Molecular Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates from Strangles Cases in Indonesia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Isolates and Reference Strains
2.2. Taxonomic Assessment of Bacterial Isolates
2.3. Bacterial DNA Extraction and Whole Genome Sequencing
2.4. SeM Typing
2.5. MLST
2.6. The cgMLST Analysis
2.7. Assessment of Antigens Used in the Strangvac® Vaccine
2.8. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and Assessment for Antimicrobial Resistance Genes
3. Results
3.1. Taxonomic Identification of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi
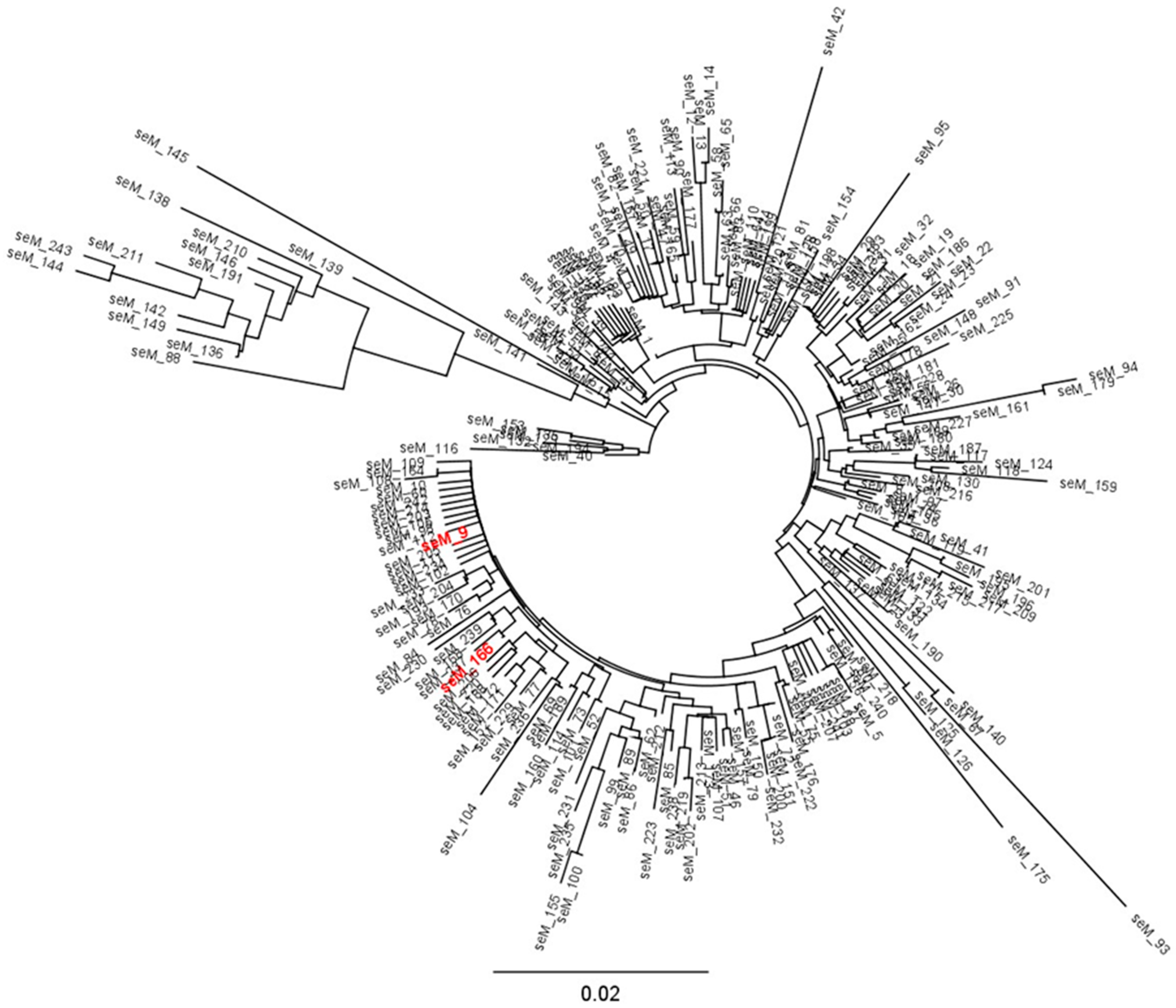
3.2. Molecular Typing of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates
3.3. Presence and Predicted Amino Acid Sequences of Strangvac® Antigens
3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and Resistance Genes of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyle, A.G.; Timoney, J.F.; Newton, J.R.; Hines, M.T.; Waller, A.S.; Buchanan, B.R. Streptococcus equi infections in horses: Guidelines for treatment, control, and prevention of strangles-revised consensus statement. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 633–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, C.; Steward, K.F.; Charbonneau, A.R.L.; Walsh, S.; Wilson, H.; Timoney, J.F.; Wernery, U.; Joseph, M.; Craig, D.; van Maanen, K.; et al. Globetrotting strangles: The unbridled national and international transmission of Streptococcus equi between horses. Microb. Genom. 2021, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringle, J.; Storm, E.; Waller, A.; Riihimäki, M. Influence of penicillin treatment of horses with strangles on seropositivity to Streptococcus equi ssp. equi-specific antibodies. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 294–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, J.R.; Wood, J.L.; Dunn, K.A.; DeBrauwere, M.N.; Chanter, N. Naturally occurring persistent and asymptomatic infection of the guttural pouches of horses with Streptococcus equi. Vet. Rec. 1997, 140, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christmann, U.; Pink, C. Lessons learned from a strangles outbreak on a large Standardbred farm. Equine Vet. Educ. 2017, 29, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waller, A.S.; Paillot, R.; Timoney, J.F. Streptococcus equi: A pathogen restricted to one host. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 60, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A.S. New perspectives for the diagnosis, control, treatment, and prevention of strangles in horses. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2014, 30, 591–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, J.R.; Verheyen, K.; Talbot, N.C.; Timoney, J.F.; Wood, J.L.; Lakhani, K.H.; Chanter, N. Control of strangles outbreaks by isolation of guttural pouch carriers identified using PCR and culture of Streptococcus equi. Equine Vet. J. 2000, 32, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waller, A. Streptococcus equi: Breaking its strangles-hold. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pringle, J.; Venner, M.; Tscheschlok, L.; Waller, A.S.; Riihimäki, M. Markers of long term silent carriers of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi in horses. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 2751–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffo, G. De Medicina Equorum. Available online: http://wellcomelibrary.org/player/b19689755 (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Sweeney, C.R.; Timoney, J.F.; Newton, J.R.; Hines, M.T. Streptococcus equi infections in horses: Guidelines for treatment, control, and prevention of strangles. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, E.; Locke, S.J.; Donahoe, J.K.; Mackin, M.A.; Carter, C.N. Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus spp. from horses: A retrospective study (2000–2010). J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2012, 24, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johns, I.C.; Adams, E.