In Vitro Assessment of Postbiotic and Probiotic Commercial Dietary Supplements Recommended for Counteracting Intestinal Dysbiosis in Dogs
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Commercial Products Tested
2.2. Batch Culture Fermentations
2.3. Selective Enumeration of Bacteria Groups, Bacterial Profiling of the Fluid Microbiota, and SCFAs Determination
2.4. Statistical Methodology
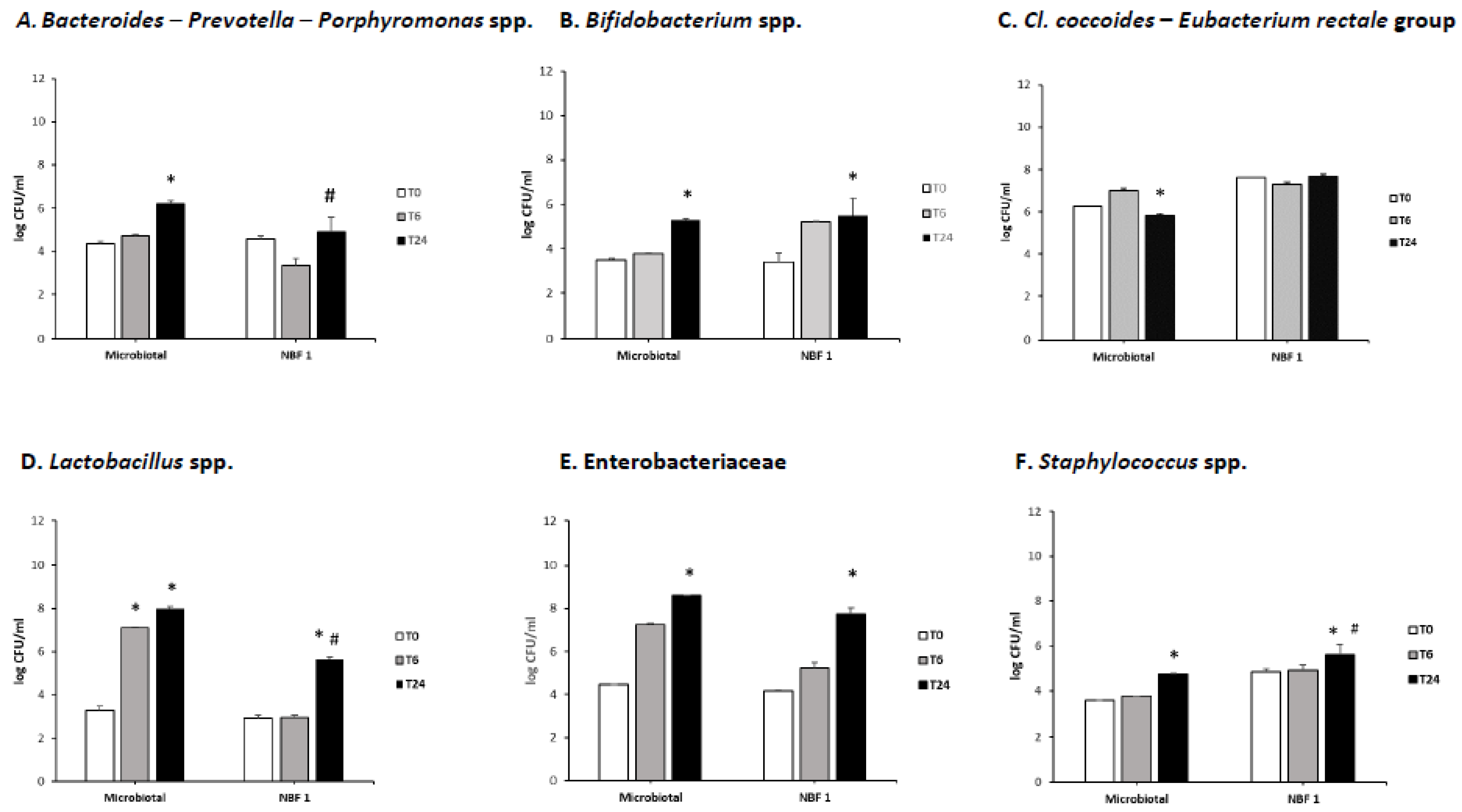
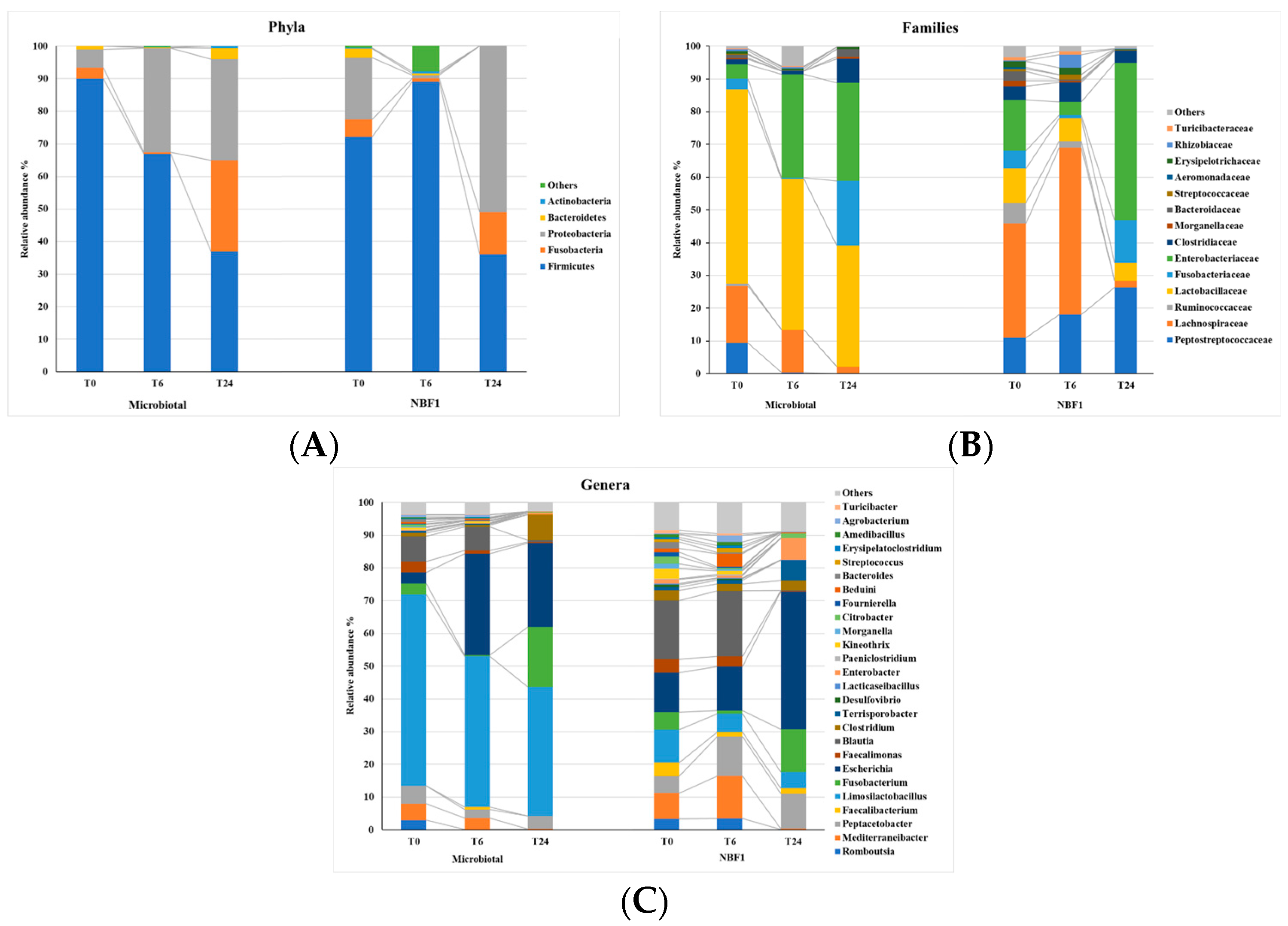
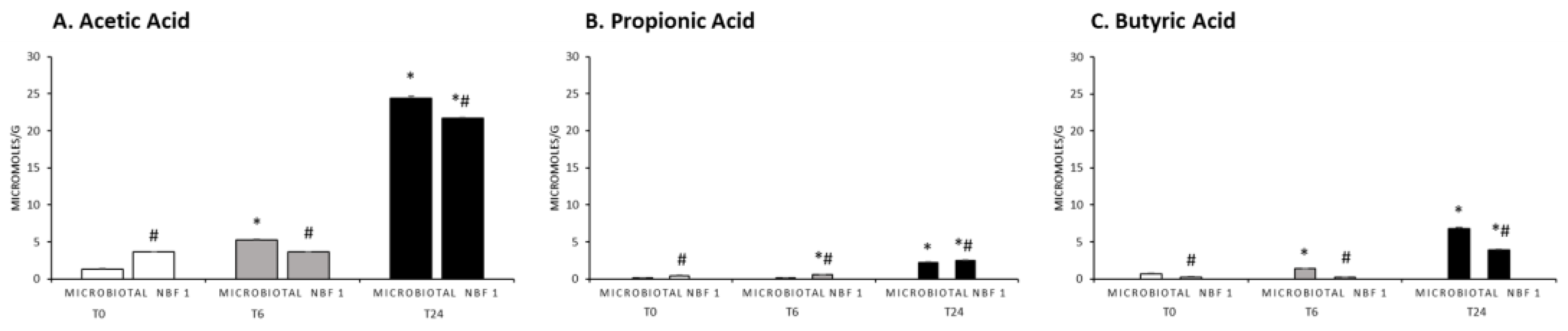
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Populations Changes
3.2. Profiling of the Fluid Microbiota by 16S Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)
3.3. SCFA Levels
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Herstad, K.M.V.; Gajardo, K.; Bakke, A.M.; Moe, L.; Ludvigsen, J.; Rudi, K. A diet change from dry food to beef induces reversible changes on the faecal microbiota in healthy, adult client-owned dogs. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.; Unterer, S.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Honneffer, J.B.; Guard, B.C.; Lidbury, J.A. The fecal microbiome and metabolome differ between dogs fed Bones and Raw Food (BARF) diets and dogs fed commercial diets. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0201279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilla, R.; Suchodolski, J.S. The Role of the Canine Gut Microbiome and Metabolome in Health and Gastrointestinal Disease. Review. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galler, A.I.; Suchodolski, J.S.; Steiner, J.M. Microbial dysbiosis and fecal metabolomic perturbations in Yorkshire Terriers with chronic enteropathy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herstad, K.M.V.; Vinje, H.; Skancke, E.; Næverdal, T.; Corral, F.; Llarena, A.; Nyquist, N.F. Effects of canine-obtained lactic-acid bacteria on the fecal microbiota and inflammatory markers in dogs receiving non-steroidal anti-inflammatory treatment. Animals 2022, 12, 2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biagi, G.; Cipollini, I.; Pompei, A.; Zaghini, G.; Matteuzzi, D. Effect of a Lactobacillus animalis strain on composition and metabolism of the intestinal microflora in adult dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaravolo, S.; Martínez-López, L.M.; Allcock, R.J.N.; Woodward, A.P.; Mansfield, C. Longitudinal survey of fecal microbiota in healthy dogs administered a commercial probiotic. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 664318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, S.S. Value of probiotics in canine and feline gastroenterology. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 51, 171–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittemore, J.C.; Price, J.M.; Moyers, T.; Suchodolski, J.S. Effects of synbiotics on the fecal microbiome and metabolomic profiles of healthy research dogs administered antibiotics: A randomized controlled trial. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 665713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, S.; Collado, M.C.; Endo, A.; Hill, C.; Lebeer, S.; Quigley, E.M.; Sanders, M.E.; Shamir, R.; Swann, J.R.; Szajewska, H.; et al. The International Scientific Association of Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 671. [Google Scholar]
- Laverde Gomez, J.A.; Mukhopadhya, I.; Duncan, S.H.; Louis, P.; Shaw, S.; Collie-Duguid, E.; Crost, E.; Juge, N.; Flint, H.J. Formate cross-feeding and cooperative metabolic interactions revealed by transcriptomics in co-cultures of acetogenic and amylolytic human colonic bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 21, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belà, B.; Coman, M.M.; Verdenelli, M.C.; Bianchi, C.; Pignataro, G.; Fiorini, D.; Silvi, S. In vitro fermentation of Cucumis sativus fructus extract by canine gut microbiota in combination with two probiotic strains. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 63, 103585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvesi, C.; Coman, M.M.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Fiorini, D.; Silvi, S. In vitro study of potential prebiotic properties of monovarietal extra virgin olive oils. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023; ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belà, B.; Pignataro, G.; Di Prinzio, R.; Di Simone, D.; Crisi, P.E.; Gramenzi, A. Effects of Lactobacillus reuteri NBF 1 DSM 32203 Supplementation on Healthy Dog Performance. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2021, 37, 29149–29163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Qu, F.; Zhu, L.H. Isolation of genomic DNAs from plants, fungi and bacteria using benzyl chloride. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993, 21, 5279–5280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avella, M.A.; Olivotto, I.; Silvi, S.; Place, A.R.; Carnevali, O. Effect of dietary probiotics on clownfish: A molecular approach to define how lactic acid bacteria modulate development in a marine fish. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R359–R371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micioni Di Bonaventura, M.V.; Coman, M.M.; Tomassoni, D.; Micioni Di Bonaventura, E.; Botticelli, L.; Gabrielli, M.G.; Rossolini, G.M.; Di Pilato, V.; Cecchini, C.; Amedei, A.; et al. Supplementation with Lactiplantibacillus plantarum IMC 510 modifies microbiota composition and prevents bodyweight gain induced by Cafeteria diet in rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scortichini, S.; Boarelli, M.C.; Silvi, S.; Fiorini, D. Development and validation of a GC-FID method for the analysis of short chain fatty acids in rat and human faeces and in fermentation fluids. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1143, 121972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, I.; Kim, M.J. Comparison of Gut Microbiota of 96 Healthy Dogs by Individual Traits: Breed, Age, and Body Condition Score. Animals 2021, 11, 2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.M.; Munoz-Munoz, J.; van Sinderen, D. Plant Glycan Metabolism by Bifidobacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 609418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.; Sarada, S.; Poornachandra, Y. Status and Future Prospects of Fructooligosaccharides as Nutraceuticals. Role Mater. Sci. Food Bioeng. 2018, 14, 451–503. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, G.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhao, K.N.; Vitetta, L. Effects of Intestinal Microbial-Elaborated Butyrate on Oncogenic Signaling Pathways. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasaly, N.; Hermoso, M.A.; Gotteland, M. Butyrate and the Fine-Tuning of Colonic Homeostasis: Implication for Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tandon, D.; Haque, M.M.; Gote, M. A prospective randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-response relationship study to investigate efficacy of fructo-oligosaccharides (FOS) on human gut microflora. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Wu, M.; Dong, Y.; Ma, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Yu, Q.; Zheng, X. In vitro fermentation of fructooligosaccharide and galactooligosaccharide and their effects on gut microbiota and SCFAs in infants. J. Funct. Foods 2022, 99, 105329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, H.; Saier, M.H.J. Gut Bacteroides species in health and disease. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1848158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, J.L.; Ji, S.Y.; Lee, S.D.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, B.; Kim, K.H. Difference of gut microbiota composition based on the body condition scores in dogs. J. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020, 62, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, ESP-0006-2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, J.L.; Yap, Y.A.; McLeod, K.H.; Mackay, C.R.; Mariño, E. Dietary metabolites and the gut microbiota: An alternative approach to control inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2016, 5, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, P.; Hold, G.L.; Flint, H.J. The gut microbiota, bacterial metabolites and colorectal cancer. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, A.; De Vadder, F.; Kovatcheva-Datchary, P.; Bäckhed, F. From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-Chain Fatty Acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell Rev. 2016, 165, 1332–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belà, B.; Coman, M.M.; Verdenelli, M.C.; Gramenzi, A.; Pignataro, G.; Fiorini, D.; Silvi, S. In Vitro Assessment of Postbiotic and Probiotic Commercial Dietary Supplements Recommended for Counteracting Intestinal Dysbiosis in Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010019
Belà B, Coman MM, Verdenelli MC, Gramenzi A, Pignataro G, Fiorini D, Silvi S. In Vitro Assessment of Postbiotic and Probiotic Commercial Dietary Supplements Recommended for Counteracting Intestinal Dysbiosis in Dogs. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(1):19. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010019
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelà, Benedetta, Maria Magdalena Coman, Maria Cristina Verdenelli, Alessandro Gramenzi, Giulia Pignataro, Dennis Fiorini, and Stefania Silvi. 2024. "In Vitro Assessment of Postbiotic and Probiotic Commercial Dietary Supplements Recommended for Counteracting Intestinal Dysbiosis in Dogs" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 1: 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010019
APA StyleBelà, B., Coman, M. M., Verdenelli, M. C., Gramenzi, A., Pignataro, G., Fiorini, D., & Silvi, S. (2024). In Vitro Assessment of Postbiotic and Probiotic Commercial Dietary Supplements Recommended for Counteracting Intestinal Dysbiosis in Dogs. Veterinary Sciences, 11(1), 19. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010019









