Establishment and Application Prospect of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Subgroup C Avian Metapneumovirus
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
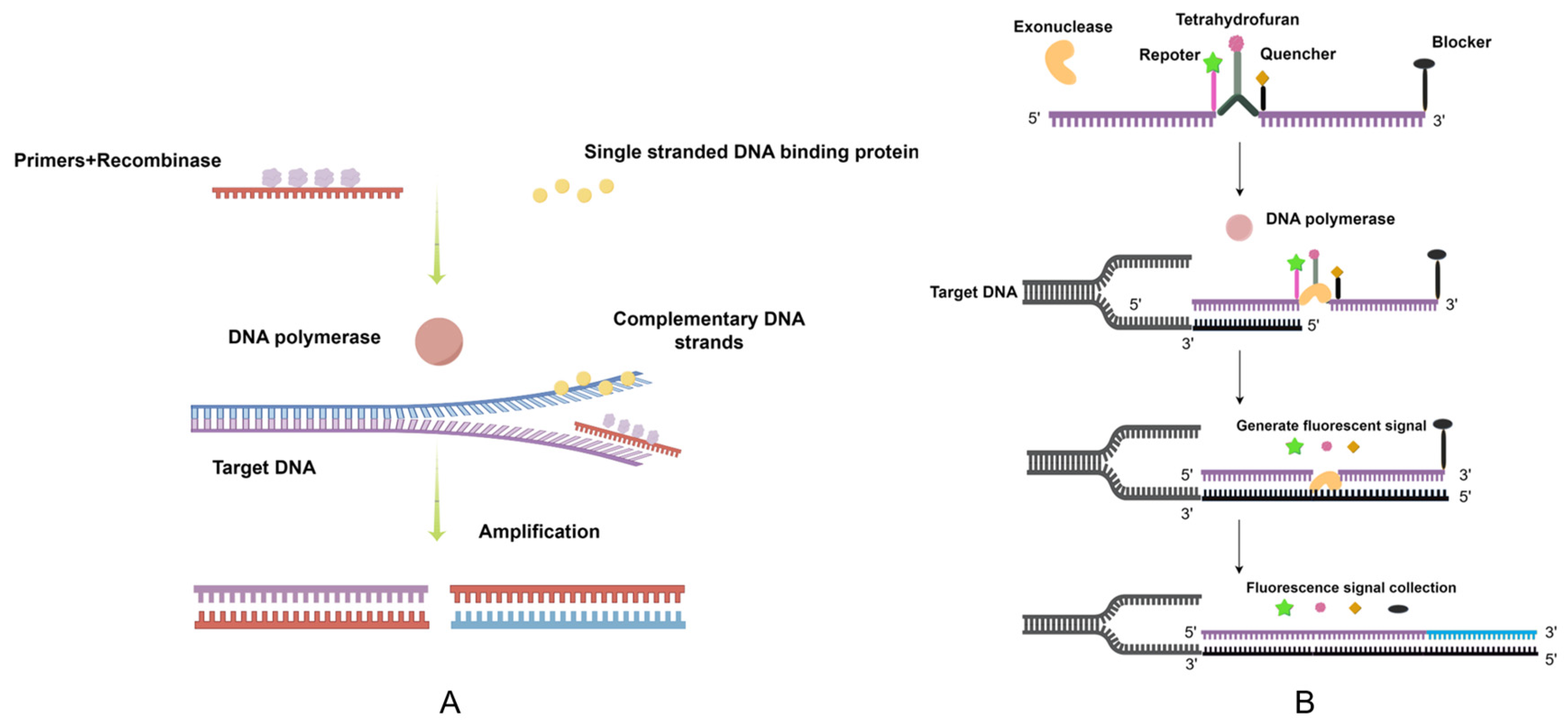
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Viruses and Clinical Samples
2.2. Primers and Probe
2.3. Plasmid Standard Generation
2.4. Validation of RT-RAA Primers
2.5. RT-RAA Reaction System Development
2.6. Assay for RT-RAA Sensitivity
2.7. Assay for RT-RAA Specificity
2.8. Assay for the RT-RAA Repeatability
2.9. Assessment of Clinical Samples Utilizing the RT-RAA Assay
3. Results
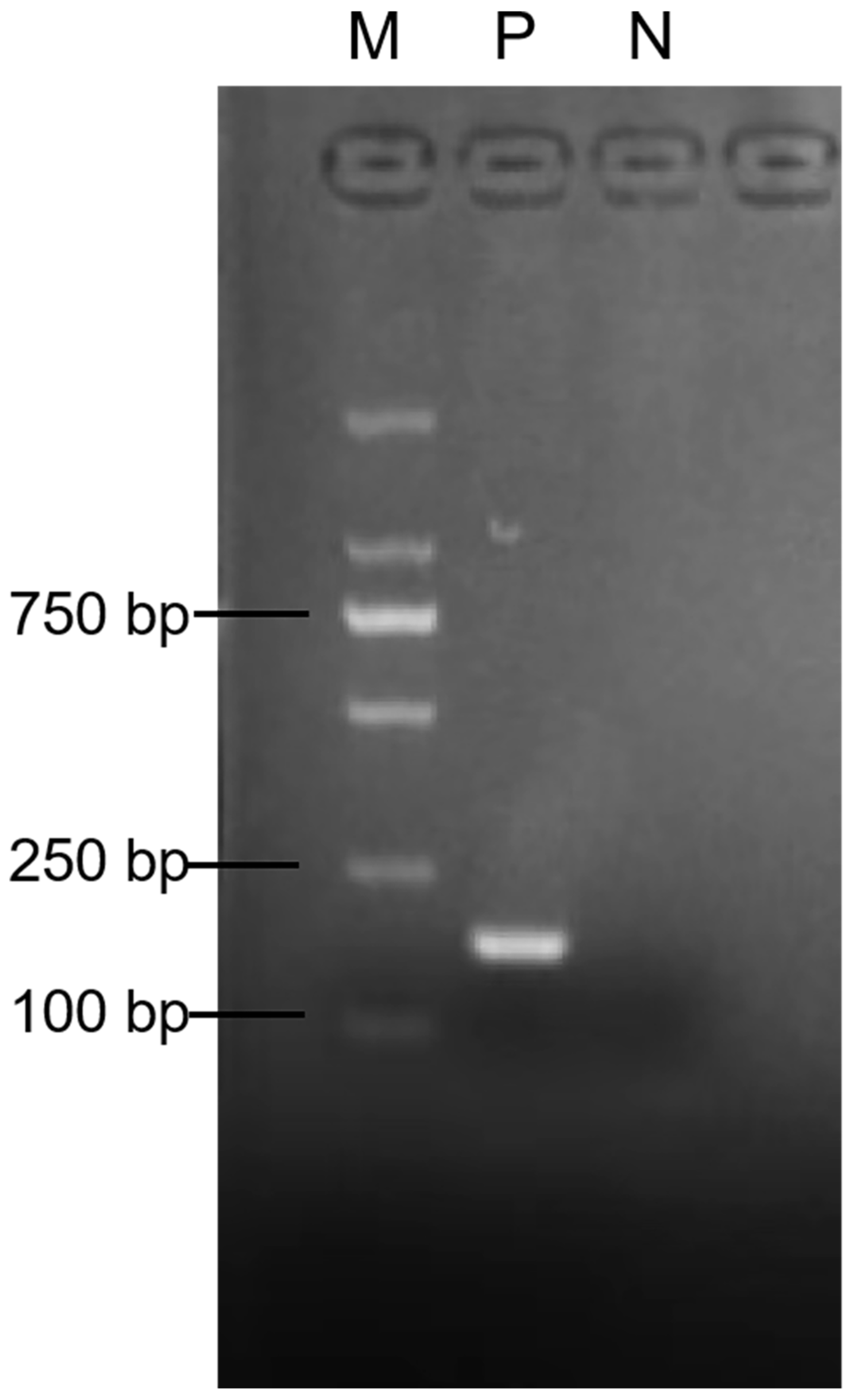
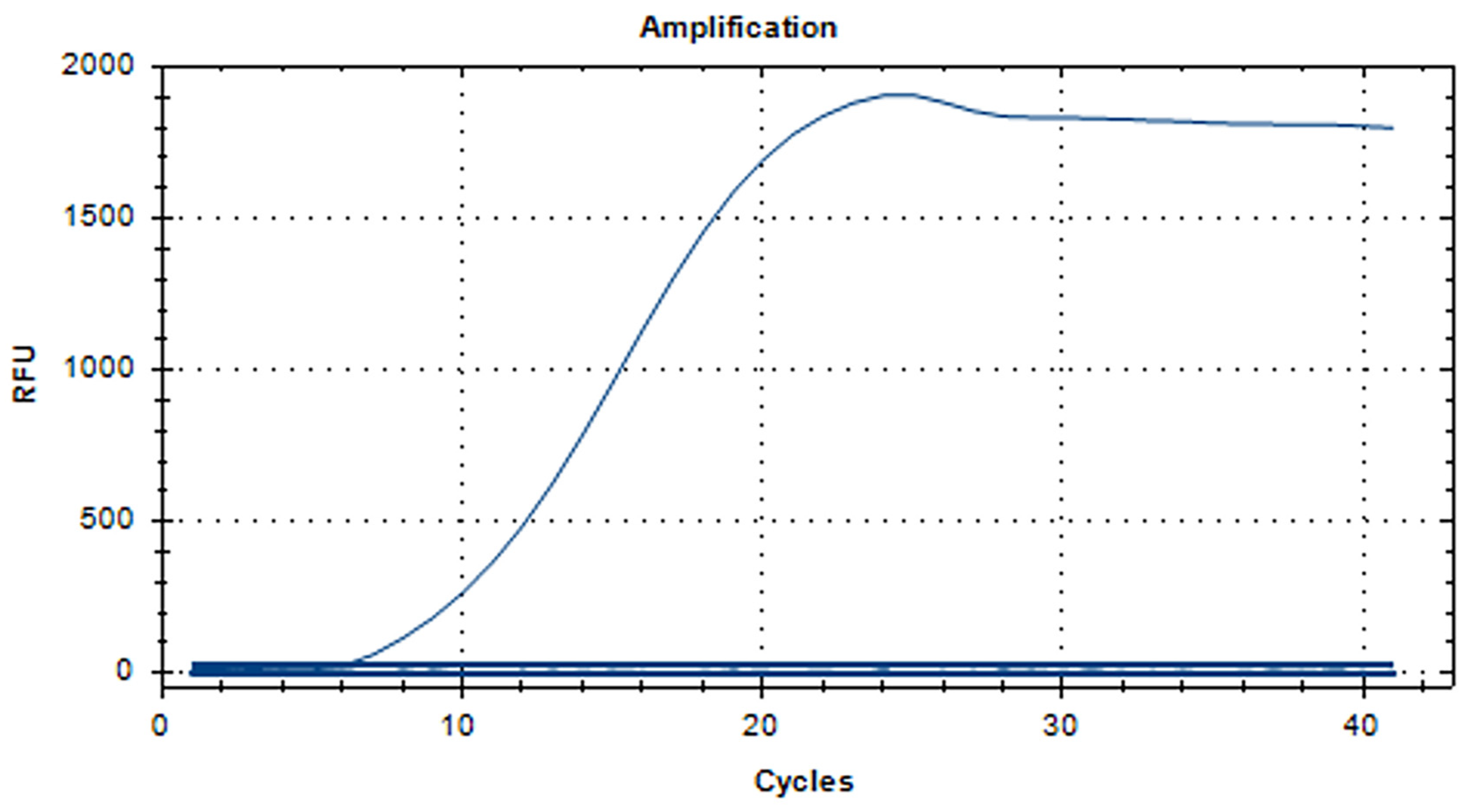
3.1. RT-RAA Primer Validation
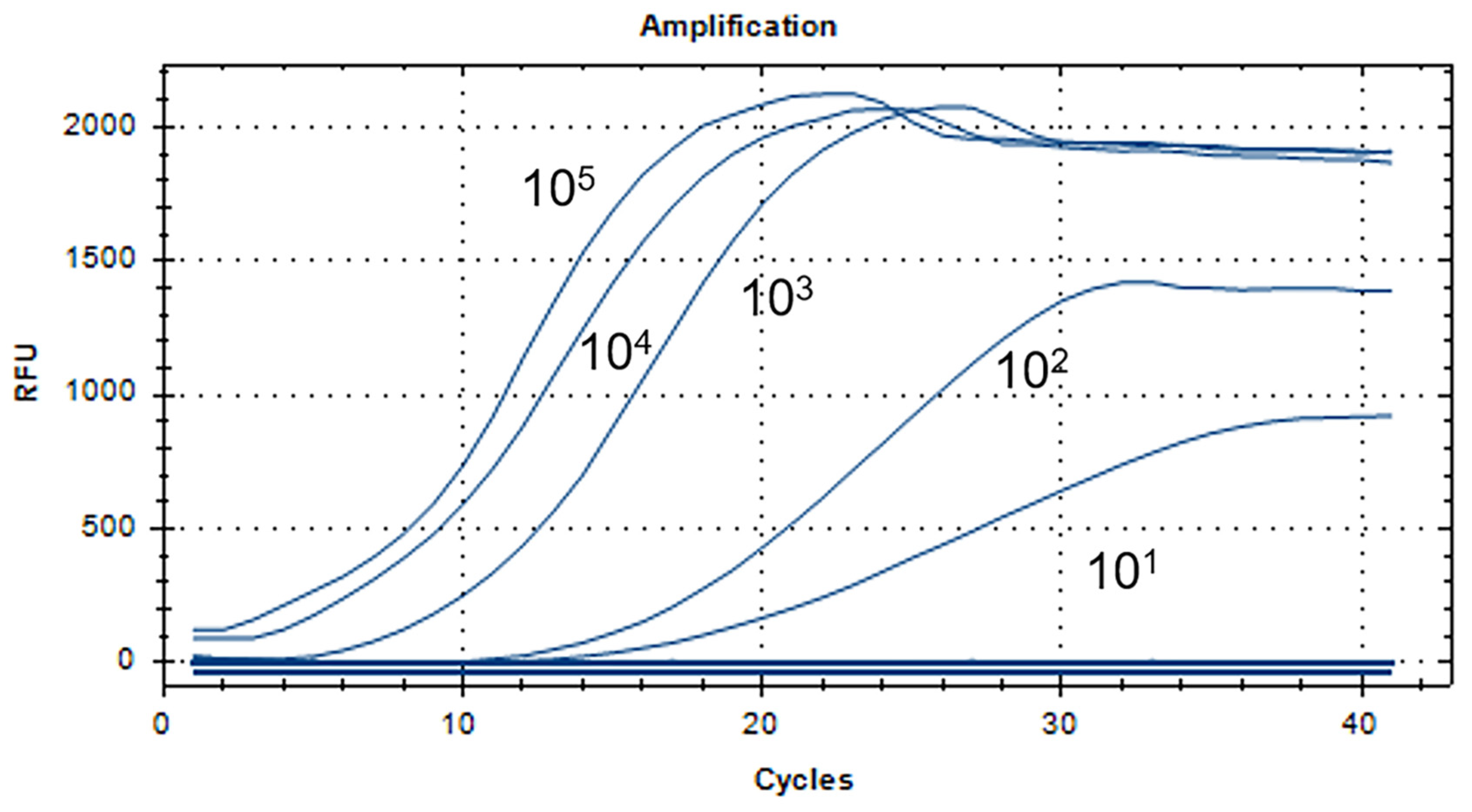
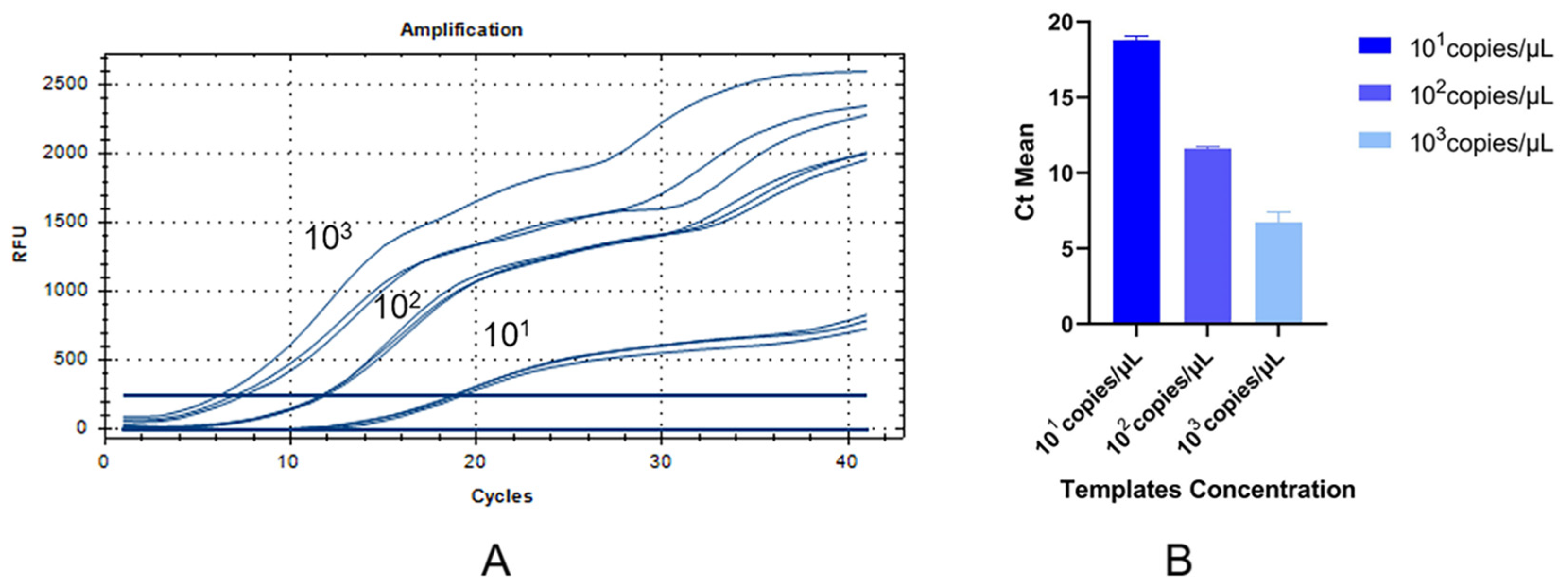
3.2. The RT-RAA Sensitivity Analysis
3.3. The RT-RAA Specificity Analysis
3.4. Repeatability of the RT-RAA
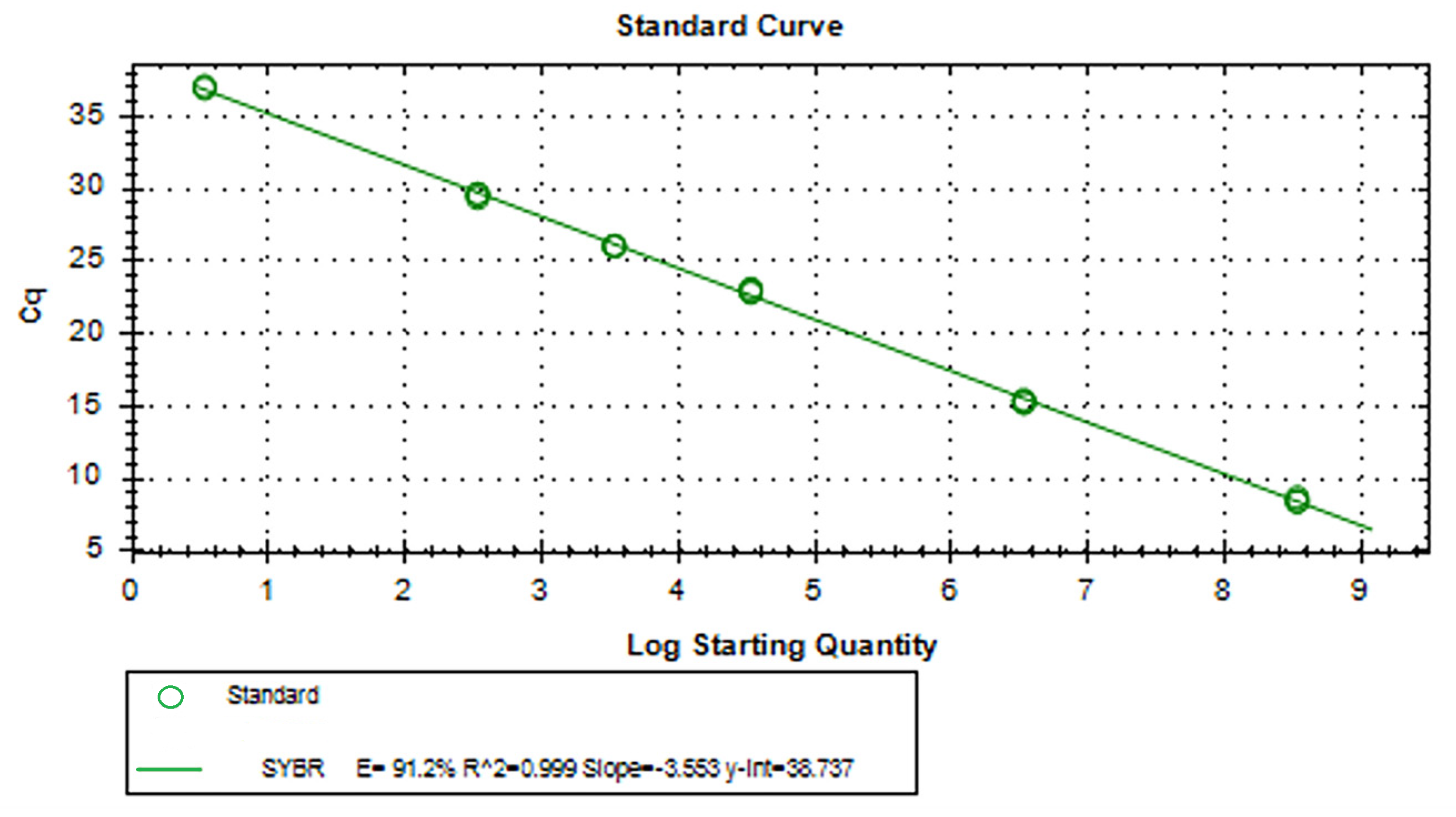
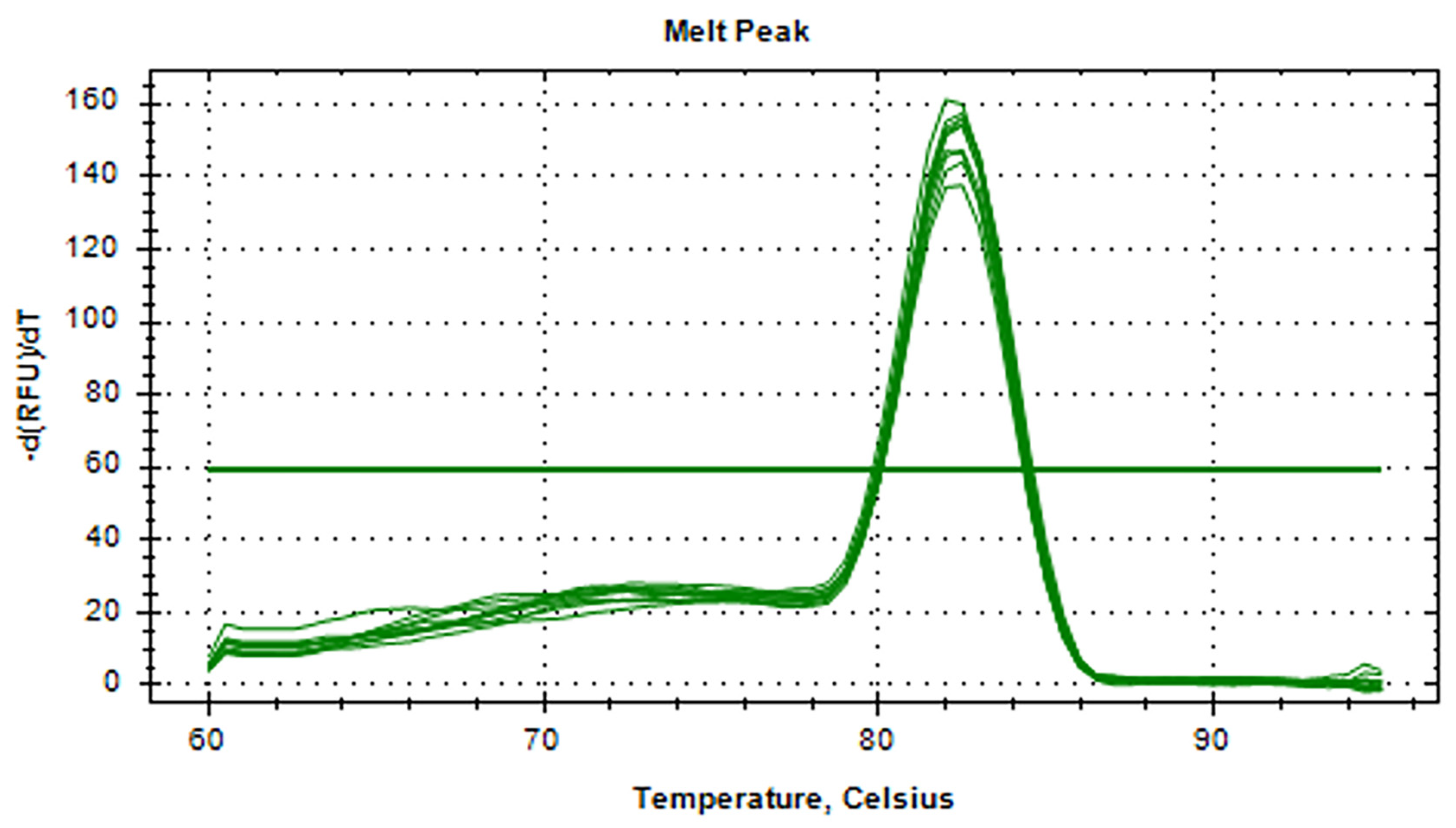
3.5. RT-qPCR Standard and Melting Curves for aMPV-C
3.6. Evaluation of Testing of Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Franzo, G.; Tucciarone, C.M.; Enache, M.; Bejan, V.; Ramon, G.; Koutoulis, K.C.; Cecchinato, M. First Report of Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype B Field Strain in a Romanian Broiler Flock during an Outbreak of Respiratory Disease. Avian Dis. 2017, 61, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.-S.; Lee, H.-J.; Jeong, S.-H.; Park, J.-Y.; Hong, Y.-H.; Lee, Y.-J.; Youn, H.-S.; Lee, D.-W.; Do, S.-H.; Park, S.-Y.; et al. Isolation and Characterization of Avian Metapneumovirus from Chickens in Korea. J. Vet. Sci. 2010, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easton, A.J.; Domachowske, J.B.; Rosenberg, H.F. Animal Pneumoviruses: Molecular Genetics and Pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 390–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buys, S.B.; du Preez, J.H.; Els, H.J. The Isolation and Attenuation of a Virus Causing Rhinotracheitis in Turkeys in South Africa. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 1989, 56, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Awad, F.; Forrester, A.; Baylis, M.; Lemiere, S.; Jones, R.; Ganapathy, K. Immune Responses and Interactions Following Simultaneous Application of Live Newcastle Disease, Infectious Bronchitis and Avian Metapneumovirus Vaccines in Specific-Pathogen-Free Chicks. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizotto, L.S.; Scagion, G.P.; Cardoso, T.C.; Simão, R.M.; Caserta, L.C.; Benassi, J.C.; Keid, L.B.; Oliveira, T.M.F.D.S.; Soares, R.M.; Arns, C.W.; et al. Complete Genome Sequence of an Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype A Strain Isolated from Chicken (Gallus gallus) in Brazil. Genome Announc. 2017, 5, e00688-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaboudi, K.; Lachheb, J. Avian Metapneumovirus Infection in Turkeys: A Review on Turkey Rhinotracheitis. J. Appl. Poult. Res. 2021, 30, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.J.; Rajashekara, G.; Jirjis, F.F.; Shaw, D.P.; Goyal, S.M.; Halvorson, D.A.; Nagaraja, K.V. Specific Detection of Avian Pneumovirus (APV) US Isolates by RT-PCR. Arch. Virol. 2000, 145, 1239–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, R.S.; LaRue, R.; Shaw, D.; Yu, Q.; Nagaraja, K.V.; Halvorson, D.A.; Njenga, M.K. A Wild Goose Metapneumovirus Containing a Large Attachment Glycoprotein Is Avirulent but Immunoprotective in Domestic Turkeys. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 14834–14842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-G.; Chung, H.-C.; Do, H.-Q.; Nguyen, T.-T.; Cao, T.-B.-P.; Truong, H.-T.; Mai, T.-N.; Le, T.-T.; Nguyen, T.-H.; Le, T.-L.; et al. Serological and Molecular Characterization of Avian Metapneumovirus in Chickens in Northern Vietnam. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hasan, B.A.; Alhatami, A.O.; Abdulwahab, H.M.; Bustani, G.S.; Hameed, M.A.; Jawad, A.H. First Report of Avian Metapneumovirus Type B in Iraqi Broiler Flocks with Swollen Head Syndrome. Vet. World 2022, 15, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habte, T.; Gerber, P.F.; Ibrahim, F.; Groves, P.J.; Walkden-Brown, S.W. Seroprevalence of Major Respiratory Diseases of Chickens in Central Ethiopia in Different Chicken Production Systems. