Repeated Administration of the Cannabinoid WIN Alters the Isoflurane-Sparing Effect of Morphine and Dexmedetomidine
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Anesthetic Procedure
2.2. Minimum Alveolar Concentration Determination
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime World Drug Report 2022; United Nations Publication: New York, NY, USA, 2022.
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Kamle, M.; Borah, R.; Sharma, B.; Pandhi, S.; Tripathi, V.; Yadav, H.S.; Devi, S.; Patil, U.; et al. Pharmacological properties, therapeutic potential, and legal status of Cannabis sativa L: An overview. Phytother. Res. 2021, 35, 6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, P.F.; Wolff, R.F.; Deshpande, S.; Di Nisio, M.; Duffy, S.; Hernandez, A.V.; Keurentjes, J.C.; Lang, S.; Misso, K.; Ryder, S.; et al. Cannabinoids for medical use: A systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2015, 313, 2456–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jugl, S.; Okpeku, A.; Costales, B.; Morris, E.J.; Alipour-Haris, G.; Hincapie-Castillo, J.M.; Stetten, N.E.; Sajdeya, R.; Keshwani, S.; Joseph, V.; et al. A mapping literature review of medical cannabis clinical outcomes and quality of evidence in approved conditions in the USA from 2016 to 2019. Med. Cannabis Cannabinoids 2021, 4, 21–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehnke, K.F.; Litinas, E.; Clauw, D.J. Medical cannabis use is associated with decreased opiate medication use in a retrospective cross-sectional survey of patients with chronic pain. J. Pain 2016, 17, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinghorn, A.; Falk, H.; Gibbons, S.; Kobayashi, J. Phytocannabinoids; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Abrams, D.I.; Couey, P.; Shade, S.B.; Kelly, M.E.; Benowitz, N.L. Cannabinoid-opioid interaction in chronic pain. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 90, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davy, A.; Fessler, J.; Fischler, M.; Le Guen, M. Dexmedetomidine and general anesthesia: A narrative literature review of its major indications for use in adults undergoing non-cardiac surgery. Minerva Anestesiol. 2017, 83, 1294–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tasbihgou, S.R.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.R. The role of dexmedetomidine in neurosurgery. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2021, 35, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, W.; Mengge, W.; Jian, X.; Changshuai, W.; Baohui, Z.; Guonian, W.; Daqing, M. Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative stress, inflammation, and immune function: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, 777–794. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Jiang, M.; Ji, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shen, W. Impact of postoperative dexmedetomidine infusion on incidence of delirium in elderly patients undergoing major elective noncardiac surgery: A randomized clinical trial. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 2911–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charan, J.; Biswas, T. How to calculate sample size for different study designs in medical research? Indian J. Psychol. Med. 2013, 35, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th ed.; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Chavez, J.R.; Ibancovichi, J.A.; Sanchez-Aparicio, P.; Acevedo-Arcique, C.M.; Moran-Muñoz, R.; Recillas-Morales, S. Effect of acetaminophen alone and in combination with morphine and tramadol on the minimum alveolar concentration of isoflurane in rats. PLoS ONE 2015, 25, e0143710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antognini, J.F.; Schwartz, K. Exaggerated anesthetic requirements in the preferentially anesthetized brain. Anesthesiology 1993, 79, 1244–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quasha, A.L.; Eger, E.I.; Tinker, J.H. Determination and applications of MAC. Anesthesiology 1980, 53, 314–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez de Segura, I.A.; Criado, A.B.; Santos, M.; Tendillo, F.J. Aspirin synergistically potentiates isoflurane minimum alveolar concentration reduction produced by morphine in the rat. Anesthesiology 1998, 89, 1489–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rioja, E.; Santos, M.; Martinez Taboada, F.; Ibancovichi, J.A.; Tendillo, F.J. Cardiorespiratory and minimum alveolar concentration sparing effects of a continuous intravenous infusion of dexmedetomidine in halothane or isoflurane anaesthetized rats. Lab. Anim. 2006, 40, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawston, J.; Borella, A.; Robinson, J.K.; Whitaker-Azmitia, P.M. Changes in hippocampal morphology following chronic treatment whith the synthetic cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2. Brain Res. 2000, 877, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanda, G.; Pontieri, F.E.; Chiara, G.D. Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common µ1 opioid receptor mechanism. Science 1997, 276, 2048–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Monteagudo, J.R.; Ibancovichi, J.A.; Sanchez-Aparicio, P.; Recillas-Morales, S.; Osorio-Avalos, J.; De Paz-Campos, M.A. Minimum Alveolar Concentration of Isoflurane in Rats Chronically Treated with the Synthetic Cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2. Animals 2022, 12, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibancovichi, J.A.; Chávez-Monteagudo, J.R.; Sánchez-Aparicio, P.; De Paz-Campos, M.A. Chronic Use of the Synthetic Cannabinoid WIN 55,212-2 55 Modifies the Isoflurane-Sparing Effect of Morphine and Dexmedetomidine. Preprints 2023, 2023010488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.E.; Oropeza, V.C.; Sparks, S.E.; Qian, Y.; Menko, A.S.; Van Bockstaele, E.J. Repeated cannabinoid administration increases indices of noradrenergic activity in rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2007, 86, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardot, M.N.; Holloway, F.A. Intermittent cold water stress analgesia in rats: Cross tolerance to morphine. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1984, 20, 631–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ide, S.; Satoyoshi, H.; Minami, M.; Satoh, M. Amelioration of the reduced antinociceptive effect of morphine in the unpredictable chronic mild stress model mice by noradrenalin but not serotonin reuptake 423 inhibitors. Mol. Pain 2015, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hine, B. Morphine and delta 9-tetrahydrocannabinol: Two way cross tolerance for antinociceptive and heart rate responses in the rat. Psychopharmacology 1985, 87, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, A.S.; Dewey, W.L. A comparison of some pharmacological actions of morphine and delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol in the mouse. Psychopharmacology 1978, 57, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corchero, J.; Manzanares, J.; Fuentes, J.A. Cannabinoid/opioid crosstalk in the central nervous system. Crit. Rev. Neurobiol. 