Wildlife Infection of Peste des Petits Ruminants Detected in China, 2024
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Peste des Petits Ruminants Epidemic in China in 2024
2.2. Clinical Symptoms of Diseased Animals
2.3. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Reverse-Transcription PCR
2.4. Reverse-Transcription PCR
2.5. Genomic Sequencing
2.6. Genomic Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
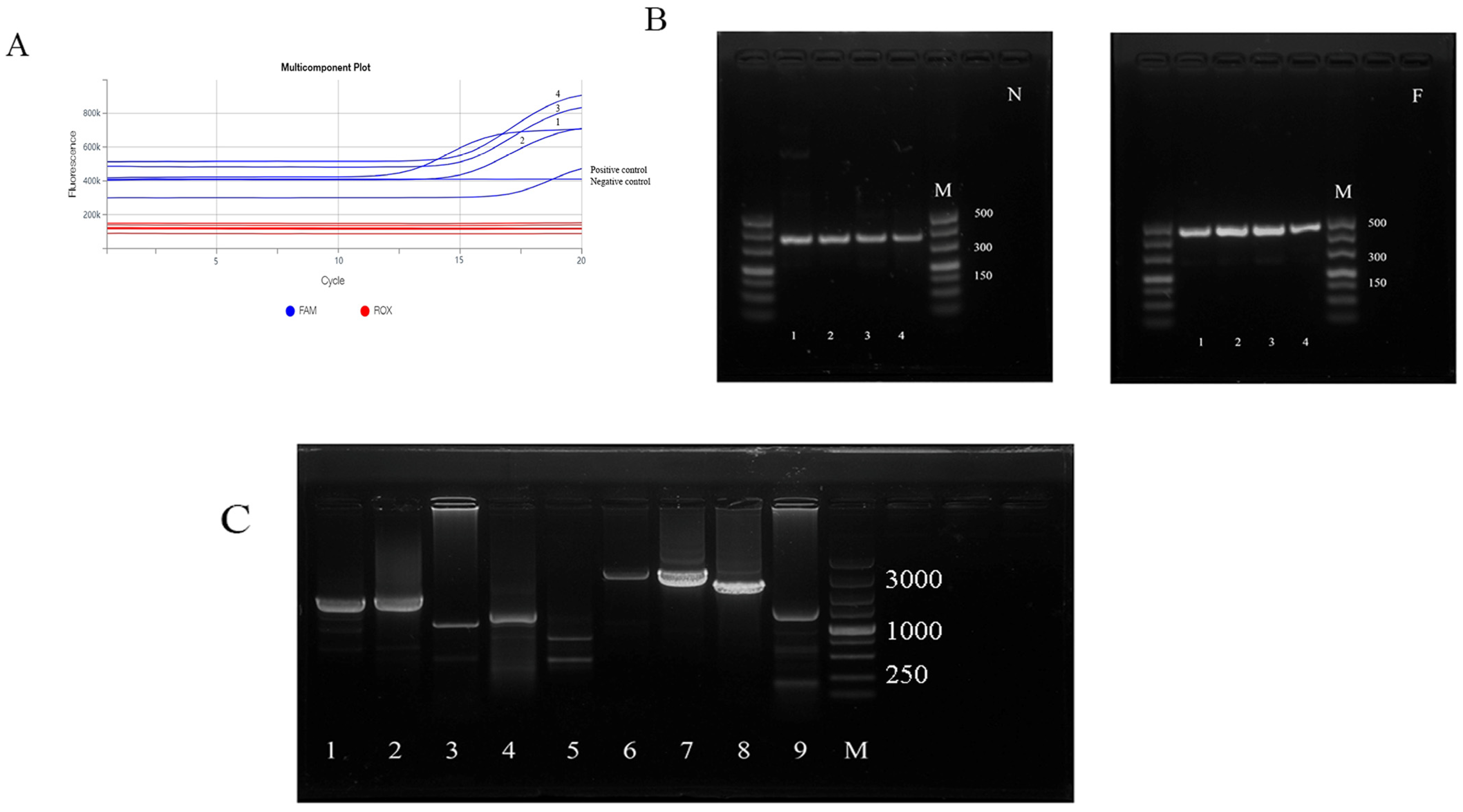
3.1. Nucleic Acid Analysis for Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus
3.2. Amplification of N and F Genes and Genomic Fragments
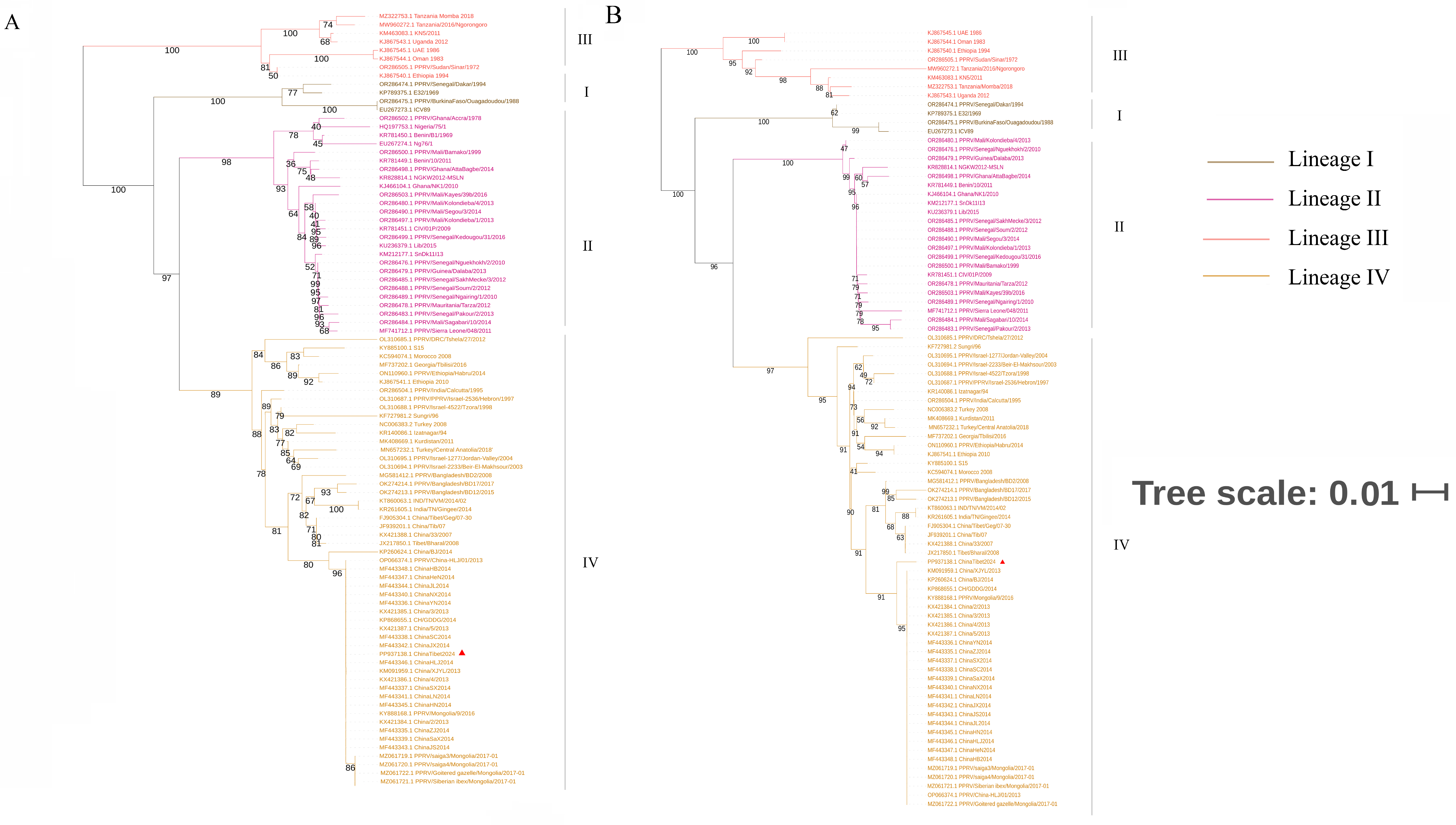
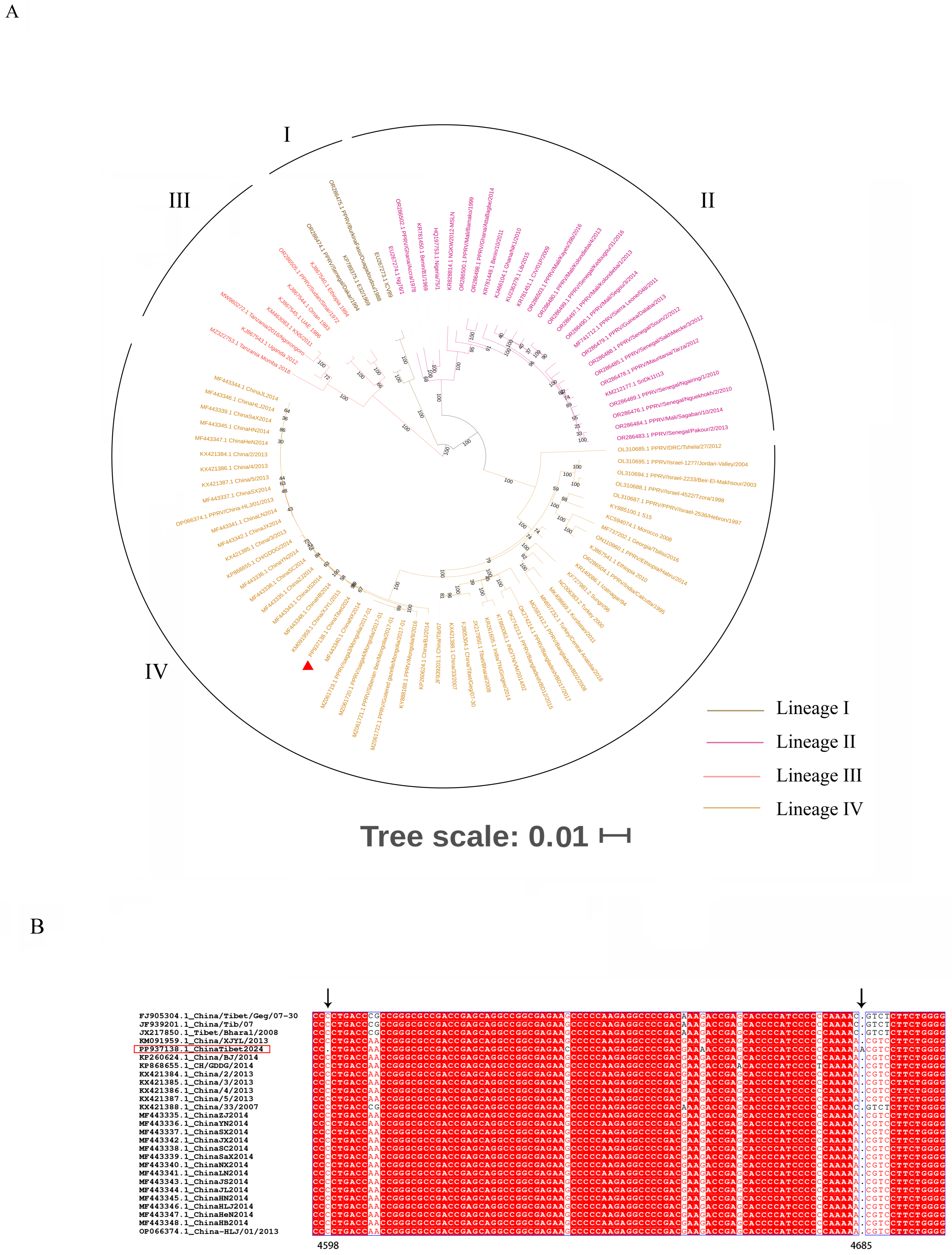
3.3. Phylogenetic Analysis and Sequence Alignment
3.4. Nucleotide and Amino Acid Diversity between ChinaTibet2024 and China/XJYL/2013
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, A.E.; Dhama, K.; Ali, Q.; Hussain, I.; Oneeb, M.; Chaudhary, U.; Wensman, J.J.; Shabbir, M.Z. Peste des petits ruminants in large ruminants, camels and unusual hosts. Vet. Q. 2020, 40, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njeumi, F. Current scenario and control initiatives for PPR at global, regional and country level according to the risk factors and socioeconomic impact. In Proceedings of the Second Regional Conference on Progressive Control of Peste Des Petits Ruminants in South Asia, Kathmandu, Nepal, 19–20 December 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gargadennec, L.; Lalanne, A. La peste des petits ruminants. Bull. Zoo Tech. Epizzoties Afr. Occident. Fr. 1942, 5, 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Dundon, W.G.; Diallo, A.; Cattoli, G. Peste des petits ruminants in Africa: A review of currently available molecular epidemiological data, 2020. Arch. Virol. 