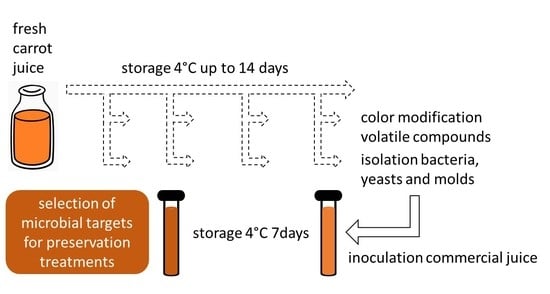
Selection of Microbial Targets for Treatments to Preserve Fresh Carrot Juice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Carrot Sampling and Processing
2.2. Physicochemical Analyses
2.3. Total Carotenoid Content
2.4. Analysis of Volatile Compounds
2.5. Microbiological Counts
2.6. Isolation and Indentification of Isolates
2.6.1. Isolation of Bacteria and PCR
2.6.2. Isolation of Fungi and PCR
2.6.3. Analysis of PCR Products
2.7. Determination of Spoilage Capacity of Isolates
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
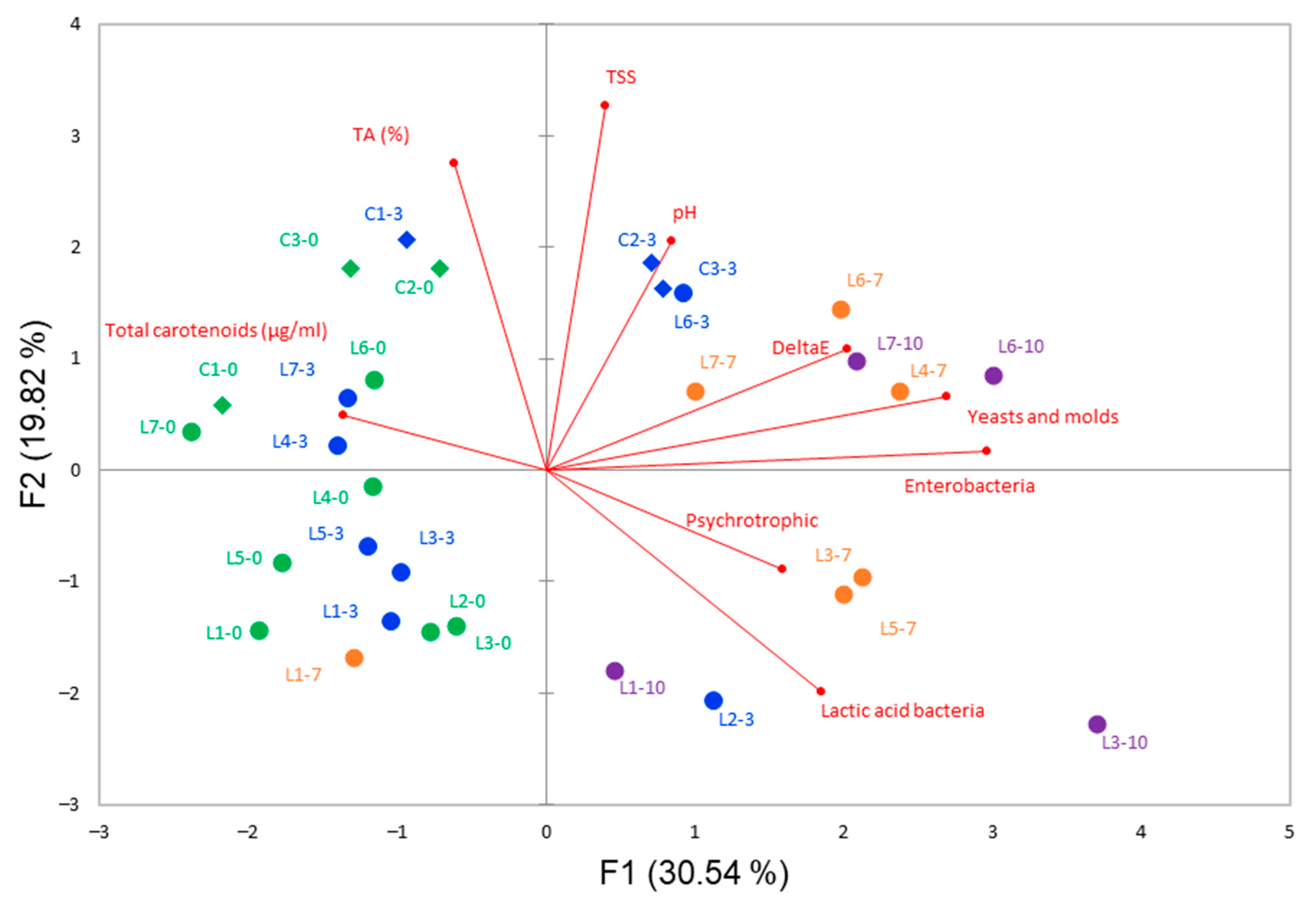
3.1. Initial Characteristics of Carrot Juices and Changes during Storage
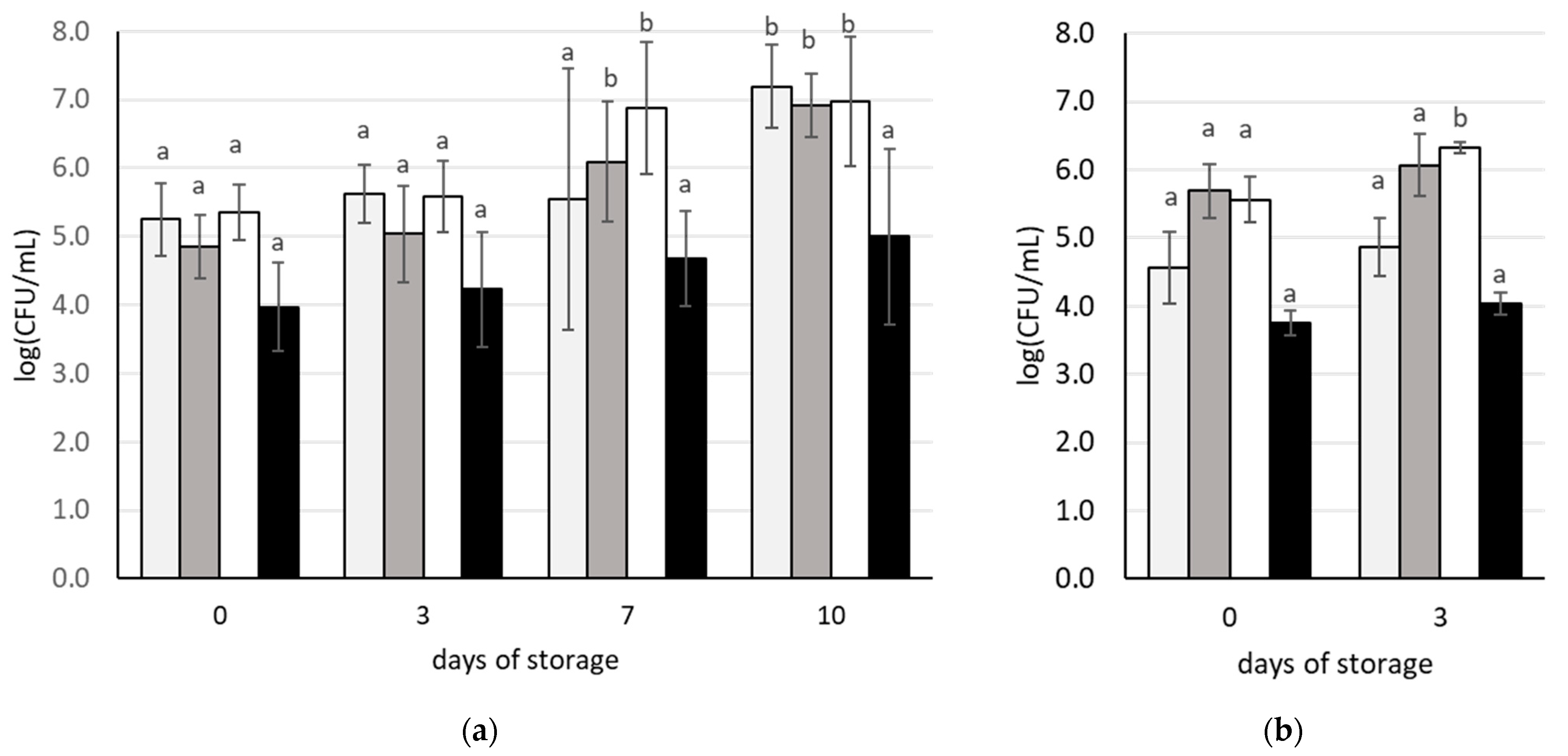
3.2. Changes in Microbial Populations during Storage of Carrot Juices
3.3. Changes in Volatile Compounds during Storage of Carrot Juices
3.4. Isolation, Identification and Characterization of Spoilage Potential of Bacteria and Fungi
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, K.D.; Karki, S.; Thakur, N.S.; Attri, S. Chemical Composition, Functional Properties and Processing of Carrot—A Review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 49, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammad, A.A.; Abd El-Khalek, H.H.; Youssef, K.A.; Abd El-Kader, R.M. Microbiological, Nutritional and Sensorial Changes in Fresh Carrot Juice Preserved by Irradiation. Hammad 2013, 11, 2224–6088. [Google Scholar]
- Riganakos, K.A.; Karabagias, I.K.; Gertzou, I.; Stahl, M. Comparison of UV-C and Thermal Treatments for the Preservation of Carrot Juice. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 42, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, M.F.; McKay, A.M.; Connolly, M.; Linton, M. The Effect of High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Microbiological Quality and Safety of Carrot Juice during Refrigerated Storage. Food Microbiol. 2012, 30, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouma, M.; Álvarez, I.; Condón, S.; Gayán, E. Pasteurization of Carrot Juice by Combining UV-C and Mild Heat: Impact on Shelf-Life and Quality Compared to Conventional Thermal Treatment. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2020, 64, 102362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Flores, H.E.; Garnica-Romo, M.G.; Bermúdez-Aguirre, D.; Pokhrel, P.R.