Abstract
Whiskey’s complex and diverse flavor stems from a range of reactions that create congeners that are primarily dependent upon the cereal source/mash bill and each stage of the process: malting, mashing, fermentation, distillation, and cask maturation. Therefore, in theory, the congener profile of a whiskey is a summation of its ingredients and the specific parameters of each stage of the manufacturing process. Congener profiles have been used as biomarkers for quality and authentication; however, to date, insufficient information has been published in relation to the extensive profiling of congeners associated with specific whiskey styles/types or the intra-and inter-variability within brands, especially in an Irish context due to the recent rapid expansion of the industry. As the ability to extract and identify congeners has progressed appreciably in recent years due to advances in extraction, chromatographic, and chemometric techniques, it is imperative that research is undertaken to gain a better understanding of the impact of specific congeners not only in relation to quality but also as biomarkers for authentication.
1. Introduction
Whisky or whiskey production (the latter generally refers to non-Scotch or Scottish whisky, but for the purpose of this review, the term whiskey will be used, unless specifically referring to Scotch whisky) has three key ingredients: water, cereal, and yeast, and follows a relatively similar fundamental process. However, as operational procedures and parameters vary greatly between styles/types and distilleries, significant potential exists for numerous distinguished and subtle differences in the final product. Choices in the selection of cereal variety, malting regime, fermentation conditions, distillation process/design, time, cask choice, and maturation environment all potentially influence the final character of the product. Not to mention blending, which further increases complexity and is a major product type within the whiskey category. These varieties result in whiskies with distinct flavors due to the presence of many multiples of potentially active flavor compounds, commonly referred to as congeners. The key congener chemical groups identified in whiskey are alcohols, esters, aldehydes, acids, phenols, lactones, terpenes, and tannins, generated at multiple stages of the process and more prominent in some than others [1].
Variable congeners and concentrations are associated with unique flavor profiles but also potentially discriminate between whiskies based on style/type, region, and authenticity. Whiskey authentication has always been a critical focus of the industry in order to combat fraud due to its popularity and classification as a premium product. Whiskey fraud is the imitation of legitimate brands through refilling, fabrication, and tampering, putting the industry’s brand integrity, consumer confidence, and profitability at risk [2]. In 2016, the European Union Intellectual Property Office (EUIPO) estimated the spirits and wine industry’s losses at GBP 1.3 billion annually (~3.3% of sales) due to counterfeit products in the EU marketplace, with some reports suggesting that as much as a third of commercial Scotch whiskies tested were fraudulent [3,4]. Imitations are often a response to increased demand, and Irish whiskey sales have increased from under 5 million cases in 2010 to over 13 million cases in 2022, i.e., from 60 million bottles to over 156 million bottles, and are forecast to increase to 24 million cases by 2030 [5]. Thus, Irish whiskey is potentially under increased threat from counterfeiting.
On the island of Ireland, the number of operational distilleries has increased from four to over forty since 2010. It is therefore imperative that safeguards to protect the overall Irish whiskey brand are suitably robust [5,6]. Whiskey fraud can be a highly refined business, making all but the most elaborate attempts difficult to identify. Identifying biomarkers of fraud is an established mechanism used to protect some specific styles/types of Scotch, but in order for this approach to be applicable for Irish whiskies, individual congeners, congener ratios, and overall congener profiles associated with particular styles/types, brands, and distilleries must first be established [2,4,7,8]. Therefore, achieving a ‘detailed congener fingerprint’ of specific batches of product offers the best way to be able to detect adulteration but also to monitor product consistency, quality, or even improve or direct flavor profiles [9]. It is therefore necessary to build a congener library of branded whiskies of all styles/types in order to be able to differentiate between genuine and fraudulent samples. These congener libraries could potentially be used to identify uniqueness and commonalities within selected whiskey categories, to better understand the production process and the source and diversity of flavor, to protect brands against fraudulent activity, and for quality control. In addition, attempting to link congeners to the cereal source may also be very beneficial in reducing the risk of fraud, especially for single malt whiskies that are only allowed to contain barley as the cereal source as per the Irish whiskey technical file [10]. While existing research on congener libraries has been extensively undertaken on Scotch and bourbon, little work has been published on Irish whiskies, especially for the many new entrants in the sector. To date, numerous chromatographic and spectroscopic techniques have been used to establish differences between whiskies and to establish congener libraries. However, recent advances in automated volatile extraction techniques, comprehensive gas chromatography (GCxGC), high resolution mass spectrometry, and chemometric analysis have significantly enhanced the capability of extracting and identifying trace level congeners in whiskey, which can be subsequently used to determine their impact on sensory perception and quality, as well as for authentication purposes.
2. Whiskey Origins
It is said that Irish Christian monks obtained the secrets of distilling from the Moors of Spain during their voyages to the Mediterranean in the 11th century [11,12,13]. Initially, the monks produced distilled alcohol based on essential oils and herbs, known as aqua vitae, and used it for medicinal purposes, translating in Gaelic to ‘Uisce Beatha’ (water of life) [12]. Irish whiskey dates back to 1405 (reported in the Annals of Clonmacnoise), 90 years before its notation in Scotland by monk Friar John Cor in 1494 [13]. In the 17th century, the shortened name ‘uiskie’ was used, changing to ‘whiskie’ in 1715 and eventually to ‘whisky’ in 1736, now widely used to denote whiskey produced in Scotland [14,15]. In 1830, Aenas Coffey invented a column still that permitted continuous, cheaper, and more efficient whiskey production, which subsequently became the bedrock of Scotch grain whisky. Consequently, Irish distillers wanted to differentiate their own product from Scotch, thus developing the marketing effect of adding an ‘e’ [14,16].
Whiskey gained accelerated popularity, not only from the impact of the column still but also from the ravaging of France’s grapes by the pest Phylloxera in 1880–1900 [16]. In the 1900s, numerous events devastated the production and sales of Irish whiskey. In 1914, World War I saw the reservation of coal and barley for the war effort. In 1916, the Easter Rising and the subsequent Irish War of Independence further impacted production. Arguably, the greatest impact on the production and sale of whiskey was prohibition in the United States of America (1920–1933) and subsequently the outbreak of World War II (1939–1945). The protectionism policies of the Irish government over this period up to the 1960s, although designed to safeguard Irish industries from cheaper imports, adversely impacted exports due to tariffs [3,13]. Efforts to rebuild Irish whiskey began with the creation of the Irish Distillers Group in 1966 by the merger of John Power & Son, John Jameson & Son, and the Cork Distillers Company, the outcome of which was to consolidate production in a new purpose-built facility in Midleton, Co. Cork, resulting in the closure of their existing distilleries. This also coincided with new government strategies for industrial growth and foreign direct investment in Ireland. Bushmills Distillery in Co. Antrim, Northern Ireland, joined the Irish Distilleries Group in 1972 [6,11]. This consolidation increased production and sales but also resulted in a more defined Irish whiskey character, which was generally smoother and sweeter than Scotch [17]. Pernod Ricard acquired Irish Distilleries in 1988, and the Bushmills Distillery was sold to Diageo in 2005. The only other Distillery that became operational at this time on the island of Ireland was Cooley Distillery in 1987 in Co. Louth, which was subsequently sold to Beam Suntory in 2012. Numerous other distilleries have opened across the island of Ireland in recent years, from craft distilleries to large-scale production operations, due to the rising demand for Irish whiskey, particularly in the USA, where Irish whiskey sales rose by 16.3% in 2021 [17]. Unlike Scotch, where every part of the whiskey process occurs at the same distillery (apart from bottling) as per the Scottish whisky technical file, not all operations need to be undertaken on the same site in Ireland [10,18]. This allowance for outsourcing to specialized bodies can result in cost reduction, assurance of quality due to specific expertise, and potentially greater product diversification.
Irish Whiskey Regulations
The Irish whiskey technical file defines whiskey as being produced by the distillation of a mash made from cereals and water (which varies according to the style or type). In summary, none of the alcohol can be of synthetic or non-agricultural origin. The whiskey must not exceed an alcohol concentration of 94.8% alcohol by volume (ABV), and its flavor profile must be representative of the raw materials used. The final distillate must have a minimum maturation period of 3 years, taking place in wooden casks (as opposed to only oak as per the Scottish whisky technical file [18]) no bigger than 700 L. The only permitted additives to the distillate are water and the additive caramel (E150a), often used to enhance color [10,19]. In order to differentiate whiskies on a national or regional scale, most countries regulate the definition of whiskey by law, incorporating appropriate procedures and practices. Therefore, production that does not adhere to the regulations cannot claim to be authentic or even whiskey and/or from the said country or region. This ensures the protection of the producer, consumer, and tax revenues for the state. In order for Irish whiskey to be recognized as both a spirit drink and of Irish origin, it must be compliant with both the legal definition under the EU 2019/787 regulation and the Irish whiskey technical file [10,20]. Both documents also detail specifications for the Geographical Indicator (GI) status of Irish whiskey approved by the European Commission in 2016. GI status not only provides an assurance of quality/tradition but potentially also offers another level of protection against fraud. In order to uphold its GI status, all types of Irish whiskey must be produced and matured on the island of Ireland, with exportation of the whiskey in any container that continues its maturation prohibited. Bottling is permitted to take place off the island of Ireland but is still subject to company controls and the use of demineralized water to ensure organoleptic properties are retained. The attainment of GI status theoretically provides protection to Irish distilleries, maintaining the culture of the Irish whiskey industry and potentially shielding the brand from fraudulent products [21,22].
Even though Ireland can be considered the birthplace of whiskey, its definition somewhat differs between countries, creating a variance in permitted processes and ingredients. As well as demonstrating a wide array of traditions and cultures, said variances can aid in identifying differing traits and hallmark predictive congeners in specific regional styles/types of whiskies. With an ever-expanding market, exceptions begin to develop in terms of processes and raw materials, provided innovation adheres to the regulations outlined in the Irish whiskey technical file [10]. Therefore, it is more imperative than ever to monitor whiskey products in order to attain a greater understanding of the congeners and their reactions that are representative of the diversity of Irish whiskey, to better understand the processes impacting flavor development, for quality control, and also to protect against fraudulent practices [7,8,23].
3. Irish Whiskey Types/Styles
Typically, there are four key types of Irish whiskey: Malt Irish Whiskey, Pot Still Irish Whiskey, Grain Irish Whiskey, and Blended Irish whiskey (Figure 1). Malt whiskey is made with 100% malted barley and typically brewed in a batch-style system using copper pot stills. [10]. The term ‘single’, refers to the fact that the whiskey comes from one distillery, with most single malt whiskies being combinations of whiskies from different casks and of varying ages, provided all whiskies in question are made with 100% malted barley and follow the process outlined in the technical file [10,24,25]. Pot Still whiskey is unique to Ireland and is a similar process to malted whiskey, with a very different mash bill consisting of a mixture of malted barley (30% or greater), unmalted/green barley (30% or greater), and no more than 5% other cereals such as oats, rye, or maize [25]. Using ‘green’ unmalted barley gives the aroma and taste of raw/cooked apples, as well as a spicy and creamy mouthfeel [10]. The practice of using green barley dates back to alleviate the fluctuating malt tax at the end of the 18th century, but more recently to avoid excessive kilning, where some enzymes can be denatured by the high temperatures used in the malting process [26]. Irish Grain whiskey can either be made with 100% maize, wheat, or rye, or more commonly mixed in combination with malted barley (~10%) in order to use the barley’s enzymes (lacking in the grain) to extract sugar from the grain [10]. The addition of exogenous enzymes is permitted in Irish whiskey production, enabling 100% maize and other grain (wheat or rye) distillates to be possible [10]. Grain whiskey is considered paler and lighter in character compared with malt whiskey, primarily due to the use of a column still and the absence of kilning [27]. Using a column still (also known as a continuous still) also contributes to a lighter character, producing a final spirit with a greater alcohol content (94.5% ABV) as more volatile components are removed (i.e., those congeners less volatile than ethanol) from increased rectification, leading to a less intense flavor.
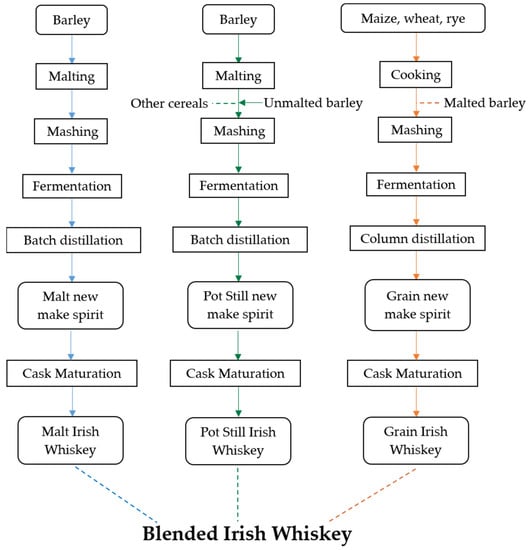
Figure 1.
Production process flow chart for Irish whiskey types.
