Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Trichinella spp. in Pigs from Cairo, Egypt
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
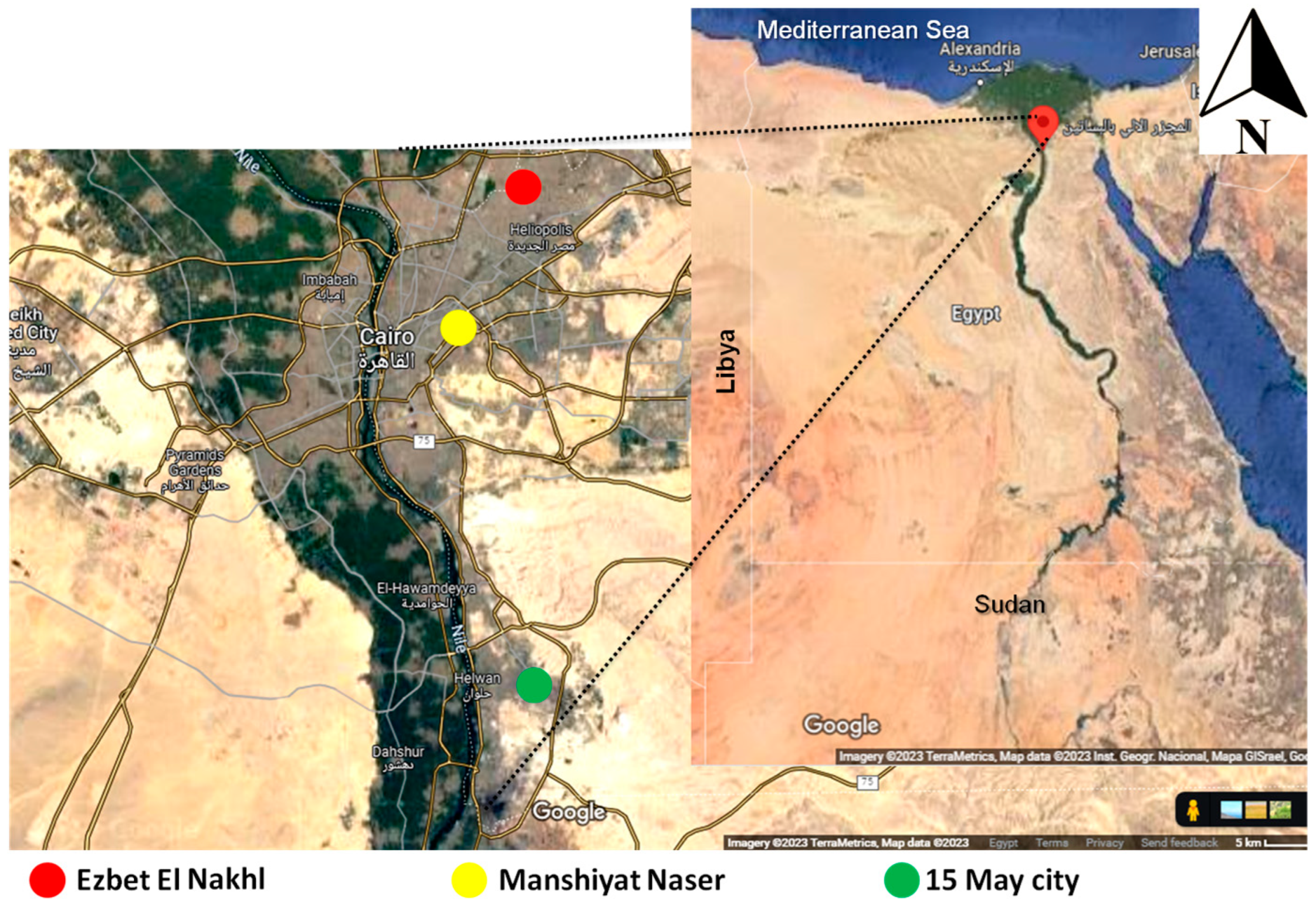
2.1. Description of the Animals and Regions of the Study
2.2. ELISAs for Screening Antibodies to T. gondii, N. caninum, and Trichinella Species in Pigs
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO. World Food and Agriculture—Statistical Yearbook 2021; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations. Population Estimates and Projections; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Available online: https://population.un.org (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- U.S. Department of State. International Religious Freedom Report for 2020: Egypt; United States Department of State, Office of International Religious Freedom: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. Available online: https://www.state.gov/reports/2020-report-on-international-religious-freedom/egypt/ (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- FAOSTAT. 2021. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QA (accessed on 23 June 2023).
