Non-Thermal Processing of a Protein Functional Beverage Using Pulsed Electric Fields: Escherichia coli Inactivation and Effect on Proteins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
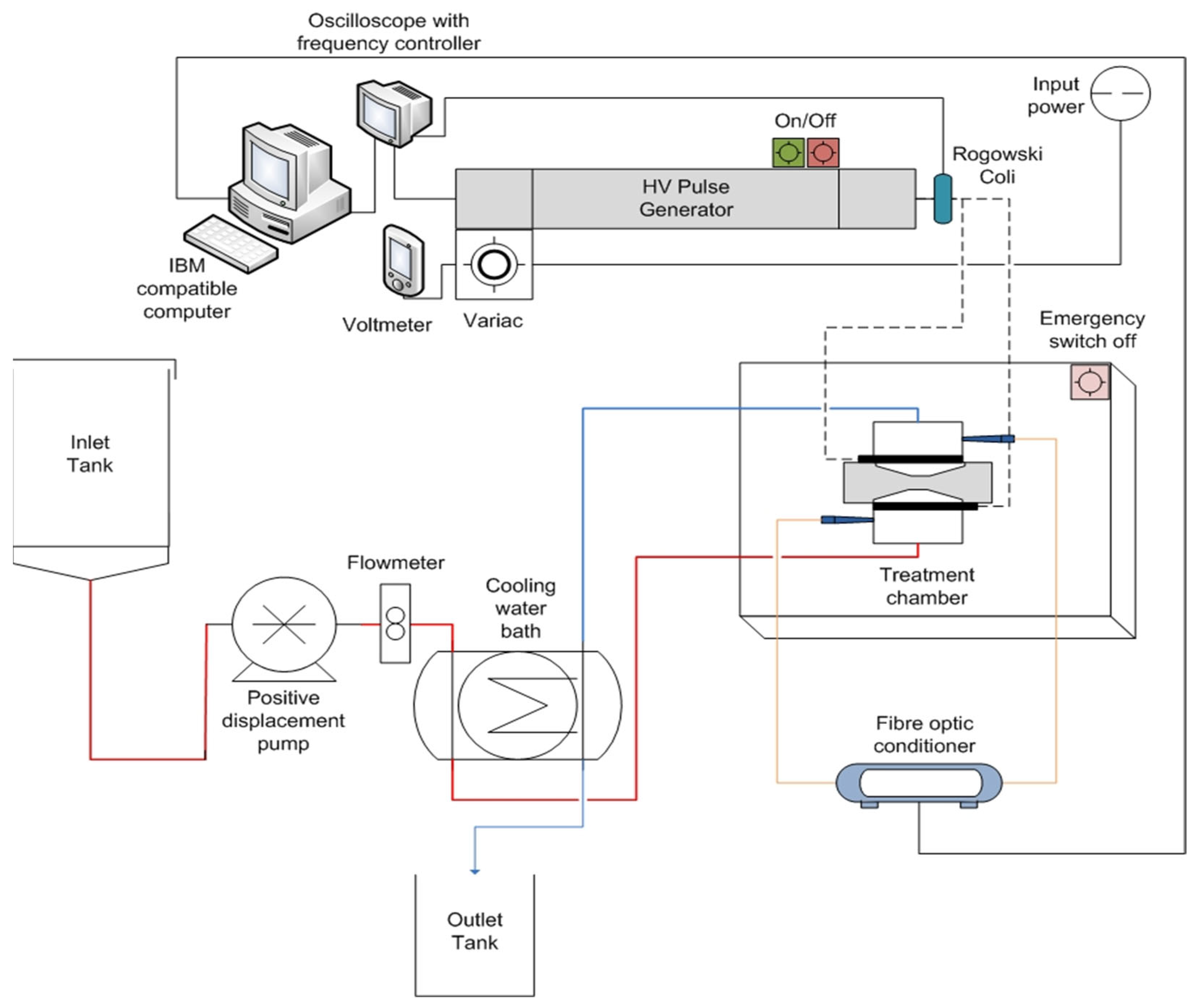
2.1. Pulsed Electric Fields Equipment
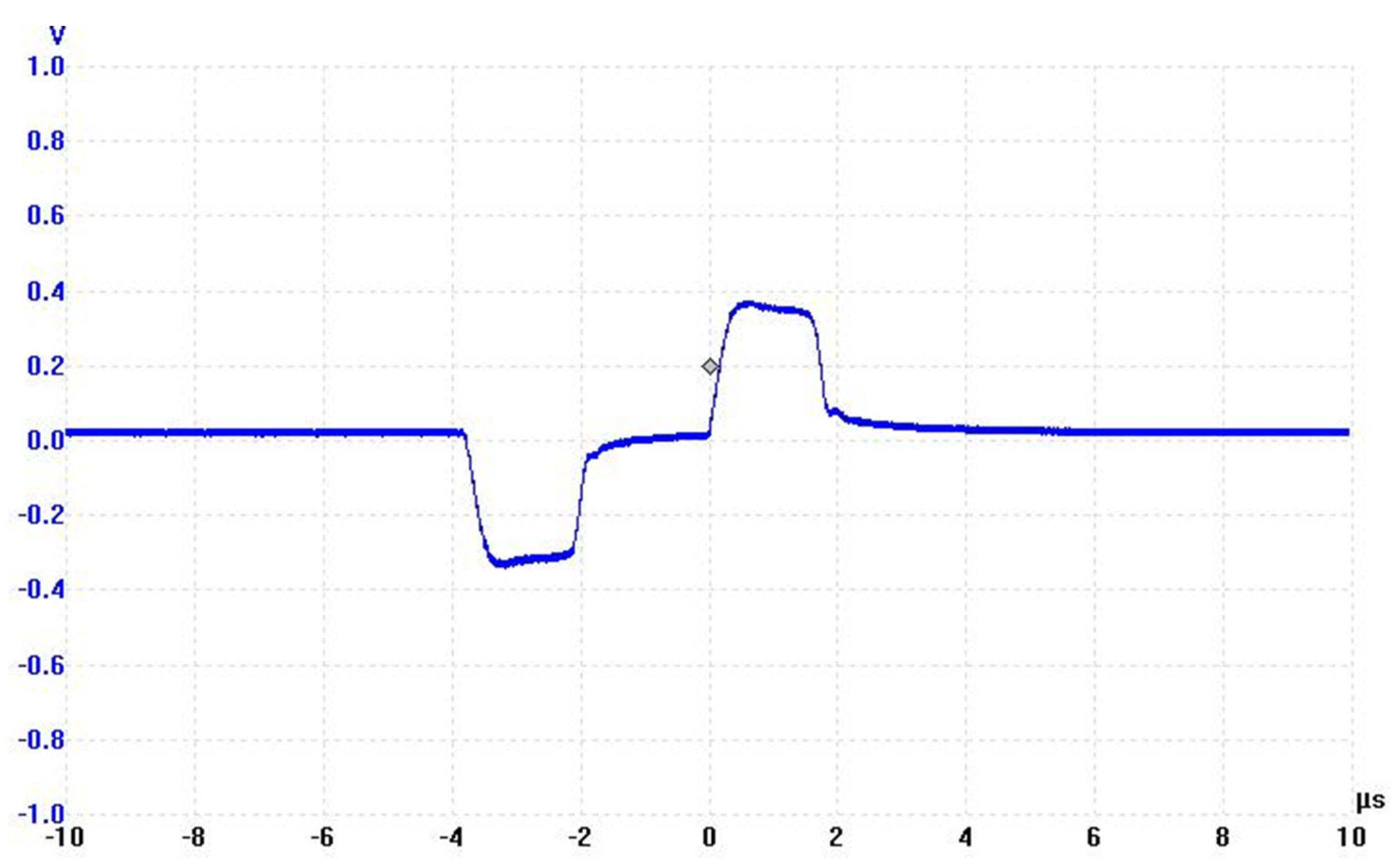
2.1.1. Pulse Generator
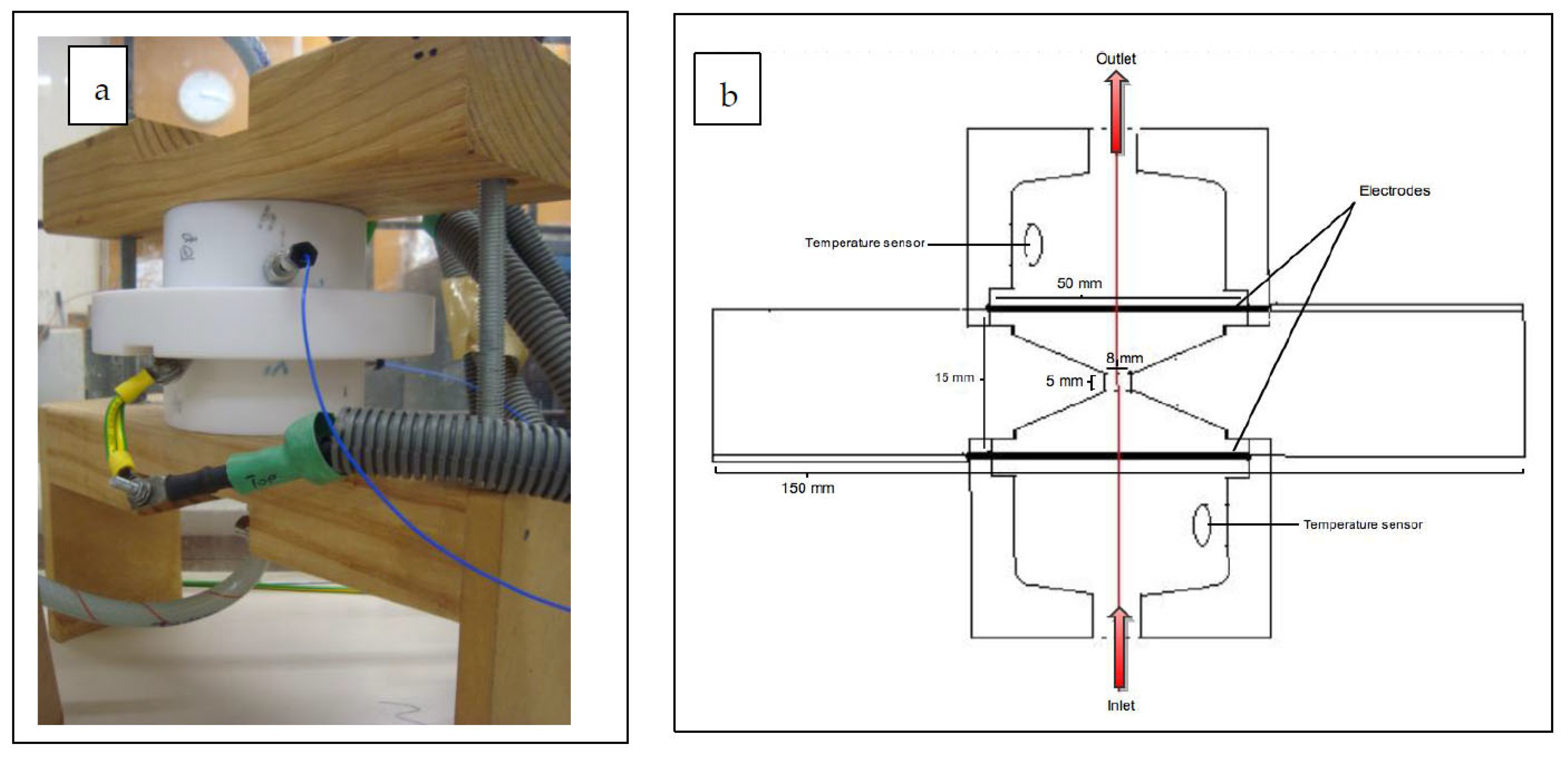
2.1.2. Treatment Chamber
2.1.3. Temperature Control and Measurements
2.2. PEF and Thermal Inactivation of E. coli Suspended in the Diluted Protein Shake beverage
2.2.1. Protein Beverage Composition and Preparation
2.2.2. Microbial Cultivation and Enumeration
2.2.3. Thermal Inactivation Experiments
2.2.4. PEF Inactivation Experiments
2.3. PEF and Thermal Processing of Proteins Solutions
2.3.1. Preparation of Whey and Soy Protein Solutions
2.3.2. Denatured Protein Quantification
2.3.3. Measurement of Surface Free Sulfhydryls (SHFs) Content in Soy Protein Solution
2.3.4. Thermal Processing of Proteins Solutions
2.3.5. PEF Processing of Protein Solutions
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PEF and Thermal Inactivation of Escherichia coli Suspended in the Diluted Protein Shake Beverage
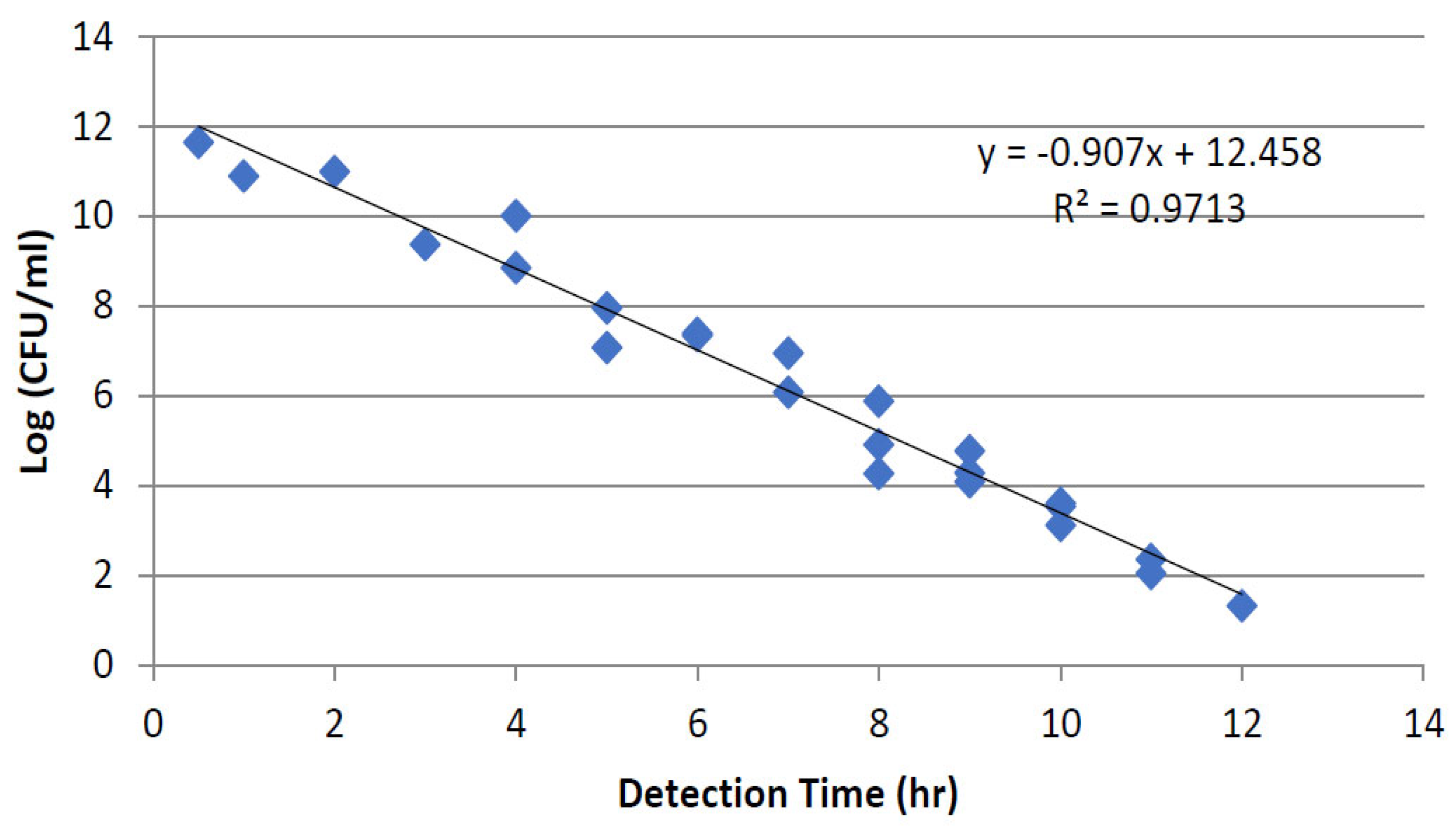
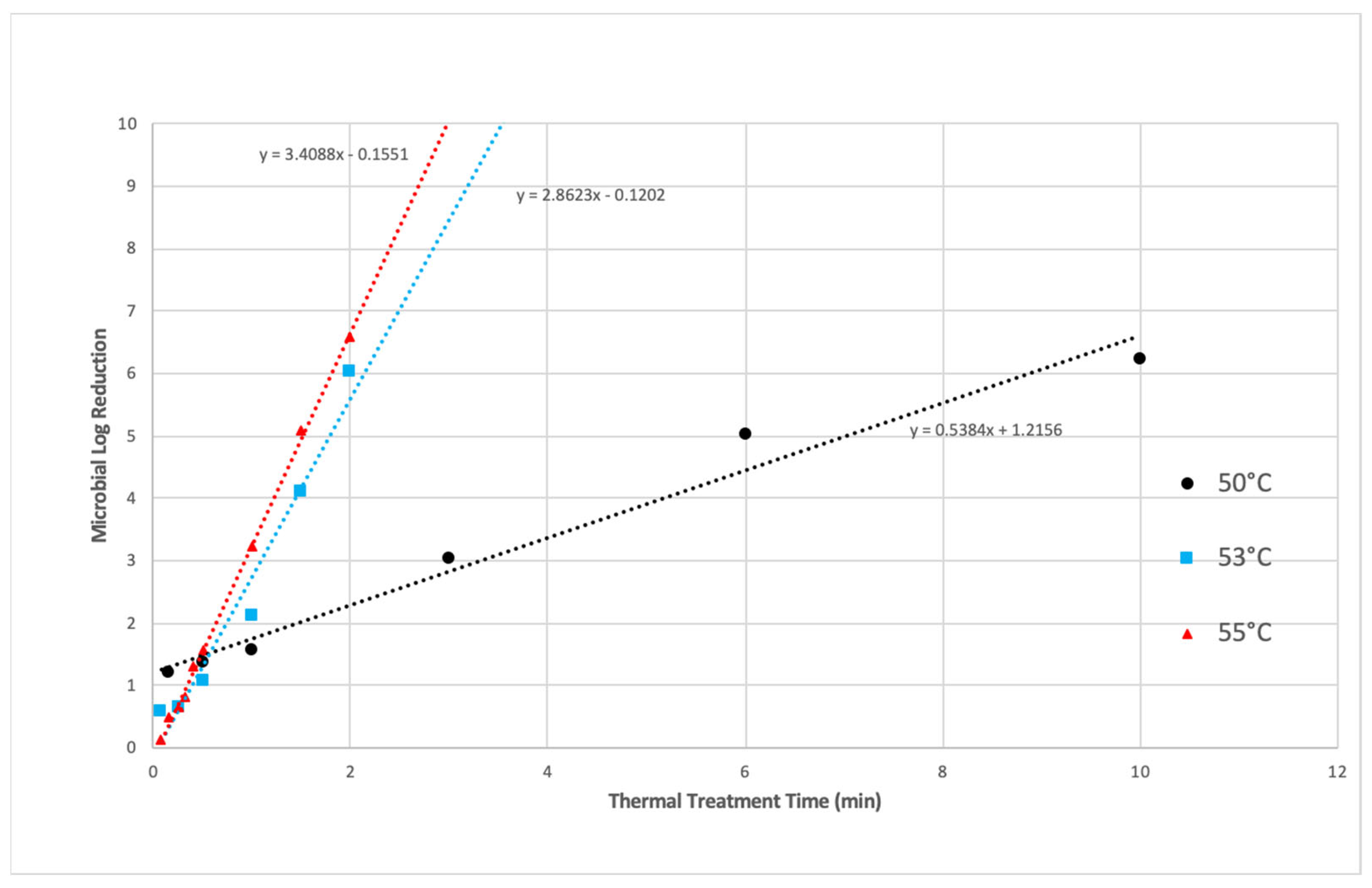
3.1.1. Thermal Inactivation
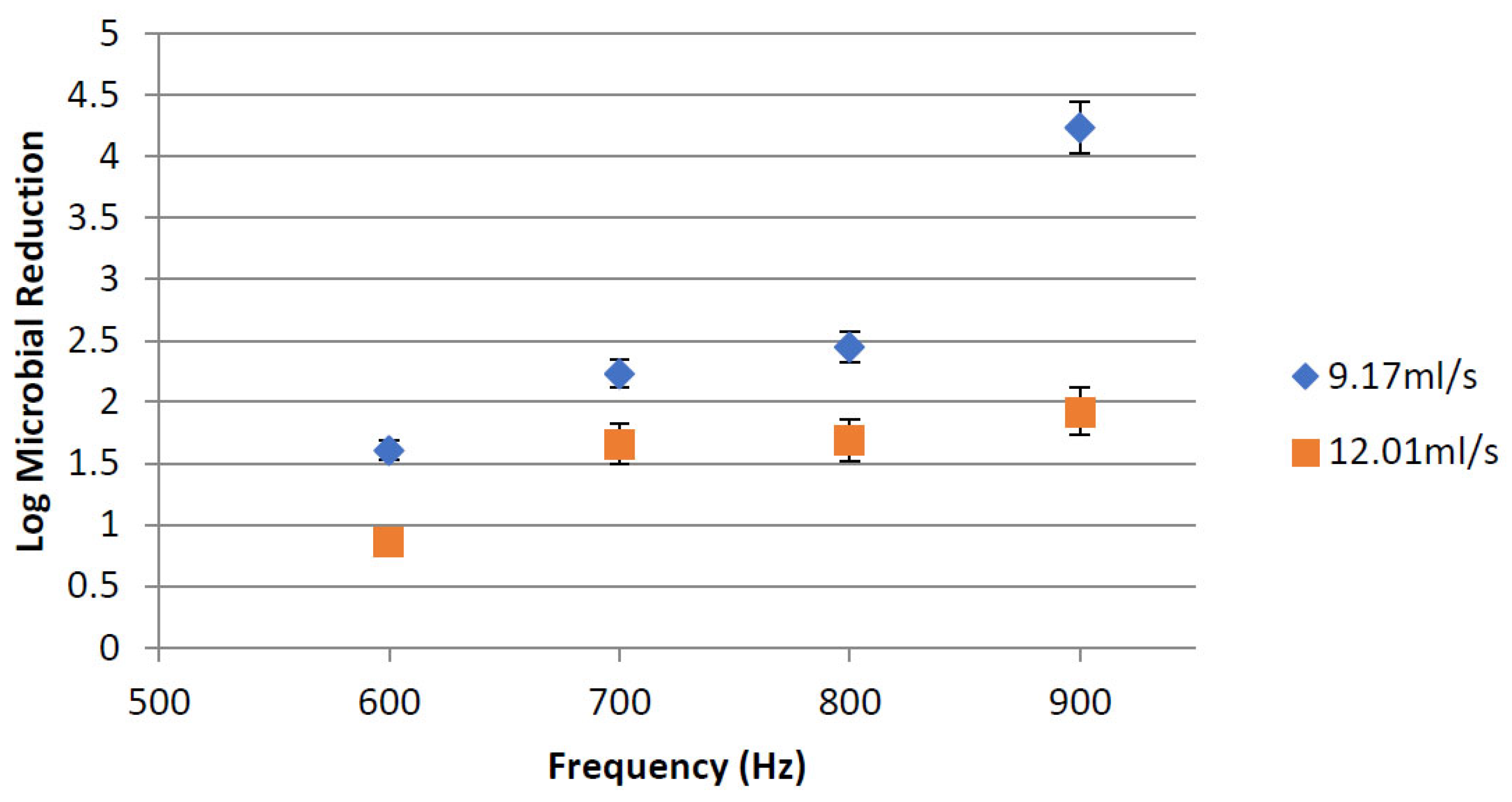
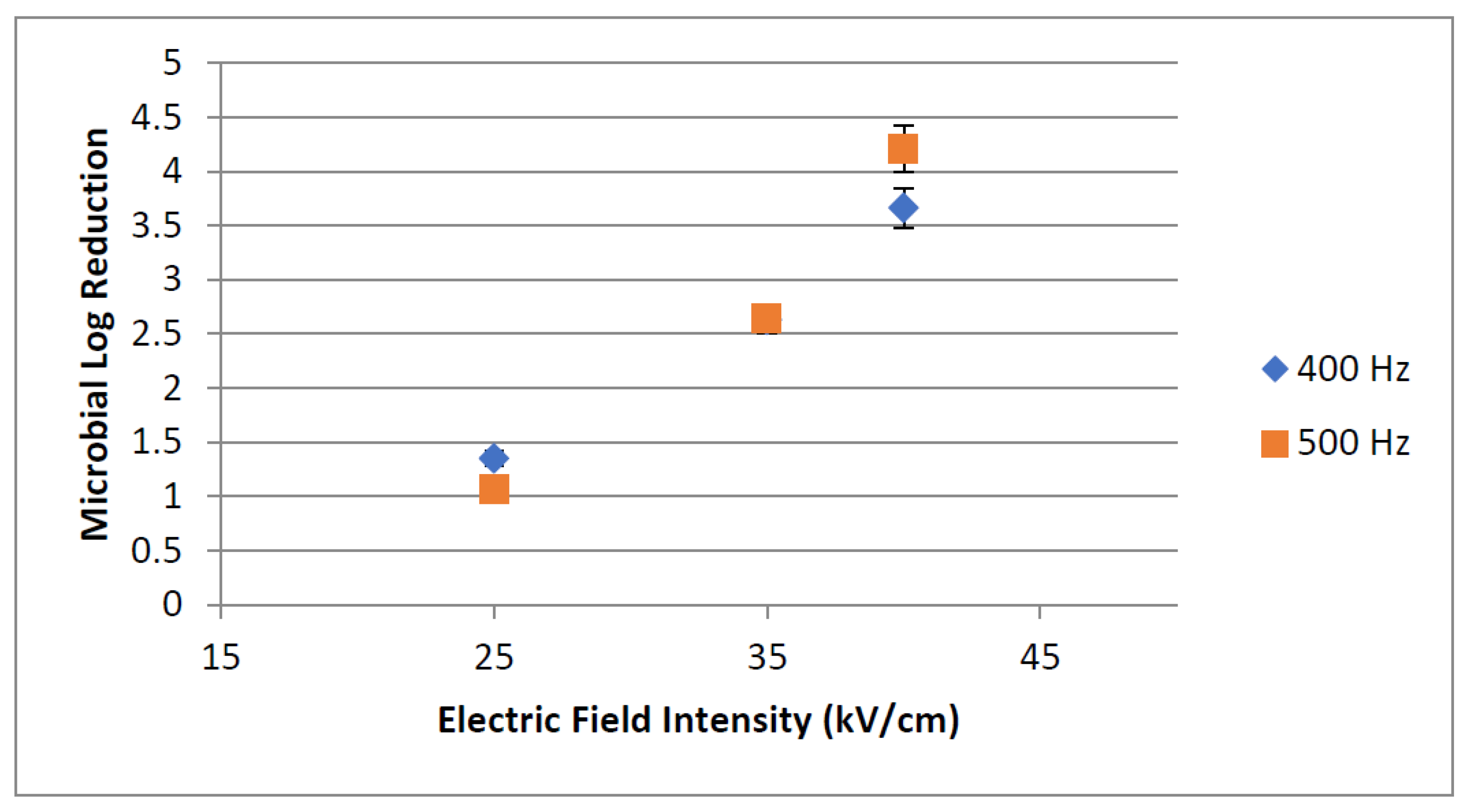
3.1.2. PEF Microbial Inactivation
Effect of Treatment Time Using Different Flow Rates and Frequencies
Effect of Electric Field Intensity
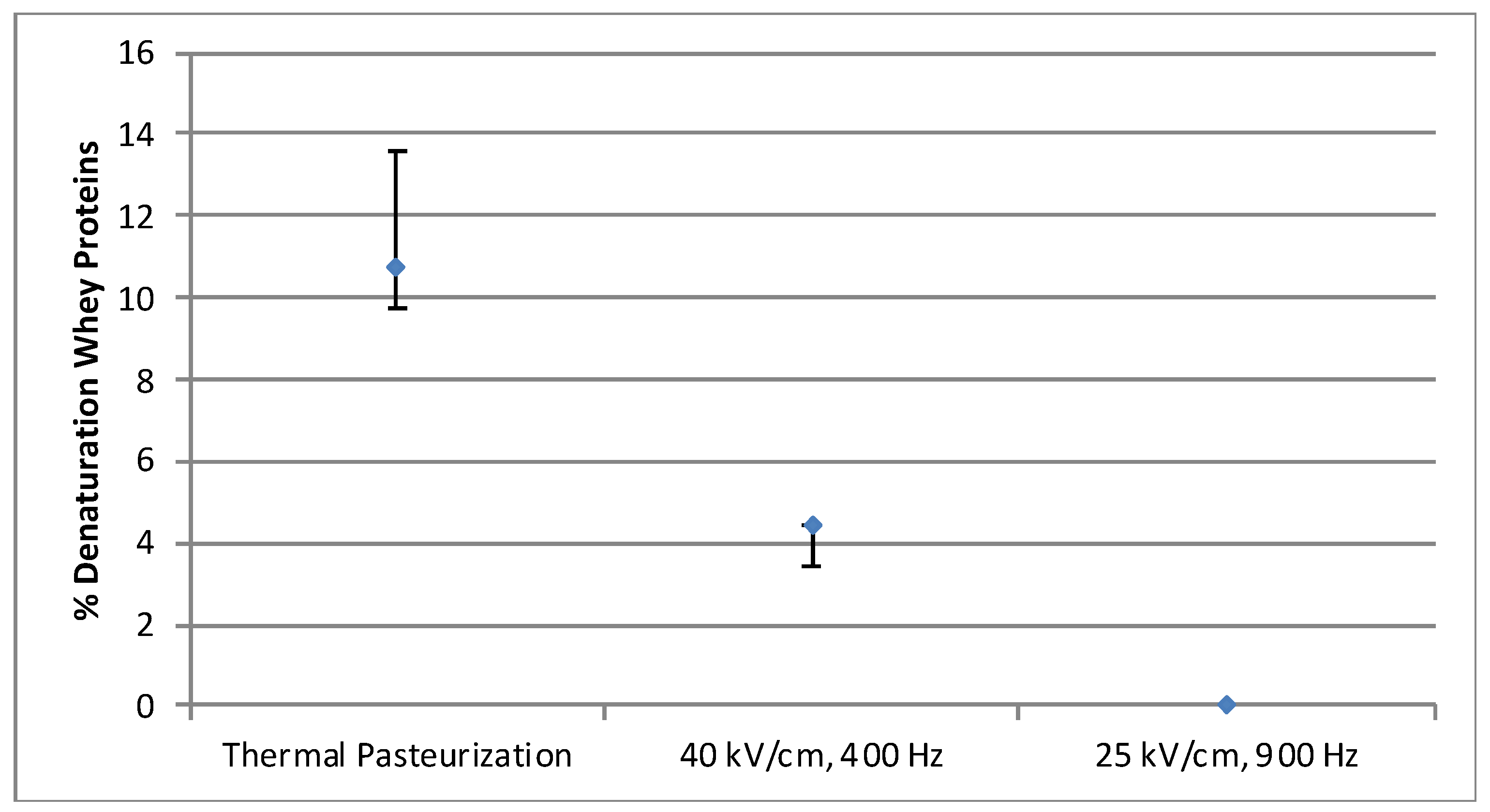
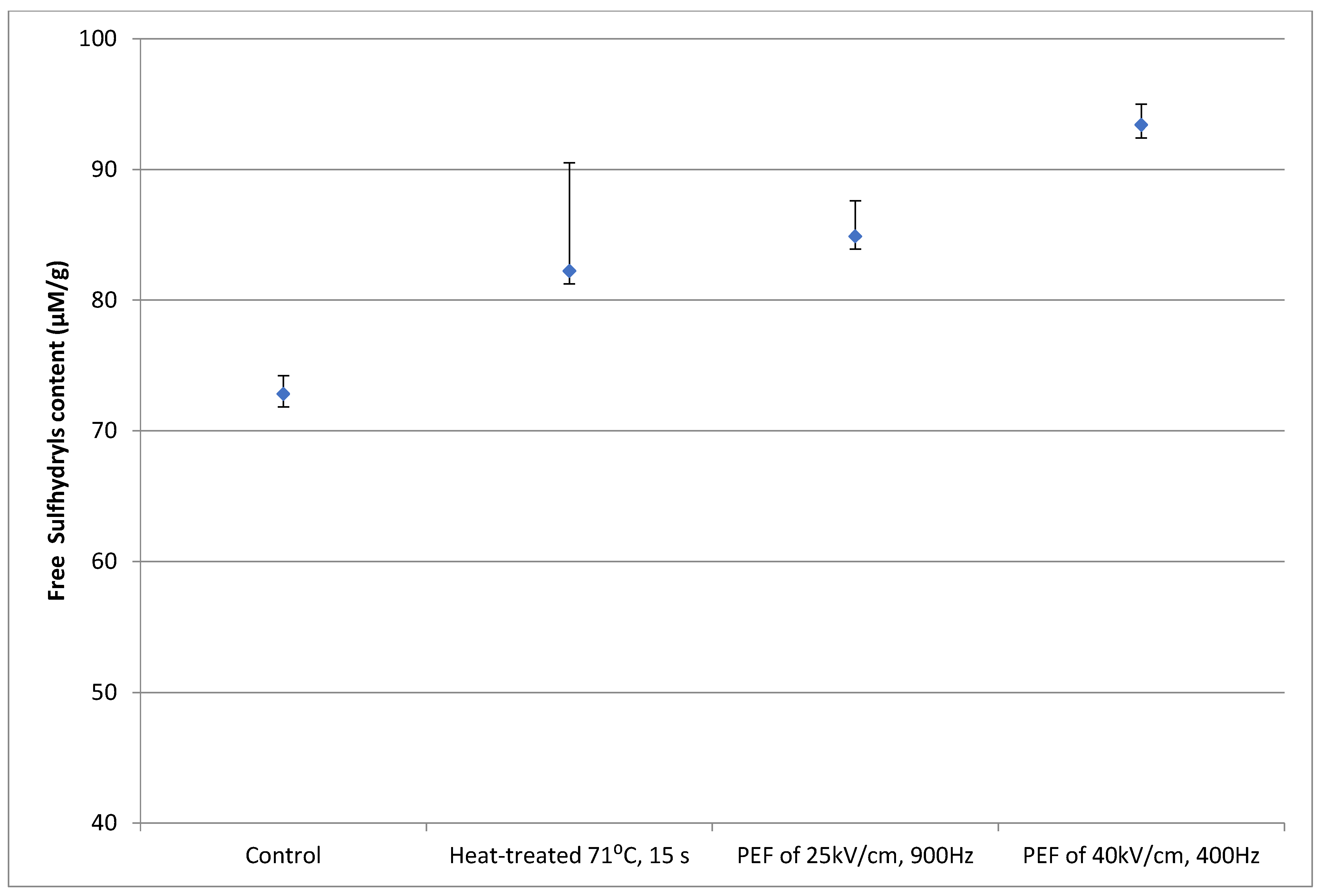
3.2. Protein denaturation
3.2.1. Whey Protein Solution
3.2.2. Soy Protein Solution
