Abstract
Listeria monocytogenes poses significant risks in acidic foods like unpasteurized fruit juices due to its capacity to survive under stressful conditions. This study evaluated L. monocytogenes survival in orange juice following acid adaptation and exposure to antimicrobial compounds. Acid adaptation was induced using glucose-supplemented or citric acid-acidified media, followed by the evaluation of pathogen survival in orange juice stored at 4 °C, 15 °C, and 25 °C. While glucose adaptation reduced the medium pH to 4.5 and enabled bacterial growth (up to 7.5 total log CFU/mL), citric acid exposure caused around 1.4 log units of reduction. Contrary to expectations, the survival of acid-adapted cells was lower than that of non-acid-adapted cells, particularly in orange juice stored at 25 °C (around 4.8 vs. 1.4 log units of reduction after 6 days). The behaviour of non-acid-adapted cells was evaluated in response to different antimicrobial compounds (citral, coumaric acid, nisin, sinapic acid, and vanillin). Nisin was the most effective, achieving a reduction of about 3.5 log units with a dose of 2 mL/L. Nisin-treated cells also showed reduced survival during simulated gastrointestinal assays (around 1.5 log units of reduction). These results challenge the assumption that acid adaptation universally enhances survival in acidic matrices and highlight nisin’s dual role in microbial control and pathogenicity mitigation. This work underscores the need for tailored stress adaptation studies and natural antimicrobial applications to improve food safety in minimally processed fruit juices.
1. Introduction
Foodborne pathogens can greatly impact public health, with Listeria monocytogenes being of particular concern due to the high mortality rate of infected individuals and its ability to thrive in food-production environments [1]. This bacterium is ubiquitous in nature, residing in various reservoirs, including soil, water, raw fruits, and food processing environments [2]. Consequently, fresh produce, such as fruits intended for juice extraction, can become contaminated. Cross-contamination during handling and extraction processes can introduce L. monocytogenes into fruit juices, especially those that are freshly squeezed, minimally processed, or unpasteurized, heightening the risk of consumer exposure.
Given the potential risks associated with L. monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods, the European Union’s Regulation No. 2073/2005 establishes a microbiological safety criterion to minimize foodborne infections [3]. This regulation stipulates that L. monocytogenes levels must remain below 100 CFU/g throughout the shelf life of ready-to-eat foods that do not support its growth. Products with pH ≤ 4.4 or aw ≤ 0.92, as well as those with a pH ≤ 5.0 and aw ≤ 0.94, are considered unable to support the growth of this pathogen by the regulation. These combinations reflect different mechanisms—either acidity alone, low water activity, or their combined inhibitory effect. However, for products that support its growth, the regulation mandates that the pathogen is not detected in 25 g of the product. Orange juice, with its inherently acidic nature (pH typically below 4.4), falls into the first category, theoretically making it unsuitable for bacterial proliferation. Despite this, several studies have shown that L. monocytogenes can survive and even grow at refrigeration temperatures in fruits and minimally processed fruit products [4,5,6]. This ability increases the risk of its persistence in fruit juices and underscores the need for effective control measures.
Furthermore, a critical concern is that L. monocytogenes can develop resistance to environmental and processing-related stresses [7]. One of the adaptive mechanisms employed by the foodborne pathogen to survive in acidic foods is acid adaptation, which involves physiological changes that enhance its resistance to low pH conditions [8]. In addition to acid stress, the antimicrobial properties of antimicrobial compounds are being increasingly explored as natural alternatives for bacterial control in food products [9,10]. Essential oils, phenolic acids, and bacteriocins have demonstrated inhibitory effects against L. monocytogenes, although their efficacy can vary depending on environmental conditions and bacterial physiological state [11,12,13,14]. An acidic environment and the presence of antimicrobial compounds are stress barriers that may affect the survival of L. monocytogenes in orange juice but also enhance its pathogenic potential, thereby raising concerns about the risk associated with unpasteurized and minimally processed fruit juices.
The objective of this study was to evaluate the survival of L. monocytogenes in orange juice under two different stress conditions: acid adaptation and exposure to antimicrobial compounds. As a first step, we assessed different methods for inducing acid adaptation and evaluated whether this adaptation influenced bacterial survival in orange juice stored at different temperatures (4, 15, and 25 °C). Afterwards, we examined the efficacy of different antimicrobial compounds (citral, coumaric acid, nisin, sinapic acid, and vanillin) in controlling the proliferation of L. monocytogenes in orange juice. Following the selection of the most effective antimicrobials, we further assessed pathogen survival and pathogenic potential. By addressing these aspects, this study contributes to a better understanding of L. monocytogenes stress responses and provides insights into potential control strategies for minimally processed fruit juices.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Culture
To obtain a fresh bacterial culture, a single L. monocytogenes serovar 4b strain (CECT 4032) colony previously grown on tryptone soy agar with 6 g/L yeast extract (TSYEA; Biokar; Allonne, France) at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 ± 1 h was inoculated into 100 mL of tryptone soy broth supplemented with 6 g/L yeast extract (TSYEB; Biokar, Allonne, France). The broth was incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 20 ± 1 h, resulting in a late stationary phase bacterial culture. Postincubation, 20 mL of the bacterial suspension was harvested and centrifuged at 9800× g for 10 min at 25 °C. The pellet was subsequently resuspended in saline solution (SS; 8.5 g/L NaCl; VWR; Radnor, PA, USA). The bacterial concentration was assessed by performing tenfold serial dilutions in saline peptone (SP; 8.5 g/L NaCl and 1 g/L peptone; Biokar), followed by plating them onto TSYEA. The plates were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 ± 2 h.