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Physico-Chemical Parameters, Bioactive Compounds and Microbial Quality of Thermo-Sonicated Carrot Juice during Storage. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 650–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aneja, K.R.; Dhiman, R.; Aggarwal, N.K.; Kumar, V.; Kaur, M. Microbes Associated with Freshly Prepared Juices of Citrus and Carrots. Int. J. Food Sci. 2014, 2014, 408085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García Carrillo, M.; Ferrario, M.; Guerrero, S. Study of the Inactivation of Some Microorganisms in Turbid Carrot-Orange Juice Blend Processed by Ultraviolet Light Assisted by Mild Heat Treatment. J. Food Eng. 2017, 212, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jin, X.; Feng, X.; Yang, H.; Fu, C. Inactivation Kinetics of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium on Organic Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Treated with Low Concentration Electrolyzed Water Combined with Short-Time Heat Treatment. Food Control 2019, 106, 106702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. Antimicrobial Mechanism of Pulsed Light for the Control of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Its Application in Carrot Juice. Food Control 2019, 106, 106751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xylia, P.; Chrysargyris, A.; Botsaris, G.; Tzortzakis, N. Mint and Pomegranate Extracts/Oils as Antibacterial Agents against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Listeria monocytogenes on Shredded Carrots. J. Food Saf. 2018, 38, e12423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokhrel, P.R.; Toniazzo, T.; Boulet, C.; Oner, M.E.; Sablani, S.S.; Tang, J.; Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V. Inactivation of Listeria innocua and Escherichia coli in Carrot Juice by Combining High Pressure Processing, Nisin, and Mild Thermal Treatments. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2019, 54, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratphitagsanti, W.; De Lamo-Castellvi, S.; Balasubramaniam, V.M.; Yousef, A.E. Efficacy of Pressure-Assisted Thermal Processing, in Combination with Organic Acids, against Bacillus amyloliquefaciens Spores Suspended in Deionized Water and Carrot Puree. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, M46–M52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tola, Y.B.; Ramaswamy, H.S. Combined Effects of High Pressure, Moderate Heat and pH on the Inactivation Kinetics of Bacillus licheniformis Spores in Carrot Juice. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K.; Buschmann, C. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Measurement and Characterization by UV-VIS Spectroscopy. Curr. Protoc. Food Anal. Chem. 2001, 1, F4.3.1–F4.3.8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S Ribosomal DNA Amplification for Phylogenetic Study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fessard, A.; Bourdon, E.; Payet, B.; Remize, F. Identification, Stress Tolerance, and Antioxidant Activity of Lactic Acid Bacteria Isolated from Tropically Grown Fruits and Leaves. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016, 62, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardes, M.; Bruns, T.D. ITS Primers with Enhanced Specificity for Basidiomycetes–Application to the Identification of Mycorrhizae and Rusts. Mol. Ecol. 1993, 2, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Lee, D.K. What is the Proper Way to Apply the Multiple Comparison Test? Korean J. Anesth. 2018, 71, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wuyts, S.; Van Beeck, W.; Oerlemans, E.F.M.; Wittouck, S.; Claes, I.J.J.; De Boeck, I.; Weckx, S.; Lievens, B.; De Vuyst, L.; Lebeer, S. Carrot Juice Fermentations as Man-Made Microbial Ecosystems Dominated by Lactic Acid Bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00134-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moreira, S.A.; Pintado, M.E.; Saraiva, J.A. Effect of a Winter Savory Leaf Extract Obtained Using High Hydrostatic Pressure on the Quality of Carrot Juice. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demir, N.; Acar, J.; Bahceci, K.S. Effects of Storage on Quality of Carrot Juices Produced with Lactofermentation and Acidification. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2004, 218, 465–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokrzycki, W.S.; Tatol, M. Colour Difference DELTA(E)—A Survey. MG&V 2011, 20, 383–411. [Google Scholar]
- Umair, M.; Jabbar, S.; Nasiru, M.M.; Senan, A.M.; Zhuang, H.; Zhang, J. Sequential Application of High-Voltage Electric Field Cold Plasma Treatment and Acid Blanching Improves the Quality of Fresh Carrot Juice (Daucus carota L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020, 68, 15311–15318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, F.; Christensen, L.P.; Edelenbos, M. Quantitative Analysis of Aroma Compounds in Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Cultivars by Capillary Gas Chromatography Using Large-Volume Injection Technique. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2001, 49, 4342–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchlinski, A.; Ibdah, M.; Ellison, S.; Yahyaa, M.; Nawade, B.; Laliberte, S.; Senalik, D.; Simon, P.; Whitehead, S.R.; Tholl, D. Diversity and Function of Terpene Synthases in the Production of Carrot Aroma and Flavor Compounds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, H.; Hu, Q.; Wang, L.; Pei, F.; Mariga, A.M.; Yang, W. Exogenous Bacterial Composition Changes Dominate Flavor Deterioration of Dried Carrots during Storage. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 134, 110833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, I.C.; dos Reis, K.C.; Menezes, E.G.T.; Borges, P.R.S.; Rodrigues, A.C.; Leal, R.; Hernandes, T.; de Carvalho, E.H.N.; Vilas Boas, E.V.D.B. Combined Effect of Starch/Montmorillonite Coating and Passive MAP in Antioxidant Activity, Total Phenolics, Organic Acids and Volatile of Fresh-Cut Carrots. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 67, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nsogning Dongmo, S.; Sacher, B.; Kollmannsberger, H.; Becker, T. Key Volatile Aroma Compounds of Lactic Acid Fermented Malt Based Beverages–Impact of Lactic Acid Bacteria Strains. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 565–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kachalkin, A.V.; Glushakova, A.M.; Venzhik, A.S. Presence of Clinically Significant Endophytic Yeasts in Agricultural Crops: Monitoring and Ecological Safety Assessment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 723, 042005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumby, K.M.; Caliani, N.S.; Jiranek, V. Yeast Diversity in the Vineyard: How It Is Defined, Measured and Influenced by Fungicides. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2021, 27, 169–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gientka, I.; Bzducha-Wróbel, A.; Stasiak-Różańska, L.; Bednarska, A.A.; Błażejak, S. The Exopolysaccharides Biosynthesis by Candida Yeast Depends on Carbon Sources. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 22, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grijseels, S.; Nielsen, J.C.; Nielsen, J.; Larsen, T.O.; Frisvad, J.C.; Nielsen, K.F.; Frandsen, R.J.N.; Workman, M. Physiological Characterization of Secondary Metabolite Producing Penicillium Cell Factories. Fungal Biol. Biotechnol. 2017, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ragaert, P.; Devlieghere, F.; Devuyst, E.; Dewulf, J.; Van Langenhove, H.; Debevere, J. Volatile Metabolite Production of Spoilage Micro-Organisms on a Mixed-Lettuce Agar during Storage at 7 °C in Air and Low Oxygen Atmosphere. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2006, 112, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löser, C.; Urit, T.; Bley, T. Perspectives for the Biotechnological Production of Ethyl Acetate by Yeasts. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5397–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Batch | Day | pH | TA (%) | TSS (°Brix) | TCC (µg/mL) | L* | a* | b* | ΔE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lab-made (n = 7) | 0 | 6.2 ± 0.4 a | 2.8 ± 0.2 b | 8.8 ± 0.7 b | 3.4 ± 1.2 a | 26.1 ± 7.5 a | 32.7 ± 5.3 a | 28.6 ± 6.2 a | 0 c |
| Company (n = 3) | 0 | 6.0 ± 0.4 a | 3.2 ± 0.1 a | 9.7 ± 0.1 a | 4.3 ± 1.3 a | 32.4 ± 3.7 a | 29.4 ± 7.7 a | 27.2 ± 5.3 a | 0 c |
| Lab-made (n = 7) | 3 | 6.1 ± 0.6 a | 2.8 ± 0.1 b | 9.0 ± 0.5 b | 3.8 ± 0.8 a | 26.0 ± 7.9 a | 31.8 ± 5.0 a | 31.6 ± 6.4 a | 5.5 ± 5.0 b |
| Company (n = 3) | 3 | 6.1 ± 0.1 a | 3.3 ± 0.1 a | 9.7 ± 0.1 a | 3.1 ± 3.0 a | 31.7 ± 2.0 a | 28.9 ± 6.8 a | 27.6 ± 4.9 a | 5.8 ± 1.4 ab |
| Lab-made (n = 7) | 7 | 6.2 ± 0.6 a | 2.8 ± 0.2 b | 8.9 ± 0.5 b | 3.2 ± 1.1 a | 27.2 ± 8.0 a | 29.4 ± 8.5 a | 29.1 ± 7.6 a | 7.1 ± 5.6 ab |
| Lab-made (n = 5) | 10 | 6.3 ± 0.3 a | 2.8 ± 0.2 b | 8.8 ± 0.6 b | 3.0 ± 1.1 a | 30.6 ± 10.4 a | 32.5 ± 2.9 a | 30.6 ± 1.7 a | 6.5 ± 2.8 ab |
| Lab-made (n = 4) | 14 | 6.2 ± 0.3 a | 2.8 ± 0.2 b | 8.9 ± 0.7 b | 2.8 ± 0.9 a | 25.2 ± 12.4 a | 29.1 ± 3.2 a | 31.2 ± 3.4 a | 11.5 ± 3.9 a |
| Volatile Compound (RI, CAS Number) * | Batch L1 | Batch L2 | Batch L3 | Batch L4 | Flavor Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| o-cymene (1287, 527-84-4) | H ** | H | H 0.002 ▼ (−42%) D10 | H 0.012 ≈ | citrus |
| α-pinene (1033, 80-56-8) | H | H < 0.0001 ▲ (+58%) D10 | H 0.004 ▼ (−27%) D10 | H 0.001 ▲ (+81%) D10 | pine, turpentine |
| p-cymene (1269, 99-87-6) | M 0.014 ≈ | H 0.027 ≈ | H 0.039 ≈ | H 0.002 ≈ | citrus, solvent |
