Development of a Rapid, Accurate, and On-Site Detection Protocol for Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Collection of Si and Seven Other Ant Species
2.2. Extraction of Genomic DNA from Eight Ant Species
2.3. Verification of a Si-specific Gene by Conventional PCR
2.4. The 4pSi-LAMP Assay Protocol
2.5. The 6pSi-LAMP Assay Protocol
2.6. Determination of Optimal Amounts of LAMP Polymerase
2.7. Detection Limit of 6pSi-LAMP Assay
2.8. The 6pSi-LAMP Assay with a Rapid Genomic Extraction Protocol
2.9. On-Site Si Diagnostic Protocol
3. Results
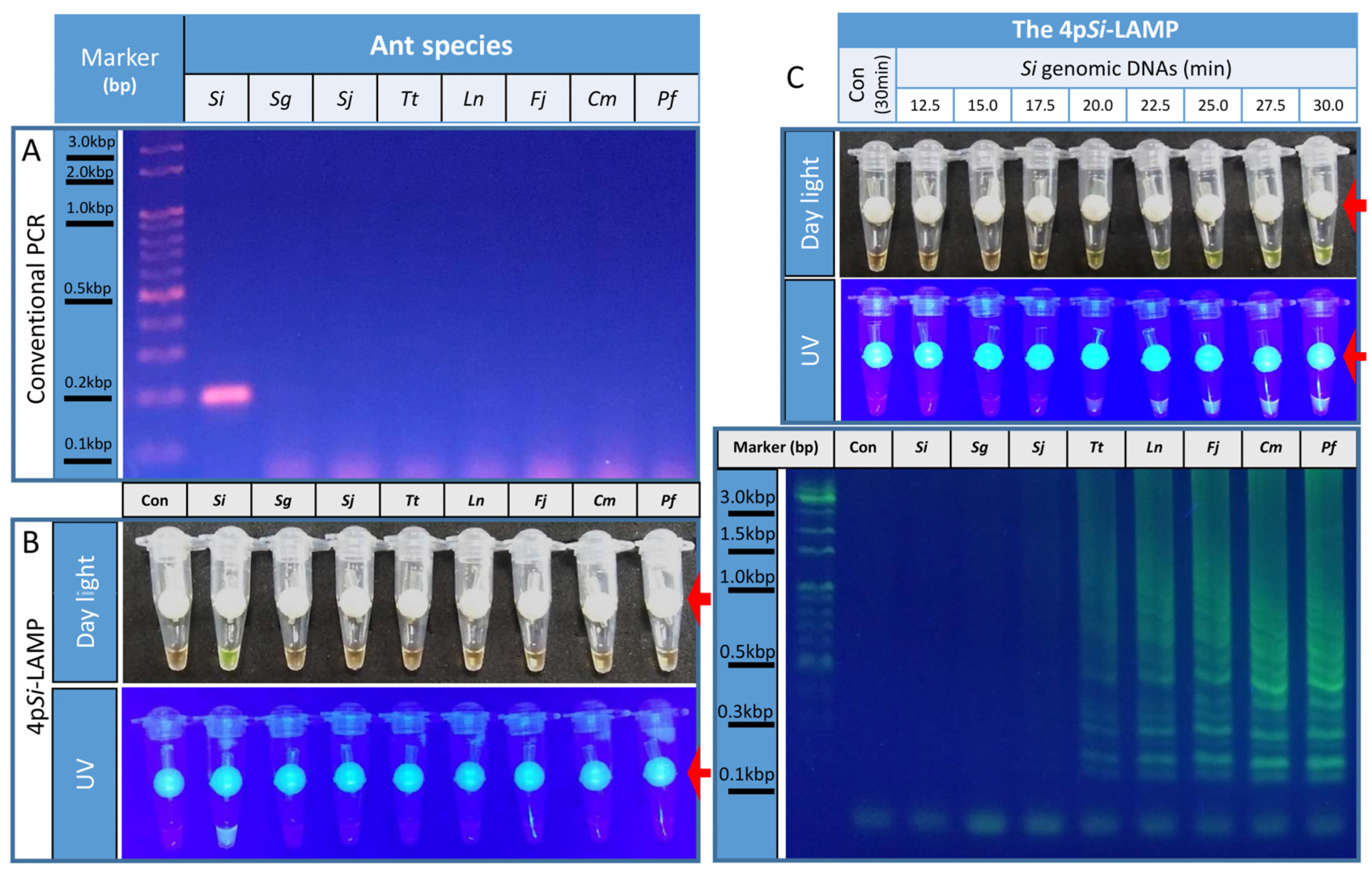
3.1. Si11977 Was a Si-Specific Biomarker
3.2. Development of a Four-Primer Si-LAMP Assay
3.3. Determination of the Optimal Incubation Periods for the 4pSi-LAMP
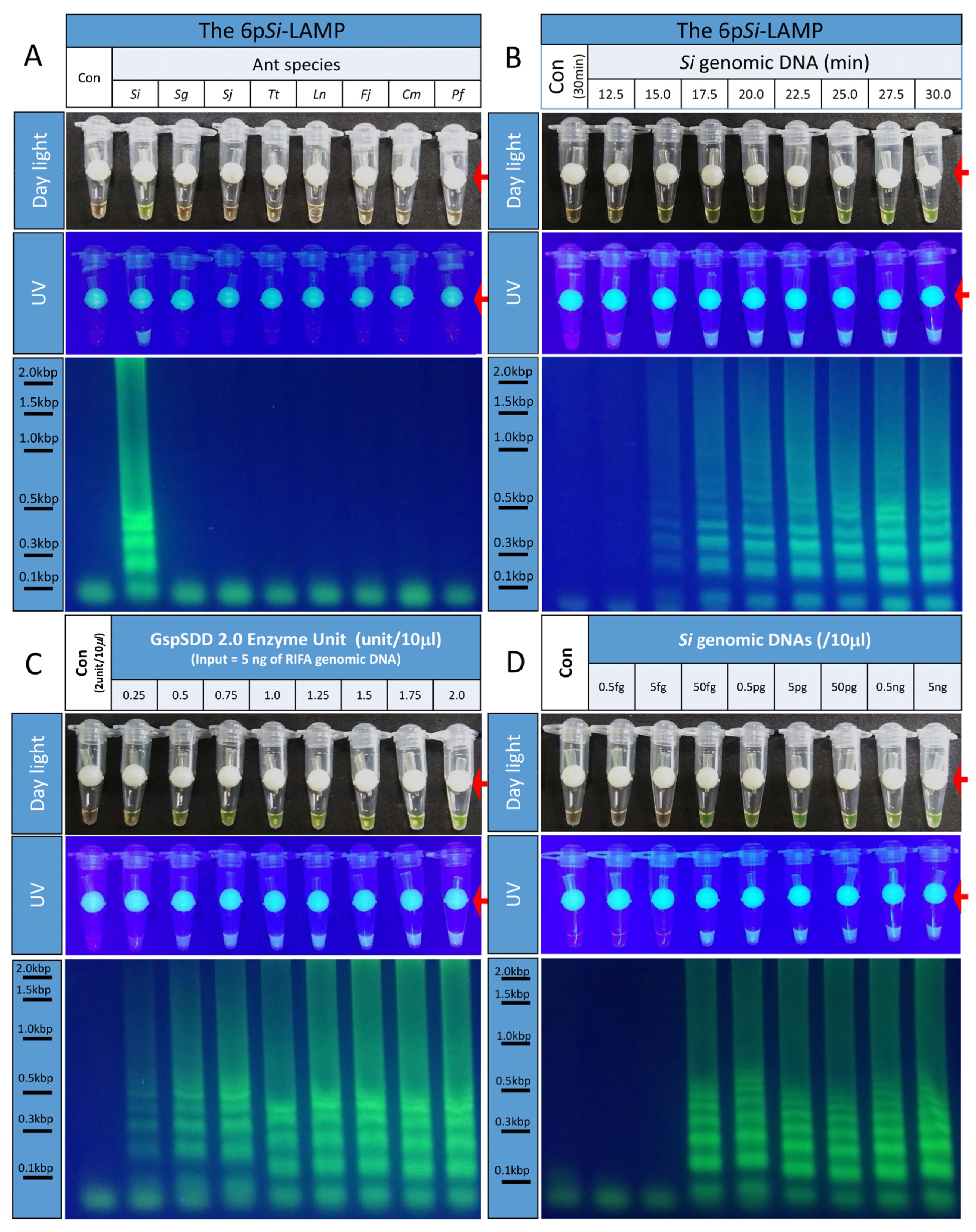
3.4. Development of the Six-Primer Si-LAMP
3.5. Reduced Incubation Periods of the 6pSi-LAMP Assay
3.6. Determination of the Optimal Amounts of GspSDD 2.0 DNA Polymerase for the 6pSi-LAMP Assay
