Boosting PRRSV-Specific Cellular Immunity: The Immunological Profiling of an Fc-Fused Multi-CTL Epitope Vaccine in Mice
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Virus Strains and Cell Lines
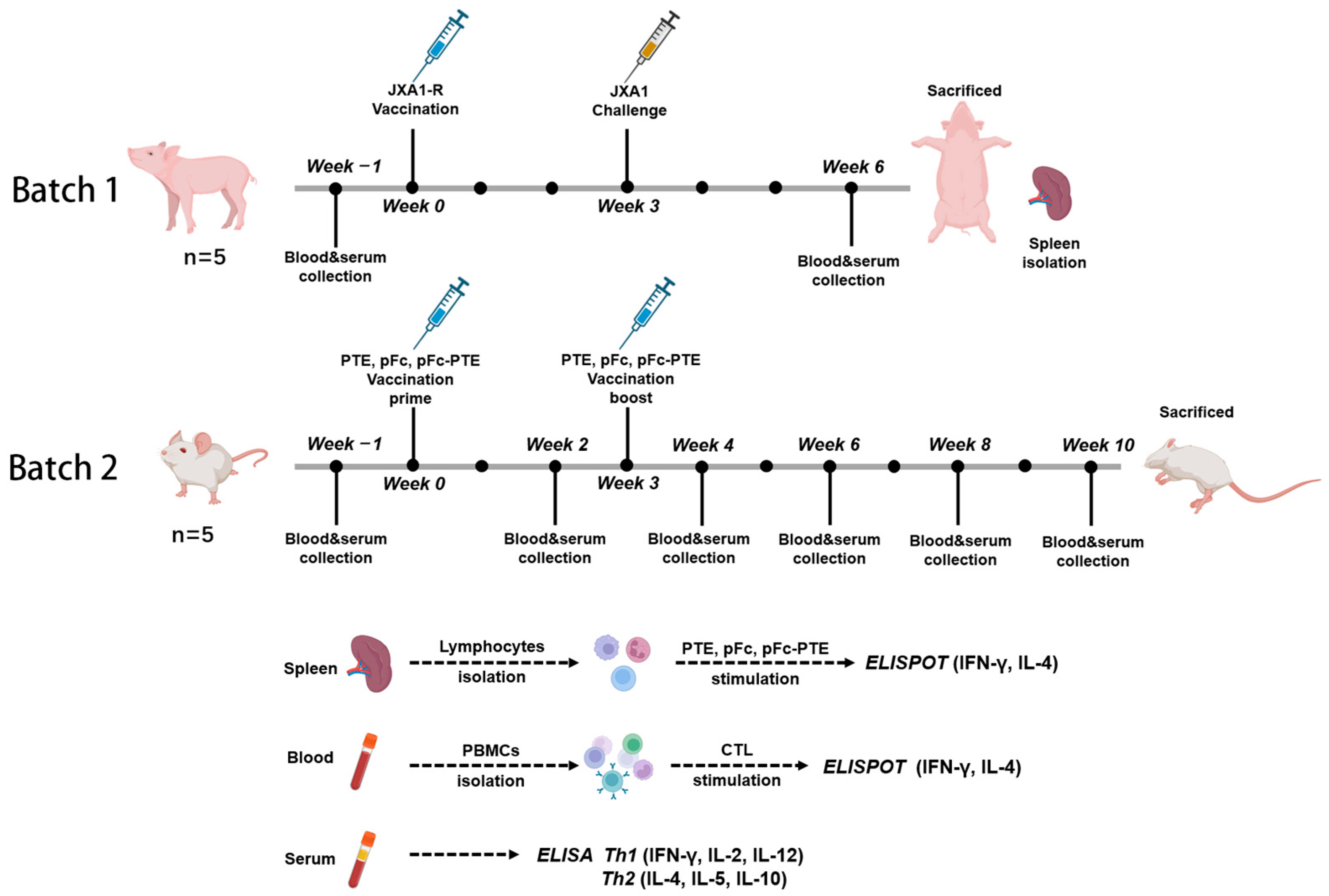
2.2. Animal Grouping and Immunization
2.3. PBMCs and Splenic Lymphocyte Isolation
2.4. ELISPOT and ELISA
2.5. Peptide Screening and Synthesis
2.6. Construction, Expression, and Purification of Fc Fusion Proteins
2.7. Evaluation Software
2.8. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
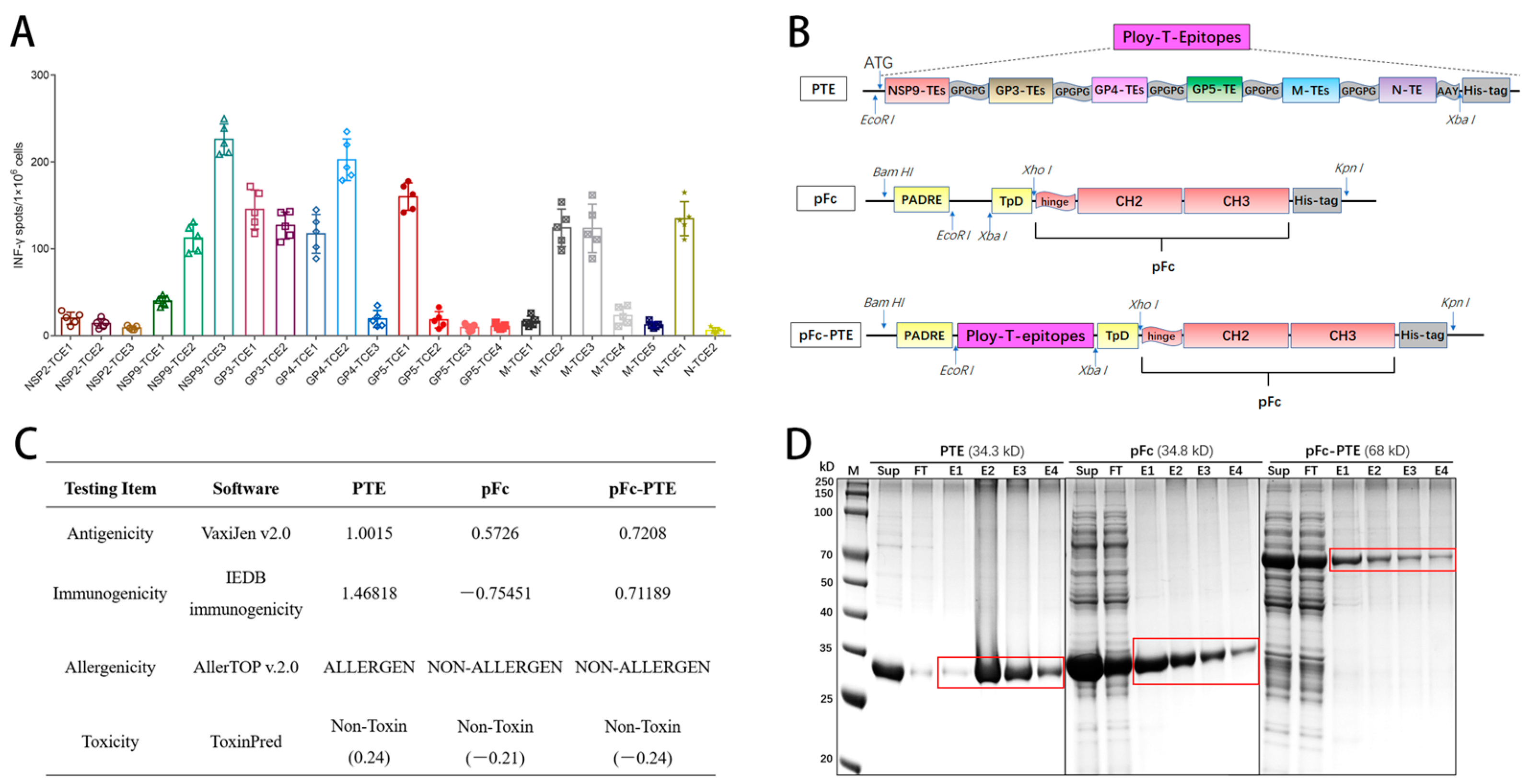
3.1. The 10 CTL Epitopes Significantly Stimulated PBMCs to Release IFN-γ
3.2. Design and Bioinformatics Analysis of Epitope Peptides Fused with Fc Protein
3.3. The Recombinant Proteins Were Successfully Expressed and Purified
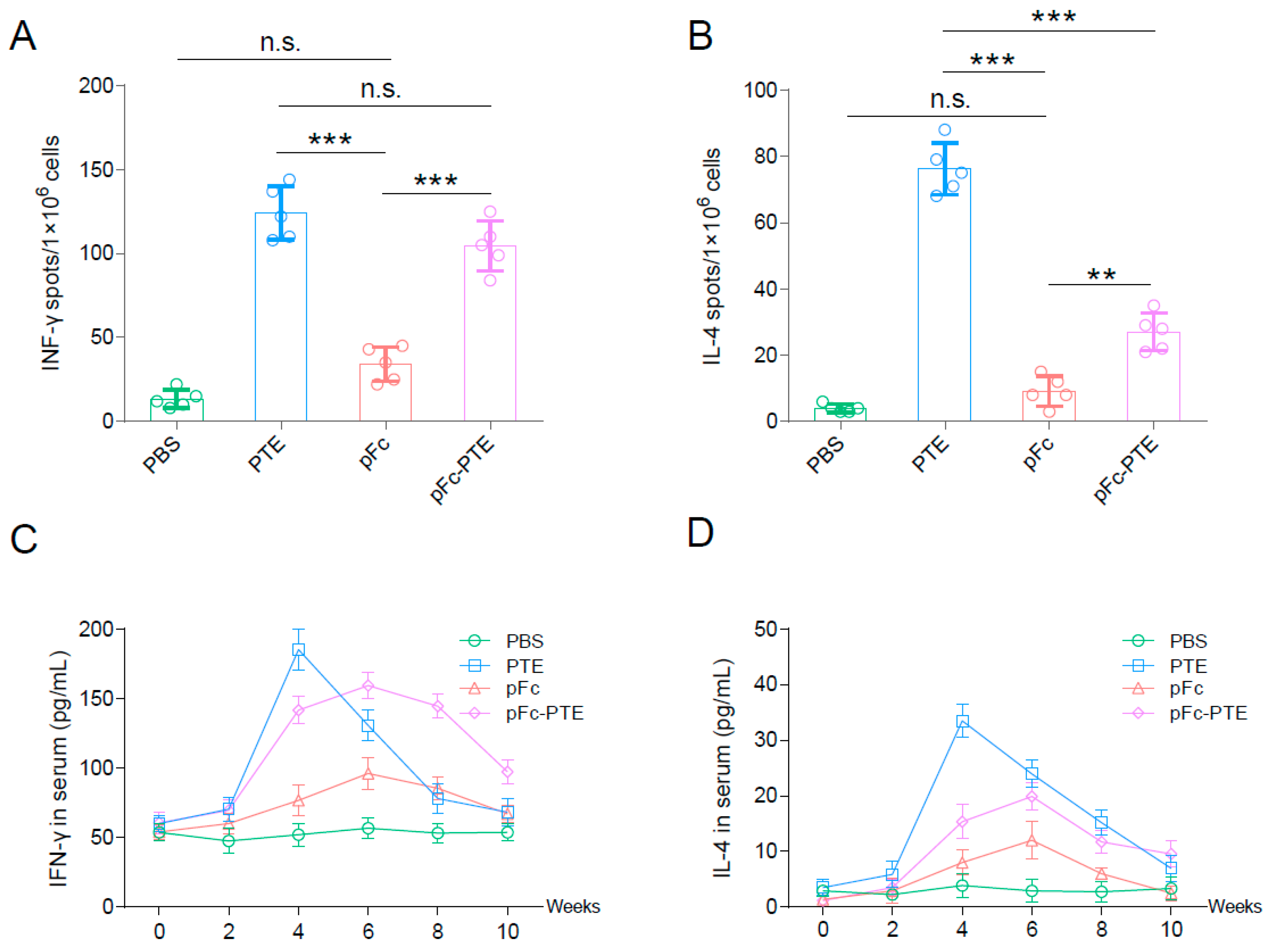
3.4. pFc-PTE Stimulated PRRSV-Specific Splenic Lymphocytes to Secrete High Levels of IFN-γ
3.5. pFc-PTE Induce a More Persistent Cellular Immune Response
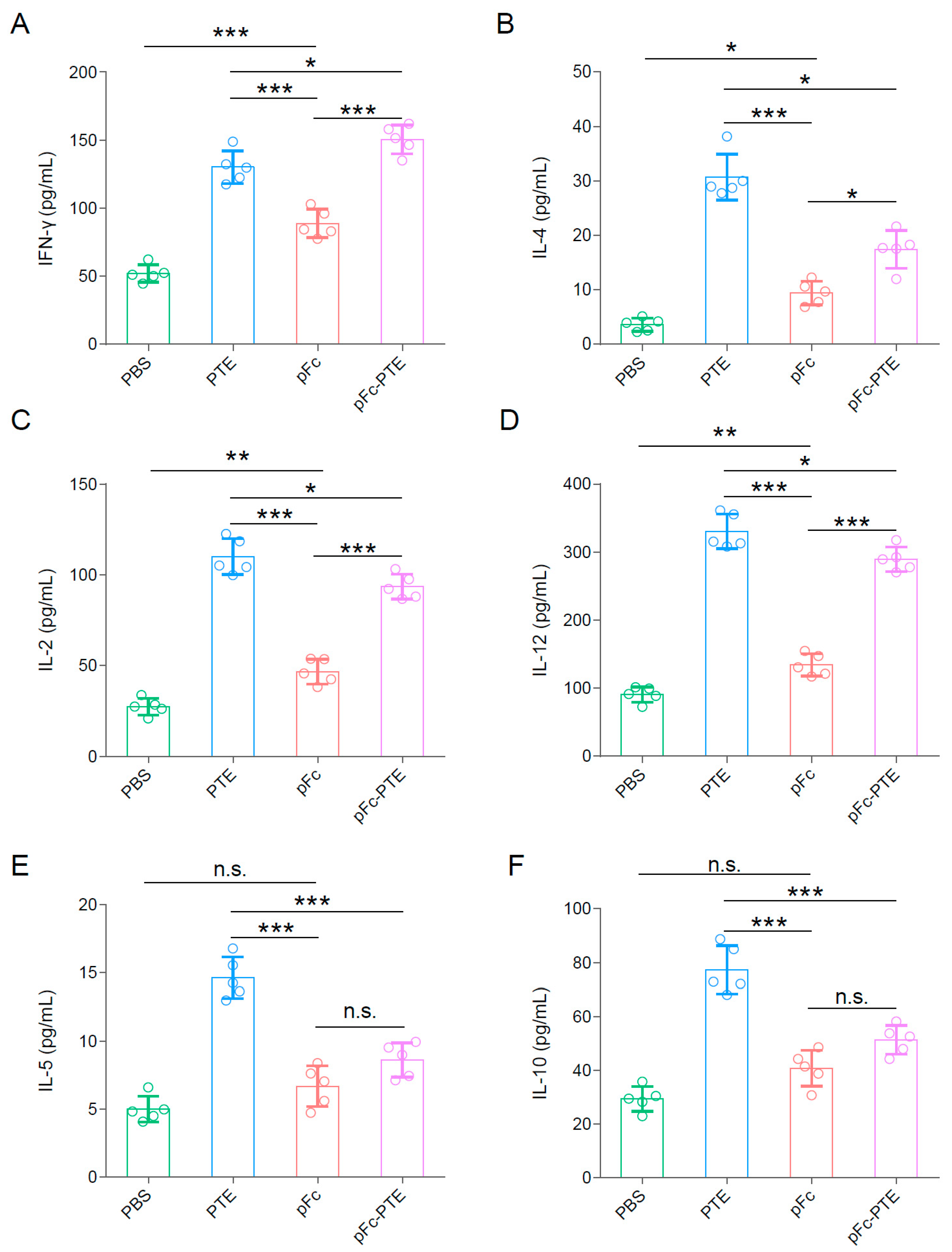
3.6. pFc-PTE Induced a Th1-Biased Immune Response
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lunney, J.K.; Fang, Y.; Ladinig, A.; Chen, N.; Li, Y.; Rowland, B.; Renukaradhya, G.J. Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus (PRRSV): Pathogenesis and Interaction with the Immune System. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2016, 4, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.Z.; Wang, F.X.; Han, X.Y.; Guo, H.; Liu, C.Y.; Hou, L.N.; Wang, Y.X.; Zheng, H.; Wang, L.; Wen, Y.J. Recent advances in the study of NADC34-like porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 950402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruedas-Torres, I.; Rodríguez-Gómez, I.M.; Sánchez-Carvajal, J.M.; Larenas-Muñoz, F.; Pallarés, F.J.; Carrasco, L.; Gómez-Laguna, J. The jigsaw of PRRSV virulence. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 260, 109168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roche, P.A.; Furuta, K. The ins and outs of MHC class II-mediated antigen processing and presentation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 203–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, M.; Cui, X.; Gao, X.; Sun, W.; Ge, X.