Feature Extraction of Shoulder Joint’s Voluntary Flexion-Extension Movement Based on Electroencephalography Signals for Power Assistance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. Feature Extraction of the EEG Signals Related to the Motion of the Shoulder Joint
2.2. Averaging Method
3. Measurement
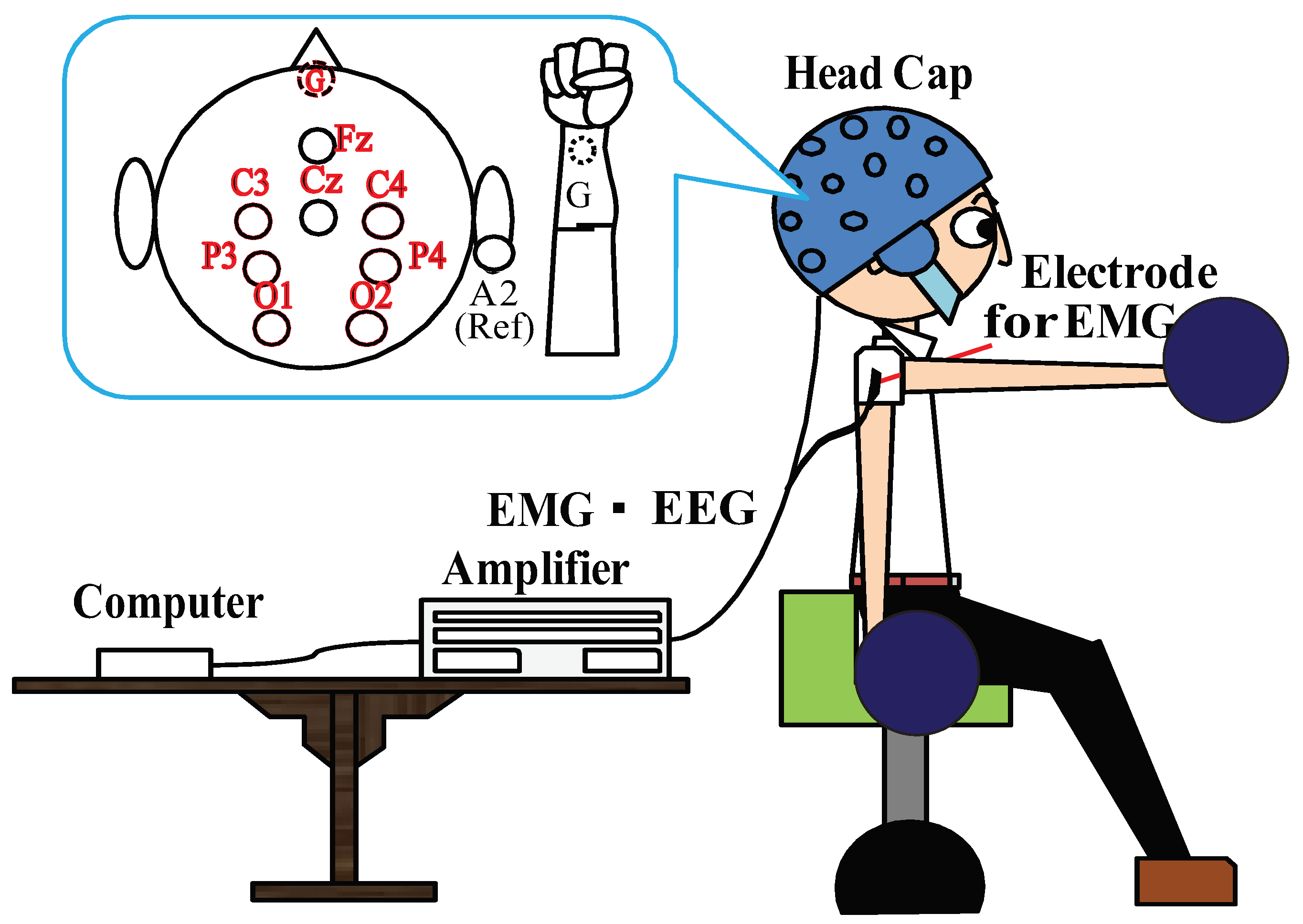
3.1. Experimental Setup
3.2. Experimental Task
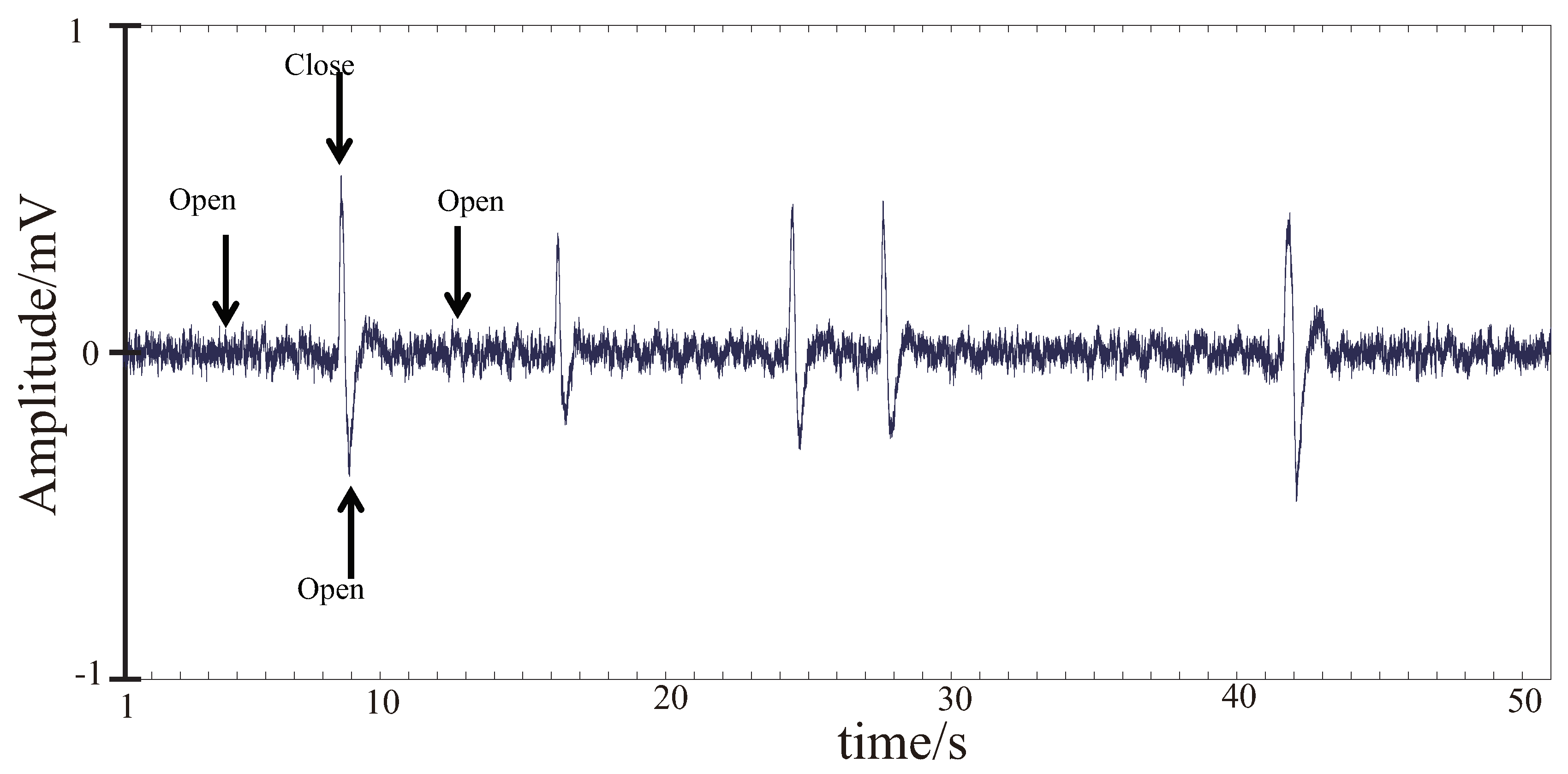
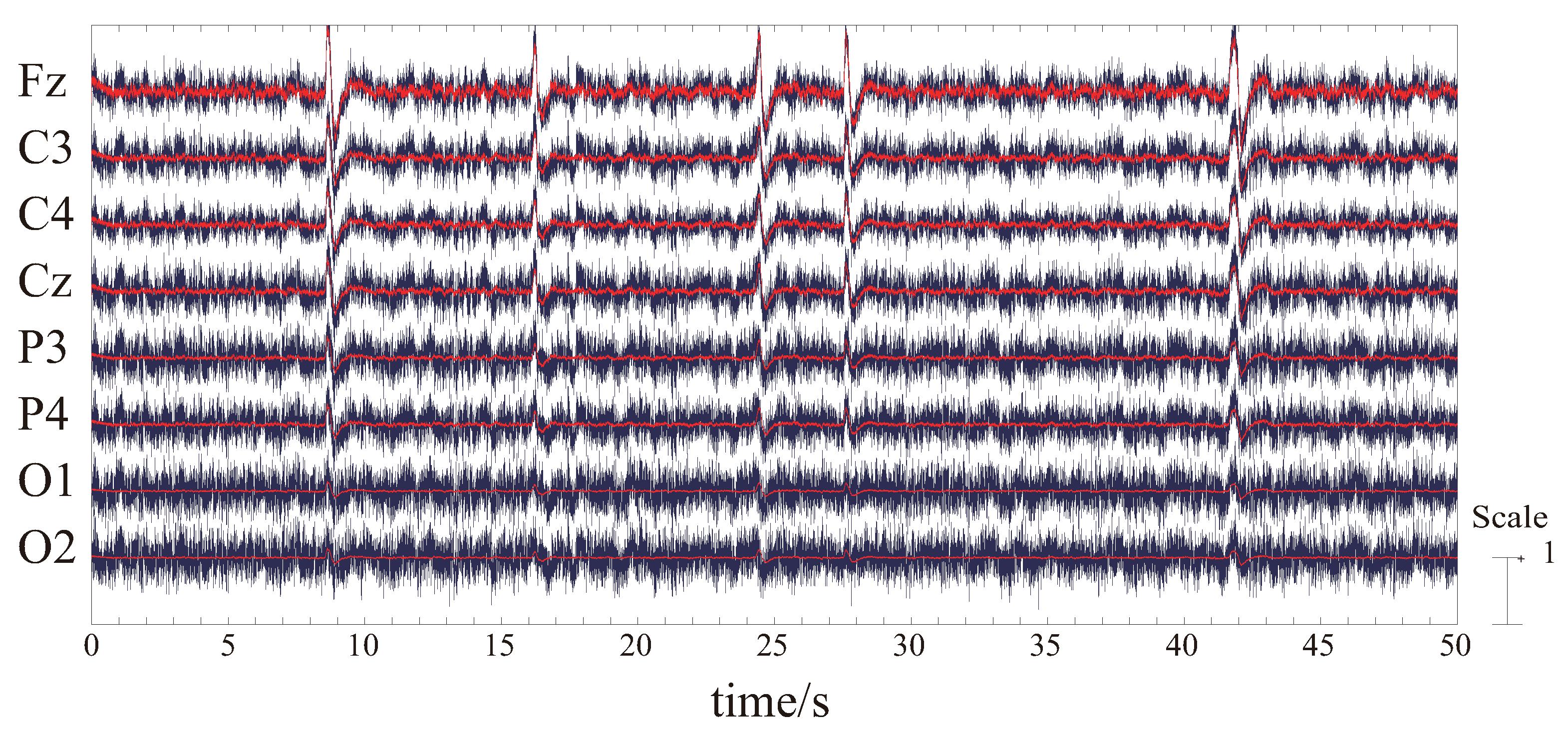