2.2. Acid Adaptation and Its Effect in Orange Juice
2.2.1. Evaluation Methods for Obtaining Acid-Adapted Cells
Two different methods were assessed for developing acid-adapted (AA) cultures, using TSYEB without glucose (TSYEB-w/o; Sigma-Aldrich; San Luis, MO, USA) as the base medium. Two formulations were tested: TSYEB-w/o supplemented with 10 g/L glucose (TSYEB-G, D-Glucose anhydrous; Fisher Scientific; Loughborough, UK) to induce fermentation, and TSYEB-w/o acidified to pH 4.5 with citric acid (TSYEB-CA). Citric acid was selected from among various organic acids, as it is the predominant organic acid naturally present in orange juice. Fresh L. monocytogenes culture was harvested by centrifugation (9800× g for 10 min at 25 °C), washed with SS, and diluted with sterile water in order to obtain a standardized inoculum suspension of approximately 4.5 × 105 CFU/mL. Then, 50 µL of this suspension was added to 20 mL of TSB-w/o (to obtain non-acid-adapted cells, NAA) or to 20 mL of TSYEB-G or TSYEB-CA (to obtain acid-adapted cells, AA) in order to achieve an initial bacterial concentration of 3 log CFU/mL. All flasks were incubated for 24 ± 2 h at 37 ± 1 °C. Initial and final populations were quantified by performing tenfold serial dilutions in SP and plating onto TSYEA. The plates were then incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 ± 2 h. The initial and final pH values of each culture condition were also determined using a GLP22 pH meter (Crison Instruments S.A.; Alella, Spain) coupled with a 2 PORE F TEMP BNC electrode (XS Instruments; Carpi, Italy).
2.2.2. Survival of Acid-Adapted and Non-Acid Adapted Pathogens in Orange Juice
The food matrix used in this study was a commercial pasteurized orange juice sourced from a supermarket in Lleida (Catalonia, Spain). The juice presented the following characteristics: pH 3.51 ± 0.02, total soluble solids of 11.6 ± 0.1 °Brix, and a titratable acidity of 7.04 ± 0.26 g citric acid/L. These physicochemical parameters were measured using the following methodology: pH was measured using a GLP22 pH-meter (Crison Instruments S.A; Barcelona, Spain) with a 2 PORE F TEMP BNC electrode (XS Instruments; Carpi, Italy); total soluble solids were assessed with a digital refractometer (Atago Co. Ltd.; Tokio, Japan) at room temperature and expressed as °Brix ± SD; titratable acidity was determined by titrating 10 mL of juice with 0.1 N NaOH (VWR) to pH 8.1, and the results expressed as g of citric acid/L ± SD.
To standardize the bacterial concentration prior to inoculation into orange juice, culture volumes were adjusted based on the final cell concentration obtained from each growth medium. For this experiment, only AA cells grown in TSYEB-G and NAA cells grown in TSYEB-w/o were used. An appropriate volume of each culture was centrifuged (9800× g, 10 min, 25 °C), washed with saline solution (SS; 8.5 g/L NaCl; VWR), and resuspended in pre-tempered to 4, 15, or 25 °C orange juice to achieve an initial population of approximately 5 log CFU/mL. Inoculated samples were stored at 4, 15, and 25 °C for a period of six days. Bacterial populations were evaluated on days 0, 1, 2, and 6 by performing tenfold serial dilutions in SP and plating them onto selective Palcam agar (Palcam Agar Base with selective supplement; Biokar). Plates were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 ± 2 h. The pH of each sample was measured at both the initial and final time points.
2.3. Antimicrobial Compounds and Their Antimicrobial Effect Against Non-Acid-Adapted Cells in Orange Juice
The preliminary assay consisted of the evaluation of the effect of 5 different antimicrobial compounds at different doses against L. monocytogenes after 48 h in orange juice stored at 4 °C (Section 2.3.2). Then, only the antimicrobial compounds and doses that showed the highest population reduction were evaluated after different timepoints in orange juice at 4 °C (Section 2.3.3). Ultimately, a single antimicrobial compound was selected to evaluate its effect on the pathogenic potential (Section 2.3.4).
2.3.1. Orange Juice Supplemented with Antimicrobial Compounds
The tested compounds included citral (Sigma-Aldrich; San Luis, MO, USA), nisin (White NisinA®, Handary; Fleurus, Belgium), p-coumaric acid (Sigma-Aldrich), sinapic acid (Sigma-Aldrich), and vanillin (Sigma-Aldrich). These compounds were incorporated into the commercial orange juice at different concentrations. As a control, orange juice without any added compounds was included. All orange juice samples were aliquoted into 20 mL portions, stored in sterile flasks, and kept at −20 °C until further use.
2.3.2. Initial Selection of Antimicrobial Compounds and Corresponding Concentrations
Based on a literature review and to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration against pathogen growth, antimicrobial compounds were added to orange juice at the following concentrations: citral at 0.25 and 0.5 mL/L; nisin at 0.5, 1, 2, and 4 mL/L; coumaric acid at 0.05, 0.1, 0.25, and 0.5 g/L; sinapic acid at 0.3, 0.45, 0.9, and 1.5 g/L; and vanillin at 0.05, 0.125, 0.25, and 0.5 g/L. Prior to pathogen inoculation, all supplemented orange juice samples were preconditioned at 4 °C. Then, 200 µL of a NAA L. monocytogenes suspension obtained by centrifugation of a culture grown in TSYEB for 24 h was added to each sample to achieve an initial bacterial concentration of approximately 5 log CFU/mL in the juice. Samples were stored at 4 °C for 48 h, with bacterial populations monitored immediately after inoculation and at the conclusion of the storage period. At each sampling point, bacterial enumeration was conducted by plating tenfold serial dilutions on TSYEA plates, followed by incubation at 37 ± 1 °C for 24–48 h.
2.3.3. Antimicrobial Activity of the Chosen Antimicrobials in Orange Juice
Based on the findings from Section 2.3.2, the most effective antimicrobial compounds were selected for further testing to determine the kinetic parameters of the microbial reduction: citral at 0.25 and 0.5 mL/L, nisin at 1 and 2 mL/L, and coumaric acid at 0.25 and 0.5 g/L. To prepare bacterial suspensions, 20 mL of bacterial culture was centrifuged at 9800× g for 10 min at 25 °C and the resulting pellets were resuspended in the same volume of sterile water. Sterile flasks containing 20 mL of either plain orange juice or orange juice supplemented with antimicrobial compounds, pre-tempered to 4 °C, were inoculated to achieve an initial bacterial concentration of approximately 5 log CFU/mL. Samples were stored at 4 °C, and bacterial populations were monitored at 0, 6, 24, 30, and 48 h by plating tenfold serial dilutions onto TSYEA. Plates were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 24 ± 2 h.