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Han, J.; Zhou, L.; et al. Attenuated Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Regains Its Fatal Virulence by Serial Passaging in Pigs or Porcine Alveolar Macrophages To Increase Its Adaptation to Target Cells. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0308422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Bai, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, L.; Yuan, S.; Yao, H.; Yang, H.; Sun, Z. High reversion potential of a cell-adapted vaccine candidate against highly pathogenic porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 227, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Dai, A.; Huang, C.; Luo, M.; Wei, C. Molecular Characteristics and Pathogenicity of a Novel Recombinant Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus Strain from NADC30-, NADC34-, and JXA1-Like Strains That Emerged in China. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0266722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renukaradhya, G.J.; Meng, X.J.; Calvert, J.G.; Roof, M.; Lager, K.M. Live porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus vaccines: Current status and future direction. Vaccine 2015, 33, 4069–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renukaradhya, G.J.; Meng, X.J.; Calvert, J.G.; Roof, M.; Lager, K.M. Inactivated and subunit vaccines against porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome: Current status and future direction. Vaccine 2015, 33, 3065–3072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malonis, R.J.; Lai, J.R.; Vergnolle, O. Peptide-Based Vaccines: Current Progress and Future Challenges. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 3210–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Peng, W.J.; Kuo, B.S.; Ho, Y.H.; Wang, M.S.; Yang, Y.T.; Chang, P.Y.; Shen, Y.H.; Hwang, K.P. Toward a pan-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine targeting conserved epitopes on spike and non-spike proteins for potent, broad and durable immune responses. PLoS Pathog 2023, 19, e1010870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGee, M.C.; Huang, W. Evolutionary conservation and positive selection of influenza A nucleoprotein CTL epitopes for universal vaccination. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 2578–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Q.M.; Tian, D.; Heffron, C.L.; Subramaniam, S.; Opriessnig, T.; Foss, D.L.; Calvert, J.G.; Meng, X.J. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes identified from a contemporary strain of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus enhance CD4+CD8+ T, CD8+ T, and γδ T cell responses. Virology 2019, 538, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, W.; Pan, C.; Cheng, P.; Wang, J.; Zhao, G.; Wu, X. Peptide-Based Vaccines for Tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 830497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizpour, S.; Pourseif, M.M.; Razmara, J.; Rafi, M.A.; Omidi, Y. Epitope-based vaccine design: A comprehensive overview of bioinformatics approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonaguro, L.; Tagliamonte, M. Peptide-based vaccine for cancer therapies. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1210044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larché, M.; Wraith, D.C. Peptide-based therapeutic vaccines for allergic and autoimmune diseases. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, S69–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Erp, E.A.; Luytjes, W.; Ferwerda, G.; van Kasteren, P.B. Fc-Mediated Antibody Effector Functions During Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection and Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, N.; Wei, X.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, R.; Li, Q.; Liang, R.; Zhang, L.; Ma, L.; Xia, C. Illumination of PRRSV Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitopes by the Three-Dimensional Structure and Peptidome of Swine Lymphocyte Antigen Class I (SLA-I). Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; He, X.; Quan, J.; Jiang, Q.; Lin, H.; Chen, H.; Qu, L. Specificity Characterization of SLA Class I Molecules Binding to Swine-Origin Viral Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte Epitope Peptides in Vitro. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashisht, K.; Goldberg, T.L.; Husmann, R.J.; Schnitzlein, W.; Zuckermann, F.A. Identification of immunodominant T-cell epitopes present in glycoprotein 5 of the North American genotype of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vaccine 2008, 26, 4747–4753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtar, H.; Eck, M.; Morgan, S.B.; Essler, S.E.; Frossard, J.P.; Ruggli, N.; Graham, S.P. Proteome-wide screening of the European porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus reveals a broad range of T cell antigen reactivity. Vaccine 2014, 32, 6828–6837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.; Xia, Q.; Zhou, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ding, P.; Qi, Y.; Wang, A. Identification of potential SLA-I-restricted CTL epitopes within the M protein of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 259, 109131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Lin, Y.; Bai, Y.; Tong, T.; Wang, Q.; Liu, N.; Liu, G.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, T.; Bu, Z.; et al. Identification of CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocyte epitopes from porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus matrix protein in BALB/c mice. Virol. J. 2011, 8, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.; Jazayeri, S.D.; Ramanathan, B.; Poh, C.L. Enhancement of Tetravalent Immune Responses to Highly Conserved Epitopes of a Dengue Peptide Vaccine Conjugated to Polystyrene Nanoparticles. Vaccines 2020, 8, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rath, T.; Baker, K.; Dumont, J.A.; Peters, R.T.; Jiang, H.; Qiao, S.W.; Lencer, W.I.; Pierce, G.F.; Blumberg, R.S. Fc-fusion proteins and FcRn: Structural insights for longer-lasting and more effective therapeutics. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2015, 35, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruterbusch, M.; Pruner, K.B.; Shehata, L.; Pepper, M. In Vivo CD4+ T Cell Differentiation and Function: Revisiting the Th1/Th2 Paradigm. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 38, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, T.; Ben-Yedidia, T. Epitope-based approaches to a universal influenza vaccine. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 54, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wang, M.; Zhou, L.; Tian, P.; Sun, Z.; Sun, J.; Wang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Jiang, D.; Wu, Y.; et al. A candidate nanoparticle vaccine comprised of multiple epitopes of the African swine fever virus elicits a robust immune response. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arieta, C.M.; Xie, Y.J.; Rothenberg, D.A.; Diao, H.; Harjanto, D.; Meda, S.; Marquart, K.; Koenitzer, B.; Sciuto, T.E.; Lobo, A.; et al. The T-cell-directed vaccine BNT162b4 encoding conserved non-spike antigens protects animals from severe SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell 2023, 186, 2392–2409.e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, C.; Wang, P.; Tian, J.; Gao, G.F.; Liu, K.; Liu, W.J. Seeing the T cell Immunity of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV: Believing the Epitope-Oriented Vaccines. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 4052–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, W.; Wu, Z.; Guo, C.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Xia, X.; Sun, H. Recombinant adenovirus-delivered soluble CD163 and sialoadhesin receptors protected pigs from porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus infection. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 219, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhou, X.; Noor, A.U.; Zhang, X.; Song, C.; Sun, H. Enhancing half-life and cytotoxicity of porcine respiratory and reproductive syndrome virus soluble receptors by taming their Fc domains. Vet. Microbiol. 