Initial Healing Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Gel and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Deep Corneal Wound in Rabbits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Experiments
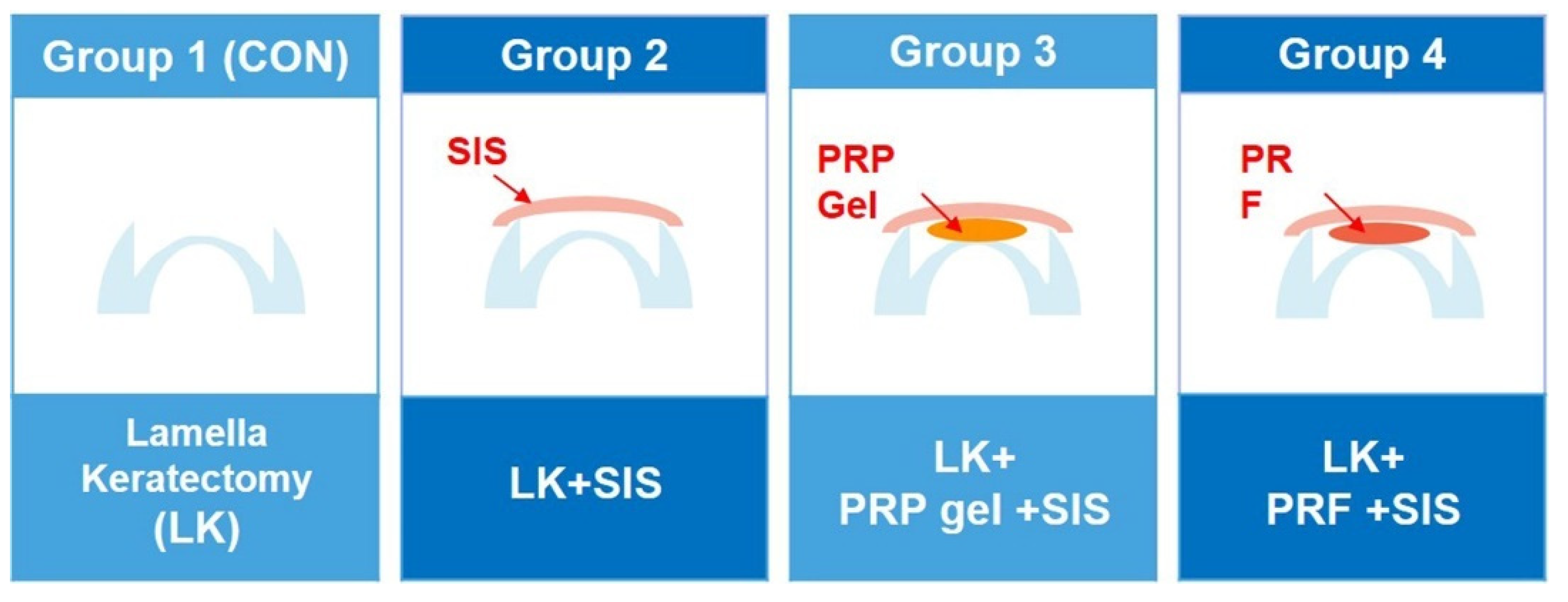
2.2. Study Design
2.3. PRP Gel Preparation
2.4. PRF Preparation
2.5. Surgical Procedures
2.6. Clinical Analysis of Cornea
2.7. Histopathologic Examination
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
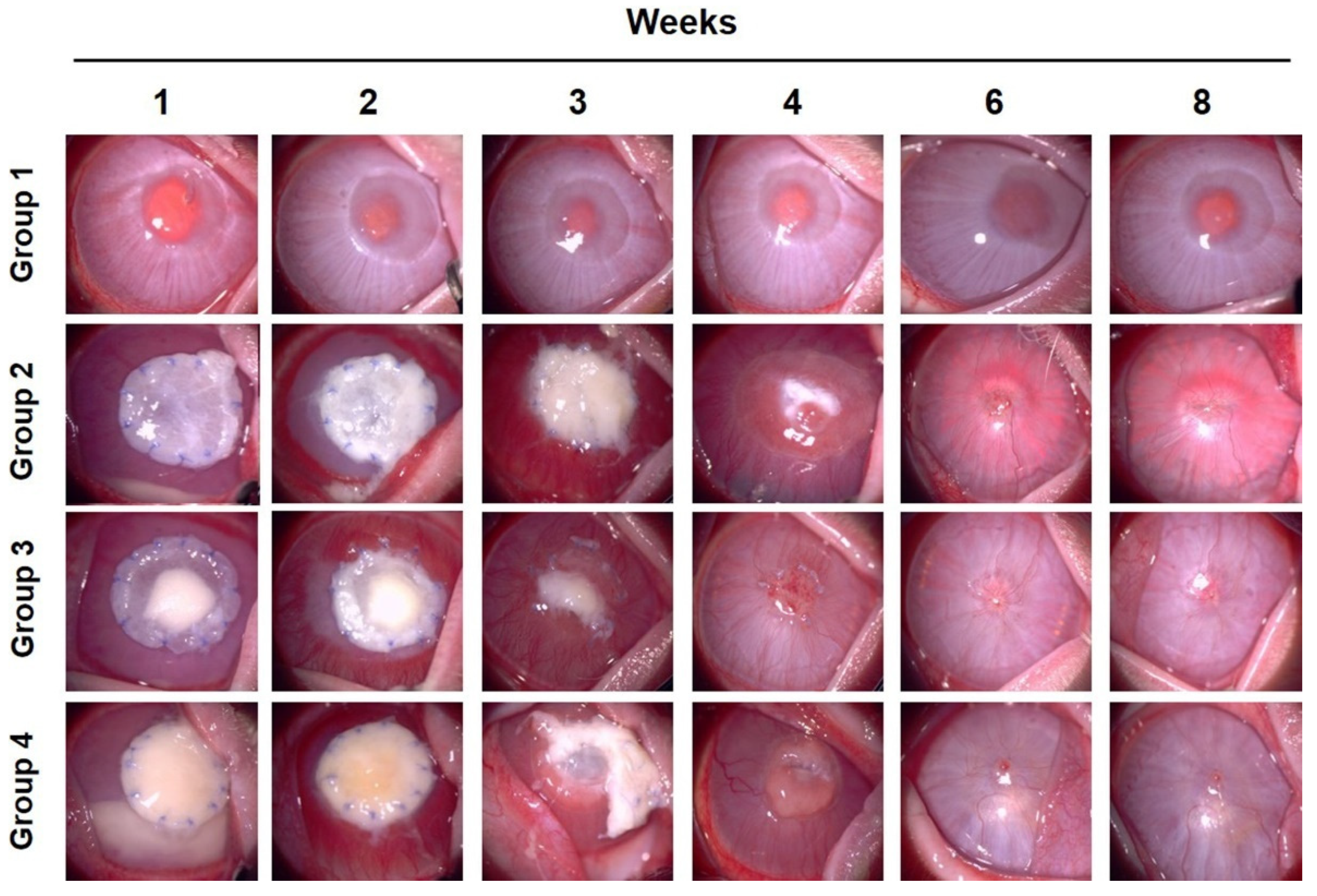
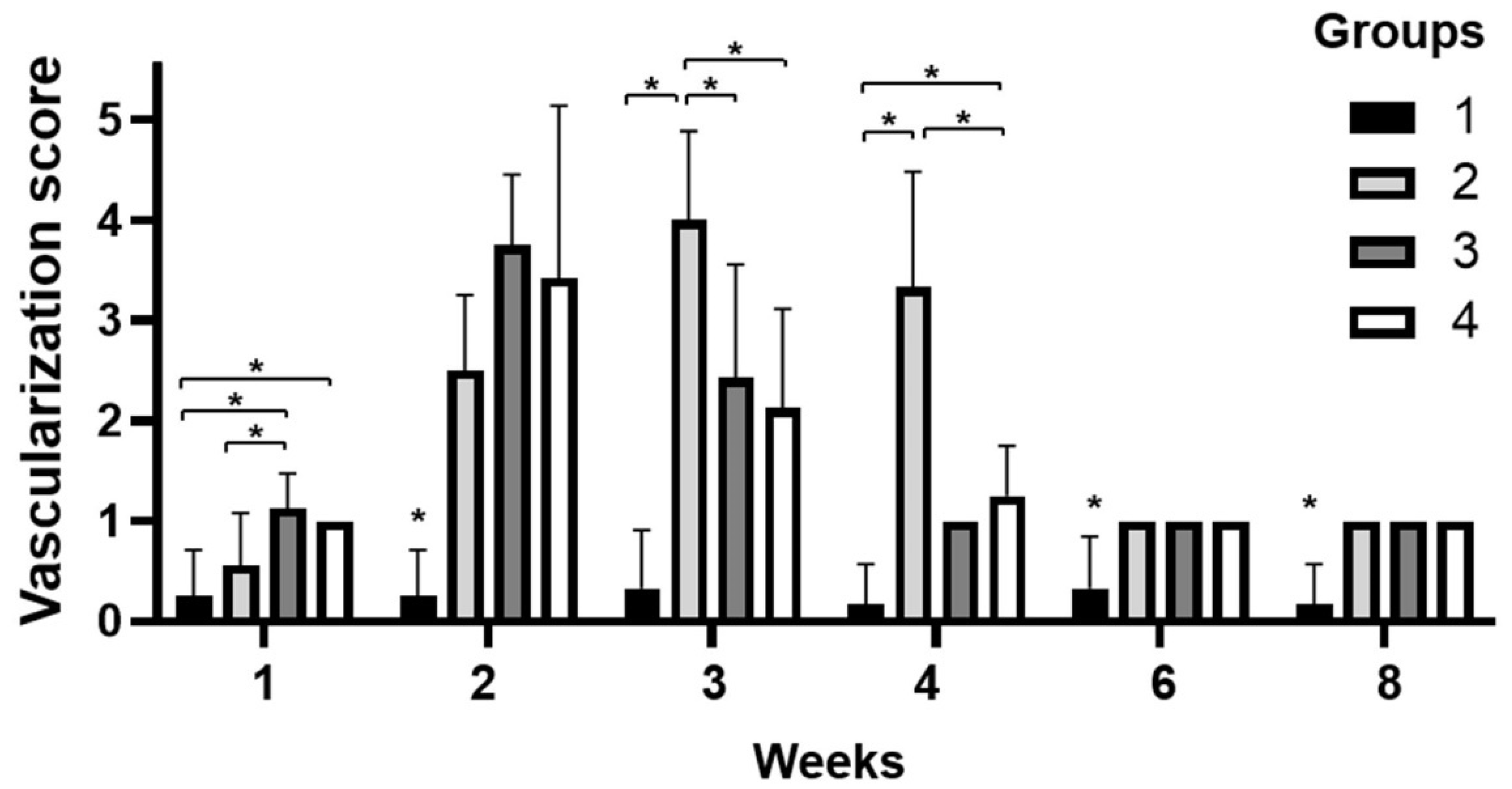
3.1. Clinical Evaluation of Corneal Vascularization, Opacity, and Complications
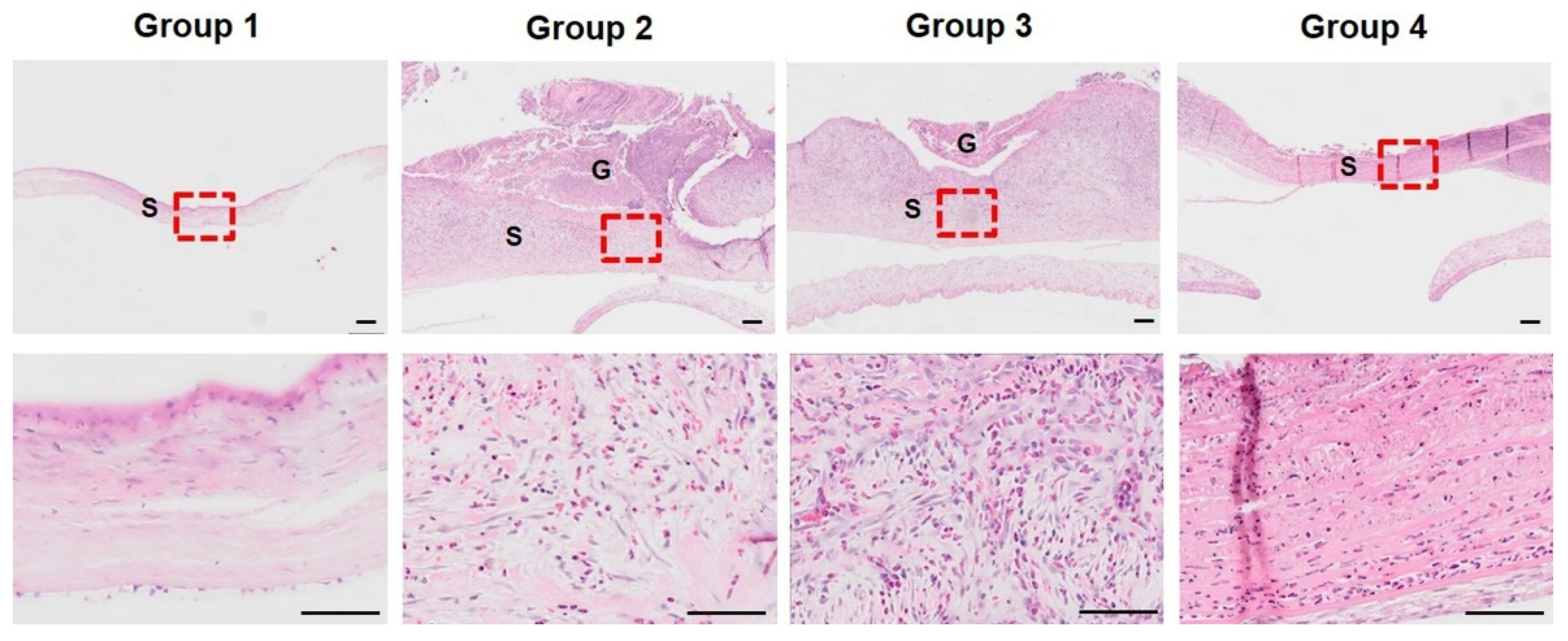
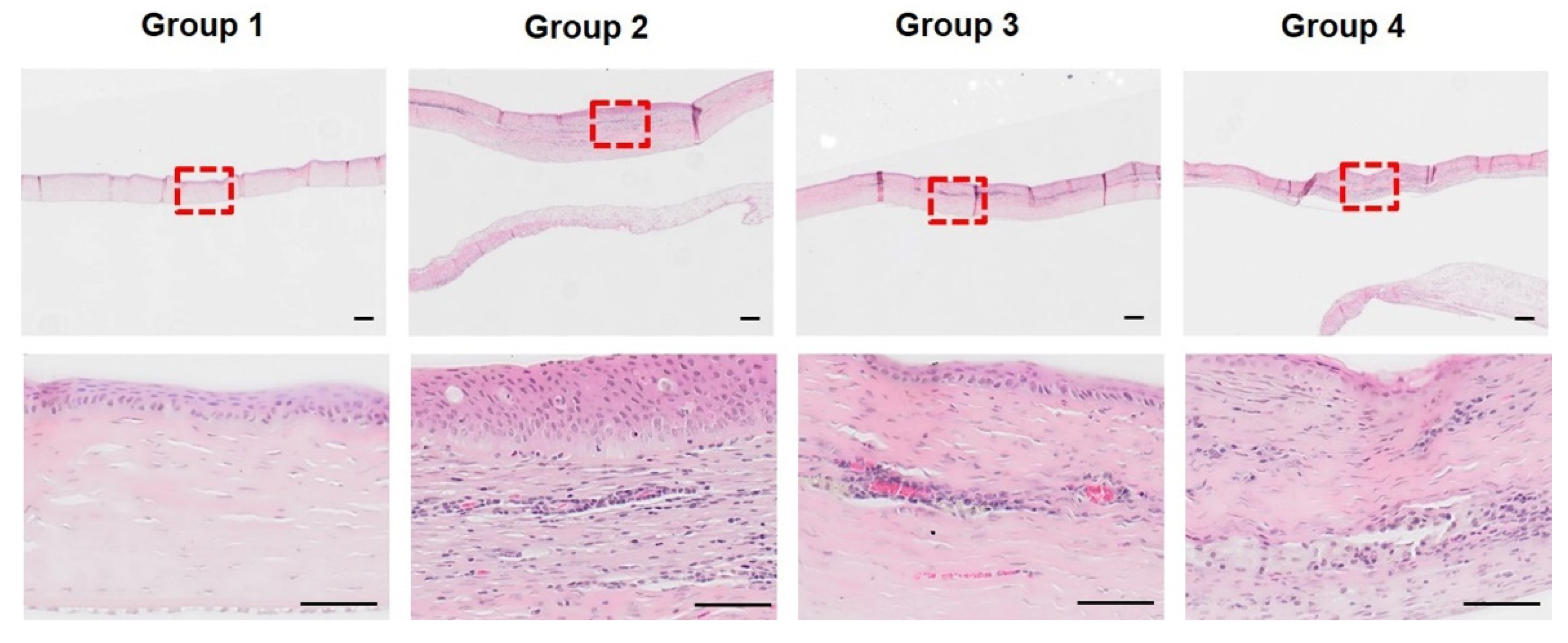
3.2. Histopathological Analysis of Initial Corneal Wound Healing Process
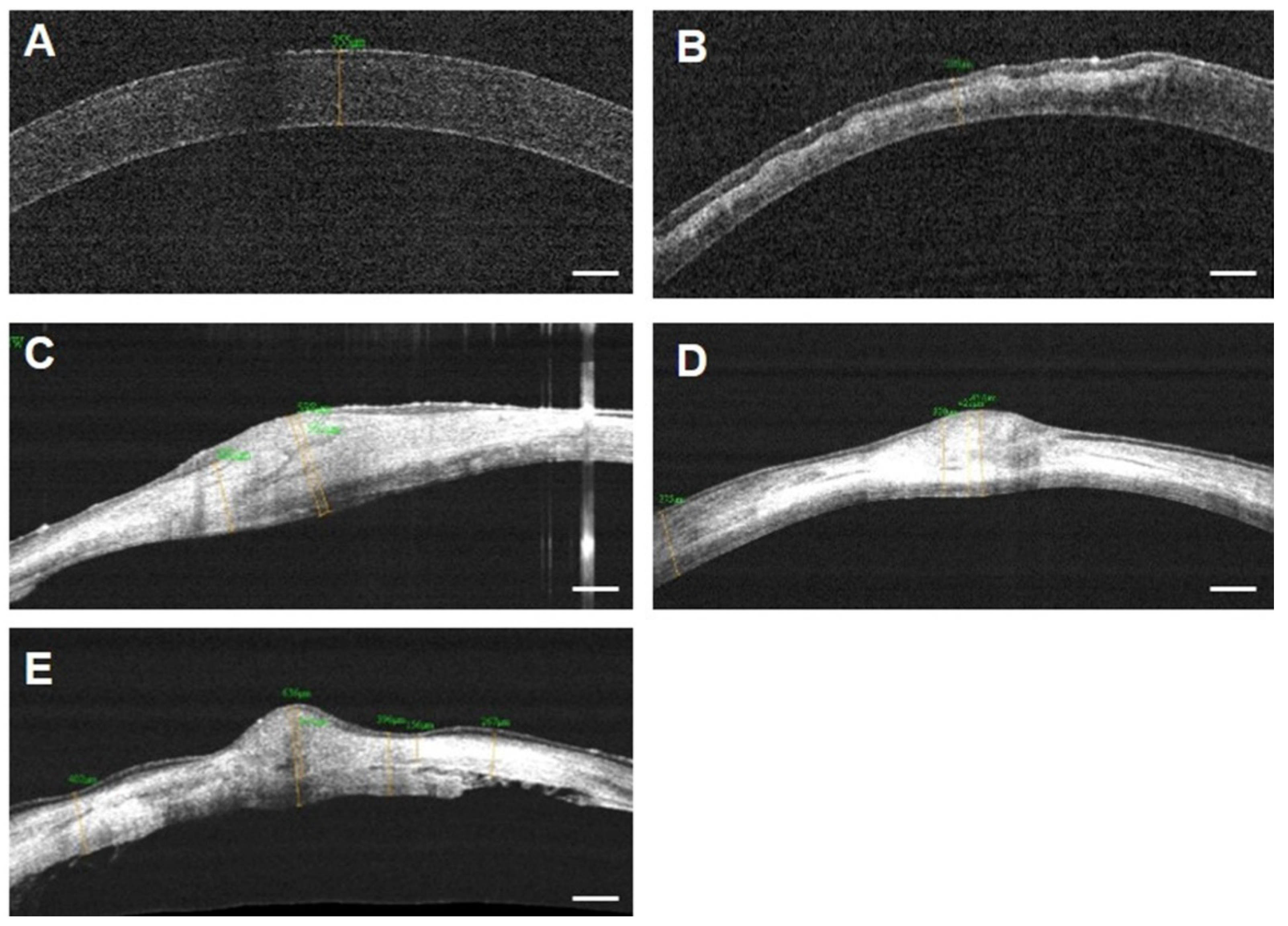
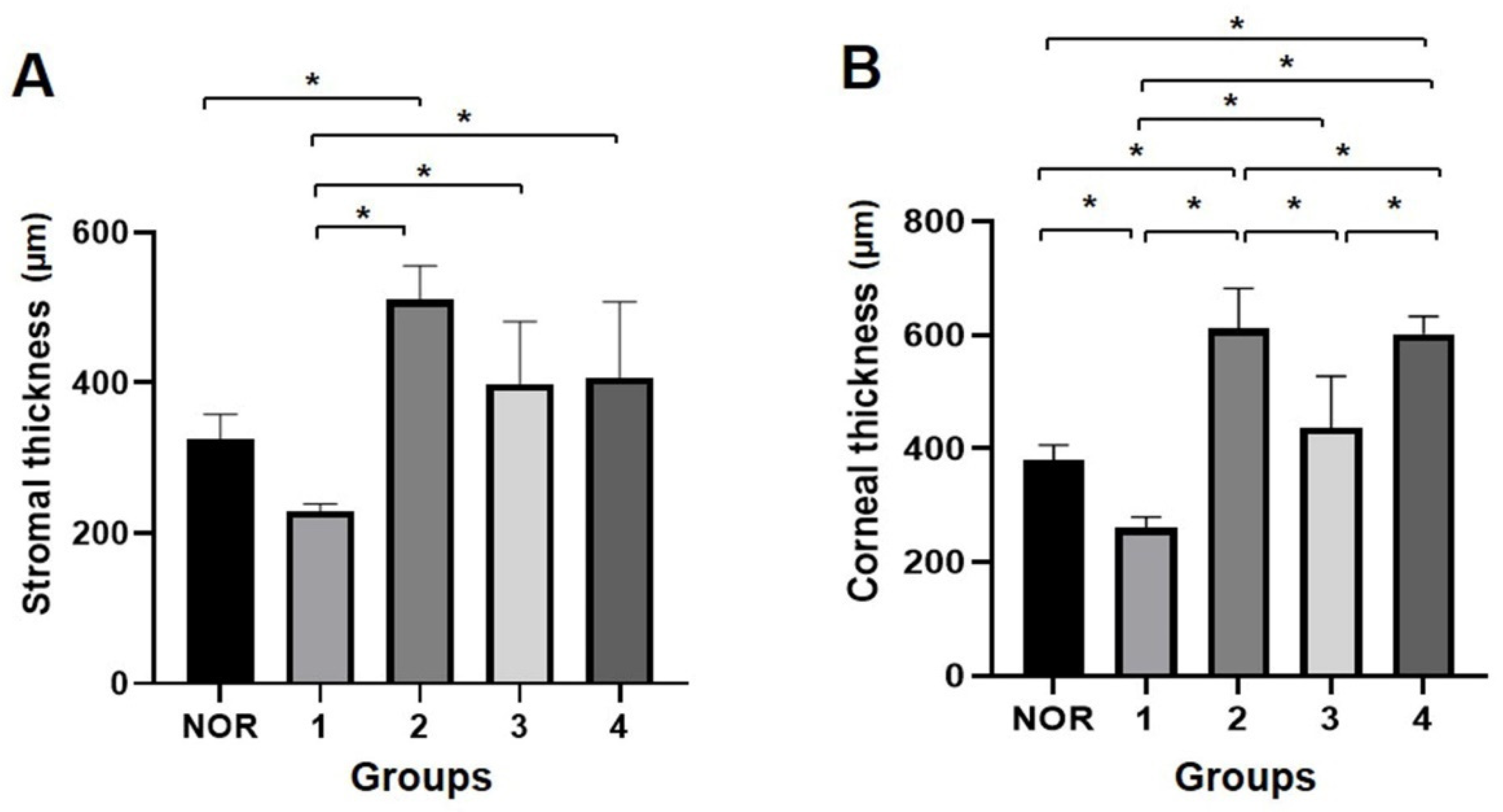
3.3. FD-OCT Examination for Corneal Thickness
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Leong, Y.; Tong, L. Barrier Function in the Ocular Surface: From Conventional Paradigms to New Opportunities. Ocul. Surf. 2015, 13, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Jong, B.B.S.; van der Meulen, I.J.E.; van Vliet, J.M.J.B.S.; Lapid-Gortzak, R.; Nieuwendaal, C.P.; van den Berg, T.J.T.P. Effects of Corneal Scars and Their Treatment with Rigid Contact Lenses on Quality of Vision. Eye Contact Lens. 2018, 44, S216–S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ljubimov, A.V.; Saghizadeh, M. Progress in corneal wound healing. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2015, 49, 17–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wilson, S.E. Corneal wound healing. