Histopathological Aspects of the Influence of Babesia microti on the Placentas of Infected Female Rats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Tissue Samples
2.2. FISH (Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization) Technique
2.3. Histopathology Examination
2.4. Semi-Thin Sections
3. Results
3.1. FISH
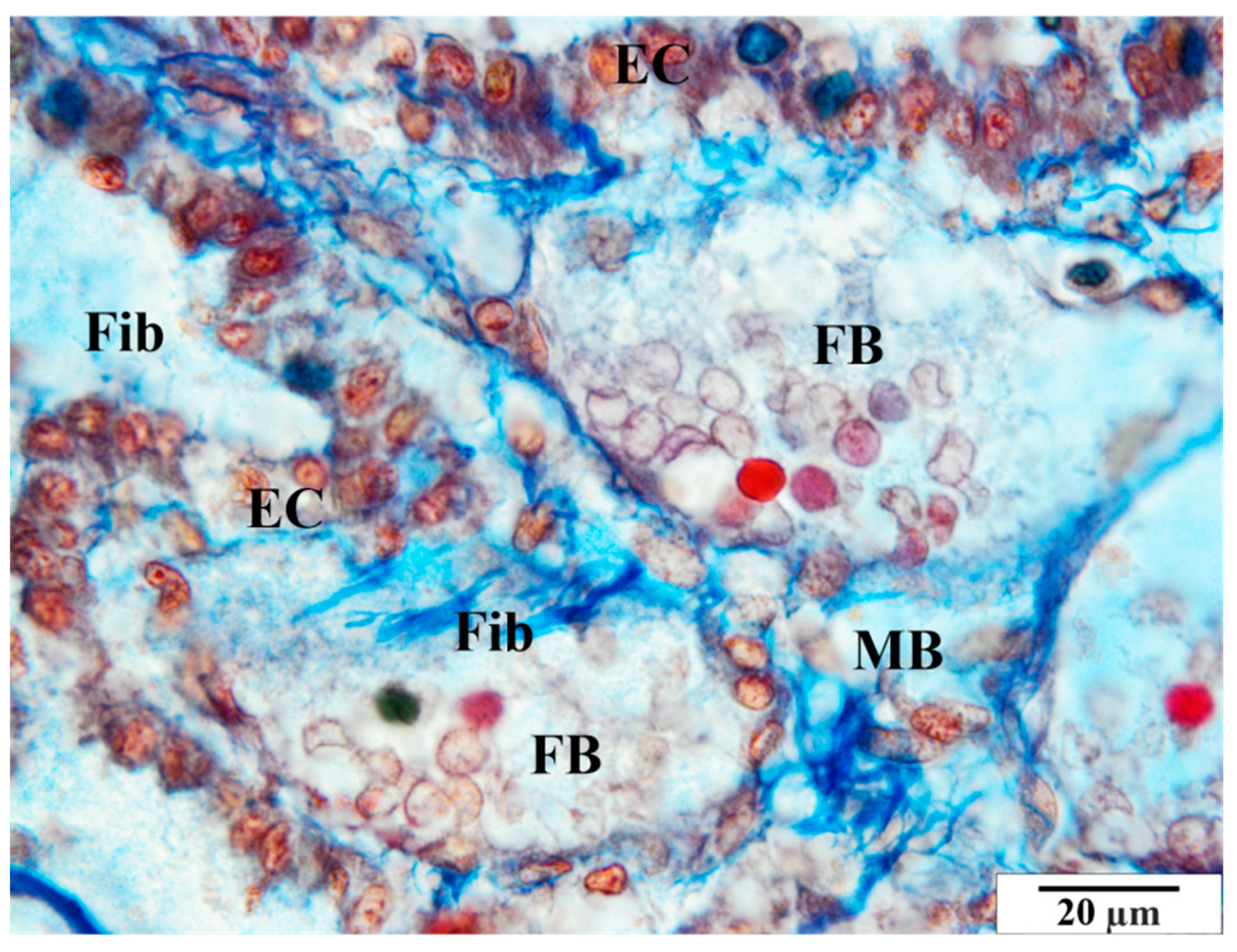
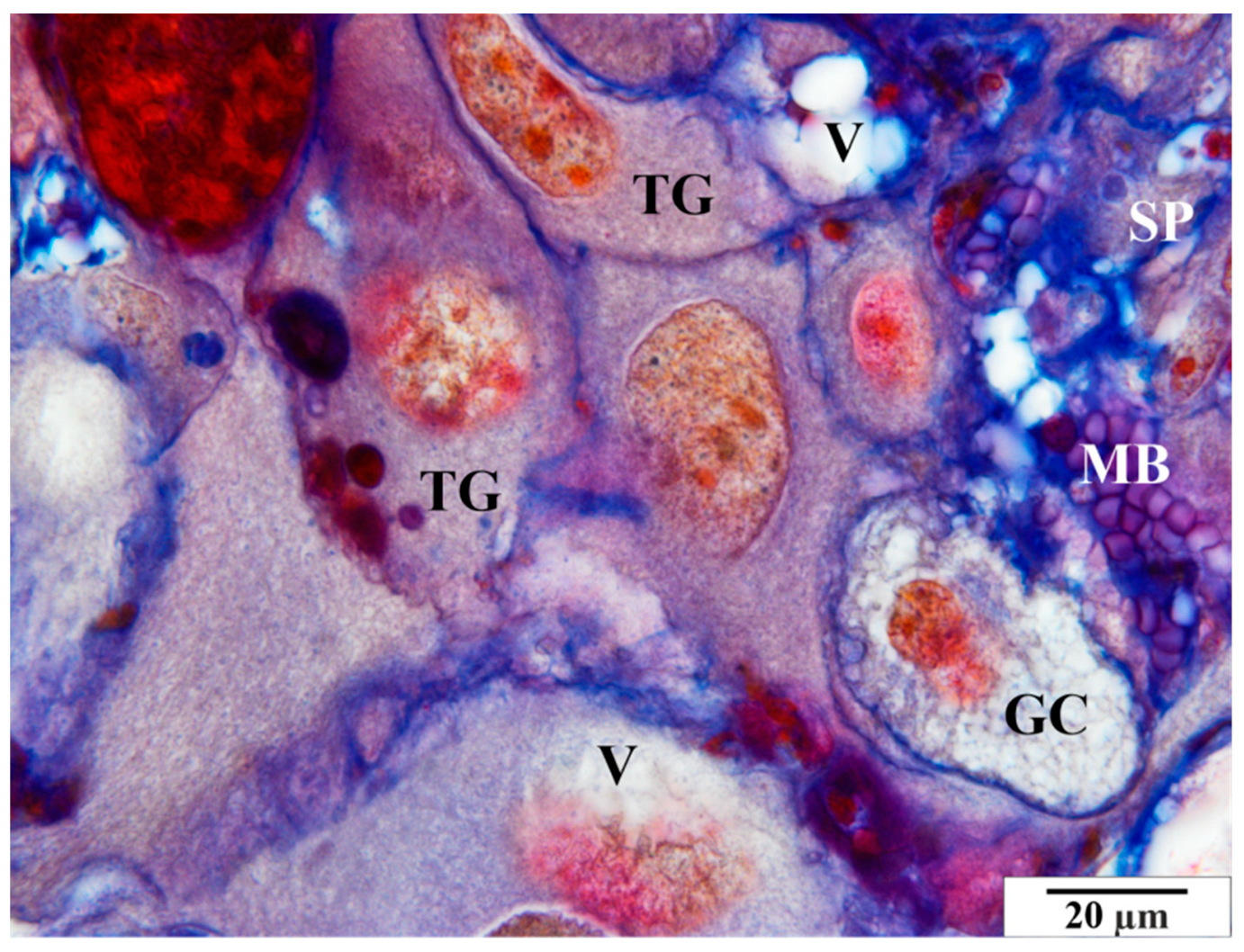
3.2. Mallory Staining
3.2.1. Control Group
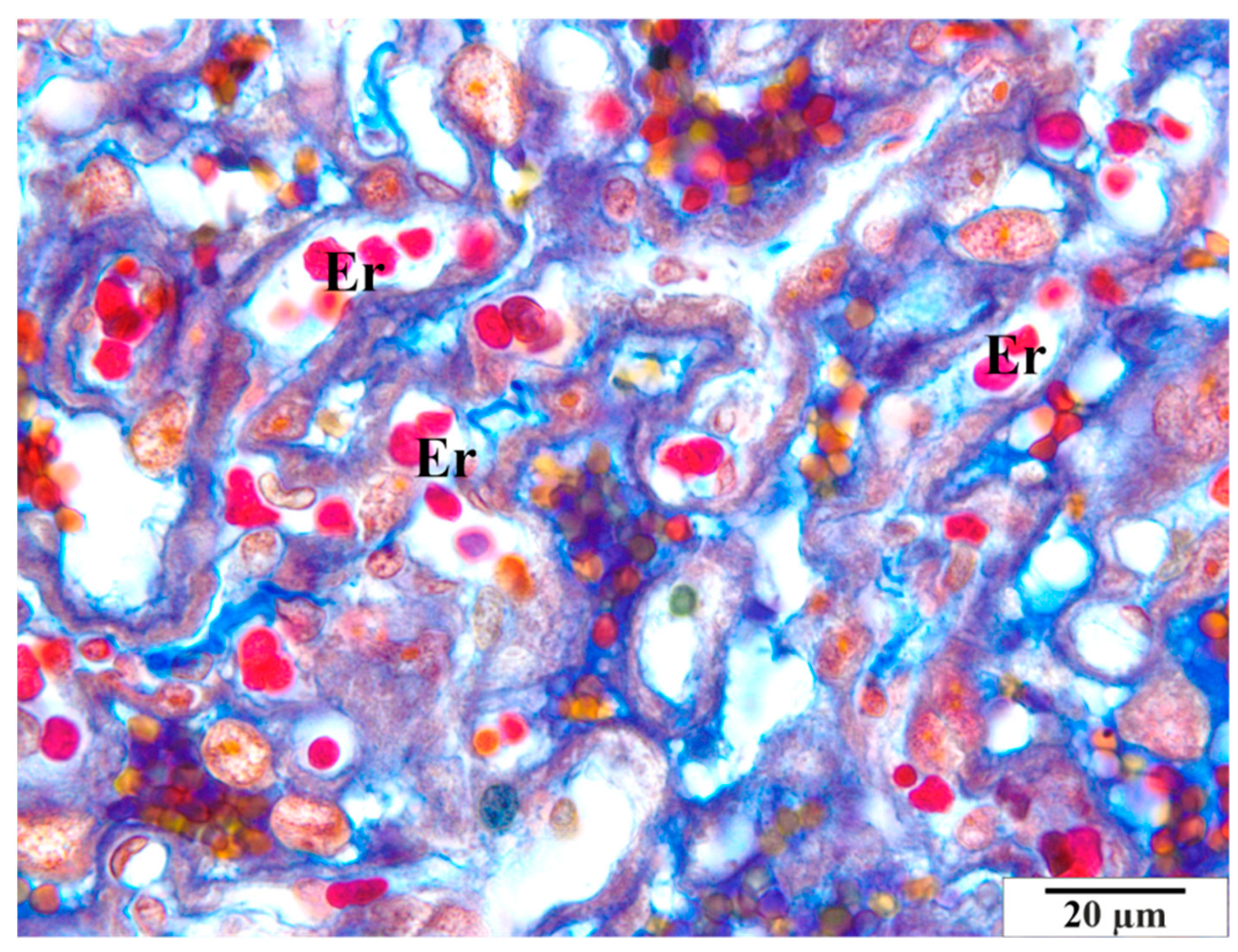
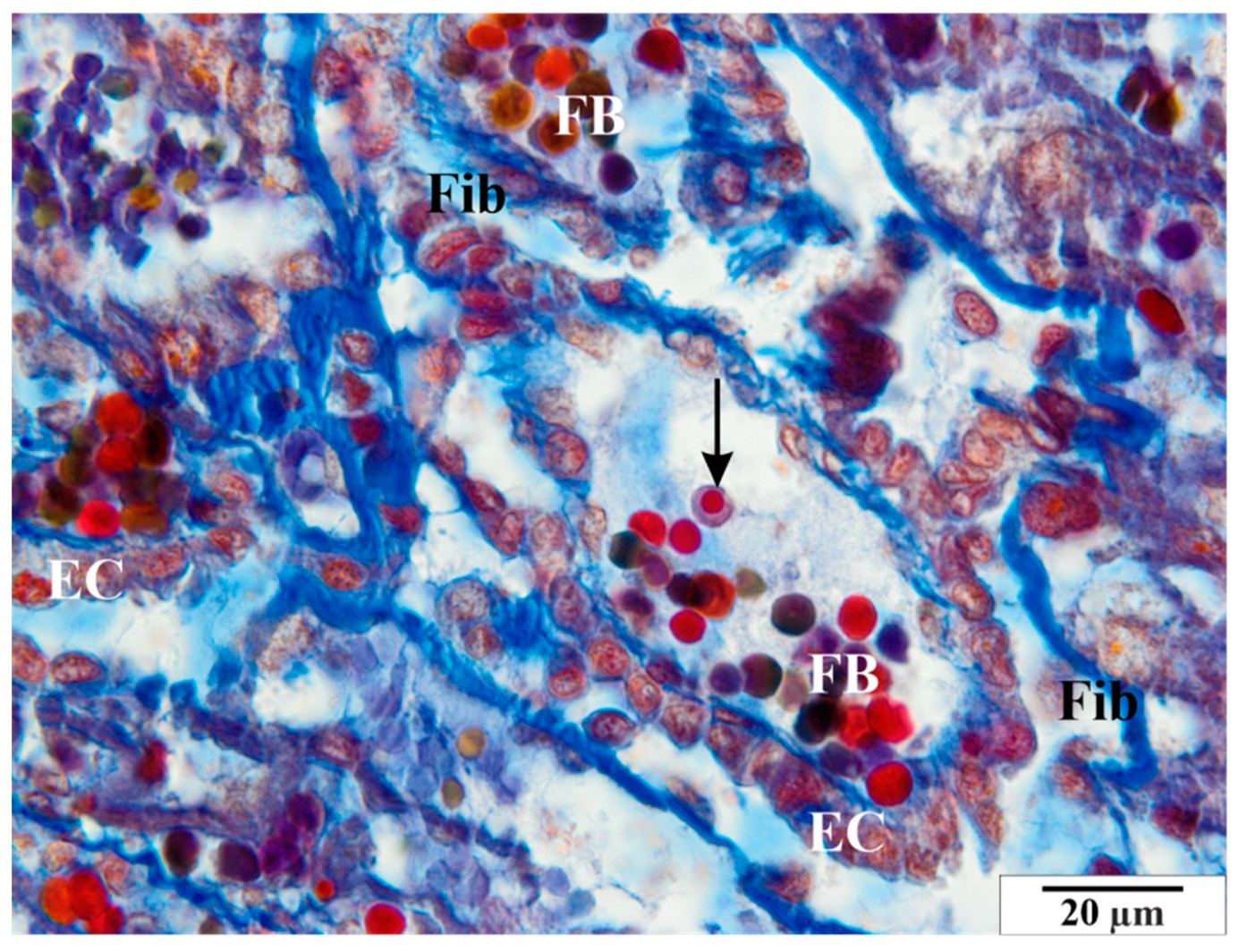
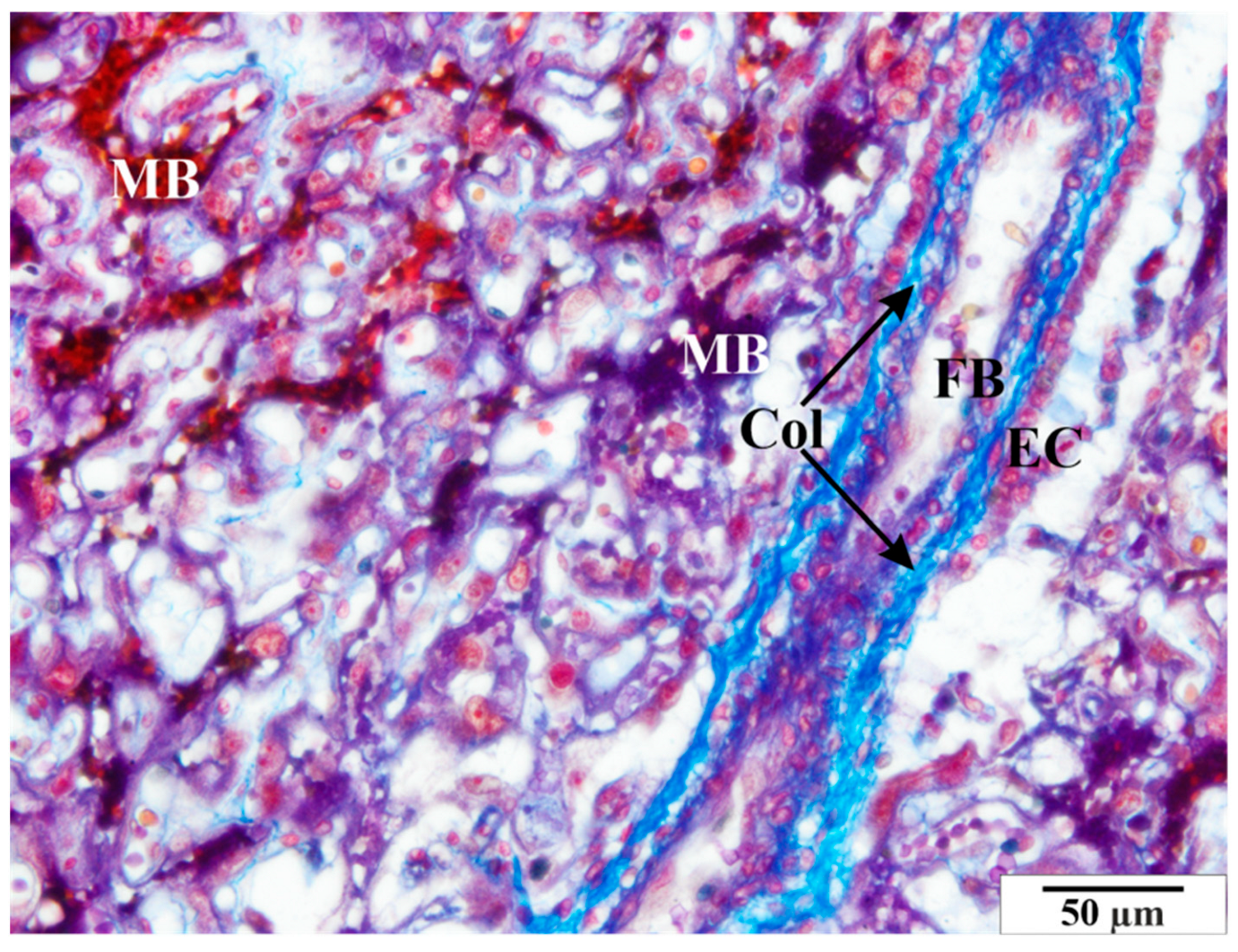
3.2.2. Infected Group
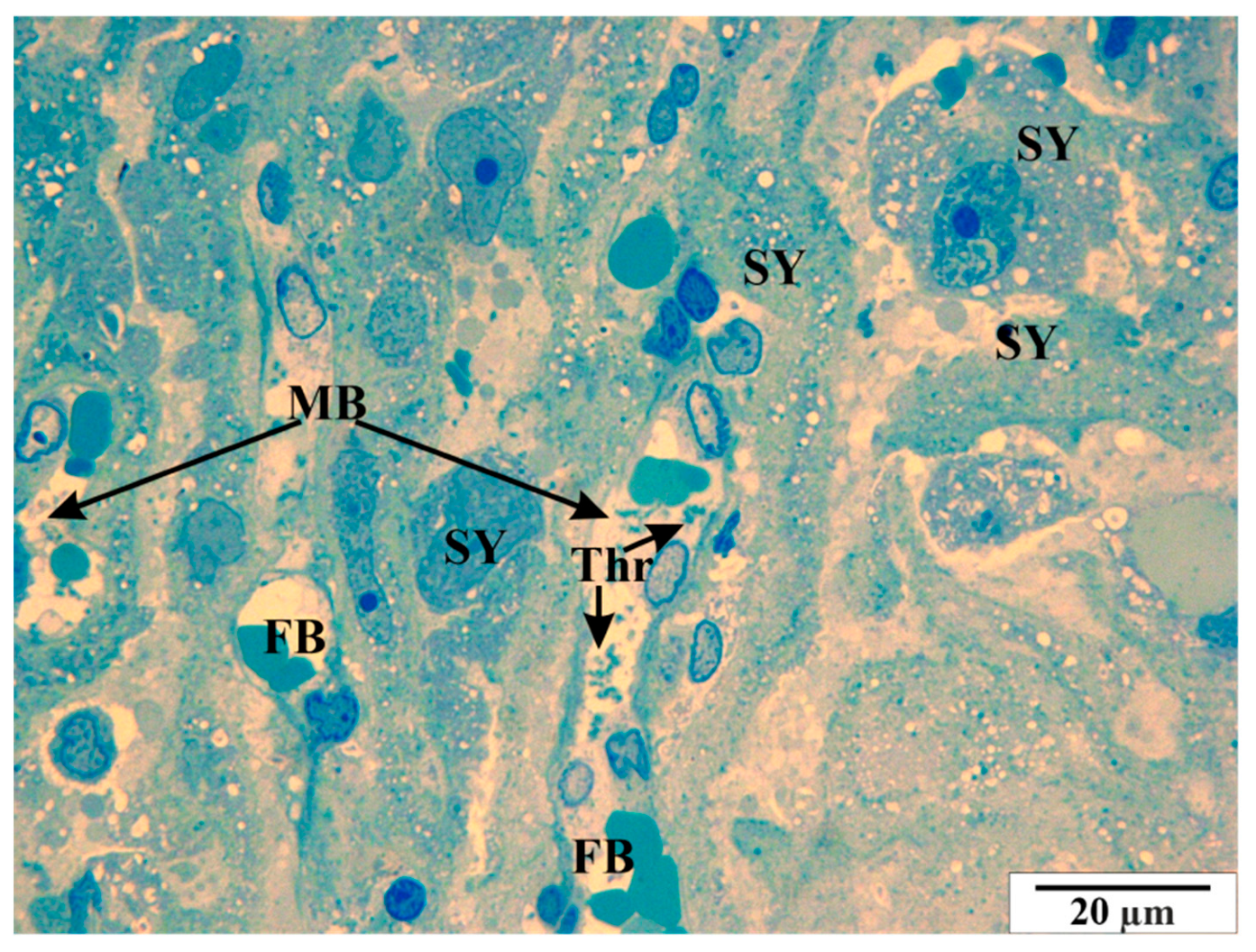
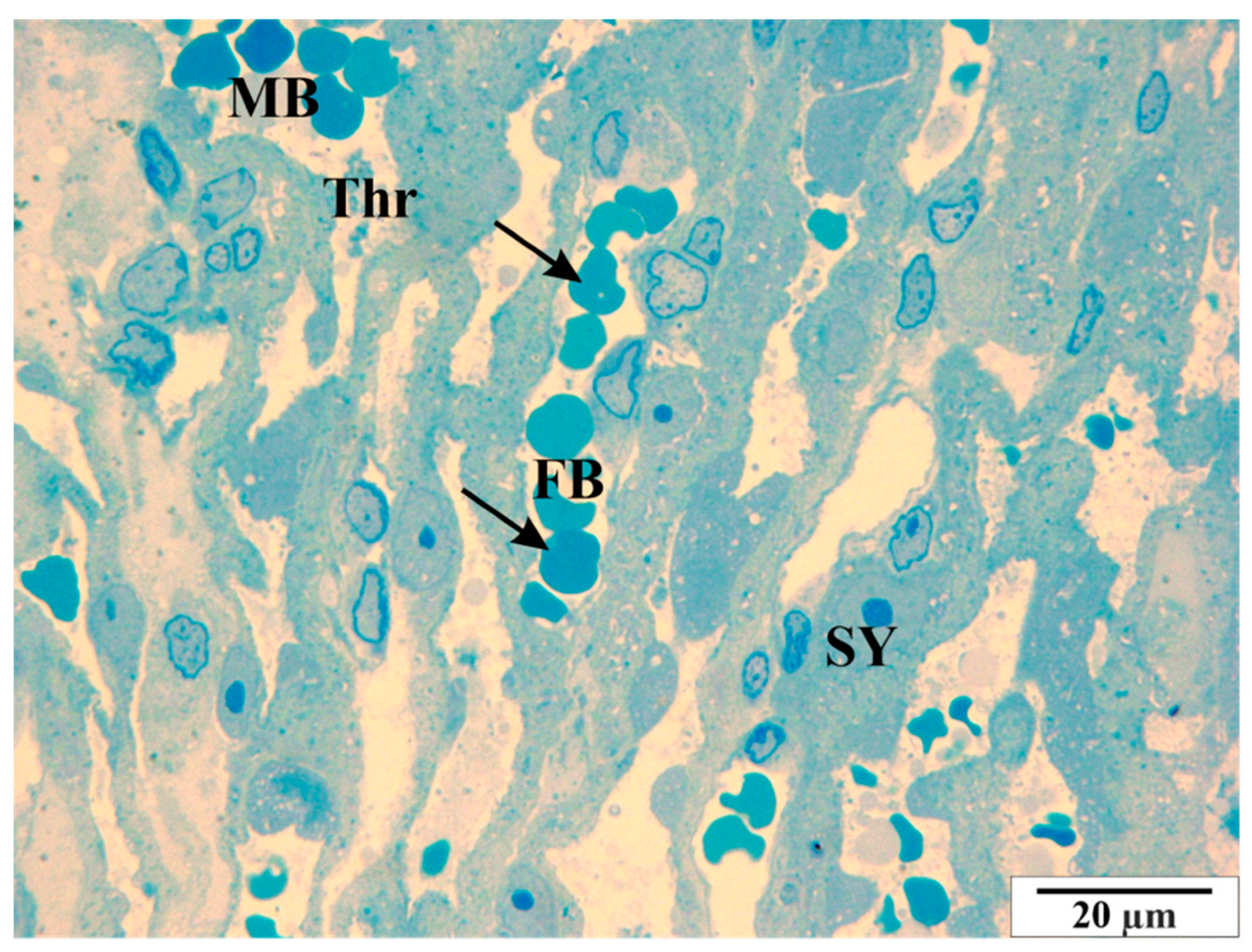
3.3. Microscopic Image of Semi-Thin Sections Stained with Methylene Blue
3.3.1. Control Group
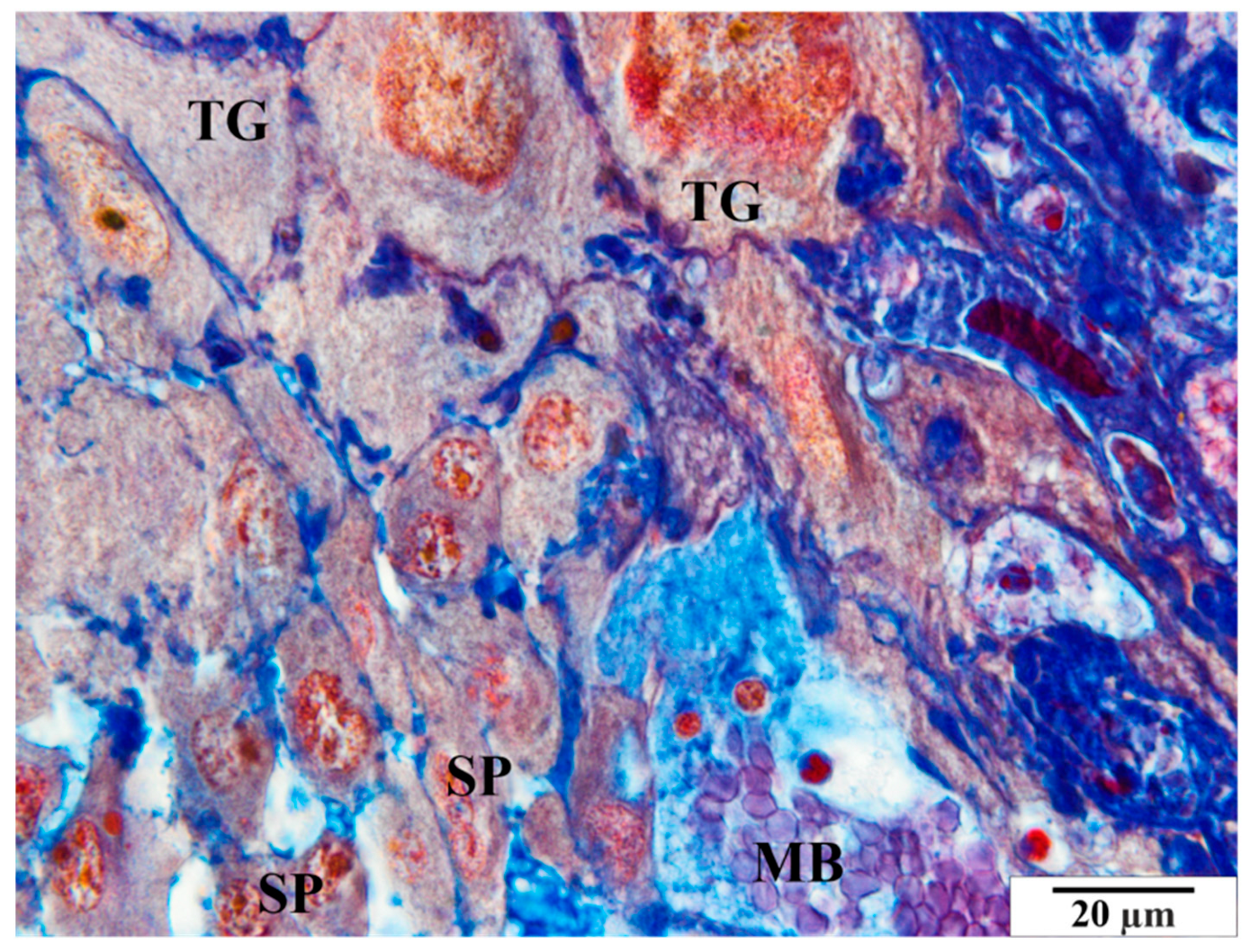
3.3.2. Study Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, J.S.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Zintl, A. Vectors of Babesiosis. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2019, 64, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moniuszko-Malinowska, A.; Swiecicka, I.; Dunaj, J.; Zajkowska, J.; Czupryna, P.; Zambrowski, G.; Chmielewska-Badora, J.; Żukiewicz-Sobczak, W.; Swierzbinska, R.; Rutkowski, K.; et al. Infection with Babesia microti in humans with non-specific symptoms in North East Poland. Infect. Dis. 2016, 48, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufts, D.M.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A. Transplacental transmission of tick-borne Babesia microti in its natural host Peromyscus leucopus. Parasites Vectors 2018, 11, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajer, A.; Dwużnik-Szarek, D. The specificity of Babesia-tick vector interactions: Recent advances and pitfalls in molecular and field studies. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalovecka, M.; Hajdusek, O.; Sojka, D.; Kopacek, P.; Malandrin, L. The Complexity of Piroplasms Life Cycles. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-García, G.; Santamaría-Espinosa, R.M.; Lira-Amaya, J.J.; Figueroa, J.V. Challenges in Tick-Borne Pathogen Detection: The Case for Babesia spp. Identification in the Tick Vector. Pathogens 2021, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, Y.; Gou, J.; Zhong, D.; Ma, L.; Yin, C.; Shu, M.; Liu, G.; Lin, Q. The Tick-Borne Pathogens: An Overview of China’s Situation. Acta Parasitol. 2023, 68, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westblade, L.F.; Simon, M.S.; Mathison, B.A.; Kirkman, L.A. Babesia microti: From Mice to Ticks to an Increasing Number of Highly Susceptible Humans. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2903–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, N.; Bhanot, P. Babesia microti-Borrelia burgdorferi Coinfection. Pathogens 2019, 8, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tołkacz, K.; Rodo, A.; Wdowiarska, A.; Bajer, A.; Bednarska, M. Impact of Babesia microti infection on the initiation and course of pregnancy in BALB/c mice. Parasites Vectors 2021, 14, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Kelly, B.; Lambert, J.S. Vector-borne diseases in pregnancy. Ther. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, 2049936120941725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulersen, M.; Brost, B.C.; Bobrovnikov, V.; Bornstein, E. Acute Babesiosis in Pregnancy: A Novel Imitator of Hemolysis, Elevated Liver Enzymes, and Low Platelet Count Syndrome. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 128, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khangura, R.K.; Williams, N.; Cooper, S.; Prabulos, A.M. Babesiosis in Pregnancy: An Imitator of HELLP Syndrome. AJP Rep. 2019, 9, e147–e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas-Pirela, M.; Medina, L.; Rojas, M.V.; Liempi, A.I.; Castillo, C.; Pérez-Pérez, E.; Guerrero-Muñoz, J.; Araneda, S.; Kemmerling, U. Congenital Transmission of Apicomplexan Parasites: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 751648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saetre, K.; Godhwani, N.; Maria, M.; Patel, D.; Wang, G.; Li, K.I.; Wormser, G.P.; Nolan, S.M. Congenital Babesiosis After Maternal Infection with Borrelia burgdorferi and Babesia microti. J. Pediatric. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2018, 7, e1–e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, S.; Goodman, K. Congenital Babesiosis From Maternal Exposure: A Case Report. J. Emerg. Med. 2019, 56, e39–e41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, A.J.; Simonsen, K.A. Babesiosis. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz, R.; Freeman, P.R. Healthy Fetal Outcomes using a Novel Treatment for Maternal Lyme Disease and Babesiosis During Consecutive Pregnancies: A Case Study and Literature Review. Arch. Med. Case Rep. 2020, 2, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, I.; Ben Mamoun, C. Treatment of Human Babesiosis: Then and Now. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, J.S.; Mark, O.; Caoili, E.; Poruri, A.; Horowitz, R.I.; Ashbaugh, A.D.; Ramasamy, R. A Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH) Test for Diagnosing Babesiosis. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wołuń-Cholewa, M.; Szymanowski, K.; Andrusiewicz, M.; Szczerba, A.; Warchoł, J.B. Trichrome Mallory’s stain may indicate differential rates of RNA synthesis in eutopic and ectopic endometrium. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2010, 48, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasik, K.; Kleczka, A.; Filipowska, S. Histopathological Analysis of Selected Organs of Rats with Congenital Babesiosis Caused by Babesia microti. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.F.; Serakides, R. Intrauterine trophoblast migration: A comparative view of humans and rodents. Cell Adh. Migr. 2016, 10, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Tsuji, N.; Sugiyama, A. Morphology and physiology of rat placenta for toxicological evaluation. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2019, 32, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bačenková, D.; Trebuňová, M.; Čížková, D.; Hudák, R.; Dosedla, E.; Findrik-Balogová, A.; Živčák, J. In Vitro Model of Human Trophoblast in Early Placentation. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, S.; Hayashi, S.; Usuda, K.; Abe, M.; Hagio, S.; Ogawa, I. Toxicological pathology in the rat placenta. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2011, 24, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charest, P.L.; Vrolyk, V.; Herst, P.; Lessard, M.; Sloboda, D.M.; Dalvai, M.; Haruna, J.; Bailey, J.L.; Benoit-Biancamano, M.O. Histomorphologic Analysis of the Late-term Rat Fetus and Placenta. Toxicol. Pathol. 2018, 46, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Gómez, R.; Ottone, N.E.; Bianchi, H.F. Morphological Features of the Human Placenta and its Free Chorionic Villi in Normal Pregnancies and those with Diabetes and High Blood Pressure. Literature Review. Int. J. Morphol. 2018, 36, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Boeldt, D.S.; Bird, I.M. Vascular adaptation in pregnancy and endothelial dysfunction in preeclampsia. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 232, R27–R44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, M.; Lipsett, B.J. Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Umbilical Cord. [Updated 2023 Jul 24]. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557389/ (accessed on 1 January 2023).
