Investigation of Extracted Plasma Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Foals with Sepsis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Processing
2.2. CfDNA Measurements on Neat Plasma
2.3. CfDNA Measurements on Extracted Plasma
2.4. Cell-Free DNA Measurement
2.5. Inter-Assay and Intra-Assay Agreement
2.6. Linearity of Dilution
2.7. Nonspecific Dye Fluorescence
2.8. Autofluorescence
2.9. cfDNA to Neutrophil Ratio
2.10. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animals
3.2. Qubit cfDNA Measurement Precision and Accuracy
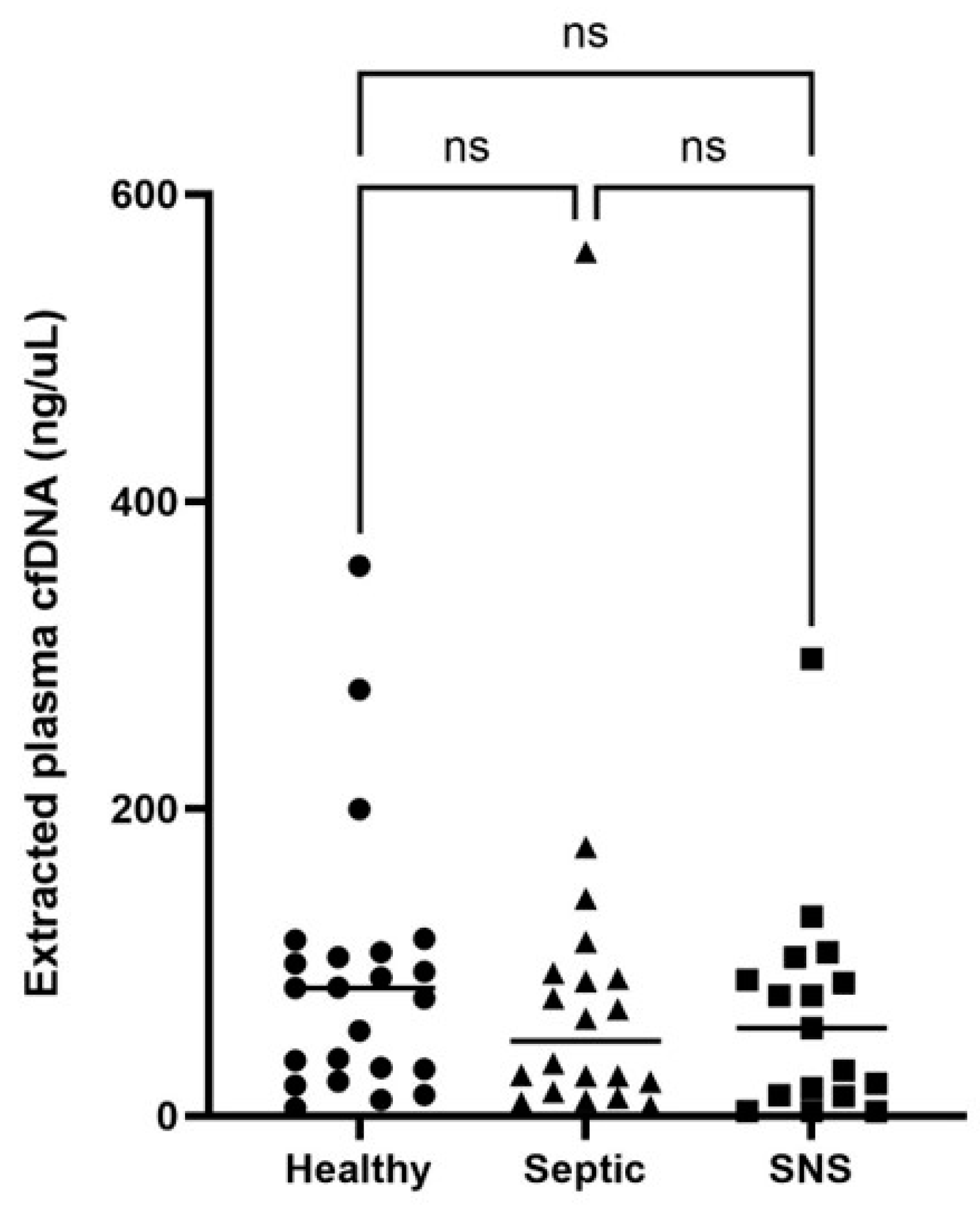
3.3. Plasma cfDNA and cfDNA:Neutrophil Ratios in Healthy, SNS and Septic Foals
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hytychová, T.; Bezděková, B. Retrospective evaluation of blood culture isolates and sepsis survival rate in foals in the Czech Republic: 50 cases (2011–2013). J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2015, 25, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colon, D.F.; Wanderley, C.W.; Franchin, M.; Silva, C.M.; Hiroki, C.H.; Castanheira, F.V.S.; Donate, P.B.; Lopes, A.H.; Volpon, L.C.; Kavaguti, S.K.; et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) exacerbate severity of infant sepsis. Crit. Care 2019, 23, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clementi, A.; Virzì, G.M.; Brocca, A.; Pastori, S.; de Cal, M.; Marcante, S.; Granata, A.; Ronco, C. The Role of Cell-Free Plasma DNA in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis. Blood Purif. 2016, 41, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson Chornenki, N.L.; Coke, R.; Kwong, A.C.; Dwivedi, D.J.; Xu, M.K.; McDonald, E.; Marshall, J.C.; Fox-Robichaud, A.E.; Charbonney, E.; Liaw, P.C. Comparison of the source and prognostic utility of cfDNA in trauma and sepsis. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2019, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayless, R.L.; Cooper, B.L.; Sheats, M.K. Investigation of plasma cell-free DNA as a potential biomarker in horses. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.H.; Tablin, F. A comparative review of neutrophil extracellular traps in sepsis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Chen, P.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, C.; He, X.; Shi, T.; Zhong, Q.; Jia, Y.; et al. Circulating Cell-Free DNAs as a Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2206789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingerhut, L.; Ohnesorge, B.; von Borstel, M.; Schumski, A.; Strutzberg-Minder, K.; Morgelin, M.; Deeg, C.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Beineke, A.; von Kockritz-Blickwede, M.; et al. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in the Pathogenesis of Equine Recurrent Uveitis (ERU). Cells 2019, 8, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colmer, S.F.; Luethy, D.; Abraham, M.; Stefanovski, D.; Hurcombe, S.D. Utility of cell-free DNA concentrations and illness severity scores to predict survival in critically ill neonatal foals. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0242635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panizzi, L.; Dittmer, K.E.; Vignes, M.; Doucet, J.S.; Gedye, K.; Waterland, M.R.; Rogers, C.W.; Sano, H.; McIlwraith, C.W.; Riley, C.B. Plasma and Synovial Fluid Cell-Free DNA Concentrations Following Induction of Osteoarthritis in Horses. Animals 2023, 13, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewer, B.D.; Koterba, A.M. Development of a scoring system for the early diagnosis of equine neonatal sepsis. Equine Vet. J. 1988, 20, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letendre, J.A.; Goggs, R. Measurement of plasma cell-free DNA concentrations in dogs with sepsis, trauma, and neoplasia. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2017, 27, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.A.; Lawson, C.M.; McMichael, M.A.; Jung, K.; O’Brien, M.; Achiel, R. Evaluation of assays for quantification of DNA in canine plasma as an indirect marker of NETosis. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2017, 46, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devonshire, A.S.; Whale, A.S.; Gutteridge, A.; Jones, G.; Cowen, S.; Foy, C.A.; Huggett, J.F. Towards standardisation of cell-free DNA measurement in plasma: Controls for extraction efficiency, fragment size bias and quantification. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 6499–6512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Barrios, C.; Nieto-Alcolado, I.; Torrente, M.; Jiménez-Sánchez, C.; Calvo, V.; Gutierrez-Sanz, L.; Palka, M.; Donoso-Navarro, E.; Provencio, M.; Romero, A. Comparison of methods for circulating cell-free DNA isolation using blood from cancer patients: Impact on biomarker testing. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloten, V.; Ruchel, N.; Bruchle, N.O.; Gasthaus, J.; Freudenmacher, N.; Steib, F.; Mijnes, J.; Eschenbruch, J.; Binnebosel, M.; Knuchel, R.; et al. Liquid biopsy in colon cancer: Comparison of different circulating DNA extraction systems following absolute quantification of KRAS mutations using Intplex allele-specific PCR. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 86253–86263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goggs, R.; Jeffery, U.; LeVine, D.N.; Li, R.H.L. Neutrophil-Extracellular Traps, Cell-Free DNA, and Immunothrombosis in Companion Animals: A Review. Vet. Pathol. 