Irish Blended whiskey is a combination of two or more of the above whiskey types or a blend of two or more of the same whiskey style/type from different distilleries. The art of blending is very important to create greater diversity and unique products, especially as only three conventional whiskey styles/types exist. Blending significantly contributes to the wide range of existing brands, creating numerous possibilities. The skill is to achieve a sensory character that retains or enhances the component aromas and tastes but, as a whole, is inseparable from the component parts and yet distinctive [10,11]. While a blend may have a recipe consisting of specific quantities of certain whiskies, these are often varied due to batch-to-batch or cask-to-cask fluctuations. A blend will rarely rely on just one type of grain or malt whiskey due to the difficulty of attaining the exact same products over time. Knowledge of the brand and/or the distillery from which it originates enables the consumer to ascertain expectations about the product prior to purchase and enhances brand loyalty, an increasingly important aspect in a competitive market [7,11].
4. Congeners and the Whiskey Process
While congener differences are the result of variations in processes and materials used, identifying the single compound or group of compounds responsible for flavor differentiation between whiskies is difficult, or maybe even impossible, due to the complexity of these products. Minor alterations in processing can influence congeners, with many reactions in different states of equilibrium, highlighting the dynamic nature of the process up to bottling [1]. Many congener groups can arise from multiple stages, as seen in Figure 2. Ultimately, each stage in the process has its own impact on the concentration of congeners in the final product, as some are only generated at specific stages in the process, while others may be generated or degraded at more than one stage. For example, phenols are strongly correlated with peated malts and are therefore thought to develop from the kilning process in malting, contributing to a smoky and medicinal flavor [28]. However, they are also known to arise during fermentation and cask maturation, and whether they are entirely responsible for the peated profile remains uncertain [1,29]. Congeners remain the most useful guide to flavor formation; however, it may be near impossible to definitively establish every congener involved in any individual whiskey due to the host of factors impacting their presence, concentration, or sensory influence. It is worth remembering that some congeners at trace levels (minute quantities) may have a greater impact on sensory perception than much more abundant congeners, as sensory perception depends primarly upon abundance and odor activity. Thus, volatile congeners will only be perceived if their concentration is above their odor threshold, which varies considerably between individual congeners.
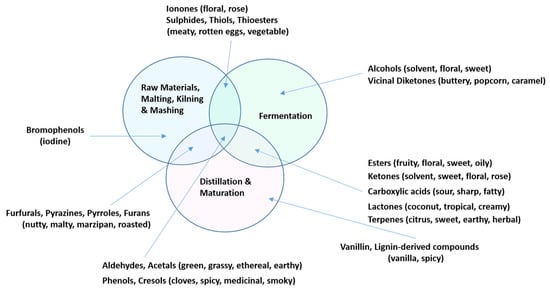
Figure 2.
Venn diagram of congeners found at various process stages based on [1].
4.1. Malting Barley
The first step of whiskey production, if barley is the main cereal source, is malting. This effectively ‘tricks’ the barley into germinating, with a hormone called gibberellic acid activating enzyme synthesis of α-amylase and β-glucanase, which start converting the starch, and additional mechanisms that also utilize the protein reserve, creating simpler starches and sugars. Other enzymes such as β-amylase and peptidases present in the starchy endosperm of the barley are activated during malting, extracting peptides and amino acids, all requisites for the yeast to grow during the fermentation stage [25,30,31]. Germination is initiated by steeping the barley in warm water (~16 °C) in cycles between air rests for up to 3 days to raise the moisture content and allow oxygen to reach the embryo until sprouting begins [11]. Traditionally, barley was left to air dry on a malting house floor, a practice still in use by some Scottish distilleries and even being recommissioned by others. Most distilleries now outsource to expert maltsters that use more modern methods, such as blowing pressurized, heated air through the barley during the air rests in order to mix the barley, as well as removing carbon dioxide by extraction.
The barley is then cured in a kiln for 24–48 h to prevent full germination and preserve sugar content (at this point, peat smoking can be introduced, which is used in the production of peated whiskies). Kilning essentially has three functions: (i) halt germination; (ii) enhance Maillard reactions (MR) between amino acids and sugars, enhancing color and flavor development; and (iii) reduce moisture from ~45% to ~4–5% whilst preserving the enzymes required for fermentation [32]. The MR is a non-enzymatic browning reaction that is critical in producing key flavor congeners such as furfurals and pyrazines, derived from pentose sugars in the cereal walls [33,34]. The MR is not a single reaction but a series of complex reactions whose pathways and products critically depend on pH and temperature. The MR takes place between reducing sugars and amino groups and is strongly accelerated by thermal energy. The resulting reaction produces an N-substituted glycosylamine, also named a Schiff base due to its carbon-to-nitrogen double bond. This unstable Schiff base isomerises by undergoing an Amadori rearrangement, giving a ketosamine with the double bond between a carbon and an oxygen [35,36]. The ketosamine can then react in a number of ways to produce different products, which can further react to give a wide range of flavor compounds (congeners). If the temperature exceeds 120 °C, caramelization reactions will also occur. Caramelization, unlike MR, is a pyrolytic reaction producing higher concentrations of volatile congeners, such as diacetyl (2,3-butanedione), which has a caramel and butterscotch aroma [37,38,39]. The barley can now be referred to as ‘malt’ due to the presence of sugars, subsequently undergoing a milling process in preparation for the next stage [28,40].
After the malt is ground, it is mixed with warm water and referred to as mash. The water source is claimed to be of great importance and is allegedly a link to the authenticity of the region of production. The mashing-in water requires minerals and trace metals for optimum fermentation conditions, above all calcium ions for α-amylase activity [11,41]. The soluble sugars are enzymatically hydrolyzed by constant agitation in large vessels (mash tuns) for several hours in controlled conditions, with the remaining malt drained off and the process repeated up to three times, raising the internal temperature each time to remove as much sugar as possible [42]. The liquids from the first two collections are used, and the third is recycled into a new batch after the malt solids (refuse) are extracted. The combined liquids are known as the ‘wort’ and are given time to cool before being transferred to the fermentation vessel [7]. Different phenolic and xylenol isomers are generated from the thermal degradation of benzoic acid derivatives in the malt or from peat smoke if used, producing a range of different aromas [29,38,43]. For example, ρ-cresol (4-methy-phenol) has a medicinal/barny attribute, ο-cresol (2-methyl-phenol) has a musty attribute, and m-cresol (3-methyl-phenol) has a woody, ethereal attribute. This also demonstrates the complexity of aroma compound analysis, as isomeric compounds (with the same empirical formula but different structural arrangements) can exhibit very different aromatic properties [29]. Varying the temperature during malting can result in variation in compounds (congeners or substrates for congeners), with some phenolic compounds such as ρ-cresol increasing concurrently with temperature whilst decreasing others such as guaiacol [38]. Other potentially important congeners, such as pyrazines, pyrroles, pyridines, and furans, also develop from MR during this stage [44]. The importance of roasting the malt was demonstrated by Marčiulionytė et al., who generated pyrazines (2-methylpyrazine, 2,3-dimethylpyrazine, 2,5-dimethylpyrazine, and 2-ethylpyrazine) and furans (furfural, 5-methylfurfural, and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural) in the distillate by incorporating 30 g of milled roasted malt at >150 °C along with 70 g of unroasted milled malt prior to mashing [36].
Amino acids come mostly from the malt and are also involved in producing aldehydes during mashing and wort boiling, which are degraded by α-carbonyls formed in the MR, leading to deamination and decarboxylation of the amino acids [45,46]. The amino acid can undergo either Strecker degradation (SD) with an α-dicarbonyl or an Amadori rearrangement (AR) with an α-hydroxycarbonyl, both of which produce Strecker aldehydes. AR-produced Strecker aldehydes will go on to produce melanoidins, brown, high molecular weight polymers, whereas SD-produced Strecker aldehydes [46,47]. Key Strecker aldehydes are 2-methylpropanal (derived from valine), 2-methybutanal (derived from isoleucine), 3-methylbutanal (derived from leucine), methional (derived from methionine), and phenylacetaldehyde (derived from phenylalanine). Benzaldehyde is also considered a Strecker aldehyde but is formed indirectly from phenylalanine [46]. Aldehydes can also originate from lipids in malted barley, as fatty acids undergo oxidation and subsequent decarboxylation to produce primary aldehydes such as octanal, nonanal, decanal, and dodecanal [48]. Aldehydes (both Strecker and fatty acid-derived) are key intermediary compounds, especially in the production of alcohols [1,11,22,23]. Alcohols with six carbons (>C6) and above can be produced from aldehydes by reduction in a sequence of enzymatic reactions known as the lipoxygenase pathway [49,50]. Some lactones, such as γ-nonalactone, may also be generated at this stage, as they are derived from hydroxy fatty acids in the malt, which are accelerated by thermal activity, imparting coconut-like flavors [51]. The lipoxygenase pathway can result in α- and β-ionones with violet-like odors, though they can also be formed through vitamin A auto-oxidation and β-carotene degradation [52,53]. Sulfur compounds and their precursors can form during the malting process, with S-methyl methionine potentially forming as early as the germination phase, the latter being subsequently converted to dimethyl sulfide (DMS) during kilning [11]. Higher kilning temperatures increase DMS production, with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) potentially forming from the oxidation of DMS.
4.2. Fermentation
Yeast fermentation is arguably the most important stage in whiskey production as it produces ethanol. However, the importance of fermentation with regard to the flavor of whiskey cannot be underestimated, as it is responsible for the production of a large number of metabolites, some of which end up as congeners or as substrates for congener formation [11,54]. Different yeast strains and various mixes, fermenter design, aeration, duration, wort composition, and the presence of contaminating bacteria are all factors that can affect the congener profile [29,39]. Once the wort has sufficiently cooled down, the yeast is added and fermented between 20 and 32 °C until the soluble sugars are metabolized into alcohol up to 5–10% volume [7,11,55].
4.2.1. Yeast and Key Congener Pathways
The difference in congener profiles between different species and within individual yeast strains is dependent on the metabolism of amino acids and proteins, sugars, and the autolysis (self-digestion) of the yeast [56]. Studies investigating the effect of different yeast strains on new-make spirits demonstrated variation in congener profiles, especially in relation to ester profiles [1,54,57,58]. Special strains of distilling yeast have been developed that can tolerate high alcohol contents [59]. Unlike distillers yeast, brewing and wine yeasts (all Saccharomyces cerevisiae) are selected to impart flavor rather than survive high alcohol content or fast conversion of alcohol [60]. Waymark and Hill reported that brewing yeast imparts more cereal and feinty characteristics to new-make spirits, whereas wine yeast imparts much lighter floral attributes [1]. However, it is not unusual for mixtures of yeast to be used in whiskey production. New-make spirits produced with mixed yeasts are thought to have more varied concentrations of congeners; in addition, differences between dried and fresh brewer’s yeast have resulted in differences in the generation of sulfur compounds [61,62].
Fermentation conditions affect the metabolism of the yeast, as do the secondary metabolite ratios and therefore the congeners they produce [54]. Thus, fermentation can be modified to either increase or decrease certain congeners [39,63,64,65]. Despite the fact that yeast fermentations are undertaken in anaerobic conditions to produce ethanol, oxygen has a pivotal role during fermentation, enabling yeast cells to produce fatty acids and sterols essential for cell membrane development [66]. Therefore, fatty acid and sterol growth is limited unless the wort is supplied with oxygen directly [11]. Ester and >C2 alcohol production relies heavily on the aerobic growth conditions of the yeast, described as the Crabtree effect [67]. Yeast can produce alcohol under aerobic conditions at high external sugar concentrations. Increased growth of yeast at higher temperatures and high oxygen levels generally results in increased alcohols and decreased esters, with the reverse effect of reduced yeast growth [68]. This is due to the yeast using up more internal fatty acids in response to increased cell function and growth, which in turn also creates additional demand for acetyl CoA for that purpose and reduces its availability for ester synthesis [69]. No two yeast strains have identical responses to these fermentation conditions, and therefore varying yeast cultures could potentially affect the flavor of the wash and ultimately the spirit [7]. Fatty acids of medium chain length such as hexanoic (C6), octanoic (C8), decanoic (C10), and dodecanoic (C12) are normally present in the wort in low concentrations and accumulate during fermentation depending on the conditions, contributing fatty, waxy, and sour characteristics if present in high enough concentrations. These medium-chain fatty acids are primarily linked to yeast activity and are thought to be excreted by the yeast into the wort. However, some may also be the result of the degradation of longer-chain acids such as palmitic and myristic acids [70].
Esters are largely formed during the active growth or exponential phase of the yeast (primary fermentation) by enzymatic condensation/esterification of short, medium, and long fatty acids with alcohols, as a water molecule is eliminated as a result of the acid and the alcohol reacting. Esters are the major congener constituents and key contributors to the flavor and aroma of whiskey and can be divided into two categories: acetate esters (ethyl acetates) and medium-chain ethyl esters [71,72,73]. The yeast forms these aroma active esters intracellularly, and as they are lipid-soluble and have a low molecular weight, they can diffuse through the plasma membrane into the fermentation medium. Diffusion of the acetate esters is rapid due to their small size, whereas diffusion of medium-chain ethyl esters is slower and dependent upon the number of carbon atoms [72]. Thus, for example, more ethyl hexanoate (C6) can cross the membrane than ethyl decanoate (C10), which is also a reason why longer-chain fatty acid ethyl esters do not proliferate in whiskey. Acetate esters are formed via ethanol or from other alcohols reacting with acetic acid, with ethyl acetate being the most abundant due to the higher concentration of ethanol [11,54]. Other ester acetates have also been shown to have a notable influence on the overall flavor profile of whiskey, such as 2-phenylethyl acetate (floral, rose) and 3-methylbutyl acetate (also known as isoamyl acetate) (banana/pear drop) [38,39,74,75]. Quantitatively, ethyl esters, mainly ethyl hexanoate, ethyl octanoate, ethyl decanoate, and ethyl dodecanoate, largely dominate the volatile composition of whiskey. Overall, these esters are some of the most prominent congeners in whiskey and demonstrate the importance of fermentation in relation to the flavor of whiskey [71,72,73,74,76,77,78]. However, high concentrations of medium-chain fatty acids and their ethyl esters can inhibit yeast growth, thus adversely impacting the fermentation process [79]. Optimal temperature and pH are prerequisites to successful esterification, hence why temperature monitoring during fermentation is essential [39,55]. Other esters and alcohols can also be produced during yeast fermentation by alcoholysis, a transesterification reaction between an ester and an alcohol [80].