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 197, 108089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamil, S.; Mohan, R.R. Corneal stromal wound healing: Major regulators and therapeutic targets. Ocul. Surf. 2021, 19, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, S.E. Corneal myofibroblast biology and pathobiology: Generation, persistence, and transparency. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 99, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mobaraki, M.; Abbasi, R.; Omidian Vandchali, S.; Ghaffari, M.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mozafari, M. Corneal Repair and Regeneration: Current Concepts and Future Directions. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2019, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sharif, Z.; Sharif, W. Corneal neovascularization: Updates on pathophysiology, investigations & management. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 63, 15–22. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Udupa, E.P.; Kumar, U.; Rao, P.; Honnegowda, T. Role of angiogenesis and angiogenic factors in acute and chronic wound healing. Plast. Aesthet Res. 2015, 2, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feizi, S.; Azari, A.A.; Safapour, S. Therapeutic approaches for corneal neovascularization. Eye Vis. 2017, 4, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golebiewska, E.M.; Poole, A.W. Platelet secretion: From haemostasis to wound healing and beyond. Blood Rev. 2014, 29, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anitua, E.; Andia, I.; Ardanza, B.; Nurden, P.; Nurden, A.T. Autologous platelets as a source of proteins for healing and tissue regeneration. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.B.; Sporn, M.B.; Assoian, R.K.; Smith, J.M.; Roche, N.S.; Wakefield, L.M.; Heine, U.I.; Liotta, L.A.; Falanga, V.; Kehrl, J.H. Transforming growth factor type beta: Rapid induction of fibrosis and angiogenesis in vivo and stimulation of collagen