Abstract
A simple and sensitive reduced graphene oxide-modified glassy carbon electrode-based electrochemical sensor was used for the concomitant determination of gallic acid (GA) and protocatechuic (PA) acid. The prepared sensor showed a significant enhancement in synergetic electro-catalytic performance towards GA and PA oxidation. A good resolution of the voltammetry peaks was obtained and a method of square wave voltammetry was developed for detection. The modified electrode was characterized by electrochemical techniques. The optimal experimental parameters were considered. GA and PA exhibited a linear increase in the peak currents with their concentrations in the range from 20 to 144 µmol·L−1 for GA and from 20 to 166 µmol·L−1 for PA, with limits of detection (S/N = 3) of 30.8 µmol·L−1 for GA and 10.2 µmol·L−1 for PA. The sensor applicability was simultaneously tested for the analytical determination of GA and PA in mango juice and exhibited a robust functionality.
1. Introduction
Gallic acid (GA, 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) and protocatechuic acid (PA, 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid), the most representative phenolic acids in fruits and vegetables, are strong antioxidants. They are present in a wide variety of fruits such as bananas, citrus fruits and mangoes as well as in green tea and several other plants. Recently, these phenolic acids have attracted great interest due to their scavenging ability against free radicals [1,2]. GA has received much attention because of its multiple biological and pharmaceutical properties, such as anti-inflammatory and antitumor activity, scavenging of free radicals and protection against cardiovascular diseases [3]. GA is mostly utilized in tanning, ink dyes, the manufacturing of paper, in the food industry, and in the drug trimethoprim in the pharmaceutical industry [4]. Therefore, the accurate determination of GA is a very important concern for human health. To date, many methods have been developed for the determination of GA, such as flow injection analysis [5], resonance light scattering [6], reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) [7], high-pressure liquid chromatography coupled with quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC–ESI–QTOF–MS/MS) [2] electrochemical sensors and nano-structured sensors [1,8,9,10]. Among these, electrochemical methods have received much attention lately, mainly due to their sensitivity, selectivity and simplicity.
Protocatechuic acid (3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid, as the naturally occurring phenolic acid) is widely present in nearly all plants. PA is found in Spanish heath, dog rose, Korean spruce, gum-tree, the traditional Chinese medicine herb shensi, ferns, buckwheat, alder, onions, garlics and relatives, and Japanese peppers [11]. It is also found in pigmented onion scales [12], carrots, and mushrooms [13]. PA derivatives have potential antioxidant activity [14]. PA has been found to have several bioactivities such as antifungal, antihepatotoxic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant [15], antibacterial [16], antidiabetic [17], anticancer [18], and antifibrotic [19] activities. Furthermore, it was found to be potent against avian influenza virus H9N2 infection [20]. PA was efficiently determined in grape juices using selective and rapid magnetic molecular imprinted solid phase extraction coupled with HPLC [21]. Trace PA from complex matrices was extracted and analyzed using high-capacity magnetic hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymers with HPLC. It was reported that the polymers that were used had high selectivity towards PA [22]. It was also determined electrochemically with a N-Butylpyridinium hexafluorophosphate ionic liquid modified carbon paste electrode, using the cyclic voltammetric method. Phosphate buffer solution (pH 2.0) was selected as the supporting electrolyte. The proposed method was applied for its detection in juice [23].
The HPLC method is utilized for the simultaneous separation, identification, and quantification of phenolic compounds including GA and PA. The following techniques have been used for the simultaneous determination of GA and PA: High-performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detector (HPLC-PDA) in Heliotropium thermophilum [24], HPLC-DAD-UV in crude grape cane extracts without pre-treatment [25], ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography-photo diode array detector (UHPLC-PDA) in wines [26], and HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS in grapes [27]. HPLC techniques are highly selective, but their procedures are complex and time-consuming. Alternatively, electrochemical methods are highly selective, simple and sensitive. Various electrochemical determination methods have been performed for PA [23,28]. The electrochemical determination of catechin, PA, and L-lactic acid mixture has been developed in the presence of ferroceneboronic acid as an electrochemical probe [29]. The determination was performed using cyclic and differential pulse voltammetric methods on a glassy carbon electrode at pH 7.0. A novel efficient nanocomposite catalyst of ZrO2/Co3O4/rGO/FTO was prepared by a reflux method and then characterized [30]. The nanocomposite electrode exhibits a synergistic catalytic effect towards the oxidation of GA, caffeic acid and PA. The proposed ZrO2/Co3O4/rGO/FTO was applied successfully for the simultaneous determination of the three acids in fruit juice, rice and tea samples with satisfactory data. The major challenge in the simultaneous determination of GA and PA is the quantification of each in the presence of the other, since they are oxidized at almost similar potentials with poor sensitivity at the glassy carbon electrode. Voltammetric responses can overlap and this makes their simultaneous determination highly difficult. To overcome this problem, modification of the glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was developed using reduced graphene oxide (rGO).