2022, 273, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Peng, K.; Tian, J.; Xu, X.; Zhou, E.; Chen, H. Immune response to Fc tagged GP5 glycoproteins of porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus. Viral Immunol. 2014, 27, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, S.; Lv, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Tabynov, K.; Zhao, Q.; Zhou, E.M. Nanobody Nb6 fused with porcine IgG Fc as the delivering tag to inhibit porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus replication in porcine alveolar macrophages. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| CTL Epitope | Reported Sequence | Reference | Corresponding Sequence in JXA1 | SLA-1 0401 | SLA-1 0801 | SLA-2 0101 | SLA-2 0401 | SLA-2 0502 | SLA-2 1001 | SLA-3 0401 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSP2-TCE1 | QTLKLPAAL | [13] | QILRLPAAL | 10 | 6 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 8 | 32 |
| NSP2-TCE2 | SIFQAPFTL | SAYQAFRIL | 15 | 8 | 8 | 4 | 6 | 0.8 | 2 | |
| NSP2-TCE3 | VVGPVGLGL | VVGPVGLGL | 6 | 8 | 15 | 32 | 15 | 7 | 32 | |
| NSP9-TCE1 | TMPPGFELY | [19] | TMPSGFELY | 1 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 4 | 8 | 5 | 32 |
| NSP9-TCE2 | YASAAAILM | [13] | YASAAAILM | 4 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| NSP9-TCE3 | YSFPGPPFF | YSFPGPPFF | 0.4 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 1 | 0.17 | 0.4 | 2 | |
| GP3-TCE1 | ITAVYQTYY | ISAVFQTYY | 0.8 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.08 | 5 | 5 | 3 | |
| GP3-TCE2 | FSFELLVNY | FSFELMVNY | 3 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 5 | 3 | 15 | |
| GP4-TCE1 | MAASFLFLL | MAASFLFLL | 9 | 8 | 2 | 7 | 0.08 | 5 | 4 | |
| GP4-TCE2 | RTAIGTPVY | RTAIGTPVY | 0.2 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 0.8 | 10 | 3 | 1.5 | |
| GP4-TCE3 | CLFAILLAT | [20] | CLFAILLAI | 32 | 9 | 32 | 32 | 6 | 10 | 32 |
| GP5-TCE1 | GLITVSAAGY | [13] | GLATVSTAGY | 0.8 | 0.1 | 6 | 1.5 | 32 | 2 | 32 |
| GP5-TCE2 | LAALICFVIRLAKNC | [20,21] | LAALICFVIRLAKNC | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 32 | 50 | 50 |
| GP5-TCE3 | KGRLYRWRSPVIVEK | [21] | KGRLYRWRSPVIVEK | 50 | 50 | 15 | 32 | 50 | 50 | 2 |
