Discrimination of Romanian Wines Based on Phenolic Composition and Identification of Potential Phenolic Biomarkers for Wine Authenticity and Traceability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Wine Samples
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Analytical Determination
2.3.1. Wine Bioactive Characteristics by UV–Vis Spectrophotometric Determinations
2.3.2. Phenolic Profile by UHPLC–ESI/HRMS
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
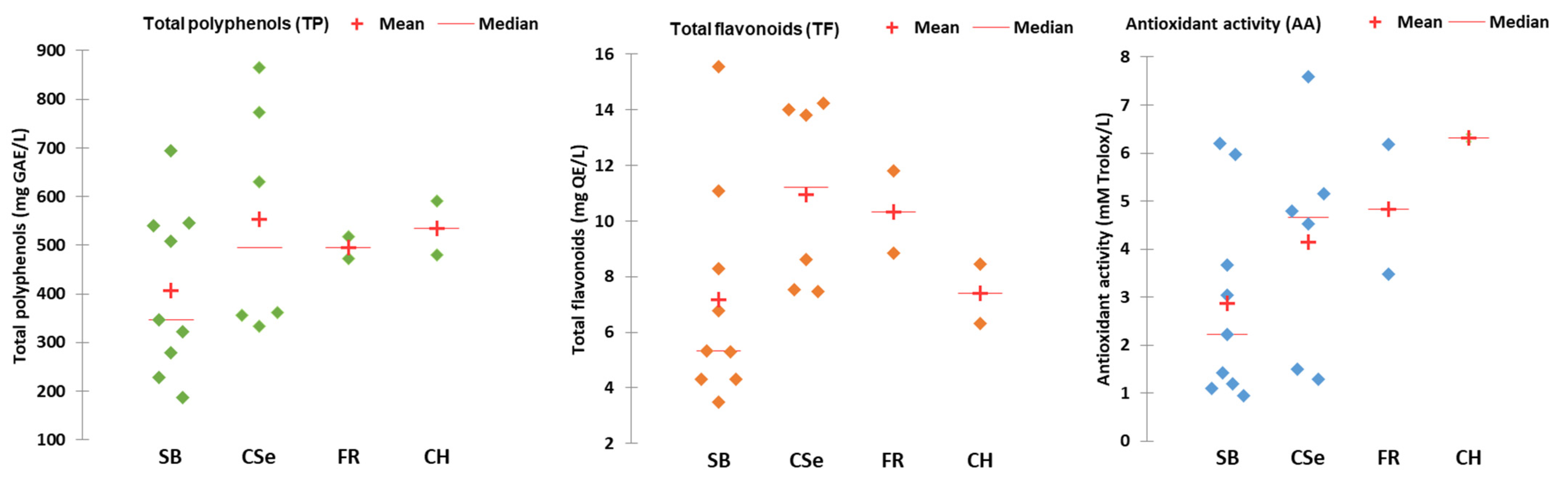
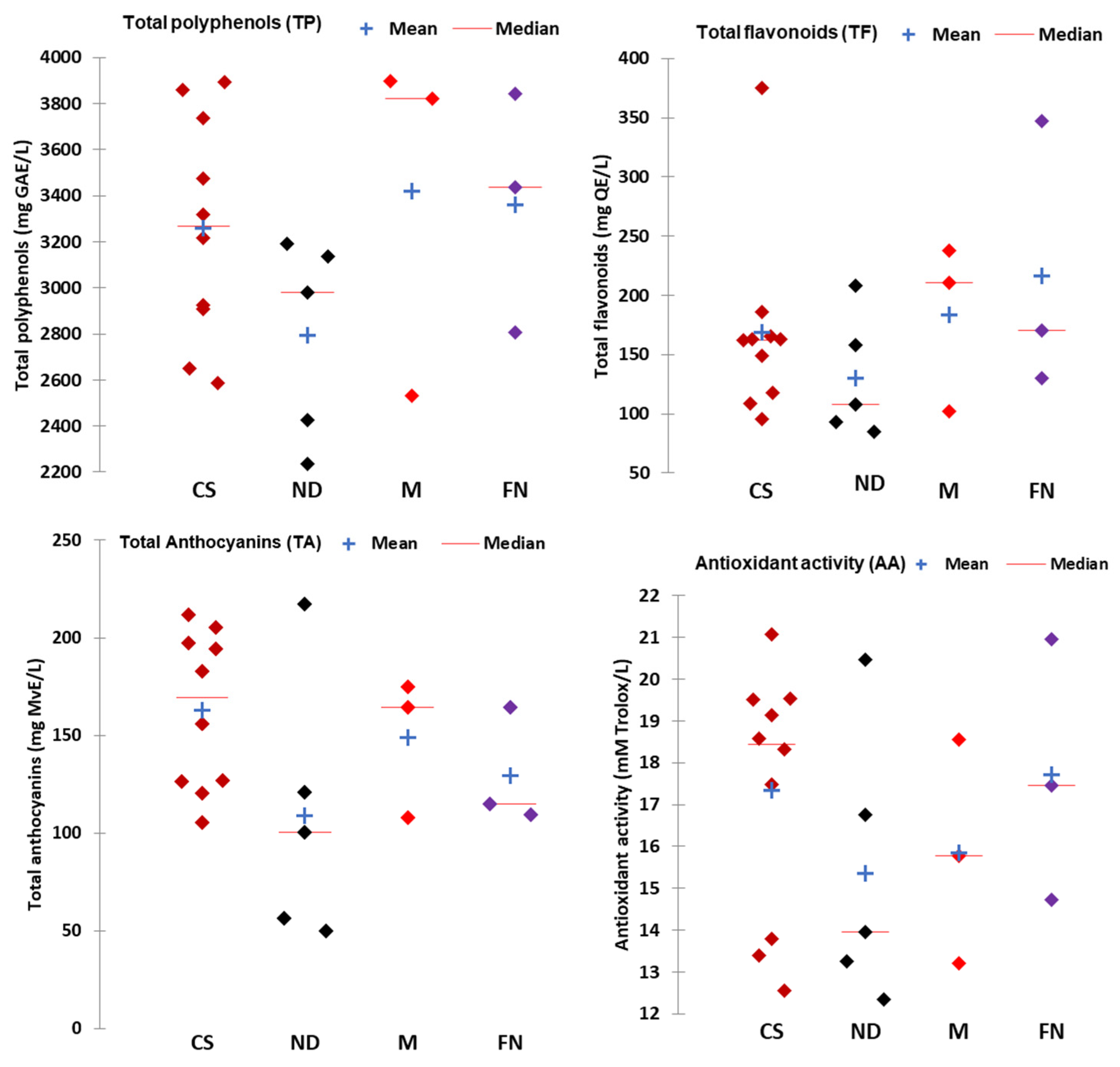
3.1. Bioactive Characteristics of White and Red Wines
3.2. Profile of Phenolic Compounds in White and Red Wines
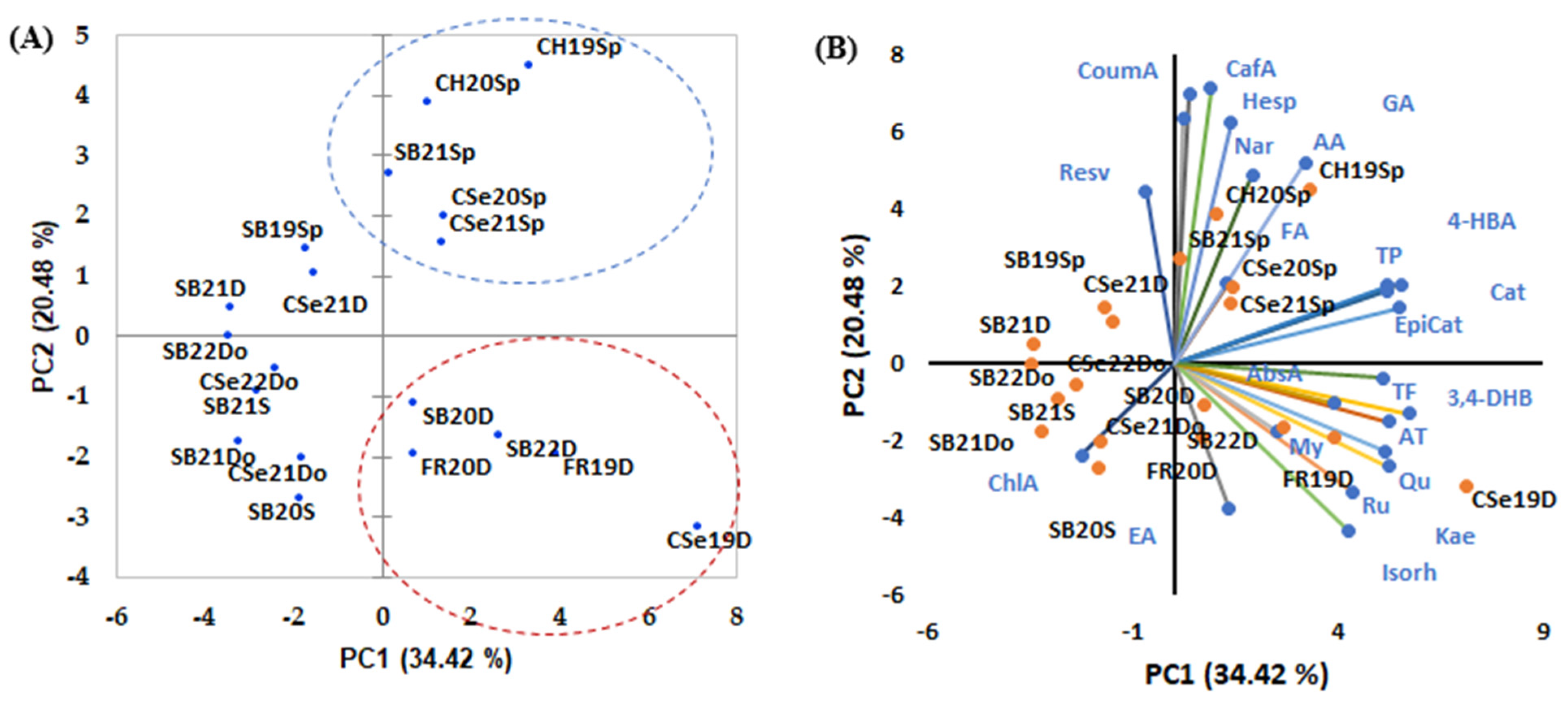
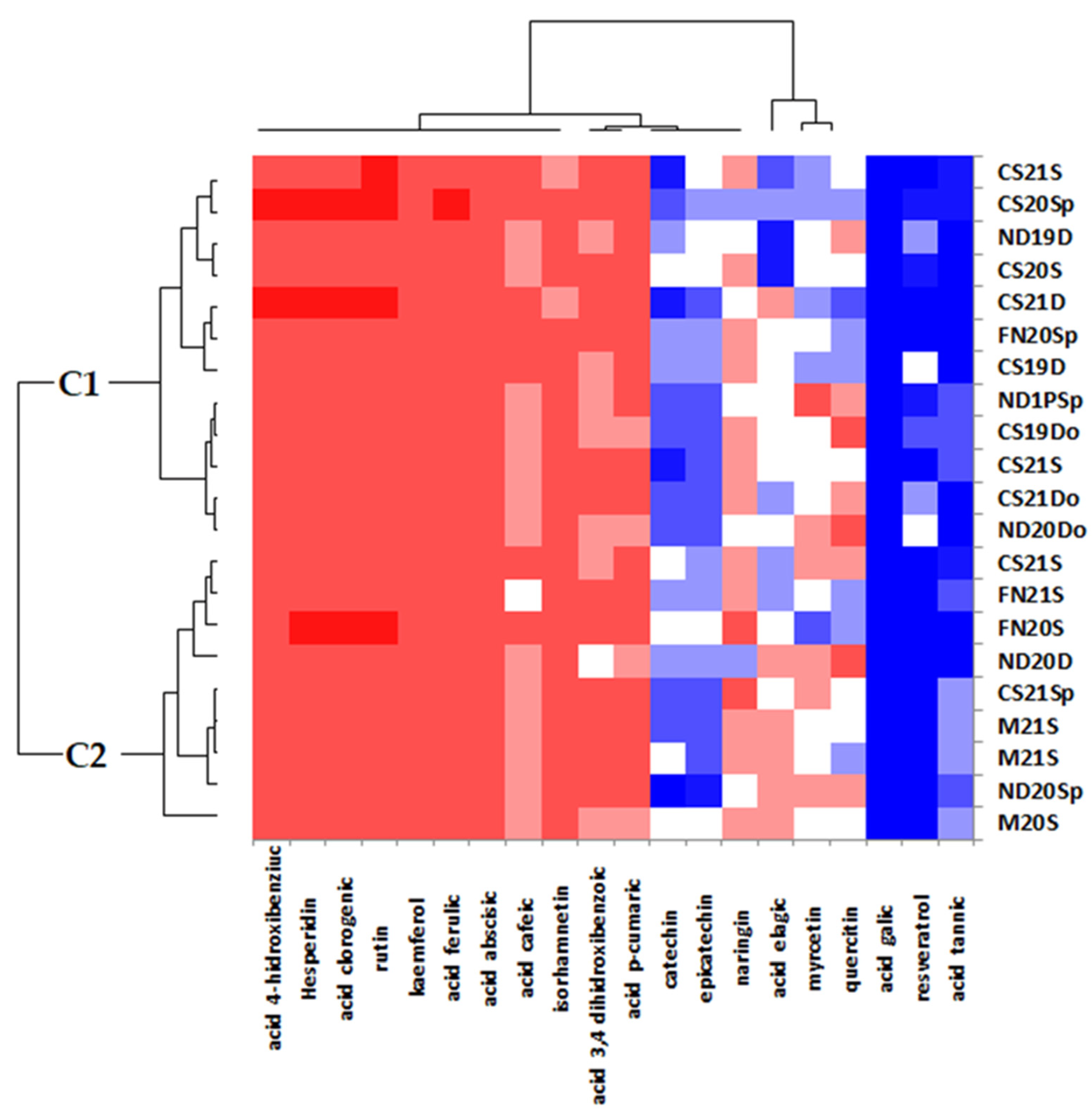
3.3. Discrimination of White Wines
3.4. Discrimination of Red Wines
3.5. Discrimination of Wines in Romanian Context and Other Surrounding Countries
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roullier-Gall, C.; Lucio, M.; Noret, L.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Gougeon, R.D. How Subtle Is the “Terroir” Effect? Chemistry-Related Signatures of Two “Climats de Bourgogne”. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urvieta, R.; Jones, G.; Buscema, F.; Bottini, R.; Fontana, A. Terroir and Vintage Discrimination of Malbec Wines Based on Phenolic Composition across Multiple Sites in Mendoza, Argentina. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koljančić, N.; Furdíková, K.; de Araújo Gomes, A.; Špánik, I. Wine Authentication: Current Progress and State of the Art. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popîrdă, A.; Luchian, C.E.; Cotea, V.V.; Colibaba, L.C.; Scutarașu, E.C.; Toader, A.M. A Review of Representative Methods Used in Wine Authentication. Agriculture 2021, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Escobar, R.; Aliaño-González, M.J.; Cantos-Villar, E. Wine Polyphenol Content and Its Influence on Wine Quality and Properties: A Review. Molecules 2021, 26, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajovic Scepanovic, R.; Wendelin, S.; Forneck, A.; Eder, R. Varietal Differentiation of Grapes Cv. ‘Vranac’, ‘Kratosija’ and ‘Cabernet Sauvignon’ from Montenegro According to Their Polyphenolic Composition. Mitteilungen Klosterneubg. 2014, 64, 9–19. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, E.-Q.; Deng, G.-F.; Guo, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B. Biological Activities of Polyphenols from Grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 622–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.-D.; Li, J.; Xiong, R.-G.; Saimaiti, A.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wu, S.-X.; Yang, Z.-J.; Shang, A.; Zhao, C.-N.; Gan, R.-Y.; et al. Bioactive Compounds, Health Benefits and Food Applications of Grape. Foods 2022, 11, 2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banc, R.; Popa, D.-S.; Cozma-Petruţ, A.; Filip, L.; Kiss, B.; Fărcaş, A.; Nagy, A.; Miere, D.; Loghin, F. Protective Effects of Wine Polyphenols on Oxidative Stress and Hepatotoxicity Induced by Acrylamide in Rats. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, M.F.; Arif, Z.; Kabir, A.; Mehmood, I.; Munir, D.; Razzaq, A.; Ali, A.; Goksen, G.; Coşier, V.; Ahmad, N.; et al. Oxidative Stress and Metabolic Diseases: Relevance and Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 994309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burin, V.M.; Ferreira-Lima, N.E.; Panceri, C.P.; Bordignon-Luiz, M.T. Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Vitis Vinifera and Vitis Labrusca Grapes: Evaluation of Different Extraction Methods. Microchem. J. 2014, 114, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beara, I.N.; Torović, L.D.; Pintać, D.Đ.; Majkić, T.M.; Orčić, D.Z.; Mimica-Dukić, N.M.; Lesjak, M.M. Polyphenolic Profile, Antioxidant and Neuroprotective Potency of Grape Juices and Wines from Fruška Gora Region (Serbia). Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20, S2552–S2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćorković, I.; Pichler, A.; Šimunović, J.; Kopjar, M. A Comprehensive Review on Polyphenols of White Wine: Impact on Wine Quality and Potential Health Benefits. Molecules 2024, 29, 5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornedo-Ortega, R.; Reyes González-Centeno, M.; Chira, K.; Jourdes, M.; Teissedre, P.-L. Phenolic Compounds of Grapes and Wines: Key Compounds and Implications in Sensory Perception. In Chemistry and Biochemistry of Winemaking, Wine Stabilization and Aging; Cosme, F., Nunes, F.M., Filipe-Ribeiro, L., Eds.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2021; ISBN 978-1-83962-575-6. [Google Scholar]
- Urcan, D.E.; Lung, M.-L.; Giacosa, S.; Torchio, F.; Ferrandino, A.; Vincenzi, S.; Río Segade, S.; Pop, N.; Rolle, L. Phenolic Substances, Flavor Compounds, and Textural Properties of Three Native Romanian Wine Grape Varieties. Int. J. Food Prop. 2016, 19, 76–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.P. Tannins and Anthocyanins: From Their Origin to Wine Analysis—A Review. S. Afr. J. Enol. Vitic. 2018, 39, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temerdashev, A.; Atapattu, S.N.; Pamunuwa, G.K. Determination and Identification of Polyphenols in Wine Using Mass Spectrometry Techniques. J. Chromatogr. Open 2024, 6, 100175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac, H.X.; Pham, T.T.; Ha, N.T.T.; Nguyen, L.L.P.; Baranyai, L.; Friedrich, L. Current Techniques for Fruit Juice and Wine Adulterant Detection and Authentication. Beverages 2023, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasvanka, K.; Tzachristas, A.; Proestos, C. 9—Quality Tools in Wine Traceability and Authenticity. In Quality Control in the Beverage Industry; Grumezescu, A.M., Holban, A.M., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 289–334. ISBN 978-0-12-816681-9. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Zhang, F.; Gutiérrez-Gamboa, G.; Ge, Q.; Xu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, Y.; Ma, T. Real Wine or Not? Protecting Wine with Traceability and Authenticity for Consumers: Chemical and Technical Basis, Technique Applications, Challenge, and Perspectives. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 6783–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arduini, S.; Chinnici, F. Advancements in Analytical Strategies for Authentication and Quality Control of Grappa and Wine Brandy with Geographical Indications. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 8092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compendium of International Methods of Wine and Must Analysis|OIV. Available online: https://www.oiv.int/standards/compendium-of-international-methods-of-wine-and-must-analysis (accessed on 7 December 2024).