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesse, S.T.; Ribó-Molina, P.; Jo, W.K.; Rautenschlein, S.; Vuong, O.; Fouchier, R.A.M.; Ludlow, M.; Osterhaus, A.D.M.E. Molecular Characterization of Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype C Detected in Wild Mallards (Anas platyrhynchos) in The Netherlands. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, 3360–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Y.; Yu, M.; Liu, P.; Hou, F.; Muhammad, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; et al. Novel Inactivated Subtype B Avian Metapneumovirus Vaccine Induced Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses. Vaccines 2020, 8, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, L.; Wei, L.; Yan, X.; Zhu, S.; Quan, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, D.; Jiang, H.; Song, J.; et al. Characterization of Avain Metapneumovirus Subgroup C Isolated from Chickens in Beijing, China. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.A.; Bonci, M.; Ricchizzi, E.; Jones, R.C.; Naylor, C.J. Identification of Two Regions within the Subtype A Avian Metapneumovirus Fusion Protein (Amino Acids 211–310 and 336–479) Recognized by Neutralizing Antibodies. Virus Res. 2009, 146, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.C.; Williams, R.A.; Baxter-Jones, C.; Savage, C.E.; Wilding, G.P. Experimental Infection of Laying Turkeys with Rhinotracheitis Virus: Distribution of Virus in the Tissues and Serological Response. Avian Pathol. 1988, 17, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biacchesi, S.; Skiadopoulos, M.H.; Yang, L.; Lamirande, E.W.; Tran, K.C.; Murphy, B.R.; Collins, P.L.; Buchholz, U.J. Recombinant Human Metapneumovirus Lacking the Small Hydrophobic SH and/or Attachment G Glycoprotein: Deletion of G Yields a Promising Vaccine Candidate. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 12877–12887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khehra, R.S.; Jones, R.C. In Vitro and In Vivo Studies on the Pathogenicity of Avian Pneumovirus for the Chicken Oviduct. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owoade, A.A.; Ducatez, M.F.; Hübschen, J.M.; Sausy, A.; Chen, H.; Guan, Y.; Muller, C.P. Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype A in China and Subtypes A and B in Nigeria. Avian Dis. 2008, 52, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Zhu, S.; Yan, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S.; She, R.; Hu, F.; Quan, R.; Liu, J. Avian Metapneumovirus Subgroup C Infection in Chickens, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2013, 19, 1092–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xing, L.; Chang, F.; Bao, Y.; Wang, S.; He, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Farooque, M.; et al. Genomic Sequence and Pathogenicity of the First Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype B Isolated from Chicken in China. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 228, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayahi, M.; Momtaz, H.; Jafari, R.A.; Zamani, P. Detection and Subtyping Avian Metapneumovirus from Turkeys in Iran. Vet. Res. Forum Int. Q. J. 2017, 8, 105–108. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Jiang, N.; Jiang, L.; Zhuang, Q.; Chen, Q.; Hou, G.; Xiao, Z.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.; et al. Establishment and Application of a Quadruple Real-Time RT-PCR for Detecting Avian Metapneumovirus. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A. Avian Pneumovirus Infections of Turkeys and Chickens. Vet. J. 2000, 160, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eterradossi, N.; Toquin, D.; Guittet, M.; Bennejean, G. Discrepancies in Turkey Rhinotracheitis ELISA Results Using Different Antigens. Vet. Rec. 1992, 131, 563–564. [Google Scholar]
