Simple Summary
Wildlife has been described as a sylvatic reservoir for a multitude of pathogens. The interactions between wild birds, domestic animals, and humans in urban areas are high, so monitoring urban birds is key for the surveillance of zoonosis such as campylobacteriosis. This infection is mainly caused by thermophilic Campylobacter spp., and it is the most reported foodborne zoonosis in the European Union. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of thermophilic Campylobacter isolates and their antimicrobial resistance pattern in urban wild birds. Results showed that 16.8% of birds were positive for Campylobacter, with 82.4% of the isolates resistant to at least one antimicrobial. The taxonomic order of individuals, main diet, age, and season of sampling were significant factors associated with Campylobacter spp. carriage. Although the prevalence of Campylobacter was low, the rate of antimicrobial-resistant isolates is worrying, so similar studies should be included in the antimicrobial resistance surveillance programs.
Abstract
The increasing urbanization of ecosystems has had a significant impact on wildlife over the last few years. Species that find an unlimited supply of food and shelter in urban areas have thrived under human presence. Wild birds have been identified as amplifying hosts and reservoirs of Campylobacter worldwide, but the information about its transmission and epidemiology is still limited. This study assessed the prevalence of Campylobacter in 137 urban birds admitted at a wildlife rescue center, with 18.8% of individuals showing positive. C. jejuni was the most frequent species (82.6%), followed by C. coli and C. lari (4.3% each). The order Passeriformes (33.3%) showed significant higher presence of Campylobacter when compared to orders Columbiformes (0%) and Ciconiiformes (17.6%), as well as in samples collected during the summer season (31.9%), from omnivorous species (36.8%) and young individuals (26.8%). Globally, Campylobacter displayed a remarkable resistance to ciprofloxacin (70.6%), tetracycline (64.7%), and nalidixic acid (52.9%). In contrast, resistance to streptomycin was low (5.8%), and all the isolates showed susceptibility to erythromycin and gentamycin. The results underline the importance of urban birds as reservoirs of thermophilic antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter and contribute to enhancing the knowledge of its distribution in urban and peri-urban ecosystems.
Keywords:
Campylobacter; antimicrobial resistance; urban wildlife; landfills; passerines; AMR; zoonoses; One Health; wild birds; wildlife 1. Introduction
The increasing urbanization of ecosystems has had a significant impact on wildlife over the last years. While some species have suffered population decline, many others have adapted and thrived under human presence [1]. Most of these species find in urban areas a supply of unlimited resources for their biological functions, and the increase in urban waste has promoted landfills as an important source of food for urban wildlife [2,3]. In this sense, due to the constant food availability and the milder winter temperatures, some migratory species such as white storks (Ciconia ciconia) have shortened or even stopped their migration in the Iberian Peninsula during the last decades [4]. Nevertheless, a diet based on urban waste may involve several risks such as nutritional deficiencies, intoxications, or the acquisition of antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) bacteria, including E. coli, Salmonella, and Campylobacter [5].
Campylobacter is the most reported foodborne zoonotic bacteria in the European Union (EU) and has significant socioeconomic repercussions on public health [6,7]. Although approximately 137,000 confirmed cases of human campylobacteriosis have been reported in the European Union in 2022 [7], the actual number could be up to 9 million per year [8]. On the other hand, human campylobacteriosis can lead to reactive arthritis and severe neurological disorders such as Guillain–Barré and Miller–Fisher syndromes [9]. Despite the high host specificity, many animals are considered natural hosts of Campylobacter, since the bacteria has been detected as a part of the normal microbiota in cattle, sheep, swine, and poultry, with the highest prevalence in the last one, which is defined as the main reservoir [10,11]. Indeed, it has been reported that more than 88% of human campylobacteriosis cases originate from poultry [12]. In addition, wild birds have also been identified as amplifying hosts and reservoirs worldwide, including Antarctica, with C. jejuni, C. lari, and C. coli as the most reported species [13,14].
Information about the transmission and epidemiology of this genus is still limited, especially in wild bird populations, although evidence about the transmission between wild birds and humans has already been published [6]. Ecological and life history traits, such as feeding habits or sociality, can influence the infection rates of Campylobacter in wild birds [13]. Among urban wild birds, Passeriformes and Columbiformes are two orders that have shown a high prevalence of infection [6,9,15,16,17]. In cities, there is a significant level of direct or indirect contact between humans and these species, particularly in parks, playgrounds, market squares, or terraces, which poses a potential risk to public health (Figure 1) [18].

Figure 1.
Urban wildlife can pose a risk due to its close contact with humans.
The dissemination of Campylobacter by wild birds becomes especially worrying when antimicrobial-resistant (AMR) strains are involved [19,20]. The increasing development and spread of AMR through the environment is concerning, since it is estimated that resistant bacteria are involved in over 5 million deaths [21]. Although the contribution to the development of resistances is not comparable to that due to livestock and human activity [22,23], several studies have reported a high proportion of AMR Campylobacter isolates, including multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains, in wild bird populations [22,24,25].
