Five-Day Supplementation with an Isotonic Beetroot Juice Drink Improves Sprint Interval Exercise and Muscle Oxygenation in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Participants
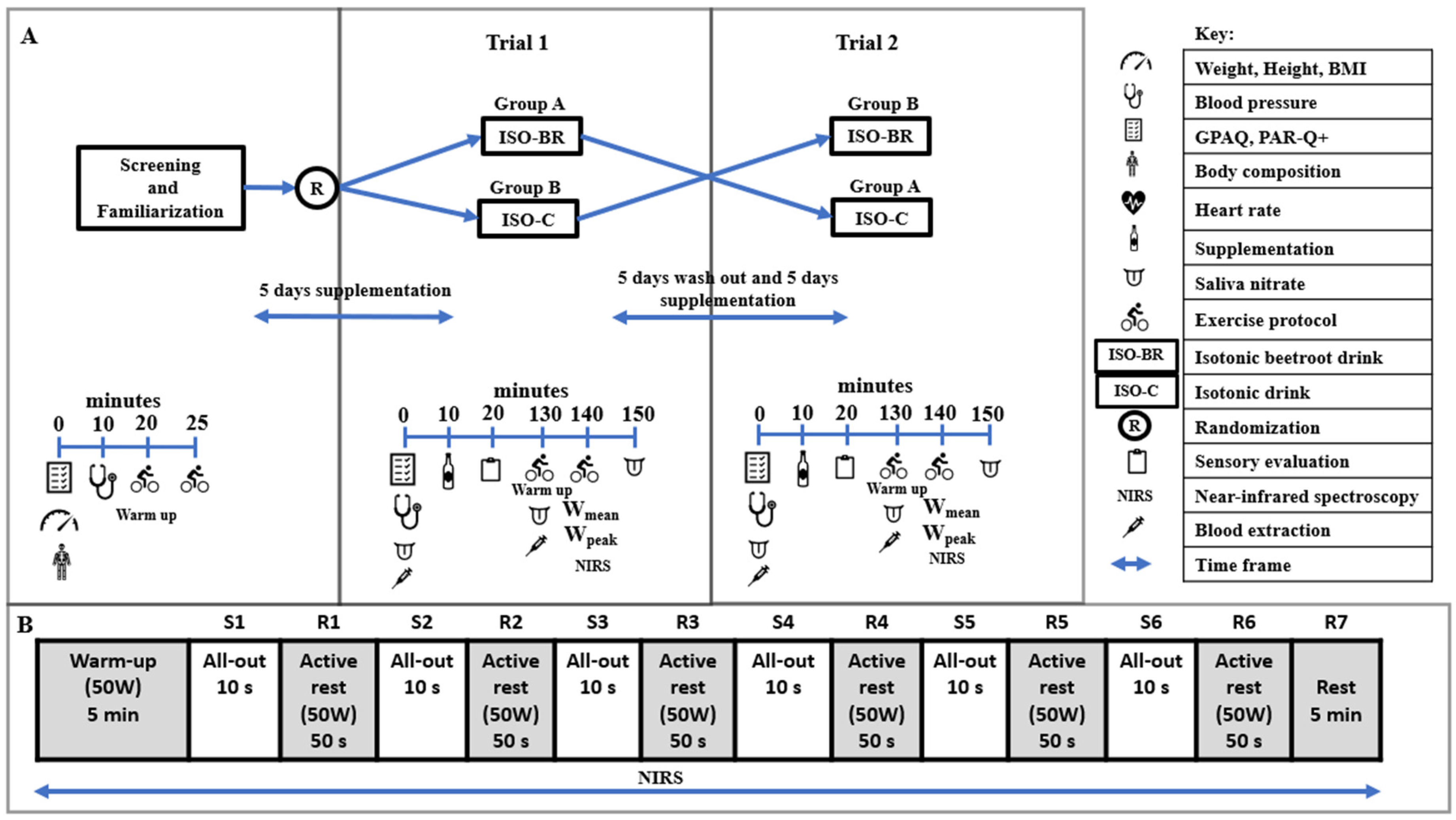
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Screening and Familiarization
2.5. Pre-Trial Experimental Control and Protocol
2.6. Exercise Protocol
2.7. NIRS Measurements
2.8. Supplementation
2.9. Sensory Evaluation
2.10. NOx Salivary Test
2.11. Blood Plasma Collection and Analysis
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
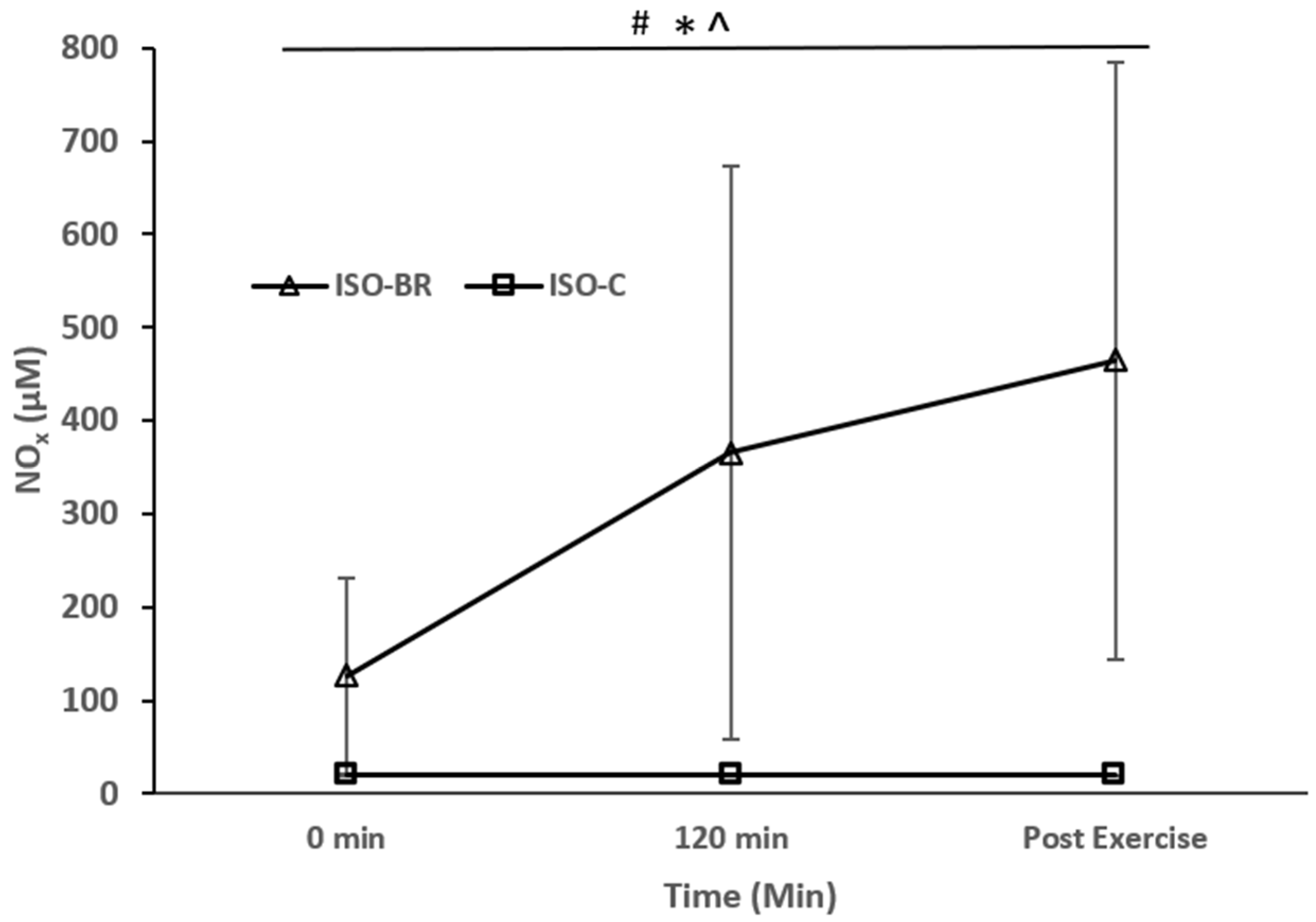
3.1. Salivary NOx Concentration
3.2. Plasma Nitrate and Nitrite Concentration
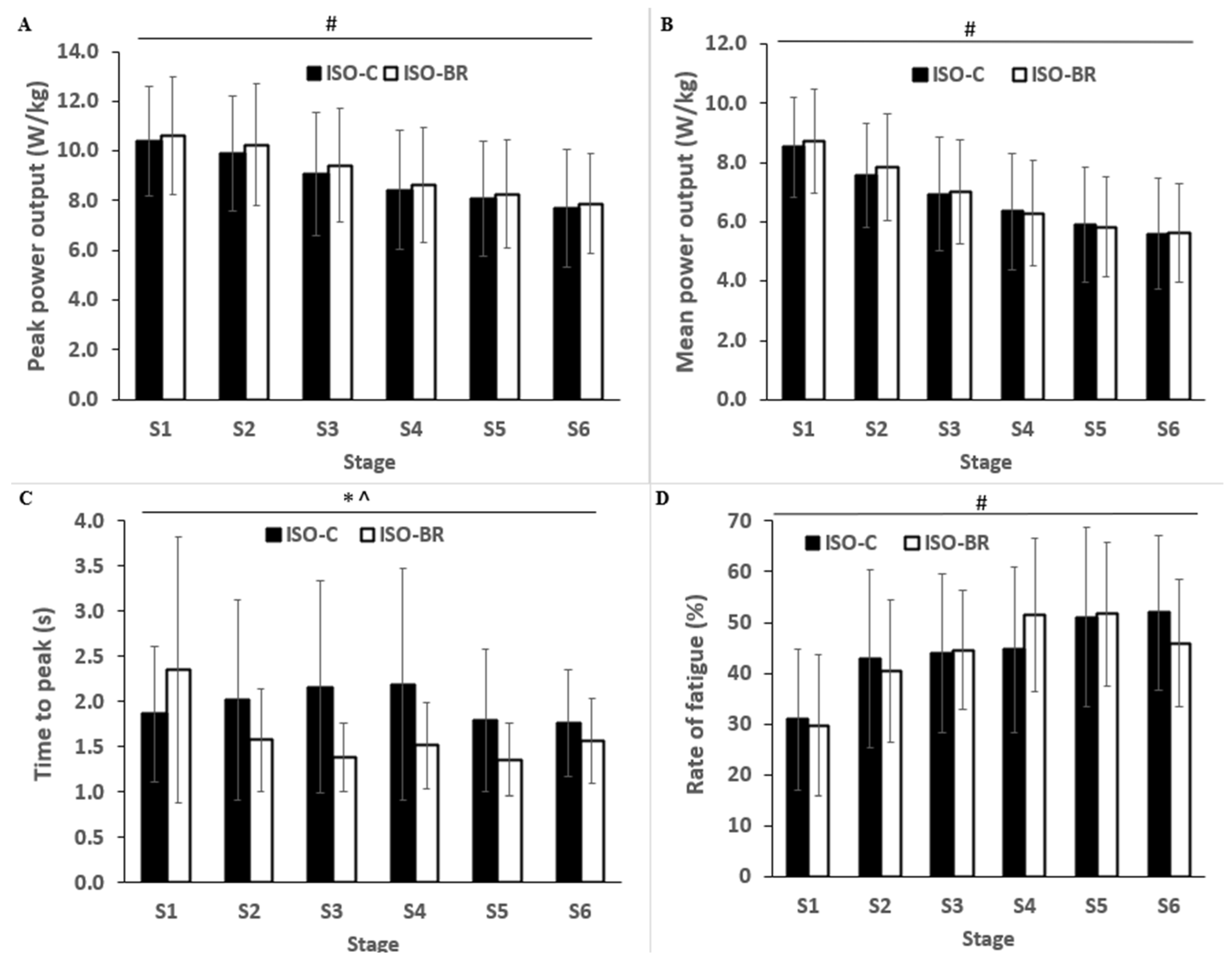
3.3. SIE Performance
3.4. Sensory Evaluation Results
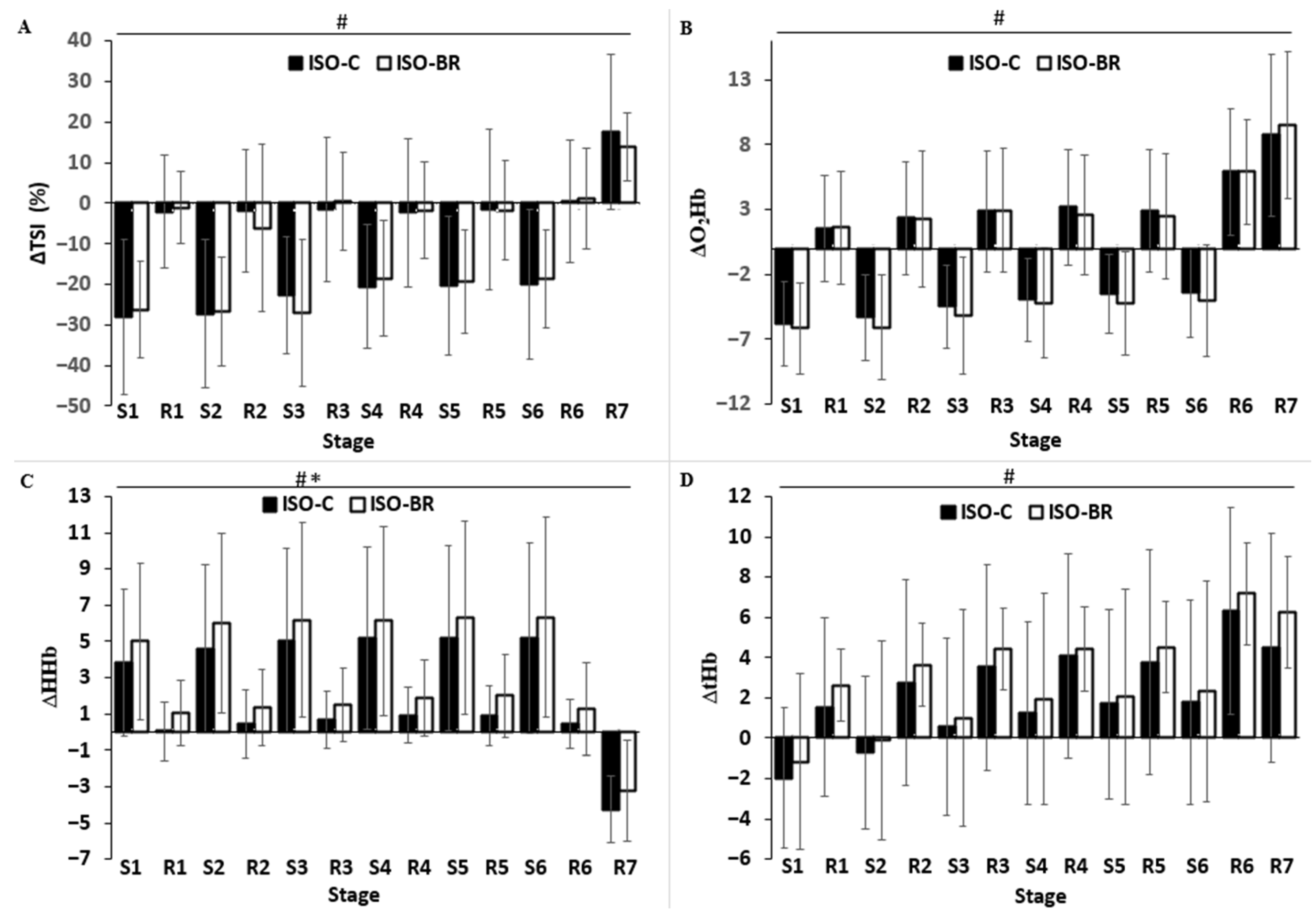
3.5. Muscle Oxygenation
4. Discussion
Practical Implications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| ∆HHb | Relative changes in deoxyhemoglobin + deoxymyoglobin |
| ∆O2Hb | Relative changes in oxyhemoglobin + oxymyoglobin |
| ∆tHb | Relative changes in total hemoglobin + myoglobin |
| ∆TSI | Relative changes in tissue saturation index |
| GMP | Good Manufacturing Practice |
| HIIT | High-intensity interval training |
| ISO-BR | Isotonic beetroot juice drink |
| ISO-C | Isotonic drink |
| NIRS | Near-infrared spectroscopy |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| NO2 | Nitrite |
| NO3 | Nitrate |
| NOx | Total nitrate and nitrite |
| PCr | Phosphocreatine |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SIE | Sprint interval exercise |
| SIT | Sprint interval training |
| O2 | Rate of oxygen uptake |
References
- Cuenca, E.; Jodra, P.; Pérez-López, A.; González-Rodríguez, L.G.; Fernandes da Silva, S.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Domínguez, R. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Performance and Fatigue in a 30-s All-Out Sprint Exercise: A Randomized, Double-Blind Cross-Over Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jodra, P.; Domínguez, R.; Sánchez-Oliver, A.J.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Bailey, S.J. Effect of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on Mood, Perceived Exertion, and Performance During a 30-Second Wingate Test. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2020, 15, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansley, K.E.; Winyard, P.G.; Fulford, J.; Vanhatalo, A.; Bailey, S.J.; Blackwell, J.R.; DiMenna, F.J.; Gilchrist, M.; Benjamin, N.; Jones, A.M. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of walking and running: A placebo-controlled study. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 110, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, S.J.; Winyard, P.; Vanhatalo, A.; Blackwell, J.R.; Dimenna, F.J.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Tarr, J.; Benjamin, N.; Jones, A.M. Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of low-intensity exercise and enhances tolerance to high-intensity exercise in humans. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 1144–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cermak, N.M.; Gibala, M.J.; van Loon, L.J.C. Nitrate Supplementation’s Improvement of 10-km Time-Trial Performance in Trained Cyclists. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2012, 22, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, P.M.; Nyberg, M.; Bangsbo, J. Influence of nitrate supplementation on VO2 kinetics and endurance of elite cyclists. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2013, 23, e21–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoon, M.W.; Hopkins, W.G.; Jones, A.M.; Martin, D.T.; Halson, S.L.; West, N.P.; Johnson, N.A.; Burke, L.M. Nitrate supplementation and high-intensity performance in competitive cyclists. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2014, 39, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonvik, K.L.; Nyakayiru, J.; Van Dijk, J.W.; Maase, K.; Ballak, S.B.; Senden, J.M.G.; Van Loon, L.J.C.; Verdijk, L.B. Repeated-sprint performance and plasma responses following beetroot juice supplementation do not differ between recreational, competitive and elite sprint athletes. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2018, 18, 524–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, G.L.; Dawson, B.; McNaughton, L.R.; Cox, G.R.; Burke, L.M.; Peeling, P. The effect of beetroot juice supplementation on repeat-sprint performance in hypoxia. J. Sports Sci. 2019, 37, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak-Chaouch, M.; Boissière, J.; Munyaneza, D.; Gamelin, F.X.; Cuvelier, G.; Berthoin, S.; Aucouturier, J. Beetroot Juice Does Not Enhance Supramaximal Intermittent Exercise Performance in Elite Endurance Athletes. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2019, 38, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, K.; Muggeridge, D.J.; Easton, C.; Ross, M.D. An acute dose of inorganic dietary nitrate does not improve high-intensity, intermittent exercise performance in temperate or hot and humid conditions. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2019, 119, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.; Wylie, L.J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Fulford, J.; Black, M.I.; Kelly, J.; McDonagh, S.T.; Carter, J.; Bailey, S.J.; Vanhatalo, A.; et al. Influence of dietary nitrate supplementation on physiological and muscle metabolic adaptations to sprint interval training. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2017, 122, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylie, L.J.; Bailey, S.J.; Kelly, J.; Blackwell, J.R.; Vanhatalo, A.; Jones, A.M. Influence of beetroot juice supplementation on intermittent exercise performance. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2016, 116, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez, R.; Maté-Muñoz, J.L.; Cuenca, E.; García-Fernández, P.; Mata-Ordoñez, F.; Lozano-Estevan, M.C.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; da Silva, S.F.; Garnacho-Castaño, M.V. Effects of beetroot juice supplementation on intermittent high-intensity exercise efforts. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muggeridge, D.J.; Howe, C.C.; Spendiff, O.; Pedlar, C.; James, P.E.; Easton, C. The effects of a single dose of concentrated beetroot juice on performance in trained flatwater kayakers. Int. J. Sport Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2013, 23, 498–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, C.L.; Henry, T.; Guelfi, K.; Dawson, B.; McNaughton, L.R.; Wallman, K. Effects of sodium phosphate and beetroot juice supplementation on repeated-sprint ability in females. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 115, 2205–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clifford, T.; Berntzen, B.; Davison, G.W.; West, D.J.; Howatson, G.; Stevenson, E.J. Effects of Beetroot Juice on Recovery of Muscle Function and Performance between Bouts of Repeated Sprint Exercise. Nutrients 2016, 8, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ernest, G.R.; Linda, R.P.; Andrew, R.C.; James, C.M. Increase in Maximal Cycling Power with Acute Dietary Nitrate Supplementation. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2016, 11, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, K.; Smee, D.; Thompson, K.G.; Rattray, B. No Improvement of Repeated-Sprint Performance with Dietary Nitrate. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.; Sim, A.; Burns, S.F. The Effect of Beetroot Ingestion on High-Intensity Interval Training: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, E.T.-C.; Iu, J.C.-K.; Sum, W.M.-K.; Wong, P.-S.; Lo, K.K.-H.; Ali, A.; Burns, S.F.; Trexler, E.T. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation and Exercise Performance: An Umbrella Review of 20 Published Systematic Reviews with Meta-analyses. Sports Med. 2025, 55, 1213–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.; Vanhatalo, A.; Kadach, S.; Wylie, L.J.; Fulford, J.; Ferguson, S.K.; Blackwell, J.R.; Bailey, S.J.; Jones, A.M. Discrete physiological effects of beetroot juice and potassium nitrate supplementation following 4-wk sprint interval training. J. Appl. Physiol. (1985) 2018, 124, 1519–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, A.M.; Vanhatalo, A.; Seals, D.R.; Rossman, M.J.; Piknova, B.; Jonvik, K.L. Dietary Nitrate and Nitric Oxide Metabolism: Mouth, Circulation, Skeletal Muscle, and Exercise Performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 280–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blot, S. Antiseptic mouthwash, the nitrate–nitrite–nitric oxide pathway, and hospital mortality: A hypothesis generating review. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiper, J.B. Fate of ingested fluids: Factors affecting gastric emptying and intestinal absorption of beverages in humans. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peri, L.; Pietraforte, D.; Scorza, G.; Napolitano, A.; Fogliano, V.; Minetti, M. Apples increase nitric oxide production by human saliva at the acidic pH of the stomach: A new biological function for polyphenols with a catechol group? Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, N.C.; Blannin, A.K.; Armstrong, E.; Rickman, M.; Gleeson, M. Carbohydrate and fluid intake affect the saliva flow rate and IgA response to cycling. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2000, 32, 2046–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siow, P.C.; Tan, W.S.K.; Henry, C.J. Impact of Isotonic Beverage on the Hydration Status of Healthy Chinese Adults in Air-Conditioned Environment. Nutrients 2017, 9, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.; Sim, R.; Sim, A.; Burns, S.F. Effects of an Isotonic Beetroot Drink on Power Output During Sprint Exercise and Jump Performance in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial. J. Diet. Suppl. 