Comparison of Xylazine and Lidocaine Infusion versus Medetomidine Continuous Rate Infusion during General Anesthesia with Isoflurane in Horses Undergoing Emergency Laparotomy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- The X group received preoperative sedation with xylazine (0.6 mg/kg i.v.) followed by butorphanol (0.02 mg/kg i.v.) and an intraoperative CRI of lidocaine (0.05 mg/kg/min i.v.) [31];
- -
- The M group received medetomidine (7 μg/kg i.v.) followed by morphine (0.1 mg/kg i.m.) and an intraoperative CRI of medetomidine (3.5 μg/kg/h i.v.) [13].
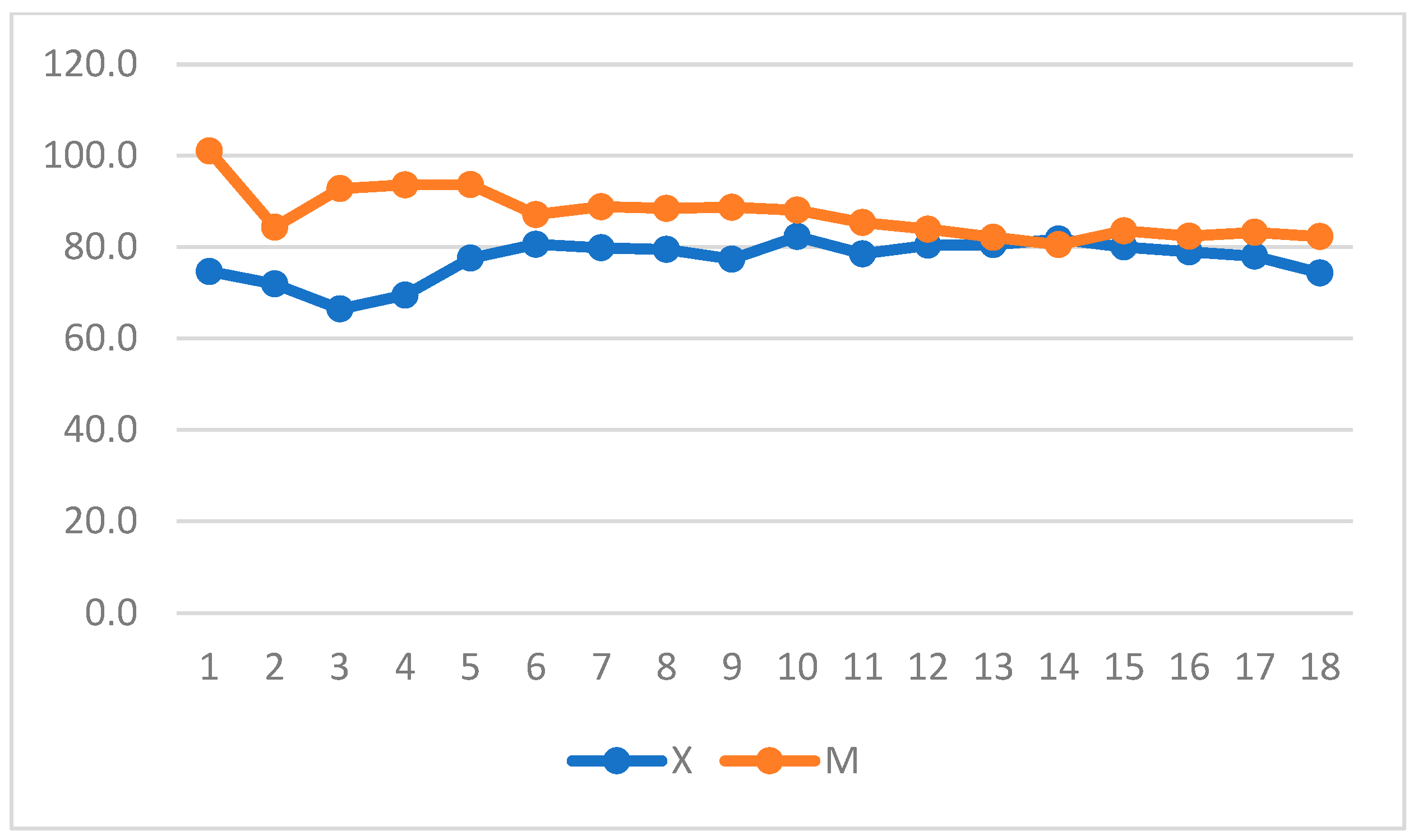
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pascoe, P.J.; McDonell, W.N.; Trim, C.M.; Van Gorder, J. Mortality Rates and Associated Factors in Equine Colic Operations—A Retrospective Study of 341 Operations. Can. Vet. J. 1983, 24, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Mee, A.M.; Cripps, P.J.; Jones, R.S. A Retrospective Study of Mortality Associated with General Anaesthesia in Horses: Emergency Procedures. Vet. Rec. 1998, 142, 307–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, G.M.; Eastment, J.K.; Wood, J.L.N.; Taylor, P.M. The Confidential Enquiry into Perioperative Equine Fatalities (CEPEF): Mortality Results of Phases 1 and 2. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2002, 29, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopster, K. Anaesthesia-Related Equine Fatalities: How Good Are We? Equine Vet. J. 2018, 50, 710–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, B. Equine Anaesthesia: An Assessment of Techniques Used in Clinical Practice. Equine Vet. J. 1969, 1, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamerling, S. Pharmacological Profile of Medetomidine in the Equine. Acta. Vet. Scand. 1991, 87, 161–162. [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen, R.; Savola, J.-M.; Saano, V.; Nyman, L. Characterization of the Selectivity, Specificity and Potency of Medetomidine as an A2-Adrenoceptor Agonist. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 150, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- England, G.; Clarke, K.; Goosens, L. A Comparison of the Sedative Effects of Medetomidine and Xylazine in the Horse. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 1991, 18, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffey, E.P.; Pascoe, P.J.; Woliner, M.J.; Berryman, E.R. Effects of Xylazine Hydrochloride during Isoflurane-Induced Anesthesia in Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 61, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.C.; Steffey, E.P. Use of Opioids for Pain and Anesthetic Management in Horses. Vet. Clin. North Am.—Equine Pract. 2002, 18, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringer, S.; Portier, K.G.; Fourel, I.