2020, 57, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polatoglou, E.; Mayer, Z.; Ungerer, V.; Bronkhorst, A.J.; Holdenrieder, S. Isolation and Quantification of Plasma Cell-Free DNA Using Different Manual and Automated Methods. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayless, R.L. Investigation of plasma cell-free dna (cfdna) as a novel biomarker of inflammation and disease severity in equine colic patients. Equine Vet. Educ. 2021, 33, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponti, G.; Maccaferri, M.; Manfredini, M.; Kaleci, S.; Mandrioli, M.; Pellacani, G.; Ozben, T.; Depenni, R.; Bianchi, G.; Pirola, G.M.; et al. The value of fluorimetry (Qubit) and spectrophotometry (NanoDrop) in the quantification of cell-free DNA (cfDNA) in malignant melanoma and prostate cancer patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 479, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoensappakit, A.; Sae-Khow, K.; Rattanaliam, P.; Vutthikraivit, N.; Pecheenbuvan, M.; Udomkarnjananun, S.; Leelahavanichkul, A. Cell-free DNA as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for adult sepsis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 19624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.N.; Stensballe, A.; Lai, J.C.; Jiang, P.; Brunse, A.; Li, Y.; Sun, J.; Mallard, C.; Skeath, T.; Embleton, N.D.; et al. Elevated levels of circulating cell-free DNA and neutrophil proteins are associated with neonatal sepsis and necrotizing enterocolitis in immature mice, pigs and infants. Innate Immun. 2017, 23, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, G.A.; Wagner, B. The development of equine immunity: Current knowledge on immunology in the young horse. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demmers, S.; Johannisson, A.; Grondahl, G.; Jensen-Waern, M. Neutrophil functions and serum IgG in growing foals. Equine Vet. J. 2001, 33, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, R.B.; Nydam, D.V.; Luna, J.A.; Bicalho, M.L.; Matychak, M.B.; Flaminio, M.J. Serum opsonization capacity, phagocytosis, and oxidative burst activity in neonatal foals in the intensive care unit. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 797–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcos, V.; Nussbaum, C.; Vitkov, L.; Hector, A.; Wiedenbauer, E.