Higher alcohols (fusel alcohols) are alcohols that have more than two carbons. Their higher molecular weights and strong intermolecular forces from hydrogen bonding (presence of –OH group) give alcohols higher boiling points than most other congeners, save carboxylic acids, which can be produced via the Ehrlich pathway (Figure 3) either via a catabolic process from amino acids or via an anabolic synthetic pathway from sugars. The choice of pathway depends on the individual’s higher alcohol level and the concentration and availability of amino acids [37,78,81]. Essentially, yeast strains absorb the amino acids and small peptides in the wort in a distinct order, from which they take the amino group (NH2) [82,83]. Key amino acids that are assimilated are valine, leucine, isoleucine, methionine, and phenylalanine [84,85]. The α-keto acids that remain enter an irreversible biochemical chain reaction to form higher alcohols [39,86]. Branched-chain (leucine, valine, isoleucine), aromatic (phenylalanine, tyrosine, tryptophan), and sulfur-containing (cysteine, methionine) amino acids are metabolized to form, for example, 1-propanol (solvent-like, fruity, sweet) from threonine, 2-methylpropanol (winey, solvent-like, bitter) from valine, 2-methylbutanol (ethereal, fatty, alcoholic) from isoleucine, 2-phenylehtanol (floral, rose, honey) from phenylalanine, and 3-methylbutanol (musty, alcoholic, cider) from leucine [55,81,87,88].
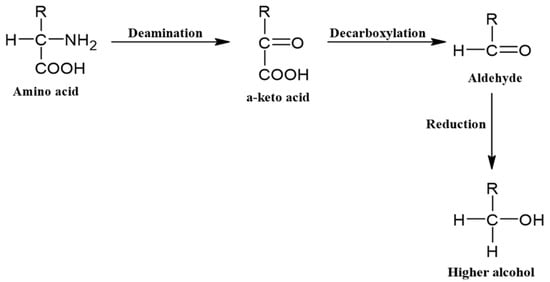
Figure 3.
The Ehrlich pathway in the production of higher alcohols.
As shown in Figure 4, each higher alcohol has a differing amino acid precursor and follows the Ehrlich pathway in that the keto acid undergoes irreversible decarboxylation to an aldehyde (fusel aldehyde), which is then reduced to an alcohol, with the prefix ‘fusel’ indicating the aldehyde is produced from the Ehrlich pathway [84]. Fusel aldehydes can also be oxidized to fusel acids, but the balance between oxidation and reduction of fusel aldehydes ultimately depends on the culture conditions, with aerobic glucose-depleted cultures with various amino acids as the sole nitrogen source preferring fusel acid production [84]. The pathways can also all derive from pyruvate, the conjugate base of α-keto acid (pyruvic acid) from glycolysis, which is an intermediate for many biochemical processes [89]. Catalysis via specific enzymes also produces the keto carboxylate ester from the acid, though this pathway is less common as it depends on the enzymes (pyruvate decarboxylases) and the amino acids present, with tryptophan, threonine, and phenylalanine precursors for pyruvate [39,46]. The only difference is that the 2-methylbutanol pathway involves a β-keto acid, an isomer of the same ketoacids as the other pathways [86]. The availability of nitrogen plays a key role in the direction that the Ehrlich pathway takes. Keto acids will favorably convert back into their respective amino acids in the presence of high initial concentrations of nitrogen, reducing the concentration of higher alcohols produced by the yeast. However, when nitrogen is limited, the concentration of higher alcohols increases [84,90]. Furthermore, high nitrogen concentrations will produce higher concentrations of H2S and acetate esters, both of which have unpleasant odors, and this can happen if the fermentation process processes too slowly [91,92].
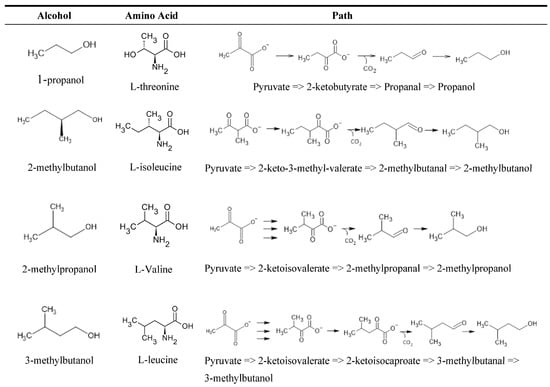
Figure 4.
Higher alcohols and their typical pathways via pyruvate.
4.2.2. Key Congeners in Fermentation
Some ketones in spirits and beer are classified as vicinal diketones (VDKs) and are key flavor congeners, which are also produced during amino acid metabolism [46]. Diacetyl (2,3-butanedione) and acetylpropionyl (2,3-pentanedione) are key examples of VDKs that can be produced at this stage and are associated with a pleasant, strong aroma of butterscotch [38,39]. Diacetyl and acetylpropionyl are derived from the oxidative decarboxylation of excess α-acetohydroxy acids that are excreted into the wort and are intermediates of the biosynthetic pathways of isoleucine, valine, and leucine in yeast [46]. Diacetyl is produced from α-acetolactic acid, involved in the synthesis of valine or leucine, with acetylpropionyl formed from α-acetohydroxybutryic acid, involved in the synthesis of isoleucine. Diacetyl can also be decarboxylated to acetoin (3-hydroxybutanone) and subsequently to 2,3,-butanediol; similarly, acetylpropionyl can be reduced to 2,3-pentanediol [11,83,93,94]. Diacetyl is often only produced at low concentrations but has a low flavor threshold, notably as low as 0.1 ppm in Scotch grain whisky [38,95]. Due to the yeast requiring oxygen for growth at the start of fermentation, higher alcohols can be partially oxidized to aldehydes and subsequently short-chain carboxylic acids. Fatty acids that come from the barley (namely linolenic, linoleic, oleic, and palmitic acids) can also produce aldehydes through lipid oxidation involving malt lipoxygenases produced from the malting step [75,96].
Oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes is often in equilibrium, demonstrating that high levels of aldehydes can also be representative of fluctuations and specificities of whiskey production. As intermediate compounds, aldehydes can also be indicative of incomplete fermentation, as high concentrations are common in low ABV spirits, as indicated by Daute et al. when investigating Scotch whisky ranging from 29.3–34.0% ABV [38]. The aroma of odor-active aldehydes varies greatly; for example, hexanal has a green, grassy note; trans-2-nonenal has a cardboard-like aroma; and trans-2-octenal has a metallic, mushroom-sawdust-like aroma [7,11,97]. A key, highly reactive aldehyde, not derived from oxidation, in generating various flavor compounds is acetaldehyde. Acetaldehyde is produced via either decarboxylation of pyruvate by the yeast as an intermediate for ethanol production or dehydrogenation of ethanol [98]. Levels are monitored regularly, as it is associated with sour-apple flavors at high concentrations [99]. Acetaldehyde is very reactive and can be involved in various reversible reactions with other compounds, such as thiols and alcohols [100]. Acetaldehyde reacts with ethanol to give diethyl acetal (1,1-diethoxyethane/acetaldehyde diethyl acetal), a compound with a low aroma threshold denoted as ethereal, sweet, and nutty [40]. Other aldehydes can react with higher alcohols to give various acetals that can have fruity aromas [75]. Acetals can either be formed reversibly via an unstable hemiacetal that subsequently reacts with another alcohol to form the acetal or irreversibly in an acidic medium [86]. Acetal formation in neutral or less acidic mediums is reversible; therefore, if the alcohol content is between 40 and 50% ABV (as is the case for most whiskies), only 15–20% of the total amount of acetaldehyde combines with ethanol [80]. Thus, the concentration of free aldehyde content in higher ABV spirits will not be reduced by acetal formation, even after prolonged maturation, and therefore, greater concentrations of acetals are often related to a distillate of higher acidity [71].
Sulfur compounds can also develop during fermentation, with two key reactions being the biosynthesis of cysteine and methionine and the reduction of sulfate salts from the wort [61]. DMSO, formed from the oxidation of DMS during kilning, is converted back to DMS by the yeast during fermentation. Much of the resulting H2S is stripped off by the evolution of CO2 during the process; however, sufficient amounts of H2S and sulfur compounds in the wash can adversely affect the quality of the distilled spirit [7]. H2S can be converted to ethanethiol by the yeast, which in turn reacts with the remaining H2S to produce methanethiol, the precursor for sulfuric compounds such as DMS, dimethyl disulfide (DMDS), and dimethyl trisulfide (DMTS) [75,101]. Sulfur compounds can have a positive contribution at low levels but begin to have a negative contribution as their concentration increases [44,61]. For example, so-called grapefruit mercaptans/thiols have a grapefruit juice character at <10 ppm but are sulfurous and rubbery at >10 ppm [12].
4.3. Distillation
At the end of fermentation, most congeners are at their most dilute in the wash, and distillation effectively concentrates the majority of congeners while eliminating others [102]. In addition to extracting volatiles from the wash, the distillation process involves a reaction stage during which congeners are formed from precursors or interact with other compounds, most of which are impacted by thermal energy, reflux, and the metal composition of the still [44]. Along with other key considerations of still design, the choice of metal can impact the overall flavor of the new spirit while also aiding in the overall efficiency of the process [11,12,29]. Copper is widely used due to its malleability, ease of cleaning, and ability to conduct heat (it disperses the heat evenly across its surface, creating a more even distillation), but it can also remove many undesirable sulfuric malodors that develop during fermentation, such as mercaptans (cabbage odors) and disulfides (burnt plastic and rotten vegetable odors) [61,101]. The sulfur binds itself to the copper, producing H2S, which in turn makes copper sulfate, which sticks to the inside of the still and is removed after distillation during cleaning to avoid contaminating the next batch [44]. Copper is also a requisite for the production of pot stills and malted whiskey in Ireland [10].
4.3.1. Pot Distillation
The distillation process consists of heating the liquid mixture (the wash) to separate it into fractions based on their volatility, aiming to increase the ethanol content and certain congeners while eliminating others, such as dissolved solids and water. Traditionally, the distillation process has two stages that take place in separate stills: the wash still and the spirit still. The wash still is bigger, and its purpose is to heat the wash. It works on the premise that alcohol has a lower boiling point (+/− 75 °C) than water, so the ethanol and other volatile substances evaporate, rise up the neck of the still, and subsequently condense [103]. Wash distillation is stopped when the distillate strength is approximately 1% (v/v) ethanol, collected as ‘low wines’, and passed into the spirit still. The first distillate recovered at the start of the distillation is known as the ‘foreshots’. Foreshots are pungent and contain a large % volume of ethanol, as well as acetone, methanol, ethyl acetate, and acetaldehyde. A demisting test can be performed to assess when foreshot recovery can cease, although most distillers make their decisions based on time [11]. Distillate collected after the foreshots is called the ‘spirit’ (or heart), and only this is selected for maturation. The last of the distillate is called the ‘feints’, and like the foreshots, it is pungent but has a much less intense aroma. The cut point from spirit to feint collection is determined by time or ethanol concentration [7,11]. Both the foreshots and feints are then recycled into the following batch of low wines, and the process is repeated. This gives the final product a more intense taste, as it allows additional congeners to come through and ensures waste is minimized [12]. Most whiskey is double distilled, i.e., the wash still is followed by the spirit still; however, some whiskey is triple distilled, which is more common in Irish whiskey. Triple distilled is either passed three times using one pot still, once in the wash still and twice in the spirit still, or three stills in series. In theory, additional distillations equate to the removal of more volatile components (congeners) while increasing the concentration of ethanol. Regardless of how many stills the spirit goes through, it is critical that the distiller switches between the fractions and collects the distillates at the right time. Collect too early or too late, and important volatiles may be lost, or highly volatile or sulfurous compounds may be carried over and adversely impact the flavor of the final spirit [101]. In pot still distillation, the alcoholic vapor will rise unimpeded through the open neck, pass through the lyne arm, enter the condenser, and return to a liquid state. Thus, this liquid tends to have a higher concentration of congeners in the distillate (Figure 5) than column stills.
