Prevalence, Infection, and Risk to Human Beings of Toxocara canis in Domestic Food-Producing Animals
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
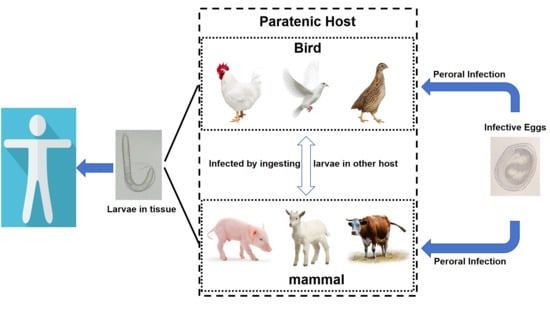
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Infection
2.1. Chicken
2.2. Pigeon
2.3. Quail
2.4. Pig
2.5. Sheep
3. Epidemiological Investigation
3.1. Chicken
3.2. Pig
3.3. Sheep
4. Case Report
4.1. Chicken
4.2. Duck
4.3. Pig
4.4. Beef
4.5. Sheep
5. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bowman, D.D. History of Toxocara and the associated larva migrans. Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 109, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, J.H. Foodborne eosinophilia due to visceral larva migrans: A disease abandoned. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2012, 27, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Macpherson, C.N. The epidemiology and public health importance of toxocariasis: A zoonosis of global importance. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 999–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, G.; Holland, C.V.; Wang, T.; Hofmann, A.; Fan, C.K.; Maizels, R.M.; Hotez, P.J.; Gasser, R.B. Human toxocariasis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, e14–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zyoud, S.H. Global toxocariasis research trends from 1932 to 2015: A bibliometric analysis. Health Res. Policy Syst. 2017, 15, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nagakura, K.; Tachibana, H.; Kaneda, Y.; Kato, Y. Toxocariasis possibly caused by ingesting raw chicken. J. Infect. Dis. 1989, 160, 735–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, K.; Saeed, I.; Permin, A.; Kapel, C.M. Zoonotic risk of Toxocara canis infection through consumption of pig or poultry viscera. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 121, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, E.A.; Rocha, R.L. Toxocariasis: Visceral larva migrans in children. J. Pediatr. 2011, 87, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiura, E.; Del Carmen Garcia Lopes, A.; da Paz, J.S.; Gava, M.G.; Flecher, M.C.; Colares, M.; de Freitas Soares, F.E.; da Fonseca, L.A.; Lacerda, T.; de Araújo, J.V.; et al. Fungi predatory activity on embryonated Toxocara canis eggs inoculated in domestic chickens (Gallus gallus domesticus) and destruction of second stage larvae. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 3301–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenji, F.; Pouryousef, A.; Fata, A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Salehi, M.; Khoshnegah, J. Seroepidemiological Study of Toxocariasis in the Owners of Domestic Cats and Dogs in Mashhad, Northeastern Iran. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2016, 11, 265–268. [Google Scholar]
- Poulle, M.L.; Bastien, M.; Richard, Y.; Josse-Dupuis, É.; Aubert, D.; Villena, I.; Knapp, J. Detection of Echinococcus multilocularis and other foodborne parasites in fox, cat and dog faeces collected in kitchen gardens in a highly endemic area for alveolar echinococcosis. Parasite 2017, 24, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.K.; Holland, C.V.; Loxton, K.; Barghouth, U. Cerebral Toxocariasis: Silent Progression to Neurodegenerative Disorders? Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 663–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Despommier, D. Toxocariasis: Clinical aspects, epidemiology, medical ecology, and molecular aspects. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnaval, J.F.; Glickman, L.T.; Dorchies, P.; Morassin, B. Highlights of human toxocariasis. Korean J. Parasitol. 2001, 39, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finsterer, J.; Auer, H. Neurotoxocarosis. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. 2007, 49, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawor, J.; Borecka, A.; Zarnowska, H.; Marczyńska, M.; Dobosz, S. Environmental and personal risk factors for toxocariasis in children with diagnosed disease in urban and rural areas of central Poland. Vet. Parasitol. 2008, 155, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, H.; Holland, C.; Taylor, M.; Magnaval, J.F.; Schantz, P.; Maizels, R. How common is human toxocariasis? Towards standardizing our knowledge. Trends Parasitol. 2009, 25, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, C.; Castelo, J.S.; Tsanaclis, A.M.; Pereira, F.E. Prevalence of Toxocara-induced liver granulomas, detected by immunohistochemistry, in a series of autopsies at a Children’s Reference Hospital in Vitoria, ES, Brazil. Virchows Arch. An Int. J. Pathol. 2007, 450, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinsky-Elefant, G.; Hirata, C.E.; Yamamoto, J.H.; Ferreira, M.U. Human toxocariasis: Diagnosis, worldwide seroprevalences and clinical expression of the systemic and ocular forms. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 2010, 104, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, S.R.; Morgan, E.R.; Prada, J.M.; Betson, M. Brain food: Rethinking food-borne toxocariasis. Parasitology 2022, 149, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimatsu, Y.; Akao, N.; Akiyoshi, H.; Kawazu, T.; Okabe, Y.; Aizawa, H. A familial case of visceral larva migrans after ingestion of raw chicken livers: Appearance of specific antibody in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of the patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2006, 75, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmeister, B.; Glaeser, S.; Flick, H.; Pornschlegel, S.; Suttorp, N.; Bergmann, F. Cerebral toxocariasis after consumption of raw duck liver. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2007, 76, 600–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, G.; Schantz, P. Toxocaral visceral larva migrans after ingestion of raw lamb liver. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1992, 15, 743–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisamatsu, Y.; Ishii, H.; Kai, N.; Amemiya, Y.; Otani, S.; Morinaga, R.; Shirai, R.; Umeki, K.; Kishi, K.; Tokimatsu, I.; et al. Case of toxocariasis showing migratory nodular shadows with halos. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi 2008, 46, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mseleku, C.; Chimonyo, M.; Slotow, R.; Mhlongo, L.C.; Ngidi, M.S.C. Contribution of Village Chickens in Sustainable and Healthy Food Systems for Children along a Rural-Urban Gradient: A Systematic Review. Foods 2023, 12, 3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henning, J.; Hla, T.; Meers, J. Interdisciplinary Communication of Infectious Disease Research-Translating Complex Epidemiological Findings into Understandable Messages for Village Chicken Farmers in Myanmar. SpringerPlus 2014, 3, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-da-Silva, D.R.; da Paz, J.S.; Fortunato, V.R.; Beltrame, M.A.; Valli, L.C.; Pereira, F.E. Natural infection of free-range chickens with the ascarid nematode Toxocara sp. Parasitol. Res. 2015, 114, 4289–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Söhsten, A.L.; da Silva, A.V.; Rubinsky-Elefant, G.; Guerra, L.M.S.M.E.M. Anti-Toxocara spp. IgY antibodies in poultry sold in street markets from Feira de Santana, Bahia, Northeastern Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Rep. 2017, 8, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merigueti, Y.F.F.B.; da Silva Raposo, R.; Zampieri, B.P.; de Lima Cerazo, L.M.; Pereira, L.; Santarém, V.A. Dispersion and infectivity of Toxocara canis eggs after passage through chicken intestine. Parasitol. Res. 2018, 117, 3481–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, H. Studies on visceral larva migrans. Infectivity of Toxocara canis larvae from paratenic host and antibody titers in rats. Med. J. Hiroshima Univ. 1987, 35, 1417–1429. [Google Scholar]
- Dutra, G.F.; Pinto, N.S.F.; da Costa de Avila, L.F.; Dutra, P.C.; de Lima Telmo, P.; Rodrigues, L.H.; Silva, A.M.W.A.; Scaini, C.J. Risk of infection by the consumption of liver of chickens inoculated with low doses of Toxocara canis eggs. Vet. Parasitol. 2014, 203, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Nino, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Katsube, Y. Parasitism of Toxocara canis larvae in chickens inoculated with the ascarid eggs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1994, 56, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gargili, A.; Tuzer, E.; Gulanber, A.; Toparlak, M.; Efil, I.; Keles, V.; Ulutas, M. Experimental visceral larva migrans in chicken with Toxocara canis. Turk. Vet. Hayvan Derg. 1999, 23, 431–433. [Google Scholar]
- Taira, K.; Permin, A.; Kapel, C.M. Establishment and migration pattern of Toxocara canis larvae in chickens. Parasitol. Res. 2003, 90, 521–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvin, T.J. Experimental Toxocara canis infections in chickens and pigeons. J. Parasitol. 1964, 50, 124–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahbar, A.; Alborzi, A.; Seifi Abad Shapoori, M. An alternative method for producing Toxocara canis second stage larvae from a paratenic host (pigeon) for mRNA extraction purpose. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 186–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Passali, D.; Motta, G.; Passali, F.M.; Nunziata, M.; Ciprandi, G. Oral quail egg homogenate in the treatment of allergic rhinitis: A first experience in clinical practice. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34, 1593–1596. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pahari, T.K.; Sasmal, N.K. Experimental infection of mice with Toxocara canis larvae obtained from Japanese quails. Int. J. Parasitol. 1990, 20, 263–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahari, T.K.; Sasmal, N.K. Experimental infection of Japanese quail with Toxocara canis larvae through earthworms. Vet. Parasitol. 