| β-pinene (1101, 127-91-3) | M 0.037 ≈ | M 0.0002 ▲ (+73%) D14 | M 0.003 ▼ (−34%) D10 | M 0.002 ▲ (+62%) D10 | pine, resin |
| (R)-1-methyl-5-(1-methylvinyl)cyclohexene (1193, 1461-27-4) | M | M | M | M | - |
| trans-γ-bisabolene (1751, 53585-13-0) | M 0.016 ≈ | M | M 0.005 ≈ | M 0.09 ≈ | soap, spicy |
| m-cymene (1238, 535-77-3) | M 0.003 ≈ | M 0.010 ≈ | M 0.003 ▼ (−29%) D10 | M 0.016 ≈ | - |
| β-myrcene (1150, 123-35-3) | L | L | L 0.008 ▼(−36%) D10 | M 0.010 ≈ | spicy, plastic |
| sabinene (1123, 3387-41-5) | M 0.024 ▼ (−93%) D14 | M 0.014 ≈ | L 0.009 ▼ (−45%) D14 | L 0.002 ≈ | pepper, turpentine |
| cis-γ-bisabolene (1743, 13062-00-5) | L | L | L | M | fat, wood |
| caryophyllene (1653, 13877-93-5) | L 0.036 ≈ | L | L | M | spicy, clove |
| 1,3,8-p-menthatriene (1457, 18368-95-1) | L | L < 0.0001 ▼ (−45%) D10 | L 0.007 ▼ (−47%) D10 | L 0.002 ▼ (−53%) D7 | turpentine, woody |
| β-thujene (1119, 28634-89-1) | L | L | L 0.017 ≈ | L | - |
| α-phellandrene (1165, 99-83-2) | L | L 0.048 ≈ | L | L | turpentine, mint |
| 3-carene (1143, 13466-78-9) | L 0.004 ▲ (+440%) D14 | L | L | L | lemon, resin |
| carveol (1756, 99-48-9) | L 0.039 ▼ (−73%) D14 | L 0.048 ≈ | L 0.032 ▲ (+140%) D7 | L 0.001 ≈ | fresh, spearmint |
| isocaryophyllene (1616, 118-65-0) | L | L | L 0.022 ▲ (not detected at D0) D14 | L < 0.0001 ▲ (not detected at D0) D10 | wood |
| p-cymenene (1475, 100-42-5) | L 0.042 ≈ | L < 0.0001 ▼ (−40%) D10 | L 0.018 ≈ | L 0.004 ≈ | balsamic, gasoline |
| tert-butyl benzene (1236, 98-06-6) | L | L 0.007 ≈ | L 0.0001 ▼ (−71%) D14 | L < 0.0001 ≈ | - |
| 2-methoxyphenol (1885, 90-05-1) | L < 0.0001 ≈ | L < 0.0001 ▲ (not detected D0) D7 | L < 0.0001 ▲ (+9152%) D10 | L < 0.0001 ▲ (+456%) D14 | smoke, medicine |
| ethanol (1006, 64-17-5) | L < 0.001 ▲ (+162%) D14 | M < 0.0001 ▼ (−35%) D10 | L | H < 0.0001 ▲ (+4057%) D7 | sweet |
| ethyl acetate (989, 141-78-6) | L 0.004 ▲ (+92%) D10 | L < 0.0001 ▲ (+1600%) D7 | L < 0.0001 ▲ (+783%) D14 | L | pineapple, ether |
| acetic acid (1509, 64-19-7) | L 0.020 ▼ (−99%) D7 | L | L 0.005 ▼ (−65%) D7 | L 0.027 ▼ (−58%) D14 | sour |
| 2-butenal (1051, 4170-30-3) | L 0.001 ▼ (+72%) D14 | L < 0.0001 ≈ | L < 0.0001 ≈ | L 0.028 ≈ | - |
| hexanal (1089, 66-25-1) | L 0.001 ≈ | L 0.025 ≈ | L < 0.0001▼ (−77%) D7 | L < 0.0001 ≈ | grass, tallow |
| 6-methyl, 5-hepten-2-one (1359, 110-93-0) | L 0.048 ≈ | L 0.027 ≈ | L 0.001 ▼ (−31%) D14 | L 0.041 ≈ | lemon, musty |