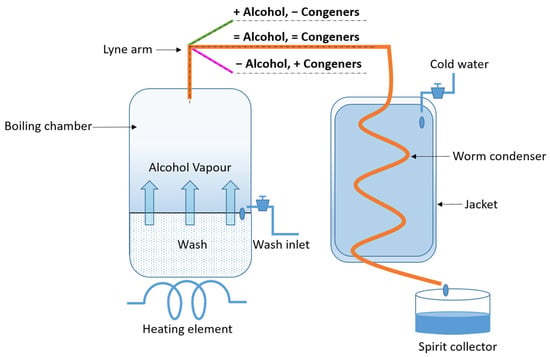
Figure 5.
Simple pot still distillation.
For batch distillation using pot stills, design parameters such as the still height, the angle and length of the lyne arm, and the type of condenser all impact the type and concentration of congeners in the final raw spirit. The angle of the lyne arm can affect the overall flavor; an upwardly sloping arm undergoes the most reflux, resulting in a lighter spirit (less congeners and higher purity of ethanol) [102]. A downwardly sloping arm will produce a heavier spirit, lower in ethanol but with more congeners [7,11,12]. Wash carryover will also be more pronounced with a downwardly sloping arm, sometimes indicated by a higher abundance of furans and pyrazines [33].
4.3.2. Continuous Distillation
Different factors come into play in either batch or continuous distillation. Continuous distillation is more associated with the process and the efficiency of the still (Figure 6). A column still has a range of plates that divide it into segments [102]. Each plate is perforated, which allows the spirit to pass through and condense into liquid in the subsequent segment, where it again vaporizes and continues through the next plates as it rises up the still. The spirit increases in ABV, with the greatest purity at the top of the still and the spent mash at the bottom. The height of the still and number of plates influence the amount of reflux, i.e., the more plates, the greater the degree of condensation and, therefore, the greater the strength of spirit with the least congeners [7,11]. In a column still, the same amount of ethanol evaporates as the amount of water that condenses; therefore, the vapor constantly increases in ethanol content and the liquid constantly loses ethanol. Ethanol concentration therefore varies from ~10% at the rectifier base to ~94% at the top of the still, and once operational balance is achieved in continuous mode, the operation will ideally be sustained for days or weeks as shutting down and restarting expends energy and efficiency [7,12]. The width and height of the still will determine the purity of the spirit and the speed at which it produces distillate [103].
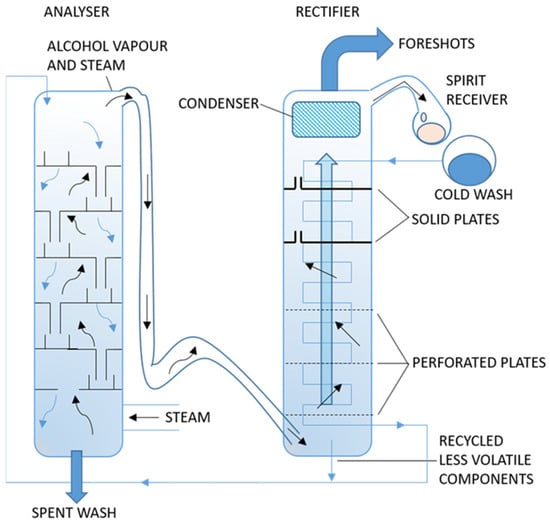
Figure 6.
Continuous distillation.
4.3.3. Congeners by Volatility
Congeners generated at this stage are generally split into three types based on their volatility in comparison to ethanol: more volatile, less volatile, or having a similar volatility to ethanol. Volatility is related to the boiling point; however, in distillation, it is also affected by ethanol concentration, polarity, and vapor pressure [7]. The volatility of many congeners is impacted by the changing ethanol concentration during distillation, especially those of equal volatility to ethanol. For example, in batch distillation, as alcoholic strength decreases throughout the run, some congeners increase in volatility over time due to changes in the polarity of the liquid [7,11,103]. The foreshots contain the most volatile congeners, including acetaldehyde, acetone, ethyl acetate, 2-methylpropanol, 3-methylbutanol, 2-methylbutanol, 1-propanol, methanol, and some ketones [12,103]. Common branched-chain aldehydes found in foreshots are 2-methylpropanal, 2-methylbutanal, and 3-methylbutanal, giving dried fruit notes as well as malty and worty notes [7,40]. Many ketones are present in the foreshots, but they tend to have high odor thresholds and are not thought to contribute significantly to aroma [80]. However, many of these ketones are key intermediates and reactive species. For example, β-damascenone, an unsaturated, cyclic ketone, is known to interact synergistically with other compounds to enhance fruity aromas and minimize negative vegetal notes, highlighting its significance in new whiskey [75]. Many aldehydes and ketones are also found in the middle and tail fractions as they increase in molecular size (and so do their boiling points), resulting in lower volatility [80,104]. Generally, in batch distillation, aldehyde and short-chain ester concentrations are determined by the primary cut from foreshots to spirit due to their high volatility, while the concentration of higher alcohols and acids is determined by the cut from spirits to feints due to their lower volatility, and therefore more are present in the recycled feints [40]. Spirit cut-off points are key to determining what esters are present and their concentration in the final spirit due to their varied volatility and carbon chain length [29]. For example, cutting early from foreshots to spirit at a high distillate strength of 75–85% ABV will lead to a spirit with a greater concentration of higher alcohols, short/medium-chain fatty acid esters, and ethyl acetate. This will result in a new spirit with predominately oily, fruity aromas, the latter giving the spirit a ‘pear drop’ aroma [7,40]. Spirit cuts and their exact timing can vary depending on the distillery/distiller, whiskey type/style, and even on a batch basis. Spirit cuts at <60% ABV later on during the distillation are thought to enhance phenol and guaiacol congener concentrations as they have lower volatility [11]. The spirit cut (middle fraction) is dominated by short to medium carbon chain (C5–C14) fatty acid ethyl esters, such as ethyl hexanoate, ethyl octanoate, ethyl decanoate, ethyl dodecanoate, and ethyl lactate [73,105]. Goss et al. identified that the predominant fatty acid ethyl esters in Scotch whiskies were medium chain (C8–C14), with esters of >C14 in trace amounts as their solubility decreases with increasing carbon chain length, but also due to the fact that mainly short/medium chain ethyl esters are generated during fermentation [106]. Shorter-chain esters of 8 carbons and less are generally associated with unique fruity aromas, such as ethyl hexanoate, which imparts apple-like, waxy, pineapple characteristics, and ethyl octanoate, which imparts apricot, winey, sour apple-like aromas [1,39]. As ester carbon chain length increases, these are more associated with soapy, oily, and waxy notes, more characteristic of ethyl dodecanoate (C12) [7,107]. The feints (tail fraction) contain congeners with less volatility than ethanol, such as phenols and nitrogen-containing compounds. Throughout the process, higher alcohols are exposed to prolonged heat after being recycled in the stills in a series of distillations and become fully oxidized, producing carboxylic acids that often dominate the feints, such as hexanoic, octanoic, decanoic, and dodecanoic acids, yielding sharp, sweaty, fatty, cheese-like notes [103]. After the volatiles have evaporated, water, proteins, carbohydrates, and higher alcohols remain in the ‘spent wash’. The predetermined second spirit cut is designed to ensure that less volatile compounds do not contaminate the final product, as these are often characterized by stale and metallic tastes but are also dependent on the desired congeners and their concentration [103]. An earlier cut has weaker, recycled feints and a less intense flavor, while a later cut will have stronger, recycled feints, the latter important for smoked whiskies to ensure phenols are incorporated in the spirit [7].
4.4. Cask Maturation
The spirit obtained from the distillation process is considered new-make spirit, which is colorless and neutral; however, it contains many congeners that have either been transferred from the malt and/or created or concentrated during fermentation or distillation, as previously discussed [5,108,109]. Maturation involves the transition of the new spirit into a more mature, mellow, and smoother product, usually achieved by diluting the spirit first in water and then transferring it to wooden casks for a minimum period of three years but often much longer [38]. The maturation stage adds to the complexity of the sensory characteristics of the whiskey. Studies of comparisons between new-made spirits and matured spirits, as well as the identification of compounds derived from wood, have demonstrated an increase in congeners that influence the final sensory character of the whiskey created during cask maturation [110,111]. Three types of reactions happen in the cask: additive, interactive, or subtractive [112]. Additive reactions introduce new compounds to the spirit or elevate their concentrations, such as when extracting compounds from the wood. Interactive is when oxygen diffuses into the casks, resulting in reactions between the molecules in the spirit and between these molecules in the spirit and molecules from wood [12]. Subtractive reactions correspond to where compounds are lost through evaporation, desorption, and oxidation—including pungent compounds that survive the distillation process, such as DMS and acrolein [11,112,113,114].
4.4.1. Wood Components
Wood is made of various polymers, the four key components being cellulose, hemicellulose, lignins, and tannins [11,108]. The latter three components have the most impact on flavor, being fully soluble in water and less soluble in pure alcohol [108]. Cellulose constitutes between 40 and 50% of wood but acts more as a transporter for extractives from the wood to the spirit [7]. Hemicellulose is more thermally labile than cellulose, consisting of several simple pentose and hexose (C5 and C6) sugars such as glucose, xylose, and arabinose. Hemicelluloses are prone to dehydration reactions, producing furaldehydes, especially furfural but also 5-methylfurfural and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, which contribute to roasted, fudge, and caramel profiles [7,11,75,115].
Tannins, or their active hydrolysable classification, ellagitannins, are key non-volatile compounds in the maturation process. These are a class of polyphenolic biomolecules that affect the whiskey by adding bitterness, astringency, and some herbaceous notes, as well as affecting color [116,117]. It is considered that compounds that intensify color have larger molecular weights and are highly conjugated, thus being more susceptible to oxidation and therefore altering color [118]. Both ellagitannins and lignins also help remove unwanted sulfur notes [57,109], most recently proven by Fracassetti et al., who concluded that tannins limited the production of volatile sulfur compounds in model wine samples [119]. Picariello et al. suggested this is due to tannins increasing oxygen consumption and therefore inhibiting sulfur compounds, minimizing sulfur dioxide production [120]. As ellagitannins are more soluble, they are readily hydrolyzed to ellagic acid, a key polyphenolic compound that increases in concentration with maturation and is thought to be an important congener that contributes to the final flavor of the whiskey [8,11,108,121]. Ellagic acid has also been proven to act as a scavenger, preventing reactive oxygen radical species from adversely affecting the whiskey by producing unwanted reaction products [122]. Comparatively, lignins are insoluble cell wall polymers and require covalent bond cleavage prior to hydrolysis, as confirmed by Conner et al., who found that the majority of linkages (ether) present in lignins compared across four different cask types (new, first fill, second fill, and exhausted) are resistant to acidolysis and hydrolysis, unlike ellagitannins [123]. The lignin degradation process is relatively slow and proceeds during maturation; thus, younger spirits tend to have high proportions of ellagitannins, whereas lignin oligomers predominate in more mature products [108]. The compounds extracted from the wood, such as aromatic aldehydes, phenols, lactones, and terpenes, generally have low to mid-range aroma thresholds and are therefore responsible for important olfactory notes. These volatiles are affected by natural factors, such as wood species and extent of seasoning, and cooperage techniques (different degrees of cask heating, etc.) [115].
4.4.2. Oak Casks
Oak casks are commonly used as they are an optimal material due to their durability and because they are impervious to liquid yet allow interaction with oxygen [124]. A lot of single-use USA oak casks are used in whiskey maturation in Ireland and Scotland, as USA laws stipulate that bourbon must be aged initially in virgin USA oak, leaving USA distilleries with a surplus of single-filled barrels [11]. These casks are ~200 L in volume and thus have a smaller surface area than traditional oak casks used for European whiskey production at ~650 L. The use of smaller-volume casks results in faster maturation rates due to increased surface area per volume of interaction between the spirit and the wood [11,12]. European oak is also widely used, but more in the form of used sherry, port, or wine casks than as virgin oak. These casks tend to be ~500 L in size and are well suited for secondary maturation because they have a lower surface area per volume than a bourbon cask and thus tend to impart a more subtle flavor characteristic, though this is time-dependent [125]. The use of seasoned casks may not have the intensity of virgin oak, but the cask is still rich in congeners containing wood extracts and ellagitannins, which are oxidized to phenolic compounds during the maturation process, helping to deliver a more subtle yet complex and balanced character to the spirit [10,11]. A potentially key source of flavor diversity for Irish whiskey is the fact that Irish whiskey can use different wood types beyond oak for maturation, whereas Scotch can only be matured and finished in variations of oak [10,18]. This has resulted in various experiments with other woods, such as cherry wood, acacia, and chestnut, among others. Tarko et al. recently highlighted the potential for various compounds in differing wood types, with high levels of eugenol and isoeugenol in chestnut wood and further variances in cherry wood and acacia [126].
4.4.3. Cask Toasting and Congeners
In some cases, casks are heated, toasted, or charred (Figure 7).
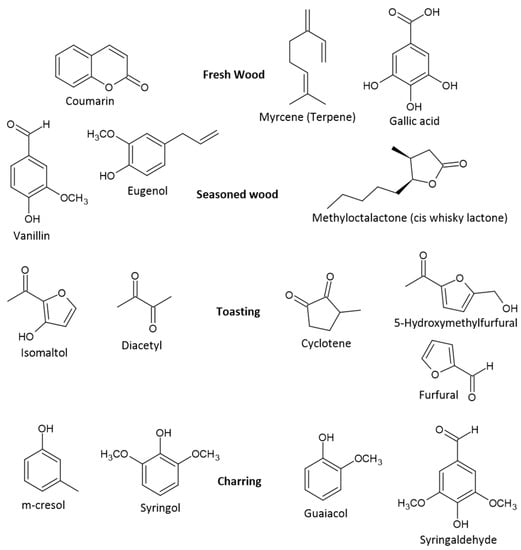
Figure 7.