2.3.4. Impact of the Selected Antimicrobial on Bacterial Pathogenicity
According to the results from Section 2.3.3, the antimicrobial compound that suppressed bacterial growth the most was nisin at 1 mL/L. The impact of the antimicrobial compound added to orange juice on pathogenic potential was assessed by evaluating bacterial survival during simulated gastrointestinal tract (GIT) exposure. Bacterial enumeration was performed at three critical stages: immediately following inoculation in orange juice (OJ), after exposure to simulated gastric fluid (post SGF), and after exposure to simulated intestinal fluid (post SIF). The assay was repeated after 24 h of storage at 4 °C. The gastrointestinal simulation followed the protocol described by Minekus et al. [15] with minor modifications. At each time point, 5 mL of inoculated orange juice (with or without antimicrobial compound) was aseptically transferred into a sterile flask. Subsequently, 9.8 mL of Simulated Gastric Fluid (SGF, pH 3.0) was added, and the mixture was homogenized. SGF was prepared by mixing 7.5 mL of electrolyte stock solution (Fisher Scientific), 1.6 mL of porcine pepsin (25,000 U/mL, Sigma-Aldrich), and 0.7 mL of CaCl2 (0.0021 M, Sigma-Aldrich), with the pH adjusted to 3.0 using 1 M HCl (Panreac S.A; Barcelona, Spain). Samples were incubated at 37 ± 1 °C for 2 h. After incubation, the pH was recorded and duplicate 0.5 mL aliquots were collected for bacterial counting (post SGF). Following this, 19.7 mL of Simulated Intestinal Fluid (SIF, pH 7.0) was added, mixed thoroughly, and the pH was adjusted to 7.0 using sodium hydroxide (NaOH, 1 mol/L; VWR). SIF was prepared using 11 mL of electrolyte stock solution (Fisher Scientific), 5 mL of pancreatin (800 U/mL, Sigma-Aldrich), 2.5 mL of bile salts (160 mM, Sigma-Aldrich), and 1.2 mL of CaCl2 (0.01 M, Sigma-Aldrich). The samples underwent a second incubation at 37 ± 1 °C for 2 h. Upon completion, the pH was measured again and duplicate 0.5 mL samples were taken for bacterial enumeration (post-SIF). Bacterial counts at all stages were determined using the previously described methodology.
2.4. Data Analysis
All the experiments were conducted in triplicate and repeated twice, resulting in a total of six replicates (n = 6). Bacterial populations during storage were quantified as colony-forming units per milliliter (CFU/mL) and subsequently transformed to logarithmic scale (log CFU/mL). Statistical analyses, including analysis of variance (ANOVA), Student’s t tests, and Tukey’s tests, were performed with JMP Pro 17 software (SAS Institute Inc.; Cary, NC, USA), with significance set at p < 0.05. To illustrate the correlations between bacterial population reductions and the tested antimicrobial compounds at different concentrations, a scatter matrix plot was created using the same software. Additionally, survival curve fitting was performed using GInaFIT 1.6 software [16]. The Weibull model is represented by Equation (1).
where δ (h) represent the scale parameter, indicating the time necessary for the first decimal reduction, and p denotes the shape parameter, which characterizes the concavity or convexity of the survival curve. Model performance was evaluated based on the root mean square error (RMSE) and the adjusted correlation coefficient (R2-adj), both of which were obtained directly from the software as standard outputs for assessing the goodness of fit.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Methods for Obtaining Acid-Adapted Cells
Figure 1 shows the growth of L. monocytogenes in different acid-adaptive media, along with the average pH values recorded at the beginning and after 24 h of incubation. In the control medium (TSYEB-w/o), L. monocytogenes reached approximately 9 log CFU/mL, whereas in the glucose-supplemented medium (TSYEB-G), the population increased by 4.4 ± 0.3 log units, reaching 7.5 log CFU/mL. The final pH of the control medium after incubation was 5.8 ± 0.2, while in the glucose-supplemented medium, it decreased to 4.5 ± 0.0. In contrast, when citric acid was present (initial pH = 4.5), L. monocytogenes populations declined by 1.4 ± 0.5 log units. The pH in the citric acid medium remained stable throughout the experiment.
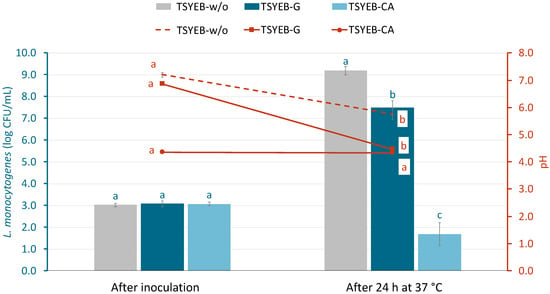
Figure 1.
Population of L. monocytogenes (log CFU/mL) and pH changes over time in different growth media: tryptone soy broth with yeast extract (TSYEB-w/o), TSYEB with 1% glucose (TSYEB-G), and TSYEB adjusted to pH 4.5 with citric acid (TSYEB-CA). Bars and markers, color-coded by treatment, depict bacterial populations (log CFU/mL), while lines correspond to pH evolution represented on the right Y-axis. Data are expressed as means with standard deviation error bars (n = 6). According to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05), different letters above the bars indicate significant differences between bacteria populations at the same timepoint. Similarly, different letters above the markers denote significant differences in pH within each medium over time, comparing before and after incubation.