-M.; Roos, D.; Kuijpers, T.; Krautgartner, W.D.; Genzel-Boroviczény, O.; Sperandio, M.; et al. Delayed but functional neutrophil extracellular trap formation in neonates. Blood 2009, 114, 4908–4911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipp, P.; Ruhnau, J.; Lange, A.; Vogelgesang, A.; Dressel, A.; Heckmann, M. Less Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Formation in Term Newborns than in Adults. Neonatology 2017, 111, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorobjeva, N.V.; Chernyak, B.V. NETosis: Molecular Mechanisms, Role in Physiology and Pathology. Biochemistry 2020, 85, 1178–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTaggart, C.; Penhale, J.; Raidala, S.L. Effect of plasma transfusion on neutrophil function in healthy and septic foals. Aust. Vet. J. 2005, 83, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, A.G.; Harris, L.A.; Owens, S.D.; Jandrey, K.E. The prognostic utility of degenerative left shifts in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, A.G.; Harris, L.A.; Owens, S.D.; Jandrey, K.E. Degenerative left shift as a prognostic tool in cats. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2014, 28, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gayle, J.M.; Cohen, N.D.; Chaffin, M.K. Factors associated with survival in septicemic foals: 65 cases (1988–1995). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letendre, J.-A.; Goggs, R. Determining prognosis in canine sepsis by bedside measurement of cell-free DNA and nucleosomes. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2018, 28, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, M.H.; Hart, K.A. Clinical Pathology in the Foal. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2020, 36, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, E.J.; Sanchez, L.C.; Giguère, S. Re-evaluation of the sepsis score in equine neonates. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 275–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusterla, N.; Mapes, S.; Byrne, B.A.; Magdesian, K.G. Detection of bloodstream infection in neonatal foals with suspected sepsis using real-time PCR. Vet. Rec. 2009, 165, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, E.S.; Lunn, D.P.; Ferris, R.A.; Horohov, D.W.; Lappin, M.R.; McCue, P.M. Detection of bacteraemia and host response in healthy neonatal foals. Equine Vet. J. 2015, 47, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, D.M.; Ruby, R.E.; Dembek, K.A.; Barr, B.S.; Reuss, S.M.; Magdesian, K.G.; Olsen, E.; Burns, T.; Slovis, N.M.; Wilkins, P.A. Evaluation of updated sepsis scoring systems and systemic inflammatory response syndrome criteria and their association with sepsis in equine neonates. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 1185–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
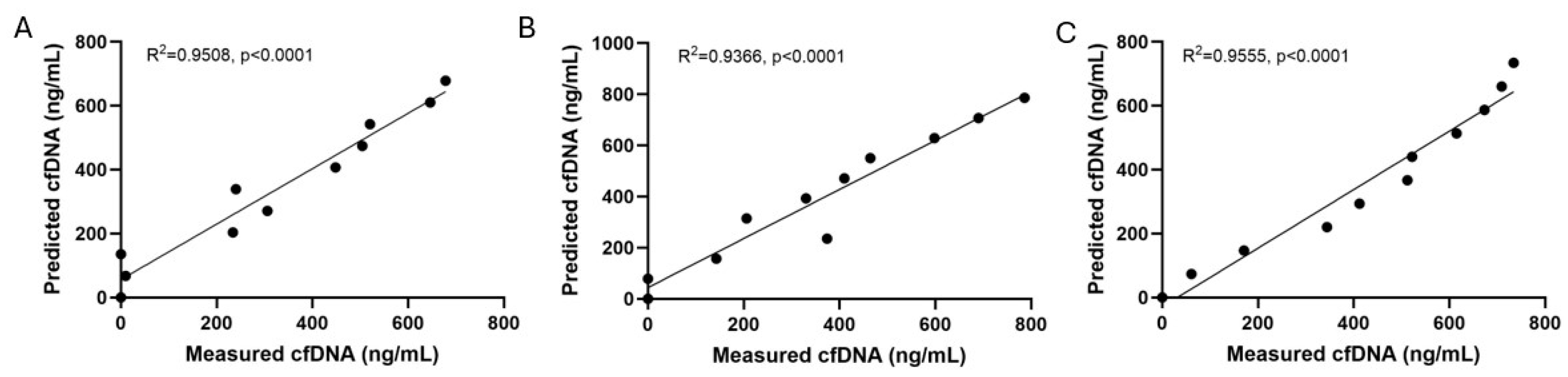
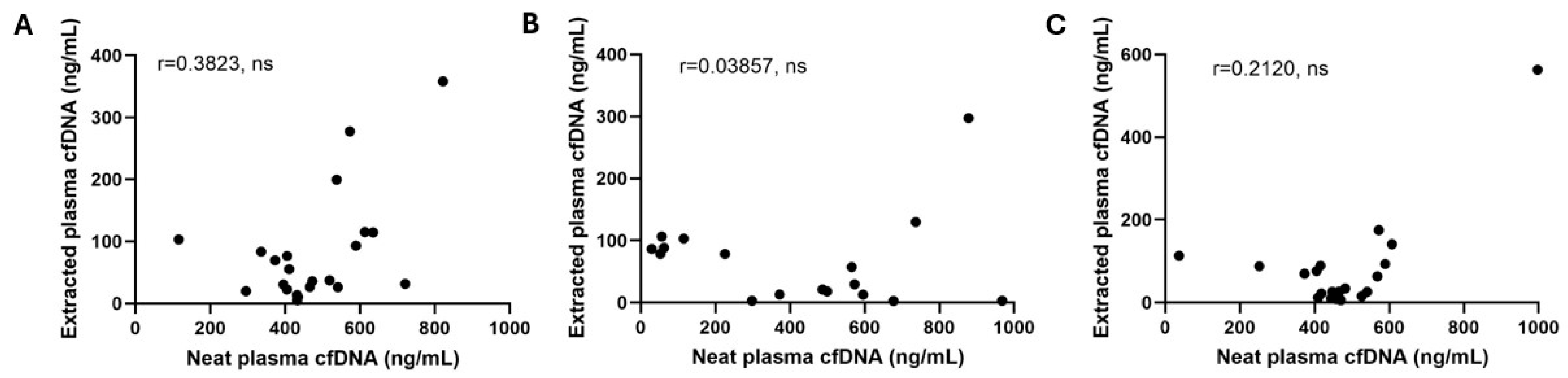

| Sample | Intra-Assay CV | Inter-Assay CV |
|---|---|---|
| 1 (SNS) | 2.54% | 9.55% |
| 2 (Healthy) | 4.37% | 18.07% |
| 3 (Septic) | 1.75% | 7.08% |
