An Overview of the Utilisation of Brewery By-Products as Generated by British Craft Breweries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Background
2.1. Spent Grain
2.2. Spent Hops/Hot Trub
2.3. Spent Yeast
2.4. Feed Hygiene Regulations
3. Methods
4. Results
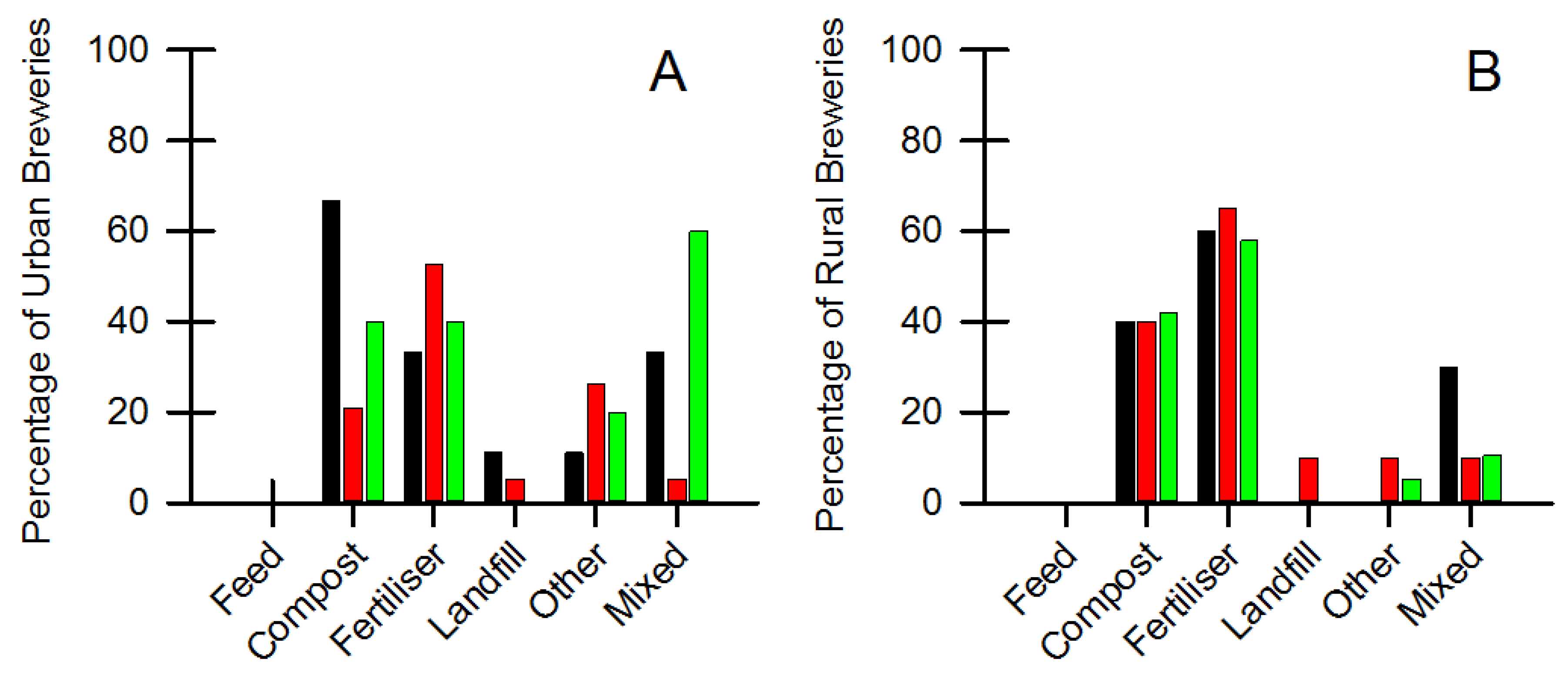
4.1. Spent Brewer’s Grain
4.2. Spent Brewer’s Yeast
4.3. Spent Brewer’s Hops/Hot Trub
5. Discussion
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dos Santos Mathias, T.R.; de Mello, P.P.M.; Servulo, E.F.C. Solid wastes in brewing process: A review. J. Brew. Distill. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Huige, N. Brewery by-products and effluents. In Handbook of Brewing, 2nd ed.; Priest, F.G., Stewart, G.G., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 656–707. [Google Scholar]
- Murray, D.W.; O’Neill, M.A. Craft beer: Penetrating a niche market. Br. Food J. 2012, 114, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewers Association (2017) Craft Brewer Defined. Available online: https://www.brewersassociation.org/statistics/craft-brewer-defined/ (accessed on 31 May 2017).