The presence of AMR in wildlife is directly related to the anthropization of ecosystems, but other transmission routes may also exist, such as environment contamination and the dissemination of antimicrobial resistance genes (ARGs) through clouds [26,27]. In urban wildlife, the environmental pressure on antimicrobial residues in cities may be the main route for AMR acquisition, highlighting the importance of including the monitoring of urban wildlife in AMR surveillance. Due to their increasingly close contact with humans, wildlife may act as a reservoir for zoonotic infections [28]. Moreover, Campylobacter can easily transfer genetic elements such as ARGs to other bacteria [24].
In this context, this study aimed to assess the prevalence of Campylobacter in urban wild birds from different species admitted at a wildlife rescue center, as well as identify strains at the species level, and determine their susceptibility to antimicrobials.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
From 2017 to 2021, 137 birds of 13 species from urban populations admitted to the Grupo de Rehabilitación para la Fauna Autóctona y su Hábitat (GREFA) Wildlife Hospital (Madrid, Spain) were examined and sampled following a standard protocol for the health status monitoring of animals. All birds were handled according to the European Directive 2010/63/EU and the Spanish Royal Decree 53/2013 [29,30]. As a part of the sanitary status analysis, a cloacal swab was aseptically collected from each individual at their arrival to assess the presence of Campylobacter, before any treatment. Samples were preserved in ferrous sulfate, sodium metabisulfite, and sodium pyruvate (250 mg/L each) medium (FBP) (Oxoid®, Basingstoke, UK) with 0.5% active charcoal (Sigma-Aldrich®, St. Louis, MO, USA) and kept frozen at −20 °C until analysis.
Furthermore, the body condition score, age, and gender of all the individuals included in the study were determined. The age of the animals was estimated based on feather development, whereupon they were grouped into young (nestlings and fledglings) or adult categories. Gender was identified by sexual dimorphism when possible. Finally, the visual body composition score (BCS) of each animal was estimated by morphometry using a zero-to-five system, where level 0 represented cachectic birds, 1 emaciated birds, level 2 under-conditioned birds, level 3 well-conditioned birds, level 4 over-conditioned birds, and level 5 obese birds [31].
2.2. Campylobacter spp. Isolation and Identification
Isolation of thermophilic Campylobacter was performed at the Central Veterinary Laboratory (LCV) of Algete (Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food) based on the ISO 10272–1:2017 procedures [32], as previously described by Mencía-Gutiérrez et al. [25]. Briefly, samples were streaked onto modified charcoal cefoperazone deoxycholate (mCCDA) and Preston agar (Oxoid®, Basingstoke, UK) and incubated in a microaerobic atmosphere at 41.5 ± 1 °C for 44 ± 4 h. The morphology and motility of all the Campylobacter-like colonies were assessed under microscopy, and Gram staining was employed for the morphology study (Panreac AppliChem®, Darmstadt, Germany). Also, biochemical tests were performed, including catalase activity, oxidase activity (MAST® ID Oxidase Strips, Amiens, France), and hippurate hydrolysis for preliminary C. jejuni identification. Moreover, microanaerobiosis and aerobiosis growth were also tested by the culture in blood agar (Oxoid®, Basingstoke, UK) at 25 ± 1 °C and 41.5 ± 1 °C for the first one, and at 37 ± 1 °C for the second one.
Campylobacter species was confirmed according to the multiplex PCR assay described by Wang et al., including the genes hipO and 23 S rRNA, present in C. jejuni; glyA, present in C. coli, C. lari, and C. upsaliensis; and sapB2 from C. fetus subsp. fetus [33]. Isolates with inconclusive results were subjected to a sequential PCR assay described by Denis et al. for simultaneous identification of C. jejuni and C. coli [34]. Samples with non-determinant results were classified as Campylobacter spp. Isolates were cryopreserved at −80 °C in the FBP medium until antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Campylobacter strains were subjected to an antimicrobial susceptibility test (AST) using the broth microdilution method. Sensititre Campylobacter EUCAMP2® plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific®, Madrid, Spain) were used according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Each strain was tested against six different antimicrobials: nalidixic acid (NAL), ciprofloxacin (CIP), erythromycin (ERY), tetracycline (TET), gentamycin (GEN), and streptomycin (STR). The susceptibility or resistance of C. jejuni and C. coli isolates to antimicrobials was determined using the epidemiological cut-off values (ECOFF) established by the European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST, 2023) (Table 1) [35]. For other Campylobacter species, the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) cut-off values for C. jejuni were applied as they were the most restrictive ones. MDR was defined as resistance to at least three different antimicrobial families [36].

Table 1.
Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) cut-off values that were employed for C. jejuni and C. coli (EUCAST, 2023).
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with two commercially available software packages: SPSS v23.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA, 2002) and Statgraphics Centurion XVI v16.2.04 (StatPoint Technologies, Inc., Warrenton, VA, USA).
Assuming a binomial distribution for Campylobacter shedding and AMR, different statistical tests were performed to assess whether there was an association with different variables. The following variables were selected for statistical analysis: (1) bird order: Ciconiiformes, Columbiformes, Passeriformes; (2) main feeding diet: insectivore, herbivore, and omnivore; (3) presence in landfill: yes or no; (4) season of sampling; and (5) age. Univariate statistical analysis was performed with Pearson chi-square χ2 test and Fisher’s exact test when appropriate for independence (p-value), using Campylobacter spp. status (absence/presence) as the dependent variable. A two-tailed p-value < 0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI95%) were also calculated. Logistic regression was also implemented to test the impact of variables with more accuracy and perform a multivariate analysis to assess the correlation between variables simultaneously.