2024, 21, 808–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowland, S.N.; Da Boit, M.; Tan, R.; Robinson, G.P.; O’Donnell, E.; James, L.J.; Bailey, S.J. Dietary Nitrate Supplementation Enhances Performance and Speeds Muscle Deoxyhaemoglobin Kinetics during an End-Sprint after Prolonged Moderate-Intensity Exercise. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcelli, S.; Ramaglia, M.; Bellistri, G.; Pavei, G.; Pugliese, L.; Montorsi, M.; Rasica, L.; Marzorati, M. Aerobic Fitness Affects the Exercise Performance Responses to Nitrate Supplementation. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKay, A.K.A.; Stellingwerff, T.; Smith, E.S.; Martin, D.T.; Mujika, I.; Goosey-Tolfrey, V.L.; Sheppard, J.; Burke, L.M. Defining Training and Performance Caliber: A Participant Classification Framework. Int. J. Sport Physiol. Perform. 2022, 17, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, T.; Bull, F. Development of the World Health Organization Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ). J. Public Health 2006, 14, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburton, D.E.; Jamnik, V.K.; Bredin, S.S.; Gledhill, N. The physical activity readiness questionnaire for everyone (PAR-Q+) and electronic physical activity readiness medical examination (ePARmed-X+). Health Fit. J. Can. 2011, 4, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kapil, V.; Haydar, S.M.; Pearl, V.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Ahluwalia, A. Physiological role for nitrate-reducing oral bacteria in blood pressure control. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 55, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenmann, E.; Held, S.; Geisler, S.; Flenker, U.; Jeffreys, I.; Zinner, C. The effect of the menstrual cycle phases on back squat performance, jumping ability and psychological state in women according to their level of performance -a randomized three-arm crossover study. BMC Sports Sci. Med. Rehabil. 2024, 16, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.Y.; Osborne, J.O.; Topranin, V.M.; Engseth, T.P.; Solli, G.S.; Valsdottir, D.; Andersson, E.; Øistuen, G.F.; Flatby, I.; Welde, B.; et al. Menstrual Cycle Phase Has No Influence on Performance-Determining Variables in Endurance-Trained Athletes: The FENDURA Project. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2024, 56, 1595–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, H.; Townsend, L.K.; Hazell, T.J. Modified sprint interval training protocols. Part, I. Physiological responses. Interval Train. 2018, 1, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danek, N.; Smolarek, M.; Michalik, K.; Zatoń, M. Comparison of Acute Responses to Two Different Cycling Sprint Interval Exercise Protocols with Different Recovery Durations. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagishi, T.; Babraj, J. Effects of reduced-volume of sprint interval training and the time course of physiological and performance adaptations. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2017, 27, 1662–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermens, H.J. Biomedical Commission des Communautés européennes, and Programme Health Research. In SENIAM: European Recommendations for Surface Electromyography: Results of the SENIAM Project, 2nd ed.; Roessingh Research and Development: Enschede, The Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Volino-Souza, M.; de Oliveira, G.V.; Barros-Santos, E.; Conte-Junior, C.A.; Alvares, T.S. The impact of beetroot juice intake on muscle oxygenation and performance during rhythmic handgrip exercise. Pharma Nutr. 2020, 14, 100215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, R.; Pennell, A.; Price, K.M.; Karl, S.T.; Seekamp-Hicks, N.G.; Paniagua, K.K.; Weiderman, G.D.; Powell, J.P.; Sharabidze, L.K.; Lincoln, I.G.; et al. Effects of Dietary Nitrate Supplementation on Performance and Muscle Oxygenation during Resistance Exercise in Men. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulos, S.; Dipla, K.; Triantafyllou, A.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Kyparos, A.; Touplikioti, P.; Vrabas, I.S.; Zafeiridis, A. Beetroot Increases Muscle Performance and Oxygenation During Sustained Isometric Exercise, but Does Not Alter Muscle Oxidative Efficiency and Microvascular Reactivity at Rest. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2018, 37, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meilgaard, M.; Civille, G.; Carr, B. Sensory Evaluation Techniques, 4th ed.; CRC Press LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Green, N.; Green, J. Compositions, Apparatus and Methods for Monitoring Biomarkers. US 2017/0219570 A1, 7 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Babateen, A.M.; Shannon, O.M.; Mathers, J.C.; Siervo, M. Validity and reliability of test strips for the measurement of salivary nitrite concentration with and without the use of mouthwash in healthy adults. Nitric Oxide 2019, 91, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modi, A.; Morou-Bermudez, E.; Vergara, J.; Patel, R.P.; Nichols, A.; Joshipura, K. Validation of two point-of-care tests against standard lab measures of NO in saliva and in serum. Nitric Oxide 2017, 64, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatarczak-Michalewska, M.; Flieger, J.; Kawka, J.; Płaziński, W.; Flieger, W.; Blicharska, E.; Majerek, D. HPLC-DAD Determination of Nitrite and Nitrate in Human Saliva Utilizing a Phosphatidylcholine Column. Molecules 2019, 24, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.; Dougall, H.; Johnston, P.; Green, S.; Brogan, R.; Leifert, C.; Smith, L.; Golden, M.; Benjamin, N. Chemical generation of nitric oxide in the mouth from the enterosalivary circulation of dietary nitrate. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flueck, J.L.; Bogdanova, A.; Mettler, S.; Perret, C. Is beetroot juice more effective than sodium nitrate? The effects of equimolar nitrate dosages of nitrate-rich beetroot juice and sodium nitrate on oxygen consumption during exercise. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2016, 41, 421–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lbban, E.; Macey, A.; Rundle, J.; Ashor, A.; Idris, I.; Siervo, M. Effects of dietary nitrate and vitamin C co-ingestion on blood pressure and hand-grip strength in young adults. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2023, 94, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, B.S.; Gago, B.; Barbosa, R.M.; Laranjinha, J. Dietary polyphenols generate nitric oxide from nitrite in the stomach and induce smooth muscle relaxation. Toxicology 2009, 265, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadach, S.; Piknova, B.; Black, M.I.; Park, J.W.; Wylie, L.J.; Stoyanov, Z.; Thomas, S.M.; McMahon, N.F.; Vanhatalo, A.; Schechter, A.N.; et al. Time course of human skeletal muscle nitrate and nitrite concentration changes following dietary nitrate ingestion. Nitric Oxide 2022, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, K.; Goodall, S.; Stone, M.; Howatson, G.; Gibson, A.S.C.; Ansley, L.E.S. Central and Peripheral Fatigue in Male Cyclists after 4-, 20-, and 40-km Time Trials. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferguson, S.K.; Holdsworth, C.T.; Wright, J.L.; Fees, A.J.; Allen, J.D.; Jones, A.M.; Musch, T.I.; Poole, D.C. Microvascular oxygen pressures in muscles comprised of different fiber types: Impact of dietary nitrate supplementation. Nitric Oxide 2015, 48, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D. Measurement of nitrite in plasma and serum: Still a challenging analytical task. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. (CCLM) 2012, 50, 2049–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.M. Dietary nitrate supplementation and exercise performance. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernardi, B.B.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Alves, R.C.; Urbinati, K.S.; McAnulty, S.R.; Junior, T.P.S. Acute Supplementation with Beetroot Juice Does Not Enhance Exercise Performance among Well-trained Athletes: A Randomized Crossover Study. J. Exerc. Physiol. Online 2018, 21, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Kokkinoplitis, K.; Chester, N. The effect of beetroot juice on repeated sprint performance and muscle force production. J. Phys. Educ. Sport 2014, 14, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K.V.C.; Costa, B.D.; Gomes, A.C.; Saunders, B.; Mota, J.F. Factors that Moderate the Effect of Nitrate Ingestion on Exercise Performance in Adults: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analyses and Meta-Regressions. Adv. Nutr. 2022, 13, 1866–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lansley, K.E.; Winyard, P.G.; Bailey, S.J.; Vanhatalo, A.; Wilkerson, D.P.; Blackwell, J.R.; Gilchrist, M.; Benjamin, N.; Jones, A.M. Acute dietary nitrate supplementation improves cycling time trial performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoon, M.W.; Jones, A.M.; Johnson, N.A.; Blackwell, J.R.; Broad, E.M.; Lundy, B.; Rice, A.J.; Burke, L.M. The Effect of Variable Doses of Inorganic Nitrate-Rich Beetroot Juice on Simulated 2000-m Rowing Performance in Trained Athletes. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2014, 9, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, R.; Garnacho-Castano, M.V.; Cuenca, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, P.; Munoz-Gonzalez, A.; de Jesus, F.; Lozano-Estevan, M.D.C.; Fernandes da Silva, S.; Veiga-Herreros, P.; Mate-Munoz, J.L. Effects of Beetroot Juice Supplementation on a 30-s High-Intensity Inertial Cycle Ergometer Test. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BILLAUT, F.; BISHOP, D.J.; SCHAERZ, S.; NOAKES, T.D. Influence of Knowledge of Sprint Number on Pacing during Repeated-Sprint Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2011, 43, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, A.; Schiffer, T.A.; Ivarsson, N.; Cheng, A.J.; Bruton, J.D.; Lundberg, J.O.; Weitzberg, E.; Westerblad, H. Dietary nitrate increases tetanic [Ca2+]i and contractile force in mouse fast-twitch muscle. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 3575–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamler, J.S.; Meissner, G. Physiology of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 209–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelofs, E.J.; Hirsch, K.R.; Trexler, E.T.; Mock, M.G.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. The effects of pomegranate extract on anaerobic exercise performance & cardiovascular responses. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broeder, C.E.; Flores, V.; Julian, B.; Wojan, F.; Tauber, R.; Schubert, L.; Salacinski, A.; Ivy, J.L. Nitric Oxide Enhancement Supplement Containing Beet Nitrite and Nitrate Benefits High Intensity Cycle Interval Training. Curr. Res. Physiol. 2021, 4, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breese, B.C.; McNarry, M.A.; Marwood, S.; Blackwell, J.R.; Bailey, S.J.; Jones, A.M. Beetroot juice supplementation speeds O2 uptake kinetics and improves exercise tolerance during severe-intensity exercise initiated from an elevated metabolic rate. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R1441–R1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, S.; Kano, Y.; Barstow, T.J.; Ferreira, L.F.; Ohmae, E.; Sudo, M.; Poole, D.C. Kinetics of muscle deoxygenation and microvascular Po2 during contractions in rat: Comparison of optical spectroscopy and phosphorescence-quenching techniques. J. Appl. Physiol. 2012, 112, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondonno, C.P.; Liu, A.H.; Croft, K.D.; Ward, N.C.; Puddey, I.B.; Woodman, R.J.; Hodgson, J.M. Short-term effects of a high nitrate diet on nitrate metabolism in healthy individuals. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1906–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Specification | ISO-C | ISO-BR |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrate content (mg/285 mL) | 0 | 400 ± 30 |
| Carbohydrate (g/285 mL) | 14.8 ± 0.5 | 17.5 ± 0.5 |
| Total sugars (g/285 mL) | 14.0 ± 0.5 | 12.2 ± 0.5 |
| Protein (g/285 mL) | 0 | 1.4 ± 0.2 |
| Sodium (mg/285 mL) | 121 ± 5 | 219 ± 5 |
| Potassium (mg/285 mL) | 39 ± 5 | 215 ± 5 |
| Initial osmolality (mOsm/kg) | 290 ± 10 | 290 ± 10 |
| Major ingredients | Sugars | Beetroot juice concentrate * |
| Minor ingredients | Citric acid, salts, vitamins (B3, B6, B12), permitted flavorings, colorings and preservative | Citric acid, salts, natural sweeteners, vitamins (C, B3, B6, B12), permitted flavorings and preservative |
| Overall Liking and Preference (7-Point Hedonic Scale) | ISO-C | ISO-BR |
|---|---|---|
| Top 3 box overall liking (T3B) Neutral overall liking (Neutral) Bottom 3 box overall liking (B3B) Average mean score | 90% 10% 0% 5.40 a | 35% 10% 55% 3.85 b |
| Preference | 80% a | 20% b |
| Variables (n = 18) | ∆TSI | p Value | ∆O2Hb | p Value | ∆HHb | p Value | ∆tHb | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | ISO-C | −28.0 ± 19.2 | 0.714 | −5.8 ± 3.2 | 0.725 | 3.8 ± 4.1 | 0.098 | −2.1 ± 3.5 | 0.551 |
| ISO-BR | −26.3 ± 11.9 | −6.1 ± 3.8 | 5.0 ± 4.3 | −1.4 ± 3.4 | |||||