2020, 165, 2147–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AhAduzzaman, M. Peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in Africa and Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the prevalence in sheep and goats between 1969 and 2018. Vet. Med. Sci. 2020, 6, 613–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banyard, A.C.; Parida, S.; Batten, C.; Oura, C.; Kwiatek, O.; Libeau, G. Global distribution of peste des petits ruminants virus and prospects for improved diagnosis and control. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 2885–2897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Bao, J.Y.; Wu, X.D.; Liu, Y.T.; Li, L.; Liu, C.J.; Suo, L.; Xie, Z.L.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Peste des petits ruminants virus in Tibet, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 299–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.Y.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, L.; Wu, X.D.; Sang, P.; Wu, G.Z.; Ding, G.Y.; Suo, L.; Liu, C.J.; Wang, J.W.; et al. Detection and genetic characterization of peste des petits ruminants virus in free-living bharals (Pseudois nayaur) in Tibet. Res. Vet. Sci. 2011, 90, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M. Role of wild small ruminants in the epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2014, 61, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu Elzein, E.M.E.; Housawi, F.M.T.; Bashareek, Y.; Gameel, A.A.; AI-Afaleq, A.I.; Anderson, E. Severe PPR infection in gazelles kept under semi-free range conditions. J. Vet. Med. Ser. B 2004, 51, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, S.; Albayrak, H. Seroprevalance of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in goitered gazelle (Gazella subgutturosa subgutturosa) in Turkey. J. Wildl. Dis. 2010, 46, 673–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Li, L.; Wu, X.D.; Liu, F.X.; Zou, Y.L.; Wang, Q.H.; Liu, C.; Bao, J.; Wang, W.; Ma, W.; et al. Diagnosis of Peste des Petits Ruminants in Wild and Domestic Animals in Xinjiang, China, 2013–2016. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2017, 64, e43–e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.Y.; Wang, Q.H.; Li, L.; Liu, C.J.; Zhang, Z.C.; Li, J.M.; Wang, S.J.; Wu, X.D.; Wang, Z.L. Evolutionary dynamics of recent peste des petits ruminants virus epidemic in China during 2013–2014. Virology 2017, 510, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.; Cao, X.; He, J.; Liu, X.; Shang, Y. Analysis and Sequence Alignment of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus ChinaSX2020. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Li, W.; Hao, F.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Sun, M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, M.; Luo, X.; Cheng, Z. Research Progress on Emerging Viral Pathogens of Small Ruminants in China during the Last Decade. Viruses 2022, 14, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Miao, Q.; Zhu, L.; Zhan, S.H.; Wang, G.J.; Liu, G.Q. First report of peste des petits ruminants virus lineage II in Hydropotes inermis, China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 65, e205–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parida, S.; Muniraju, M.; Mahapatra, M.; Muthuchelvan, D.; Buczkowski, H.; Banyard, A.C. Peste des petits ruminants. Vet. Microbiol. 2015, 181, 90–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, B.; Liang, R.; Zhang, S.; Sun, X.; Li, F.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, H.; Bao, S.; Zhong, J.; Li, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal characteristics analysis and potential distribution prediction of peste des petits ruminants (PPR) in China from 2007–2018. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2022, 69, 2747–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camilla, T.O.B.; Sarah, H.; Shatar, M.; Shatar, M.; Shiilegdamba, E.; Damdinjav, B.; Fine, A.; Willett, B.; Kock, R.; Bataille, A. Molecular epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants virus emergence in critically endangered Mongolian saiga antelope and other wild ungulates. Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab062. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.X.; Li, J.M.; Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z. Peste des petits ruminants in China since its first outbreak in 2007: A 10-year review. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2018, 65, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhar, P.; Sreenivasa, B.P.; Barrett, T.; Corteyn, M.; Singh, R.P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K. Recent epidemiology of peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV). Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 88, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, K.; Amr, E. Toward peste des petits virus (PPRV) eradication: Diagnostic approaches, novel vaccines, and control strategies. Virus Res. 2019, 274, 197774. [Google Scholar]
- Kaushik, R.; Shaila, M.S. Cellular casein kinase II-mediated phosphorylation of rinderpest virus P protein is a prerequisite for its role in replication/transcription of the genome. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikia, P.; Gopinath, M.; Shaila, M.S. Phosphorylation status of the phosphoprotein P of rinderpest virus modulates transcription and replication of the genome. Arch. Virol. 2008, 153, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Region | Length (bp) | Nucleotide Variable Sites | Diversity (%) | Encoding Amino Acid | Amino Acid Variable Sites | Diversity (%) | Amino Acid Position | Amino Acid Mutation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leader | 52 | 2 | 3.85 | / | / | / | / | / |
| N 3′ UTR | 52 | 2 | 3.85 | / | / | / | / | / |
| N cds | 1578 | 15 | 0.95 | 525 | 2 | 0.38 | 442 | I-T |
| 515 | S-N | |||||||
| N 5′ UTR | 59 | 2 | 3.39 | / | / | / | / | / |
| P 3′ UTR | 59 | 1 | 1.69 | / | / | / | / | / |
| P cds | 1530 | 10 | 0.65 | 509 | 7 | 1.38 | 30 | R-K |
| 93 | A-T | |||||||
| 140 | V-I | |||||||
| 174 | N-D | |||||||
| 248 | I-T | |||||||
| 266 | N-S | |||||||
| 339 | I-L | |||||||
| P 5′ UTR | 66 | 1 | 1.52 | / | / | / | / | / |
| M 3′ UTR | 32 | 0 | 0.00 | / | / | / | / | / |
| M cds | 1008 | 5 | 0.50 | 335 | 0 | 0 | / | / |
| M 5′ UTR | 443 | 18 | 4.06 | / | / | / | / | / |