3. Results
A total of 137 individual birds from 13 urban avian species and 3 orders (Ciconiiformes, Columbiformes, and Passeriformes) were analyzed for Campylobacter carriage. A total of 23 Campylobacter isolates were recovered from 8 out of the 13 urban species (61.5%), with an individual prevalence of 16.8% (CI95% 11.4–23.9%). The most frequent species was C. jejuni (82.6%), followed by C. coli and C. lari (4.3% each). Two isolates could not be identified at the species level (8.7%). Further details about the distribution of Campylobacter among the different orders and species are shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Campylobacter prevalence and species regarding urban bird species.
Chi-square and Fisher’s exact test showed a significant relationship between four variables and prevalence rates of Campylobacter: order, feeding, season of sampling, and age (Table 3). A subsequent univariate logistic regression analysis was performed excluding the Campylobacter-free categories to investigate the association between variables with greater accuracy. Overall, the age of individuals and season of sampling resulted in key variables on the Campylobacter epidemiology: the proportion of Campylobacter was 3.47 times higher in young individuals than in adults (p = 0.01) and 8.28 times higher in individuals sampled during summer than in other seasons (p = 0.002) (Figure 2). According to the taxonomic order, a tendency was detected in Passeriformes, being 2.33 times more positive to Campylobacter spp. than Ciconiiformes (p = 0.102). The rest of the variables (diet and presence in landfill) were not significantly associated with Campylobacter prevalence. Gender and body condition scores were assessed but discarded as independent variables due to the high number of animals of unknown gender (missing = 103) and the high percentage (90%) of animals classified in only one of the 5 possible categories in the case of body condition.

Table 3.
Factors associated with Campylobacter spp. presence in urban birds.
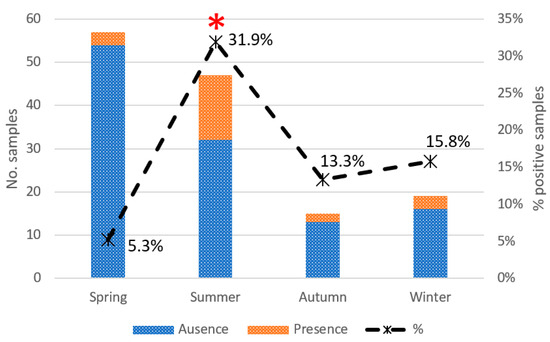
Figure 2.
Campylobacter prevalence by season in urban birds (* p < 0.01). Bars indicate the total number of samples, with different colors depending on the absence (dark) or presence (light) of Campylobacter. The dashed line indicates the percentage of positive samples about the total number of samples.
A multivariate analysis was later performed including the risk factors identified as significant in the univariate logistic regression: season (summer vs. spring) and age (young vs. adult), but also the trend detected for the order in the case of Passeriformes with respect to Ciconiiformes (Table 3). A statistically significant difference was observed in the case of young individuals and samples collected during the summer. Finally, separate logistic regression analyses were performed for adult and young individuals to assess a possible co-linearity with the effect of season. A significant correlation was observed between seasonality and young birds but not in the case of adults.
On the other hand, only 17 Campylobacter isolates out of 23 isolates could be subjected to AST; it was not possible to recover 6 isolates (4 C. jejuni and 2 Campylobacter spp.) from FBP cryovials. Results showed that 82.4% (14/17; CI95%: 58.2–94.6%) of all the Campylobacter isolates analyzed for AST were resistant to at least one antimicrobial, and only three isolates were pansusceptible (17.6%). Globally, Campylobacter displayed a remarkable resistance to CIP (70.6%), TET (64.7%), and NAL (52.9%) and a low resistance to STR (5.8%). All isolates were susceptible to ERY and GEN. The results of AST are summarized in Table 4. The statistical analysis revealed that, among all the species, white storks tended to have higher rates of resistant Campylobacter (p = 0.052), while not significantly different.

Table 4.
Results of antimicrobial susceptibility testing (AST) of Campylobacter isolates from urban birds.
Among the resistant isolates (n = 14), 12 were identified as C. jejuni, 1 as C. coli, and 1 as C. lari. The antimicrobial resistance patterns of Campylobacter isolates are summarized in Table 5 and Figure 3. No MDR isolates were detected.

Table 5.
Antimicrobial resistance profiles of Campylobacter isolates from urban birds.
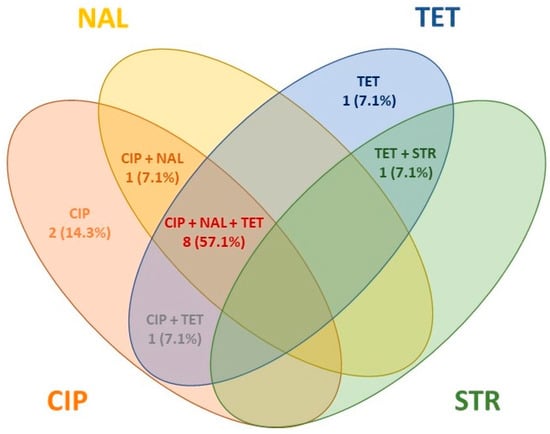
Figure 3.