| 4 (SNS) | 2.14% | 10.78% |
| 5 (Healthy) | 1.88% | 15.74% |
| 6 (Healthy) | 7.75% | 16.50% |
| Average | 3.4% | 12.95% |
| Sample | cfDNA before Turbo DNase (ng/mL) | cfDNA after Turbo DNase (ng/mL) | % Degraded | Autofluorescence | % Autofluorescence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 (Healthy) | 720.6 | 29.8 | 95.9% | -- | -- |
| 2 (Healthy) | 411 | 374 | 9% | 195 | 47.4% |
| 3 (Healthy) | 466 | -- | -- | 255 | 54.7% |
| 4 (Healthy) | 370 | 42.4 | 88.54% | -- | -- |
| 5 (Healthy) | 668 | 29.8 | 95.54% | -- | -- |
| 6 (Healthy) | 454 | 374 | 17.62% | -- | -- |
| 7 (SNS) | 526.6 | 32 | 93.9% | 121 | 22.98% |
| 8 (SNS) | 310 | 43 | 86.1% | 272 | 87.7% |
| 9 (Septic) | 382 | 42.4 | 88.9% | 255 | 66.8% |
| 10 (Septic) | 875 | 103 | 88.2% | 332 | 37.9% |
| 11 (Septic) | 492 | 32 | 93.50% | -- | -- |
| 12 (Septic) | 568 | 103 | 81.87% | -- | -- |
| Average | -- | -- | 76.3% | -- | 52.9% |
| Foal Category | Median (Range) cfDNA (ng/mL) | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy (SS ≤ 5) (n = 23) | 83.2 (5.28 to 358.1) | 31.34 to 103.2 |
| Sick non-septic (SS 6–11) (n = 17) | 57.2 (2.92 to 297.4) | 13.3 to 88.6 |
| Septic (SS ≥ 12) (n = 20) | 48.73 (6.44 to 562.7) | 22.2 to 89.46 |
| Foal Category | Median (Range) cfDNA:Neutrophil Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval |
|---|---|---|
| Healthy (SS ≤ 5) (n = 21) | 0.01265 (0.001272 to 0.06156) | 0.004979 to 0.02337 |
| Sick non-septic (SS 6–11) (n = 17) | 0.007179 (0.0003255 to 0.03511) | 0.002522 to 0.01878 |
| Septic (SS ≥ 12) (n = 17) | 0.008 (0.001844 to 0.08487) | 0.003341 to 0.02235 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hobbs, K.J.; Cooper, B.L.; Dembek, K.; Sheats, M.K. Investigation of Extracted Plasma Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Foals with Sepsis. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080346
Hobbs KJ, Cooper BL, Dembek K, Sheats MK. Investigation of Extracted Plasma Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Foals with Sepsis. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(8):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080346
Chicago/Turabian StyleHobbs, Kallie J., Bethanie L. Cooper, Katarzyna Dembek, and M. Katie Sheats. 2024. "Investigation of Extracted Plasma Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Foals with Sepsis" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 8: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080346
APA StyleHobbs, K. J., Cooper, B. L., Dembek, K., & Sheats, M. K. (2024). Investigation of Extracted Plasma Cell-Free DNA as a Biomarker in Foals with Sepsis. Veterinary Sciences, 11(8), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11080346








