Wine Cork Closures Impacts on Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS) and Precursors (DMSP) Equilibrium of Different Shiraz Wines during Accelerated Bottle Ageing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Wines
2.3. Wine Sampling
2.3.1. Wine Closures
2.3.2. Wine Bottling
2.3.3. Accelerated Ageing Mode
2.4. Chemical Analysis
2.4.1. Oenological Parameters
2.4.2. Analysis of Volatile Sulfur Compounds by SPME-GC-MS/MS
Sample Preparation
Analysis by SPME-GC-MS/MS
Analytical Validation
2.4.3. Analysis of DMSP by GC-MS/MS
3. Results
3.1. Analytical Validation of SPME-GC-MS/MS Analysis
3.2. Characterization of VSC during Accelerated Wine Bottle Ageing
3.2.1. Initial Characterization of Wines
3.2.2. Final Characterization of Wines
Evolution of VSC
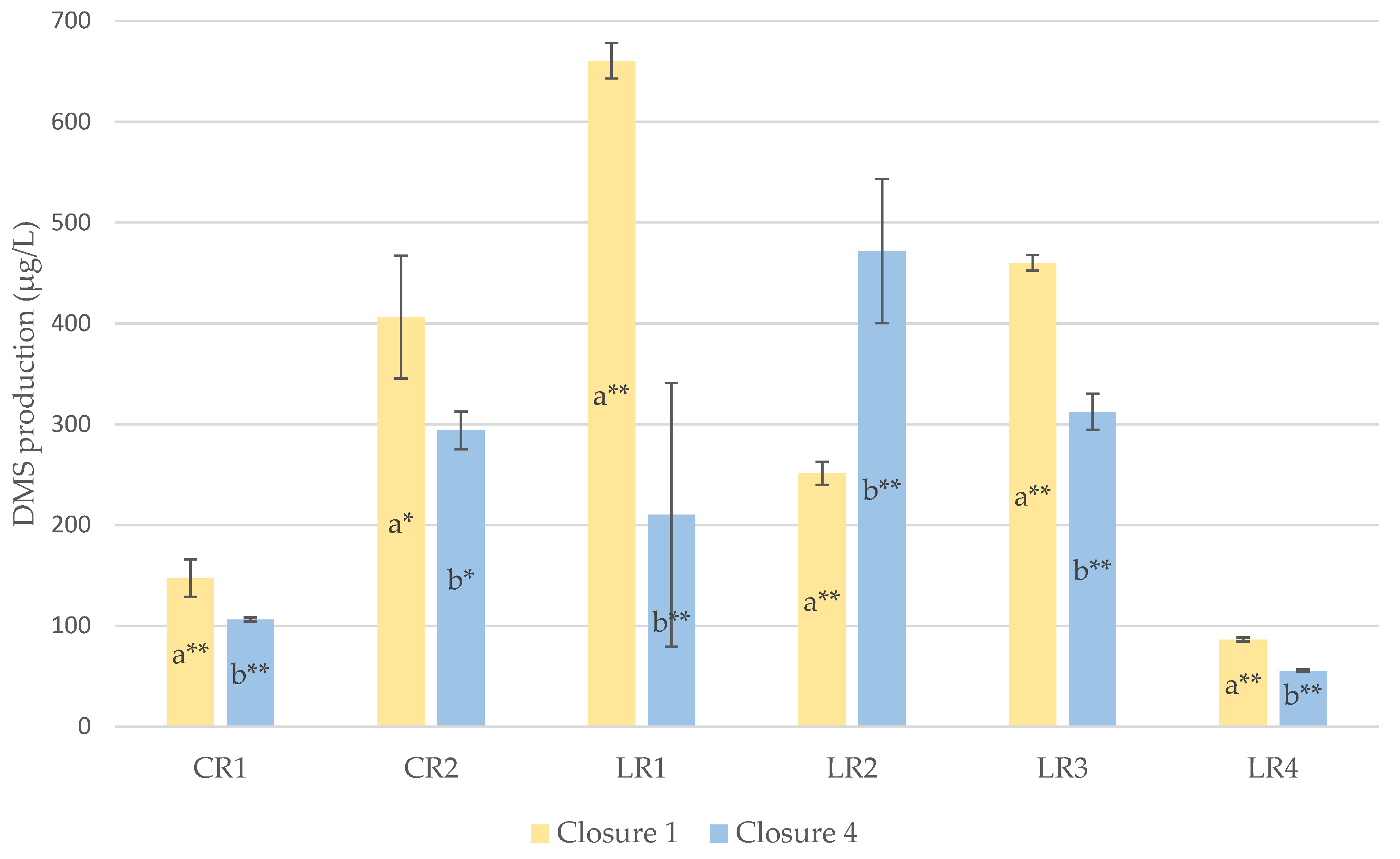
Evolution of DMS
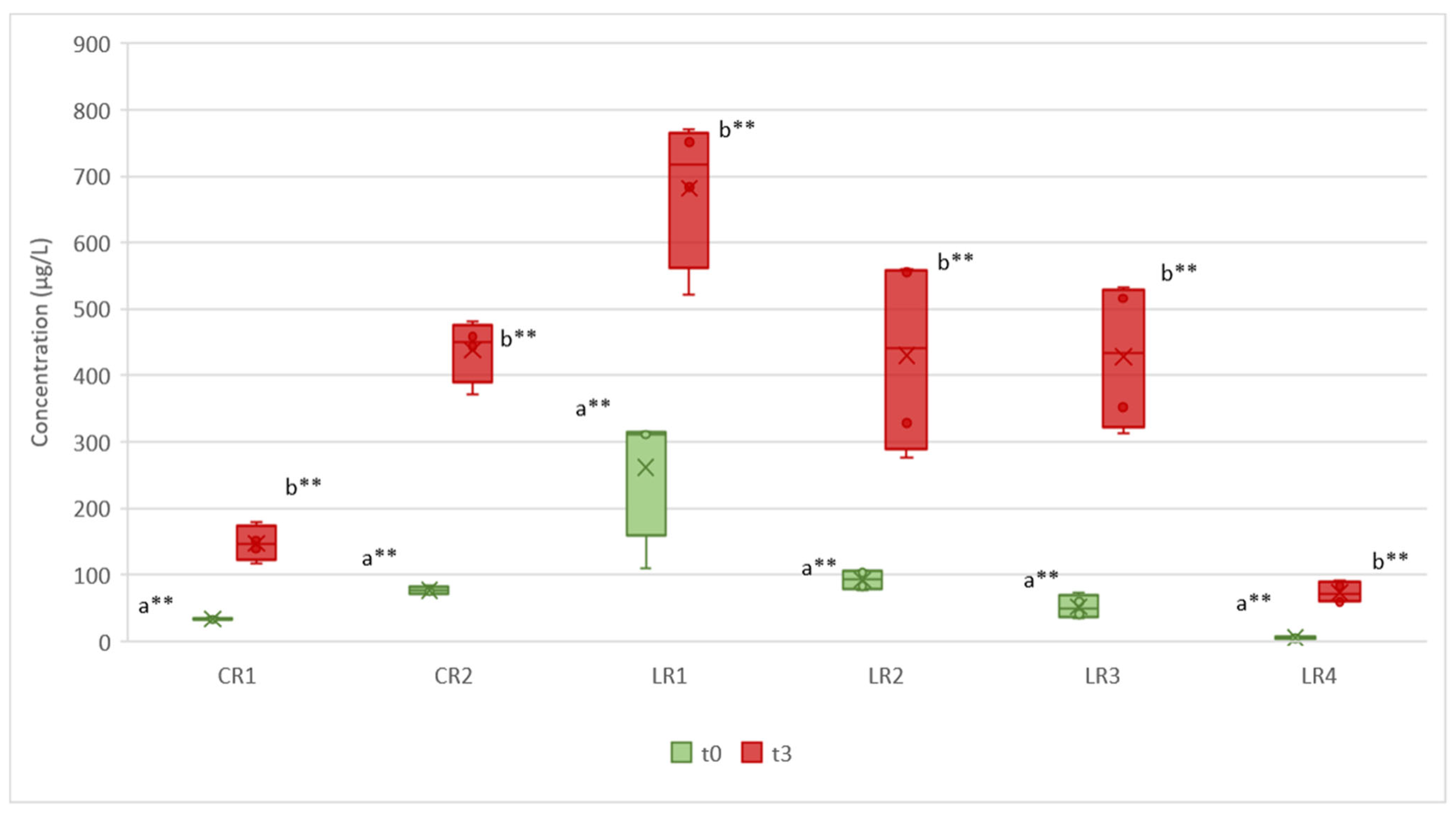
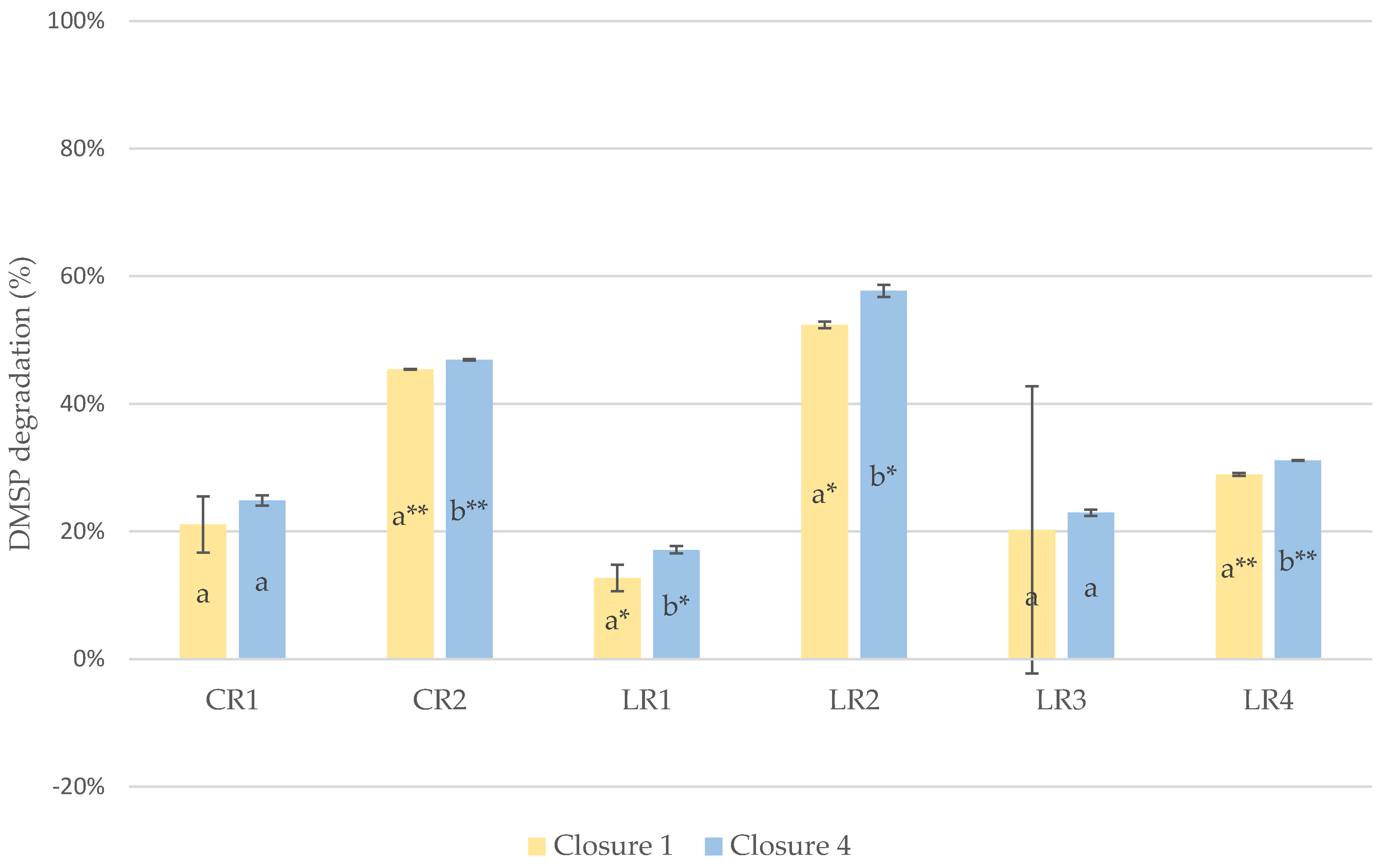
Evolution of DMSP
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolution of DMS
4.2. Evolution of DMSP
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du Plessis, C.; Loubser, G. The bouquet of “late harvest” wine. Agrochemophysica 1974, 6, 49–51. [Google Scholar]
- Marais, J. Effect of storage time and temperature on the formation of dimethyl sulphide and on white wine quality. J. Marais 1979, 18, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
- Spedding, D. The influence of dimethyl sulphide and carbon disulphide in the bouquet of wines. J. Grapevine Res. 1982, 21, 240–246. [Google Scholar]
- De Mora, S.; Knowles, S.; Eschenbruch, R.; Torrey, W. Dimethyl sulphide in some Australian red wines. Vitis 1987, 26, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Escudero, A.; Campo, E.; Fariña, L.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V. Analytical Characterization of the Aroma of Five Premium Red Wines. Insights into the Role of Odor Families and the Concept of Fruitiness of Wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 4501–4510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segurel, M.A.; Razungles, A.J.; Riou, C.; Salles, M.; Baumes, R.L. Contribution of dimethyl sulfide to the aroma of Syrah and Grenache Noir wines and estimation of its potential in grapes of these varieties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 