| GP5-TCE4 | FDWAVETFVLYPVAT | [22] | FDWAVETFVIFPVLT | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| M-TCE1 | AVKQGVVNL | [23] | AVKQGVVNL | 15 | 9 | 15 | 32 | 32 | 4 | 15 |
| M-TCE2 | YSAIETWKF | YSAIETWKF | 1.5 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0.8 | 6 | 15 | |
| M-TCE3 | STNKVALTM | [13] | STNRVALTM | 0.5 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 3 | 1 |
| M-TCE4 | KFITSRCRL | [24] | KFITSRCRL | 32 | 32 | 10 | 50 | 32 | 32 | 5 |
| M-TCE5 | FGYMTFVHF | FGYMTFVHF | 32 | 9 | 9 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 6 | |
| N-TCE1 | FSLPTQHTV | [20] | FSLPTQHTV | 15 | 15 | 9 | 16 | 0.3 | 15 | 9 |
| N-TCE2 | NPEKPHFPL | NPEKPHFPL | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 7 | 50 | 50 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lei, X.; Ban, J.; Wu, Z.; Cao, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, R.; Lu, H.; Zhu, S. Boosting PRRSV-Specific Cellular Immunity: The Immunological Profiling of an Fc-Fused Multi-CTL Epitope Vaccine in Mice. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060274
Lei X, Ban J, Wu Z, Cao S, Zhou M, Zhang L, Zhu R, Lu H, Zhu S. Boosting PRRSV-Specific Cellular Immunity: The Immunological Profiling of an Fc-Fused Multi-CTL Epitope Vaccine in Mice. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(6):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060274
Chicago/Turabian StyleLei, Xinnuo, Jinzhao Ban, Zhi Wu, Shinuo Cao, Mo Zhou, Li Zhang, Rui Zhu, Huipeng Lu, and Shanyuan Zhu. 2024. "Boosting PRRSV-Specific Cellular Immunity: The Immunological Profiling of an Fc-Fused Multi-CTL Epitope Vaccine in Mice" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 6: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060274
APA StyleLei, X., Ban, J., Wu, Z., Cao, S., Zhou, M., Zhang, L., Zhu, R., Lu, H., & Zhu, S. (2024). Boosting PRRSV-Specific Cellular Immunity: The Immunological Profiling of an Fc-Fused Multi-CTL Epitope Vaccine in Mice. Veterinary Sciences, 11(6), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11060274