Recently, graphene electrodes have received enormous interest. This is due to their unique properties, such as wide potential windows, inertness as a catalyst and good electro-catalytic activity. Thus, owing to these remarkable properties, they and their derivatives are promising candidates for the fabrication of electronic devices [30]. Among these derivatives, reduced graphene oxide is one of the best candidates. This is attributed to its reasonably reduced number of functionalities and many remaining electroactive sites. Reduced graphene oxide also offers a wide and interesting range of advantages, such as cheap and reliable preparation, large surface area, the possibility of functionalization, and good biocompatibility. Reduced graphene oxide composite is widely used as a building block of electrochemical sensors for the simultaneous determination of phenolic compounds. Mostly, reduced graphene oxide is prepared by the chemical reduction of graphene oxide, employing hazardous or corrosive reducing agents which bring impurities. As a result, the degradation of the electronic properties and weakening of the electrochemical performance of graphene occur due to the partial removal of oxygenated species. Thus, rGO is prepared using the green and convenient electrochemical reduction method. This method shows improved electrochemical performance and, in addition, a thin film of rGO can be prepared [31].
In this work, the electrochemical preparation of rGO elaborated an electrochemical sensor with satisfying selectivity, reproducibility and stability. The applicability of the sensor was tested for simultaneous quantification of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid in a real mango juice sample.
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
All chemicals were of Analytical Reagents (AR) products. GA, PA, potassium hexacyanoferrate and the acids of buffer solutions were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (Paris, France). Double-distilled water was used in this work. The 10.0 mM aqueous stock solutions of GA and PA were freshly prepared before use and the measured solutions were obtained prepared by dilution. The test solution was degassed prior to and during the electrochemical experiments with pure nitrogen.
2.2. Instruments
Cyclic and square wave voltammetric experiments were performed utilizing an Autolab Potentiostat/Galvanostat (PGSTAT128N) (Eco Chemie BV, Utrecht, The Netherlands) coupled with NOVA 1.10 software (Metrohm Autolab B.V., Utrecht, The Netherlands). Three electrodes, the working (bare or modified glassy carbon electrodes), the reference (Ag/AgCl, aq. KCl, 3.5 M) and the auxiliary Pt wire electrodes, were used. The pH of the solutions was measured with a pH-meter (HI 2210, HANNA Instruments, Bucharest, Romania) using a combined pH reference electrode.
2.3. Preparation of the rGO/GCE
The surface of the glassy carbon electrode was polished with 0.05 μm alumina in water using a polishing cloth until a mirror finish was achieved on the electrode surface and then it was rinsed thoroughly with double-distilled water. After that, the clean electrode was subjected to an ultrasonic bath of water and ethanol to assure the complete removal of any surface-bound impurities and then it was dried under ambient air conditions. Graphite oxide (GO) was prepared from natural graphite flakes by a modified version of the Hummer method [32]. The reduced graphene oxide (rGO)-modified electrode was prepared as follows: 1.0 mg·mL−1 GO powder was dispersed homogeneously in bi-distilled water by ultrasonication for 45 min to obtain a graphene oxide suspension. The rGO-modified electrode was then prepared by the electrochemical reduction of the GO suspension to form an insoluble thin layer of rGO on the surface of the GC electrode. This was conducted by repetitive cyclic voltammetry (CV) scanning from 0 to −1.0 V at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1 in the degassed 0.04 M Britton–Robinson buffer solution (B–R) (pH 5.25) for 15 cycles. After that, the electrode was then carefully washed several times with water to remove the electrolyte and the monomer, and then dried at room temperature. The rGO/GCE was cleaned electrochemically after each measurement, using cyclic voltammetric scanning in a potential range of a 0.2 to 1.0 V window for 15 cycles at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1.