| α, α,4-trimethylbenzene methanol (1883, 1197-01-9) | L 0.013 ▼ (−99%) D14 | L 0.030 ≈ | L 0.014 ≈ | L < 0.0001▲ (+277%) D10 | cherry, camphor |
| Number of Isolates with Same Source and Same Effects on Juice | Isolation Source (Carrot) | Population Increase in Carrot Juice (log CFU/mL) | pH Value | Odor Modification | Isolate Reference and Bacterium Identification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A | N/A * | N/A | 4.42 | no | N/A (control not inoculated) |
| 6 | Surface before washing | 2.4–3.4 | 4.35–4.54 | yes | 49d04 Leuconostoc sp., 1a01 Pseudomonas sp., 2a02 Pseudomonas moraviensis, 52d07 Pseudomonas veronii, 25b10, 72e12 n.d. ** |
| 3 | Juice, day of preparation | 2.7–3.0 | 4.51–4.55 | no | 50d05 Pseudomonas putida, 4a04, 10a09 n.d. |
| 21 | Juice, day of preparation | 2.6–3.4 | 4.35–4.54 | yes | 56d09 Enterobacteriaceae, 31c02 and 70e10 Leuconostoc citreum, 57d10 and 43c10 Leuconostoc mesenteroides, 30c01 Leuconostoc miyukkimchii, 37c07 Pseudomonas fluorescens, 7a07 Pseudomonas fragi, 46d02 and 3a03 P. moraviensis, 34c05 P. veronii, 35c06, 5a05, 6a06, 20b05, 73f01, 38c08, 32c03, 33c04, 26b11 and 15a12 n.d. |
| 2 | Juice, stored for 3 days | 2.8–3.0 | 4.37–4.51 | no | 51d06 and 22b07 Pseudomonas sp. |
| 15 | Juice, stored for 3 days | 2.4–3.4 | 4.35–4.51 | yes | 11a10 Enterobacteriaceae, 24b09 Erwinia sp., 74f02 L. citreum, 44c11 P. fluorescens, 42c09 Pseudomonas libanensis, 39c12 L. miyukkimchi, 45d01 Pseudomonas protegens, 65e05, 18b03, 71e11, 61e01, 19b04, 47d03, 62e02 and 21b06 n.d. |
| 9 | Juice, stored for 7 days | 2.5–3.3 | 4.40–4.51 | yes | 63e03 Enterobacteriaceae, 55d08 Leclercia sp., 8a08, 16b01, 66e06, 38e08, 67e07, 13a11 and 27b12 n.d. |
| 1 | Juice, stored for 10 days | 3.1 | 4.40 | no | 64e04 n.d. |
| 2 | Juice, stored for 10 days | 3.0–3.1 | 4.42–4.46 | yes | 69e09 Weissella soli, 23b08 n.d. |
| 3 | Juice, stored for 14 days | 3.0–3.4 | 4.40–4.45 | yes | 59d12 L. mesenteroides, 17b02 Pseudomonas sp., 58d11 n.d. |
| Isolate Reference and Identification | Isolation from Carrot Juice: Time after Preparation | Growth in Carrot Juice * | pH Value | Texture Modification | Gas Production | Color Difference to Day 0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N/A ** (control not inoculated) | N/A | N/A | 4.6 | no | no | 0.5 |
| 6A6 Debaryomyces hansenii | Day 0 | +/− | 4.4 | no | no | n.d. *** |
