Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs and Cats: Treatment, Complications and Prognosis
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Medical Management of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts
3. Surgical Treatment of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts
3.1. Suture Ligation
3.2. Gradual Attenuation
3.3. Percutaneous Transvenous Coil Embolization
4. Complications after Congenital Portosystemic Shunt Attenuation
5. Long-Term Post-operative Care
6. Prognosis and Outcome
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weisse, C.; Berent, A. Hepatic Vascular Anomalies. In Textbook of Veterinary Internal Medicine; Ettinger, S., Feldman, E., Cote, E., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017; pp. 1639–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Berent, A.; Tobias, K. Hepatic Vascular Anomalies. In Veterinary Surgery: Small Animal; Johnston, S., Tobias, K., Eds.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2018; pp. 1852–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Mehl, M.L.; Kyles, A.E.; Hardie, E.M.; Kass, P.H.; Adin, C.; Flynn, A.K.; De Cock, H.E.; Gregory, C.R. Evaluation of Ameroid Ring Constrictors for Treatment for Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: 168 Cases (1995–2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2005, 226, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bostwick, D.R.; Twedt, D.C. Intrahepatic and Extrahepatic Portal Venous Anomalies in Dogs: 52 Cases (1982–1992). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1995, 206, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weisse, C.; Berent, A.C.; Todd, K.; Solomon, J.A.; Cope, C. Endovascular Evaluation and Treatment of Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: 100 Cases (2001–2011). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 244, 78–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, K.M.; Rohrbach, B.W. Association of Breed with the Diagnosis of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: 2,400 Cases (1980–2002). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 1636–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holford, A.L.; Tobias, K.M.; Bartges, J.W.; Johnson, B.M. Adrenal Response to Adrenocorticotropic Hormone in Dogs before and after Surgical Attenuation of a Single Congenital Portosystemic Shunt. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 832–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berent, A.C.; Tobias, K.M. Portosystemic Vascular Anomalies. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2009, 39, 513–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivers, M.; Lipscomb, V. Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Cats: Investigation, Diagnosis and Stabilisation. J. Feline Med. Surg. 2011, 13, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayton, W.A.; Westgarth, C.; Scase, T.; Price, D.J.; Bexfield, N.H. Histopathological Frequency of Feline Hepatobiliary Disease in the UK. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, J.T.; Bohling, M.W.; Tillson, M.D.; Wright, J.C.; Ballagas, A.J. Portosystemic Shunts: Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Treatment of 64 Cases (1993–2001). J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2003, 39, 169–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, S.N.; Dunning, M.D.; McKinley, T.J.; Goodfellow, M.R.; Kelman, K.R.; Freitag, T.; O’Neill, E.J.; Hall, E.J.; Watson, P.J.; Jeffery, N.D. Comparison of Survival after Surgical or Medical Treatment in Dogs with a Congenital Portosystemic Shunt. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2010, 236, 1215–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhalgh, S.N.; Reeve, J.A.; Johnstone, T.; Goodfellow, M.R.; Dunning, M.D.; O’Neill, E.J.; Hall, E.J.; Watson, P.J.; Jeffery, N.D. Long-Term Survival and Quality of Life in Dogs with Clinical Signs Associated with a Congenital Portosystemic Shunt after Surgical or Medical Treatment. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwingenberger, A.L.; Daniel, L.; Steffey, M.A.; Mayhew, P.D.; Mayhew, K.N.; Culp, W.T.N.; Hunt, G.B. Correlation Between Liver Volume, Portal Vascular Anatomy, and Hepatic Perfusion in Dogs With Congenital Portosystemic Shunt Before and After Placement of Ameroid Constrictors. Vet. Surg. 2014, 43, 926–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.J.; Herrtage, M.E. Medical Management of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in 27 Dogs-a Retrospective Study. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1998, 39, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivers, M.S.; Lipscomb, V.J. Hepatic Vascular Disorders. In Feline Gastroenterology; Procoli, F., Allenspach, K.A., Salavati Schmitz, S., Eds.; Edra S.p.A.: Milano, Italy, 2021; pp. 346–359. [Google Scholar]