formation in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 4167–4171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tandon, A.; Tovey, J.C.K.; Sharma, A.; Gupta, R.; Mohan, R.R. Role of Transforming Growth Factor Beta in Corneal Function, Biology and Pathology. Curr. Mol. Med. 2010, 10, 565–578. [Google Scholar]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Arnalich-Montiel, F.; Rodriguez, A.E. The Role of “Eye Platelet Rich Plasma” (E-Prp) for Wound Healing in Ophthalmology. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2012, 13, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnalich, F.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Luque-Rio, A.; Alio, J.L. Solid Platelet Rich Plasma in Corneal Surgery. Ophthalmol 2016, 5, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Conca, V.; Abad-Collado, M.; Hueso-Abancens, J.R.; Mengual-Verdú, E.; Piñero, D.P.; Aguirre-Balsalobre, F.; Molina, J.C. Efficacy and safety of treatment of hyposecretory dry eye with platelet-rich plasma. Acta Ophthalmol. 2019, 97, e170–e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alio, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Martinez, L. Bovine Pericardium Membrane (Tutopatch) Combined with Solid Platelet-Rich Plasma for the Management of Perforated Corneal Ulcers. Cornea 2013, 32, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alio, J.L.; Abad, M.; Artola, A.; Rodriguez-Prats, J.L.; Pastor, S.; Ruiz-Colecha, J. Use of Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Dormant Corneal Ulcers. Ophthalmology 2007, 114, 1286–1293.