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Sepulveda, D. Present Status and the future of PEF Technology. In Novel Food Processing Technologies; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V., Tapia, M.S., Cano, M.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Gusbeth, C.; Frey, W.; Volkmann, H.; Schwartz, T.; Bluhm, H. Pulsed electric field treatment for bacteria reduction and its impact on hospital wastewater. Chemosphere 2009, 75, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monfort, S.; Gayán, E.; Saldaña, G.; Puértolas, E.; Condón, S.; Raso, J.; Álvarez, I. Inactivation of Salmonella Typhimurium and Staphylococcus aureus by pulsed electric fields in liquid whole egg. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, A.; Hamilton, W. Effects of high eletric fields on microorganisms. Lysis of erythrocytes and protoplasts. Biochemica. Biophysica. Acta 1968, 163, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, A.; Hamilton, W. Effects of high electric fields on microorganisms: Killing of bacteria and yeast. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1967, 148, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, J.E.; Pearlman, J.S. Methods and Apparatus for Extending the Shelf Life of Fluid Food Products. U.S. Patent No. 4,695,472, 22 September 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, R.P.; Murray, W. Pulsed High Electric Field Sterilization. In Proceedings of the 7th Pulsed Power Conference, Monterey, CA, USA, 11–14 June 1989; pp. 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Belloso, O.; Vega-Mercado, H.; Qin, B.L.