3.7. Determining the Detection Limits for the 6pSi-LAMP Assay
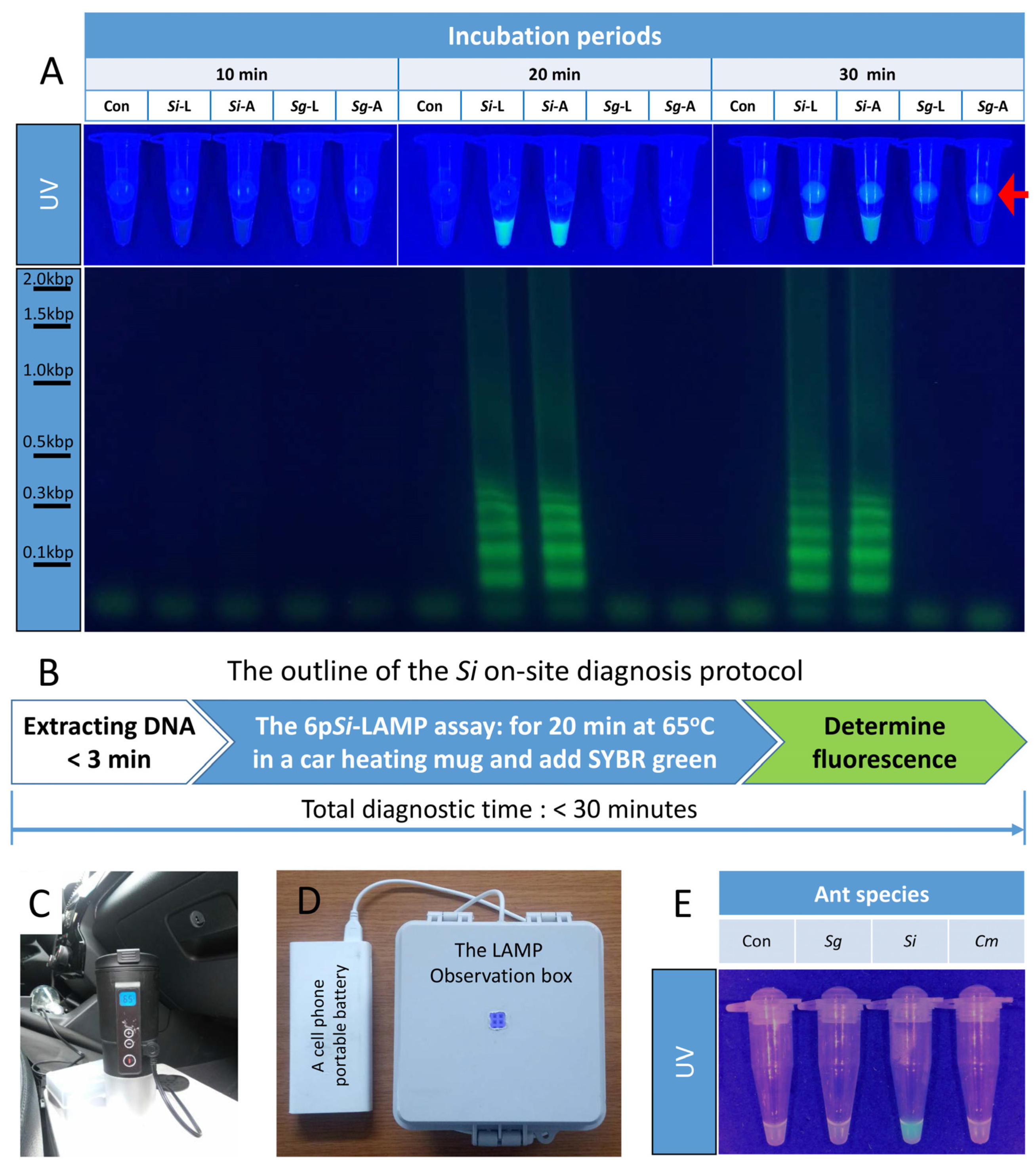
3.8. The 6pSi-LAMP Assays with Si Genomic DNA Rapidly Extracted with Quick Genomic DNA Extraction Solution
3.9. The Si On-Site Diagnosis Protocol
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Early, R.; Bradley, B.A.; Dukes, J.S.; Lawler, J.J.; Olden, J.D.; Blumenthal, D.M.; Gonzalez, P.; Grosholz, E.D.; Ibañez, I.; Miller, L.P.; et al. Global threats from invasive alien species in the twenty-first century and national response capacities. Nat. Commun. 2016, 23, 12485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowe, S.; Browne, M.; Boudjelas, S.; De Poorter, M. 100 of the World’s Worst Invasive Alien Species: A Selection from the Global Invasive Species Database; The Invasive Species Specialist Group (ISSG) a Specialist Group of the Species Survival Commission (SSC) of the World Conservation Union (IUCN): Auckland, New Zealand, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ujiyama, S.; Tsuji, K. Controlling