- Mussatto, S.I. Brewer’s spent grain: A valuable feedstock for industrial applications. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 1264–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fărcaş, A.; Tofană, M.; Socaci, S.; Mudura, E.; Scrob, S.; Salanţă, L.; Mureşan, V. Brewers’ spent grain—A new potential ingredient for functional foods. J. Agroaliment. Proc. Technol. 2014, 20, 137–141. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.R.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Brewery wastes. Strategies for sustainability. A review. Asp. Appl. Biol. 2006, 80, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Stocks, C.; Barker, A.J.; Guy, S. The composting of brewery sludge. J. Inst. Brew. 2002, 108, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller-Reinspach, H.W. Emissions during the combustion of spent brewer’s grains. Brauwelt 1989, 129, 2316–2319. [Google Scholar]
- Deublein, D.; Steinhauser, A. Biogas from Waste and Renewable Resources: An Introduction; John Wiley & Sons: Weinheim, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- O’Rourke, T. Making the most of your hops. New Brewer. 1994, 11, 20–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bedini, S.; Flamini, G.; Girardi, J.; Cosci, F.; Conti, B. Not just for beer: Evaluation of spent hops (Humulus lupulus L.) as a source of eco-friendly repellents for insect pests of stored foods. J. Pest Sci. 2015, 88, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djuragic, O.; Levic, J.; Serdanovic, S. Use of new feed from brewery by-products for breeding layers. Romanian Biotechnol. Lett. 2010, 15, 5559–5565. [Google Scholar]
- Aliyu, S.; Bala, M. Brewer’s spent grain: A review of its potentials and applications. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 324–331. [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hamed, U.; Seddighi, H.; Thomas, K. Economic returns of using brewery’s spent grain in animal feed. World Acad. Sci. Eng. Technol. 2011, 50, 695–698. [Google Scholar]
- Newbold, C.J.; Wallace, R.J.; McIntosh, F.M. Mode of action of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a feed additive for ruminants. Br. J. Nutr. 1996, 76, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, L. Feed Additives for Pigs. U.S. Patent Application No. 10/175,054, 18 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Pinho, O.; Vieira, E.; Tavarela, J.G. Brewer’s Saccharomyces yeast biomass: Characteristics and potential applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 21, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munch, P.; Hofmann, T.; Schieberle, P. Comparison of key odorants generated by thermal treatment of commercial and self-prepared yeast extracts: Influence of the amino acid composition on odorant formation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1997, 45, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sombutyanuchit, P.; Suphantharika, M.; Verduyn, C. Preparation of 5′-GMP-rich yeast extracts from spent brewer’s yeast. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2001, 17, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, E.F.; Carvalho, J.; Pinto, E.; Cunha, S.; Almeida, A.A.; Ferreira, I.M. Nutritive value, antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds profile of brewer’s spent yeast extract. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 52, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food Standards Agency. Feed Hygiene Regulation (183/2005): How to Apply for Approval or Registration, and Related Information. 2013. Available online: https://www.food.gov.uk/businessindustry/farmingfood/animalfeed/animalfeedlegislation/approvregfeedguidance (accessed on 31 May 2017).
- BFBI. BFBI Feed Assurance Scheme. 2016. Available online: http://www.bfbi.org.uk/training/bfbi-feed-assurance-scheme (accessed on 31 May 2017).
- Henderson, N. Silage additives. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 1993, 4, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy & Sons. Ammonium Tetraformate Solution—Spent Grain Treatment. 2015. Available online: http://blog.murphyandson.co.uk/category/spent-grain-treatment/ (accessed on 31 May 2017).