- Shalaby, E.A. Prospects of effective microorganisms technology in wastes treatment in Egypt. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2011, 1, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redding, R.W. The pig and the chicken in the Middle East: Modeling human subsistence behavior in the archaeological record using historical and animal husbandry data. J. Archaeol. Res. 2015, 23, 325–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenter, A.M.; Heckeroth, A.R.; Weiss, L.M. Toxoplasma gondii: From animals to humans. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 1217–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis of Animals and Humans, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Elmore, S.A.; Jones, J.L.; Conrad, P.A.; Patton, S.; Lindsay, D.S.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasma gondii: Epidemiology, feline clinical aspects, and prevention. Trends Parasitol. 2010, 26, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Weigel, R.M.; Siegel, A.M.; Thulliez, P.; Kitron, U.D.; Mitchell, M.A.; Mannelli, A.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E.; Shen, S.K.; Kwok, O.C.H.; et al. Sources and reservoirs of Toxoplasma gondii infection on 47 swine farms in Illinois. J. Parasitol. 1995, 81, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.; Kwok, O.C.; Hill, D.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. All about Toxoplasma gondii infections in pigs: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 288, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, M.; Fakhri, Y.; Riahi, S.M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Namroodi, S.; Taghipour, A.; Spotin, A.; Gamble, H.R.; Rostami, A. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 269, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maronpot, R.R.; Botros, B.A.M. Toxoplasma serologic survey in man and domestic animals in Egypt. J. Egypt. Public Health Assoc. 1972, 47, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Rifaat, M.A.; Morsy, T.A.; Sadek, M.S.M.; Azab, M.E.; Khaled, M.L.M.; Safar, E.H. Incidence of toxoplasmosis among farm animals in north coastal zone of Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1979, 9, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ghattas, S.S. Studies on Toxoplasma gondii Infecting Slaughtered Pigs in Egypt. MSc. Thesis, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Barakat, A.M.; El Fadaly, H.A.; Shaapan, R.M.; Khalil, F.A.M. Occupational health hazard of Egyptian employees in contact with wastage nourished swine. J. Am. Sci. 2011, 7, 808–903. [Google Scholar]
- El Moghazy, F.M.; Kandil, O.M.; Shaapan, R.M. Toxoplasma gondii: Comparison of some serological tests for detection in sera of naturally infected pigs. World J. Zool. 2011, 6, 204–208. [Google Scholar]
- Hassanain, M.A.; El-Fadaly, H.A.; Hassanain, N.A.; Shaapan, R.M.; Barakat, A.M.; Abd El-Razik, K.A. Serological and molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis in human and animals. World J. Medical Sci. 2013, 9, 243–247. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Hafeez, E.H.; Kamal, A.M.; Abdelgelil, N.H.; Abdel-Fatah, M. Parasites transmitted to human by ingestion of different types of meat, El-Minia City, El-Minia Governorate, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, M.H.S. Studies on Parasitic Infections among Egyptian pigs. MSc. Thesis, Benha University, Benha, Egypt, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Abbas, I.E.; Villena, I.; Dubey, J.P. A review on toxoplasmosis in humans and animals from Egypt. Parasitology 2020, 147, 135–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, B.A.M.; Moch, R.W.; Barsoum, I.S. Toxoplasmosis in Egypt: Isolation of Toxoplasma gondii from a pig. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1973, 76, 259–261. [Google Scholar]