- Tzachristas, A.; Pasvanka, K.; Calokerinos, A.; Proestos, C. Polyphenols: Natural Antioxidants to Be Used as a Quality Tool in Wine Authenticity. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, E.; Cosme, F.; Rivero-Pérez, M.D.; Jordão, A.M.; González-SanJosé, M.L. Influence of Wine Region Provenance on Phenolic Composition, Antioxidant Capacity and Radical Scavenger Activity of Traditional Portuguese Red Grape Varieties. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2015, 241, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkyte, V.; Longo, E.; Windisch, G.; Boselli, E. Phenolic Compounds as Markers of Wine Quality and Authenticity. Foods 2020, 9, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stój, A.; Kapusta, I.; Domagała, D. Classification of Red Wines Produced from Zweigelt and Rondo Grape Varieties Based on the Analysis of Phenolic Compounds by UPLC-PDA-MS/MS. Molecules 2020, 25, 1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.-L.; Xia, N.-Y.; Wang, Y.-C.; Zhang, H.-L.; Yang, W.-M.; Duan, C.-Q.; Pan, Q.-H. Evolution of Aroma Profiles in Vitis vinifera L. Marselan and Merlot from Grapes to Wines and Difference between Varieties. Molecules 2024, 29, 3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.; Pereira, J.A.; Silva, P.; Perestrelo, R.; Câmara, J.S. Food Fingerprints—A Valuable Tool to Monitor Food Authenticity and Safety. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranaweera, R.K.R.; Capone, D.L.; Bastian, S.E.P.; Cozzolino, D.; Jeffery, D.W. A Review of Wine Authentication Using Spectroscopic Approaches in Combination with Chemometrics. Molecules 2021, 26, 4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttl, L.; Bechynska, K.; Ehlers, M.; Kadlec, V.; Navratilova, K.; Dzuman, Z.; Fauhl-Hassek, C.; Hajslova, J. Critical Assessment of Chemometric Models Employed for Varietal Authentication of Wine Based on UHPLC-HRMS Data. Food Control 2023, 143, 109336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Llopart, A.; Saurina, J. Characterization of Sparkling Wines According to Polyphenolic Profiles Obtained by HPLC-UV/Vis and Principal Component Analysis. Foods 2019, 8, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geană, E.-I.; Sandru, C.; Stanciu, V.; Ionete, R.E. Elemental Profile and 87Sr/86Sr Isotope Ratio as Fingerprints for Geographical Traceability of Wines: An Approach on Romanian Wines. Food Anal. Methods 2017, 10, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geana, E.I.; Marinescu, A.; Iordache, A.M.; Sandru, C.; Ionete, R.E.; Bala, C. Differentiation of Romanian Wines on Geographical Origin and Wine Variety by Elemental Composition and Phenolic Components. Food Anal. Methods 2014, 7, 2064–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miricioiu, M.G.; Ionete, R.E.; Costinel, D.; Simova, S.; Gerginova, D.; Botoran, O.R. Metabolic Profiling and Stable Isotope Analysis of Wines: Pilot Study for Cross-Border Authentication. Foods 2024, 13, 3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geana, E.I.; Popescu, R.; Costinel, D.; Dinca, O.R.; Ionete, R.E.; Stefanescu, I.; Artem, V.; Bala, C. Classification of Red Wines Using Suitable Markers Coupled with Multivariate Statistic Analysis. Food Chem. 2016, 192, 1015–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BANC, R.; LOGHIN, F.; MIERE, D.; FETEA, F.; SOCACIU, C. Romanian Wines Quality and Authenticity Using FT-MIR Spectroscopy Coupled with Multivariate Data Analysis. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2014, 42, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geana, E.I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Apetrei, C.; Artem, V. Application of Spectroscopic UV-Vis and FT-IR Screening Techniques Coupled with Multivariate Statistical Analysis for Red Wine Authentication: Varietal and Vintage Year Discrimination. Molecules 2019, 24, 4166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magdas, D.A.; Cinta Pinzaru, S.; Guyon, F.; Feher, I.; Cozar, B.I. Application of SERS