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Jeon, S.H.; Park, J.; Chung, J.; Choung, Y.; Choung, H.; Kim, E.; Choung, P. Platelet-Rich Fibrin is a Bioscaffold and Reservoir of Growth Factors for Tissue Regeneration. Tissue Eng. Part. A 2010, 17, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Perez, K.; Dym, H. Clinical Uses of Platelet-Rich Fibrin in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 64, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahmanpour, S.; Ghasemi, P.M.; Sadeghi-Naini, M.; Kashani, I.R. Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma & Platelet-Rich Fibrin with and without Stromal Cell-Derived Factor-1 on Repairing Full-Thickness Cartilage Defects in Knees of Rabbits. Iran. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 41, 507–517. [Google Scholar]
- Chuang, M.; Ho, L.; Kuo, T.; Sheu, S.; Liu, Y.; Lin, P.; Tsai, Y.; Yang, C.; Chu, C.; Lin, S. Regenerative Potential of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Releasate Combined with Adipose Tissue–Derived Stem Cells in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Injury Model. Cell Transplant. 2020, 29, 96368972091943–963689720919438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurger, M.; Once, G.; Yilmaz, E.; Demir, S.; Calik, I.; Say, Y.; Kavakli, A.; Key, S.; Gurbuz, M.U.; Bingollu, O. The effect of the platelet-rich plasma and ozone therapy on tendon-to-bone healing in the rabbit rotator cuff repair model. J. Orthop Surg. Res. 2021, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faot, F.; Deprez, S.; Vandamme, K.; Camargos, G.V.; Pinto, N.; Wouters, J.; van den Oord, J.; Quirynen, M.; Duyck, J. The effect of L-PRF membranes on bone healing in rabbit tibiae bone defects: Micro-CT and biomarker results. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Altmann, S.; Emanuel, A.; Toomey, M.; McIntyre, K.; Covert, J.; Dubielzig, R.R.; Leatherberry, G.; Murphy, C.J.; Kodihalli, S.; Brandt, C.R. A Quantitative Rabbit Model of Vaccinia Keratitis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 4531–4540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mannis, M.J.; Holland, E.J. Cornea, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 1505–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Avadhanam, V.S.; Liu, C.S. A brief review of Boston type-1 and osteo-odonto keratoprostheses. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 99, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, M.; Kuffova, L.; Forrester, J.V.; Lagali, N.; Fagerholm, P.; Gantxegui, N.G.; Fuchsluger, T.A. Biosynthetic Alternatives to Human Donor Tissue; Chapter 66; Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers: New Delhi, India, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, S.L.; Sidney, L.E.; Dunphy, S.E.; Rose, J.B.; Hopkinson, A. Keeping an eye on decellularized corneas: A review of methods, characterization and applications. J. Funct. Biomater. 2013, 4, 114–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uwamaliya, J.; Carrier, P.; Proulx, S.; Deschambeault, A.; Audet, C.; Auger, F.A.; Germain, L. Reconstruction of a Human Cornea by the Self-Assembly Approach of Tissue Engineering Using the Three Native Cell Types. Mol. Vis. 2010, 16, 2192–2201. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.T.; Dart, J.K.; Holland, E.J.; Kinoshita, S. Corneal transplantation. Lancet 2012, 379, 1749–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.A.; Ringuette, R.; Wallace, V.A.; Griffith, M. Autologous fibrin glue as an encapsulating scaffold for delivery of retinal progenitor cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 2, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fagerholm, P.; Lagali, N.S.; Merrett, K.; Jackson, W.B.; Munger, R.; Liu, Y.; Polarek, J.W.; Söderqvist, M.; Griffith, M. A biosynthetic alternative to human donor tissue for inducing corneal regeneration: 24-month follow-up of a phase 1 