Compounds common with different degrees of wood toasting.
Cask heating breaks down wood polymers to: (i) enhance the extraction of flavor compounds; (ii) degrade undesirable wood-derived flavor components; or (iii) create a layer of active carbon from intense charring, a more vigorous burning of the wood to a point where the surface breaks and the interior of the cask blackens [11,115,126]. Cask heating imparts sweeter and smokier flavors by promoting more vanillin and phenol generation from lignin and tannin degradation [112,115]. The active carbon also acts as a catalyst for the removal of some unwanted compounds (especially sulfur compounds) and enhances the continuation of lignin and hemicellulose degradation [7,11,112,127]. The compounds produced are both time- and temperature-dependent. Light toasting is performed at approximately 120 °C for up to 90 min, medium toasting between 120 and 230 °C, and high toasting >230 °C for more than 15 min [126]. Lignin degradation is initiated via stronger and more prolonged toasting, creating higher concentrations of key volatiles such as phenols, phenyl ketones, and aldehydes such as syringaldehyde, coniferaldehyde, and vanillin (Figure 8) [11,38]. Ethanol reacts with lignins, some of which break down to yield coniferyl and sinapic alcohols, which in turn are oxidized to cinnamaldehydes (coniferaldehyde and sinapaldehyde) [7,128]. These cinnamaldehydes possess a double bond in the side chain and are further oxidized to benzaldehydes (vanillin and syringaldehyde) [115,128]. These aromatic aldehydes are thought to be markers of a better-quality spirit; their concentration is dependent on the type of cask and degree of charring, as these affect compound extraction and alcoholysis of the lignin [126]. Excessive cask heating can result in increased concentrations of phenols, such as guaiacol and syringol, which have more smoky, medicinal, and spiced characteristics that can overpower and dominate the flavor of whiskey [11]. Correspondingly, heat treatment of oak aids lactone extraction, which derives from the thermal degradation of lipids in the wood. Light to medium toasting is often used to extract lactones as they are commonly found in the heartwood of the oak, and light toasting only affects the top 2 mm layer due to the poor thermal conductivity of wood [126]. Two key lactone isomers of interest are known as oak or whiskey lactones: cis and trans β-methyl-γ-octalactone [115]. These whiskey lactones have characteristic coconut, spice, and nutty aromas depending on the specific isomer and are important, especially in older whiskies, as the extraction process takes time in the cask [38,110,129]. Conner et al. compared charred with uncharred oak in the maturation of Scotch malt whisky and found that charring generated both whiskey lactone isomers (β-methyl-γ-octalactone) [129].
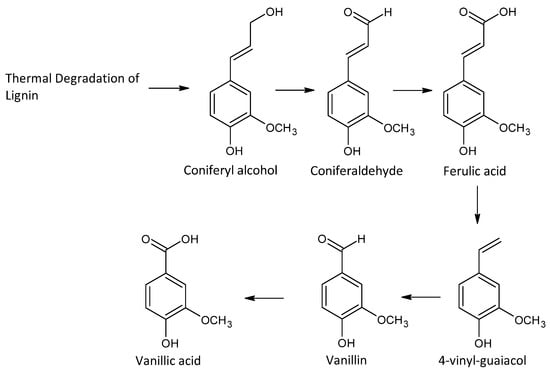
Figure 8.
Production of vanillin through lignin degradation.
However, it is commonly concluded that at the beginning of toasting, the quantity of γ-lactones increases, but if the toasting is prolonged or excessive, total destruction of these lactones can occur [115,130]. Prida et al. deduced from a study that the main factor influencing whiskey lactone oak extractive levels and their concentrations is the oak species used in the cask [109]. The investigation demonstrated differences in whiskey lactones within the same oak species as well as in comparison to other oak species, either being richer in the cis or trans isomer, not both. This suggests that the formation of each isomer is made at the expense of the other, implying their synthesis is not independent [109]. The cis-oak lactone has an aroma threshold much lower than that of its trans counterpart [11]. Furthermore, differing ratios of these whiskey lactones have been demonstrated to alter flavor. A greater abundance of the cis-to-trans-whiskey lactone (8:1) is common in American oak, as is having ellagic acid and gallic acid, compared with European oak. It is therefore suggested that spirits maturing in American oak can have creamier, more coconut-like aromas [115,130,131]. Other lactones, such as γ-lactones (sweet, hay-like, coumaric, coconut), and specifically γ- and δ-nonalactones (coconut, creamy, waxy), and γ-decalactones (peach, coconut, buttery), are also thought to positively impact whiskey flavor [11,38,74,130].
4.4.4. Terpenes
Terpenes, or ‘terpenoids’, mostly monoterpenes in terms of whiskey, are also key to the overall aroma profile. Terpenes in whiskey originate from three potential sources: (i) raw materials in both free and bound states (cereal sources); (ii) microbial pathways (yeast and some bacteria during fermentation); and (iii) various oxidation and degradation of wood polymers during maturation [7,71,126]. Geraniol (floral), camphor (antiseptic), limonene (citrus), myrcene (lemongrass), linalool (floral), citronellol (citrus lemon), and carophyllene (sweet, cloves, woody) are typical examples of terpenes contributing sensory characteristics during maturation. Enantiomers, chiral molecules that are mirror images of themselves, of congeners such as linalool and citranellol are often present in whiskey but produce very different aromas and have different aroma thresholds. One enantiomer of linalool (sweet orange, floral aroma) is perceived at 7.4 ppb, and the other (woody, lavender-like aroma) is perceived at 0.8 ppb [132]. The alcohol content at the start of the maturation process, or collection strength, varies between types of whiskey and the preference of the distillery; malts are typically 68–71% ABV and >94% ABV for grain [11]. Traditionally, spirits are diluted to 63.5% ABV as spirit concentration effects how the liquid interacts with the wood, and this alcohol strength has been previously found to be optimal for Scottish and Irish climates, giving a more consistent, balanced flavor over time [25]. However, some distillers mature at collection strength, perhaps to extract more lipophilic/hydrophobic compounds (lactones and vanillin) or perhaps because filling at higher ethanol concentrations delays the inevitable decrease of both the strength of the maturing spirit and the volume in the cask [11,133,134]. As discussed, alcohol strength at cask filling is important as it can impact congener solubility due to differences in the polarity of congeners. Therefore, different compounds in the wood are extracted at different rates depending on the alcohol content of the distillate [108,135]. The reactions that take place in the cask are primarily catalyzed by the acidic environment that develops within the cask via alcohol and aldehyde oxidation, as well as non-volatile dicarboxylic acid extraction from the wood with water [116]. The typical pH of matured whiskey is often 4–4.5, as maturation time is directly correlated with increased acidity. However, acids are not commonly found in mature whiskey, as they react with alcohols to form esters (mainly ethanol-forming ethyl esters) and also undergo oxidation to form aldehydes. Thus, esters and some specific aldehydes increase with cask maturation [11,136]. As previously mentioned, acetic acid is primarily produced during fermentation but can also be extracted from the cask. Linolenic acid can also be present from the cereal source earlier in the process, but it is also extracted from the cask. Linolenic acid is insoluble in water and very sensitive to oxidation to low-molecular-weight primary aldehydes [11,38,137]. Fruity and floral aromatic esters can also originate from the hydrolysis of hemicellulose acetyl groups and wood charring [109]. Esterification reactions produce acetate and diethyl esters, such as diethyl succinate. Diethyl succinate is of interest as, despite its high molecular mass and high boiling point, its high polarity and reactivity enable it to impart a similar aroma detection threshold to smaller, more volatile esters. Previous studies have highlighted that it increases in concentration with maturation in both spirits and wines and thus may be a biomarker for age. It has the floral, fruity characteristics of cooked apples and the tropical plant ylang [138,139,140]. Ethyl acetate at higher concentrations gives a more solvent-like and vinegar-like note, while at lower concentrations it can impart pear-like, soft fruit aromas [7,40,141]. In warmer climates, both the wood and the liquid expand, resulting in increased interaction and accelerating cask maturation, but at the cost of greater evaporation. In colder climates, the wood contracts and cask maturation is prolonged, but losses to evaporation are less [142]. If the liquid’s alcohol temperature decreases to ≤7 °C, long-chain esters begin to separate from the alcohols and form a sediment, or ‘haze’, as they become insoluble. Chill filtering is widely practiced to remove wood particles or any other insoluble material prior to bottling. However, it is argued that chill filtration can alter the flavor [10,11,38]. Overall, the temperate oceanic climate of Ireland and Scotland is ideally suited to maturation as it is typically not prone to extremes, which, as mentioned, can potentially adversely impact maturation [25].
5. Congeners as Biomarkers of Fraud and Authentication
Identification of congeners not only serves the purpose of brand protection but also allows for a deeper understanding at a molecular level of those most responsible for the flavor of whiskey. As mentioned, congeners are a summation of the process and cereals used; therefore, congener analysis can potentially be used to identify distinctive whiskey traits that may be representative of brands, distilleries, and whiskey types/styles. Congeners can be divided into volatile and non-volatile, with volatile congeners having a much greater impact on the overall sensory character of whiskey due to the fact that we can perceive many times more aromatic volatile compounds than non-volatile tastants and the significant range and abundance (from ng/L to several g/L) of different volatile congeners present [12,74]. Congeners differ in terms of volatility, molecular weight, vapor pressure, and polarity, which consequently influences their ease of extraction and separation [143]. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS) is the most common method used for the analysis of whiskey congeners [6,40,73,74,75,76,97,110,111,143,144,145,146]. It allows for the identification and quantification of a wide range of trace analytes, demonstrating sensitivity and depth that many other techniques lack. The links between volatile congeners and perceived aroma can be difficult to discern as so many factors are involved. Typically, in foods and beverages, only a small portion of volatile compounds contribute to sensory perception, as they need to be present at a concentration above their aroma threshold in order to do so [147]. One useful approach to help identify those key aromaactive congeners contributing to sensory perception is the use of gas chromatography olfactometry (GC-O), where trained human assessors are used as an additional detector [148]. Although not a perfect solution to identify the relationships between volatiles and the complete sensory characteristics of the product, it certainly aids in better defining the impact of most individual aromatic congeners and is also very beneficial in identifying malodors [149].
As well as assessing unique compounds for distinction between styles/types of whiskey, investigating the abundance ratios of some specific congeners has also been used to identify potential fraudulent products [7,11,40]. Blends are generally quite difficult to identify and compare due to the huge variance in grains, malting, distillation, and cask maturation techniques used to create the individual component whiskies of the blend. Therefore, ranges and ratios of specific congeners have been used for authentication rather than identifying exact concentrations, and from this, attempts have been made to verify whether a greater proportion of grain, such as maize, wheat, oats, raw barley, or malted barley, has been used [7,8,11]. Furthermore, ranges or ratios of specific congeners can be used to identify counterfeits; however, for this approach to be successful, representative volatile congener profiles must exist for that whiskey style/type, requiring a significant amount of analysis to be undertaken on a wide range of representative samples [7]. Higher alcohols are often used for discrimination between whiskies of different brands, regions, and styles/types of whiskey, namely 2-methylpropanol, 2-methylbutanol, and 3-methylbutanol, due to their low concentrations in grain whiskies due to the higher distillation efficiency of column stills [3,5,8,15]. Therefore, grain whiskies tend to have higher levels of 1-propanol and 2-methylpropanol, and thus, ratios of 2-methylbutanol and 3-methylbutanol to 2-methylpropanol can aid in differentiation between styles and types [11]. Authenticity approaches that only compare 2-methylbutanol and 3-methylbutanol concentrations as a ratio are not as effective, as ratios can be relatively similar across different whiskies even though the higher alcohol concentrations differ [7]. However, higher levels of 2-methylbutanol and 3-methylbutanol in blends can demonstrate a higher percentage of malt whiskey content in the blend, and this may be representative of some specific brands [8,150].