- Conaghan, P.; O’Kiely, P.; O’Mara, F.P. Conservation characteristics of wilted perennial ryegrass silage made using biological or chemical additives. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 628–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, A.F.; Broderick, G.A.; Colmenero, J.O.; Reynal, S.M. Effects of feeding formate-treated alfalfa silage or red clover silage on omasal nutrient flow and microbial protein synthesis in lactating dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 1392–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K.M.; Steffen, E.J.; Arendt, E.K. Brewers’ spent grain: A review with an emphasis on food and health. J. Inst. Brew. 2016, 122, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mussatto, S.I. Biotechnological potential of brewing industry by-products. In Biotechnology for Agro-Industrial Residues Utilisation; Singh-Nee Nigam, P., Pandey, A., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 313–326. [Google Scholar]
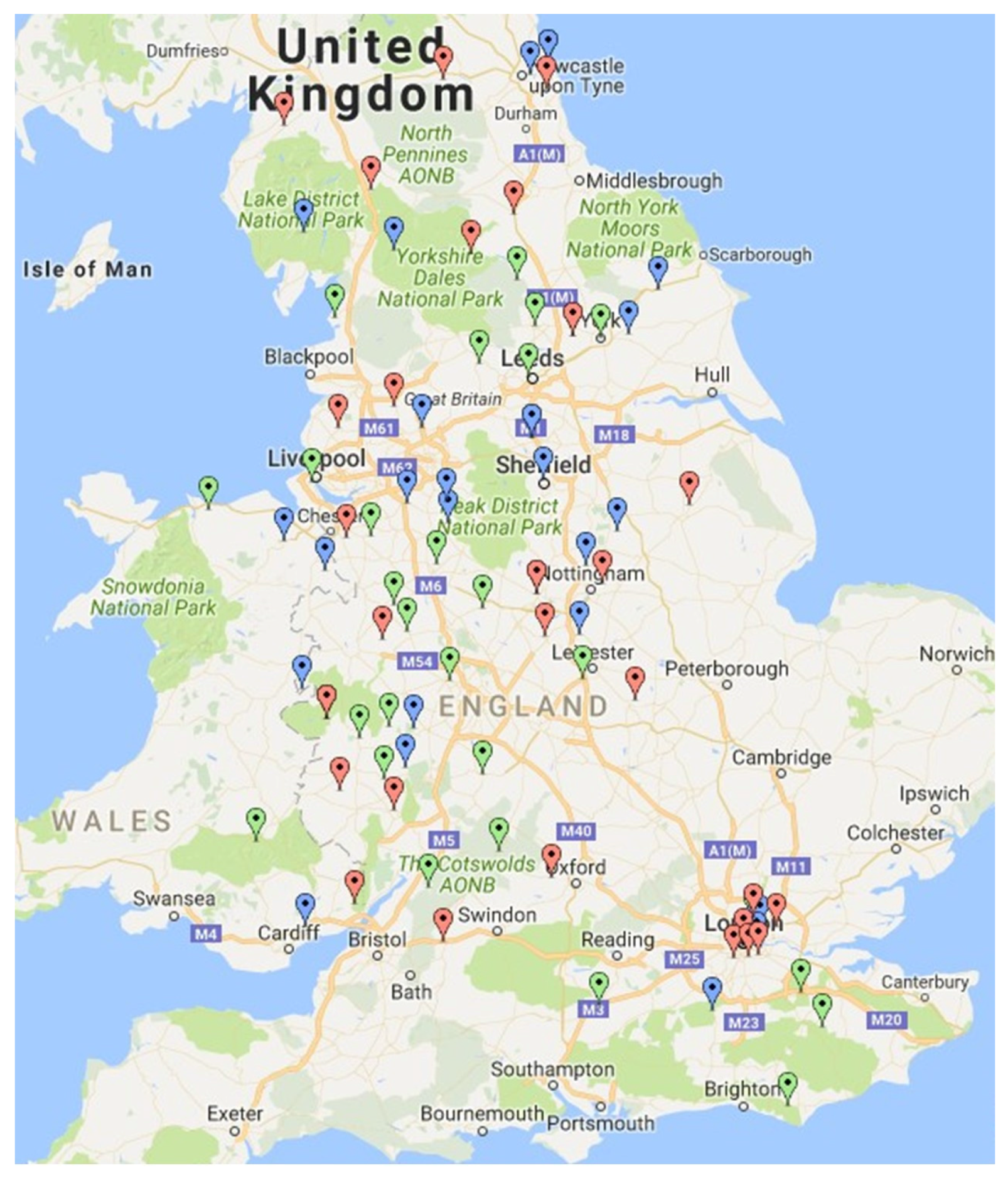
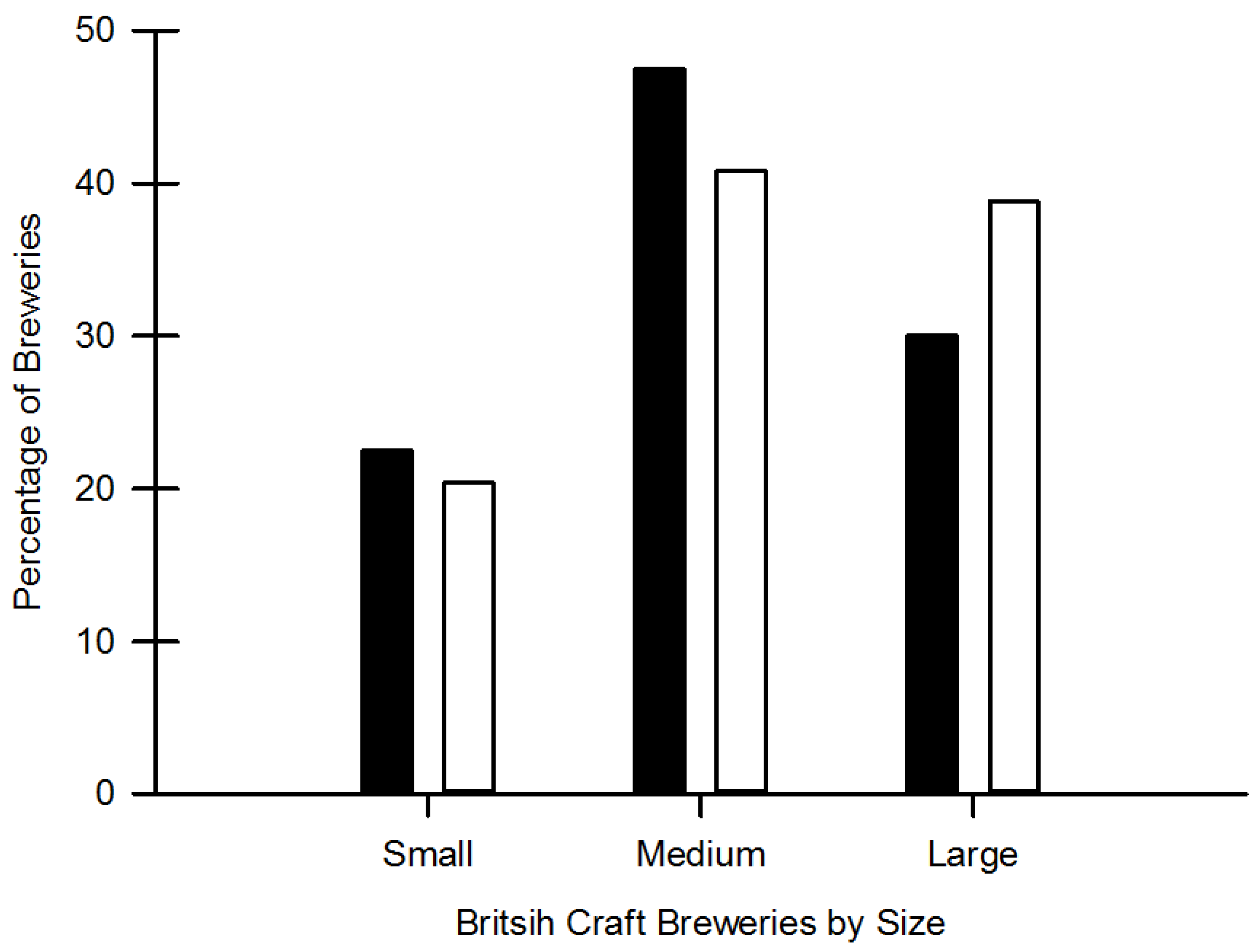
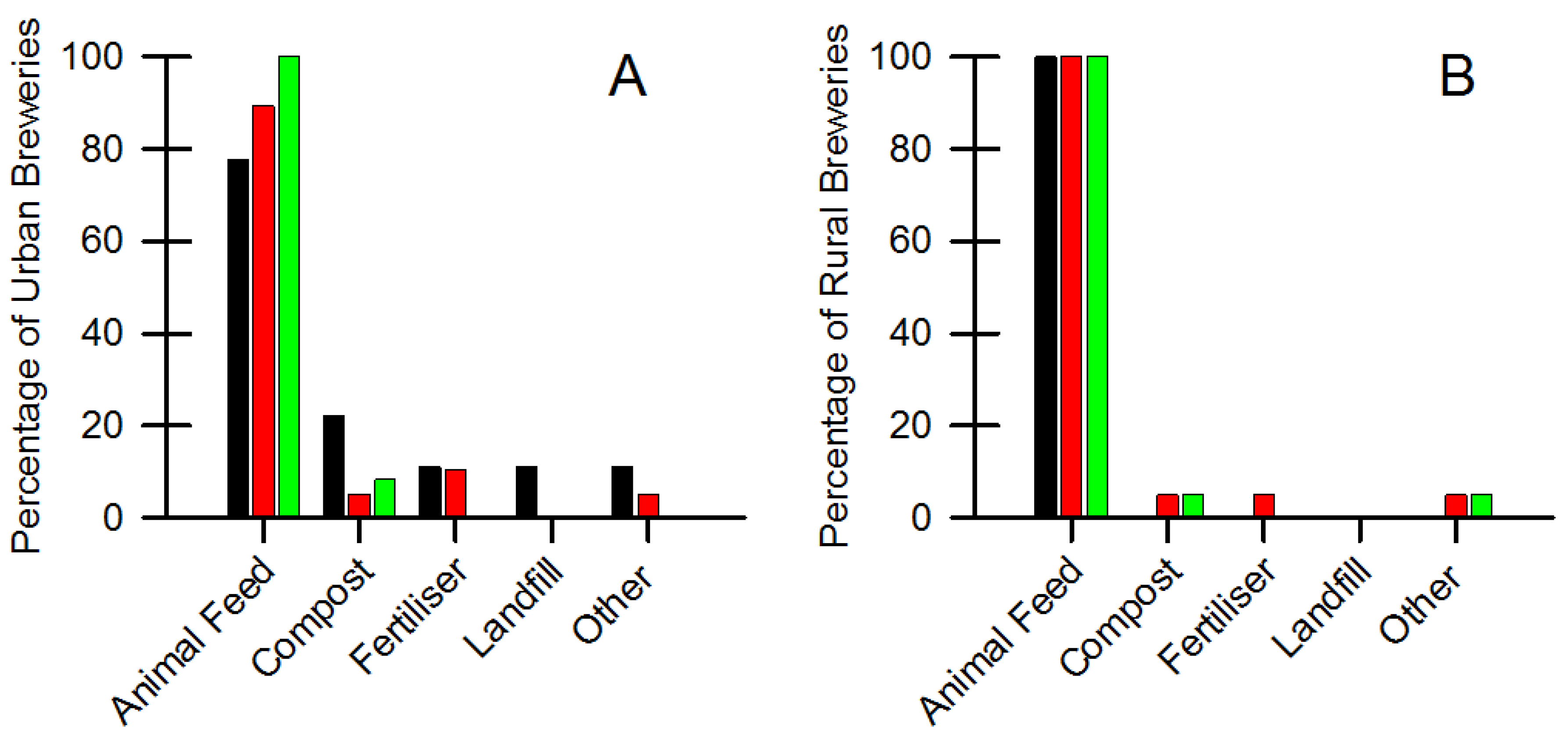
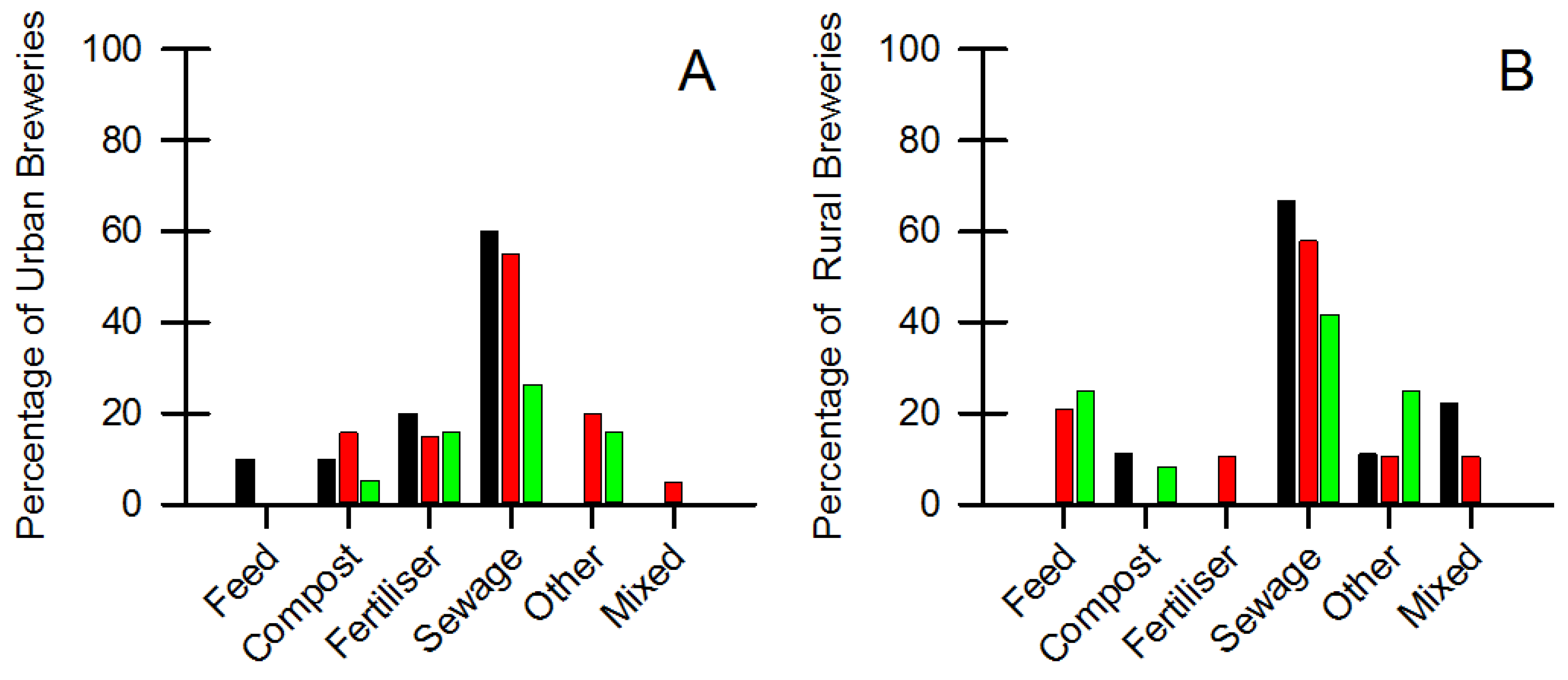
| Brewery; Location & Size | Frequency of Spent Grain Removal from Brewery Site | Cost Involved in Removal of Spent Grain from Brewery Site | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | 2–3/Week | Weekly | When Required | Brewery Incurs No Cost | Brewery Facilitates Disposal | Brewery Incurs All Costs | Brewery Receives Payment | |
| Urban-S | 11.1% | 11.1% | 66.7% | 11.1% | 55.6% | 44.4% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Urban-M | 15.8% | 52.6% | 26.3% | 5.3% | 89.5% | 10.5% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Urban-L | 25.0% | 75.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 75.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% | 25.0% |