- Mekkes, D.R.; De Wit, J.J. Comparison of Three Commercial ELISA Kits for the Detection of Turkey Rhinotracheitis Virus Antibodies. Avian Pathol. 1998, 27, 301–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Yu, Z.; Jiao, S.; Liu, Y.; Ni, H.; Wang, Y. Development of a Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Porcine Circovirus 3. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 282, 113904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, F.; Yang, X.; Xu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhou, L.; Ge, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, X.; Yang, H. Development of a Fluorescent Probe-based Real-time Reverse Transcription Recombinase-aided Amplification Assay for the Rapid Detection of Classical Swine Fever Virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2021, 68, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Nie, M.; Deng, H.; Lai, S.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, Z. Establishment of a Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Detection Method for Porcine Group a Rotavirus. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 954657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Shen, X.; Li, M.; Qi, J.; Wang, R.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, R.; Fan, T.; Bai, X.; Fan, G.; et al. Applicability of Duplex Real Time and Lateral Flow Strip Reverse-Transcription Recombinase Aided Amplification Assays for the Detection of Enterovirus 71 and Coxsackievirus A16. Virol. J. 2019, 16, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, T. Research Note: Application of Reverse-Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification-Lateral Flow Dipstick Method in the Detection of Infectious Bursal Disease Virus. Poult. Sci. 2023, 102, 102306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Ma, W.; Jiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Ismail, R.G.; Zhou, T.; Fan, Z. Reverse Transcription-Recombinase-Aided Amplification and CRISPR/Cas12a-Based Visual Detection of Maize Chlorotic Mottle Virus. Phytopathol. Res. 2022, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rausch, F.; Tanneberger, F.; Abd El Wahed, A.; Truyen, U. Validation of the Efficacy of Air Purifiers Using Molecular Techniques. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhuang, Q.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, F.; Chen, Q.; Zhao, R.; Li, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, J.; Hou, G.; et al. Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Avian Influenza Virus. Virus Genes 2023, 59, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudi, S. Turkey Rhinotracheitis. CABI Compend. 2022, 60956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.; Huggins, M.; Woods, M.; Orbell, S.; Mockett, A. Protection Provided by a Commercially Available Vaccine against Different Strains of Turkey Rhinotracheitis Virus. Vet. Rec. 1995, 136, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, C.J.; Lupini, C.; Brown, P.A. Charged Amino Acids in the AMPV Fusion Protein Have More Influence on Induced Protection than Deletion of the SH or G Genes. Vaccine 2010, 28, 6800–6807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Roth, J.P.; Estevez, C.N.; Zsak, L.; Liu, B.; Yu, Q. Generation and Evaluation of a Recombinant Newcastle Disease Virus Expressing the Glycoprotein (G) of Avian Metapneumovirus Subgroup C as a Bivalent Vaccine in Turkeys. Vaccine 2011, 29, 8624–8633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patnayak, D.P.; Goyal, S.M. Cold-Adapted Strain of Avian Pneumovirus as a Vaccine in One-Day-Old Turkeys and the Effect of Inoculation Routes. Avian Dis. 2004, 48, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbenstroth, D.; Dalgaard, T.S.; Kothlow, S.; Juul-Madsen, H.R.; Rautenschlein, S. Effects of Cyclosporin A Induced T-Lymphocyte Depletion on the Course of Avian Metapneumovirus (aMPV) Infection in Turkeys. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2010, 34, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, R.M.; Khatri, M.; Sharma, J.M. Protection against Avian Metapneumovirus Subtype C in Turkeys Immunized via the Respiratory Tract with Inactivated Virus. Vaccine 2011, 29, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Zhao, C. Epidemiological Investigation of Avian Metapneumovirus Insome Areas of China in 2020. Chin. J. Prev. Vet. Med. 2022, 44, 712–717. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Fan, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, S.; Zhao, M. Development of Recombinase Aided Amplification Combined with Disposable Nucleic Acid Test Strip for Rapid Detection of Porcine Circovirus Type 2. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 676294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Chen, Y.; Ding, X.; Liu, X.; Lu, H.; Guo, C.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Z.; Huang, J.; Fan, Z.; et al. Rapid and Visual Detection of Type 2 Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Syndrome Virus by Real-Time Fluorescence-Based Reverse Transcription Recombinase-Aided Amplification. Viruses 2022, 14, 2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Kong, J.; Yao, Z.; Sun, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Huang, H.; Wang, J.; et al. A New Rapid and Sensitive Method for Detecting Chicken Infectious Anemia Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 994651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, M.; Huggins, M.B.; Mudzamiri, R.; Heincz, U. Avian Metapneumovirus Excretion in Vaccinated and Non-Vaccinated Specified Pathogen Free Laying Chickens. Avian Pathol. 2004, 33, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Suderman, M.; Koziuk, J.; Ojkic, D.; Berhane, Y. Development of A Recombinant Nucleocapsid Based Indirect ELISA for the Detection of Antibodies to Avian Metapneumovirus Subtypes, A, B, and C. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2021, 231, 110151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, J.K.A.; Huggins, M.B.; Orbell, S.J.; Senne, D.A. Preliminary Antigenic Characterization of an Avian Pneumovirus Isolated from Commercial Turkeys in Colorado, USA. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 607–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Primer | Sequence (5′-3′) | Localization | Size of Product (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|
| RAA-F | CTATGCGGAGAGATACTGTATGCCAAGC | 139–166 | 175 |