3.2. Acid-Adapted and Non-Acid Adapted Pathogen’s Survival in Orange Juice
After observing a population reduction in AA cells that had been adapted in a medium enriched with citric acid, and based on the results from Section 3.1, bacterial growth in a TSYEB-G medium was selected as the method for L. monocytogenes acid adaptation. Therefore, the glucose-based adaptation method was used in this experiment. Figure 2 depicts the behaviour of AA and NAA L. monocytogenes in orange juice stored at 4, 15 and 25 °C. At the initial time point, no significant differences were observed among the initial populations of L. monocytogenes, with an average bacterial population of 5.5 ± 0.1 log CFU/mL. After 2 days of storage, the AA L. monocytogenes population decreased by nearly 2 log units in juice at 25 °C, whereas at the other temperatures (both AA and NAA populations), bacterial levels either remained stable or showed only a minor reduction of approximately 0.4 log units. By day 6, AA populations were lower than their control counterparts at all storage temperatures. For instance, NAA populations remained stable at 4 °C and 15 °C, while AA populations decreased by 0.6 ± 0.3 and 1.3 ± 0.2 log units, respectively. At 25 °C, AA populations showed a significant reduction of 4.8 ± 0.2 log units in comparison with the 1.4 ± 0.2 log units decrease in NAA populations.
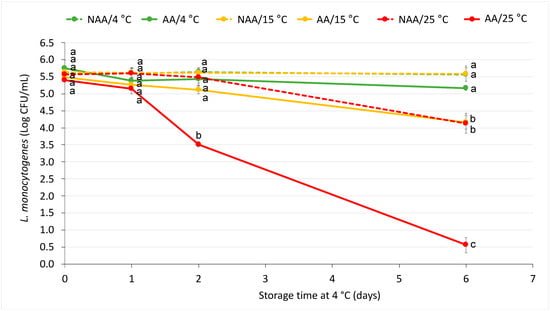
Figure 2.
Acid-adapted (AA) and non-acid-adapted (NAA) L. monocytogenes’s survival in orange juice stored for 6 days at three different temperatures (4, 15 and 25 °C). Markers represent means and error bars represent standard errors of the mean (n = 6). Different letters represent significant differences between samples at the same timepoint according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05).
3.3. Preliminary Selection of Antimicrobial Compounds and Their Concentrations
Figure 3 represents the antimicrobial effects of several antimicrobial compounds added to orange juice as measured by the NAA L. monocytogenes population reduction, expressed in log CFU/mL, across different doses. Among the tested treatments, orange juice with nisin exhibited the highest antimicrobial activity, achieving reductions of up to approximately 3.9 ± 0.4 log units at higher doses (2 and 4 g/L) after 48 h at 4 °C. In contrast, citral and coumaric acid exhibited moderate levels of population reduction, with maximum reductions around 2.0 ± 0.1 log units at higher doses. On the other hand, sinapic acid and vanillin showed limited effectiveness, with reductions similar to those observed in orange juice without any antimicrobial compound, remaining below 1 log unit of reduction across all tested doses.
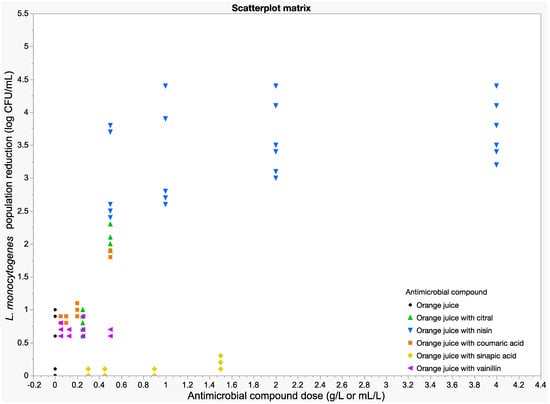
Figure 3.
Bacterial population reductions of NAA L. monocytogenes after 48 h at 4 °C in orange juice supplemented with various antimicrobial compounds at different concentrations.
3.4. Antimicrobial Effect of the Selected Antimicrobials in Orange Juice
Figure 4 shows L. monocytogenes’s logarithmic reduction in orange juice with and without citral, nisin and coumaric acid at different concentrations at 4 °C. Overall, L. monocytogenes in orange juice without any compound showed minimal reduction over time (<0.5 log units of reduction), maintaining relatively stable levels compared to the other conditions. The addition of low doses of citral and coumaric acid (0.25 mL/L and 0.25 g/L, respectively) resulted in a gradual decrease in the bacterial population, although less pronounced than for the other compounds. The addition of low doses of nisin (1 mL/L) led to a similar reduction observed with higher loses of citral and coumaric acid, particularly in the early storage stages. The highest decline was observed with the addition of 2 mL/L of nisin, reaching a reduction of around 3.5 log units by the end of the experiment (48 h).
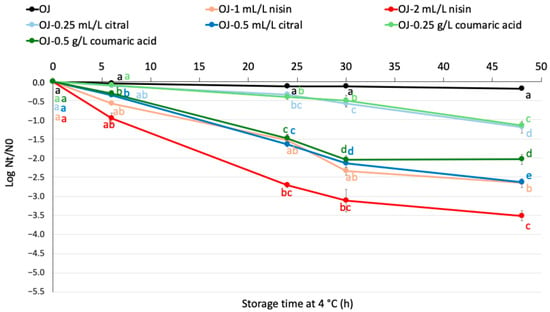
Figure 4.
Logarithmic reduction of NAA L. monocytogenes population (log Nt/N0) in plain orange juice and orange juice supplemented with varying concentrations of antimicrobial compounds during storage at 4 °C. Data points represent means, with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean (n = 6). Different letters denote significant differences over the storage period according to Tukey’s test (p < 0.05). OJ: orange juice.
The observed microbial behavior is related to the kinetic parameters obtained after fitting the microbial data to the Weibull model. Table 1 presents the statistical indices and parameters obtained from the Weibull model fitted to the survival curves of L. monocytogenes in orange juice subjected to various antimicrobial treatments and stored at 4 °C. The best fit was observed for 0.5 mL/L citral, with the highest R2-adj (0.972) and a relatively low RMSE (0.181), suggesting a strong correlation and predictive capacity. Treatments with the lowest dose of citral and coumaric acid (0.25 mL-g/L) showed similar performances, with high δ values (almost 45 h), indicating slower microbial inactivation. In contrast, 2 mL/L nisin showed the lowest δ (around 3.5 h), reflecting the rapid decline in bacterial population noted in Figure 4.