-L. Trends in antimicrobial resistance in equine bacterial isolates: 1999–2012. Vet. Rec. 2015, 176, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, C.; Greenwood, S.; Boison, J.O.; Chirino-Trejo, M.; Dowling, P.M. Bacterial isolates from equine infections in western Canada (1998–2003). Can. Vet. J. 2008, 49, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Hage, C.M.; Bannai, H.; Wiethoelter, A.K.; Firestone, S.M.; Heislers, C.M.; Allen, J.L.; Waller, A.S.; Gilkerson, J.R. Serological responses of Australian horses using a commercial duplex indirect ELISA following vaccination against strangles. Aust. Vet. J. 2019, 97, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Waller, A.S.; Frykberg, L.; Flock, M.; Zachrisson, O.; Guss, B.; Flock, J.-I. Intramuscular vaccination with Strangvac is safe and induces protection against equine strangles caused by Streptococcus equi. Vaccine 2020, 38, 4861–4868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. CVMP Assessment Report for Strangvac (EMEA/V/C/005309/0000): Vaccine Common Name: Streptococcus equi Vaccine (Recombinant Proteins). 2021. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/assessment-report/strangvac-epar-public-assessment-report_en.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Timoney, J.F. The pathogenic equine streptococci. Vet. Res. 2004, 35, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, M.T.G.; Heather, Z.; Paillot, R.; Steward, K.F.; Webb, K.; Ainslie, F.; Jourdan, T.; Bason, N.C.; Holroyd, N.E.; Mungall, K.; et al. Genomic evidence for the evolution of Streptococcus equi: Host restriction, increased virulence, and genetic exchange with human pathogens. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, C.; Bugg, M.; Robinson, C.; Mitchell, Z.; Davis-Poynter, N.; Newton, J.R.; Jolley, K.A.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Waller, A.S. Sequence variation of the SeM gene of Streptococcus equi allows discrimination of the source of strangles outbreaks. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivens, P.A.S.; Matthews, D.; Webb, K.; Newton, J.R.; Steward, K.; Waller, A.S.; Robinson, C.; Slater, J.D. Molecular characterisation of ‘strangles’ outbreaks in the UK: The use of M-protein typing of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi. Equine Vet. J. 2011, 43, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, T.; Kuwamoto, Y.; Wada, R.; Sugita, S.; Kakuda, T.; Takai, S.; Higuchi, T.; Timoney, J.F. Variation in the N-terminal region of an M-like protein of Streptococcus equi and evaluation of its potential as a tool in epidemiologic studies. Am. J. Vet. Res. 2005, 66, 2167–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, M.; Lynagh, Y.; Woods, C.; Owen, P. The fibrinogen-binding protein (FgBP) of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi additionally binds IgG and contributes to virulence in a mouse model. Microbiology 2001, 147, 3311–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webb, K.; Jolley, K.A.; Mitchell, Z.; Robinson, C.; Newton, J.R.; Maiden, M.C.J.; Waller, A. Development of an unambiguous and discriminatory multilocus sequence typing scheme for the Streptococcus zooepidemicus group. Microbiology 2008, 154, 3016–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsdóttir, S.; Harris, S.R.; Svansson, V.; Gunnarsson, E.; Sigurðardóttir, Ó.G.; Gammeljord, K.; Steward, K.F.; Newton, J.R.; Robinson, C.; Charbonneau, A.R.L.; et al. Genomic dissection of an Icelandic epidemic of respiratory disease in horses and associated zoonotic cases. mBio 2017, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parkinson, N.J.; Robin, C.; Newton, J.R.; Slater, J.; Waller, A.S. Molecular epidemiology of strangles outbreaks in the UK during 2010. Vet. Rec. 2011, 168, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidayat, R.; Alhadi, F. Identifikasi Streptococcus equi dari kuda yang diduga menderita strangles: (Identification of Streptococcus equi from horses suspected strangles). J. Ilmu Pertan. Indones. 2012, 17, 199–203. [Google Scholar]