Antimicrobial resistance patterns found in Campylobacter isolates.
4. Discussion
Although some authors consider that the role of wild birds as a reservoir for enteric pathogens may be overestimated [37], others have reported similarities among Campylobacter strains isolated from both humans and wildlife [17]. Likewise, several studies have confirmed the presence of the same Campylobacter genotypes in wild birds, domestic animals, and humans [6,24,38]. Therefore, the monitoring of wild birds during ringing activities or upon admission to rescue centers would be a very valuable tool for assessing the distribution of these bacteria in the environment.
The presence of Campylobacter spp. in fecal samples of urban birds belonging to the orders Ciconiiformes, Columbiformes, and Passeriformes has been previously evaluated, but the individual prevalence found in this study (16.8%) differs from the findings of other authors. Du et al. reported a prevalence of 10.96% in birds from urban and suburban areas of Beijing [24], while Ramonaite et al. detected a prevalence of 36.2% in fresh fecal samples of free-living urban birds in Lithuania [39]. This difference between both studies could be due to two circumstances. First, while the first study included urban wild birds from 33 different species, the second one focused only on two species (crows and pigeons). The second reason could be that Ramonaite et al. included a selective enrichment step to detect stressed thermophilic Campylobacter isolates in the samples [39]. Most of the studies about Campylobacter prevalence in wild animals often exhibit heterogeneous results among species or taxonomic groups, even within the same study, as observed in this work [40]. On the other hand, the prevalence of Campylobacter seems to be linked to the biology and evolution of the avian species, reflecting the evolutionary commensal association between Campylobacter and birds [13]. In general, the order Passeriformes exhibited the highest infection rate, being particularly notable in the Corvidae family, as observed by other authors [26,41,42]. The presence of two different Campylobacter species (C. jejuni and C. lari) within this family has also been previously reported [43]. Crows, which commonly have a high prevalence of Campylobacter [40,44], are omnivorous and opportunistic scavengers, and it has been described that individuals from peri-urban areas with a greater amount of anthropogenic waste in their stomach contents had a higher prevalence of Campylobacter compared to those from rural areas [45]. Similar associations have been observed in white storks with feeding habits in landfills, which have been linked to a higher prevalence and a broader spectrum of Campylobacter species [46]. In the Iberian Peninsula, there is a close relationship between resident populations of white storks and landfills, which could explain the higher prevalence observed in this study, compared to the findings of Szczepanska et al. in Poland (7.6%) [46]. However, the present results did not confirm the association between the presence of Campylobacter and feeding in landfills. Surprisingly, none of the Columbiformes included in this study was positive for Campylobacter, which contrasts with most of the literature [24,38,41,43]. Columbiformes are herbivorous species that may primarily acquire Campylobacter infection through contaminated vegetables and surfaces. Specifically, ringdove (Columba palumbus) and collared dove (Streptopelia decaocto) are birds inhabiting rural areas with lesser interaction with human wastes, which reduces the acquisition of bacteria such as Campylobacter [47].
Moreover, differences found among bird species could be related to their body temperature average. In 2022, Casalino et al. reported a strong association between body temperature and Campylobacter presence, with a high prevalence in species whose average body temperature ranged from 40.7 to 41.8 °C. Out of this body temperature range, Campylobacter was not found [48]. It is well-known that body temperature is higher in small birds [49] such as passerines, which showed the highest prevalence (33.3%). However, the average body temperatures of most of the species included in this study are unknown; therefore, it would be an interesting aspect to evaluate in future studies.
In this study, Campylobacter rate infection also seems to be influenced by season and weather conditions. Some studies have reported a higher prevalence of Campylobacter in wild birds through the spring/early summer months [25,50], when carriers might increase the pathogen fecal shedding during the moment of acute stress related to the breeding season, infecting in turn their partners or even their offspring. Likewise, a peak of campylobacteriosis cases in humans and domestic animals is often observed during the warmer months of the year, which agrees with the present results [10,38,51]. Also, the age of the animals has been previously addressed as a significant factor in the Campylobacter infection rates, thus it was included as a variable in the statistical analysis of this study. Results showed a higher prevalence in young individuals (26.8%) than in adults (9.8%). According to our results, Colles et al. observed that the prevalence of Campylobacter was significantly higher in the younger starlings, but while younger starlings showed a greater variety of Campylobacter species (C. jejuni, C. coli, and C. lari) compared to adult birds, C. jejuni was the most prevalent species in young birds (14/15), and only one isolate of C. coli was observed [50]. On the contrary, some studies have found no significant correlation between the age of the birds and the presence of Campylobacter spp. [38,52]. Separate logistic regression analyses were performed for adults and chicks to evaluate the effect of the summer season. This was significant only for young birds, indicating a correlation between the two categories, where the highest prevalence of chicks could be attributed to a higher prevalence of Campylobacter fecal shedding during the summer season. Although it would be desirable to carry out studies specifically focused on this subject, most research is often conducted as part of ringing programs or time-limited captures for animal welfare reasons. Previous research has also indicated that C. jejuni is more frequently detected in younger individuals, while C. coli is more common in adults [53]. However, the number of non-C. jejuni isolates obtained in the present study (1 C. coli in young birds, 1 C. lari in adults) were limited, making it impossible to draw any definitive conclusions.