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Development of a Xylazine Constant Rate Infusion with or without Butorphanol for Standing Sedation of Horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2012, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Clarke, K.W.; Vainio, O.; Aliabadi, F.; Demuth, D. Pharmacokinetics of Medetomidine in Ponies and Elaboration of a Medetomidine Infusion Regime Which Provides a Constant Level of Sedation. Res. Vet. Sci. 1999, 67, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalchofner, K.S.; Ringer, S.K.; Boller, J.; Kästner, S.B.R.; Lischer, C.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Clinical Assessment of Anesthesia with Isoflurane and Medetomidine in 300 Equidae. Pferdeheilkunde 2006, 22, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Neges, K.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Müller, J.; Fürst, A.; Kästner, S. The Isoflurane Sparing Effect of a Medetomidine Constant Rate Infusion in Horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2003, 30, 92–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gozalo-Marcilla, M.; Gasthuys, F.; Schauvliege, S. Partial Intravenous Anaesthesia in the Horse: A Review of Intravenous Agents Used to Supplement Equine Inhalation Anaesthesia: Part 2: Opioids and Alpha-2 Adrenoceptor Agonists. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2015, 42, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creighton, C.M.; Lemke, K.A.; Lamont, L.A.; Horney, B.S.; Riley, C.B. Comparison of the Effects of Xylazine Bolus versus Medetomidine Constant Rate Infusion on Cardiopulmonary Function and Depth of Anesthesia in Horses Anesthetized with Isoflurane. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2012, 240, 991–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steffey, E.P.; Howland Jr, D. Cardiovascular Effects of Halothane in the Horse. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1978, 39, 611–615. [Google Scholar]
- Menzies, M.P.L.; Ringer, S.K.; Conrot, A.; Theurillat, R.; Kluge, K.; Kutter, A.P.N.; Jackson, M.; Thormann, W.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Cardiopulmonary Effects and Anaesthesia Recovery Quality in Horses Anaesthetized with Isoflurane and Low-dose S-ketamine or Medetomidine Infusions. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2016, 43, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valverde, A.; Doherty, T.J.; Hernández, J.; Davies, W. Effect of Lidocaine on the Minimum Alveolar Concentration of Isoflurane in Dogs. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2004, 31, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doherty, T.J.; Frazier, D.L. Effect of Intravenous Lidocaine on Halothane Minimum Alveolar Concentration in Ponies. Equine Vet. J. 1998, 30, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikiti, T.B.; Hellebrekers, L.J.; Van Dijk, P. Effects of Intravenous Lidocaine on Isoflurane Concentration, Physiological Parameters, Metabolic Parameters and Stress-related Hormones in Horses Undergoing Surgery. J. Vet. Med. Ser. A 2003, 50, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driessen, B. Intravenöse Lidokain-Infusion Bei Der Kombinationsnarkose in Der Bauchhöhlenchirurgie: Hintergrund Und Klinische Erfahrungen. Pferdeheilkunde 2005, 21, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Valverde, A.; Gunkel, C.; Doherty, T.J.; Giguère, S.; Pollak, A.S. Effect of a Constant Rate Infusion of Lidocaine on the Quality of Recovery from Sevoflurane or Isoflurane General Anaesthesia in Horses. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 37, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, J.C.; White, K.L.; Johnson, C.B.; Taylor, P.M.; Doherty, T.J.; Waterman-Pearson, A.E. Investigation of the EEG Effects of Intravenous Lidocaine during Halothane Anaesthesia in Ponies. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2005, 32, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, S.A.; Sanchez, L.C.; Merritt, A.M.; Doherty, T.J. Effect of Systemic Lidocaine on Visceral and Somatic Nociception in Conscious Horses. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 37, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwood, L.L. Postoperative Management of the Large Colon Volvulus Patient. Vet. Clin. Equine Pract. 2004, 20, 167–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hoogmoed, L.M.; Nieto, J.E.; Snyder, J.R.; Harmon, F.A. Survey of Prokinetic Use in Horses with Gastrointestinal Injury. Vet. Surg. 2004, 33, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.D.; Lester, G.D.; Sanchez, L.C.; Merritt, A.M.; Roussel, A.J. Evaluation of Risk Factors Associated with Development of Postoperative Ileus in Horses. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 225, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brianceau, P.; Chevalier, H.; Karas, A.; Court, M.H.; Bassage, L.; Kirker-Head, C.; Provost, P.; Paradis, M.R. Intravenous Lidocaine and Small-intestinal Size, Abdominal Fluid, and Outcome after Colic Surgery in Horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2002, 16, 736–741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malone, E.; Ensink, J.O.S.; Turner, T.; Wilson, J.; Andrews, F.; Keegan, K.; Lumsden, J. Intravenous Continuous Infusion of Lidocaine for Treatment of Equine Ileus. Vet. Surg. 2006, 35, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nannarone, S.; Spadavecchia, C. Evaluation of the Clinical Efficacy of Two Partial Intravenous Anesthetic Protocols, Compared with Isoflurane Alone, to Maintain General Anesthesia in Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2012, 73, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringer, S.K.; Kalchofner, K.; Boller, J.; Fürst, A.