clinical study. Sci. Transl Med. 2010, 2, 46ra61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uzunalli, G.; Soran, Z.; Erkal, T.S.; Dagdas, Y.S.; Dinc, E.; Hondur, A.M.; Bilgihan, K.; Aydin, B.; Guler, M.O.; Tekinay, A.B. Bioactive self-assembled peptide nanofibers for corneal stroma regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Islam, M.M.; Ravichandran, R.; Olsen, D.; Ljunggren, M.K.; Fagerholm, P.; Lee, C.; Griffith, M.; Phopase, J. Self-assembled collagen-like-peptide implants as alternatives to human donor corneal transplantation. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 55745–55749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isidan, A.; Liu, S.; Li, P.; Lashmet, M.; Smith, L.J.; Hara, H.; Cooper, D.K.; Ekser, B. Decellularization methods for developing porcine corneal xenografts and future perspectives. Xenotransplantation 2019, 26, e12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letko, E.; Stechschulte, S.U.; Kenyon, K.R.; Sadeq, N.; Romero, T.R.; Samson, C.M.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Harper, S.L.; Primack, J.D.; Azar, D.T. Amniotic membrane inlay and overlay grafting for corneal epithelial defects and stromal ulcers. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2001, 119, 659–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goulle, F. Use of porcine small intestinal submucosa for corneal reconstruction in dogs and cats: 106 cases. J. Small Anim. Pr. 2012, 53, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, A.V.; Boveland, S.D.; Rodriguez Galarza, R.; Moore, P.A. Corneoconjunctival transposition with and without ACell® for deep corneal ulcer repair in 18 dogs. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2020, 23, 884–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashena, Z.; Holmes, C.; Nanavaty, M.A. Pericardium patch graft for severe corneal wound burn. J. Curr. Ophthalmol. 