- Dubey, J.P.; Schares, G.; Ortega-Mora, L. Epidemiology and control of neosporosis and Neospora caninum. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 323–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Hemphill, A.; Calero-Bernal, R.; Schares, G. Neosporosis in Animals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fereig, R.M.; Nishikawa, Y. From signaling pathways to distinct immune responses: Key factors for establishing or combating Neospora caninum infection in different susceptible hosts. Pathogens 2020, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Schares, G. Neosporosis in animals—The last five years. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 180, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, B.Z.; Lv, Q.Y.; Ge, M.; Li, R.C.; Zhu, X.Q.; Liu, G.H. First report of Neospora caninum infection in pigs in China. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 67, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snak, A.; Junior, G.S.; Pilati, G.V.T.; Kroetz, C.C.; Consoni, W.; Cristani, J.; de Moura, A.B. Does Neospora caninum cause reproductive problems in pigs? Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 275, 108934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snak, A.; Henrique, S.M.; Sebolt, A.P.R.; Cristani, J.; Sato, M.E.; Miletti, L.C.; de Moura, A.B. Experimental infection of tachyzoites of the NC1 strain of Neospora caninum in female swine. Parasitol. Res. 2021, 120, 1049–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Schares, G. Diagnosis of bovine neosporosis. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 140, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinnott, F.A.; Monte, L.G.; Collares, T.F.; Silveira, R.M.; Borsuk, S. Review on the immunological and molecular diagnosis of neosporosis (years 2011–2016). Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 239, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozio, E.; Zarlenga, D.S. New pieces of the Trichinella puzzle. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 983–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, K.D.; Pozio, E. Worldwide occurrence and impact of human trichinellosis, 1986–2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Rosa, G.; Pozio, E.; Rossi, P.; Murrell, K.D. Allozyme analysis of Trichinella isolates from various host species and geographical regions. J. Parasitol. 1992, 78, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, E.S.; Youseef, A.G.; Mubarak, A.G.; Mawas, A.S.; Khalifa, F.A.; Felefel, W. Epidemiological perspective associated with principal risk factors of Trichinella spiralis infection in pigs and humans in Egypt. Vet. World 2022, 15, 1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loutfy, N.F.; Awad, O.M.; El-Masry, A.G.; Kandil, G.M. Study on rodents infestation in Alexandria and prevalence of Trichinella spiralis infection among them. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 897–909. [Google Scholar]
- Mikhail, E.M.; Mansour, N.S.; Awadalla, H.N. Identification of Trichinella isolates from naturally infected stray dogs in Egypt. J. Parasitol. 1994, 80, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassien, M.; Abd EL-Rahman, H.; Ibrahim, A.; Mousa, M. Prevalence of encysted larvae of Trichinella spiralis in pork and beef meat products with special reference to the effect of rapid heat treatment on their viability. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 1989, 21, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Morsy, T.A.; Ibrahim, B.B.; Haridy, F.M.; Rifaat, M.M. Trichinella encysted larvae in slaughtered pigs in Cairo (1995–1999). J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sayed, A.S.; Hussein, A.A.; Arafa, M.I.; Abdo, B.R.N. Epidemiological study on trichinellosis in pigs and man in Upper Egypt. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2010, 56, 280–287. [Google Scholar]
- Dyab, A.K.; Ahmed, M.A.; Abdelazeem, A.G. Prevalence and histopathology of Trichinella spiralis larvae of slaughtered pigs in Cairo governorate, Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 2019, 49, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azab, M.E.; Morsy, T.A.; Abdel-Aal, T.M.; Safar, E.H.; Makaram, S.S.; El Hady, H.M.; Kamel, A.A. Current prevalence of trichinosis in pigs in Egypt. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1988, 18, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- OIE/World Organisation for Animal Health. Trichinellosis (Infection with Trichinella spp.), Chapter 2.1.20 Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals, World Organization for Animal Health. 2017. Available online: https://www.oie.int/eng/normes/mmanual/A_00013.htm (accessed on 13 June 2023).