It has been described that gut microbiota composition differs substantially between young and adult birds [54], and although some progress is being made in the wild bird’s microbiota understanding [55], studies regarding the role of bacterial diversity on the presence of Campylobacter spp. are still scarce [54]. Nevertheless, previous studies have confirmed that gut microbiota diversity is strongly affected by the urban transformation of the feeding area, and even though the factors that contribute to intraspecies and interspecies variations are still unknown, feeding on human waste could significantly influence the avian gut microbial community [55].
Similarly, diet can influence the infection rate of Campylobacter among bird species [14]. Omnivorous and insectivorous birds showed a statistically significant higher prevalence compared to herbivorous birds, which agrees with recent studies [44,48]. Some authors confirmed that omnivorous birds, in particular those that forage on the ground, had higher proportions of Campylobacter [44]. Moreover, one of the feeding sources for omnivorous birds is garbage, which could increase the exposure of these animals to Campylobacter strains of human origin [3].
The dynamics of AMR in wildlife present a potential hazard to human and animal health, particularly considering that approximately 40% of emerging human diseases are estimated to have originated in wildlife [47]. Over the last decade, clinically relevant antimicrobial-resistant strains, including those from Campylobacter spp., have been isolated from various wildlife species [16,41]. In our study, CIP was the antimicrobial with the highest resistance rate, followed by TET and NAL, which agrees with other authors’ findings [13,22,24,44,56]. The combination of these three antimicrobials was the most frequent resistance pattern (CIP-NAL-TET). Fluoroquinolones, such as CIP and NAL, have been commonly used in the treatment of campylobacteriosis, but their effectiveness has decreased due to the rapid selection of CIP-resistant Campylobacter isolates [57]. However, CIP remains one of the first-line antimicrobials used in avian medicine, and the spread of CIP-resistant genes can complicate the resolution of infectious diseases. High rates of TET-resistant Campylobacter isolates have also been described in wild birds [22]. The transmission of tetracycline resistance seems to be associated with avian reservoirs due to the high average body temperature, which can promote the conjugation of plasmids carrying TET resistance [58]. The increase in fluoroquinolone-resistant and tetracycline-resistant Campylobacter isolates in public health has led to the use of other antimicrobial families, such as macrolides, for campylobacteriosis complications, but their effectiveness can be compromised by the increase in AMR strains. Fortunately, neither ERY-resistant nor MDR strains were identified in this work, although some authors have reported MDR rates up to 33% in Campylobacter isolates from wild birds [17,24]. The order Ciconiiformes showed the highest rate of AMR, with 91.7% of the isolates tested to AST (12 C. jejuni and 1 C. coli), showing resistance to at least one antimicrobial agent. In the Iberian Peninsula, white storks commonly rely on landfills as a food source [59] and exhibit altered migration patterns, with many individuals shortening or even stopping migration to Africa. In this sense, it has been suggested that open landfills or wastewater sites could be key for the acquisition and dissemination of AMR among wildlife since they are high-risk environments for the presence of antibiotic residues and antimicrobial-resistant bacteria [3,60,61]. Despite a moderate prevalence in our study and an omnivorous diet with occasional scavenging and presence in landfills, the Corvidae family did not show alarming results concerning AMR.
5. Conclusions
The findings of this study underline the relevance of urban birds as reservoirs of antimicrobial-resistant Campylobacter strains that could be disseminated in the environment and transmitted to other animals and humans, with significant implications for public health. The acquired data contribute to enhancing the knowledge of the Campylobacter distribution in wild birds of urban and peri-urban ecosystems. Our results confirm the seasonality of Campylobacter prevalence and highlight the role of taxonomic order, diet, and age of animals as key factors in its distribution among wild birds. Further research should be undertaken on the epidemiology of Campylobacter in wild birds.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.M.-G., M.M. and B.M.-M.; methodology, F.J.G.-P., I.P.-C., A.M.-G. and N.P.-T.; formal analysis, A.M.-G.; investigation, A.M.-G. and B.M.-M.; resources, F.G., F.J.G.-P. and I.P.-C.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M.-G. and B.M.-M.; writing—review and editing, F.J.G.-P., N.P.-T. and M.M.; visualization, A.M.-G.; supervision, B.M.-M. and M.M.; funding acquisition, F.G. and F.J.G.-P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Ministry of Ecological Transition (MITECO) of Spain.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study because of the standard protocol for the sanitary status analysis of animals admitted to the GREFA Wildlife Hospital. Therefore, no extra handling of the animals was necessary to collect the samples, and no extra samples were collected outside the hospital’s standard work protocol. For this reason, according to the current legislation at the time of the research (Directive 2010/63/EU), it is not mandatory to have the approval of an Ethics Committee.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request from the corresponding author (A.M.-G.).