2021, 33, 342. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, J.; Yao, K.; Kim, J.C. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rabbit corneal alkali burn model: Engraftment and involvement in wound healing. Eye 2006, 20, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zemba, M.; Stamate, A.; Tataru, C.P.; Branisteanu, D.C.; Balta, F. Conjunctival flap surgery in the management of ocular surface disease (Review). Exp. Med. 2020, 20, 3412–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- SAIKA, S. TGFβ pathobiology in the eye. Lab. Investig. 2006, 86, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelghany, A.A.; Bahrawy, M.E.; Alio, J.L. Combined Platelet Rich Plasma and Amniotic membrane in the treatment of Perforated Corneal Ulcers. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 32, 2148–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choukroun, J.; Diss, A.; Simonpieri, A.; Girard, M.; Schoeffler, C.; Dohan, S.L.; Dohan, A.J.; Mouhyi, J.; Dohan, D.M. Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF): A second-generation platelet concentrate. Part IV: Clinical effects on tissue healing. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2006, 101, e56–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can, M.; Dereli Can, G.; Cagil, N.; Cakmak, H.; Sungu, N. Urgent Therapeutic Grafting of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Membrane in Descemetocele. Cornea 2016, 35, 1245–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, C.; Kaya, A.; Akgül, Y. Normal values of haematological and some biochemical parameters in serum and urine of New Zealand White rabbits. World Rabbit Sci. 2012, 20, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrova, Y.; Petrov, V.; Georgieva, T.M.; Ceciliani, F. Blood fibrinogen concentrations in New Zealand white rabbits during the first year of life. Bulg. J. Vet. Med. 2018, 21, 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodde, J.P.; Record, R.D.; Liang, H.A.; Badylak, S.F. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Porcine-Derived Extracellular Matrix. Endothelium 2001, 8, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voytik-Harbin, S.L.; Brightman, A.O.; Kraine, M.R.; Waisner, B.; Badylak, S.F. Identification of extractable growth factors from small intestinal submucosa. J. Cell Biochem. 1997, 67, 478–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.-Y.; Kim, S.; Park, K.-M. Initial Healing Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Gel and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Deep Corneal Wound in Rabbits. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080405
Choi S-Y, Kim S, Park K-M. Initial Healing Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Gel and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Deep Corneal Wound in Rabbits. Bioengineering. 2022; 9(8):405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080405
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Seo-Young, Soochong Kim, and Kyung-Mee Park. 2022. "Initial Healing Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Gel and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Deep Corneal Wound in Rabbits" Bioengineering 9, no. 8: 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080405
APA StyleChoi, S.-Y., Kim, S., & Park, K.-M. (2022). Initial Healing Effects of Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Gel and Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF) in the Deep Corneal Wound in Rabbits. Bioengineering, 9(8), 405. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering9080405