2004, 16, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.-Y.; Liu, G.; Lin, J.-H.; Jin, Y.-P. Efficacy and Safety of Dexmedetomidine Premedication in Balanced Anesthesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis in Dogs. Animals 2021, 11, 3254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, E.L.; Samra, S. Dexmedetomidine and neuroprotection. Semin. Anesth. Perioper. Med. Pain 2006, 25, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segal, I.S.; Vickery, R.G.; Walton, J.K.; Doze, V.A.; Maze, M. Dexmedetomidine diminishes halothane anesthetic requirements in rats through a postsynaptic alpha2—Adrenergic receptor. Anesthesiology 1988, 69, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eger, E.I., II; Xing, Y.; Laster, M.J.; Sonner, J.M. α-2 Adrenoreceptors probably do not mediate the immobility produced by inhaled anesthetics. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 1661–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


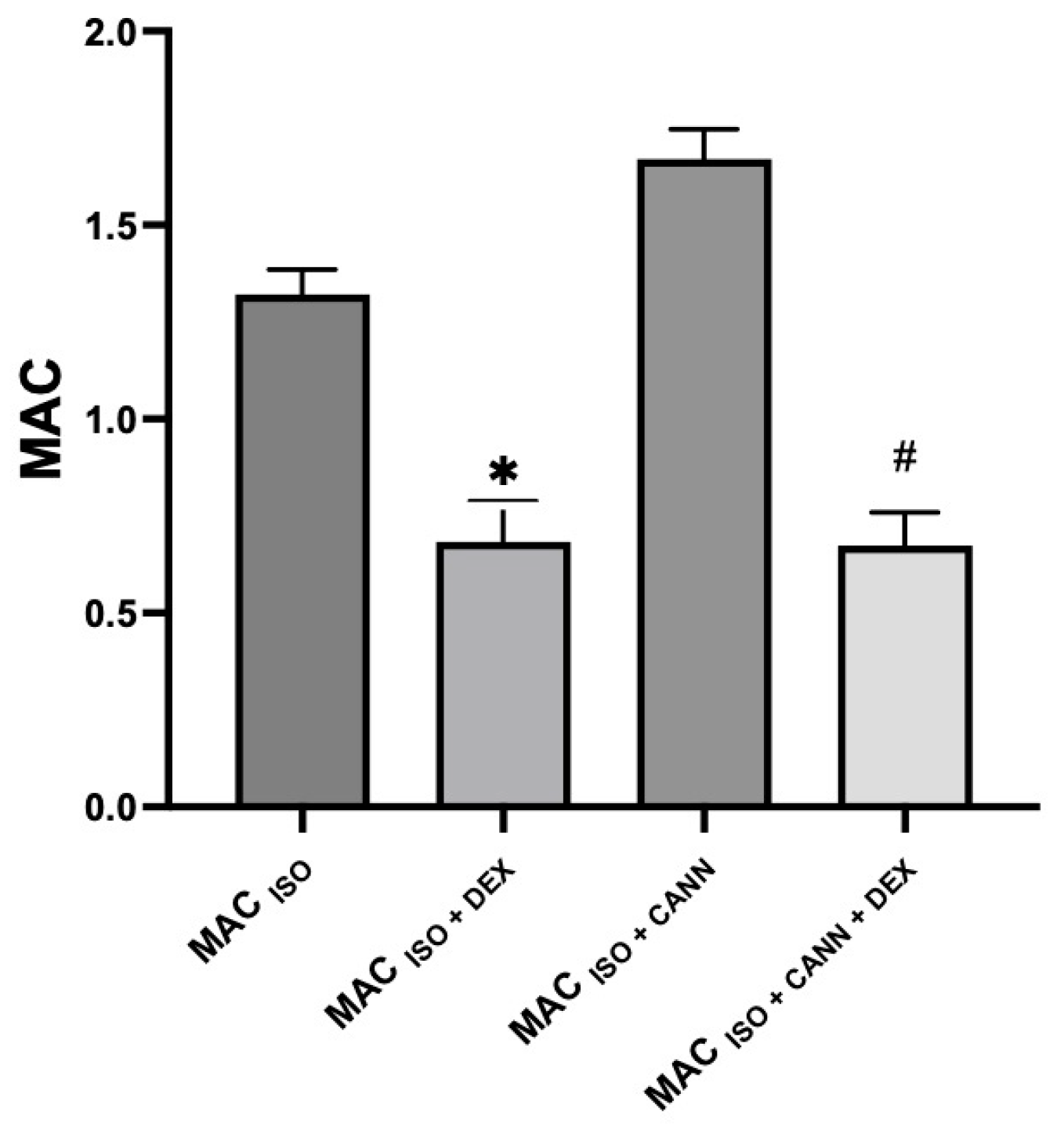
| Group | MAC% | SD | % MAC Increase (↑) or Decrease (↓) | p-Value | 95% CI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAC (ISO) | 1.32 | 0.06 | - | 1.27–1.37 | |
| MAC (ISO + CANN) | 1.69 * | 0.09 | ↑ 28% | <0.0001 | 1.61–1.76 |
| MAC (ISO + MOR) | 0.97 * | 0.02 | ↓ 26% | <0.0001 | 0.95–0.99 |
| MAC (ISO + CANN + MOR) | 1.55 + | 0.08 | ↓ 8% | 0.0094 | 1.47–1.62 |
| MAC (ISO + DEX) | 0.68 * | 0.10 | ↓ 48% | <0.0001 | 0.59–0.77 |
| MAC (ISO + CANN + DEX) | 0.67 + | 0.08 | ↓ 60% | <0.0001 | 0.60–0.74 |
| Value | MAC (ISO) | MAC (ISO + CANN) | MAC (ISO + MOR) | MAC (ISO + CANN + MOR) | MAC (ISO + DEX) | MAC (ISO + CANN + DEX) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heart rate (bpm) | 401 ± 8 | 403 ± 7 | 399 ± 8 | 401 ± 11 | 303 ± 16 * | 297 ± 21 + |
| MAP (mmHg) | 93 ± 8 | 90 ± 9 | 91 ± 7 | 92 ± 8 | 86 ± 7 | 84 ± 11 |
| Temperature °C | 37.7 ± 0.07 | 37.6 ± 0.12 | 37.2 ± 0.11 | 37.4 ± 0.09 | 37.4 ± 0.10 | 37.5 ± 0.08 |
| pH | 7.3 ± 03 | 7.3 ± 0.04 | 7.4 ± 0.02 | 7.3 ± 0.02 | 7.3 ± 0.06 | 7.3 ± 0.09 |
| PaO2 (mmHg) | 301 ± 34 | 295 ± 8 | 299 ± 12 | 289 ± 10 | 291 ± 16 | 289 ± 13 |
| PaCo2 (mmHg) | 37 ± 4 | 37 ± 1 | 38 ± 2 | 38 ± 4 | 32 ± 2 | 37 ± 7 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ibancovichi, J.A.; Chávez-Monteagudo, J.R.; Sánchez-Aparicio, P.; De Paz-Campos, M.A. Repeated Administration of the Cannabinoid WIN Alters the Isoflurane-Sparing Effect of Morphine and Dexmedetomidine. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050310
Ibancovichi JA, Chávez-Monteagudo JR, Sánchez-Aparicio P, De Paz-Campos MA. Repeated Administration of the Cannabinoid WIN Alters the Isoflurane-Sparing Effect of Morphine and Dexmedetomidine. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(5):310. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050310
Chicago/Turabian StyleIbancovichi, José Antonio, Julio Raúl Chávez-Monteagudo, Pedro Sánchez-Aparicio, and Marco Antonio De Paz-Campos. 2023. "Repeated Administration of the Cannabinoid WIN Alters the Isoflurane-Sparing Effect of Morphine and Dexmedetomidine" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 5: 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050310
APA StyleIbancovichi, J. A., Chávez-Monteagudo, J. R., Sánchez-Aparicio, P., & De Paz-Campos, M. A. (2023). Repeated Administration of the Cannabinoid WIN Alters the Isoflurane-Sparing Effect of Morphine and Dexmedetomidine. Veterinary Sciences, 10(5), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10050310