| Rural-S | 20.0% | 50.0% | 20.0% | 10.0% | 70.0% | 20.0% | 0.0% | 10.0% |
| Rural-M | 25.0% | 40.0% | 35.0% | 0.0% | 90.0% | 5.0% | 0.0% | 5.0% |
| Rural-L | 42.1% | 31.6% | 26.3% | 0.0% | 73.7% | 10.5% | 0.0% | 5.2% |
| Brewery: Location & Size | Frequency of Spent Yeast Removal from Brewery Site | Cost Involved in Removal of Spent Yeast from Brewery Site | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | 2–3/Week | Weekly | When Required | Brewery Incurs No Cost | Brewery Facilitates Disposal | Brewery Incurs All Costs | Brewery Receives Payment | |
| Urban-S | 55.6% | 11.1% | 22.2% | 11.1% | 77.8% | 11.1% | 11.1% | 0.0% |
| Urban-M | 21.0% | 57.9% | 15.8% | 5.3% | 57.9% | 10.5% | 31.6% | 0.0% |
| Urban-L | 16.7% | 25.0% | 8.3% | 50.0% | 50.0% | 16.7% | 16.7% | 16.7% |
| Rural-S | 50.0% | 40.0% | 10.0% | 0.0% | 80.0% | 10.0% | 10.0% | 0.0% |