| R1 | ISO-C | 25.9 ± 12.0 | 0.786 | 7.3 ± 5.0 | 0.489 | −3.8 ± 3.5 | 0.665 | 3.4 ± 2.4 | 0.783 |
| ISO-BR | 25.2 ± 11.7 | 7.8 ± 5.1 | −4.0 ± 3.7 | 3.6 ± 2.4 | |||||
| S2 | ISO-C | −25.1 ± 12.0 | 0.886 | −6.9 ± 5.0 | 0.161 | 4.6 ± 4.0 | 0.381 | −2.3 ± 1.9 | 0.507 |
| ISO-BR | −25.5 ± 13.6 | −7.7 ± 5.3 | 5.0 ± 4.3 | −2.6 ± 1.8 | |||||
| R2 | ISO-C | 25.4 ± 15.6 | 0.450 | 7.7 ± 5.5 | 0.285 | −4.2 ± 4.0 | 0.409 | 3.5 ± 2.4 | 0.782 |
| ISO-BR | 20.4 ± 24.3 | 8.4 ± 5.9 | −4.6 ± 4.1 | 3.7 ± 2.4 | |||||
| S3 | ISO-C | −21.0 ± 7.9 | 0.970 | −6.8 ± 5.1 | 0.306 | 4.6 ± 4.5 | 0.689 | −2.2 ± 1.5 | 0.432 |
| ISO-BR | −20.9 ± 13.0 | −7.5 ± 5.8 | 4.8 ± 4.6 | −2.5 ± 1.8 | |||||
| R3 | ISO-C | 21.4 ± 9.4 | 0.173 | 7.4 ± 5.4 | 0.131 | −4.4 ± 4.4 | 0.439 | 3.0 ± 1.8 | 0.262 |
| ISO-BR | 27.6 ± 23.0 | 8.1 ± 5.7 | −4.7 ± 4.6 | 3.4 ± 1.9 | |||||
| S4 | ISO-C | −19.1 ± 8.5 | 0.971 | −6.8 ± 5.1 | 0.515 | 4.5 ± 4.4 | 0.766 | −2.3 ± 1.3 | 0.683 |
| ISO-BR | −19.2 ± 11.3 | −7.1 ± 5.5 | 4.6 ± 4.4 | −2.4 ± 1.8 | |||||
| R4 | ISO-C | 18.3 ± 8.9 | 0.660 | 7.1 ± 5.1 | 0.473 | −4.3 ± 4.4 | 0.973 | 2.9 ± 1.5 | 0.331 |
| ISO-BR | 16.9 ± 11.9 | 6.8 ± 5.4 | −4.3 ± 4.4 | 2.5 ± 2.1 | |||||
| S5 | ISO-C | −18.1 ± 7.8 | 0.858 | −6.7 ± 4.9 | 0.749 | 4.3 ± 4.4 | 0.670 | −2.4 ± 1.2 | 0.965 |
| ISO-BR | −17.7 ± 10.5 | −6.8 ± 5.8 | 4.5 ± 4.6 | −2.3 ± 1.8 | |||||
| R5 | ISO-C | 18.8 ± 8.5 | 0.607 | 6.4 ± 5.0 | 0.591 | −4.3 ± 4.2 | 0.986 | 2.0 ± 1.9 | 0.426 |
| ISO-BR | 17.6 ± 9.9 | 6.8 ± 5.8 | −4.3 ± 4.6 | 2.4 ± 2.1 | |||||
| S6 | ISO-C | −18.4 ± 10.7 | 0.563 | −6.3 ± 5.1 | 0.670 | 4.3 ± 4.4 | 0.930 | −1.9 ± 1.5 | 0.624 |
| ISO-BR | −16.8 ± 10.3 | −6.5 ± 5.9 | 4.3 ± 4.7 | −2.1 ± 2.0 | |||||
| R6 | ISO-C | 20.4 ± 10.4 | 0.836 | 9.3 ± 5.9 | 0.389 | −4.8 ± 5.1 | 0.505 | 4.6 ± 3.0 | 0.657 |
| ISO-BR | 19.8 ± 11.2 | 9.9 ± 6.3 | −5.1 ± 5.4 | 4.9 ± 2.3 | |||||
| R7 | ISO-C | 17.1 ± 14.7 | 0.247 | 2.8 ± 4.3 | 0.427 | −4.7 ± 2.2 | 0.697 | −1.4 ± 4.0 | 0.488 |
| ISO-BR | 12.8 ± 8.3 | 3.6 ± 3.9 | −4.5 ± 2.5 | −0.8 ± 4.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wong, T.H.; Ooi, D.S.Q.; Burns, S.F. Five-Day Supplementation with an Isotonic Beetroot Juice Drink Improves Sprint Interval Exercise and Muscle Oxygenation in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Beverages 2025, 11, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11040097
Wong TH, Ooi DSQ, Burns SF. Five-Day Supplementation with an Isotonic Beetroot Juice Drink Improves Sprint Interval Exercise and Muscle Oxygenation in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Beverages. 2025; 11(4):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11040097
Chicago/Turabian StyleWong, Tak Hiong, Delicia Shu Qin Ooi, and Stephen F. Burns. 2025. "Five-Day Supplementation with an Isotonic Beetroot Juice Drink Improves Sprint Interval Exercise and Muscle Oxygenation in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial" Beverages 11, no. 4: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11040097
APA StyleWong, T. H., Ooi, D. S. Q., & Burns, S. F. (2025). Five-Day Supplementation with an Isotonic Beetroot Juice Drink Improves Sprint Interval Exercise and Muscle Oxygenation in Physically Active Individuals: A Randomized Crossover Trial. Beverages, 11(4), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11040097