2.4. Sample Preparation
An amount of 2.0 g of pulp from golden yellow mango (The Governorate of Ismailia, Egypt) was first treated with 30% ethanol aqueous solution and then sonicated for 30 min. The solution was later filtered through Whatman paper (No. 1). After removing the lipophilic impurities by filtration, 1.0 mL of the filtrate was diluted to 25 mL (B–R) (pH 2.1) which was directly added to the electrochemical cell. The square wave voltammogram was then recorded.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrochemical Synthesis and Characterization of the rGO/GCE
Figure 1 illustrates the repetitive CV cycles for the electrochemical reduction of GO-modified GCE. The voltammogram shows a cathodic reduction wave at around −0.68 V in the first cycle which was ascribed to the reduction of the surface oxygen groups [33]. During the second cycle, the reduction wave is shifted negatively and its current starts to drop exceptionally. On progressing the CV scans, the decrease of current continues until a stable baseline current is reached. This indicates that the surface-oxygen species are successfully reduced.
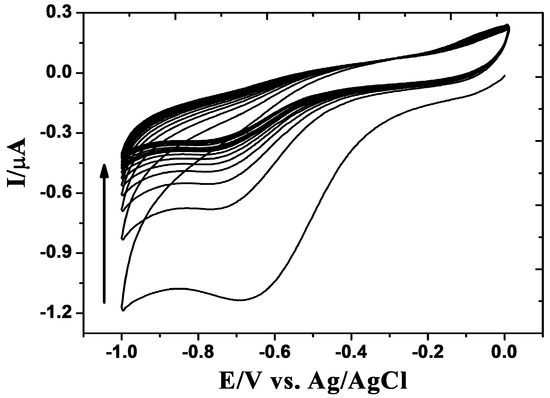
Figure 1.
Repetitive cyclic voltammetry (CV) synthesis of the reduced graphene oxide/glassy carbon electrode (rGO/GCE) from graphene oxide in 0.04 M Britton–Robinson buffer solution (pH 5.25) at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1.
In order to investigate the electrochemical properties of the concerned electrodes (the bare GCE and rGO/GCE), cyclic voltammetric measurements were performed using [K3Fe(CN)6] as the electrochemical probe. Figure 2 presents the cyclic voltammograms obtained by the two studied electrodes of 1 mM [K3Fe(CN)6] solution in 0.2 M KCl solution. On comparing the bare GCE with the rGO/GCE, the redox peak currents increase, whereas the peak-to-peak separation (ΔEP) decreases using the rGO/GCE. The observed values of ΔEP for the bare and modified GCEs are 172 and 83 mV, respectively. This clearly reveals that the electron transfer on the rGO surface is much easier than for the bare GCE. This might be due to the large surface area as well as the high electric conductivity of rGO. The electrochemical properties of the modified GC electrode were investigated by CV.
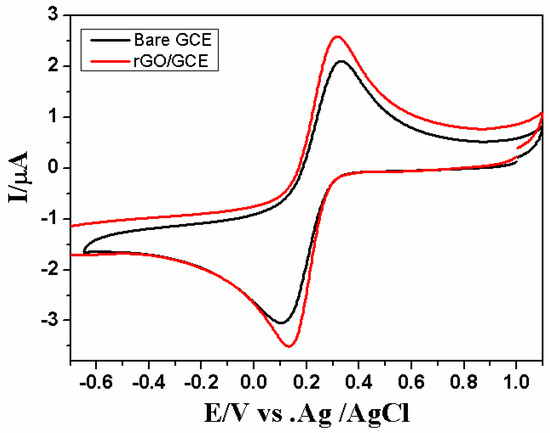
Figure 2.
Cyclic voltammograms of 1.0 mmol·L−1 [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− in 0.2 mol·L−1 KCl at the GCE and rGO/GCE at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1.
The cyclic voltammograms (CVs) of 1.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− solution were recorded at different scan rates (data not shown) in order to determine the effective active area of the subject electrode using the Randles–Sevcik equation [34]:
where Ip is the peak current (A), n is the number of electrons in the electrode reaction (n = 1), A is the surface area of the electrode (cm2), Do is the diffusion coefficient (Do = 7.6 × 10−6 cm2·s−1), Co is the concentration of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− (Co = 1.0 × 10−6 mol·cm−3), and ν is the scan rate (V·s−1). The active surface area was calculated to be 0.051 and 0.073 cm2 for the bare and modified electrodes, respectively. These results indicate that the active surface area of the modified GC electrode is increased by the presence of graphene (×1.45 more).