Table 1.
Model parameters and statistical indices derived from the Weibull model fitting of L. monocytogenes survival curves in orange juice containing various antimicrobial compounds during storage at 4 °C.
3.5. Impact of the Selected Antimicrobials on Bacterial Pathogenicity
Figure 5 shows the survival of NAA L. monocytogenes in orange juice with and without the addition of 1 mL/L of nisin following simulated gastrointestinal tract (GIT) exposure. Assessments were conducted both immediately after inoculation and after 24 h of juice storage at 4 °C. Notably, although both juices were inoculated with the same concentration of pathogen, the initial population in the nisin-treated orange juice was lower than that in the untreated juice. Despite this, a greater reduction was observed throughout the GIT simulation in the nisin-treated juice. The total decrease from OJ to post SIF was 3.4 ± 0.1 log units in juice supplemented with nisin, compared to 2.2 ± 0.1 log units in the control. After 24 h of storage at 4 °C, the population in orange juice with nisin had already decreased by approximately 1 log unit, whereas in the untreated juice, the reduction was less than 0.5 log units. When considering only the reduction during the GIT simulation, both treatments showed comparable decreases (2.7 ± 0.1 log units). However, due to the lower initial population in the nisin-treated juice prior to the GIT exposure, the final concentration after simulated intestinal fluid (post SIF) was more than 3 log units lower than that of the control.
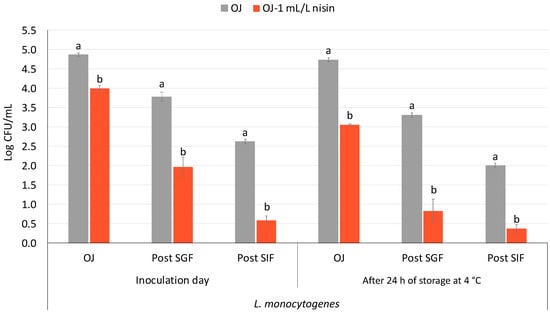
Figure 5.
Population of NAA L. monocytogenes in orange juice and orange juice with nisin (1 mL/L nisin) following exposure to a simulated gastrointestinal tract (GIT) before and after 24 h of juice storage at 4 °C. Bars represent mean values, with error bars indicating the standard error of the mean (n = 6). Distinct letters denote statistically significant differences between plain orange juice (grey bars) and orange juice supplemented with nisin (orange bars) at each sampling point—orange juice (OJ), after exposure to simulated gastric fluid (post-SGF), and after exposure to simulated intestinal fluid (post-SIF)—as determined by Student’s t-test (p < 0.05).
4. Discussion
The ability of L. monocytogenes to adapt to stressful environments is relevant for food security, particularly in acidic food products such as fruit juices. In this study, we evaluated the survival of this foodborne pathogen in orange juice under two different stress conditions: acid adaptation and exposure to antimicrobial compounds.
To induce acid adaptation, we evaluated two different approaches, exposure to a glucose-supplemented medium (TSYEB-G) and exposure to a citric acid-acidified medium (TSYEB-CA, pH 4.5). The ability of citric acid to trigger an acid tolerance response more effectively than other organic acids has been demonstrated in pathogens such as Salmonella [17]. The use of a mildly acidic growth medium has been shown to provide moderate stress conditions that effectively induce an adaptive acid stress response in subsequent highly acidic environments [18]. However, in our study, this method did not support bacterial growth, suggesting that citric acid and immediate exposure to an acidic pH had a strong inhibitory effect on L. monocytogenes under the tested conditions. Alternative approaches for effective acid adaptation through exposure to mildly acidic environments could involve acidification with non-cytotoxic acidic buffers [19] or other acids such as HCl or lactic acid [20,21].
Consequently, the glucose-based method was selected for further experimentation. A previous study [22] evaluated the same acid adaptation method (1% glucose) with Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli O157:H7. Foodborne pathogens exhibited increased survival in orange juice after acid adaptation. Contrary to the initial hypothesis, the results of this study revealed that acid adaptation negatively impacted the survival of L. monocytogenes in orange juice, particularly at 25 °C. This suggests that the acid stress experienced during adaptation may have weakened the bacterial cells, rendering them less capable of surviving subsequent exposure to the acidic environment of orange juice. These findings contrast with previous study by Karabiyikli et al. [23] and Topalcengiz et al. [24], who demonstrated that acid adaptation conferred increased tolerance to fruit juices in L. monocytogenes. In their study, acid adaptation was achieved by culturing the bacteria twice in BHI broth supplemented with 1% glucose at 37 °C for 18 h. The discrepancy may be attributed to differences in adaptation methods or experimental conditions.
Another possible explanation for the reduced survival of L. monocytogenes in fruit juice following acid adaptation is that exposure to glucose-supplemented medium, followed by a subsequent pH drop to sublethal levels, may have induced cellular damage. Arvaniti et al. [25] demonstrated in their study that after prolonged acid stress, the pathogen sustains sublethal damage, which negatively affects its subsequent survival at both 20 and 4 °C. Additionally, acid stress can lead to physiological trade-offs, where energy resources are redirected toward stress response mechanisms rather than cellular maintenance and repair [26], eventually increasing bacterial susceptibility under a subsequent hostile environment. Future studies could employ techniques such as transcriptomic or proteomic analyses to identify damage markers in acid-adapted cells after exposure in food matrices.
Given that acid adaptation did not confer increased survival in orange juice, it was not considered a relevant factor when evaluating the effect of natural antimicrobials. This decision was based on the observation that adaptation did not provide a survival advantage, making it unnecessary to differentiate between AA and NAA cells in the antimicrobial assays.