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. A Clinical Comparison of Two Anaesthetic Protocols Using Lidocaine or Medetomidine in Horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2007, 34, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pöppel, N.; Hopster, K.; Geburek, F.; Kästner, S. Influence of Ketamine or Xylazine Supplementation on Isoflurane Anaesthetized Horses-a Controlled Clinical Trial. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2015, 42, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devisscher, L.; Schauvliege, S.; Dewulf, J.; Gasthuys, F. Romifidine as a Constant Rate Infusion in Isoflurane Anaesthetized Horses: A Clinical Study. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2010, 37, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauvliege, S.; Marcilla, M.G.; Verryken, K.; Duchateau, L.; Devisscher, L.; Gasthuys, F. Effects of a Constant Rate Infusion of Detomidine on Cardiovascular Function, Isoflurane Requirements and Recovery Quality in Horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2011, 38, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacks, M.; Ringer, S.K.; Bischofberger, A.S.; Berchtold, S.M.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Clinical Comparison of Dexmedetomidine and Medetomidine for Isoflurane Balanced Anaesthesia in Horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2017, 44, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, K.; Tsubakishita, S.; Futaoka, S.; Ueda, I.; Hamaguchi, H.; Seno, T.; Katoh, S.; Izumisawa, Y.; Kotani, T.; Muir, W.W. Cardiovascular Effects of Medetomidine, Detomidine and Xylazine in Horses. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2000, 62, 1025–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Bettschart, R.W.; Vainio, O.; Marlin, D.; Clarke, K.W. Cardiopulmonary Effects of a Two Hour Medetomidine Infusion and Its Antagonism by Atipamezole in Horses and Ponies. J. Vet. Anaesth. 1999, 26, 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringer, S.K.; Schwarzwald, C.C.; Portier, K.G.; Ritter, A.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Effects on Cardiopulmonary Function and Oxygen Delivery of Doses of Romifidine and Xylazine Followed by Constant Rate Infusions in Standing Horses. Vet. J. 2013, 195, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Dicht, S.; Vullo, C.; Frotzler, A.; Kuemmerle, J.M.; Ringer, S.K. A Clinical Study on the Effect in Horses during Medetomidine–Isoflurane Anaesthesia, of Butorphanol Constant Rate Infusion on Isoflurane Requirements, on Cardiopulmonary Function and on Recovery Characteristics. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2011, 38, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.; Clutton, R.E.; Blissitt, K.J.; Chase-Topping, M.E. Effects of Peri-Operative Morphine Administration during Halothane Anaesthesia in Horses. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2005, 32, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLARKE, K.W.; PATON, B.S. Combined Use of Detomidine with Opiates in the Horse. Equine Vet. J. 1988, 20, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corletto, F.; Raisis, A.A.; Brearley, J.C. Comparison of Morphine and Butorphanol as Pre-Anaesthetic Agents in Combination with Romifidine for Field Castration in Ponies. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2005, 32, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannarone, S.; Cenani, A.; Gialletti, R.; Pepe, M. Clinical Comparison of Two Regimens of Lidocaine Infusion in Horses Undergoing Laparotomy for Colic. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2015, 42, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.A.; Lin, H.C.; Hanson, R.R.; Hayes, T.L. Effects of Intravenous Lidocaine Overdose on Cardiac Electrical Activity and Blood Pressure in the Horse. Equine Vet. J. 2001, 33, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Ba, Z.F.; Chaudry, I.H. Hepatic Extraction of Indocyanine Green Is Depressed Early in Sepsis despite Increased Hepatic Blood Flow and Cardiac Output. Arch. Surg. 1991, 126, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feary, D.J.; Mama, K.R.; Wagner, A.E.; Thomasy, S. Influence of General Anesthesia on Pharmacokinetics of Intravenous Lidocaine Infusion in Horses. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 574–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grubb, T.L.; Muir III, W.W. Anaesthetic Emergencies and Complications—Part 1. Equine Vet. Educ. 1998, 10, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, A.E. Complications in Equine Anesthesia. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2008, 24, 735–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidwell, L.A.; Bramlage, L.R.; Rood, W.A. Equine Perioperative Fatalities Associated with General Anaesthesia at a Private Practice–a Retrospective Case Series. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2007, 34, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navas de Solís, C.; McKenzie, H.C. Serum Concentrations of Lidocaine and Its Metabolites MEGX and GX During and After Prolonged Intravenous Infusion of Lidocaine in Horses after Colic Surgery. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2007, 27, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, E.J.; McKenzie, H.C.; Brown, J.A.; De Solis, C.N. Serum Concentrations of Lidocaine and Its Metabolites after Prolonged Infusion in Healthy Horses. Equine Vet. J. 2008, 40, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valverde, A.; Black, B.; Cribb, N.C.; Hathway, A.; Daw, A. Assessment of Unassisted Recovery from Repeated General Isoflurane Anesthesia in Horses Following Post-Anesthetic Administration of Xylazine or Acepromazine or a Combination of Xylazine and Ketamine. Vet. Anaesth. Analg. 2013, 40, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kälin, I.; Henze, I.S.; Ringer, S.K.; Torgerson, P.R.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R. Comparison of Recovery Quality Following Medetomidine versus Xylazine Balanced Isoflurane Anaesthesia in Horses: A Retrospective Analysis. Animals 2021, 11, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, S.; Hopster, K.; Sill, V.; Rohn, K.; Kästner, S.B.R. Comparison between Head-tail-rope Assisted and Unassisted Recoveries in Healthy Horses Undergoing General Anesthesia for Elective Surgeries. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rüegg, M.; Bettschart-Wolfensberger, R.; Hartnack, S.; Junge, H.K.; Theiss, F.; Ringer, S.K. Comparison of Non-Assisted versus Head and Tail Rope-Assisted Recovery after Emergency Abdominal Surgery in Horses. Pferdeheilkunde 2016, 32, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glitz, F.; Lorber, K.; Oppen, T.V.; Bubeck, K.; Bartmann, C.P.; Deegen, E. Recovery Phase of Horses after General Anesthesia with Inhalants with and without Postanesthetic Sedation with Xylazine (Rompun®). Pferdeheilkunde Equine Med. 2001, 17, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, M.J. What Really Causes Colic in Horses? Epidemiology’s Role in Elucidating the Ultimate Multi-Factorial Disease. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 413–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeves, M.J.; Salman, M.D.; Smith, G. Risk Factors for Equine Acute Abdominal Disease (Colic): Results from a Multi-Center Case-Control Study. Prev. Vet. Med. 1996, 26, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straticò, P.; Varasano, V.; Palozzo, A.; Guerri, G.; Celani, G.; Revelant, O.; Petrizzi, L. Retrospective Study on Risk Factors and Short-Term Outcome of Horses Referred for Colic from 2016 to 2022. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, N.; Gibbs, P.; Woods, A. Dietary and Other Management Factors Associated with Equine Colic. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc 1999, 45, 96–98. [Google Scholar]
- Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Kopral, C.A.; Seitzinger, A.H.; Garber, L.P.; Forde, K.; White, N.A. Estimate of the National Incidence of and Operation-Level Risk Factors for Colic among Horses in the United States, Spring 1998 to Spring 1999. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 219, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, N.P.; Smith, J.; Edwards, G.B.; Proudman, C.J. Equine Surgical Colic: Risk Factors for Postoperative Complications. Equine Vet. J. 2002, 34, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, D.C.; Pinchbeck, G.L.; Proudman, C.J.; Clough, H.E. Is Equine Colic Seasonal? Novel Application of a Model Based Approach. BMC Vet. Res. 2006, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kaya, G.; Sommerfeld-Stur, I.; Iben, C. Risk Factors of Colic in Horses in Austria. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2009, 93, 339–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, G.A.; Ertzman-Ginsburg, R.; Steinman, A.; Milgram, J. Initial Investigation of Mortality Rates and Prognostic Indicators in Horses with Colic in Israel: A Retrospective Study. Equine Vet. J. 2009, 41, 482–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtis, L.; Burford, J.H.; England, G.C.W.; Freeman, S.L. Risk Factors for Acute Abdominal Pain (Colic) in the Adult Horse: A Scoping Review of Risk Factors, and a Systematic Review of the Effect of Management-Related Changes. PLoS ONE. 2019, 14, e0219307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bowden, A.; England, G.C.W.; Brennan, M.L.; Mair, T.S.; Furness, W.A.; Freeman, S.L.; Burford, J.H. Indicators of Critical’ Outcomes in 941 Horses Seen out-of-Hours’ for Colic. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruíz-López, P.; Cuypers, C.; Schauvliege, S. Xylazine Infusion during Equine Colic Anesthesia with Isoflurane and Lidocaine: A Retrospective Study. Animals 2023, 13, 2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitehair, K.J.; Steffey, E.P.; Willits, N.H.; Woliner, M.J. Recovery of Horses from Inhalation Anesthesia. Am. J. Veter. Res. 1993, 54, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


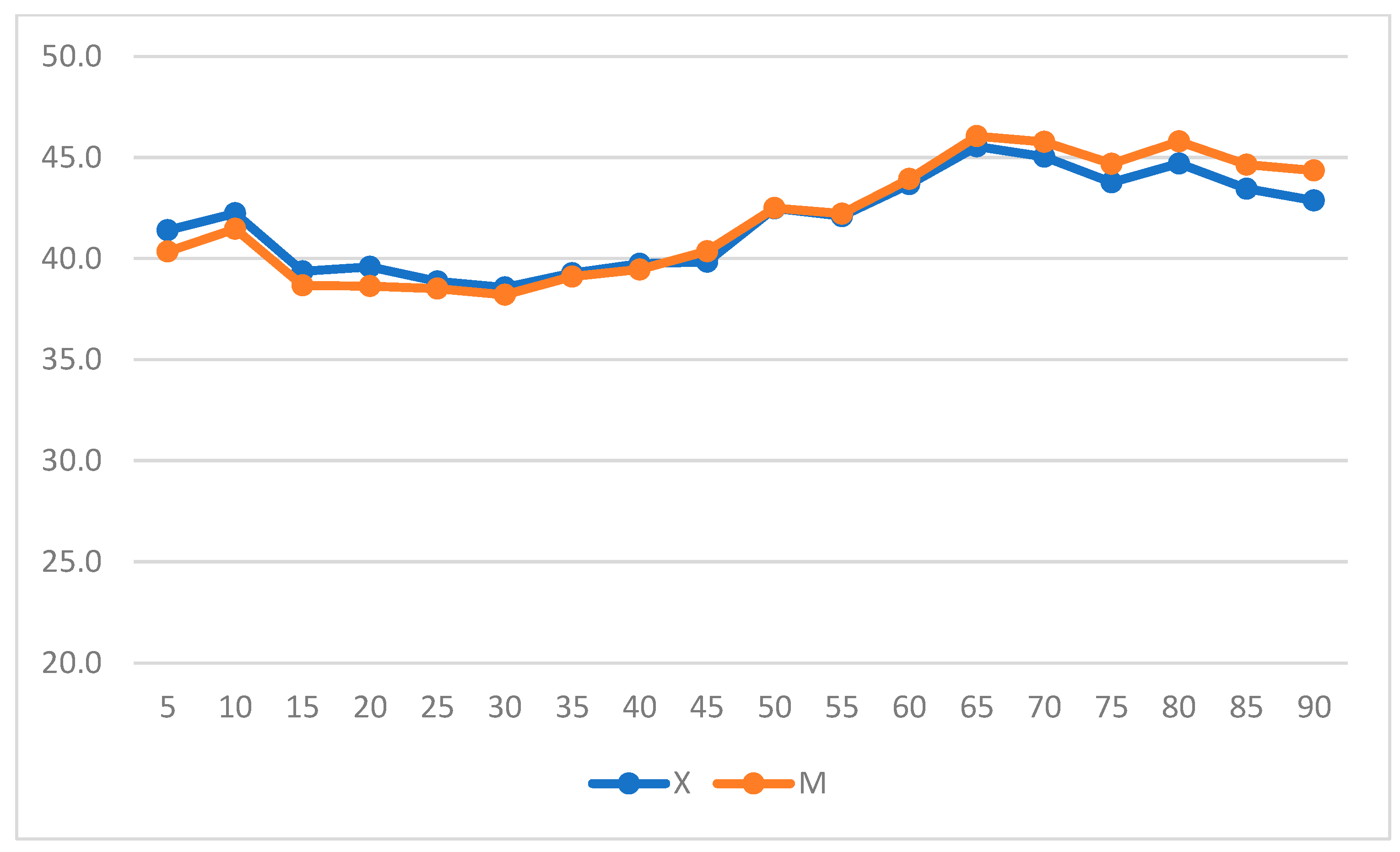
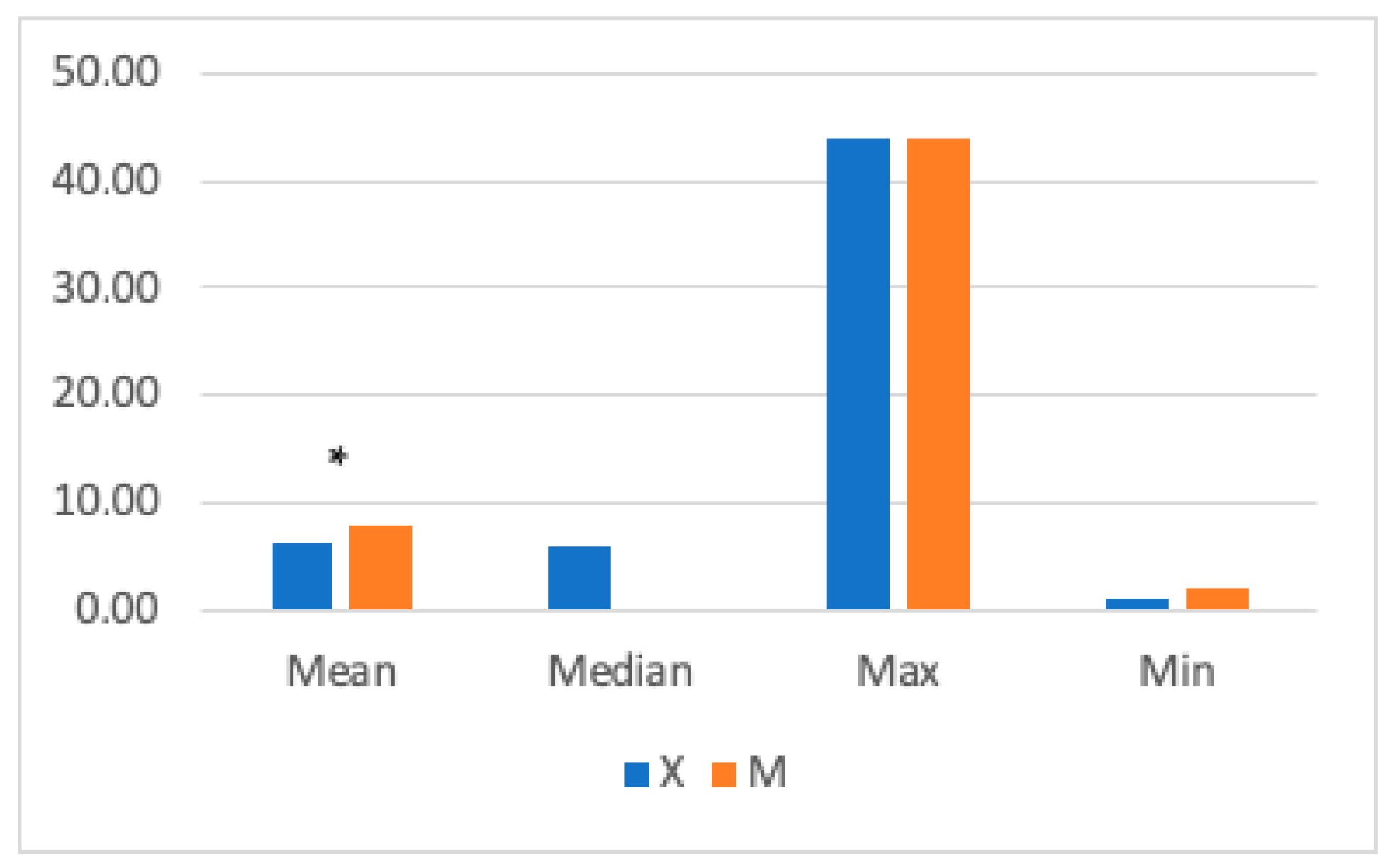
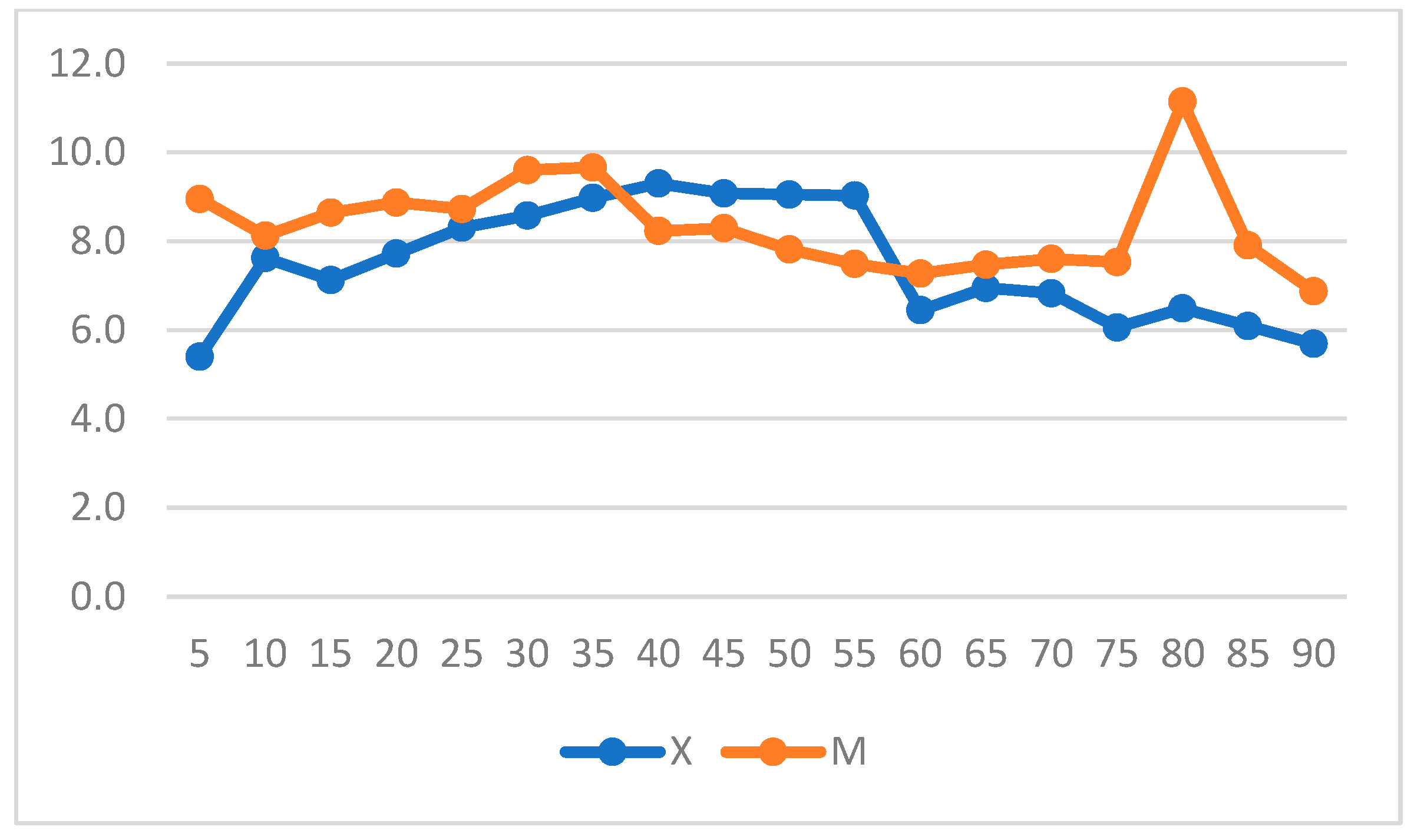

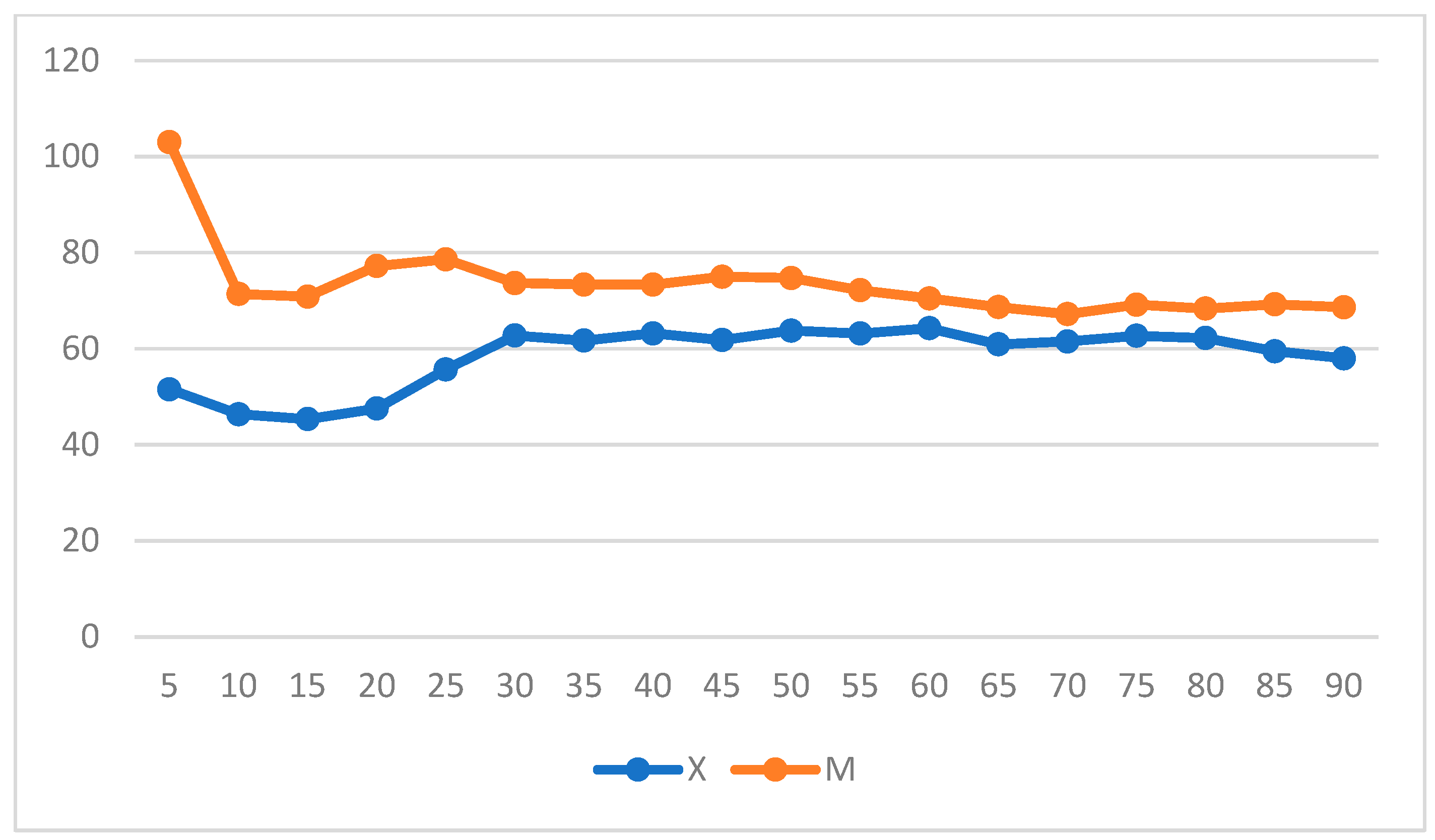
| Score | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Excellent recovery | The horse is capable of standing at first attempt. |
| 2 | Very good | The horse remained calm; two attempts to stand. |
| 3 | Good | The horse remained calm; >2 attempts. |
| 4 | Poor | Excitement during recovery with danger to the horse; >2 attempts. |
| 5 | Very poor | Severe excitement during recovery with injury to the horse. |
| Variable | Group X | Group M | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 14 ± 10 years | 10 ± 5 | 0.270 |
| Weight | 460.3 ± 136.53 | 462.5 ± 115 | 0.215 |
| Female | 39.1% (18) | 30.4% (14) | 0.25 |
| Male | 60.9% (27) | 43.5% (20) | |
| Unknown gender | 0 | 52.2% (12) |
