Applications of Machine Learning for Wine Recognition Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Set
2.2. 1H-NMR Spectra Acquisition
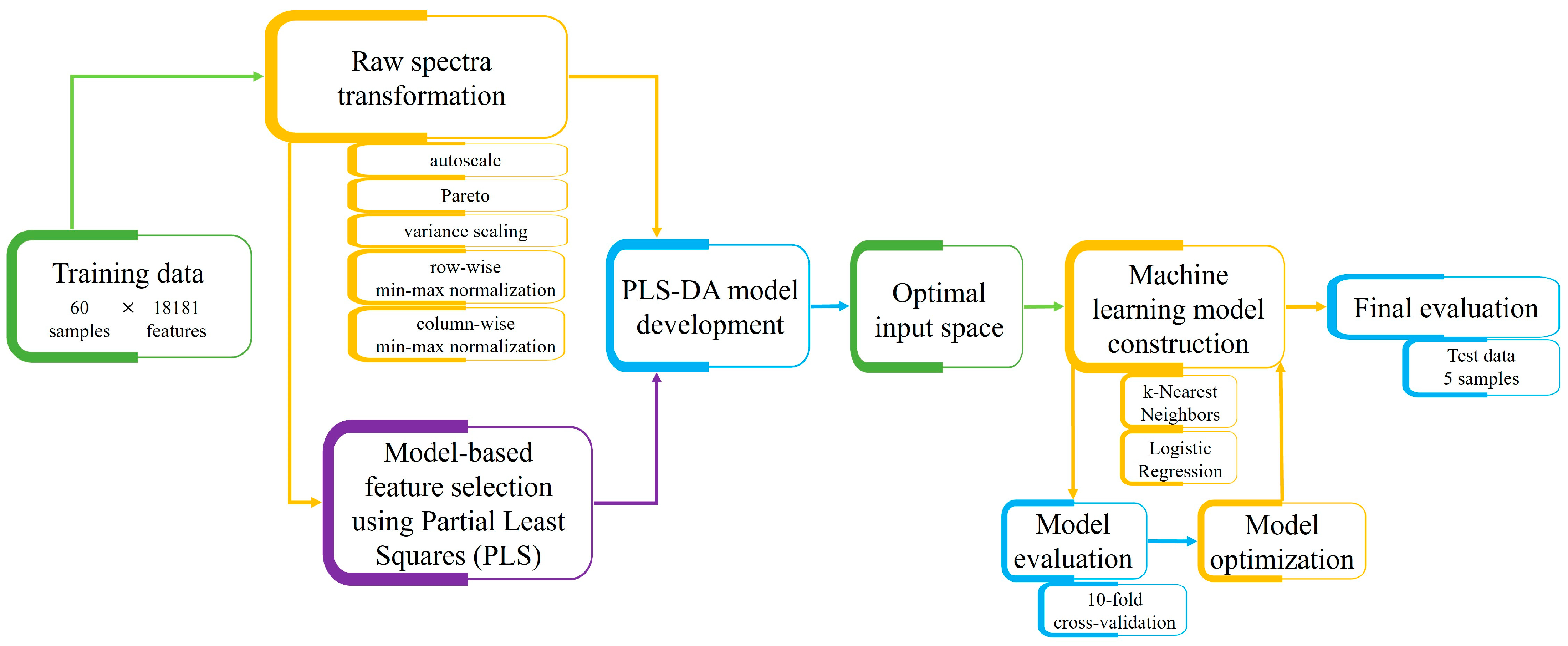
2.3. Experimental Data Preprocessing
2.3.1. Raw Spectra Transformation Techniques
2.3.2. Data Dimensionality Reduction
2.4. Machine Learning-Based Analysis
2.4.1. K-Nearest Neighbors
2.4.2. Logistic Regression
2.4.3. Performance Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
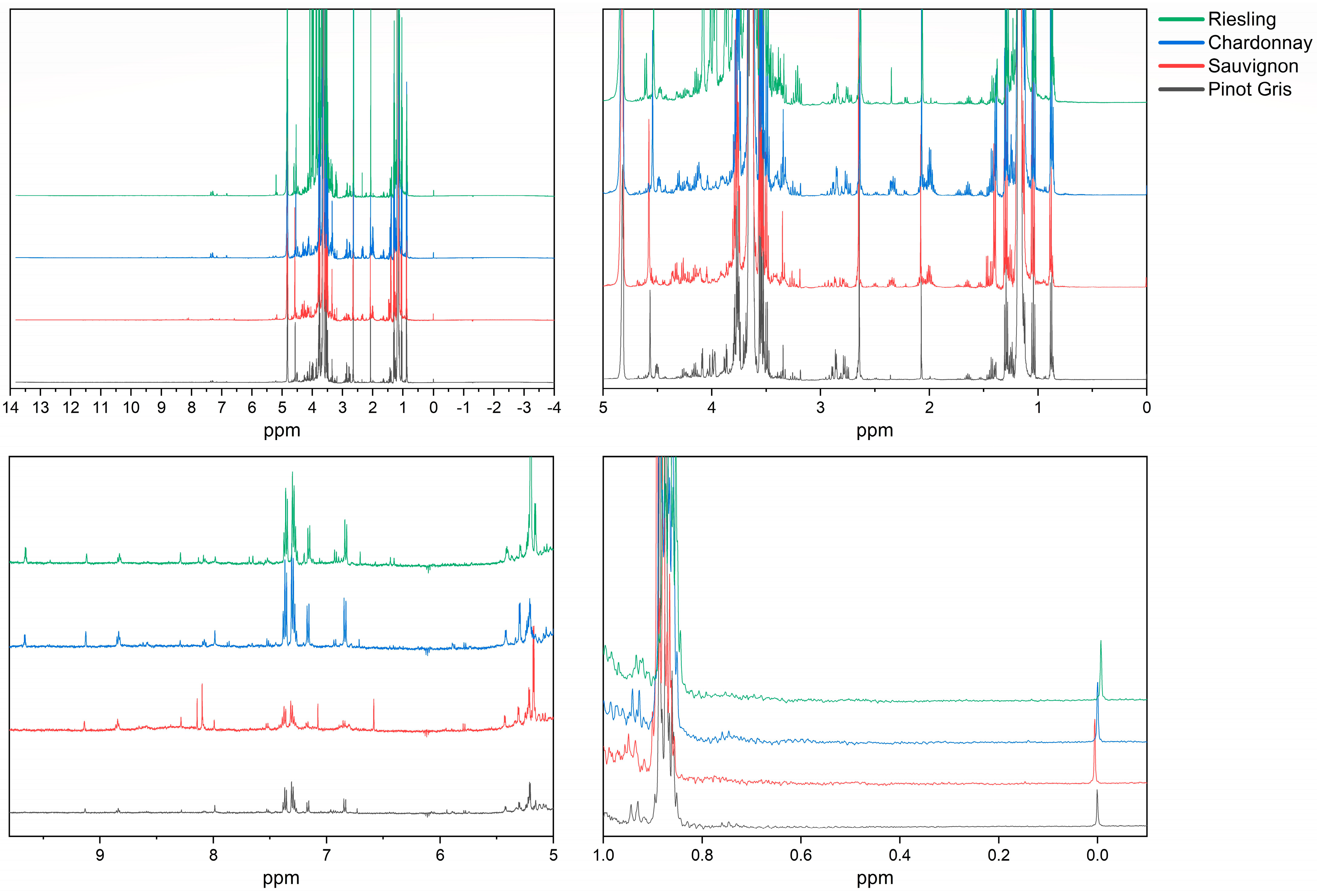
3.1. Experimental Spectra
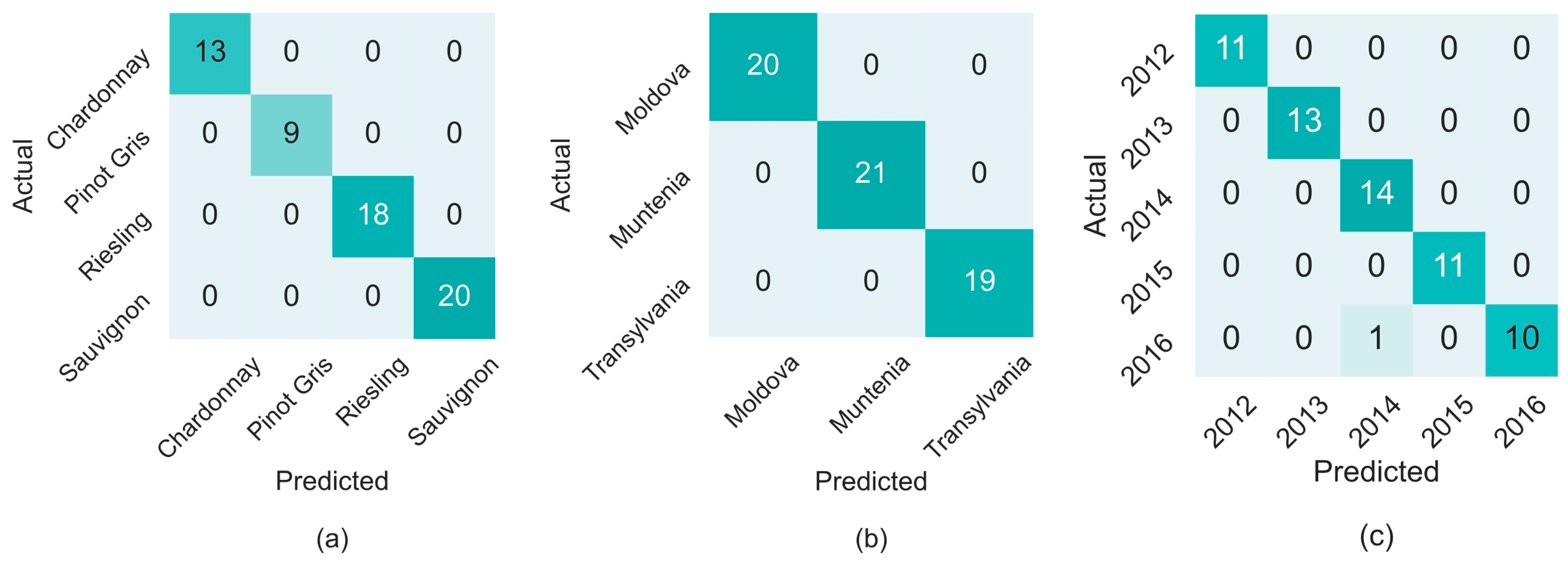
3.2. Varietal Differentiation
3.3. Geographical Classification
3.4. Harvesting Year Discrimination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moore, J.C.; Spink, J.; Lipp, M. Development and application of a database of food ingredient fraud and economically motivated adulteration from 1980 to 2010. J. Food Sci. 2012, 77, R118–R126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyev, P.A.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Riedl, J.; Esslinger, S.; Bontempo, L.; Camin, F. NMR spectroscopy in wine authentication: An official control perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2040–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S. Chapter 6—Chemical constituents of grapes and wine. In Wine Science, 5th ed.; Jackson, R.S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 375–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, F.; Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Ge, Q.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Ma, T. Real Wine or Not? Protecting Wine with Traceability and Authenticity for Consumers: Chemical and Technical Basis, Technique Applications, Challenge, and Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 62, 6783–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koljančić, N.; Furdíková, K.; de Araújo Gomes, A.; Špánik, I. Wine authentication: Current progress and state of the art. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camin, F.; Boner, M.; Bontempo, L.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Kelly, S.D.; Riedl, J.; Rossmann, A. Stable isotope techniques for verifying the declared geographical origin of food in legal cases. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 61, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basalekou, M.; Pappas, C.; Tarantilis, P.; Kotseridis, Y.; Kallithraka, S. Wine authentication with Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy: A feasibility study on variety, type of barrel wood and ageing time classification. Int. J. Food Sci. 2017, 52, 1307–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Tian, F.; Chen, C.; Wu, W.; Tian, X.; Chen, C.; Lv, X. Identification of Chinese red wine origins based on Raman spectroscopy and deep learning. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2023, 291, 122355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevin, C.J.; Dambergs, R.G.; Fergusson, A.J.; Cozzolino, D. Varietal discrimination of Australian wines by means of mid-infrared spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 621, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Cinta Pinzaru, S.; Guyon, F.; Feher, I.; Cozar, B.I. Application of SERS technique in white wines discrimination. Food Control 2018, 92, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godelmann, R.; Fang, F.; Humpfer, E.; Schütz, B.; Bansbach, M.; Schäfer, H.; Spraul, M. Targeted and nontargeted wine analysis by 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Differentiation of important parameters: Grape variety, geographical origin, year of vintage. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5610–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadi, M.; Zira, A.; Magiatis, P.; Haroutounian, S.A.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Mikros, E. 1H NMR-based metabonomics for the classification of Greek wines according to variety, region, and vintage. Comparison with HPLC data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 11067–11074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, M.; Horn, B.; Raeke, J.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Hermann, A.; Brockmeyer, J.; Riedl, J. Towards harmonization of non-targeted 1H NMR spectroscopy-based wine authentication: Instrument comparison. Food Control 2022, 132, 108508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suciu, R.C.; Zarbo, L.; Guyon, F.; Magdas, D.A. Application of fluorescence spectroscopy using classical right angle technique in white wines classification. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azcarate, S.M.; de Araújo Gomes, A.; Alcaraz, M.R.; de Araújo, M.C.U.; Camiña, J.M.; Goicoechea, H.C. Modeling excitation–emission fluorescence matrices with pattern recognition algorithms for classification of Argentine white wines according grape variety. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranaweera, R.K.R.; Capone, D.L.; Bastian, S.E.P.; Cozzolino, D.; Jeffery, D.W. A Review of Wine Authentication Using Spectroscopic Approaches in Combination with Chemometrics. Molecules 2021, 26, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friebolin, H. Basic One-and Two-Dimensional NMR Spectroscopy, 4th ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lolli, V.; Caligiani, A. How NMR contributes to food authentication: Current trends and perspectives. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2024, 58, 101200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balthazar, C.F.; Guimarães, J.T.; Rocha, R.S.; Pimentel, T.C.; Neto, R.P.C.; Tavares, M.I.B.; Graça, J.S.; Alves Filho, E.G.; Freitas, M.Q.; Esmerino, E.A.; et al. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance as an Analytical Tool for Monitoring the Quality and Authenticity of Dairy Foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, A.; Blanchet, L.; Buydens, L.M.C.; Wijmenga, S.S. NMR and pattern recognition methods in metabolomics: From data acquisition to biomarker discovery: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 750, 82–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascellani, A.; Hoca, G.; Babisz, M.; Krska, P.; Kloucek, P.; Havlik, J. 1H NMR chemometric models for classification of Czech wine type and variety. Food Chem. 2021, 339, 127852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esslinger, S.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Wittkowski, R. Authentication of Wine by 1H-NMR Spectroscopy: Opportunities and Challenges. In Advances in Wine Research; Ebeler, S.B., Sacks, G., Vidal, S., Winterhalter, P., Eds.; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 85–108. [Google Scholar]
- Hategan, A.R.; Guyon, F.; Magdas, D.A. The improvement of honey recognition models built on 1H NMR fingerprint through a new proposed approach for feature selection. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 114, 104786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Pirnau, A.; Feher, I.; Guyon, F.; Cozar, B.I. Alternative approach of applying 1H NMR in conjunction with chemometrics for wine classification. LWT 2019, 109, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roger, J.M.; Boulet, J.C.; Zeaiter, M.; Rutledge, D.N. Pre-processing methods. In Comprehensive Chemometrics; Brown, S., Tauler, R., Walczak, B., Eds.; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2020; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Eigenvector Research Wiki, Selectvars. Available online: https://wiki.eigenvector.com/index.php?title=Selectvars (accessed on 22 November 2024).