The antimicrobial efficacy of the tested compounds varied significantly in this study. Sinapic acid and vanillin showed limited effectiveness against L. monocytogenes, even at increasing concentrations. Like other phenolic acids, sinapic acid has gained attention for its antimicrobial properties against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria [27]. It has also been reported to inhibit L. monocytogenes biofilm formation [28]. However, its antimicrobial effect in fruit juice has not been previously studied, making its inclusion in this study particularly relevant. Despite this, no inhibitory effect was observed under the tested conditions (0.3–1.5 g/L in orange juice at 4 °C for 48 h). Differences in findings between the studies may be attributed to factors such as the method of application (alone, in combination, or encapsulated), the composition of the food matrix, storage conditions, and interactions with other substances [29], and the specific L. monocytogenes strains used, since previous research has employed a variety of strains, which may differ from the one used in this study. Similarly, vanillin (0.05–0.5 g/L) did not show significant inhibition in this study. As with sinapic acid, previous studies on vanillin also used different L. monocytogenes strains, which could partly explain the variability in its antimicrobial activity observed. In addition, vanillin’s efficacy has been reported to depend on the physicochemical characteristics of the matrix, such as pH and juice type [30,31]. Further studies are needed to optimize its application in fruit juices.
In contrast to the limited antimicrobial effect observed with sinapic acid and vanillin, scatter matrix results showed a clear dose-dependent relationship for citral and coumaric acid, with higher concentrations leading to greater reductions in L. monocytogenes populations. Previous studies have investigated the antimicrobial effects of citral and coumaric acid against foodborne pathogens [32,33]. Citral exerts its effect by disrupting membrane integrity, while coumaric acid penetrates the cell in its undissociated form, acidifying the cytoplasm and leading to cell death [34,35]. These findings align with our results. However, higher concentrations (0.5 mL/L) were necessary to achieve reductions of approximately 2.5 log units in orange juice after 48 h at 4 °C. It has been reported that high levels of essential oils like citral can alter the sensory characteristics of the food matrix, potentially affecting consumer acceptance [36]. To overcome these challenges, combined treatments or delivery technologies such as encapsulation could enhance antimicrobial efficacy while maintaining sensory attributes [37,38,39].
Nisin exhibited the highest antimicrobial activity, achieving final reductions of approximately 2.5 log units of L. monocytogenes population in orange juice at relatively low concentrations. This result aligns with previous studies showing that nisin effectively disrupts bacterial cell membranes and inhibits peptidoglycan synthesis [40]. Similar reductions, close to 4 log units, were observed by Lee et al. [41] in orange juice containing solid nisin (1 g/L) stored at 25 °C, demonstrating the bacteriocin’s inhibitory effect even at higher temperatures than those analysed in this study.
Notably, despite the bacterial survival curves in orange juice treated with 1 mL/L of nisin being fitted using the Weibull model, the goodness of fit was poor, with R2 values close to 0.500. This suggests that the model could not adequately describe the observed bacterial behavior. The high variability between replicates is likely due to the sublethal concentration of nisin, which may have caused cellular injury rather than complete inactivation. Sublethally injured cells can behave unpredictably—some may recover and resume growth, while others may die—thus complicating the modeling process [42]. In contrast, the 2 mL/L nisin treatment resulted in more consistent bacterial reductions and better model fits, suggesting that this higher concentration was more effective at inactivating the majority of the L. monocytogenes population.
Additionally, research has shown that adding nisin to different fruit juices does not alter their sensory properties and remains stable in all samples for 30 days at 4 °C [12]. This represents a significant advantage when considering nisin as a promising alternative for controlling microbial contamination in fruit juices. The demonstrated stability and antimicrobial activity of nisin under acidic conditions further support its application as a natural preservative in these beverages.
The impact of nisin on pathogenic potential was particularly noteworthy. While its antimicrobial properties have been widely studied, to the best of our knowledge, no research has specifically evaluated its effect on L. monocytogenes survival through the gastrointestinal tract when added to fruit juice. Simulated gastrointestinal assays revealed that L. monocytogenes populations in orange juice with 1 mL/L of nisin were significantly reduced after exposure to gastrointestinal conditions (3.4 ± 0.1 log units), compared to untreated juice (2.2 ± 0.1 log units). Akritidou et al. [43] evaluated L. monocytogenes survival through the gastrointestinal tract under in vitro conditions, considering the proportion of injured populations. Their findings indicated that a substantial fraction of bacterial cells was sublethally damaged at the end of the intestinal phase and that bile acids exerted a stronger bactericidal effect when prior exposure to acidity was more severe. This could explain the greater reduction in L. monocytogenes populations observed in nisin-treated juice, suggesting a synergistic effect between the acidic pH of orange juice, the components of gastrointestinal fluids, and nisin’s specific mechanism of action, which involves pore formation in bacterial membranes [44]. These findings reinforce the use of nisin as a potential strategy against L. monocytogenes, given that foodborne pathogens can develop tolerance mechanisms to the gastrointestinal tract after exposure to sublethal stresses during food processing [45].