IP = (2.69 × 105) n3/2 A Do1/2 Co ν1/2
3.2. Electrochemical Oxidation of GA and PA
The electrochemical behavior of a solution mixture of 0.1 mM GA and PA was characterized at the GCE and rGO/GCE in Britton–Robinson buffer solution (pH 2.1) at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1 (Figure 3). On one hand, no separation of the anodic peaks corresponding to the oxidation of the two acids was obtained at the bare GCE, making the determination of the individual concentration of the acids not possible from the obtained merged peaks. On the other hand, at the modified electrode (rGO/GCE), two oxidation peaks appeared at different potentials of 555 and 650 mV with peaks separation (ΔEp) of 95 mV, corresponding to the oxidation of GA and PA, respectively. The ΔEp is large enough for the selective and simultaneous determination of GA and PA in their solution mixture. Furthermore, a remarkable increase in the peak current responses is observed with values of 12.58 and 21.44 µA for GA and PA, respectively. This enhancement in the peak currents using the rGO/GCE is attributed to the high active surface area and to the excellent electrical conductivity of reduced graphene oxide, which increases the electron transfer kinetics between the electrode and the analytes. The obtained results confirm that the rGO/GCE enhances the oxidation of the two acids, making the simultaneous determination of GA and PA in the coexistence system feasible. Thus, the rGO/GCE-based electrochemical sensor was used for simultaneous determination with good selectivity as well as high sensitivity.

Figure 3.
CVs of 0.10 mM GA and 0.10 mM PA in B–R solution (pH 2.1) at a scan rate of 50 mV·s−1.
3.3. Effects of pH and Scan Rate on the Electrochemistry of GA and PA
The evolution of the oxidation peak potentials for GA and PA versus pH was studied by cyclic voltammetry between pH values 2.1 and 6.1 of B–R at the rGO/GCE (data not shown). It was revealed that the oxidation potentials of both acids were shifted negatively with the increasing pH of the solution. This shift is attributed to the participation of protons in the electrode reactions [35]. Linear relationships between the peak potential and the pH value were obtained with slope values of −52 and −50 mV/pH for GA and PA, respectively. These slopes are close to the value for the Nernst system, i.e., −59 mV/pH at 25 °C. This indicates that the overall electrode reaction proceeds through a transfer of an equal number of electrons and protons, two electrons and two protons as shown in Scheme 1 [36,37]. Also, the anodic peak currents of the two species decrease gradually as the pH increases. This trend could be explained as follows: at low pH, the proton concentration is high and increases with the decreasing pH of the solution. This influences the ease of oxidation and enhances mass transport to the electrode surface and, in turn, increases the oxidation current. On further increase of the pH, the current begins to decrease which may be due to the repulsive interaction between the positively charged electrode surface and the highly protonated GA and PA species. Consequently, a B–R buffer solution of pH 2.1 was chosen for the sensitive determination in subsequent experiments.

Scheme 1.
The oxidation mechanism of polyphenol.
The effect of the scan rate on the electrochemical peak current of GA and PA at the rGO/GCE in the range of 10 to 290 mV·s−1 was investigated by CV (Figure 4). A linear log–log variation, log peak current (log Ip) versus log scan rate (log υ) is obtained for both acids with a slope value of 0.48 and 0.41 for GA and PA, respectively. This indicates that the electrochemical oxidation of GA and PA is a diffusion-controlled process in nature.

Figure 4.
Cyclic voltammetry of the rGO/GCE in 0.04 M B–R (pH 2.1) containing (A) 0.1 mM GA and (B) 0.1 mM PA at different scan rates (10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 80, 90, 120, 150, 170, 190, 200, 230, 270 and 290 mV·s−1).