| RAA-R | TTTGCCTTTACCAAGGGAGTATGTCTTG | 285–313 | |
| RAA-P | CCACATTGGGAGCACGGCGTACACAGCGAGA[FAM-dT][THF]C[BHQ-dT]AAAGAACTCAGGTAG-[C3Spacer] | ||
| qPCR-F | TGCGGAGAGATACTGTATGCCAAG | 141–165 | 141 |
| qPCR-R | ATACTGCCTGCACTTCACTACCTG | 257–281 | |
| PCR-F | TTCAGGGGATTCAGCTTAGTGAC | 8–30 | 515 |
| PCR-R | GATGCCAGCTTCGTGAAGATT | 502–522 |
| Templates (Copies/µL) | Average ± SD | CV% |
|---|---|---|
| 101 | 18.79 ± 0.27 | 1.44% |
| 102 | 11.60 ± 0.14 | 1.21% |
| 103 | 6.74 ± 0.66 | 9.79% |
| Sample | Known | RT-RAA | RT-qPCR | Coincidence Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | 10 | 10 | 10 | 100 |
| Negative | 30 | 30 | 30 | 100 |
| Total | 40 | 40 | 40 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Dong, M.; Li, T.; Dai, Z.; Li, H.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, X. Establishment and Application Prospect of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Subgroup C Avian Metapneumovirus. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030122
Bai Y, Wu X, Liu J, Wang Z, Dong M, Li T, Dai Z, Li H, Xie Q, Zhang X. Establishment and Application Prospect of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Subgroup C Avian Metapneumovirus. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(3):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030122
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Yuhang, Xiuhong Wu, Jiajia Liu, Zhanxin Wang, Mengyue Dong, Tong Li, Zhenkai Dai, Hongxin Li, Qingmei Xie, and Xinheng Zhang. 2024. "Establishment and Application Prospect of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Subgroup C Avian Metapneumovirus" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 3: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030122
APA StyleBai, Y., Wu, X., Liu, J., Wang, Z., Dong, M., Li, T., Dai, Z., Li, H., Xie, Q., & Zhang, X. (2024). Establishment and Application Prospect of Reverse Transcriptase Recombinase-Aided Amplification Assay for Subgroup C Avian Metapneumovirus. Veterinary Sciences, 11(3), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11030122