These results have significant implications for food safety, particularly in unpasteurized or minimally processed fruit juices like orange juice. The demonstrated efficacy of nisin offers a promising approach for microbial control. Additionally, combining nisin with other antimicrobial compounds such as citral or coumaric acid could enhance antimicrobial activity by targeting multiple bacterial resistance mechanisms. Future research should focus on understanding the molecular mechanisms underlying L. monocytogenes adaptation to acidic environments and evaluating the long-term stability and sensory effects of organic antimicrobials in fruit juice. Investigating synergistic interactions between different antimicrobials could further improve their efficacy while reducing required concentrations. Additionally, consumer acceptance and regulatory considerations will be crucial for the successful incorporation of these natural preservatives into commercial products.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrated that acid adaptation using glucose-supplemented media did not enhance L. monocytogenes survival in orange juice, with AA populations declining by 4.8 log units at 25 °C compared to 1.4 log units for NAA cells. These findings contrast with earlier reports of improved acid tolerance, suggesting that adaptation outcomes depend on methodology and environmental conditions. Nisin emerged as a potent antimicrobial, reducing bacterial populations by 3.5 log units at 2 g/L and impairing pathogenicity during gastrointestinal simulation (around 1.5 log reduction postintestinal exposure). Citral and coumaric acid showed moderate efficacy (around 2.0 log units of reductions), while sinapic acid and vanillin were ineffective. Future research should explore molecular mechanisms behind stress adaptation variability and evaluate synergies between natural antimicrobials (e.g., nisin and citral) to enhance microbial control. Such insights are critical for designing robust food safety strategies that address the complex interplay between pathogen physiology, antimicrobial interventions, and matrix-specific factors in minimally processed fruit juices.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.B.B., P.C.-M., I.V. and I.A.; methodology, M.B.B. and P.C.-M.; software, M.B.B.; validation, M.B.B., P.C.-M. and I.A.; formal analysis, M.B.B. and P.C.-M.; investigation, M.B.B. and P.C.-M.; resources, I.V. and I.A.; data curation, M.B.B.; writing—original draft preparation, M.B.B.; writing—review and editing, P.C.-M. and I.A.; visualization, M.B.B.; supervision, I.V. and I.A.; project administration, I.V. and I.A.; funding acquisition, I.V. and I.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was financially supported by the Spanish Government (Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad, research project QUALISAFEJUICE, PID2019-106645RB-I00). Agència de Gestió d’Ajuts Universitaris i de Recerca (AGAUR) supported the PhD grant of M. B Bainotti (2022FI_B1 00225).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Osek, J.; Lachtara, B.; Wieczorek, K. Listeria monocytogenes—How This Pathogen Survives in Food-Production Environments? Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 866462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Townsend, A.; Strawn, L.K.; Chapman, B.J.; Dunn, L.L. A Systematic Review of Listeria Species and Listeria monocytogenes Prevalence, Persistence, and Diversity throughout the Fresh Produce Supply Chain. Foods 2021, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Union Regulation (EC). No 2073/2005 of 15 November 2005 on Microbiological Criteria for Foodstuffs. J. Eur. Union 2005, 338, 1–26. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Ziegler, M.; Rüegg, S.; Stephan, R.; Guldimann, C. Growth Potential of Listeria monocytogenes in Six Different RTE Fruit Products: Impact of Food Matrix, Storage Temperature and Shelf Life. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2018, 7, 7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zheng, J.; Nou, X. Growth and Survival of Salmonella enterica and Listeria monocytogenes on Fresh-Cut Produce and Their Juice Extracts: Impacts and Interactions of Food Matrices and Temperature Abuse Conditions. Food Control 2019, 100, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nangul, A.; Bozkurt, H.; Gupta, S.; Woolf, A.; Phan-thien, K.-y.; McConchie, R.; Fletcher, G.C. Decline of Listeria monocytogenes on Fresh Apples during Long-Term, Low-Temperature Simulated International Sea-Freight Transport. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 341, 109069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiktorczyk-Kapischke, N.; Skowron, K.; Grudlewska-Buda, K.; Wałecka-Zacharska, E.; Korkus, J.; Gospodarek-Komkowska, E. Adaptive Response of Listeria monocytogenes to the Stress Factors in the Food Processing Environment. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 710085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, T.; Buys, E.M. Listeria monocytogenes Pathogenesis: The Role of Stress Adaptation. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruzzi, L.; Campaniello, D.; Speranza, B.; Corbo, M.R.; Sinigaglia, M.; Bevilacqua, A. Thermal Treatments for Fruit and Vegetable Juices and Beverages: A Literature Overview. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2017, 16, 668–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A.; Georgescu, C.; Turcuş, V.; Olah, N.K.; Mathe, E. An Overview of Natural Antimicrobials Role in Food. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 143, 922–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.; Domingues, F. The Antimicrobial Action of Resveratrol against Listeria monocytogenes in Food-Based Models and Its Antibiofilm Properties. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2016, 96, 4531–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira Junior, A.A.; Silva de Araújo Couto, H.G.; Barbosa, A.A.T.; Carnelossi, M.A.G.; de Moura, T.R. Stability, Antimicrobial Activity, and Effect of Nisin on the Physico-Chemical Properties of Fruit Juices. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 211, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usaga, J.; Acosta, Ó.; Churey, J.J.; Padilla-Zakour, O.I.; Worobo, R.W. Evaluation of High Pressure Processing (HPP) Inactivation of Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica, and Listeria monocytogenes in Acid and Acidified Juices and Beverages. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 339, 109034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawacka, I.; Olejnik-Schmidt, A.; Schmidt, M.; Sip, A. Natural Plant-Derived Chemical Compounds as Listeria monocytogenes Inhibitors In Vitro and in Food Model Systems. Pathogens 2020, 10, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minekus, M.; Alminger, M.; Alvito, P.; Ballance, S.; Bohn, T.; Bourlieu, C.; Carrière, F.; Boutrou, R.; Corredig, M.; Dupont, D.; et al. A Standardised Static in Vitro Digestion Method Suitable for Food—An International Consensus. Food Funct. 2014, 5, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geeraerd, A.H.; Valdramidis, V.P.; Van Impe, J.F. GInaFiT, a Freeware Tool to Assess Non-Log-Linear Microbial Survivor Curves. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2005, 102, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Ordóñez, A.; Fernández, A.; Bernardo, A.; López, M. Comparison of Acids on the Induction of an Acid Tolerance Response in Salmonella Typhimurium, Consequences for Food Safety. Meat Sci. 2009, 81, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, J.W.; Hall, H.K. Adaptive Acidification Tolerance Response of Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 1990, 172, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tian, S.; Wu, Y.; Li, H.; Bai, L.