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Bisong, E. Logistic Regression. In Building Machine Learning and Deep Learning Models on Google Cloud Platform; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hategan, A.R.; David, M.; Pirnau, A.; Cozar, B.; Cinta-Pinzaru, S.; Guyon, F.; Magdas, D.A. Fusing 1H NMR and Raman experimental data for the improvement of wine recognition models. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gougeon, L.; Da Costa, G.; Le Mao, I.; Ma, W.; Teissedre, P.L.; Guyon, F.; Richard, T. Wine analysis and authenticity using 1H-NMR metabolomics data: Application to Chinese wines. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 11, 3425–3434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambina, P.; Spinella, A.; Lo Papa, G.; Chillura Martino, D.F.; Lo Meo, P.; Cinquanta, L.; Conte, P. 1H-NMR Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics to Classify Wines According to Different Grape Varieties and Different Terroirs. Agriculture 2024, 14, 749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Zhong, Q.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Pfister, M.K.H.; Horn, B.; Huang, Z. Classification of Chinese wine varieties using 1H NMR spectroscopy combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Food Control 2018, 88, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Preprocessing Method | Number of Variables | True Positives | Accuracy (CV) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar discrimination | ||||||||||||
| Chardonnay (13) | Pinot Gris (9) | Riesling (18) | Sauvignon (20) | |||||||||
| autoscale | 18,181 | 6 | 3 | 8 | 12 | 0.48 | ||||||
| Pareto | 18,181 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 0.36 | ||||||
| variance scaling | 18,181 | 6 | 1 | 12 | 9 | 0.46 | ||||||
| min–max scaling (row-wise) | 18,181 | 6 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 0.33 | ||||||
| min–max scaling (column-wise) | 18,181 | 5 | 1 | 13 | 5 | 0.40 | ||||||
| Geographical origin discrimination | ||||||||||||
| Moldova (20) | Muntenia (21) | Transylvania (19) | ||||||||||
| autoscale | 18,181 | 7 | 14 | 15 | 0.60 | |||||||
| Pareto | 18,181 | 8 | 7 | 13 | 0.46 | |||||||
| variance scaling | 18,181 | 9 | 11 | 15 | 0.58 | |||||||
| min–max scaling (row-wise) | 18,181 | 8 | 4 | 10 | 0.36 | |||||||
| min–max scaling (column-wise) | 18,181 | 6 | 16 | 13 | 0.58 | |||||||
| Vintage discrimination | ||||||||||||
| 2012 (11) | 2013 (13) | 2014 (14) | 2015 (11) | 2016 (11) | ||||||||
| autoscale | 18,181 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 0.41 | |||||
| Pareto | 18,181 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 1 | 0.25 | |||||
| variance scaling | 18,181 | 4 | 3 | 6 | 3 | 2 | 0.30 | |||||
| min–max scaling (row-wise) | 18,181 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 7 | 2 | 0.41 | |||||