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Inactivation of E. coli suspended in liquid egg using pulsed electric fields. J. Food Process. Preserv. 1997, 21, 193–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina, L.D.; Jin, Z.T.; Zhang, Q.H.; Yousef, A.E. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in milk by pulsed electric field. J. Food Prot. 1998, 61, 1203–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gongora-Nieto, M.M.; Seignour, L.; Riquet, P.; Davidson, P.M.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Hurdle Approach for the Inactivation of Pseudomonas Fluorescens in Liquid Whole Egg. In Proceedings of the IFT Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 22–26 June 1996; Insitute of Food Technologists: Chicago, IL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gongora-Nieto, M.M.; Seignour, L.; Riquet, P.; Davidson, P.M.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Nonthermal inactivation of Pseudomonas fluorescens in liquid whole egg. Pulsed Electr. Fields Food Process. Fundam. Asp. Appl. 2001, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Miranda, M.L.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Inactivation of Listeria innocua in liquid whole egg by pulsed electric fields and nisin. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1999, 51, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Molina, J.J.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Inactivation of Listeria innocua by Combining Pulsed Electric Fields and Acetic Acid In Skim Milk. In Proceedings of the IFT Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 22–26 June 1996; Insitute of Food Technologists: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Mañas, P.; Barsotti, L.; Cheftel, J.C. Microbial inactivation by pulsed electric fields in a batch treatment chamber: Effects of some electrical parameters and food constituents. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2000, 2, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Mittal, G.S.; Griffiths, M.W. Pasteurization of milk using pulsed electrical field and antimicrobials. J. Food Sci. 2002, 67, 2304–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiali, M.; Ngadi, M.O.; Smith, J.P.; Raghavan, V.G. Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157: H7 and Salmonella enteritidis in liquid egg white using pulsed electric field. J. Food Sci. 2006, 71, M88–M94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega-Mercado, H.; Gongora-Nieto, M.M.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Pulsed Electric Field in Food Preservation. In Handbook of Food Preservation; Rahman, M.S., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 783–813. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Diaz, M.D.; Barsotti, L.; Dumay, E.; Cheftel, J.C. Effects of pulsed electric fields on ovalbumin solutions and dialyzed egg white. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2332–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, O.E.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Structure/function modification of B-lactoglobulin and egg white proteins by pulsed electric field. Presented at the IFT Annual Meeting, New Orleans, LA, USA, 22–26 June 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Martin-Belloso, O.; Bendicho, S.; Elez-Martinez, P. Does High-Intensity Pulsed Electric Fields Induce Changes in Enzymatic Activity, Protein Conformation, and Vitamin and Flavor Stability. In Novel Food Processing Technologies; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V., Tapia, M.S., Cano, M.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Mañas, P.; Vercet, A. Effect of PEF on Enzymes and Food Constituents. In Pulsed Electric Fields Technology for the Food Industry: Fundamental and Applications; Raso, J., Heinz, V., Eds.; Springer Science and Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 131–149. [Google Scholar]
- Vanga, S.K.; Wang, J.; Jayaram, S.; Raghavan, V. Effects of Pulsed Electric Fields and Ultrasound Processing on Proteins and Enzymes: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA BIOHAZ Panel (EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards); Koutsoumanis, K.; Alvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Bolton, D.; Bover-Cid, S.; Chemaly, M.; Davies, R.; De Cesare, A.; Herman, L.; Hilbert, F.; et al. Scientific Opinion on the efficacy and safety of high-pressure processing of food. EFSA J. 2022, 20, 7128. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhafaji, S. An Investigation on the Non-Thermal Pasteurization Using Pulsed Electric Fields. Ph.D. Thesis, The University of Aucklan, Auckland, New Zealand, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Alkhafaji, S.R.; Farid, M. An investigation on pulsed electric fields technology using new treatment chamber design. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2007, 8, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothakamury, U.; Monsalve-Gonzalez, A.