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Dong, Q. Strain Variability in Growth and Thermal Inactivation Characteristics of Listeria monocytogenes Strains after Acid Adaptation. J. Food Prot. 2021, 84, 2229–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolfe, C.A.; Anderson, N.M.; Black, D.G.; Lee, A. Barotolerance of Acid-Adapted and Cold-Adapted Bacterial Isolates of E. coli O157:H7, Salmonella spp., and L. monocytogenes in an Acidic Buffer Model. J. Food Prot. 2023, 86, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Dong, P.; Liang, R.; Mao, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, X. Acid Tolerance Response of Listeria monocytogenes in Various External PHs with Different Concentrations of Lactic Acid. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2020, 17, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bainotti, M.B.; Colás-Medà, P.; Viñas, I.; Alegre, I. Effect of Antimicrobial Compounds on the Survival and Pathogenic Potential of Acid-Adapted Salmonella Enteritidis and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in Orange Juice. Antibiotics 2025, 14, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabiyikli, Ş.; Değırmencı, H.; Karapinar, M. Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes in Black Mulberry (Morus Nigra) Juice. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2017, 41, e12840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalcengiz, Z.; Danyluk, M.D. Thermal Inactivation Responses of Acid Adapted and Non-Adapted Stationary Phase Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli (STEC), Salmonella spp. and Listeria monocytogenes in Orange Juice. Food Control 2017, 72, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvaniti, M.; Tsakanikas, P.; Papadopoulou, V.; Giannakopoulou, A.; Skandamis, P. Listeria monocytogenes Sublethal Injury and Viable-but-Nonculturable State Induced by Acidic Conditions and Disinfectants. Microbiol. Spectr. 2021, 9, e01377-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, N.; Liu, L. Microbial Response to Acid Stress: Mechanisms and Applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kincses, A.; Ghazal, T.S.A.; Hohmann, J. Synergistic Effect of Phenylpropanoids and Flavonoids with Antibiotics against Gram-Positive and Gram-Negative Bacterial Strains. Pharm. Biol. 2024, 62, 659–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Dasagrandhi, C.; Kang, E.H.; Eom, S.H.; Kim, Y.M. In Vitro Antibacterial and Early Stage Biofilm Inhibitory Potential of an Edible Chitosan and Its Phenolic Conjugates against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Listeria monocytogenes. 3 Biotech 2018, 8, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamuz, S.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Dzuvor, C.K.O.; Zhang, W.; Sant’Ana, A.S.; Lorenzo, J.M. The Role of Phenolic Compounds against Listeria Monocytogenes in Food. A Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 110, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.D.; Delaquis, P.; Toivonen, P.; Stanich, K. Effect of Vanillin on the Fate of Listeria monocytogenes and Escherichia coli O157:H7 in a Model Apple Juice Medium and in Apple Juice. Food Microbiol. 2006, 23, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, S.; Guerrero, S.; Alzamora, S.M. Combined Use of Ultrasound and Natural Antimicrobials To Inactivate Listeria monocytogenes in Orange Juice. J. Food Prot. 2007, 70, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Angulo, A.B.; Zanini, S.F.; Rosenthal, A.; Rodrigo, D.; Klein, G.; Martínez, A. Comparative Study of the Effects of Citral on the Growth and Injury of Listeria innocua and Listeria monocytogenes Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0114026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, X.; Du, H.; Li, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhu, Z. A Transparent P-Coumaric Acid-Grafted-Chitosan Coating with Antimicrobial, Antioxidant and Antifogging Properties for Fruit Packaging Applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 339, 122238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Bai, M.; Fang, H.; Aziz, T.; Shami, A.; Al-Asmari, F.; Al-Joufi, F.A.; Alwethaynani, M.S.; Cui, H. Mechanistic Insights into Citral-Induced Cellular Damage and Its Antibacterial Efficacy against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Biosci. 2025, 68, 106435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pernin, A.; Guillier, L.; Dubois-Brissonnet, F. Inhibitory Activity of Phenolic Acids against Listeria monocytogenes: Deciphering the Mechanisms of Action Using Three Different Models. Food Microbiol. 2019, 80, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.L.; da Cruz Almeida, E.T.; de Sousa Guedes, J.P. The Potential of the Incorporation of Essential Oils and Their Individual Constituents to Improve Microbial Safety in Juices: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2016, 15, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyague, L.; Macedo, R.E.F.; Meca, G.; Holley, R.A.; Luciano, F.B. Combination of Phenolic Acids and Essential Oils against Listeria monocytogenes. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 64, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Vadivel, V. Citral and Linalool Nanoemulsions: Impact of Synergism and Ripening Inhibitors on the Stability and Antibacterial Activity against Listeria monocytogenes. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luciano, W.A.; Pimentel, T.C.; Bezerril, F.F.; Barão, C.E.; Marcolino, V.A.; de Siqueira Ferraz Carvalho, R.; dos Santos Lima, M.; Martín-Belloso, O.; Magnani, M. Effect of Citral Nanoemulsion on the Inactivation of Listeria monocytogenes and Sensory Properties of Fresh-Cut Melon and Papaya during Storage. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2023, 384, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Singh, P.; Joshi, A.S.; Tabassum, N.; Jeong, G.J.; Bamunuarachchi, N.I.; Mijakovic, I.; Kim, Y.M. Multiple Potential Strategies for the Application of Nisin and Derivatives. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 49, 628–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.H.; Khan, I.; Oh, D.H. Evaluation of the Efficacy of Nisin-Loaded Chitosan Nanoparticles against Foodborne Pathogens in Orange Juice. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 55, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalchayanand, N.; Hanlin, M.B.; Ray, B. Sublethal Injury Makes Gram-Negative and Resistant Gram-Positive Bacteria Sensitive to the Bacteriocins, Pediocin AcH and Nisin. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 1992, 15, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akritidou, T.; Akkermans, S.; Gaspari, S.; Azraini, N.D.; Smet, C.; Van de Wiele, T.; Van Impe, J.F.M. Effect of Gastric PH and Bile Acids on the Survival of Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella Typhimurium during Simulated Gastrointestinal Digestion. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 82, 103161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumariya, R.; Garsa, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sood, S.K.; Akhtar, N.; Patel, S. Bacteriocins: Classification, Synthesis, Mechanism of Action and Resistance Development in Food Spoilage Causing Bacteria. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, N.; Bhunia, A.K. Food-Associated Stress Primes Foodborne Pathogens for the Gastrointestinal Phase of Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 382666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).