- Office International des Epizooties. Self-Declaration of an Equine Disease Free Zone in Jakarta, Indonesia, for the Purpose of Facilitating the Equestrian Competitions in the Framework of the 18th Asian Games 2018. Available online: https://www.oie.int/fileadmin/Home/eng/Animal_Health_in_the_World/docs/pdf/Self-declarations/Indonesia_selfdeclaration_EDFZ_Final.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2022).
- Ministry of Agriculture, Republic of Indonesia. Decree of the Minister of Agriculture Number 235/Kpts/PK.320/3/2018 Regarding Notifiable Animal Diseases on Horses. 2018. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Animal_Health_in_the_World/docs/pdf/Self-declarations/Indonesia_selfdeclaration_EDFZ_Final.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Harris, S.R.; Robinson, C.; Steward, K.F.; Webb, K.S.; Paillot, R.; Parkhill, J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Waller, A.S. Genome specialization and decay of the strangles pathogen, Streptococcus equi, is driven by persistent infection. Genome Res. 2015, 25, 1360–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frosth, S.; Morris, E.R.A.; Wilson, H.; Frykberg, L.; Jacobsson, K.; Parkhill, J.; Flock, J.-I.; Wood, T.; Guss, B.; Aanensen, D.M.; et al. Conservation of vaccine antigen sequences encoded by sequenced strains of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. Equine Vet. J. 2022, 55, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, E.R.A.; Boyle, A.G.; Riihimäki, M.; Aspán, A.; Anis, E.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Ivanov, I.; Bordin, A.I.; Pringle, J.; Cohen, N.D. Differences in the genome, methylome, and transcriptome do not differentiate isolates of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi from horses with acute clinical signs from isolates of inapparent carriers. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, E.R.A.; Hillhouse, A.E.; Konganti, K.; Wu, J.; Lawhon, S.D.; Bordin, A.I.; Cohen, N.D. Comparison of whole genome sequences of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi from an outbreak in Texas with isolates from within the region, Kentucky, USA, and other countries. Vet. Microbiol. 2020, 243, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordoni, G.; Williams, A.; Durham, A.; Florio, D.; Zanoni, R.G.; La Ragione, R.M. Rapid diagnosis of strangles (Streptococcus equi subspecies equi) using PCR. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 102, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, S.; Okada, Y.; Maruyama, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Takahashi, T.; Nakamura, M.; Ezaki, T.; Morita, H. Direct and rapid detection of Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae DNA in animals by PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1994, 32, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehr, J.T.; Dieterich, C.; Reinert, K. Flexbar 3.0—SIMD and multicore parallelization. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2941–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolenko, S.I.; Korobeynikov, A.I.; Alekseyev, M.A. BayesHammer: Bayesian clustering for error correction in single-cell sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: Rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolley, K.A.; Bray, J.E.; Maiden, M.C.J. Open-access bacterial population genomics: BIGSdb software, the PubMLST.org website and their applications. Wellcome Open Res. 2018, 3, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradis, E.; Claude, J.; Strimmer, K. APE: Analyses of Phylogenetics and Evolution in R language. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argimón, S.; Abudahab, K.; Goater, R.J.E.; Fedosejev, A.; Bhai, J.; Glasner, C.; Feil, E.J.; Holden, M.T.G.; Yeats, C.A.; Grundmann, H.; et al. Microreact: Visualizing and sharing data for genomic epidemiology and phylogeography. Microb. Genom. 2016, 2, e000093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guss, B.; Flock, M.; Frykberg, L.; Waller, A.S.; Robinson, C.; Smith, K.C.; Flock, J.-I. Getting to grips with strangles: An effective multi-component recombinant vaccine for the protection of horses from Streptococcus equi infection. PLoS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Frykberg, L.; Flock, M.; Guss, B.; Waller, A.S.; Flock, J.