- Herrick, E.J.; Bordoni, B. Embryology, Placenta. 2023 May 1. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Belkacemi, L.; Jelks, A.; Chen, C.H.; Ross, M.G.; Desai, M. Altered placental development in undernourished rats: Role of maternal glucocorticoids. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2011, 9, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, Y.; Fujiwara, H.; Konishi, I. Mechanism of maternal vascular remodeling during human pregnancy. Reprod. Med. Biol. 2011, 11, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homer, M.J.; Aguilar-Delfin, I.; Telford, S.R., III; Krause, P.J.; Persing, D.H. Babesiosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 451–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bednarska, M.; Bajer, A.; Drozdowska, A.; Mierzejewska, E.J.; Tolkacz, K.; Welc-Falęciak, R. Vertical Transmission of Babesia microti in BALB/c Mice: Preliminary Report. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; O’Bryan, J.; Krause, P.J. The Global Emergence of Human Babesiosis. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyari, F.; Mbaya, A.W.; Adamu, L.; Malgwi, S.A.; Zango, M.K. Prevalence of Babesia infection and hematological changes in Camelus dromedarius slaughtered in Maiduguri, Borno state. Res. J. Vet. Sci. 2021, 14, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeilnejad, B.; Tavassoli, M.; Samiei, A.; Abbasi, A.; Shafipour, A.; Esmaeilnejad, N. Histopathological changes and oxidative damage in hepatic tissue of rats experimentally infected with Babesia bigemina. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 21, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano-Gallego, L.; Sainz, Á.; Roura, X.; Estrada-Peña, A.; Miró, G. A review of canine babesiosis: The European perspective. Parasites Vectors 2016, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, L.J.; Barnes, M.; Tang, H.; Pritchard, M.T.; Nagy, L.E. Kupffer cells in the liver. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 785–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertyńska, M.; Okła, H.; Jasik, K.; Urbańska-Jasik, D.; Pol, P. Interactions between Babesia microti merozoites and rat kidney cells in a short-term in vitro culture and animal model. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, E.; Krause, P.J. Human babesiosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2397–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokic, V.; Akoolo, L.; Parveen, N. Babesia microti Infection Changes Host Spleen Architecture and Is Cleared by a Th1 Immune Response. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okła, H.; Jasik, K.P.; Urbańska-Jasik, D.; Słodki, J.; Rozwadowska, B.; Grelowski, M.; Chmielik, E.; Słodki, A.; Albertyńska, M.; Grajoszek, A. Rat spleen in the course of Babesia microti invasion: Histological and submicroscopic studies. Acta Protozool. 2017, 56, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vannier, E.G.; Diuk-Wasser, M.A.; Ben Mamoun, C.; Krause, P.J. Babesiosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 29, 357–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Cai, Y.C.; Chen, S.H.; Chen, J.X.; Guo, J.; Chen, M.X.; Ai, L.; Chu, Y.H.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, X.N. Establishment of the experimental animal model of Babesia microti. Zhongguo Ji Sheng Chong Xue Yu Ji Sheng Chong Bing Za Zhi 2012, 30, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Cai, Y.C.; Chen, M.X.; Chen, S.H.; Chen, J.X. Enhanced phosphatidylserine exposure and erythropoiesis in Babesia microti-infected mice. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1083467, Erratum in Front Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1157549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okła, H.; Jasik, K.P.; Słodki, J.; Rozwadowska, B.; Słodki, A.; Jurzak, M.; Pierzchała, E. Hepatic tissue changes in rats due to chronic invasion of Babesia microti. Folia Biol. 2014, 62, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djokic, V.; Rocha, S.C.; Parveen, N. Lessons Learned for Pathogenesis, Immunology, and Disease of Erythrocytic Parasites: Plasmodium and Babesia. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 685239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnetti, L.; Townsend, R.L.; Deisting, B.M.; Haynes, J.M.; Dodd, R.Y.; Stramer, S.L. The impact of Babesia microti blood donation screening. Transfusion 2019, 59, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abittan, B.; Nizam, A.; Oey, M.; Callan, F.; Simmonds, L.; Pachtman, S.L. A Case of Babesiosis in a Pregnant Patient Treated with Red Blood Cell Exchange Transfusion. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 2019, 9869323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbowiak, G. Zoonotic reservoir of Babesia microti in Poland. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2004, 53, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Puri, A.; Bajpai, S.; Meredith, S.; Aravind, L.; Krause, P.J.; Kumar, S. Babesia microti: Pathogen Genomics, Genetic Variability, Immunodominant Antigens, and Pathogenesis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 697669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goethert, H.K. What Babesia microti Is Now. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jasik, K.P.; Kleczka, A.; Franielczyk, A. Histopathological Aspects of the Influence of Babesia microti on the Placentas of Infected Female Rats. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010018
Jasik KP, Kleczka A, Franielczyk A. Histopathological Aspects of the Influence of Babesia microti on the Placentas of Infected Female Rats. Veterinary Sciences. 2024; 11(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleJasik, Krzysztof P., Anna Kleczka, and Aleksandra Franielczyk. 2024. "Histopathological Aspects of the Influence of Babesia microti on the Placentas of Infected Female Rats" Veterinary Sciences 11, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010018
APA StyleJasik, K. P., Kleczka, A., & Franielczyk, A. (2024). Histopathological Aspects of the Influence of Babesia microti on the Placentas of Infected Female Rats. Veterinary Sciences, 11(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci11010018