- Fereig, R.M.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; El-Alfy, E.S.; El-Diasty, M.; Elsayed, A.; Mahmoud, H.Y.; Ali, A.O.; Ahmed, A.; Mossaad, E.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; et al. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in camels recently imported to Egypt from Sudan and a global systematic review. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1042279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereig, R.M.; Wareth, G.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; Mazeed, A.M.; El-Diasty, M.; Abdelkhalek, A.; Mahmoud, H.Y.; Ali, A.O.; El-Tayeb, A.; Alsayeqh, A.F.; et al. Seroprevalence of specific antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum, and Brucella spp. in sheep and goats in Egypt. Animals 2022, 12, 3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montoya, J.G. Laboratory diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection and toxoplasmosis. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, S73–S82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, R.A.M.; Torrecilhas, A.C.; Marciano, M.A.M.; Mazuz, M.L.; Pereira-Chioccola, V.L.; Fux, B. Toxoplasmosis in human and animals around the world. Diagnosis and perspectives in the one health approach. Acta Trop. 2022, 231, 106432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, A.; Karanis, P.; Fallahi, S. Advances in serological, imaging techniques and molecular diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infection 2018, 46, 303–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, D.B.; Fereig, R.M.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; Shahat, M.S.; Arafa, W.M.; Aboelhadid, S.M.; Mohamed, A.E.; Metwally, S.; Abas, O.; Suo, X.; et al. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum antibodies in dogs and cats from Egypt and risk factor analysis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metwally, S.; Hamada, R.; Sobhy, K.; Frey, C.F.; Fereig, R.M. Seroprevalence and risk factors analysis of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii in cattle of Beheira, Egypt. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1122092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerges, A.A.; MONA, S.; Fathi, A.; Mohamed, H.; Abou-gazia, K.H.A.; Mohamed, H.F. Detection of Neospora caninum and Coxiella burnetii antibodies in milk and serum of infected dairy cattle. Assiut Vet. Med. J. 2018, 64, 49–57. [Google Scholar]
- El-Mohamady, R.S.; Gerges, A.M.; Abd-Elhafeiz, Y.G.M. Investigation of the association between bovine viral diarrhea virus and Neospora caninum as a cause of abortion in cattle. J. Applied Vet. Sci. 2022, 7, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selim, A.; Abdelhady, A. Neosporosis among Egyptian camels and its associated risk factors. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartova, E.; Sedlak, K. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum in slaughtered pigs in the Czech Republic. Parasitology 2011, 138, 1369–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, L.M.; Minervino, A.H.H.; Monger, S.D.G.B.; Soares, H.S.; Portela, J.M.; Ferreira, J.I.G.D.S.; Gennari, S.M.; Pereira, W.L.A. Occurrence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii and anti-Neospora caninum antibodies in pigs in the State of Pará, Brazil. Rev. Bras. Parasitol. Vet. 2021, 30, e017520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa, L.; Gazzonis, A.L.; Allievi, C.; Zanzani, S.A.; Mortarino, M.; Manfredi, M.T. Prevalence of Neospora caninum antibodies in fattening pigs and sows from intensive farms in northern Italy. Parasitol. Res. 2022, 121, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, T.; Ai, J.; Yang, J.; Zhu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qin, Q.; Kang, M.; Sun, Y.; et al. Seroepidemiology of Neosporosis in various animals in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 953380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Romand, S.; Hilali, M.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Thulliez, P. Seroprevalence of antibodies to Neospora caniuum and Toxoplasma gondii in water buffaloes (Bubalus bubalis) from Egypt. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 527–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilali, M.; Romand, S.; Thulliez, P.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Dubey, J.P. Prevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in sera from camels from Egypt. Vet. Parasitol. 1998, 75, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Huang, P.; Salem, T.A.; Talaat, R.M.; Nasr, M.I.; Xuan, X.; Nishikawa, Y. Prevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in Northern Egypt. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fereig, R.M.; AbouLaila, M.R.; Mohamed, S.G.; Mahmoud, H.Y.; Ali, A.O.; Ali, A.F.; Hilali, M.; Zaid, A.; Mohamed, A.E.A.; Nishikawa, Y. Serological detection and epidemiology of Neospora caninum and Cryptosporidium parvum antibodies in cattle in southern Egypt. Acta Trop. 2016, 162, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.M.; Abdel-Rahman, A.A.; Bishr, N.M. Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum and Toxoplasma gondii IgG and IgM antibodies among buffaloes and cattle from Menoufia Province, Egypt. J. Parasit. Dis. 2021, 45, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selim, A.; Khater, H.; Almohammed, H.I. A recent update about seroprevalence of ovine neosporosis in Northern Egypt and its associated risk factors. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Al-Araby, M.; Elmishmishy, B.; El-Alfy, E.S. Gastrointestinal parasites of cats in Egypt: High prevalence high zoonotic risk. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, I.; Baghdadi, H.B.; Rizk, M.A.; El-Alfy, E.S.; Elmishmishy, B.; Gwida, M. Gastrointestinal Parasites of Dogs in Egypt: An update on the prevalence in Dakahlia governorate and a meta-analysis for the published data from the country. Animals 2023, 13, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.Y.; Abou-EL-Roos, M.E.A.; El-Madawy, R.S. An approach for detection of Neospora caninum infection in aborted bovine fetuses in Egypt. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2009, Feb., 266–281. [Google Scholar]
- Gazzonis, A.L.; Garcia, G.A.; Zanzani, S.A.; Mora, L.M.O.; Invernizzi, A.; Manfred, M.T. Neospora caninum infection in sheep and goats from north-eastern Italy and associated risk factors. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 140, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udonsom, R.; Supanta, J.; Tanglakmankhong, O.; Ngoenphisutsin, K.; Nishikawa, Y.; Fereig, R.M.; Jirapattharasate, C. Toxoplasma gondii and Neospora caninum prevalence and risk factors on goat farms in Kanchanaburi province, Thailand. Vet. Integr. Sci. 2021, 19, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintanilla-Gozalo, A.; Pereira-Bueno, J.; Tabares, E.; Innes, E.A.; González-Paniello, R.; Ortega-Mora, L.M. Seroprevalence of Neospora caninum infection in dairy and beef cattle in Spain. Int. J. Parasitol. 1999, 29, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozio, E. Searching for Trichinella: Not all pigs are created equal. Trends Parasitol. 2014, 30, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murrell, K.D. The dynamics of Trichinella spiralis epidemiology: Out to pasture? Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 231, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, H.R.; Bessonov, A.S.; Cuperlovic, K.; Gajadhar, A.A.; Van Knapen, F.; Noeckler, K.; Schenone, H.; Zhu, X. International Commission on Trichinellosis: Recommendations on methods for the control of Trichinella in domestic and wild animals intended for human consumption. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 93, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Knapen, F. Control of trichinellosis by inspection and farm management practices. Vet. Parasitol. 2000, 93, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alban, L.; Petersen, J.V. Ensuring a negligible risk of Trichinella in pig farming from a control perspective. Vet. Parasitol. 2016, 231, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslahi, A.V.; KarimiPourSaryazdi, A.; Olfatifar, M.; de Carvalho, L.M.M.; Foroutan, M.; Karim, M.R.; Badri, M.; Ketzis, J.K. Global prevalence of Trichinella in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 8, 2466–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therizol, M.; Levy, R.; Coulbois, J.; Brochard, C.; Berque, A.; Betourne, C. Trichinose aigue. A propos de quelques cas récents importés d’Egypte. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1975, 68, 407–415. [Google Scholar]