-I. Strangvac: A recombinant fusion protein vaccine that protects against strangles, caused by Streptococcus equi. Vaccine 2018, 36, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Test for Bacteria Isolated from Animals, 5th ed.; CLSI VET01S ED5; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sadaka, C.; Kanellos, T.; Guardabassi, L.; Boucher, J.; Watts, J.L. Evaluation of veterinary-specific interpretive criteria for susceptibility testing of Streptococcus equi subspecies with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim-sulfadiazine. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 326–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, S.; Silley, P.; Simjee, S.; Woodford, N.; van Duijkeren, E.; Johnson, A.P.; Gaastra, W. Editorial: Assessing the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacteria obtained from animals. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 601–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bortolaia, V.; Kaas, R.S.; Ruppe, E.; Roberts, M.C.; Schwarz, S.; Cattoir, V.; Philippon, A.; Allesoe, R.L.; Rebelo, A.R.; Florensa, A.F.; et al. ResFinder 4.0 for predictions of phenotypes from genotypes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 3491–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alber, J.; El-Sayed, A.; Lämmler, C.; Hassan, A.A.; Weiss, R.; Zschöck, M. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction for identification and differentiation of Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus and Streptococcus equi subsp. equi. J. Vet. Med. B Infect. Dis. Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heather, Z.; Holden, M.T.G.; Steward, K.F.; Parkhill, J.; Song, L.; Challis, G.L.; Robinson, C.; Davis-Poynter, N.; Waller, A.S. A novel streptococcal integrative conjugative element involved in iron acquisition. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 1274–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasuya, K.; Tanaka, N.; Oshima, F.; Fujisawa, N.; Saito, M.; Tagami, K.; Niwa, H.; Sasai, K. Genetic analysis of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi isolated from horses imported into Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2019, 81, 924–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindahl, S.; Söderlund, R.; Frosth, S.; Pringle, J.; Båverud, V.; Aspán, A. Tracing outbreaks of Streptococcus equi infection (strangles) in horses using sequence variation in the seM gene and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 153, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libardoni, F.; Vielmo, A.; Farias, L.; Matter, L.B.; Pötter, L.; Spilki, F.R.; de Vargas, A.C. Diversity of seM in Streptococcus equi subsp. equi isolated from strangles outbreaks. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 162, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Gao, N.; Waller, A.S.; Cook, F.R.; Fan, S.; Yuan, D.; Du, Y.; Li, F.; Norimine, J.; Zhu, W. An outbreak of strangles associated with a novel genotype of Streptococcus equi subspecies equi in donkeys in China during 2018. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanter, N.; Talbot, N.C.; Newton, J.R.; Hewson, D.; Verheyen, K. Streptococcus equi with truncated M-proteins isolated from outwardly healthy horses. Microbiology 2000, 146 Pt 6, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, R.; Taku, A.K.; Gangil, R.; Sharma, R.K. Molecular characterization of virulence genes of Streptococcus equi subsp. equi and Streptococcus equi subsp. zooepidemicus in equines. Vet. World 2016, 9, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonpitak, W.; Sornklien, C.; Wutthiwithayaphong, S. Characterization of a Streptococcus equi ssp. equi isolate from a strangles outbreak in Thailand. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2016, 38, 30–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Office International des Epizooties. World Animal Health Publication and Handistatus II (Dataset for 2004). Available online: http://web.oie.int/hs2/sit_mald_cont.asp?c_mald=160&c_cont=3&annee=2004# (accessed on 13 January 2021).