In terms of analysis, traditionally, Irish whiskey has often been considered to have a less complex matrix of congeners in comparison to Scotch. As Scotland and Ireland have similar terrain and climates, it is often concluded that this must relate to Irish whiskies traditionally undergoing triple distillation rather than double distillation [7,8,23,74,151]. However, as mentioned, Irish whiskey is not always triple distilled, with many new Irish distillers only double distilling in an attempt to promote flavor diversification. Studies comparing Scotch single malts and blends often compare multiple Scotch samples to single Irish samples and are therefore unlikely to fairly represent the differentiation of Irish whiskey. The diversity of Irish whiskey has likely increased in recent years due to the growth of the industry. Higher alcohols, such as 2- and 3-methylbutanol and propanol, have been key indicators in comparison studies and have often been used to discriminate Irish whiskey from other whiskies [8,77]. Phenols have been identified as potentially important congeners in whiskey, but especially so for peated whiskey [1,28]. Recently, White et al. investigated phenolic acids in a range of Irish whiskies, including single pot stills, single malts aged in different casks within one distillery, and multiple whiskies from the same distillery. These authors reported variance in congener profiles and concentrations across the evaluated samples and highlighted the diversity of Irish whiskies across distilleries within Ireland but also within the same distillery based on phenolic acid content [136]. As an example of congeners as good biomarkers for specific spirits, furfural, 1-octanol, 4-vinylguaiacol, γ-nonalactone, and ethyl isovalerate were considered by Wisniewska et al. as significant variables to distinguish bourbon, Scotch, and Irish whiskies [76]. These authors found that furfural was absent only in Irish whiskey, with ethyl isovalerate (ethyl 3-methylbutanoate) absent only in Scotch. The bourbon samples contained 1-octanol, 4-vinylguaiacol, and γ-nonalactone, which were absent in all the other samples. Ferracane et al. also compared blended and single malt Scotch to Irish whiskey, highlighting significant variance in six ethyl esters, an aldehyde, an acetal, and two alcohols [144]. Notably higher concentrations of ethyl 3-methylbutanoate, ethyl 2-methylbutanoate, 2-nonanol, and diethyl acetal were detected in the Irish whiskey compared with the Scotch samples, with higher concentrations of 3-methylbutanol and (E)-2-nonenal detected in the single malt Scotch. Interestingly, ethyl butanoate, ethyl hexanoate, ethyl octanoate, and ethyl dodecanoate dominated the volatile profile of Scotch blended whisky in comparison to the other samples. This may be due to the high proportion of grain whisky in the blend. Esters can potentially act as indicators of cereal sources and therefore region, as total ester content often varies among Scotch whisky, Irish whiskey, and bourbon [7,8,11]. However, these differences also likely reflect different process parameters due to tradition, a specific type or style of whiskey, or a specific type/style of whiskey or region. Bourbon is considered to contain fewer esters than Scotch and Irish whiskies, as solids are not separated before fermentation [61,152]. Furthermore, the typical phenolic contents of Scotch malt whisky tend to be lower than those of bourbon (<20 ppm compared with ≤60 ppm), presumably due to the higher levels of extractives in the new casks used in bourbon [11]. However, o-, m-, and ρ-cresol appear to be higher in Scotch malt whisky in comparison to Canadian whiskey or bourbon, potentially due to differing kilning techniques and the use of peat during malting [151]. Another study found that phenols were lower in Canadian whiskies in comparison studies with other whiskies, and these authors suggested that eugenol is a good biomarker for bourbon as it is consistently higher in concentration compared with other whiskies [153]. However, most, if not all, congener relationships within different whiskey products are not exact due to the myriad of potential factors influencing their presence and concentration. The ability to differentiate whiskies and demonstrate quality and variety on a national as well as global scale is of equal importance in the industry. Stupak et al. assessed the volatile profiles of authentic Scotch that varied in type/style (71 malts, 77 blends) and cask maturation (23 malts that had been matured in more than one type of cask), as well as pre-identified fraudulent whiskies (20 samples), in what can be considered the biggest whiskey sample comparison to date [6]. The authors suggested cis-damascenone, phenylmethanol, 2,4,-ditert-butylphenol, propiovanillone, ethyl vanillate, and vanillin as potential marker compounds to distinguish the samples, with the latter three strongly associated with the cask maturation. As such, age appeared to be the key factor in their ability to discriminate the selected whiskies, with the youngest malt (8 years) more similar to the blended whiskies and the oldest ‘premium’ blend (21 years) most representative of the malted whiskies. Syringaldehyde, ethyl dodecanoate, and 1,3,-diacetyl benzene were either absent or at low concentrations in the fraudulent whiskies, as well as having high concentrations of flavoring agents such as benzaldehyde and ethyl vanillin, likely an attempt to mimic authentic whiskey [6]. However, congeners that are structurally similar or even identical can complicate identification and authentication between samples. 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural is not only present from hemicellulose degradation but also in added caramel (E150a additive caramel) permitted for use in Irish whiskey and Scotch [8]. Furthermore, high concentrations of ethyl vanillate and propiovanillone were suggested to be characteristic of malts and blends consisting of a high proportion of malt whiskey. However, vanillin and phenylmethanol have also been identified as potential better biomarkers for blends, despite having higher average concentrations in malt whiskies [6,8]. Authentic whiskies also contain vanillin derived from the wood; fraudulent samples can also contain vanillin from the addition of commercial flavorings. These will be different in structure, but the concentration from addition will likely be much higher than that derived from wood, and concentration alone may be indicative of fraudulent activity [154]. Therefore, it is important to be able to distinguish these compounds, which differ slightly in structure but act as markers for different whiskey types. Separation of whiskies via maturation congeners relies wholly on time as a factor, whereas studies on new-make spirits have the potential to reveal much more about the early stages in the process, especially cereal source, fermentation, and distillation.
Fermentation and maturation have long been the subject of debate over whether either specific stage of the whiskey process is more important to the final flavor of the bottled product. Congeners associated with the maturation process have been used for authentication purposes, as well as establishing congener variation within different wood species or from different port, sherry, or bourbon-filled casks of the same species, and for differences that arise with maturation time [110,111,155,156]. Contrastingly, rather than focusing on differentiation and identification between whiskies, fermentation studies take a different approach by providing information on the experimental outcomes of varied fermentations that could potentially provide unique whiskey flavor profiles that could be used as biomarkers for authentication. Therefore, studies have investigated the effects of different yeast types, wort pre-treatments, the influence of bacteria on new-made spirits, and producing grain whiskey from wheat [1,27,54,75,86,157].
6. Conclusions
Whiskey is a complex product with many different flavor profiles arising from variations in ingredients, production, and maturation processes. Fermentation and cask maturation are known as key stages for congener development and variation and thus have received the most research to date in terms of flavor development and as indicators for authentication. As the sensitivity and capability of analytical instruments and methods evolve, it is possible to attain much more information in relation to the congeners responsible for differing sensory characteristics and as potential biomarkers for authentication. This trend will continue in tandem with more rapid, non-destructive analytical procedures for assessing both quality and fraud. Despite the global nature of the whiskey business, very little in-depth research has been published in relation to congener profiling in comparison to some other beverages and food products. Many research studies undertaken to date on whiskey authentication only involve a relatively small number of samples, often taken as representative of a particular whiskey style/type and such approaches can fail to take intra- and inter-brand variations into consideration, which are very likely due to the host of factors that influence the final congener profile. Thus, much more detailed research into the flavor profiles of whiskey is required. Currently, Irish whiskey is undergoing a massive expansion that has resulted in a need for both new and existing distilleries to differentiate from competitors in order to provide unique yet authentic product(s) in order to expand existing markets and develop new ones. The Irish whiskey industry in particular faces significant challenges in relation to managing and understanding the impacts of escalating popularity and expansion: (i) greater diversity, mainly due to options of cask maturation and increased blending options; (ii) growth of pot still whiskey and associated mash bills; and (iii) increasing premiumization due to greater availability of more mature stock from a wider range of distilleries.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.N.K. and C.O.; Investigation, T.J.K., K.N.K.; writing, review and editing, T.J.K., K.N.K. and C.O.; visualization, K.N.K.; funding acquisition; K.N.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Teagasc—Project 1376: Identification of Biomarkers to Authenticate Irish Whiskey and to Safeguard against Fraudulent Practices and the associated Walsh Scholarship Congener Analysis of Whiskey 2021057.
Acknowledgments
I would like to acknowledge the support given by colleagues within the flavor chemistry facility at Teagasc Food Research Centre, Moorepark, Fermoy, Co. Cork, Ireland.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Waymark, C.; Hill, A.E. The influence of Yeast Strain on Whisky New Make Spirit Aroma. Fermentation 2021, 7, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.L.; Hughes, D.M.; Badu-Tawiah, A.K.; Eccles, R.; Goodall, I.; Maher, S. Rapid Scotch Whisky Analysis and Authentication using Desorption Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionisation Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, A.C.; Ni Neill, C.; Geoghegan, S.; Currivan, S.; Deasy, M.; Cozzolino, D. A brief history of Whiskey Adulteration and the role of Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics in the Detection of Modern Whiskey Fraud. Beverages 2020, 6, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EUIPO. The Economic Cost of IPR Infringement in Spirits and Wine. 2016. Available online: https://euipo.europa.eu/tunnel-web/secure/webdav.guest/document_library/observatory/resources/research-and-studies/ip_infringement/study8/wines_and_spirtis_en.pdf (accessed on 29 September 2022).
- Drinks Ireland. Irish Whiskey Global Report. Drinks Industry Ireland. Available online: https://www.ibec.ie/drinksireland/news-insights-and-events/news/2022/10/25/irish-whiskey-association-publishes (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Stupak, M.; Goodall, I.; Tomaniova, M.; Pulkrabova, J.; Hsjslova, J. A novel approach to assess the quality and authenticity of Scotch Whisky based on gas chromatography coupled to high resolution mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1042, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aylott, R. Whisky Analysis. In Whisky: Technology, Production and Marketing, 1st ed.; Russell, I., Bamforth, C.W., Stewart, G.G., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2003; pp. 277–304. [Google Scholar]
- Aylott, R.I.; MacKenzie, W.M. Analytical strategies to confirm the Generic Authenticity of Scotch Whisky. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stead, S.; Jandova, R.; Eccles, R.; Goodall, I. Rapid Determination of Whisky Brands Using the DART QDa with LiveID System for Alcoholic Beverage Quality Control Testing; Waters Corporation: Milford, MA, USA; Scotch Whisky Research Institute: Edinburgh, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Technical File Setting out the Specifications with Which Irish whiskey/Uisce Beatha Eireannach/Irish Whisky Must Comply. Available online: https://www.gov.ie/pdf/?file=https://assets.gov.ie/91238/e4d51392-dcab-45af-a8e5-39bc0fc4de14.pdf#page=1 (accessed on 17 January 2022).
- Buxton, I.; Hughes, P.S. The Science and Commerce of Whisky, 2nd ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, G.H. The Flavor–Chemistry Association. In Whisky Science: A Condensed Distillation, 1st ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magee, M. Irish Whiskey: A 1000 Year Tradition, 2nd ed.; O’Brien Press: Dublin, Ireland, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Piggott, J. Whisky. In Current Developments in Biotechnology and Bioengineering: Food and Beverages Industry, 1st ed.; Pandey, A., Du, G., Sanroman, M., Soccol, C., Dussap, C.-G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 435–450. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewska, P.; Dymerski, T.; Wardencki, W.; Namiesnik, J. Chemical composition analysis and authentication of whisky. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlaczyk, A.; Gajek, M.; Jozwik, K.; Szynkowska, M.I. Multielemental analysis of various kinds of whisky. Molecules 2019, 24, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBEC IRISH Whiskey Trade Report 2021. Available online: https://www.ibec.ie/drinksireland/news-insights-and-events/news/2021/07/01/irish-whiskey-international-trade-report-2021 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Technical File for Scottish Whisky. Available online: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/5fd36667e90e07662ed92c85/Scotch_Whisky_Technical_File_-_June_2019.pdf (accessed on 25 January 2022).
- FSAI. Labelling of Irish Whiskey [pdf] Dublin: Food Safety Authority of Ireland. 2019. Available online: https://www.ibec.ie/drinksireland/irish-whiskey/your-association/technical/regulations-governing-irish-whiskey (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- European Parliament and Council. Regulation (EU) 2019/787 of The European Parliament and of The Council of April 2019 on the Definition, Description, Presentation, Labelling and the Protection of Geographical Indications of Spirit Drinks and Repealing Council Regulation (ECC) No 110/2008. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2019, 787, 3. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content (accessed on 6 March 2023).
- Appendix Irish Whiskey G.I.-Scheme of Revenue Verification Checks. Irish Tax and Customs. 1–9. Available online: https://www.revenue.ie/en/companies-and-charities/documents/excise/whiskey-verification-checks.pdf (accessed on 14 January 2022).