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank the Laboratorio Central de Veterinaria (LCV), Grupo de Estudio de Medicina y Conservación de Animales Salvajes (GEMAS) Research Group, and all the GREFA volunteers for their technical support. We would like to extend special thanks to Cristina Andreu from the Methodology and Statistics Advisory Group of the European University of Madrid for her advice.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have influenced the work reported in this paper.
References
- Miranda, A.C. Mechanisms of Behavioural Change in Urban Animals: The Role of Microevolution and Phenotypic Plasticity. In Ecology and Conservation of Birds in Urban Environments; Murgui, E., Hedblom, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 113–132. ISBN 978-3-319-43314-1. [Google Scholar]
- Plaza, P.I.; Lambertucci, S.A. How Are Garbage Dumps Impacting Vertebrate Demography, Health, and Conservation? Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 12, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Maldonado, B.; Vega, S.; Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Lorenzo-Rebenaque, L.; de Frutos, C.; González, F.; Revuelta, L.; Marin, C. Urban Birds: An Important Source of Antimicrobial Resistant Salmonella Strains in Central Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 72, 101519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, N.I.; Correia, R.A.; Silva, J.P.; Pacheco, C.; Catry, I.; Atkinson, P.W.; Gill, J.A.; Franco, A.M.A. Are White Storks Addicted to Junk Food? Impacts of Landfill Use on the Movement and Behaviour of Resident White Storks (Ciconia ciconia) from a Partially Migratory Population. Mov. Ecol. 2016, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, P.I.; Lambertucci, S.A. More Massive but Potentially Less Healthy: Black Vultures Feeding in Rubbish Dumps Differed in Clinical and Biochemical Parameters with Wild Feeding Birds. PeerJ 2018, 6, e4645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, B.; Kang, M.; Jang, H. Genetic Characterization and Epidemiological Implications of Campylobacter Isolates from Wild Birds in South Korea. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2019, 66, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA); European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). The European Union One Health 2022 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. 2023, 21, e8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Havelaar, A.H.; Ivarsson, S.; Löfdahl, M.; Nauta, M.J. Estimating the True Incidence of Campylobacteriosis and Salmonellosis in the European Union, 2009. Epidemiol. Infect. 2013, 141, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera-Ramírez, A.M.; McEwan, N.R.; Stanley, K.; Nava-Diaz, R.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G. A Systematic Review on the Role of Wildlife as Carriers and Spreaders of Campylobacter spp. Animals 2023, 13, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority; European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. The European Union One Health 2021 Zoonoses Report. EFSA J. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. 2022, 20, e07666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamura, M.; Kaneko, M.; Ojima, S.; Sano, H.; Shindo, J.; Shirafuji, H.; Yamamoto, S.; Tanabe, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Hu, D.-L. Differential Distribution of Salmonella Serovars and Campylobacter spp. Isolates in Free-Living Crows and Broiler Chickens in Aomori, Japan. Microbes Environ. 2018, 33, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maëssar, M.; Tedersoo, T.; Meremäe, K.; Roasto, M. The Source Attribution Analysis Revealed the Prevalent Role of Poultry over Cattle and Wild Birds in Human Campylobacteriosis Cases in the Baltic States. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0235841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minias, P. Contrasting Patterns of Campylobacter and Salmonella Distribution in Wild Birds: A Comparative Analysis. J. Avian Biol. 2020, 51, e02426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldenström, J.; Broman, T.; Carlsson, I.; Hasselquist, D.; Achterberg, R.P.; Wagenaar, J.A.; Olsen, B. Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni, Campylobacter lari, and Campylobacter coli in Different Ecological Guilds and Taxa of Migrating Birds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 5911–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greig, J.; Rajić, A.; Young, I.; Mascarenhas, M.; Waddell, L.; LeJeune, J. A Scoping Review of the Role of Wildlife in the Transmission of Bacterial Pathogens and Antimicrobial Resistance to the Food Chain. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-K.; Oh, J.-Y.; Jeong, O.-M.; Moon, O.-K.; Kang, M.-S.; Jung, B.-Y.; An, B.-K.; Youn, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-R.; Jang, I.; et al. Prevalence of Campylobacter Species in Wild Birds of South Korea. Avian Pathol. 2017, 46, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.A.; Gulhan, T. Campylobacter in Wild Birds: Is It an Animal and Public Health Concern? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 812591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, N.P.; Midwinter, A.; Holland, B.; Collins-Emerson, J.; Pattison, R.; Colles, F.; Carter, P. Molecular Epidemiology of Campylobacter jejuni Isolates from Wild-Bird Fecal Material in Children’s Playgrounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 779–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawiec, M.; Woźniak-Biel, A.; Bednarski, M.; Wieliczko, A. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Genotypic Characteristic of Campylobacter spp. Isolates from Free-Living Birds in Poland. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2017, 17, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kürekci, C.; Sakin, F.; Epping, L.; Knüver, M.-T.; Semmler, T.; Stingl, K. Characterization of Campylobacter spp. Strains Isolated From Wild Birds in Turkey. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 712106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Holm, M.; Frost, I.; Hasso-Agopsowicz, M.; Abbas, K. Global and Regional Burden of Attributable and Associated Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance Avertable by Vaccination: Modelling Study. BMJ Glob. Health 2023, 8, e011341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marotta, F.; Garofolo, G.; Di Marcantonio, L.; Di Serafino, G.; Neri, D.; Romantini, R.; Sacchini, L.; Alessiani, A.; Di Donato, G.; Nuvoloni, R.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance Genotypes and Phenotypes of Campylobacter jejuni Isolated in Italy from Humans, Birds from Wild and Urban Habitats, and Poultry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepanska, B.; Andrzejewska, M.; Spica, D.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli Isolated from Children and Environmental Sources in Urban and Suburban Areas. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Luo, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, C.; Li, M.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Chang, H.; Ji, J.; Sen, K.; et al. Emergence of Genetic Diversity and Multi-Drug Resistant Campylobacter jejuni From Wild Birds in Beijing, China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mencía-Gutiérrez, A.; Martín-Maldonado, B.; Pastor-Tiburón, N.; Moraleda, V.; González, F.; García-Peña, F.J.; Pérez-Cobo, I.; Revuelta, L.; Marín, M. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter from Wild Birds of Prey in Spain. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 79, 101712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryjanowski, P.; Nowakowski, J.J.; Indykiewicz, P.; Andrzejewska, M.; Śpica, D.; Sandecki, R.; Mitrus, C.; Goławski, A.; Dulisz, B.; Dziarska, J.; et al. Campylobacter in Wintering Great Tits Parus Major in Poland. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 7570–7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, F.; Péguilhan, R.; Turgeon, N.; Veillette, M.; Baray, J.-L.; Deguillaume, L.; Amato, P.; Duchaine, C. Quantification of Antibiotic Resistance Genes (ARGs) in Clouds at a Mountain Site (Puy de Dôme, Central France). Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, A.; Hughes, J.M. Critical Importance of a One Health Approach to Antimicrobial Resistance. EcoHealth 2019, 16, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royal Decree 53/2013, 1 February, By which Establish the Basic Standards for the Protection of Animals Used in Experimen-tation and Other Scientific Purposes, Including Teaching [Real Decreto 53/2013, de 1 de Febrero, por el que se Establecen las Normas Básicas Aplicables para la Protección de los Animales Utilizados en Experimentación y otros Fines Científicos, Incluyendo la Docencia]. BOE 34, de 8 de Febrero de 2013]. Available online: https://www.boe.es/eli/es/rd/2013/02/01/53/con (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Directive 2010/63/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2010 on the Protection of Animals Used for Scientific Purposes. OJEU L276, 33–79. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2010/63/oj (accessed on 7 May 2023).
- Ritchie, B.W.; Harrison, G.J.; Harrison, L.R. (Eds.) Avian Medicine: Principles and Application; Wingers Publishing Incorporated: Lake Worth, FL, USA, 1994; ISBN 978-0-9636996-0-2. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 10272-1:2017; Microbiology of the Food Chain. Horizontal Method for Detection and Enumeration of Campylobacter spp. Part 1: Detection Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63225.html (accessed on 7 May 2024).
- Wang, G.; Clark, C.G.; Taylor, T.M.; Pucknell, C.; Barton, C.; Price, L.; Woodward, D.L.; Rodgers, F.G. Colony Multiplex PCR Assay for Identification and Differentiation of Campylobacter jejuni, C. coli, C. lari, C. upsaliensis, and C. fetus subsp. fetus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 4744–4747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denis, M.; Soumet, C.; Rivoal, K.; Ermel, G.; Blivet, D.; Salvat, G.; Colin, P. Development of a m-PCR Assay for Simultaneous Identification of Campylobacter jejuni and C. coli. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 29, 406–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. Data from the EUCAST MIC Distribution Website. Available online: https://www.eucast.org/ (accessed on 18 June 2023).