| min–max scaling (column-wise) | 18,181 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0.31 | |||||
| Preprocessing Method | Number of Variables | True Positives | Accuracy (CV) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivar discrimination | ||||||||||||
| Chardonnay (13) | Pinot Gris (9) | Riesling (18) | Sauvignon (20) | |||||||||
| autoscale | 210 | 13 | 9 | 18 | 20 | 1.00 | ||||||
| Pareto | 915 | 6 | 4 | 13 | 10 | 0.55 | ||||||
| variance scaling | 176 | 13 | 9 | 18 | 20 | 1.00 | ||||||
| min–max scaling (row-wise) | 10,000 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 0.35 | ||||||
| min–max scaling (column-wise) | 734 | 11 | 6 | 16 | 17 | 0.83 | ||||||
| Geographical origin discrimination | ||||||||||||
| Moldova (20) | Muntenia (21) | Transylvania (19) | ||||||||||
| autoscale | 512 | 19 | 21 | 19 | 0.98 | |||||||
| Pareto | 277 | 13 | 17 | 14 | 0.73 | |||||||
| variance scaling | 800 | 20 | 21 | 19 | 1.00 | |||||||
| min–max scaling (row-wise) | 3025 | 12 | 7 | 8 | 0.45 | |||||||
| min–max scaling (column-wise) | 509 | 19 | 20 | 14 | 0.88 | |||||||
| Vintage discrimination | ||||||||||||
| 2012 (11) | 2013 (13) | 2014 (14) | 2015 (11) | 2016 (11) | ||||||||
| autoscale | 252 | 11 | 13 | 13 | 11 | 11 | 0.98 | |||||
| Pareto | 503 | 4 | 6 | 9 | 8 | 5 | 0.53 | |||||
| variance scaling | 277 | 11 | 12 | 14 | 11 | 11 | 0.98 | |||||
| min–max scaling (row-wise) | 152 | 5 | 1 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 0.40 | |||||
| min–max scaling (column-wise) | 18,181 | 6 | 3 | 7 | 1 | 2 | 0.31 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hategan, A.R.; Pirnau, A.; Magdas, D.A. Applications of Machine Learning for Wine Recognition Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. Beverages 2025, 11, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020045
Hategan AR, Pirnau A, Magdas DA. Applications of Machine Learning for Wine Recognition Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. Beverages. 2025; 11(2):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020045
Chicago/Turabian StyleHategan, Ariana Raluca, Adrian Pirnau, and Dana Alina Magdas. 2025. "Applications of Machine Learning for Wine Recognition Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy" Beverages 11, no. 2: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020045
APA StyleHategan, A. R., Pirnau, A., & Magdas, D. A. (2025). Applications of Machine Learning for Wine Recognition Based on 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. Beverages, 11(2), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020045