- Khoo, L.; Maswati, M.A.; Roseliza, R.; Rosnah, Y.; Saifu Nazri, R.; Ramlan, M. Isolation of Streptococcus equi during Strangles in Peninsular Malaysia. Malays. J. Vet. Res. 2011, 2, 27–32. [Google Scholar]
- Directorate General of Livestock and Animal Health Resources Indonesia. Horse Population by Province in Indonesia, 2014–2018. 2019. Available online: https://www.pertanian.go.id/Data5tahun/ATAPNAK2017(pdf)/102-Pop_Kuda_Prop.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Peraturan Menteri Pertanian Republik Indonesia Nomor 28/Permentan/KR.120/6/2018 Tentang Tindakan Karantina Hewan Terhadap Pemasukan Dan Pengeluaran Kuda Untuk Perlombaan (Animal Quarantine Measures on the Entry and Exit of Horses for Competition). 2018. Available online: https://www.melleq.com/peraturan/peraturan_242bn846-2018.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Agricultural Quarantine Agency, Republic of Indonesia. Keputusan Kepala Badan Karantina Pertanian Nomor 1332/KPTS/KR.120/K/07/2018 Tentang Pedoman Tindakan Karantina Untuk Perlombaan Internasional Equestrian Sesuai Dengan Ketentuan EDFZ. 2018. Available online: https://samarinda.karantina.pertanian.go.id/files/2352%20Kepka%20Barantan%20-%202018%20-%20No.%201332%20-%20Pedoman%20TK%20untuk%20Equestrian%20sesuai%20EDFZ.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Marlefzena, M. Kajian Equine Infectious Anemia Pada Kuda Impor di Bandar Udara Internasional Soekarno-Hatta. Master’s Thesis, IPB University, Bogor, Indonesia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tscheschlok, L.; Venner, M.; Steward, K.; Böse, R.; Riihimäki, M.; Pringle, J. Decreased clinical severity of strangles in weanlings associated with restricted seroconversion to optimized Streptococcus equi ssp equi assays. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2018, 32, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- British Equine Veterinary Association. Practice Policy: Dose and Routes of Administration of Common Antimicrobials (Protect Me). Available online: https://www.beva.org.uk/Protect-Me (accessed on 10 December 2022).
- Haggett, E.F.; Wilson, W.D. Overview of the use of antimicrobials for the treatment of bacterial infections in horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2008, 20, 433–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Morales, C.; Gomez, D.E.; Renaud, D.; Arroyo, L.G. Streptococcus equi culture prevalence, associated risk factors and antimicrobial susceptibility in a horse population from Colombia. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2022, 111, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, D.; Portis, E.; Keane, C.; Hallberg, J.; Bryson, L.; Sweeney, M.; Boner, P. In vitro susceptibility of ceftiofur against Streptococcus equi subsp zooepidemicus and subsp equi isolated from horses with lower respiratory disease in Europe since 2002. Vet. Ther. 2009, 10, E1–E10. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine: Ranking of Medically Important Antimicrobials for Risk Management of Antimicrobial Resistance Due to Non Human Use; 6th Revision 2018; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; ISBN 978-92-4-151552-8.