| 26C1 Didymella sp./Phoma sp. | Day 0 | +/− | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| 28C3 Didymella sp./Phoma sp. | Day 0 | - | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| 30C5 Didymella sp./Phoma sp. | Day 0 | + | 4.4 | no | no | n.d. |
| 4A4 Talaromyces funiculosus | Day 0 | + | 4.4 | no | no | n.d. |
| 5A5 Talaromyces sp. | Day 0 | + | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| U Debaryomyces hansenii | Day 3 | +/− | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| 25B12 Papiliotrema flavescens | Day 3 | - | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| 29C4 Rhodotorula mucilaginosa | Day 3 | + | 4.3 | no | yes | n.d. |
| 33C8 Candida sp. | Day 7 | + | 4.3 | no | no | n.d. |
| 32C7 Cladosporium sp. | Day 7 | + | 4.3 | no | no | n.d. |
| 34C9 Cladosporium sp. | Day 7 | + | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| 37C11 Penicillium sp. | Day 7 | + | 4.5 | no | yes | 2.3 |
| 13B1 Hanseniasopra uvarum | Day 7 | +/− | 4.5 | no | no | n.d. |
| 36 Meyerozyma guillermondii | Day 7 | + | 4.3 | yes | no | 0.3 |
| 35C10 Penicillium sp. | Day 7 | + | 4.4 | no | yes | n.d. |
| 31C6 Pichia fermentans | Day 7 | + | 4.3 | no | yes | n.d. |
| 39D1 P. fermentans | Day 7 | + | 4.3 | no | yes | 3.1 |
| 40D2 P. fermentans | Day 7 | + | 4.4 | no | no | n.d. |
| Mix 36 + 37C11 + 39D1 | N/A | + | 4.3 | n.d. | yes | 1.9 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leneveu-Jenvrin, C.; Quentin, B.; Messaaf, F.-E.; Hoarau, M.; Lebrun, M.; Remize, F. Selection of Microbial Targets for Treatments to Preserve Fresh Carrot Juice. Beverages 2022, 8, 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010017
Leneveu-Jenvrin C, Quentin B, Messaaf F-E, Hoarau M, Lebrun M, Remize F. Selection of Microbial Targets for Treatments to Preserve Fresh Carrot Juice. Beverages. 2022; 8(1):17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010017
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeneveu-Jenvrin, Charlène, Baptiste Quentin, Fatima-Ezzahra Messaaf, Mathilde Hoarau, Marc Lebrun, and Fabienne Remize. 2022. "Selection of Microbial Targets for Treatments to Preserve Fresh Carrot Juice" Beverages 8, no. 1: 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010017
APA StyleLeneveu-Jenvrin, C., Quentin, B., Messaaf, F.-E., Hoarau, M., Lebrun, M., & Remize, F. (2022). Selection of Microbial Targets for Treatments to Preserve Fresh Carrot Juice. Beverages, 8(1), 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages8010017