3.4. Simultaneous Determination of GA and PA
The analytical performance of the subject sensor was studied using square wave voltammetry (SWV) for the simultaneous determination of GA and PA in their mixture, due to its higher sensitivity and better resolution than the CV (Figure 5). The key experimental parameters, such as frequency, amplitude and step potential, were optimized (not shown). The calibration plots of GA and PA show a linear increase of the current responses of the two species increasing their concentration (Figure 5). The linear regression equations are:
and
Ipa (µA) = 0.005 CGA (µM) + 1.11 × 10−7 (R2 = 0.95)
Ipa (µA) = 0.012 CPA (µM) + 2.27 × 10−7 (R2 = 0.996)
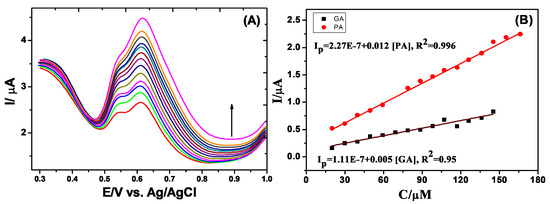
Figure 5.
(A) SWV profiles at the rGO/GCE in 0.04 M B–R buffer (pH 2.10) for different concentrations of GA and PA, and the (B) calibration plots.
Furthermore, the linear variations range from 20 to 144 µmol·L−1 for GA and from 20 to 166 µmol·L−1 for PA, with detection limits (S/N = 3) of 30.8 µmol·L−1 for GA and 10.2 µmol·L−1 for PA. Also, the limits of quantitation (LOQ, S/N = 10) obtained are 93.4 µmol·L−1 for GA and 31.0 µmol·L−1 for PA. These results illustrate that the proposed sensor possesses good analytical performance and the simultaneous quantification of GA and PA in the samples can be done successfully by the voltammetric method.
3.5. Interference, Repeatability and Stability Studies
The interference of the 100-fold concentration of the coexisting substances (such as citric acid, tartaric acid, glucose, ascorbic acid and oxalic acid) on the concomitant determination of GA and PA (0.1 mmol·L−1) in B–R solution (pH 2.1) was investigated. Less than 5% current variation was observed, suggesting that no interference occurs. Moreover, the relative standard deviation (RSD) of the current corresponding oxidation peak was equal to 4.85% for 10 continuous measurements. In addition to that, the rGO/GCE activity remained constant during the minimum period of two weeks for the simultaneous determination of GA and PA. These results indicate that the rGO/GCE displayed good stability and repeatability concerning the detection of the subject analytes.
Finally, the stability of the modified electrode was measured daily for 21 days. The peak current remained 94% of its original value during the three weeks, showing that the rGO/GCE electrochemical sensor has very good stability.
3.6. Analysis of Real Samples
The GA and PA content in a commercial mango sample was determined with the developed square wave voltammetric method in order to validate the use of the sensor based on the rGO/GCE for the simultaneous determination of GA and PA in a real sample. The standard addition method was employed in order to quantify the quantities of the gallic and protocatechuic acids in the sample with standard solutions of the acids using the earlier described method, considering the optimal parameters, and then the voltammograms were recorded. The obtained results are shown in Figure 6. In these experiments, successive amounts of standard GA and PA solutions were added to the test solution. The total content of GA and PA in the dried commercial mango sample is expressed as milligrams of GA and PA equivalents. It was estimated to be 2.4 mg·g−1 dry weight (DW) and 5.4 mg·g−1 DW for GA and PA, respectively.
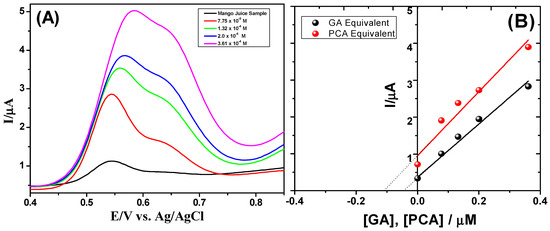
Figure 6.
(A) Square wave voltammograms of a mango sample in B–R solution in optimal conditions: pH 2.1 at frequency 25 Hz and successive additions of standards GA and PA; (B) Standard addition plots of GA and PA in a mango sample.
4. Conclusions
A reliable and simple electrochemical method was presented in this study for the simultaneous determination of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid using the electrochemically synthesized reduced graphene oxide. The rGO/GCE exhibited much improved electrocatalytic oxidation behavior and good resolution towards the selective oxidation of these acids. The outstanding electrocatalytic properties of the rGO/GCE probably make it a promising candidate for the sensitive and selective electrochemical sensing of these acids in fruit juice (mango).