Technique in White Wines Discrimination. Food Control 2018, 92, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdas, D.A.; Guyon, F.; Feher, I.; Pinzaru, S.C. Wine Discrimination Based on Chemometric Analysis of Untargeted Markers Using FT-Raman Spectroscopy. Food Control 2018, 85, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geană, E.I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Artem, V.; Apetrei, C. Wine Varietal Discrimination and Classification Using a Voltammetric Sensor Array Based on Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes in Conjunction with Chemometric Analysis. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geană, E.-I.; Artem, V.; Apetrei, C. Discrimination and Classification of Wines Based on Polypyrrole Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes Coupled with Multivariate Data Analysis. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2021, 96, 103704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geana, E.I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Artem, V.; Apetrei, C. Characterization and Classification of Wines Based on Spectrophotometric Determination of Wine Bioactive Properties. Cient Period. 2019, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Durst, R.W.; Wrolstad, R.E. Collaborators: Determination of Total Monomeric Anthocyanin Pigment Content of Fruit Juices, Beverages, Natural Colorants, and Wines by the pH Differential Method: Collaborative Study. J. AOAC Int. 2005, 88, 1269–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onache, P.A.; Geana, E.I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Florea, A.; Sumedrea, D.I.; Ionete, R.E.; Tița, O. Bioactive Phytochemical Composi-tion of Grape Pomace Resulted from Different White and Red Grape Cultivars. Separations 2022, 9, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, E.; Dobrei, A. Anthocyanins and Phenolics in Cabernet Sauvignon and Pinot Noir Wines. J. Hortic. For.Biotechnol. 2015, 19, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Hosu, A.; Cristea, V.M.; Cimpoiu, C. Analysis of Total Phenolic, Flavonoids, Anthocyanins and Tannins Content in Romanian Red Wines: Prediction of Antioxidant Activities and Classification of Wines Using Artificial Neural Networks. Food Chem. 2014, 150, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onache, P.A.; Florea, A.; Geana, E.-I.; Ciucure, C.T.; Ionete, R.E.; Sumedrea, D.I.; Tița, O. Assessment of Bioactive Phenolic Compounds in Musts and the Corresponding Wines of White and Red Grape Varieties. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giosanu, D.; Bărbuceanu, M.; Anghel, M.; Vîjan, L. The determination of the content of phenolic compounds from different romanian wines using folin-ciocîlteu method. Curr. Trends Nat. Sci. 2018, 7, 155–159. [Google Scholar]
- Dumitru, B.F.; Bunea, C.I.; Călugăr, A.; Donici, A. Phenolic, anthocyanin composition and color measurement at red wines from dealu bujorului vineyard. Agricultura 2019, 109, 14–28. [Google Scholar]
- Lisov, N.; Čakar, U.; Milenković, D.; Čebela, M.; Vuković, G.; Despotović, S.; Petrović, A. The Influence of Cabernet Sauvignon Ripeness, Healthy State and Maceration Time on Wine and Fermented Pomace Phenolic Profile. Fermentation 2023, 9, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beara, I.; Majkić, T.; Milovanović, L.; Svirčev, E.; Torović, L. Polyphenolic Profile and in Vitro Biological Activity of Serbian Orange (Skin Fermented White) Wines. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, D.; Yoncheva, T.; Iliev, A. Study on the content of phenolic compounds, anthocyanins and antioxidant activity of red grapes and wines from central northern Bulgaria. Agric. For. 2023, 69, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanova, M.; Atanassova, S.; Atanasov, V.; Grozeva, N. Content of Polyphenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Potential of Some Bulgarian Red Grape Varieties and Red Wines, Determined by HPLC, UV, and NIR Spectroscopy. Agriculture 2020, 10, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrček, I.V.; Bojić, M.; Žuntar, I.; Mendaš, G.; Medić-Šarić, M. Phenol Content, Antioxidant Activity and Metal Composition of Croatian Wines Deriving from Organically and Conventionally Grown Grapes. Food Chem. 2011, 124, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banc, R.; Loghin, F.; Miere, D.; Ranga, F.; Socaciu, C. Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Activity of Red, Rosé and White Wines Originating from Romanian Grape Cultivars. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2020, 48, 716–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosu, A.; Floare-Avram, V.; Magdas, D.A.; Feher, I.; Inceu, M.; Cimpoiu, C. The Influence of the Variety, Vineyard, and Vintage on the Romanian White Wines Quality. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artem, V.; Antoce, A.O.; Geana, E.-I.; Ionete, R.E. Study of the Impact of Vine Cultivation Technology on the Feteasca Neagra Wine Phenolic Composition and Antioxidant Properties. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 59, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitić, M.N.; Souquet, J.M.; Obradović, M.V.; Mitić, S.S. Phytochemical Profiles and Antioxidant Activities of Serbian Table and Wine Grapes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchian, C.E.; Colibaba, C.L.; Codreanu, M.; Tudose-Sandu-Ville, Ş.; Niculaua, M.; Cotea, V.V. Assay of Antioxidant Capacity and Phenolic Compounds in Some Romanian and Cypriot Wine. Not. Bot. Horti Agrobot. Cluj-Napoca 2018, 46, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alecu, A.; Albu, C.; Litescu, S.C.; Eremia, S.A.V.; Radu, G.L. Phenolic and Anthocyanin Profile of Valea Calugareasca Red Wines by HPLC-PDA-MS and MALDI-TOF Analysis. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodișan, B.F.; Ranga, F.; Biriș-Dorhoi, E.-S.; Fărcaș, A.-C.; Tofană, M. Comparative Assessment of Phenolic Compounds from Authentic Wine Varieties from North-Western Romania from the 2021-2022 Harvest. BUASVMCN-FST 2023, 80, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, R.; Šćepanović, R.P.; Raičević, D.; Popović, T.; Korntheuer, K.; Wendelin, S.; Forneck, A.; Philipp, C. Study of the Effects of Climatic Conditions on the Phenolic Content and Antioxidant Activity of Austrian and Montenegrin Red Wines. OENO One 2023, 57, 69–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova-Petropulos, V.; Hermosín-Gutiérrez, I.; Boros, B.; Stefova, M.; Stafilov, T.; Vojnoski, B.; Dörnyei, Á.; Kilár, F. Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity of Macedonian Red Wines. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2015, 41, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukić, I.; Radeka, S.; Budić-Leto, I.; Bubola, M.; Vrhovsek, U. Targeted UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS Profiling of Phenolic Compounds for Differentiation of Monovarietal Wines and Corroboration of Particular Varietal Typicity Concepts. Food Chem. 2019, 300, 125251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radovanovic, A.; Jovancicevic, B.; Arsic, B.; Radovanovic, B.; Bukarica, L.G. Application of Non-Supervised Pattern Recognition Techniques to Classify Cabernet Sauvignon Wines from the Balkan Region Based on Individual Phenolic Compounds. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2016, 49, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-C.; Tian, M.-B.; Han, X.; Shi, N.; Li, H.-Q.; Cheng, C.-F.; Chen, W.; Li, S.-D.; He, F.; Duan, C.-Q.; et al. The Key Role of Vineyard Parcel in Shaping Flavonoid Profiles and Color Characteristics of Cabernet Sauvignon Wines Combined with the Influence of Harvest Ripeness, Vintage and Bottle Aging. Food Chem. X 2023, 19, 100772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| White Wines | Red Wines | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variety | Area | Year | Code | Variety | Area | Year | Code |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Sâmburești | 2020 | SB20S | Merlot | Sâmburești | 2020 | M20S |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Sâmburești | 2021 | SB21S | Merlot | Sâmburești | 2021 | M21S |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Dobrușa | 2021 | SB21Do | Merlot | Sâmburești | 2021 | M21S |
| Crampoșie Selecționată | Dobrușa | 2021 | CSe21Do | Fetească Neagră | Sâmburești | 2020 | FN20S |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Dobrușa | 2022 | SB22Do | Cabernet Sauvignon | Sâmburești | 2020 | CS20S |
| Crampoșie Selecționată | Dobrușa | 2022 | CSe22Do | Cabernet Sauvignon | Sâmburești | 2021 | CS21S |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Spârleni | 2019 | SB19Sp | Cabernet Sauvignon | Sâmburești | 2021 | CS21S |
| Chardonnay | Spârleni | 2019 | CH19Sp | Cabernet Sauvignon | Sâmburești | 2021 | CS21S |
| Crampoșie Selecționată | Spârleni | 2020 | CSe20Sp | Fetească Neagră | Sâmburești | 2021 | FN21S |
| Chardonnay | Spârleni | 2020 | CH20Sp | Cabernet Sauvignon | Dobrușa | 2019 | CS19Do |
| Crampoșie Selecționată | Spârleni | 2021 | CSe21Sp | Negru de Drăgașani | Dobrușa | 2020 | ND20Do |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Spârleni | 2021 | SB21Sp | Cabernet Sauvignon | Dobrușa | 2021 | CS21Do |
| Crampoșie Selecționată | Drăgășani | 2019 | CSe19D | Negru de Drăgășani | Spârleni | 2019 | ND1PSp |
| Fetească Regală | Drăgășani | 2019 | FR19D | Negru de Drăgașani | Spârleni | 2020 | ND20Sp |
| Fetească Regală | Drăgășani | 2020 | FR20D | Cabernet Sauvignon | Spârleni | 2020 | CS20Sp |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Drăgășani | 2020 | SB20D | Fetească Neagră | Spârleni | 2020 | FN20Sp |
| Crampoșie Selecționată | Drăgășani | 2021 | CSe21D | Cabernet Sauvignon | Spârleni | 2021 | CS21Sp |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Drăgășani | 2021 | SB21D | Negru de Drăgașani | Drăgășani | 2020 | ND20D |
| Sauvignon Blanc | Drăgășani | 2022 | SB22D | Negru de Drăgașani | Drăgășani | 2019 | ND19D |
| Cabernet Sauvignon | Drăgășani | 2019 | CS19D | ||||
| Cabernet Sauvignon | Drăgășani | 2021 | CS21D | ||||
| No | Compound | Retention Time (min) | Formula | Exact Mass | Accurate Mass (M-H)− | Experimental Adduct Ion (m/z) | Mass Fragments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids | |||||||
| 1 | Gallic acid | 1.94 | C7H6O5 | 170.0215 | 169.0142 | 169.0133 | 125.0231 |
| 2 | 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 4.25 | C7H6O4 | 154.0266 | 153.0193 | 153.0184 | 109.0281 |
| 3 | 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 6.96 | C7H6O3 | 138.0316 | 137.0243 | 137.0233 | 118.9650, 96.9588, 71.0124 |
| 4 | Caffeic acid | 7.98 | C9H8O4 | 180.0422 | 179.0349 | 179.0343 | 135.044 |
| 5 | Chlorogenic acid | 7.90 | C16H18O9 | 354.0950 | 353.0877 | 353.0880 | 191.0553 |