- Power, A.C.; Jones, J.; NiNeil, C.; Geoghegan, S.; Warren, S.; Currivan, S.; Cozzolino, D. What’s in this drink? Classification and adulterant detection in Irish Whiskey samples using near infrared spectroscopy combined with chemometrics. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 5256–5263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisniewska, P.; Boque, R.; Borras, E.; Busto, O.; Wardencki, W.; Namiesnik, J.; Dymerski, T. Authentication of whisky due to its botanical origin and way of production by instrumental analysis and multivariate classification methods. Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2017, 173, 849–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, T.P. Production of Scotch and Irish whiskies: Their history and evolution. In The Alcohol Textbook, 4th ed.; Jacques, K.A., Lyons, T.P., Kelsall, D.R., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2003; pp. 193–222. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, F. A Glass Apart: Irish Single Pot Still Whiskey, 1st ed.; The Images Publishing Group: Mulgrave, Australia, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Harris, C. The Irish Brewing Industry, c. 1780–1930: An Archaeology. Ph.D. Thesis, University College Cork, Cork, Ireland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, S.; Vyrne, J.L.; Murphy, B.; Whelan, S.J.; Carroll, J.P.; Ryan, D. The optimisation of cook parameters to spirit whiskey production from native Irish Wheat: A response surface method approach. Foods 2022, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathgate, G.N. The influence of malt and wort processing on spirit character: The lost styles of Scotch malt whisky. J. Inst. Brew. 2019, 125, 200–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piggott, J.R. Whisky, Whiskey and Bourbon: Composition and Analysis of Whisky. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Caballero, B., Finglas, P.M., Toldrá, F., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, UK, 2016; pp. 514–518. [Google Scholar]
- Bathgate, G.N. A review of malting and malt processing for whisky distillation. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrispeels, M.J.; Varner, J.E. Gibberellic acid-enhanced synthesis and release of α-amylase and ribonuclease by isolate barley and aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1967, 42, 398–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, G. Starch in Brewing Applications. In Food Science, Technology and Nutrition, Starch in Food, 2nd ed.; Sjoo, M., Nilsson, L., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2018; pp. 633–659. [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd, E.; Linforth, R.S.T.; Jack, F.; Cook, D.J. Origins of the perceived nutty character of new-make malt whisky spirit. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauer, A.; Elss, S.; Frischmann, M.; Tellez, P.; Pischestsrieder, M. Influence of Thermally Processed Carbohydrate/Amino Acid Mixtures on the Fermentation by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 2042–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerny, C. The Aroma Side of the Maillard Reaction. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1126, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marčiulionytė, R.; Johnston, C.; Maskell, D.L.; Mayo, J.; Robertson, D.; Griggs, D.; Holmes, C.P. Roasted Malt for Distilling: Impact on Malt Whisky New Make Spirit Production and Aroma Volatile Development. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2022, 80, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coghe, S.; Gheeraert, B.; Michiels, A.; Delvaux, F.R. Development of Maillard reaction related characteristics during malt roasting. J. Inst. Brew. 2006, 112, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monica Lee, K.Y.; Paterson, A.; Piggott, J.R.; Richardson, G.D. Origins of Flavour in Whiskies and Revised Flavour Wheel: A Review. J. Inst. Brew. 2001, 107, 287–313. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, G.S. The Production of Secondary Metabolites with Flavour Potential during Brewing and Distilling Wort Fermentations. Fermentation 2017, 3, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daute, M.; Jack, F.; Baxter, I.; Harrison, B.; Grigor, J.; Walker, G. Comparison of three approaches to assess the flavour characteristics of Scotch Whisky Spirit. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, S.M.; Liang, G.; Zhu, J.; Lu, B.; Peng, L.-X.; Wang, Q.-Y.; Wei, Y.-T.; Zhou, G.-P.; Huang, R.-B. Influence of Calcium ions on the Thermal characteristics of a-amylase from thermophilic anoxybacillus sp. GXS-BL. Protein Pept. Lett. 2019, 26, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Huang, W.; Wang, X.; Tang, T.; Hua, Z.; Yan, G. Improvement of alcoholic fermentation by calcium ions under enological conditions involves the increment of plasma membrane H(+)-ATPase activity. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 26, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Kleine-Benne, E. Determining Phenolic Compounds in Whisky using Direct Large Volume Injection and Stir Bar Sorptive Extraction. [pdf] 2012. Gerstel. Available online: https://www.gerstelus.com/applications/determining-phenolic-compounds-in-whiskey-using-direct-large-volume-injection-and-stir-bar-sorptive-extraction/ (accessed on 3 August 2022).
- Furusawa, T. The Formation and Reactions of Sulphur Compounds During Distillation. Ph.D. Thesis, Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Fontana, M.; Buiatti, S. 25-Amino Acids in Beer. In Beer in Health and Disease Prevention, 1st ed.; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Barlington, MA, USA, 2009; pp. 273–284. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.M.; Guido, L.F. Impact of Wort Amino Acids on Beer Flavour: A Review. Fermentation 2018, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobis, A.; Kwasnicki, M.; Lehnhardt, F.; Hellwig, M.; Henle, T.; Becker, T.; Gastl, M. A Comprehensive Evaluation of Flavor Instability of Beer (Part 2): The Influence of De Novo Formation of Aging Aldehydes. Foods 2021, 10, 2668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchhaupt, M.; Lahne, F.; Etschmann, M.M.W.; Schrader, J. 37-Biotechnological Production of Fatty Aldehydes. In Flavour Science: Proceedings from XIII Weurman Flavour Research Symposium, 1st ed.; Ferreira, V., Lopez, R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 195–199. [Google Scholar]
- Bravi, E.; Marconi, O.; Perretti, G.; Fantozzi, P. Influence of barley variety and malting process on lipid content of malt. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.M.; Faria, M.; Sá, F.; Barros, F.; Araújo, I.M. C6-alcohols as varietal markers for assessment of wine origin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 563, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, S.; Dong, J.; Fan, W.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Chang, Z.; Tian, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, S. The influence of LOX-less barley malt on the flavour stability of wort and beer. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christoph, N.; Bauer-Christoph, C. Flavour of Spirit Drinks: Raw Materials, Fermentation, Distillation, and Ageing. In Flavours and Fragrances Chemistry, Bioprocessing and Sustainability; Berger, R.G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 219–239. [Google Scholar]
- LaRoe, E.G.; Shipley, P.A. Whiskey composition: Formation of alpha-and beta-ionone by the thermal decomposition of beta-carotene. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1970, 18, 174–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daute, M.; Jack, F.; Harrison, B.; Walker, G. Experimental whisky fermentations: Influence of wort pre-treatments. Foods 2021, 10, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korhola, M.; Harju, K.; Lehtonen, M. Fermentation. In The Science and Technology of Whiskies; Piggott, J.R., Sharp, R., Duncan, R.E.B., Eds.; Longman Group UK Ltd.: Harlow, UK, 1989; pp. 89–118. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.M.; Hill, A.E. Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Production of Whisk(e)y. Beverages 2016, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, G.M.; Stewart, G.G. Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the Production of Fermented Beverages. Beverages 2016, 2, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotar, A.M.; Semeniuc, C.A.; Mudura, E.; Coldea, T.; Pop, C.L. Identification of Microbial Contamination Sources in Distilled Spirits. Bull. Univ. Agric. Sci. Vet. Med. Cluj Napoca 2012, 69, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umego, E.C.; Barry-Ryan, C. Overview of the Irish brewing and distilling sector: Processing inputs supply and quality requirements. Brew. Sci. 2022, 75, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Bindon, K.A.; Kassara, S.; Solomon, M.; Bartel, C.; Smith, P.A.; Barker, A.; Curtin, C. Commercial Saccharomyces cerevisiae Yeast Strains Significantly Impact Shiraz Tannin and Polysaccharide Composition with Implications for Wine Colour and Astringency. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanikawa, A.; Sugimoto, T. A narrative review of sulphur compounds in whisk(e)y. Molecules 2022, 27, 1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yomo, H.; Noguchi, Y.; Yonezawa, T. Effect on new-make spirit character due to the performance of brewer’s yeast—(I) physiological changes of yeast during propagation and brewing. In Distilled Spirits: Production, Technology and Innovation; Bryce, J.H., Piggott, J.R., Stewart, G.G., Eds.; Nottingham University Press: Nottingham, UK, 2008; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Dong, J.; Yin, H.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, R.; Wan, X.; Chen, P.; Hou, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, L. Wort composition and its impact on the flavour-active higher alcohol and ester formation of beer—A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2014, 120, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, O.S.; Stewart, G.G. Effect of malt wort, very-high-gravity malt wort, and very-high-gravity adjunct wort on volatile production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 1999, 57, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Peddie, H.A.B. Ester formation in brewery fermentations. J. Inst. Brew. 1990, 96, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharczyk, K.; Tuszynski, T. The effect of wort aeration on fermentation, maturation and volatile components of beer produced on an industrial scale. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 123, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, T.; Morley, A. An evolutionary perspective on the Crabtree effect. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2014, 1, 17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dashko, S.; Zhou, N.; Compagno, C.; Piskur, J. Why, when, and how did yeast evolve alcoholic fermentation? FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 826–832. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yilmaztekin, M.; Cabaroglu, T.; Erten, H. Effects of Fermentation Temperature and Aeration on Production of Natural Isoamyl Acetate by Williopsis saturnus var. saturnus. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 870802. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, G.T.; Kirsop, B.H. The origin of the medium fatty acids present in beer. J. Inst. Brew. 1977, 83, 241–243. [Google Scholar]
- Plutowska, B.; Biernacka, P.; Wardencki, W. Identification of Volatile Compounds in Raw Spirits of Different Organoleptic Quality. J. Inst. Brew. 2010, 116, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saerens, S.M.G.; Delvaux, F.R.; Verstrepen, K.J.; Thevelein, J.M. Production and biological function of volatile esters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb. Biotechnol. 2010, 3, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, E.S.P.; Cardoso, D.R.; Franco, D.W. Quantitative ester analysis in cachaca and distilled spirits by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5488–5493. [Google Scholar]
- Camara, J.S.; Marques, J.C.; Perestrelo, R.M.; Rodrigues, F.; Oliveira, L.; Andrade, P.; Caldeira, M. Comparative study of the whisky aroma profile based on headspace solid phase microextraction using different fibre coatings. J. Chrom. A 2007, 1150, 198–207. [Google Scholar]
- Kyraleou, M.; Herb, D.; O’Reilly, G.; Conway, N.; Bryan, T.; Kilcawley, K.N. The Impact of Terroir on the Flavour of Single Malt Whisk(e)y New Make Spirit. Foods 2021, 10, 443. [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewska, P.; Sliwinska, M.; Dymerski, T.; Wardencki, W.; Namiesnik, J. Comparison of an Electronic Nose Based on Ultrafast Gas Chromatography, Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Gas Chromatography, and Sensory Evaluation for an Analysis of Type of Whisky. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 2710104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Arjona, D.; González-Gallero, V.; Pablos, F.; Gonzalez, A.G. Authentication and differentiation of Irish whiskeys by higher-alcohol congener analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 1999, 381, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perestrelo, R.; Caldeira, M.; Rodrigues, F.; Pereira, J.A.M.; Camara, J.S. DLLµE/GC-MS as a Powerful Analytical Approach to Establish the Volatilomic Composition of Different Whiskeys. Beverages 2022, 8, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csutoras, C.; Bakos-Barczi, N.; Burkus, B. Medium chain fatty acids and fatty acid esters as potential makers of alcoholic fermentation of white wines. Acta Aliment. 2022, 51, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patinios, C.; Lanza, L.; Corino, I.; Franssen, M.C.R.; Van Der Oost, J.; Weusthius, R.A.; Kengen, S.W.M. Eat1-Like alcohol acyl transferases from yeasts have high alcoholysis and thiolysis activity. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 579844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodda, L.N.; Beyer, J.; Gerostamoulos, D.; Drummer, O.H. Alcohol congener analysis and the source of alcohol: A review. Forensic. Sci. Med. Pathol. 2013, 9, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.; Pierce, J.S. Absorption of amino acids from wort by yeasts. J. Inst. Brew. 1964, 70, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogerus, K.; Gibson, B.R. 125th Anniversary Review: Diacetyl and its control during brewery fermentation. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 86–97. [Google Scholar]
- Hazelwood, L.A.; Daran, J.-M.; Van Maris, A.J.A.; Pronk, J.T.; Dickinson, J.R. The Ehrlich Pathway for Fusel Alcohol Production: A Century of Research on Saccharomyces cerevisiae Metabolism. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2259–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravasio, D.; Wendland, J.; Walther, A. Major contributor of the Ehrlich pathway for 2-phenylethanol/rose flavor production in Ashbya gossypii. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014, 14, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosowski, G.; Mikulski, D.; Macko, D.; Miklaszewska, B.; Kotarska, K.; Czuprynski, B. Influence of various yeast strains and selected starchy raw materials on production of higher alcohols during the alcoholic fermentation process. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 240, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Robles, I.W.; Cook, D.J. The impact of maturation on concentrations of key odour active compounds which determine the aroma of tequila. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Huang, J.; Jin, Y.; Wu, C.; Zhou, R. Effect of oak matrix (barrel and toasted chips) on the volatiles in Goji (Lycium Chinese) wine. J. Inst. Brew. 2017, 124, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, J.; Brigham, C. Solvent production by engineered Ralstonia eutropha: Channeling carbon to biofuel. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 5012–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godillot, J.; Sanchez, I.; Perez, M.; Picou, C.; Galeote, V.; Sablayrolles, J.-M.; Farines, V.; Mouret, J.-R. The Timing of Nitrogen Addition Impacts Yeast Genes Expression and the Production of Aroma Compounds during Wine Fermentation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 829786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Ferreira, A.; Barbosa, C.; Falco, V.; Leao, C.; Mendes-Faia, A. The production of hydrogen sulphide and other aroma compounds by wine strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in synthetic media with different nitrogen concentrations. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 36, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, E.E.; De Billerbeck, G.M.; Simoea, D.A.; Schuler, A.; Francois, J.M.; De Morais Jr, M.A. Influence of nitrogen supply on the production of higher alcohols/esters and expression of flavour-related genes in cachaça fermentation. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eram, M.S.; Ma, K. Decarboxylation of Pyruvate to Acetaldehyde for Ethanol Production by Hyperthermophiles. Biomolecules 2013, 3, 578–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, H.; Yoon, M.K.; Han, J.; Kim, Y.-S. Evaluation of volatile organic compounds in alcoholic beverages consumed in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Niu, C.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, Y. Simultaneous determination of diethylacetal and acetaldehyde during beer fermentation and storage process. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 4733–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, R.; Power, A.; Chapman, J.; Chandra, S.; Cozzolino, D. A Review on the Source of Lipids and Their Interactions during Beer Fermentation that Affect Beer Quality. Fermentation 2018, 4, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanikawa, A.; Hosoi, K.; Kato, T.; Nakagawa, K. Identification of green note compounds in malt whisky using multidimensional gas chromatography. Flavour Frag. J. 2002, 17, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Bars, D.; Yvon, M. Formation of diacetyl and acetoin by Lactococcus lactis via aspartate catabolism. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, B.; Vidgren, V.; Peddinti; Korgerus, K. Diacetyl control during brewery fermentation via adaptive laboratory engineering of the lager yeast Saccharomyces pastorianus. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 45, 1103–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcerek, M.; Pielech-Przybylska, K.; Dziekonska-Kubczak, U.; Patelski, P.; Strak, E. Fermentation Results and Chemical Composition of Agricultural Distillates Obtained from Rye and Barley Grains and the Corresponding Malts as a Source of Amylolytic Enzymes and Starch. Molecules 2016, 21, 1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, B.; Fagnen, O.; Jack, F.; Brosnan, J. The Impact of Copper in Different Parts of Malt Whisky Pot Stills on New Make Spirit Composition and Aroma. J. Inst. Brew. 2011, 117, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, B. The Art of Distilling, Revised and Updated: An Enthusiastic Guide to the Artisan Distillers of Whiskey, Vodka, Gin, and Other Potent Potables, 2nd ed.; Owens, B., Dikty, A., Faulkner, A., Eds.; Quarto: Beverley, MA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nicol, D. Batch Distillation. In The Science and Technology of Whiskies; Piggott, J.R., Sharp, R., Duncan, R.E.B., Eds.; Longman Group UK Ltd.: Harlow, UK, 1989; pp. 118–149. [Google Scholar]
- Buttery, R.G.; Ling, L.; Guadagni, D.G. Volatilities of Aldehydes, Ketones, and Esters in Dilute Water Solution. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1969, 17, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzer, D.A.; Cica, K.H.; Blesic, M.; Murtic, M.S.; Mrvcic, J.; Spaho, N. Alcoholic fermentation as a source of congeners in fruit spirits. Foods 2023, 12, 1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, K.A.; Alharethi, R.; Laposata, M. Fatty acid ethyl ester synthesis in the preparation of scotch whiskey. Alcohol 1999, 17, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boothroyd, E.L.; Linforth, R.S.H.; Cook, D.J. Effects of Ethanol and Long-Chain Ethyl Ester Concentrations on Volatile Partitioning in a Whisky Model System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 9959–9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viriot, C.; Scalbert, A.; Lapierre, C.; Moutounet, M. Ellagitannins and Lignins in Aging of Spirits in Oak Barrels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1993, 41, 1872–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prida, A.; Ducousso, A.; Petit, R.J.; Nepveu, G.; Puech, J.-L. Variation in wood volatile compounds in a mixed oak stand: Strong species and spatial differentiation in whisky-lactone content. Ann. For. Sci. 2007, 64, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, J.E.; Zimmerman, L.B.; Gardner, M.A.; Lowe, L.E. Analysis of Whiskey by Dispersive Liquid−Liquid Microextraction Coupled with Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry: An Upper Division Analytical Chemistry Experiment Guided by Green Chemistry. J. Chem. Educ. 2016, 93, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, H.A.; Elkins, J.T. Comparison of unaged and barrel aged whiskies from the same Mash Bill using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Brew. Distilling 2019, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, V. A Whisky Tour. Chemistry World. 2008, pp. 40–44. Available online: https://www.rsc.org/images/whisky_tcm18-138981.pdf (accessed on 21 October 2022).