7084–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anocibar Beloqui, A. Contribution à l’étude des composés soufrés volatils des vins rouges. Doctoral Dissertation, Université de Bordeaux 2, Bordeaux, France, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Leppänen, O.; Denslow, J.; Ronkainen, P. A gas chromatographic method for the accurate determination of low concentrations of volatile sulphur compounds in alcoholic beverages. J. Inst. Brew. 1979, 85, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loubser, G.; Du Plessis, C. The quantitative determination and some values of dimethyl sulfide in white table wines. Vitis 1976, 15, 248–252. [Google Scholar]
- Loscos, N.; Ségurel, M.; Dagan, L.; Sommerer, N.; Marlin, T.; Baumes, R. Identification of S-methylmethionine in Petit Manseng grapes as dimethyl sulphide precursor in wine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 621, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mora, S.; Eschenbruch, R.; Knowles, S.; Spedding, D. The formation of dimethyl sulphide during fermentation using a wine yeast. Food Microbiol. 1986, 3, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekker, M.Z.; Wilkes, E.N.; Smith, P.A. Evaluation of putative precursors of key ‘reductive’compounds in wines post-bottling. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 676–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segurel, M.A.; Razungles, A.J.; Riou, C.; Trigueiro, M.G.; Baumes, R.L. Ability of possible DMS precursors to release DMS during wine aging and in the conditions of heat-alkaline treatment. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2637–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, P.; Saucier, C.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Glories, Y. Impact of storage position on oxygen ingress through different closures into wine bottles. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6741–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capone, D.; Skouroumounis, G.K.; Barker, D.; McLean, H.; Pollnitz, A.; Sefton, M. Absorption of chloroanisoles from wine by corks and by other materials. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 1999, 5, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blake, A.; Kotseridis, Y.; Brindle, I.D.; Inglis, D.; Sears, M.; Pickering, G.J. Effect of closure and packaging type on 3-alkyl-2-methoxypyrazines and other impact odorants of Riesling and Cabernet Franc wines. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 4680–4690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.A.; Jourdes, M.l.; Darriet, P.; Teissedre, P.-L. Scalping of light volatile sulfur compounds by wine closures. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 10952–10956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, M.C.; He, J.; Peck, J.; Soles, R. Comparison of Screw Cap and Cork Closure Effect on Volatile Sulfur Development during Post-Bottle Ageing. In Flavour Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 267–271. [Google Scholar]
- Lopes, P.; Silva, M.A.; Pons, A.; Tominaga, T.; Lavigne, V.; Saucier, C.; Darriet, P.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Dubourdieu, D. Impact of oxygen dissolved at bottling and transmitted through closures on the composition and sensory properties of a Sauvignon blanc wine during bottle storage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 10261–10270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugliano, M.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Vidal, S.; Capone, D.; Siebert, T.; Dieval, J.-B.; Aagaard, O.; Waters, E.J. Evolution of 3-mercaptohexanol, hydrogen sulfide, and methyl mercaptan during bottle storage of Sauvignon blanc wines. Effect of glutathione, copper, oxygen exposure, and closure-derived oxygen. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 2564–2572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugliano, M.; Dieval, J.-B.; Siebert, T.E.; Kwiatkowski, M.; Aagaard, O.; Vidal, S.; Waters, E.J. Oxygen consumption and development of volatile sulfur compounds during bottle aging of two Shiraz wines. Influence of pre-and postbottling controlled oxygen exposure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8561–8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedrizzi, B.; Magno, F.; Badocco, D.; Nicolini, G.; Versini, G. Aging effects and grape variety dependence on the content of sulfur volatiles in wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 10880–10887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slaghenaufi, D.; Tonidandel, L.; Moser, S.; Villegas, T.R.; Larcher, R. Rapid analysis of 27 volatile sulfur