invasive ant species: A theoretical strategy for efficient monitoring in the early stage of invasion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Park, Y.; Kim, W.J.; Kim, A.-Y.; Nguyen, P.; Lyu, D.P.; Lee, H.S.; Koh, Y.H. Developing molecular diagnostics for detection of red imported fire ants using two genes, Sinv11108 and Sinv11977. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 102, e21610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council, I.S. Fact Sheet: Red Fire Ants; Invasive Species Council: Katoomba, NSW, Australia, 2017; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Blaser, S.; Diem, H.; von Felten, A.; Gueuning, M.; Andreou, M.; Boonham, N.; Tomlinson, J.; Müller, P.; Utzinger, J.; Frey, J.E.; et al. From laboratory to point of entry: Development and implementation of a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)-based genetic identification system to prevent introduction of quarantine insect species. Pest Manag. Sci. 2018, 74, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Pena, S.; Chacón-Cardosa, M.C.; Resendez-Perez, D. Identification of fire ants (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) from northeastern Mexico with morphology and molecular markers. Fla. Entomol. 2009, 92, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoemaker, D.D.; Ahrens, M.E.; Ross, K.G. Molecular phylogeny of fire ants of the Solenopsis saevissima species-group based on mtDNA sequences. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2006, 38, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles, S.M.; Strong, C.A.; Callcott, A.-M.A. Development of a lateral flow immunoassay for rapid field detection of the red imported fire ant, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 4693–4703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agdia. InvictDetect™ ImmunoStrip detection kit for Solenopsis invicta. Agdia, Ed. 2017. Available online: https://orders.agdia.com/insect-diagnostics (accessed on 1 June 2022).