| 6 | t-Ferulic acid | 8.89 | C10H10O4 | 194.0579 | 193.0506 | 193.0499 | 178.0262, 134.0361 |
| 7 | p-Coumaric acid | 8.69 | C9H8O3 | 164.0473 | 163.0400 | 163.0389 | 119.0489 |
| Derivatives of phenolic acids | |||||||
| 8 | Tannic acid | 7.30 | C76H52O46 | 183.0290 | 182.0217 | 182.0217 | 140.0104, 111.0075, 59.0124 |
| 9 | Ellagic acid | 9.71 | C14H6O8 | 302.0062 | 300.9989 | 300.9993 | 300.9990 |
| 10 | Abscisic acid | 9.99 | C15H20O4 | 264.1361 | 263.1289 | 263.1289 | 179.9803, 191.9454 |
| Flavonoids | |||||||
| 11 | Catechin | 7.53 | C15H14O6 | 290.0790 | 289.0717 | 289.0716 | 109.0282, 123.0349, 125.0232, 137.0232, 151.0390, 203.0708 |
| 12 | Epi-catechin | 8.12 | C15H14O6 | 290.0790 | 289.0717 | ||
| 13 | Naringin | 9.24 | C27H32O14 | 580.1791 | 579.1722 | 579.1722 | 363.0722 |
| 14 | Hesperidin | 9.32 | C28H34O15 | 610.1897 | 609.1824 | 609.1828 | 377.0876 |
| 15 | Rutin | 9.41 | C27H30O16 | 610.1533 | 609.1465 | 609.1465 | 345.0616 |
| 16 | Myricetin | 8.12 | C15H10O8 | 318.0375 | 317.0310 | 317.0310 | 178.9986, 164.9263, 151.0036, 137.0244, 107.0125 |
| 17 | Quercetin | 10.68 | C15H10O7 | 302.2357 | 301.0354 | 301.0351 | 151.0226, 178.9977, 121.0282, 107.0125 |
| 18 | Kaempferol | 11.60 | C15H10O6 | 286.0477 | 285.0404 | 285.0403 | 151.0389, 117.0180 |
| 19 | Isorhamnetin | 11.79 | C16H12O7 | 316.0582 | 315.0509 | 315.0510 | 300.0277 |
| Stilbens | |||||||
| 20 | t-Resveratrol | 9.97 | C14H12O3 | 228.0786 | 227.0713 | 227.0708 | 185.0813, 143.0337 |
| Phenolic Compounds (mg/L) | Sauvignon Blanc (SB) (n = 9) | Crâmpoșie Selecționată (CSe) (n = 6) | Fetească Regală (FR) (n = 2) | Chardonnay (CH) (n = 2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids | ||||
| Gallic acid | 7.81 (0.67–21.05) | 9.11 (1.96–18.97) | 2.34 (1.40–3.28) | 15.41 (14.58–16.23) |
| 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 0.74 (0.27–2.15) | 0.99 (0.43–2.08) | 1.38 (1.09–1.67) | 0.97 (0.96–0.99) |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 0.13 (0.04–0.38) | 0.17 (0.06–0.32) | 0.23 (0.19–0.27) | 0.30 (0.28–0.33) |
| Caffeic acid | 3.34 (1.44–6.51) | 3.53 (0.92–7.88) | 1.36 (1.32–1.40) | 8.01 (7.99–8.03) |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.03 (0.02–0.05) | 0.02 (0.01–0.03) | 0.02 (0.02–0.03) | 0.02 (0.02–0.02) |
| t-Ferulic acid | 0.46 (0.11–0.73) | 1.54 (0.94–2.52) | 0.58 (0.52–0.64) | 0.63 (0.63–0.63) |
| p-Coumaric acid | 1.26 (0.31–3.00) | 1.29 (0.19–3.38) | 0.38 (0.36–0.40) | 2.96 (2.74–3.18) |
| Derivatives of phenolic acids | ||||
| Tannic acid | 0.89 (0.45–1.41) | 1.50 (1.02–2.83) | 2.13 (1.92–2.33) | 1.59 (1.42–1.77) |
| Ellagic acid | 0.39 (0.17–0.78) | 0.74 (0.15–1.22) | 0.42 (0.34–0.50) | 0.31 (0.30–0.32) |
| Abscisic acid | 0.21 (0.13–0.29) | 0.19 (0.13–0.35) | 0.32 (0.29–0.34) | 0.31 (0.24–0.39) |
| Flavonoids | ||||
| Catechin | 1.22 (0.32–3.03) | 1.45 (0.33–3.41) | 1.72 (1.18–2.25) | 2.86 (1.76–3.96) |
| Epicatechin | 1.10 (0.31–2.94) | 1.39 (0.32–2.59) | 2.75 (2.19–3.31) | 2.78 (1.71–3.85) |
| Naringin | 0.02 (<LD–0.13) | <LD–0.01 | <LD | 0.91 (0.24–1.57) |
| Hesperidin | <LD–0.01 | 0.01 (<LD–0.02) | <LD | 0.04 (0.03–0.05) |
| Rutin | 0.02 (<LD–0.11) | 0.03 (0.01–0.07) | 0.05 (0.04–0.06) | <LD |
| Myricetin | 0.01 (<LD–0.02) | 0.01 (<LD–0.01) | 0.01 (0.01–0.01) | 0.01 (0.01–0.01) |
| Quercetin | 0.01 (<LD–0.05) | 0.06 (<LD–0.28) | 0.10 (0.05–0.15) | 0.04 (0.01–0.07) |
| Kaempferol | <LD–0.01 | 0.01 (<LD–0.02) | 0.01 (<LD–0.02) | 0.01 (0.01–0.01) |
| Isorhamnetin | 0.01 (<LD–0.01) | 0.01 (<LD–0.03) | 0.01 (0.01–0.01) | 0.01 (<LD–0.01) |
| Stilbene | ||||