1991, 39, 337–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, S.; Sotoyama, T.; Hayasaka, S.; Kameyama, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Katsube, Y. Parasitism of Toxocara canis larvae in Japanese quails by inoculation of the ascarid eggs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1991, 53, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Katsube, Y. Infectivity of Toxocara canis larvae from Japanese quails in mice. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 1994, 56, 399–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Done, J.T.; Richardson, M.D.; Gibson, T.E. Experimental visceral larva migrans in the pig. Res. Vet. Sci. 1960, 1, 133–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helwigh, A.B.; Lind, P.; Nansen, P. Visceral larva migrans: Migratory pattern of Toxocara canis in pigs. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sommerfelt, I.E.; Rosa, A.; Duchene, A.; Degregorio, O.; López, C.; Pisanú, A.; Torres, R.D. Toxocara canis in experimentally infected pigs: Migratory pattern and tissue lesions. Vet. Parasitol. 2004, 125, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taira, K.; Saeed, I.; Lind, P.; Murrell, K.D.; Kapel, C.M. Population dynamics of Toxocara canis in pigs receiving a single or multiple infection. Parasitology 2003, 127 Pt 6, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasmal, N.K.; Acharya, S.; Laha, R. Larval migration of Toxocara canis in piglets and transfer of larvae from infected porcine tissue to mice. J. Helminthol. 2008, 82, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardón, R.; Cuéllar, C.; Guillén, J.L. Larval distribution of Toxocara canis in BALB/c mice at nine weeks and one year post-inoculation. J. Helminthol. 1994, 68, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayate, C.S.; Rehmann, B.; Ahmed, M.S. Migration of ascarids in sheep. Pakistan J. Zool. 1973, 5, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Aldawek, A.M.; Levkut, M.; Revajová, V.; Kolodzieyski, L.; Seveiková, Z.; Dubinský, P. Larval toxocarosis in sheep: The immunohistochemical characterization of lesions in some affected organs. Vet. Parasitol. 2002, 105, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shehada, M.N.; Al-Zubaidy, B.A.; Herbert, I.V. The migration of larval Toxocara canis in white mice I. Migration through the intestine in primary infection. Vet. Parasitol. 1984, 17, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweatman, G.K.; Hensall, T.C.; Manktelow, B.W. Experimental observations on parasitic liver white spot in New Zealand sheep. N. Z. Vet. J. 1962, 10, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.T.; Min, H.K.; Chung, P.R.; Chang, J.K. Studies on the inducing possibility of human visceral larva migrans associated with eating habit of raw liver of domestic animals. Korean J. Parasitol. 1976, 14, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, A.C.; Rubinsky-Elefant, G.; Merigueti, Y.F.F.B.; da Silveira Batista, A.; Santarém, V.A. Frequency of anti-Toxocara antibodies in broiler chickens in southern Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2018, 27, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zibaei, M.; Sadjjadi, S.M.; Maraghi, S. The occurrence of Toxocara species in naturally infected broiler chickens revealed by molecular approaches. J. Helminthol. 2017, 91, 633–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shokri, E.; Haniloo, A.; Zibaei, M.; Pezeshki, A.; Mansori, K.; Taira, K. Detection of Toxocara species larvae in four Iranian free-range broiler farms. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nourian, A.A.; Amiri, M.; Ataeian, A.; Haniloo, A.; Mosavinasab, S.N.; Badali, H. Seroepidemiological study for toxocariasis among children in Zanjan-northwest of Iran. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2008, 11, 1844–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P. Toxocara and ascaris infection in British pigs: A serological survey. Vet. Rec. 1979, 104, 526–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lloyd, S. Seroprevalence of Toxocara canis in sheep in Wales. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 137, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarém, V.A.; Chesine, P.A.; Lamers, B.E.; Rubinsky-Elefant, G.; Giuffrida, R. Anti-Toxocara spp. antibodies in sheep from southeastern Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 179, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantzoura, V.; Diakou, A.; Kouam, M.K.; Feidas, H.; Theodoropoulou, H.; Theodoropoulos, G. Seroprevalence and risk factors associated with zoonotic parasitic infections in small ruminants in the Greek temperate environment. Parasitol. Int. 2013, 62, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassier, G.L.; Borsuk, S.; Pappen, F.; Scaini, C.J.; Gallina, T.; Villela, M.M.; da Rosa Farias, N.A.; Benavides, M.V.; Berne, M.E.A. Toxocara spp. seroprevalence in sheep from southern Brazil. Parasitol. Res. 2013, 112, 3181–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, E.R.; de Araujo, L.B.; de Leão e Neves Eduardo, A.M. Human Toxocariasis: Secondary Data Analysis. Ann. Clin. Cytol. Pathol. 2017, 3, 1075. [Google Scholar]