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.; Swanson, B. Inactivation of Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus in model foods by pulsed electric field technology. Food Res. Int. 1995, 28, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Zhang, Q.H.; Chism, G.W. Development of protein fortified fruit beverage and its quality when processed with pulsed electric field treatment. J. Food Qual. 1997, 21, 459–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Chem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar]
- Hollar, C.M.; Parris, N.; Hsieh, A.; Cockley, K.D. Factors affecting the denaturation and aggregation of whey proteins in heated whey protein concentrate mixtures. J. Dairy Sci. 1995, 78, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breveridge, T.; Toma, S.J.; Nakai, S. Determination of SH- and SS-groups in some food proteins using Ellman’s reagent. J. Food Sci. 1974, 39, 49–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Mo, H. Effects of pulsed electric fields on physiochemical properties of soybean protein isolates. Swiss Soc. Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 1167–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue sulfhydryl goups. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Ramaswamy, H.S. Evaluation of Phosphatase Inactivation Kinetics in Milk Under Continuous Flow Microwave and Conventional Heating Conditions. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeantet, R.; Baron, F.; Nau, F.; Roignant, M.; Brule, G. High intensity pulsed electric fields applied to egg white: Effect on Salmonella enteritidis inactivation and protein denaturation. J. Food Prot. 1999, 62, 1381–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulsheger, H.; Pottel, J.; Niemann, E. Killing of bacteria with electric pulses of high field strength. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 1981, 20, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, A.; Hori, Y. Destruction of living cells by pulsed high-voltage application. IEEE Trans. Ind. Gen. Appl. 1988, 24, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.L.; Pothakamury, U.R.; Vega-Mercado, H.; Martin-Belloso, O.M.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.V.; Swanson, B.G. Food pasteurization using high-intensity pulsed electric field. Food Technol. 1995, 12, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Grahl, T.; Markl, H. Killing of microorganisms by pulsed electric fields. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1996, 45, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothakamury, U.; Vega, H.; Zhang, Q.; Barbosa-Canovas, G.; Swanson, B. Effect of growth stage and processing temperature on the inactivation of Escherichia coli by pulsed electric fields. J. Food Prot. 1996, 59, 1167–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sensoy, I.; Zhang, Q.; Sastry, S. Inactivation kinetics of Salmonella dublin by pulsed electric field. J. Food Process. Eng. 1997, 20, 367–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, V.; Phillips, S.T.; Zenker, M.; Knorr, D. Inactivation of Bacillus subtilis by high-intensity pulsed electric fields under close to isothermal conditions. J. Food Biotechnol. 1999, 13, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, B.Y.; Sundararajan, S.; Mis Solval, K.; Espinoza-Rodezno, L.; Aryana, K.; Sathivel, S. Effects of pulsed electric fields and thermal pasteurization on physiochemical and quality properties of carrot juice. J. Food Qual. 2013, 38, 1556–1564. [Google Scholar]