| t-Resveratrol | 1.34 (0.33–3.56) | 2.12 (0.42–5.77) | 0.27 (0.26–0.29) | 2.04 (1.45–2.63) |
| Phenolic Compounds (mg/L) | Cabernet Sauvignon (CS) (n = 10) | Negru de Drăgășani (ND) (n = 5) | Merlot (M) (n = 3) | Fetească Neagră (FN) (n = 3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenolic acids | ||||
| Gallic acid | 54.51 (33.11–69.54) | 59.06 (43.17–68.62) | 63.02 (45.34–72.25) | 56.32 (42.37–64.07) |
| 3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid | 2.74 (1.51–6.78) | 4.10 (2.90–6.94) | 1.87 (1.65–2.29) | 2.25 (1.50–3.29) |
| 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid | 0.53 (0.33–0.93) | 0.85 (0.661.21) | 0.35 (0.31–0.38) | 0.42 (0.33–0.57) |
| Caffeic acid | 3.37 (2.01–5.14) | 3.60 (2.874.53) | 6.16 (3.45–7.84) | 5.87 (3.17–11.25) |
| Chlorogenic acid | 0.10 (0.06–0.16) | 0.09 (0.070.10) | 0.08 (0.08–0.09) | 0.22 (0.15–0.35) |
| t-Ferulic acid | 0.97 (0.34–1.58) | 0.74 (0.580.92) | 1.05 (0.50–1.35) | 0.91 (0.64–1.33) |
| p-Coumaric acid | 2.07 (0.98–3.87) | 2.27 (1.193.05) | 2.44 (2.37–2.55) | 2.64 (1.85–3.06) |
| Derivatives of phenolic acids | ||||
| Tannic acid | 22.54 (11.18–28.50) | 22.33 (18.03–25.35) | 16.12 (15.61–16.41) | 31.42 (24.65–40.34) |
| Ellagic acid | 11.39 (4.54–19.41) | 8.53 (2.92–16.31) | 5.82 (4.99–6.55) | 13.44 (10.22–18.07) |
| Abscisic acid | 1.28 (1.04–1.41) | 1.17 (1.08–1.28) | 1.19 (1.18–1.20) | 1.09 (1.00–1.14) |
| Flavonoids | ||||
| Catechin | 15.98 (7.26–23.12) | 16.63 (8.86–30.15) | 15.80 (9.25–24.67) | 14.71 (10.79–16.88) |
| Epicatechin | 14.57 (7.05–21.34) | 16.14 (8.60–29.26) | 18.45 (8.98–23.94) | 14.27 (10.47–16.38) |
| Naringin | 5.60 (1.72–13.47) | 8.14 (6.58–9.68) | 4.16 (3.99–4.33) | 5.60 (3.72–7.93) |
| Hesperidin | 0.17 (0.10–0.24) | 0.19 (0.13–0.25) | 0.22 (0.21–0.24) | 0.22 (0.19–0.24) |
| Rutin | 0.08 (0.05–0.11) | 0.07 (0.05–0.12) | 0.07 (0.06–0.08) | 0.11 (0.08–0.14) |
| Myricetin | 9.52 (6.01–13.67) | 4.91 (1.77–7.78) | 9.55 (9.38–9.68) | 13.28 (9.45–15.64) |
| Quercetin | 8.67 (0.97–13.62) | 3.18 (0.04–6.56) | 12.32 (9.03–14.24) | 14.15 (12.75–15.42) |
| Kaempferol | 0.73 (0.06–1.57) | 0.15 (0.03–0.50) | 1.07 (0.31–1.47) | 1.29 (0.84–1.64) |
| Isorhamnetin | 2.67 (0.31–4.44) | 0.87 (0.04–1.75) | 2.50 (1.98–3.02) | 2.73 (2.43–3.23) |
| Stilbene | ||||
| t-Resveratrol | 23.51 (7.94–51.33) | 22.49 (10.51–41.92) | 55.70 (44.90–72.84) | 38.08 (27.89–50.67) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ciucure, C.-T.; Miricioiu, M.G.; Geana, E.-I. Discrimination of Romanian Wines Based on Phenolic Composition and Identification of Potential Phenolic Biomarkers for Wine Authenticity and Traceability. Beverages 2025, 11, 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020044
Ciucure C-T, Miricioiu MG, Geana E-I. Discrimination of Romanian Wines Based on Phenolic Composition and Identification of Potential Phenolic Biomarkers for Wine Authenticity and Traceability. Beverages. 2025; 11(2):44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020044
Chicago/Turabian StyleCiucure, Corina-Teodora, Marius Gheorghe Miricioiu, and Elisabeta-Irina Geana. 2025. "Discrimination of Romanian Wines Based on Phenolic Composition and Identification of Potential Phenolic Biomarkers for Wine Authenticity and Traceability" Beverages 11, no. 2: 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020044
APA StyleCiucure, C.-T., Miricioiu, M. G., & Geana, E.-I. (2025). Discrimination of Romanian Wines Based on Phenolic Composition and Identification of Potential Phenolic Biomarkers for Wine Authenticity and Traceability. Beverages, 11(2), 44. https://doi.org/10.3390/beverages11020044