- Folmer, O.; Black, M.; Hoeh, W.; Lutz, R.; Vrijenhoek, R. DNA primers for amplification of mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit I from diverse metazoan invertebrates. Mol. Mar. Biol. Biotechnol. 1994, 3, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima, N.; Sakamoto, Y.; Goka, K. Rapid detection of the red fire ant Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2019, 54, 319–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becherer, L.; Borst, N.; Bakheit, M.; Frischmann, S.; Zengerle, R.; Stetten, F.v. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP)—Review and classification of methods for sequence-specific detection. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 717–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardinge, P.; Murray, J.A.H. Reduced false positives and improved reporting of loop-mediated isothermal amplification using quenched fluorescent primers. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagamine, K.; Hase, T.; Notomi, T. Accelerated reaction by loop-mediated isothermal amplification using loop primers. Mol. Cell. Probes 2002, 16, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomita, N.; Mori, Y.; Kanda, H.; Notomi, T. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) of gene sequences and simple visual detection of products. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przybylska, A.; Fiedler, Ż.; Kucharczyk, H.; Obrępalska-Stęplowska, A. Detection of the quarantine species Thrips palmi by loop-mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Ahuja, A.; Rao, U.; Somvanshi, V.S. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification based identification of entomopathogenic nematodes Heterorhabditis spp. and Steinernema spp. from soil DNA. BioControl 2021, 66, 701–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahuja, A.; Somvanshi, V.S. Diagnosis of plant-parasitic nematodes using loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): A review. Crop Prot. 2021, 147, 105459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omer, Z.S.; Wallenhammar, A.-C.; Viketoft, M. Development of Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Assay for Rapid Detection and Analysis of the Root-Knot Nematode Meloidogyne hapla in Soil. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waliullah, S.; Bell, J.; Jagdale, G.; Stackhouse, T.; Hajihassani, A.; Brenneman, T.; Ali, M.E. Rapid detection of pecan root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne partityla, in laboratory and field conditions using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Tanaka, H.; Suzuki, K.; Fukuta, S.; Kato, S.; Ohno, T. Multiplex loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay for the identification of three major whitefly species in the greenhouse. J. Appl. Entomol. 2018, 142, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurm, Y.; Wang, J.; Riba-Grognuz, O.; Corona, M.; Nygaard, S.; Hunt, B.G.; Ingram, K.K.; Falquet, L.; Nipitwattanaphon, M.; Gotzek, D.; et al. The genome of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; Kim, A.-Y.; Han, H.R.; Moon, Y.S.; Koh, Y.H. Development of two alternative Loop-mediated isothermal amplification tools for detecting pathogenic pine wood nematodes. For. Pathol. 2015, 45, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Hur, J.H.; Lee, G.S.; Choi, M.-Y.; Koh, Y.H. Rapid and highly accurate detection of Drosophila suzukii, spotted wing Drosophila (Diptera: Drosophilidae) by loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2016, 19, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osabutey, A.F.; Seo, B.Y.; Kim, A.-Y.; Ha, T.A.T.; Jung, J.K.; Goergen, G.; Owusu, E.O.; Lee, G.-S.; Koh, Y.H. Identification of a fall armyworm (Spodoptera frugiperda)-specific gene and development of a rapid and sensitive loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.H.; Hur, J.H.; Heckel, D.G.; Kim, J.; Koh, Y.H. Development of a highly accurate and sensitive diagnostic tool for pyrethroid-resistant chimeric P450 CYP337B3 of Helicoverpa armigera using loop-mediated isothermal amplification. Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 99, e21504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doorenweerd, C.; San Jose, M.; Barr, N.; Leblanc, L.; Rubinoff, D. Highly variable COI haplotype diversity between three species of invasive pest fruit fly reflects remarkably incongruent demographic histories. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Name | Nucleotide Sequences |
|---|---|
| Si11977-F3 | CTAAAACCCCACGCCACTCACC |
| Si11977-B3 | TTCGGAGAAGTTGCCGACAATGG |
| Si11977-FIP | CGGGTTTCCTTTGTTTGGGGGACGCAACCACCGTTCATC |
| Si11977-BIP | AAGACACTTTCGTCCCTGCGCTCGCACATACACTTGCATCG |
| Si11977-LF | GATCCCGTCTCAGTCGTCGAT |
| Si11977-LB | ATCCTGACGAGGCCCATTC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, A.-Y.; Koh, Y.H. Development of a Rapid, Accurate, and On-Site Detection Protocol for Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bioengineering 2022, 9, 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090434
Kim A-Y, Koh YH. Development of a Rapid, Accurate, and On-Site Detection Protocol for Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bioengineering. 2022; 9(9):434. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090434
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, A-Young, and Young Ho Koh. 2022. "Development of a Rapid, Accurate, and On-Site Detection Protocol for Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae)" Bioengineering 9, no. 9: 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090434
APA StyleKim, A.-Y., & Koh, Y. H. (2022). Development of a Rapid, Accurate, and On-Site Detection Protocol for Red Imported Fire Ants, Solenopsis invicta (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Bioengineering, 9(9), 434. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9090434