- Fujii, Y.; Mataki, H.; Koreeda, Y.; Kawabata, T.; Hamada, M.; Nakashioya, J.; Tomiyama, Y.; Kawabata, M. A case of pulmonary toxocariasis successfully treated with ivermectin. Nihon Kokyuki Gakkai Zasshi. 2011, 49, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomoda, Y.; Futami, S.; Sumida, K.; Tanaka, K. Neglected parasitic infection: Toxocariasis. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr2018224492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimmig, P.; Naser, K.; Frank, W. Seroepidemiologische Untersuchungen zur Toxokariasis des Menschen [Seroepidemiologic studies of human toxocariasis]. Zentralbl Hyg. Umweltmed. 1991, 191, 406–422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fan, C.K.; Hung, C.C.; Du, W.Y.; Liao, C.W.; Su, K.E. Seroepidemiology of Toxocara canis infection among mountain aboriginal schoolchildren living in contaminated districts in eastern Taiwan. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2004, 9, 1312–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vortel, V.; Pavelka, I.; Uhliková, M.; Hübner, J.; Zezulka, B. Larval toxocariasis in a 40-year-old man with detection of larvae in a liver biopsy. Cesk Patol. 1983, 19, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoshikawa, M.; Nishiofuku, M.; Moriya, K.; Ouji, Y.; Ishizaka, S.; Kasahara, K.; Mikasa, K.I.; Hirai, T.; Mizuno, Y.; Ogawa, S.; et al. A familial case of visceral toxocariasis due to consumption of raw bovine liver. Parasitol. Int. 2008, 57, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.; Lim, J.H.; Choi, D.C.; Lee, K.S.; Paik, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Choi, Y.H.; Huh, S. Transmission of Toxocara canis via ingestion of raw cow liver: A cross-sectional study in healthy adults. Korean J. Parasitol. 2012, 50, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuhashi, Y.; Naitou, K.; Yamauchi, S.; Naruse, H.; Matsuoka, Y.; Nakamura-Uchiyama, F.; Hiromatsu, K. A case of the myelitis due to Toxocara canis infection complicated with cervical spondylosis. No Shinkei Geka. 2006, 34, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, M.G.; Haseeb, M.A. Reduced cognitive function in children with toxocariasis in a nationally representative sample of the United States. Int. J. Parasitol. 2012, 42, 1159–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, J.; Cicero, C.E.; Rateau, G.; Quattrocchi, G.; Marin, B.; Bruno, E.; Dalmay, F.; Druet-Cabanac, M.; Nicoletti, A.; Preux, P.M. Updated evidence of the association between toxocariasis and epilepsy: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghipour, A.; Habibpour, H.; Mirzapour, A.; Rostami, A. Toxocara infection/exposure and the risk of schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 115, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.K. Pathogenesis of cerebral toxocariasis and neurodegenerative diseases. Adv. Parasitol. 2020, 109, 233–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitamura, M.; Fukuoka, M.; Haruta, Y.; Koarada, S.; Tada, Y.; Nagasawa, K. A case of visceral larva migrans due to Toxocara canis showing varied manifestations. Kansenshogaku Zasshi 2007, 81, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambe, D.; Takeoka, K.; Ogawa, K.; Doi, K.; Maruyama, H.; Yoshida, A.; Suenaga, T.; Kageyama, T. Treatment-resistant neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders associated with Toxocara canis infection: A case report. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2017, 13, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierra, M.F.; Ricoy, G.; Sosa, S.; Colavecchia, S.B.; Santillán, G.; López, C.M.; Mundo, S.L.; Sommerfelt, I.E. Humoral immune response of pigs infected with Toxocara cati. Exp. Parasitol. 2020, 218, 107997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Han, Q. Prevalence, Infection, and Risk to Human Beings of Toxocara canis in Domestic Food-Producing Animals. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020083
Xu J, Han Q. Prevalence, Infection, and Risk to Human Beings of Toxocara canis in Domestic Food-Producing Animals. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(2):83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020083
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jingyun, and Qian Han. 2024. "Prevalence, Infection, and Risk to Human Beings of Toxocara canis in Domestic Food-Producing Animals" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 2: 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020083
APA StyleXu, J., & Han, Q. (2024). Prevalence, Infection, and Risk to Human Beings of Toxocara canis in Domestic Food-Producing Animals. Veterinary Sciences, 11(2), 83. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11020083