- Tivers, M.S.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Brockman, D.J. Treatment of Intrahepatic Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: A Systematic Review. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 58, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gow, A.G. Hepatic Encephalopathy. Vet. Clin. N. Am.—Small Anim. Pract. 2017, 47, 585–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Center, S.A. Nutritional Support for Dogs and Cats with Hepatobiliary Disease. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 2733S–2746S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflamme, D.P. Nutritional Management of Liver Disease. In Kirk’s Current Veterinary Therapy XIII; Bonagura, J.D., Ed.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2000; pp. 693–697. [Google Scholar]
- Laflamme, D.P.; Allen, S.W.; Huber, T.L. Apparent Dietary Protein Requirement of Dogs with Portosystemic Shunt. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1993, 54, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lidbury, J.A.; Cook, A.K.; Steiner, J.M. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs and Cats. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care (San Antonio) 2016, 26, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proot, S.; Biourge, V.; Teske, E.; Rothuizen, J. Soy Protein Isolate versus Meat-Based Low-Protein Diet for Dogs with Congenital Portosystemic Shunts. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2009, 23, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marks, S.L. Nutritional Management of Hepatobiliary Diseases. In Applied Veterinary Clinical Nutrition; Fascetti, A.J., Delaney, S.J., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 235–250. [Google Scholar]
- Elwir, S.; Rahimi, R.S. Hepatic Encephalopathy: An Update on the Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Options. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerber, T.; Schomerus, H. Hepatic Encephalopathy in Liver Cirrhosis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Management. Drugs 2000, 60, 1353–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, A.; Perumpail, R.B.; Kumari, R.; Younossi, Z.M.; Wong, R.J.; Ahmed, A. Advances in Cirrhosis: Optimizing the Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 2871–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phongsamran, P.V.; Kim, J.W.; Cupo Abbott, J.; Rosenblatt, A. Pharmacotherapy for Hepatic Encephalopathy. Drugs 2010, 70, 1131–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, G.; Devriendt, N.; de Rooster, H.; Paepe, D. Comparison of Diet, Lactulose, and Metronidazole Combinations in the Control of Pre-Surgical Clinical Signs in Dogs with Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, N.M.; Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.; Poordad, F.; Neff, G.; Leevy, C.B.; Sigal, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Beavers, K.; Frederick, T.; et al. Rifaximin Treatment in Hepatic Encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miglio, F.; Valpiani, D.; Rossellini, S.R.; Ferrieri, A.; Canova, N. Rifaximin, a Non-Absorbable Rifamycin, for the Treatment of Hepatic Encephalopathy. A Double-Blind, Randomised Trial. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1997, 13, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falls, E.L.; Milovancev, M.; Hunt, G.B.; Daniel, L.; Mehl, M.L.; Schmiedt, C.W. Long-Term Outcome after Surgical Ameroid Ring Constrictor Placement for Treatment of Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2013, 42, 951–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case, J.B.; Marvel, S.J.; Stiles, M.C.; Maisenbacher, H.W.; Toskich, B.B.; Smeak, D.D.; Monnet, E.L. Outcomes of Cellophane Banding or Percutaneous Transvenous Coil Embolization of Canine Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, O59–O66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraun, M.B.; Nelson, L.L.; Hauptman, J.G.; Nelson, N.C. Analysis of the Relationship of Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Morphology with Clinical Variables in Dogs: 53 Cases (2009–2012). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 540–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häussinger, D.; Butz, M.; Schnitzler, A.; Görg, B. Pathomechanisms in Hepatic Encephalopathy. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 1087–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.S.; Hughes, R.D.; Harrison, P.M.; Murata, Y.; Pannell, L.; Jones, E.A.; Williams, R.; Skolnick, P. Elevated Brain Concentrations of 1,4-Benzodiazepines in Fulminant Hepatic Failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakti, G.; Fisch, H.U.; Karlaganis, G.; Minder, C.; Bircher, J. Mechanism of the Excessive Sedative Response of Cirrhotics to Benzodiazepines: Model Experiments with Triazolam. Hepatology 1987, 7, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahboucha, S.; Butterworth, R.F. The Neurosteroid System: Implication in the Pathophysiology of Hepatic Encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrein, R.; Leishman, B.; Bentzinger, C.; Roncari, G. Flumazenil in Benzodiazepine Antagonism. Actions and Clinical Use in Intoxications and Anaesthesiology. Med. Toxicol. Adverse Drug Exp. 1987, 2, 411–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulenok, C.; Bernard, B.; Cadranel, J.F.; Thabut, D.; Di Martino, V.; Opolon, P.; Poynard, T. Flumazenil vs. Placebo in Hepatic Encephalopathy in Patients with Cirrhosis: A Meta-Analysis. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002, 16, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, H.P.; Legemate, D.A.; Van Den Brom, W.; Rothuizen, J. Improvement of Chronic Hepatic Encephalopathy in Dogs by the Benzodiazepine-Receptor Partial Inverse Agonist Sarmazenil, but Not by the Antagonist Flumazenil. Metab. Brain Dis. 1998, 13, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, V.J.; Lee, K.C.; Lamb, C.R.; Brockman, D.J. Association of Mesenteric Portovenographic Findings with Outcome in Cats Receiving Surgical Treatment for Single Congenital Portosystemic Shunts. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2009, 234, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.C.L.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Lamb, C.R.; Gregory, S.P.; Guitian, J.; Brockman, D.J. Association of Portovenographic Findings with Outcome in Dogs Receiving Surgical Treatment for Single Congenital Portosystemic Shunts: 45 Cases (2000–2004). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 1122–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummeling, A.; Vrakking, D.J.E.; Rothuizen, J.; Gerritsen, K.M.; van Sluijs, F.J. Hepatic Volume Measurements in Dogs with Extrahepatic Congenital Portosystemic Shunts before and after Surgical Attenuation. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.B.; Culp, W.T.N.; Mayhew, K.N.; Mayhew, P.; Steffey, M.A.; Zwingenberger, A. Evaluation of in Vivo Behavior of Ameroid Ring Constrictors in Dogs with Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts Using Computed Tomography. Vet. Surg. 2014, 43, 834–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivers, M.S.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Smith, K.C.; Wheeler-Jones, C.P.D.; House, A.K. Markers of Hepatic Regeneration Associated with Surgical Attenuation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. J. 2014, 200, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adin, C.A.; Sereda, C.W.; Thompson, M.S.; Wheeler, J.L.; Archer, L.L. Outcome Associated with Use of a Percutaneously Controlled Hydraulic Occluder for Treatment of Dogs with Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 1749–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, D.; Seim, H.; MacPhail, C.; Monnet, E. Evaluation of Cellophane Banding with and without Intraoperative Attenuation for Treatment of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 228, 1355–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kummeling, A.; Van Sluijs, F.J.; Rothuizen, J. Prognostic Implications of the Degree of Shunt Narrowing and of the Portal Vein Diameter in Dogs with Congenital Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 2004, 33, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereda, C.W.; Adin, C.A. Methods of Gradual Vascular Occlusion and Their Applications in Treatment of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: A Review. Vet. Surg. 2005, 34, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.B.; Kummeling, A.; Tisdall, P.L.C.; Marchevsky, A.M.; Liptak, J.M.; Youmans, K.R.; Goldsmid, S.E.; Beck, J.A. Outcomes of Cellophane Banding for Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in 106 Dogs and 5 Cats. Vet. Surg. 2004, 33, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, V.J.; Jones, H.J.; Brockman, D.J. Complications and Long-Term Outcomes of the Ligation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in 49 Cats. Vet. Rec. 2007, 160, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swalec, K.M.; Smeak, D.D. Partial versus Complete Attenuation of Single Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 1990, 19, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hottinger, H.A.; Walshaw, R.; Hauptman, J.G. Long-Term Results of Complete and Partial Ligation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 1995, 24, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, G.B.; Hughes, J. Outcomes after Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Ligation in 49 Dogs. Aust. Vet. J. 1999, 77, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.B.; Bellenger, C.R.; Pearson, M.R.B. Transportal Approach for Attenuating Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 1996, 25, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.N.; Burton, C.A.; McEvoy, F.J. Surgical Treatment of Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in 45 Dogs. Vet. Rec. 1998, 142, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, G.; Rolla, E.C.; Zotti, A.; Caldin, M. Three-Dimensional Multislice Helical Computed Tomography Techniques for Canine Extra-Hepatic Portosystemic Shunt Assessment. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2006, 47, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolini, G. Anomalies of the Portal Venous System in Dogs and Cats as Seen on Multidetector-Row Computed Tomography: An Overview and Systematization Proposal. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.S.; Monnet, E.; Powers, B.E.; Twedt, D.C. Histologic Examination of Hepatic Biopsy Samples as a Prognostic Indicator in Dogs Undergoing Surgical Correction of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts: 64 Cases (1997–2005). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 232, 1511–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Gundy, T.E.; Boothe, H.W.; Wolf, A. Results of Surgical Management of Feline Portosystemic Shunts. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1990, 26, 55–62. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, J.; Bunch, S.; Komtebedde, J. Feline Portosystemic Vascular Shunts. In Kirk’s Current Veterinary Therapy XII Small Animal Practice; Bonagura, J., Ed.; WB Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1995; pp. 915–919. [Google Scholar]
- Kyles, A.E.; Gregory, C.R.; Jackson, J.; Ilkiw, J.E.; Pascoe, P.J.; Adin, C.; Samii, V.F.; Herrgesell, E. Evaluation of a Portocaval Venograft and Ameroid Ring for the Occlusion of Intrahepatic Portocaval Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2001, 30, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazoglou, L.G.; Monnet, E.; Seim, H.B. Survival and Prognostic Indicators for Dogs with Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts: 32 Cases (1990–2000). Vet. Surg. 2002, 31, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tivers, M.S.; Lipscomb, V.J.; Bristow, P.; Brockman, D.J. Intrahepatic Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: Short- and Long-Term Outcome of Suture Attenuation. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2018, 59, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breznock, E.M. Surgical Manipulation of Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1979, 174, 819–826. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, R.A.; Freeman, L.E. Identification and Surgical Management of Portosystemic Shunts in the Dog and Cat. Semin. Vet. Med. Surg. (Small Anim.) 1987, 2, 302–306. [Google Scholar]
- Swalec, K.M.; Smeak, D.D.; Brown, J. Effects of Mechanical and Pharmacologic Manipulations on Portal Pressure, Central Venous Pressure, and Heart Rate in Dogs. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1991, 52, 1327–1335. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, S.L.; Gregory, C.R.; Snyder, J.R.; Whiting, P.G.; Strack, D.; Breznock, E.M. Splanchnic Surface Oximetry during Experimental Portal Hypertension and Surgical Manipulation of Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 1991, 20, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.N.; MacDonald, N.J.; Burton, C.A. Use of Intraoperative Mesenteric Portovenography in Congenital Portosystemic Shunt Surgery. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2003, 44, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buob, S.; Johnston, A.N.; Webster, C.R. Portal Hypertension: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 169–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews, K.; Gofton, N. Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Occlusion in the Dog: Gross Observations during Surgical Correction. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1988, 24, 387–394. [Google Scholar]
- Burton, C.A.; White, R.N. Portovenogram Findings in Cases of Elevated Bile Acid Concentrations Following Correction of Portosystemic Shunts. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2001, 42, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayanuma, H.; Koyama, R.; Kanai, E. Feasibility of Complete Surgical Ligation on 72 Dogs with Singular Extrahepatic Congenital Portosystemic Shunt Based on Portal Pressure and Comparison of Intraoperative Mesenteric Portovenography. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 361–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vechten, B.J.; Komtebedde, J.; Koblik, P.D. Use of Transcolonic Portal Scintigraphy to Monitor Blood Flow and Progressive Postoperative Attenuation of Partially Ligated Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1994, 204, 1770–1774. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vogt, J.C.; Krahwinkel, D.J.; Bright, R.M.; Daniel, G.B.; Toal, R.L.; Rohrbach, B. Gradual Occlusion of Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs and Cats Using the Ameroid Constrictor. Vet. Surg. 1996, 25, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, S.T.; Ellison, G.W.; Long, M.; Van Gilder, J. A Comparison of the Ameroid Constrictor versus Ligation in the Surgical Management of Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2001, 37, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurn, S.D.; Edwards, G.A. Perioperative Outcomes after Three Different Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Attenuation Techniques in Dogs: Partial Ligation, Complete Ligation and Ameroid Constrictor Placement. Aust. Vet. J. 2003, 81, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tobias, K. Portosystemic Shunts and Other Hepatic Vascular Anomalies. In Textbook of Small Animal Surgery; Slatter, D., Ed.; Saunders Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2003; pp. 727–751. [Google Scholar]
- Harari, J.; Lincoln, J.; Alexander, J.; Miller, J. Lateral Thoracotomy and Cellophane Handing of a Congenital Portoazygous Shunt in a Dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1990, 31, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youmans, K.R.; Hunt, G.B. Cellophane Banding for the Gradual Attenuation of Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Eleven Dogs. Aust. Vet. J. 1998, 76, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youmans, K.R.; Hunt, G.B. Experimental Evaluation of Four Methods of Progressive Venous Attenuation in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 1999, 28, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landon, B.P.; Abraham, L.A.; Charles, J.A. Use of Transcolonic Portal Scintigraphy to Evaluate Efficacy of Cellophane Banding of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in 16 Dogs. Aust. Vet. J. 2008, 86, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, D.; Bellah, J.R.; Diaz, R. Results of Surgical Management of Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: 20 Cases (1985–1990). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1992, 201, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar]
- Cabassu, J.; Seim, H.B.; MacPhail, C.M.; Monnet, E. Outcomes of Cats Undergoing Surgical Attenuation of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts through Cellophane Banding: 9 Cases (2000–2007). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2011, 238, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiasovic, M.; Chanoit, G.P.A.; Meakin, L.B.; Tivers, M.S. Outcomes of Dogs Treated for Extrahepatic Congenital Portosystemic Shunts with Thin Film Banding or Ameroid Ring Constrictor. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traverson, M.; Lussier, B.; Huneault, L.; Gatineau, M. Comparative Outcomes between Ameroid Ring Constrictor and Cellophane Banding for Treatment of Single Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in 49 Dogs (1998–2012). Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiente, P.; Trehy, M.; White, R.; Nelissen, P.; Demetriou, J.; Stanzani, G.; de la Puerta, B. Complications and Outcome of Cats with Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts Treated with Thin Film: Thirty-Four Cases (2008–2017). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otomo, A.; Singh, A.; Jeong, J.; Dobberstein, R.; Lundhild, A.; Peter, E.; Brisson, B.; Oblak, M.; Milovancev, M. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes of Dogs with Single Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts Attenuated with Thin Film Banding or Ameroid Ring Constrictors. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, M.L.; Ellison, G.W.; Giglio, R.F.; Batich, C.D.; Berry, C.R.; Case, J.B.; Kim, S.E. Gradual Attenuation of a Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt with a Self-Retaining Polyacrylic Acid-Silicone Device in 6 Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Partington, B.P.; Partington, C.R.; Biller, D.S.; Toshach, K. Transvenous Coil Embolization for Treatment of Patent Ductus Venosus in a Dog. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1993, 202, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leveille, R.; Pibarot, P.; Soulez, G.; Wisner, E.R. Transvenous Coil Embolization of an Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in a Dog: A Naturally Occurring Model of Portosystemic Malformations in Humans. Pediatr. Radiol. 2000, 30, 607–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asano, K.; Watari, T.; Kuwabara, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Teshima, K.; Kato, Y.; Tanaka, S. Successful Treatment by Percutaneous Transvenous Coil Embolization in a Small-Breed Dog with Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2003, 65, 1269–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leveille, R.; Johnson, S.E.; Birchard, S.J. Transvenous Coil Embolization of Portosystemic Shunt in Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2003, 44, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, W.T.N.; Zwingenberger, A.L.; Giuffrida, M.A.; Wisner, E.R.; Hunt, G.B.; Steffey, M.A.; Mayhew, P.D.; Marks, S.L. Prospective Evaluation of Outcome of Dogs with Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts Treated via Percutaneous Transvenous Coil Embolization. Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Plassmann, M.; Rauber, K. Intrahepatic Venous Collaterals Preventing Successful Stent-Supported Coil Embolization of Intrahepatic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2009, 50, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo, J.M. Portosystemic Shunt in a Dog. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2000, 41, 516–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bussadori, R.; Bussadori, C.; Milla, L.; Rodrı, A.; Gonzalo-orden, M. Transvenous Coil Embolisation for the Treatment of Single Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Six Dogs. Vet. J. 2008, 176, 221–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivers, M.S.; Upjohn, M.M.; House, A.K.; Brockman, D.J.; Lipscomb, V.J. Treatment of Extrahepatic Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs—What Is the Evidence Base? J. Small Anim. Pract. 2012, 53, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, G.; Charalambous, M.; Devriendt, N.; de Rooster, H.; Mortier, F.; Paepe, D. Treatment of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 1865–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolschrijn, C.F.; Mahapokai, W.; Rothuizen, J.; Meyer, H.P.; van Sluijs, F.J. Gauged Attenuation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts: Results in 160 Dogs and 15 Cats. Vet. Q. 2000, 22, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, D. Critical Care Management of the Portosystemic Shunt Patient. Compend. Contin. Educ. Pract. Vet. 1994, 16, 879–892. [Google Scholar]
- Brunson, B.W.; Case, J.B.; Ellison, G.W.; Fox-Alvarez, W.A.; Kim, S.E.; Winter, M.; Garcia-Pereira, F.L.; Farina, L.L. Evaluation of Surgical Outcome, Complications, and Mortality in Dogs Undergoing Preoperative Computed Tomography Angiography for Diagnosis of an Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt: 124 Cases (2005–2014). Can. Vet. J. 2016, 57, 59. [Google Scholar]
- Tisdall, P.L.; Hunt, G.B.; Youmans, K.R.; Malik, R. Neurological Dysfunction in Dogs Following Attenuation of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 41, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, K.J.; Levine, J.M.; Peycke, L.E.; Thompson, J.A.; Cohen, N.D. Incidence of Postoperative Seizures with and without Levetiracetam Pretreatment in Dogs Undergoing Portosystemic Shunt Attenuation. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2011, 25, 1379–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardie, E.M.; Kornegay, J.N.; Cullen, J.M. Status Epilepticus after Ligation of Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 1990, 19, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyles, A.E.; Hardie, E.M.; Mehl, M.; Gregory, C.R. Evaluation of Ameroid Ring Constrictors for the Management of Single Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Cats: 23 Cases (1996–2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havig, M.; Tobias, K.M. Outcome of Ameroid Constrictor Occlusion of Single Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Cats: 12 Cases (1993–2000). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 220, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, R.; Tivers, M.S.; Fowkes, R.C.; Lipscomb, V.J. Incidence and Risk Factors for Neurological Signs after Attenuation of a Single Congenital Portosystemic Shunt in 50 Cats. Vet. Surg. 2021, 50, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullins, R.A.; Sanchez Villamil, C.; Selmic, L.E.; Tivers, M.S.; Case, J.B.; Singh, A.; Thieman Mankin, K.M.; Anderson, D.M.; White, R.N.; Pratschke, K.M.; et al. Prognostic Factors for Short-Term Survival of Dogs That Experience Postattenuation Seizures after Surgical Correction of Single Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts: 93 Cases (2005–2018). Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 958–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, R.; Tivers, M.S.; Adamantos, S.E.; Harcourt-Brown, T.R.; Fowkes, R.C.; Lipscomb, V.J. Incidence and Risk Factors for Neurological Signs after Attenuation of Single Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in 253 Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2018, 47, 745–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yool, D.A.; Kirby, B.M. Neurological Dysfunction in Three Dogs and One Cat Following Attenuation of Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 43, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronson, L.R.; Gacad, R.C.; Kaminsky-Russ, K.; Gregory, C.R.; Mullen, K.D. Endogenous Benzodiazepine Activity in the Peripheral and Portal Blood of Dogs with Congenital Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 1997, 26, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torisu, S.; Washizu, M.; Hasegawa, D.; Orima, H. Sustained Severe Hypoglycemia during Surgery as a Genesis of Global Brain Damage in Post Ligation Seizure of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts Dogs. In Proceedings of the Research Abstract Program of the 24th Annual ACVIM Forum, Louisville, KY, USA, 31 May–3 June 2006; p. 753. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, M.L.; MacPhail, C.M.; Monnet, E. Incidence of Postoperative Neurologic Complications in Pugs Following Portosystemic Shunt Attenuation Surgery. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 2018, 54, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, R.A.; Sanchez Villamil, C.; de Rooster, H.; Kummeling, A.; White, R.N.; Thieman Mankin, K.M.; Tivers, M.S.; Yool, D.A.; Anderson, D.M.; Pratschke, K.M.; et al. Effect of Prophylactic Treatment with Levetiracetam on the Incidence of Postattenuation Seizures in Dogs Undergoing Surgical Management of Single Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 2019, 48, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matushek, K.; Bjorling, D.; Mathews, K. Generalized Motor Seizures after Portosystemic Shunt Ligation in Dogs: Five Cases (1981–1988). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1990, 196, 2014–2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gommeren, K.; Claeys, S.; de Rooster, H.; Hamaide, A.; Daminet, S. Outcome from Status Epilepticus after Portosystemic Shunt Attenuation in 3 Dogs Treated with Propofol and Phenobarbital. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2010, 20, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, G.B. Effect of Breed on Anatomy of Portosystemic Shunts Resulting from Congenital Diseases in Dogs and Cats: A Review of 242 Cases. Aust. Vet. J. 2004, 82, 746–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, N.C.; Nelson, L.L. Imaging and Clinical Outcomes in 20 Dogs Treated with Thin Film Banding for Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. Surg. 2016, 45, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallarino, N.; Pil, S.; Devriendt, N.; Or, M.; Vandermeulen, E.; Serrano, G.; Paepe, D.; Bosmans, T.; De Rooster, H. Diagnostic Value of Blood Variables Following Attenuation of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in Dogs. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Straten, G.; Spee, B.; Rothuizen, J.; van Straten, M.; Favier, R.P. Diagnostic Value of the Rectal Ammonia Tolerance Test, Fasting Plasma Ammonia and Fasting Plasma Bile Acids for Canine Portosystemic Shunting. Vet. J. 2015, 204, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devriendt, N.; Serrano, G.; Meyer, E.; Demeyere, K.; Paepe, D.; Vandermeulen, E.; Stock, E.; de Rooster, H. Serum Hyaluronic Acid, a Marker for Improved Liver Perfusion after Gradual Surgical Attenuation of Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Closure in Dogs. Vet. J. 2021, 268, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devriendt, N.; Serrano, G.; Croubels, S.; Stock, E.; Vandermeulen, E.; Paepe, D.; von Luckner, J.; de Rooster, H. Evaluation of Serum Lidocaine/Monoethylglycylxylidide Concentration to Assess Shunt Closure in Dogs with Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, G.; Devriendt, N.; Paepe, D.; de Rooster, H. Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 as a Marker of Improved Liver Function and Surgical Outcome in Dogs with Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts. Vet. J. 2021, 274, 105716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toulza, O.; Center, S.; Brooks, M.B.; Erb, H.N.; Warner, K.L.; Deal, W. Evaluation of Plasma Protein C Activity for Detection of Hepatobiliary Disease and Portosystemic Shunting in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2006, 229, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bristow, P.; Lipscomb, V.; Kummeling, A.; Packer, R.; Gerrits, H.; Homan, K.; Ortiz, V.; Newson, K.; Tivers, M. Health-Related Quality of Life Following Surgical Attenuation of Congenital Portosystemic Shunts versus Healthy Controls. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 60, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szatmári, V.; Rothuizen, J.; van den Ingh, T.S.G. a M.; van Sluijs, F.J.; Voorhout, G. Ultrasonographic Findings in Dogs with Hyperammonemia: 90 Cases (2000–2002). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2004, 224, 717–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sura, P.A.; Tobias, K.M.; Morandi, F.; Daniel, G.B.; Echandi, R.L. Comparison of 99mTcO4(-) Trans-Splenic Portal Scintigraphy with per-Rectal Portal Scintigraphy for Diagnosis of Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs. Vet. Surg. 2007, 36, 654–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunch, S.E.; Johnson, S.E.; Cullen, J.M. Idiopathic Noncirrhotic Portal Hypertension in Dogs: 33 Cases (1982–1998). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2001, 218, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglin, E.V.; Lux, C.N.; Sun, X.; Folk, C.A.; Fazio, C. Clinical Characteristics of, Prognostic Factors for, and Long-Term Outcome of Dogs with Multiple Acquired Portosystemic Shunts: 72 Cases (2000–2018). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2022, 260, S30–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, M. Unusual Haemodynamics in Two Dogs and Two Cats with Portosystemic Shunt—Implications for Distinguishing between Congenital and Acquired Conditions. Open Vet. J. 2017, 7, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agg, E.J. Acquired Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in a Young Dog. Can. Vet. J. 2006, 47, 697. [Google Scholar]
- Boothe, H.W.; Howe, L.M.; Edwards, J.F.; Slater, M.R. Multiple Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs: 30 Cases (1981–1993). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1996, 208, 1849–1854. [Google Scholar]
- Worley, D.R.; Holt, D.E. Clinical Outcome of Congenital Extrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Attenuation in Dogs Aged Five Years and Older: 17 Cases (1992–2005). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2008, 232, 722–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szatmári, V.; van Sluijs, F.J.; Rothuizen, J.; Voorhout, G. Intraoperative Ultrasonography of the Portal Vein during Attenuation of Intrahepatic Portocaval Shunts in Dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 222, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, S.R.; Williams, J.M.; Niles, J.D. Outcomes of Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts Occluded with Ameroid Constrictors in Nine Dogs and One Cat. Vet. Surg. 2006, 35, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehl, M.L.; Kyles, A.E.; Case, J.B.; Kass, P.H.; Zwingenberger, A.; Gregory, C.R. Surgical Management of Left-Divisional Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunts: Outcome after Partial Ligation of, or Ameroid Ring Constrictor Placement on, the Left Hepatic Vein in Twenty-Eight Dogs (1995–2005). Vet. Surg. 2007, 36, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisse, C.; Schwartz, K.; Stronger, R.; Mondschein, J.I.; Solomon, J.A. Transjugular Coil Embolization of an Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt in a Cat. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 221, 1287–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palerme, J.S.; Brown, J.C.; Marks, S.L.; Birkenheuer, A.J. Splenosystemic Shunts in Cats: A Retrospective of 33 Cases (2004–2011). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
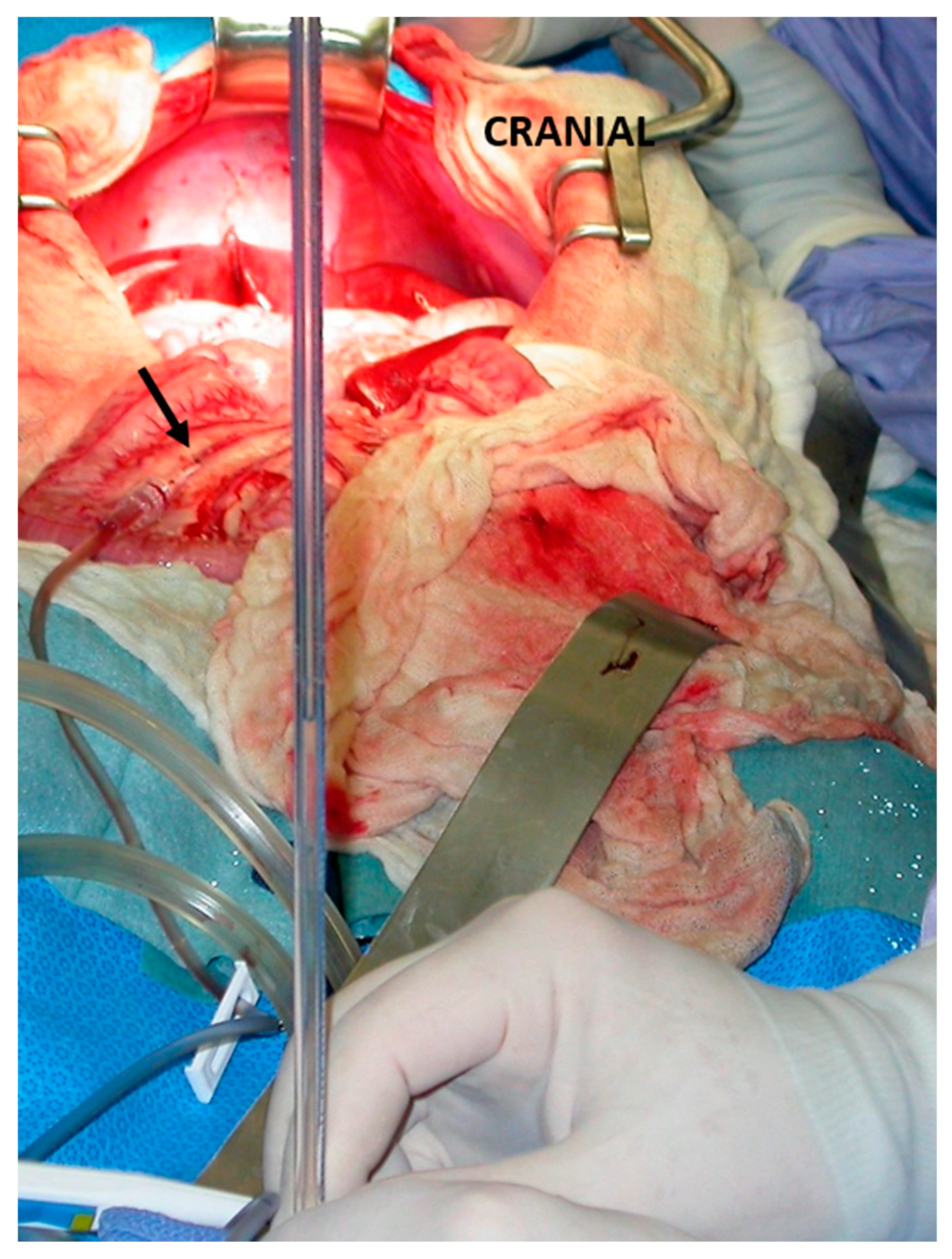

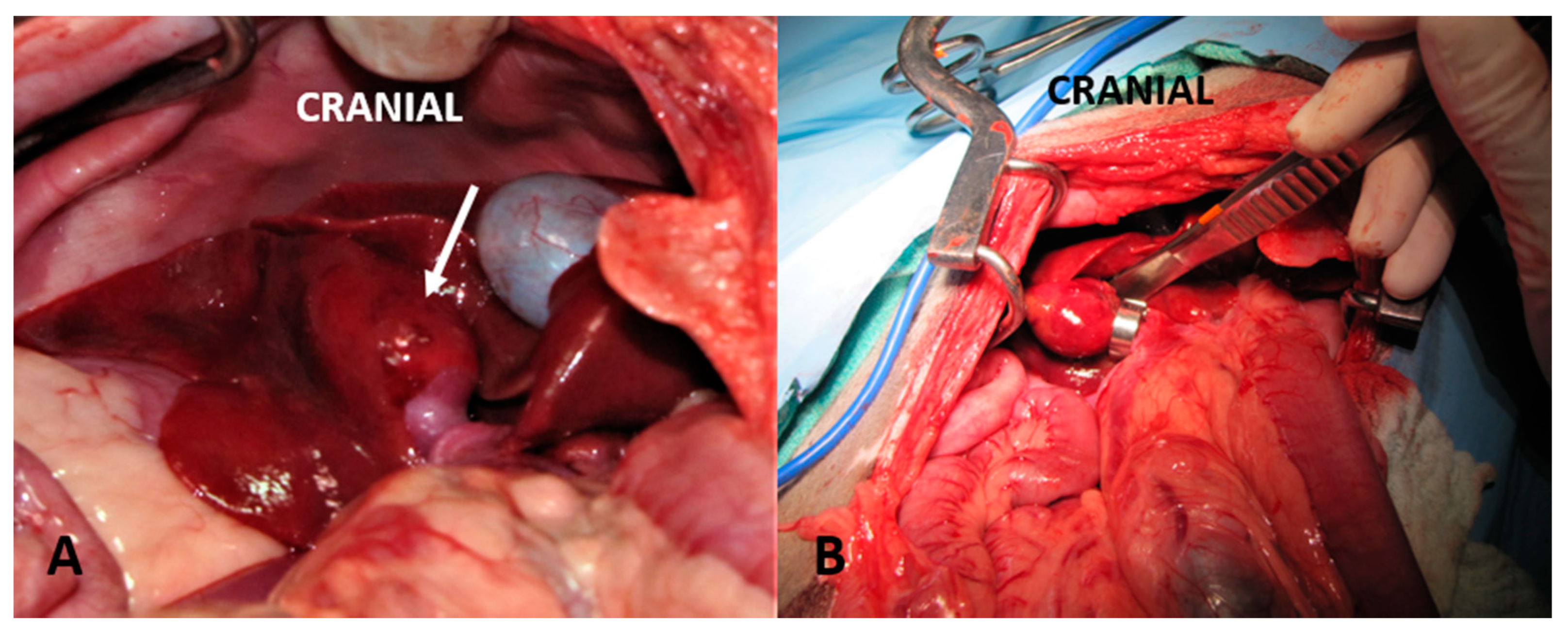

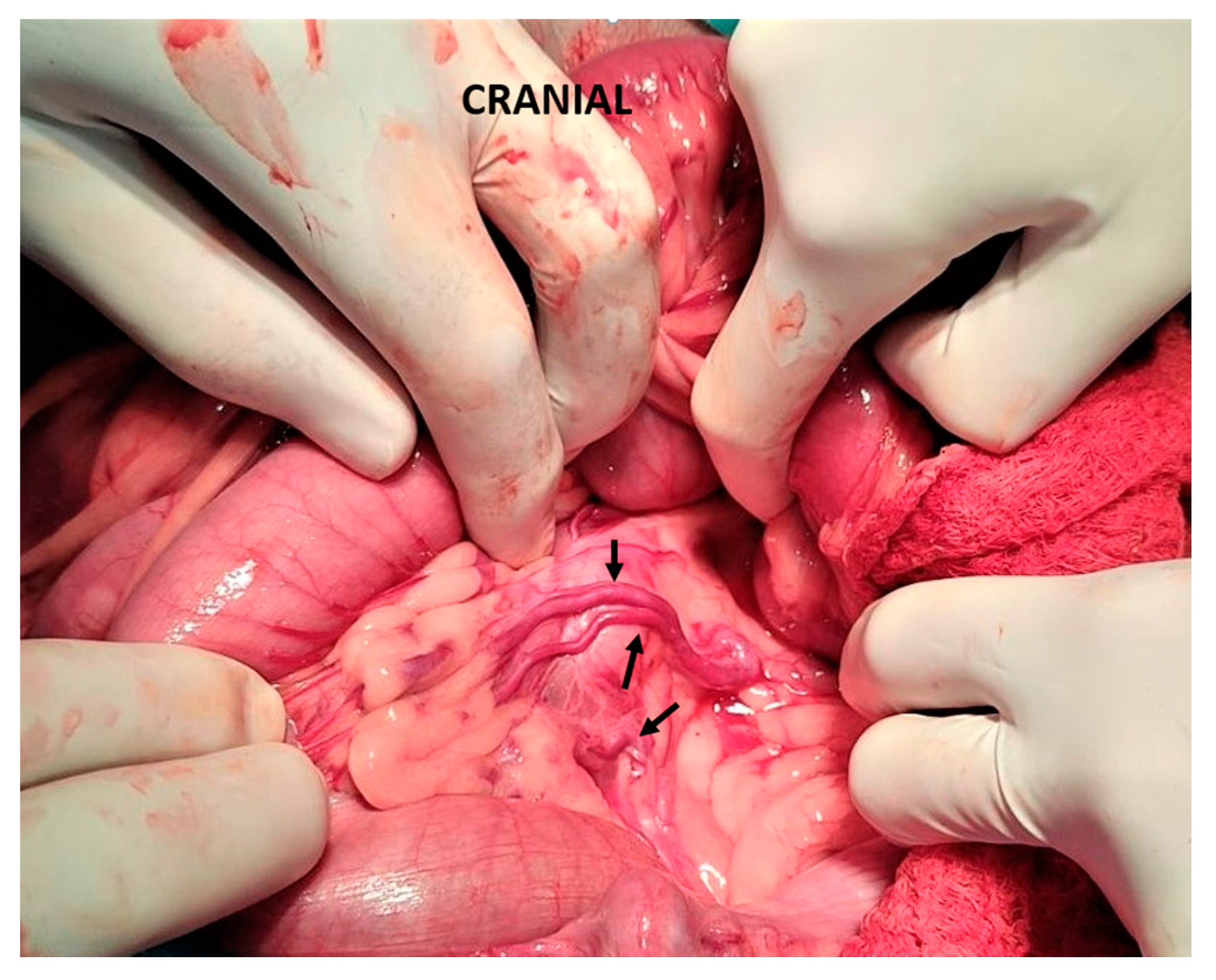
| Antibiotics | |
|---|---|
| Metronidazole | 7.5 mg/kg PO q12h |
| Amoxicillin | 22 mg/kg PO, IV, IM, or SC q12h |
| Ampicillin | 22 mg/kg IV q6h |
| Neomycin (avoid in case of intestinal bleeding, ulcerations, or renal failure; ototoxic, nephrotoxic) | 20 mg/kg PO q12h |
| Non-absorbable disaccharides | |
| Lactulose | Orally: 2.5 to 25 mL PO q8h (two or three soft stools per day) Dogs: typically start at 0.5 mL/kg PO q8h Cats: typically start at 2.5–5 mL/cat PO q8h Rectally: cleansing enemas with water (5–10 mL/kg), followed by retention enemas (30% lactulose solution; 10–15 mL/kg), retained for 30 min to 1 h |
| Lactitol | 0.5 to 0.75 g/kg PO q12h |
| Gastroprotectants | |
| Proton pump inhibitors | |
| Omeprazole | 0.9–1 mg/kg PO or IV q12h |
| Esomeprazole | 1 mg/kg PO or IV q12h |
| Sucralfate | 1 g/25 kg PO q8hr |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Konstantinidis, A.O.; Adamama-Moraitou, K.K.; Patsikas, M.N.; Papazoglou, L.G. Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs and Cats: Treatment, Complications and Prognosis. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050346
Konstantinidis AO, Adamama-Moraitou KK, Patsikas MN, Papazoglou LG. Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs and Cats: Treatment, Complications and Prognosis. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(5):346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050346
Chicago/Turabian StyleKonstantinidis, Alexandros O., Katerina K. Adamama-Moraitou, Michail N. Patsikas, and Lysimachos G. Papazoglou. 2023. "Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs and Cats: Treatment, Complications and Prognosis" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 5: 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050346
APA StyleKonstantinidis, A. O., Adamama-Moraitou, K. K., Patsikas, M. N., & Papazoglou, L. G. (2023). Congenital Portosystemic Shunts in Dogs and Cats: Treatment, Complications and Prognosis. Veterinary Sciences, 10(5), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050346