- Antonios, S.N.; Salem, S.A. A case report of human trichinosis in Tanta. J. Egypt. Soc. Parasitol. 1989, 19, 363–364. [Google Scholar]
- Pozio, E. World distribution of Trichinella spp. infections in animals and humans. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 149, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamble, H.R.; Anderson, W.R.; Graham, C.E.; Murrell, K.D. Diagnosis of swine trichinosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using an excretory—secretory antigen. Vet. Parasitol. 1983, 13, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nöckler, K.; Serrano, F.J.; Boireau, P.; Kapel, C.M.O.; Pozio, E. Experimental studies in pigs on Trichinella detection in different diagnostic matrices. Vet. Parasitol. 2005, 132, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapel, C.M.O.; Gamble, H.R. Infectivity, persistence, and antibody response to domestic and sylvatic Trichinella spp. in experimentally infected pigs. Int. J. Parasitol. 2000, 30, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapel, C.M. Sylvatic and domestic Trichinella spp. in wild boars; infectivity, muscle larvae distribution, and antibody response. J. Parasitol. 2001, 87, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozio, E.; Merialdi, G.; Licata, E.; Della Casa, G.; Fabiani, M.; Amati, M.; Cherchi, S.; Ramini, M.; Faeti, V.; Interisano, M.; et al. Differences in larval survival and IgG response patterns in long-lasting infections by Trichinella spiralis, Trichinella britovi and Trichinella pseudospiralis in pigs. Parasites Vectors 2020, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi, N.V.; Dorny, P.; La Rosa, G.; Long, T.T.; Van, C.N.; Pozio, E. High prevalence of anti-Trichinella IgG in domestic pigs of the Son La province, Vietnam. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Infectious Agent | ELISA Test Kit $ | Antigen | Serum Dilution | Conjugate | Sensitivity * | Specificity * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Toxoplasma gondii | ID Screen® Toxoplasmosis Indirect Multispecies | P30 antigen | 1:10 | Anti-multi-species IgG-HRP | 98.36% (95% CI: 95.29–99.44) | 99.42% (95% CI: 98.8–100) |
| Neospora caninum | ID Screen® Neospora caninum competition Multispecies | Purified extract of Neospora caninum | 1:2 | Anti-N. caninum-HRP (detects IgG or IgM) | 100% (95% CI: 98.8–100) | 100% (95% CI: 99.63–100) |
| Trichinella species | ID Screen® Trichinella Indirect Multispecies | Trichinella E/S antigen | 1:20 | Anti-multi-species-HRP (detects IgG or IgM) | 90.7% (95% CI: 89.1–92.4) | 100% (95% CI: 98.95–100) |
| Type of Infection | No. Tested | No. Negative (%) | No. Doubtful (%) | No. Positive (%) | 95% CI * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. gondii | 332 | 152 (45.8) | 28 (8.4) | 152 (45.8) | 40.4–51.3 |
| N. caninum | 332 | 217 (65.4) | 22 (6.6) | 93 (28.0) | 23.3–33.2 |
| Trichinella spp. | 332 | 327 (98.5) | 1 (0.3) | 4 (1.2) | 0.4–3.3 |
| T. gondii + N. caninum | 332 | 251 (75.6) | 19 (5.7) | 62 (18.7) | 14.7–23.4 |
| Analyzed Factor | No. Tested | No. Negative (%) | No. Positive (%) | OR (95% CI) * | p-Value # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 200 | 105 (52.5) | 95 (47.5) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Male | 132 | 75 (56.8) | 57 (43.2) | 0.8 (0.5–1.3) | 0.499 |
| Breeding place | |||||
| Ezbet El Nakhl | 184 | 119 (64.7) | 65 (35.3) | 3.8 (1.8–7.9) | 0.0003 |
| Manshiyat Naser | 108 | 48 (44.4) | 60 (55.6) | 0.6 (0.3–1.3) | 0.259 |
| 15 May city | 40 | 13 (32.5) | 27 (67.5) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Analyzed Factor | No. of Tested | No. of Negative (%) | No. of Positive (%) | OR (95% CI) * | p-Value # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 200 | 124 (62) | 76 (38) | Ref | Ref |