compounds in wine by headspace solid-phase microextraction gas chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 3706–3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OIV. Recueil des Méthodes Internationales D’analyse des vins et des Moûts Volume 2; OIV: Paris, France, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Roland, A.; Schneider, R. Development and validation of a high-throughput analysis of glutathione in grapes, musts and wines by Stable Isotope Dilution Assay and LC–MS/MS. Food Chem. 2015, 177, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Royer Dupré, N.; Schneider, R.; Payan, J.-C.; Salançon, E.; Razungles, A. Effects of vine water status on dimethyl sulfur potential, ammonium, and amino acid contents in Grenache noir grapes (Vitis vinifera). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2760–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekker, M.Z.; Mierczynska-Vasilev, A.; Smith, P.A.; Wilkes, E.N. The effects of pH and copper on the formation of volatile sulfur compounds in Chardonnay and Shiraz wines post-bottling. Food Chem. 2016, 207, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lytra, G.; Tempere, S.; Zhang, S.; Marchand, S.; de REVEL, G.; Barbe, J.-C. Olfactory impact of dimethyl sulfide on red wine fruity esters aroma expression in model solution. Oeno One 2014, 48, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, L.; Schneider, R. Le sulfure de diméthyle: Quels moyens pour gérer ses teneurs dans les vins en bouteilles? Arome Du Vin Proc. 2012, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
| Wine | Denomination of Origin | Vintage Year | Ageing Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| CR1 | Côtes-du-Rhône | 2020 | Tank |
| CR2 | Côtes-du-Rhône | 2019 | Barrel |
| LR1 | Languedoc-Roussillon | 2019 | Barrel |
| LR2 | Languedoc-Roussillon | 2019 | Tank |
| LR3 | Languedoc-Roussillon | 2019 | Barrel |
| LR4 | Languedoc-Roussillon | 2019 | Barrel |
| Closure | Closure 1 | Closure 2 | Closure 3 | Closure 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OIR (mg O2) | 0.91 ± 0.04 | 1.92 ± 0.21 | 1.98 ± 0.32 | 2.31 ± 0.20 |
| OTR (mg O2/year) | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 1.07 ± 0.29 | 1.15 ± 0.40 | 1.79 ± 0.36 |