- Nuriyanto, R.; Uli, E.; Hardjopangarso, S.; Unang, U.; Kurniawan, W.; Prasetyo, A. Indeks Obat Hewan Indonesia Edisi XII (Indonesian Veterinary Drug Index), 12th ed.; Asosiasi Obat Hewan Indonesia (ASOHI): Jakarta, Indonesia, 2019; ISBN 978-602-72974-8-7. [Google Scholar]

| Isolate ID | Original Name | Date of Sampling (DD-MM-YYYY) | Horse | Location | MALDI-TOF MS Scores | PCR Results | seM Typing | MLST | cgMLST | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | Age (Years) | Sex | Specimen | Farm | Province | dt | edt | sodA | ICESe2 | ICESz1 | Allele | Peptide | ST | BAPS Cluster | |||
| IHIT39386 | DAR001/18 | 02-06-2018 | 1 | 5 | F | PML | A | East Java | 2.42 | 2.43 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| IHIT39393 | DAR002/18 | 21-07-2018 | 2 | 4 | M | N | B | West Java | 2.09 | 2.28 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| IHIT39392 | DAR004/18 | 21-07-2018 | 3 | 5 | M | N | B | West Java | 2.18 | 2.35 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| IHIT39391 | DAR008/18 | 09-10-2018 | 4 | 8 | F | PML | C | Central Java | 2.05 | 2.35 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| IHIT39394 | DAR010/18 | 09-10-2018 | 5 | nd | nd | N | C | Central Java | 2.02 | 2.28 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| IHIT39395 | DAR011/18 | 22-11-2018 | 6 | nd | nd | N | D | West Java | 2.42 | 2.44 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| IHIT39396 | DAR012/18 | 22-11-2018 | 7 | 8 | nd | N | D | West Java | 2.24 | 2.42 | + | + | - | 166 | 159 | 179 | 2 |
| Antimicrobial Substance | Antimicrobial Class | Number of Isolates with the Respective MIC Value (µg/mL) | Percentage (%) | MIC50 (µg/mL) | MIC90 (µg/mL) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.016 | 0.03 | 0.06 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 | 16 | 32 | 64 | 128 | S | I | R | ||||
| Penicillin G * | Beta-lactams | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | ≤0.0625 | ≤0.0625 | ||||||
| Amoxicillin/Clavulanic acid | Beta-lactams | 6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | ≤2/1 | 4 | ||||||||||
| Ampicillin ** | Beta-lactams | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | ≤0.25 | ≤0.25 | |||||||
| Ceftiofur ** | Beta-lactams | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | ≤0.125 | ≤0.125 | ||||||||
| Cephalothin | Beta-lactams | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | ≤1 | ≤1 | |||||||||
| Enrofloxacin ** | Fluoroquinolons | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Florfenicol | Phenicols | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | ≤1 | 2 | ||||||||||
| Gentamicin | Aminoglycosides | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 2 | - | - | - | 4 | 8 | |||||||
| Spectinomycin | Aminoglycosides | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 4 | - | - | - | >64 | >64 | ||||||||
| Trimethoprim/Sulfa-methoxazole **** | Folate pathways inhibitors | 0 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 28.6 | 57.1 | 14.3 | 1/19 | >2/38 | |||||||||
| Tetracycline *** | Tetracyclines | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | ≤0.125 | 0.5 | |||||||
| Tiamulin | Pleuromutilins | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | 2 | 2 | ||||||
| Erythromycin *** | Macrolides | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | - | - | ≤0.125 | ≤0.125 | ||||||||
| Tilmicosin | Macrolides | 0 | 5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | 1 | 4 | ||||||||
| Tulathromycin | Macrolides | 0 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | - | - | - | 4 | 8 | |||||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rotinsulu, D.A.; Ewers, C.; Kerner, K.; Amrozi, A.; Soejoedono, R.D.; Semmler, T.; Bauerfeind, R. Molecular Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates from Strangles Cases in Indonesia. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010049
Rotinsulu DA, Ewers C, Kerner K, Amrozi A, Soejoedono RD, Semmler T, Bauerfeind R. Molecular Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates from Strangles Cases in Indonesia. Veterinary Sciences. 2023; 10(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleRotinsulu, Dordia Anindita, Christa Ewers, Katharina Kerner, Amrozi Amrozi, Retno Damayanti Soejoedono, Torsten Semmler, and Rolf Bauerfeind. 2023. "Molecular Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates from Strangles Cases in Indonesia" Veterinary Sciences 10, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010049
APA StyleRotinsulu, D. A., Ewers, C., Kerner, K., Amrozi, A., Soejoedono, R. D., Semmler, T., & Bauerfeind, R. (2023). Molecular Features and Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Streptococcus equi ssp. equi Isolates from Strangles Cases in Indonesia. Veterinary Sciences, 10(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci10010049