| F 3′ UTR | 640 | 27 | 4.22 | / | / | / | / | / |
| F cds | 1641 | 10 | 0.61 | 546 | 1 | 0.18 | 401 | S-N |
| F 5′ UTR | 136 | 7 | 5.15 | / | / | / | / | / |
| H 3′ UTR | 20 | 0 | 0.00 | / | / | / | / | / |
| H cds | 1830 | 18 | 0.98 | 609 | 5 | 0.82 | 27 | R-K |
| 309 | S-N | |||||||
| 438 | P-L | |||||||
| 488 | R-K | |||||||
| 609 | V-A | |||||||
| H 5′ UTR | 107 | 2 | 1.87 | / | / | / | / | / |
| L 3′ UTR | 22 | 0 | 0.00 | / | / | / | / | / |
| L cds | 6552 | 40 | 0.61 | 2183 | 8 | 0.37 | 78 | S-G |
| 122 | H-R | |||||||
| 138 | G-S | |||||||
| 843 | V-I | |||||||
| 1122 | G-A | |||||||
| 1621 | S-G | |||||||
| 2114 | P-S | |||||||
| 2162 | T-A | |||||||
| L 5′ UTR | 69 | 0 | 0.00 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Trailer | 37 | 0 | 0.00 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Total | 15,933 | 160 | 1.00 | 4707 | 23 | 0.49 | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Qu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Ren, W.; Liu, S.; Zou, Y.; Su, N.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z. Wildlife Infection of Peste des Petits Ruminants Detected in China, 2024. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100489
Xu J, Qu Z, Wang Y, Ren W, Liu S, Zou Y, Su N, Bao J, Wang Z. Wildlife Infection of Peste des Petits Ruminants Detected in China, 2024. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(10):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100489
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jiao, Zebin Qu, Yingli Wang, Weijie Ren, Shan Liu, Yanli Zou, Na Su, Jingyue Bao, and Zhiliang Wang. 2024. "Wildlife Infection of Peste des Petits Ruminants Detected in China, 2024" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 10: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100489
APA StyleXu, J., Qu, Z., Wang, Y., Ren, W., Liu, S., Zou, Y., Su, N., Bao, J., & Wang, Z. (2024). Wildlife Infection of Peste des Petits Ruminants Detected in China, 2024. Veterinary Sciences, 11(10), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11100489