| LOD | LOQ | R2 | Linearity | Repeatability (n = 5) | Accuracy (n = 3) | Intermediate Reproducibility | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µg/L | µg/L | Min µg/L | Max µg/L | RSD % | Low RSD % | High RSD % | RSD % | ||
| DMS | 9 | 30 | 0.914 | 60.0 | 480.0 | 17% | 93% | 95% | 18% |
| EtSH | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.922 | 25.2 | 201.6 | 19% | 95% | 97% | 19% |
| DES | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.962 | 13.4 | 107.2 | 24% | 100% | 100% | 17% |
| SMTA | 0.03 | 0.1 | 0.979 | 70.0 | 560.0 | 10% | 92% | 96% | 8% |
| ETA | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.880 | 13.4 | 107.2 | 14% | 90% | 96% | 40% |
| DMDS | 0.007 | 0.02 | 0.941 | 16.3 | 130.4 | 4% | 100% | 100% | 16% |
| DEDS | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.967 | 15.5 | 124.0 | 4% | 100% | 100% | 12% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De La Burgade, R.; Nolleau, V.; Godet, T.; Galy, N.; Tixador, D.; Loisel, C.; Sommerer, N.; Roland, A. Wine Cork Closures Impacts on Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS) and Precursors (DMSP) Equilibrium of Different Shiraz Wines during Accelerated Bottle Ageing. Beverages 2023, 9, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010015
De La Burgade R, Nolleau V, Godet T, Galy N, Tixador D, Loisel C, Sommerer N, Roland A. Wine Cork Closures Impacts on Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS) and Precursors (DMSP) Equilibrium of Different Shiraz Wines during Accelerated Bottle Ageing. Beverages. 2023; 9(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe La Burgade, Rémi, Valérie Nolleau, Teddy Godet, Nicolas Galy, Dimitri Tixador, Christophe Loisel, Nicolas Sommerer, and Aurélie Roland. 2023. "Wine Cork Closures Impacts on Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS) and Precursors (DMSP) Equilibrium of Different Shiraz Wines during Accelerated Bottle Ageing" Beverages 9, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010015
APA StyleDe La Burgade, R., Nolleau, V., Godet, T., Galy, N., Tixador, D., Loisel, C., Sommerer, N., & Roland, A. (2023). Wine Cork Closures Impacts on Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS) and Precursors (DMSP) Equilibrium of Different Shiraz Wines during Accelerated Bottle Ageing. Beverages, 9(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages9010015