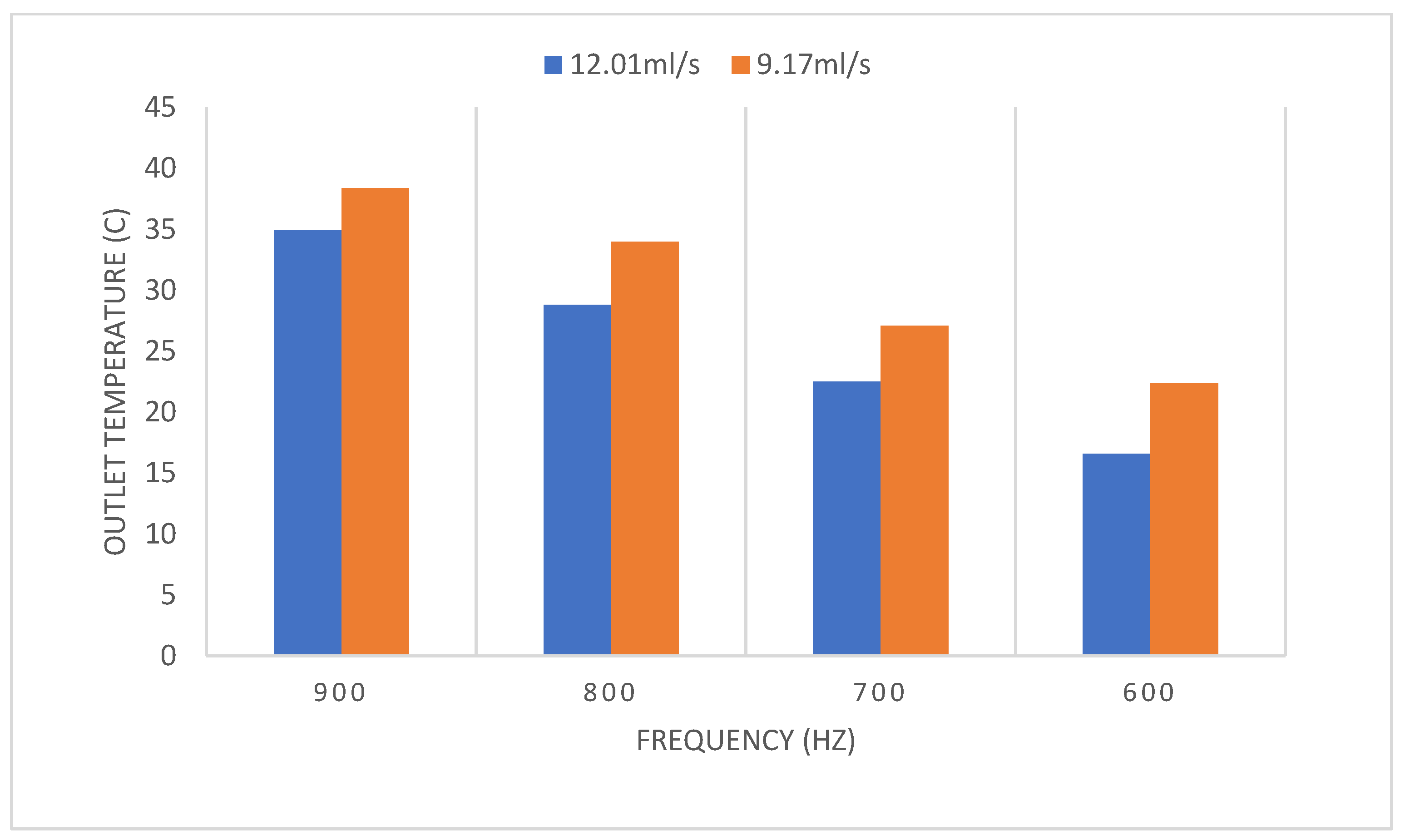
| Energy | 570 kJ (136 cal) |
| Protein | 17.5 g |
| Fat total | 1.1 g |
| Saturated | 0.5 g |
| Carbohydrates total | 14 g |
| Sugars | 12 g |
| Na | 223 mg |
| K | 558 mg |
| Ca | 426 mg |
| Fiber | 0.6 g |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alzahrani, M.; Silva, F.V.M.; Alkhafaji, S. Non-Thermal Processing of a Protein Functional Beverage Using Pulsed Electric Fields: Escherichia coli Inactivation and Effect on Proteins. Beverages 2022, 8, 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8040068
Alzahrani M, Silva FVM, Alkhafaji S. Non-Thermal Processing of a Protein Functional Beverage Using Pulsed Electric Fields: Escherichia coli Inactivation and Effect on Proteins. Beverages. 2022; 8(4):68. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8040068
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlzahrani, Mona, Filipa V. M. Silva, and Sally Alkhafaji. 2022. "Non-Thermal Processing of a Protein Functional Beverage Using Pulsed Electric Fields: Escherichia coli Inactivation and Effect on Proteins" Beverages 8, no. 4: 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8040068
APA StyleAlzahrani, M., Silva, F. V. M., & Alkhafaji, S. (2022). Non-Thermal Processing of a Protein Functional Beverage Using Pulsed Electric Fields: Escherichia coli Inactivation and Effect on Proteins. Beverages, 8(4), 68. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8040068