| Male | 132 | 115 (87.1) | 17 (12.9) | 4.1 (2.3–7.4) | <0.0001 |
| Breeding place | |||||
| Ezbet El Nakhl | 184 | 160 (87) | 24 (13) | Ref. | Ref. |
| Manshiyat Naser | 108 | 50 (46.3) | 58 (53.7) | 7.7 (4.4–13.7) | <0.0001 |
| 15 May city | 40 | 29 (72.5) | 11 (27.5) | 2.5 (1.1–5.7) | 0.031 |
| Animals | Location | Study Year | No. Tested | No. Positive (%) | Diagnostic Method | History | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Buffaloes | Cairo slaughterhouse | 1995 | 75 | 51 (68) | NAT | NS | [58] |
| Camels | Cairo slaughterhouse | 1995 | 161 | 6 (3.7) | NAT | NS | [59] |
| Cattle | Sharkia | NS | 93 | 19 (20.43) | ELISA | NS | [60] |
| Cattle | Qena and Sohag | 2014–2015 | 301 | 57 (18.9) | ELISA | NS | [61] |
| Cattle | Fayoum, Giza, Beni-Swief, and Menia | 2017 | 100 | 29 (29) 1 | ELISA | Infertility and abortion | [51] |
| Camels | Red Sea, Qalyubia, Kafr, and El Sheikh | 2018–2019 | 282 | 31 (11) | ELISA | 150 camels had a history of abortion | [53] |
| Cattle | Menoufia | 2017–2018 | 262 | 32 (12.21) 1 39 (14.89) 2 3 (1.5) 3 | ELISA | NS | [62] |
| Buffaloes | 244 | 17 (6.97) 1 33(13.52) 2 12 (4.92) 3 | |||||
| Sheep | Alexandria, Gharbia, Menofia, and Qalyubia | 2017–2018 | 430 | 37 (8.6) | ELISA | NS | [63] |
| Cattle | Giza, El Fayoum, and Beni Suef | 116 | 35 (30.17) | ELISA | Aborted bovine fetuses | [52] | |
| Camels | Aswan | 2018–2021 | 460 | 18 (3.9) | ELISA | NS | [44] |
| Sheep and Goats | Dakahlia, Beni Suef, Qena, and Red Sea | 2016–2021 | 239 121 | 37 (15.5) 6 (5) | ELISA | NS | [45] |
| Dogs and Cats | Variable | 2019–2022 | 172 51 | 10 (5.8) 2 (3.9) | ELISA | - | [49] |
| Cattle | Beheira | 358 | 88 (24.6) | ELISA | NS | [50] |
| Sample Types | Governorates | Study Year | No. Tested | No. Positive (%) | Diagnostic Methods | Species | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pork sausage | Alexandria | NS | 100 | 6 (6) 4 (4) | Trichinoscope Digestion method | T. spiralis | [38] |
| abattoir meat | Assiut and Sohag | 2006–2007 | 150 | 6 (4) 5 (3.33) | Trichinoscope Digestion methods | T. spiralis | [40] |
| abattoir meat | El-Minia | 2014–2015 | 100 | 0 | Muscle squash and digestion methods | - | [19] |
| abattoir meat | Cairo | 2018–2019 | 184 | 2 (1.08) | Trichinoscopic and histopathological examination | T. spiralis | [41] |
| abattoir inspection | Cairo | 2020 | 33,812 * | 359 (1.06) | Trichinoscopic examination | Trichinella sp. | [35] |
| abattoir meat | Cairo | 2020 | 170 | 6 (3.35) 4 (2.35) | Digestion methods Trichinoscope | T. spiralis# | [35] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fereig, R.M.; El-Alfy, E.-S.; Abdelbaky, H.H.; Abdel-Hamid, N.H.; Mazeed, A.M.; Menshawy, A.M.S.; Kelany, M.A.; El-Diasty, M.; Alawfi, B.S.; Frey, C.F. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Trichinella spp. in Pigs from Cairo, Egypt. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120675
Fereig RM, El-Alfy E-S, Abdelbaky HH, Abdel-Hamid NH, Mazeed AM, Menshawy AMS, Kelany MA, El-Diasty M, Alawfi BS, Frey CF. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Trichinella spp. in Pigs from Cairo, Egypt. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(12):675. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120675
Chicago/Turabian StyleFereig, Ragab M., El-Sayed El-Alfy, Hanan H. Abdelbaky, Nour H. Abdel-Hamid, Amira M. Mazeed, Ahmed M. S. Menshawy, Mohamed A. Kelany, Mohamed El-Diasty, Bader S. Alawfi, and Caroline F. Frey. 2023. "Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Trichinella spp. in Pigs from Cairo, Egypt" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 12: 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120675
APA StyleFereig, R. M., El-Alfy, E.-S., Abdelbaky, H. H., Abdel-Hamid, N. H., Mazeed, A. M., Menshawy, A. M. S., Kelany, M. A., El-Diasty, M., Alawfi, B. S., & Frey, C. F. (2023). Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii, Neospora caninum and Trichinella spp. in Pigs from Cairo, Egypt. Veterinary Sciences, 10(12), 675. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10120675