- Coldea, T.E.; Mudura, E.; Socaciu, C. Advances in Distilled Beverages Authenticity and Quality Testing. In Ideas and Applications Toward Sample Preparation for Food and Beverage Analysis; Stauffer, M.T., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, D.E.; Baugh, W.D.; Conner, H.A. Studies on the Formation of Acrolein in Distillery Mashes. Appl. Microbiol. 1954, 2, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadahia, E.; Fernandez de Simon, B.; Jalocha, J. Volatile Compounds in Spanish, French, and American Oak Woods after Natural Seasoning and Toasting. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5923–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittari, E.; Moio, L.; Piombino, P. Interactions between Polyphenols and Volatile Compounds in Wine: A Literature Review on Physicochemical and Sensory Insights. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, S.; Brandao, E.; Guerreiro, C.; Soares, S.; Mateus, N.; De Freitas, V. Tannins in food: Insights into the molecular perception of astringency and bitter taste. Molecules 2020, 25, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadrat, M.; Emo, C.; Lavergne, J.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Chira, K. Impact of Barrel Toasting on Ellagitannin Composition of Aged Cognac Eaux-de-Vie. Molecules 2022, 27, 2531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracassetti, D.; Limbo, S.; Pellegrino, L.; Tirelli, A. Light-induced reactions of methionine and riboflavin in model wine: Effects of hydrolysable tannins and sulfur dioxide. Food Chem. 2019, 298, 124952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picariello, L.; Rinaldi, A.; Forino, M.; Errichiello, F.; Moio, L.; Gambuti, A. Effect of Different Enological Tannins on Oxygen Consumption, Phenolic Compounds, Color and Astringency Evolution of Aglianico Wine. Molecules 2020, 25, 4607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Yoshida, T.; Hatano, T.; Ito, H. Ellagitannins renewed the concept of tannins. In Chemistry and Biology of Ellagitannins: An Underestimated Class of Bioactive Plant Polyphenols; Quideau, S., Ed.; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2009; pp. 1–54. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, K.; Taguchi, A.; Koshimizu, S.; Suwa, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Shirasaka, N.; Yoshizumi, H. Reactive Oxygen Scavenging Activity of Matured Whiskey and Its Active Polyphenols. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, J.M.; Paterson, A.; Piggott, J.R. Analysis of Lignin from Oak Casks Used for the Maturation of Scotch Whisky. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1992, 60, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegarus, D.I.; Calugar, A.; Tanase, C.; Musca, A.; Botoran, O.R.; Manolache, M.; Babes, A.C.; Bunea, C.; Gal, E.; Bunea, A.; et al. Influence of Oak Chips and Oak Barrel Ageing on Volatile Profile in Chardonnay Wine of Romania. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 3691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcárcel-Muñoz, M.J.; Guerrero-Chavinet, M.; Garcia-Moreno, M.V.; Rodriguez-Dodero, M.C.; Guillen-Sanchez, D.A. Comparative Evaluation of Brandy de Jerez Aged in American Oak Barrels with Different Times of Use. Foods 2021, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarko, T.; Frankowski, F.; Duda-Chodak, A. The impact of compounds extracted from wood on the quality of alcoholic beverages. Molecules 2023, 28, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollihue, J.; Pook, V.G.; DeBolt, S. Sources of variation in bourbon whiskey barrels: A review. J. Inst. Brew. 2021, 127, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffrey, J.D.E. Aging of Whiskey Spirits in Barrels of Non-Traditional Volume. Master’s Thesis, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Conner, J.M.; Paterson, A.; Piggott, J.R. Changes in wood extractives from oak cask staves through maturation of scotch malt whisky. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1993, 62, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanikawa, A.; Hosoi, K.; Takise, I.; Kato, T. Detection of γ -lactones in malt whisky. J. Inst. Brew. 2000, 106, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feuillat, F.; Keller, R. Variability of oak wood (Quercus robur L., Quercus petraea Liebl.) anatomy relating to cask properties. Am. J. Enol. Vitic. 1997, 48, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrau, F.M.; Medina, K.; Boido, E.; Farina, L.; Gaggero, C.; Dellacassa, E.; Versini, G.; Henschke, P.A. De novo synthesis of monoterpenes by Saccharomyces cerevisiae wine yeasts. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2005, 243, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, B.C.G.; Friedman, R. Dilution of whisky—The molecular perspective. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, R.J.; Ochoa, A.; Kerth, C.R.; Miller, R.K.; Murray, S.C. Assessing the impact of corn variety and Texas terroir on flavor and alcohol yield in new-make bourbon whiskey. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivas, N.; Vivas de Gaulejac, N.; Vitry, C.; Mouche, C.; Kahn, N.; Nonier-Bourden, M.F.; Absalon, C. Impact of ethanol content on the scavenging activities of oak wood C-glycosidic ellagitannins. Application to the evaluation of the nutritional status of spirits. J. Inst. Brew. 2013, 119, 116–125. [Google Scholar]
- White, B.; Symth, M.R.; Lunte, C.E. Determination of phenolic acids in a range of Irish whiskies, including single pot stills and aged single malts, using capillary electrophoresis with field amplified sample stacking. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.T.; Watt, C.M. Acetic and formic acids emitted from wood samples and their effect on selected materials in museum environments. Corros. Sci. 2010, 52, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes-Dieguez, S.; Rodriguez-Solana, R.; Dominguez, J.M.; Diaz, E. Impact odorants and sensory profile of young red wines from four Galician (NW of Spain) traditional cultivars. J. Inst. Brew. 2015, 121, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ubeda, C.; Kania-Zelada, I.; Del Barrio-Galan, R.; Medel-Maraboli, M.; Gil, M.; Pena-Neira, A. Study of the changes in volatile compounds, aroma and sensory attributes during the production process of sparkling wine by traditional method. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brizuela, N.S.; Bravo-Ferrada, B.M.; Curilen, Y.; Delfederico, L.; Caballero, A.; Semorile, L.; Angeles Pozo-Bayo, M.; Tymczyszyn, E.E. Advantages of using blend cultures of native L. plantarum and O. oeni strains to induce malolactic fermentation of Patagonian Malbec wine. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; CAcho, J.; Ferreira, V. Solid phase extraction, multidimensional gas chromatography mass spectrometry determination of four novel aroma powerful ethyl esters: Assessment of their occurrence and importance in wine and other alcoholic beverages. J. Chromatogr. A 2007, 1140, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, A.; Zhao, K.; Hu, Y.; Yang, G.; Kuang, B.; Xiong, X.; Yang, Z.; Zheng, Q. Influence of Electrochemical Oxidation on the Maturation Process of the Distilled Spirit. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 18349–18355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemsley, E.K.; Defernez, M.; Marini, F. Multivariate statistics: Considerations and confidences in food authenticity problems. Food Control 2019, 105, 102–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferracane, A.; Manousi, N.; Tranchida, P.Q.; Zachariadis, G.A.; Mondello, L.; Rosenberg, E. Exploring the volatile profile of whiskey samples using solid-phase microextraction Arrow and comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2022, 1676, 463241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelen, H.H.; Majcher, M.; Szwengiel, A. Key odorants in peated malt whisky and its differentiation from other whisky types using profiling of flavour and volatile compounds. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 107, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cody, R.B.; Fukudome, T.; Ubukata, M. Integrated data analysis making use of the total information from gas chromatography and high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometry to identify qualitative differences between two whisky samples. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2022, 36, e9225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunkel, A.; Steinhaus, M.; Kotthoff, M.; Nowak, B.; Krautwurst, D.; Schieberle, P.; Hofmann, T. Nature’s Chemical Signatures in Human Olfaction: A Foodborne Perspective for Future Biotechnology. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7124–7143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zellner, B.d.; Dugo, P.; Dugo, G.; Mondello, L. Gas chromatography–olfactometry in food flavour analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1186, 123–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.; Correia, E.; Dinis, L.-T.; Vilela, A. An Overview of Sensory Characterization Techniques: From Classical Descriptive Analysis to the Emergence of Novel Profiling Methods. Foods 2022, 11, 255. [Google Scholar]
- Aylott, R.I.; Clyne, A.H.; Fox, A.P.; Walker, D.A. Analytical strategies to confirm Scottish Whisky Authenticity. Analyst 1994, 119, 1741–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, G.; James, K.J.; MacNamara, K.; Stack, M.A. Characterisation of whiskeys using solid-phase microextraction with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 896, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poisson, L.; Schieberle, P. Characterization of the Most Odor-Active Compounds in an American Bourbon Whisky by Application of the Aroma Extract Dilution Analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5813–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtonen, M. Phenols in whisky. Chromatographia 1982, 16, 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, M.; Vitali, L.; Oliviera, M.A.L.; Costa, A.C.O.; Micke, G.A. A Rapid Sample Screening Method for Authenticity Control of Whiskey Using Capillary Electrophoresis with Online Preconcentration. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 6882–6888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullier-Gall, C.; Signoret, J.; Coelho, C.; Hemmler, D.; Kajdan, M.; Lucio, M.; Schafer, B.; Gougeon, R.D.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Influence of regionality and maturation time on the chemical fingerprint of whisky. Food Chem. 2020, 323, 126748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roullier-Gall, C.; Signoret, J.; Hemmler, D.; Witting, M.A.; Kanawati, B.; Schafer, B.; Gougeon, R.D.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P. Usage of FT-ICR-MS Metabolomics for Characterizing the Chemical Signatures of Barrel-Aged Whisky. Front Chem. 2018, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James Reid, S.; Speers, R.A.; Willoughby, N.; Lumsden, W.B.; Maskell, D.L. Pre-fermentation of malt whisky wort using Lactobacillus and its influence on new-make spirit character. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).