Author Contributions
The following statement illustrates the individual’s contributions of each author. E.F.N. and R.A.-H. have set up the conceptualization, while A.B. and E.F.N. have performed the methodology, software, validation, formal analysis, investigation, and data curation. R.A.-H. has written the original draft preparation, while F.G. and E.F.N. have performed the writing-review & editing as well as supervision.
Funding
This research was funded by the Science & Technology Development Fund [STDF], Egypt, grant number [5361].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Ghaani, M.; Nasirizadeh, N.; Ardakani, S.A.Y.; Mehrjardi, F.Z.; Scampicchiod, M.; Farris, S. Development of an electrochemical nanosensor for the determination of gallic acid in food. J. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singha, A.; Kumar, B.; Pharmaceut, J. Identification and characterization of phenolics and terpenoids from ethanolic extracts of Phyllanthus species by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mudnic, I.; Modun, D.; Rastija, V.; Vukovic, J.; Brizic, I.; Katalinic, V.; Kozina, B.; Medic-Saric, M.; Boban, M. Antioxidative and vasodilatory effects of phenolic acids in wine. Food Chem. 2010, 119, 1205–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarjit, A.; Wang, Y.; Dykes, G.A. Antimicrobial activity of gallic acid against thermophilic Campylobacter is strain specific and associated with a loss of calcium Ions. Food Microbiol. 2015, 46, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phakthong, W.; Liawruangrath, B.; Liawruangrath, S. Determination of gallic acid with rhodanine by reverse flow injection analysis using simplex optimization. Talanta 2014, 130, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Chen, D.; Wel, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhao, J. A Simple and Sensitive Assay of Gallic Acid Based on Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance Light Scattering of Silver Nanoparticles through Modified Tollens Process. Anal. Sci. 2011, 27, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narumi, K.; Sonoda, J.I.; Shiotani, K.; Shigeru, M.; Shibata, M.; Kawachi, A.; Tomishige, E.; Sato, K.; Motoya, T. Simultaneous detection of green tea catechins and gallic acid in human serum after ingestion of green tea tablets using ion-pair high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J. Chromatogr. B 2014, 945, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hamid, R.; Newair, F.E. Adsorptive stripping voltammetric determination of gallic acid using an electrochemical sensor based on polyepinephrine/glassy carbon electrode and its determination in black tea sample. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 704, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, S.; Jagannathan, M.; Kadir, M.R.A.; Palanivel, S.; Hadibarata, T.; Yusoff, A.R.M. A new electro-generated o-dianisidine derivative stabilized MWCNT-modified GCE for low potential gallic acid detection. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 45996–46006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sum, Y.L.; Chen, S.H. Sensitive and selective determination of gallic acid in green tea samples based on an electrochemical platform of poly(melamine) film. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 901, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hur, J.M.; Park, J.G.; Yang, K.H.; Park, J.C.; Park, J.R.; Chun, S.S.; Choi, J.S.; Choi, J.W. Effect of Methanol Extract of Zanthoxylum piperitum Leaves and of Its Compound, Protocatechuic Acid, on Hepatic Drug Metabolizing Enzymes and Lipid Peroxidation in Rats. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitaglione, P.; Donnarumma, G.; Napolitano, A.; Galvano, F.; Gallo, A.; Scalfi, L.; Fogliano, V. Protocatechuic acid is the major human metabolite of cyanidin-glucosides. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2043–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, S.; Bais, S. A Review on Protocatechuic Acid and Its Pharmacological Potential. ISRN Pharmacol. 2014, 2014, 952943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, S. Antioxidant Activity and Mechanism of Protocatechuic Acid in vitro. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2011, 1, 232–244. [Google Scholar]
- Vari, R.; D’Archivio, M.; Filesi, C.; Carotenuto, S.; Scazzocchio, B.; Santangelo, C.; Giovannini, C.; Masella, R. Protocatechuic acid induces antioxidant/detoxifying enzyme expression through JNK-mediated Nrf2 activation in murine macrophages. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, C.Y.; Yin, M.C. Antibacterial effects of roselle calyx extracts and protocatechuic acid in ground beef and apple juice. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2009, 6, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scazzocchio, B.; Var, R.; Filesi, C.; D’Archivio, M.; Santangelo, C.; Giovannini, C.; Iacovelli, A.; Silecchia, G.; Volti, G.L.; Galvano, F. Cyanidin-3-O-β-glucoside and protocatechuic acid exert insulin-like effects by upregulating PPARγ activity in human omental adipocytes. Diabetes 2011, 60, 2234–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, M. Potential cancer chemopreventive activity of protocatechuic acid. J. Exp. Clin. Med. 2011, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, W.; Zhu, H.; Hou, J. Antifibrotic effects of protocatechuic aldehyde on experimental liver fibrosis. Pharm. Biol. 2012, 50, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, C.; Shi, N.