| Outcome | Group X % (n) | Group M % (n) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duration of anesthesia (min) | 105.4 ± 36.58 | 111.1 ± 38.42 | 0.664 |
| Duration of surgery (min) | 79.6 ± 36.43 | 90.1 ± 32.70 | 0.598 |
| Time to extubation (min) | 18.8 ± 13.87 | 16.8 ± 10.6 | 0.055 |
| Time in sternal recumbency (min) | 35.6 ± 17.23 | 43.42 ± 17.04 | 0.815 |
| Time to standing | 58.6 ± 27.82 | 79.5 ± 49.18 | 0.042 * |
| Score | Group X % (n) | Group M % (n) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 41.9% (13) | 90.5% (19) | 0.24 |
| 2 | 19.4% (6) | 4.8% (1) | |
| 3 | 16.1% (5) | 4.8% (1) | |
| 4 | 16.1% (5) | 0 | |
| 5 | 6.4% (2) | 0 |
| Outcome | Group X % (n) (n = 5) | Group M % (n) (n = 46) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 66.7% (30) | 71.7% (33) | 0.255 |
| Intraoperative euthanasia | 33.3% (15) | 21.7% (10) | |
| Post-operative death | 0 | 6.6% (3) |
| Variable | Group X | Group M | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| MAC-Iso | 1.2 ± 0.24 | 1.2 ± 0.32 | 0.5 |
| PET-CO2 | 42.7 ± 11.67 | 42 ± 8.66 | 0.3 |
| SAP | 111.5 ± 23 | 112.2 ± 25.35 | 0.6 |
| MAP | 78.8 ± 18.71 | 85 ± 21.29 | 0.01 * |
| DAP | 59.68 ± 19.12 | 70.43 ± 20.09 | 0.02 * |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Straticò, P.; Guerri, G.; Bandera, L.; Celani, G.; Di Nunzio, L.; Petrizzi, L.; Varasano, V. Comparison of Xylazine and Lidocaine Infusion versus Medetomidine Continuous Rate Infusion during General Anesthesia with Isoflurane in Horses Undergoing Emergency Laparotomy. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050196
Straticò P, Guerri G, Bandera L, Celani G, Di Nunzio L, Petrizzi L, Varasano V. Comparison of Xylazine and Lidocaine Infusion versus Medetomidine Continuous Rate Infusion during General Anesthesia with Isoflurane in Horses Undergoing Emergency Laparotomy. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(5):196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050196
Chicago/Turabian StyleStraticò, Paola, Giulia Guerri, Lorenza Bandera, Gianluca Celani, Laura Di Nunzio, Lucio Petrizzi, and Vincenzo Varasano. 2024. "Comparison of Xylazine and Lidocaine Infusion versus Medetomidine Continuous Rate Infusion during General Anesthesia with Isoflurane in Horses Undergoing Emergency Laparotomy" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 5: 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050196
APA StyleStraticò, P., Guerri, G., Bandera, L., Celani, G., Di Nunzio, L., Petrizzi, L., & Varasano, V. (2024). Comparison of Xylazine and Lidocaine Infusion versus Medetomidine Continuous Rate Infusion during General Anesthesia with Isoflurane in Horses Undergoing Emergency Laparotomy. Veterinary Sciences, 11(5), 196. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11050196