- Magiorakos, A.-P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, O.M.; Snyder, W.E.; Owen, J.P. Are We Overestimating Risk of Enteric Pathogen Spillover from Wild Birds to Humans? Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2020, 95, 652–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hald, B.; Skov, M.N.; Nielsen, E.M.; Rahbek, C.; Madsen, J.J.; Wainø, M.; Chriél, M.; Nordentoft, S.; Baggesen, D.L.; Madsen, M. Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Wild Birds on Danish Livestock Farms. Acta Vet. Scand. 2016, 58, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramonaite, S.; Kudirkiene, E.; Tamuleviciene, E.; Leviniene, G.; Malakauskas, A.; Gölz, G.; Alter, T.; Malakauskas, M. Prevalence and Genotypes of Campylobacter jejuni from Urban Environmental Sources in Comparison with Clinical Isolates from Children. J. Med. Microbiol. 2014, 63, 1205–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, J.I.; Shriver, W.G. Prevalence of Three Campylobacter Species, C. jejuni, C. coli, and C. lari, Using Multilocus Sequence Typing in Wild Birds of the Mid-Atlantic Region, USA. J. Wildl. Dis. 2014, 50, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troxler, S.; Hess, C.; Konicek, C.; Knotek, Z.; Barták, P.; Hess, M. Microdilution Testing Reveals Considerable and Diverse Antimicrobial Resistance of Escherichia coli, Thermophilic Campylobacter spp. and Salmonella spp. Isolated from Wild Birds Present in Urban Areas. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2017, 63, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekian, M.; Shagholian, J.; Hosseinpour, Z. Pathogen Presence in Wild Birds Inhabiting Landfills in Central Iran. EcoHealth 2021, 18, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konicek, C.; Vodrážka, P.; Barták, P.; Knotek, Z.; Hess, C.; Račka, K.; Hess, M.; Troxler, S. Detection of Zoonotic Pathogens in Wild Birds in the Cross-Border Region Austria–Czech Republic. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hock, L.; Herold, M.; Walczak, C.; Schoos, A.; Penny, C.; Cauchie, H.-M.; Ragimbeau, C. Environmental Dynamics of Campylobacter jejuni Genotypes Circulating in Luxembourg: What Is the Role of Wild Birds? Microb. Genom. 2023, 9, mgen001031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, K.; Kubokura, Y.; Kaneko, K.; Totake, Y.; Ogawa, M. Occurrence of Campylobacter jejuni in Free-Living Wild Birds from Japan. J. Wildl. Dis. 1988, 24, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szczepańska, B.; Kamiński, P.; Andrzejewska, M.; Śpica, D.; Kartanas, E.; Ulrich, W.; Jerzak, L.; Kasprzak, M.; Bocheński, M.; Klawe, J.J. Prevalence, Virulence, and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in White Stork Ciconia ciconia in Poland. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2015, 12, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, K.E.; Williams, N.J.; Bennett, M. ‘Disperse Abroad in the Land’: The Role of Wildlife in the Dissemination of Antimicrobial Resistance. Biol. Lett. 2016, 12, 20160137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casalino, G.; D’Amico, F.; Dinardo, F.R.; Bozzo, G.; Napoletano, V.; Camarda, A.; Bove, A.; Lombardi, R.; D’Onghia, F.P.; Circella, E. Prevalence and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in Wild Birds from a Wildlife Rescue Centre. Animals 2022, 12, 2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deeming, D.C.; Du Feu, C.R. Measurement of Brood Patch Temperature of British Passerines Using an Infrared Thermometer. Bird Study 2008, 55, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colles, F.M.; McCarthy, N.D.; Howe, J.C.; Devereux, C.L.; Gosler, A.G.; Maiden, M.C.J. Dynamics of Campylobacter Colonization of a Natural Host, Sturnus vulgaris (European Starling). Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohan, V. Faeco-Prevalence of Campylobacter jejuni in Urban Wild Birds and Pets in New Zealand. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado-Tarifa, E.; Torralbo, A.; Borge, C.; Cerdà-Cuéllar, M.; Ayats, T.; Carbonero, A.; García-Bocanegra, I. Genetic Diversity and Antimicrobial Resistance of Campylobacter and Salmonella Strains Isolated from Decoys and Raptors. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glünder, G.; Neumann, U.; Braune, S. Occurrence of Campylobacter spp. in Young Gulls, Duration of Campylobacter Infection and Reinfection by Contact. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 1992, 39, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grond, K.; Sandercock, B.K.; Jumpponen, A.; Zeglin, L.H. The Avian Gut Microbiota: Community, Physiology and Function in Wild Birds. J. Avian Biol. 2018, 49, e01788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Chen, J.; Liu, K.; Tang, M.; Yang, Y. The Avian Gut Microbiota: Diversity, Influencing Factors, and Future Directions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 934272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksomaitiene, J.; Ramonaite, S.; Tamuleviciene, E.; Novoslavskij, A.; Alter, T.; Malakauskas, M. Overlap of Antibiotic Resistant Campylobacter jejuni MLST Genotypes Isolated From Humans, Broiler Products, Dairy Cattle and Wild Birds in Lithuania. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Feye, K.M.; Shi, Z.; Pavlidis, H.O.; Kogut, M.; Ashworth, A.J.; Ricke, S.C. A Historical Review on Antibiotic Resistance of Foodborne Campylobacter. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuevas-Ferrando, E.; Guirado, P.; Miró, E.; Iglesias-Torrens, Y.; Navarro, F.; Alioto, T.S.; Gómez-Garrido, J.; Madrid, C.; Balsalobre, C. Tetracycline Resistance Transmission in Campylobacter Is Promoted at Temperatures Resembling the Avian Reservoir. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 244, 108652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineda-Pampliega, J.; Ramiro, Y.; Herrera-Dueñas, A.; Martinez-Haro, M.; Hernández, J.M.; Aguirre, J.I.; Höfle, U. A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Evaluation of the Effects of Foraging on Landfills on White Stork Nestlings. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 775, 145197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Maldonado, B.; Rodríguez-Alcázar, P.; Fernández-Novo, A.; González, F.; Pastor, N.; López, I.; Suárez, L.; Moraleda, V.; Aranaz, A. Urban Birds as Antimicrobial Resistance Sentinels: White Storks Showed Higher Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia coli Levels Than Seagulls in Central Spain. Animals 2022, 12, 2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zothanpuia; Zomuansangi, R.; Leo, V.V.; Passari, A.K.; Yadav, M.K.; Singh, B.P. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Profiling of Bacterial Communities Recovered from Effluents of Municipal Solid Waste Dumping Site. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).