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Wang, B.; Compans, R.W.; He, C. Protocatechuic acid, a novel active substance against avian Influenza virus H9N2 infection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e111004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S. Efficient Determination of Protocatechuic Acid in Fruit Juices by Selective and Rapid Magnetic Molecular Imprinted Solid Phase Extraction Coupled with HPLC. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 8221–8228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, S.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X. High-capacity magnetic hollow porous molecularly imprinted polymers for specific extraction of protocatechuic acid. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1404, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Jiang, Q.; Xi, M.; Jiao, K. Determination of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid by electrocatalytic oxidation at an ionic liquid modified electrode. Microchim. Acta 2009, 166, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.; Kadioğlu, A.; Sağlam, A.; Yaşar, A. Determination of phenolic acids and rutin in Heliotropium thermophilum by high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode array detection. Instrum. Sci. Technol. 2017, 45, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Wan, L.; Wu, C.; Fang, Y.; Han, G.; Li, H.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, H. Simultaneous Determination of 14 Phenolic Compounds in Grape Canes by HPLC-DAD-UV Using Wavelength Switching Detection. Molecules 2013, 18, 14241–14257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.L.; Pereiraa, J.; Woutera, V.G.; Giro, C.; Câmara, J.S. A fast method using a new hydrophilic-lipophilic balanced sorbent in combination with ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography for quantification of significant bioactive metabolites in wines. Talanta 2011, 86, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicoleti, I.; Bello, C.; de Rossi, A.; Corrandini, D. Identification and Quantification of Phenolic Compounds in Grapes by HPLC-PDA-ESI-MS on a Semimicro Separation Scale. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8801–8808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Hua, Y.; You, Q.; Shi, S. Novel molecular imprinted polymers over magnetic mesoporous silica microspheres for selective and efficient determination of protocatechuic acid in Syzygium aromatic. Food Chem. 2015, 178, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Cai, M.; Du, X. Electrochemical determination of catechin, protocatechuic acid, and L-lactic acid based on voltammetric response of ferroceneboronic acid. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puangjan, A.; Chaiyasith, S. An efficient ZrO2/Co3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of gallic acid, caffeic acid and protocatechuic acid natural antioxidants. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 211, 273–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liscio, A.; Veronese, G.P.; Treossi, E.; Suriano, F.; Rosella, F.; Bellani, V.; Rizzoli, R.; Samori, P.; Palermo, V. Charge transport in graphene–polythiophene blends as studied by Kelvin Probe Force Microscopy and transistor characterization. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 2924–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, D.; Huang, J.; You, T. Simultaneous determination of dopamine, ascorbic acid and uric acid at electrochemically reduced graphene oxide modified electrode. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 193, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roghani-Mamaqani, H.; Haddadi-Asl, V.; Khezri, K.; Salami-Kalajahi, M. Polystyrene-grafted graphene nanoplatelets with various graft densities by atom transfer radical polymerization from the edge carboxyl groups. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 24439–24452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Deng, S.; Lei, J.; Jub, H.; Gunasekarana, S. Electrochemical synthesis of reduced graphene sheet–AuPd alloy nanoparticle composites for enzymatic biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.F.; Xie, F.; Hu, R.F. Electrochemical study of brucine on an electrode modified with magnetic carbon-coated nickel nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Hamid, R.; Newair, E.F. Electrochemical behavior of antioxidants: I. Mechanistic study on electrochemical oxidation of gallic acid in aqueous solutions at glassy-carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 657, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, H.; Ueda, M.; Nagano, S.; Tsujino, Y.; Koyama, J.; Osakai, T. Mechanistic Study of the Oxidation of Caffeic Acid by Digital Simulation of Cyclic Voltammograms. J. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 303, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).