| Rural-M | 35.0% | 20.0% | 40.0% | 5.0% | 75.0% | 10.0% | 15.0% | 0.0% |
| Rural-L | 26.3% | 42.1% | 15.8% | 15.8% | 52.6% | 10.5% | 36.8% | 0.0% |
| Brewery: Location & Size | Frequency of Spent Hops Removal from Brewery Site | Cost Involved in Removal of Spent Hops from Brewery Site | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily | 2–3/Week | Weekly | When Required | Brewery Incurs No Cost | Brewery Facilitates Disposal | Brewery Incurs All Costs | Brewery Receives Payment | |
| Urban-S | 0.0% | 11.1% | 77.8% | 11.1% | 55.6% | 22.2% | 11.1% | 11.1% |
| Urban-M | 15.8% | 47.4% | 21.1% | 15.8% | 68.4% | 10.5% | 21.1% | 0.0% |
| Urban-L | 16.7% | 66.7% | 8.3% | 8.3% | 75.0% | 0.0% | 16.7% | 8.3% |
| Rural-S | 40.0% | 20.0% | 30.0% | 10.0% | 80.0% | 20.0% | 0.0% | 0.0% |
| Rural-M | 30.0% | 20.0% | 50.0% | 0.0% | 90.0% | 5.0% | 5.0% | 0.0% |
| Rural-L | 10.5% | 21.1% | 36.8% | 31.6% | 63.2% | 15.8% | 15.8% | 5.2% |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kerby, C.; Vriesekoop, F. An Overview of the Utilisation of Brewery By-Products as Generated by British Craft Breweries. Beverages 2017, 3, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3020024
Kerby C, Vriesekoop F. An Overview of the Utilisation of Brewery By-Products as Generated by British Craft Breweries. Beverages. 2017; 3(2):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3020024
Chicago/Turabian StyleKerby, Clare, and Frank Vriesekoop. 2017. "An Overview of the Utilisation of Brewery By-Products as Generated by British Craft Breweries" Beverages 3, no. 2: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3020024
APA StyleKerby, C., & Vriesekoop, F. (2017). An Overview of the Utilisation of Brewery By-Products as Generated by British Craft Breweries. Beverages, 3(2), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages3020024