3.3. EEG and EMG Signal Processing
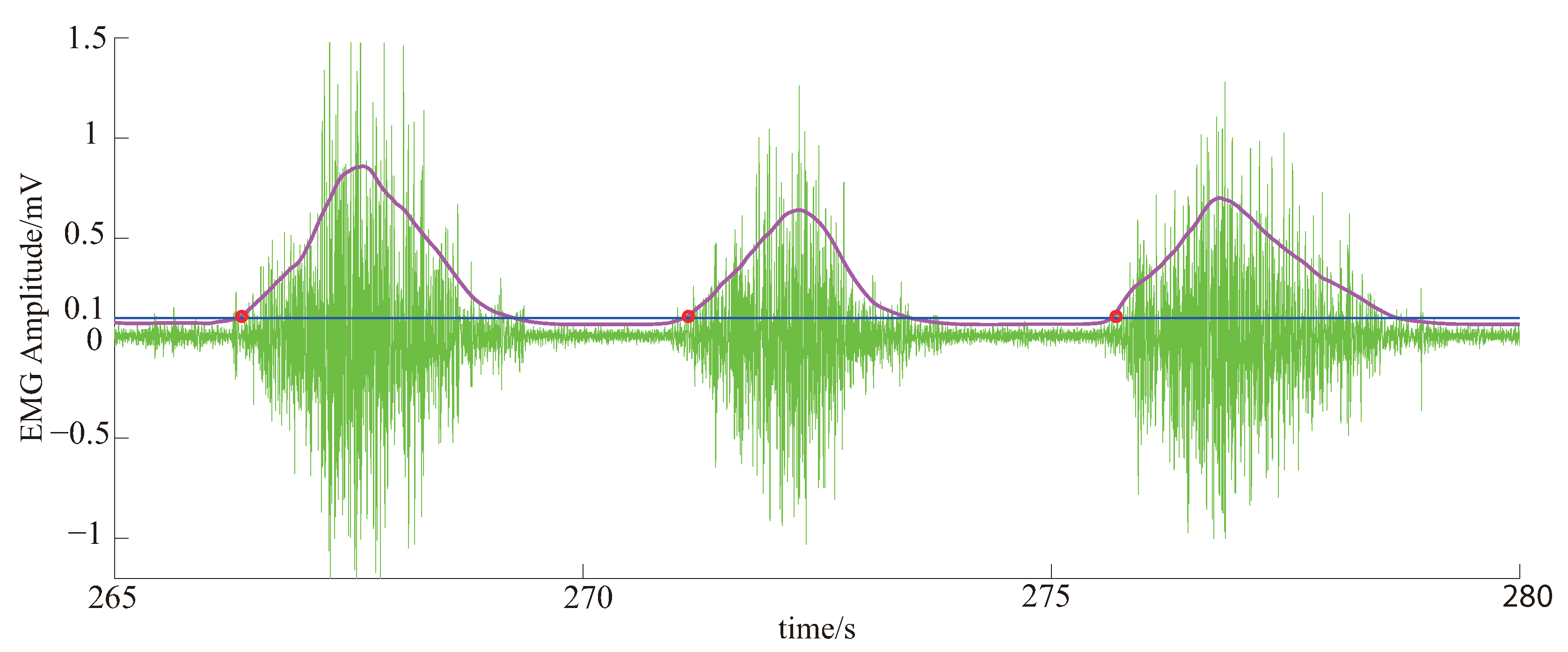
3.3.1. EMG Signal Processing
3.3.2. EEG Signal Processing
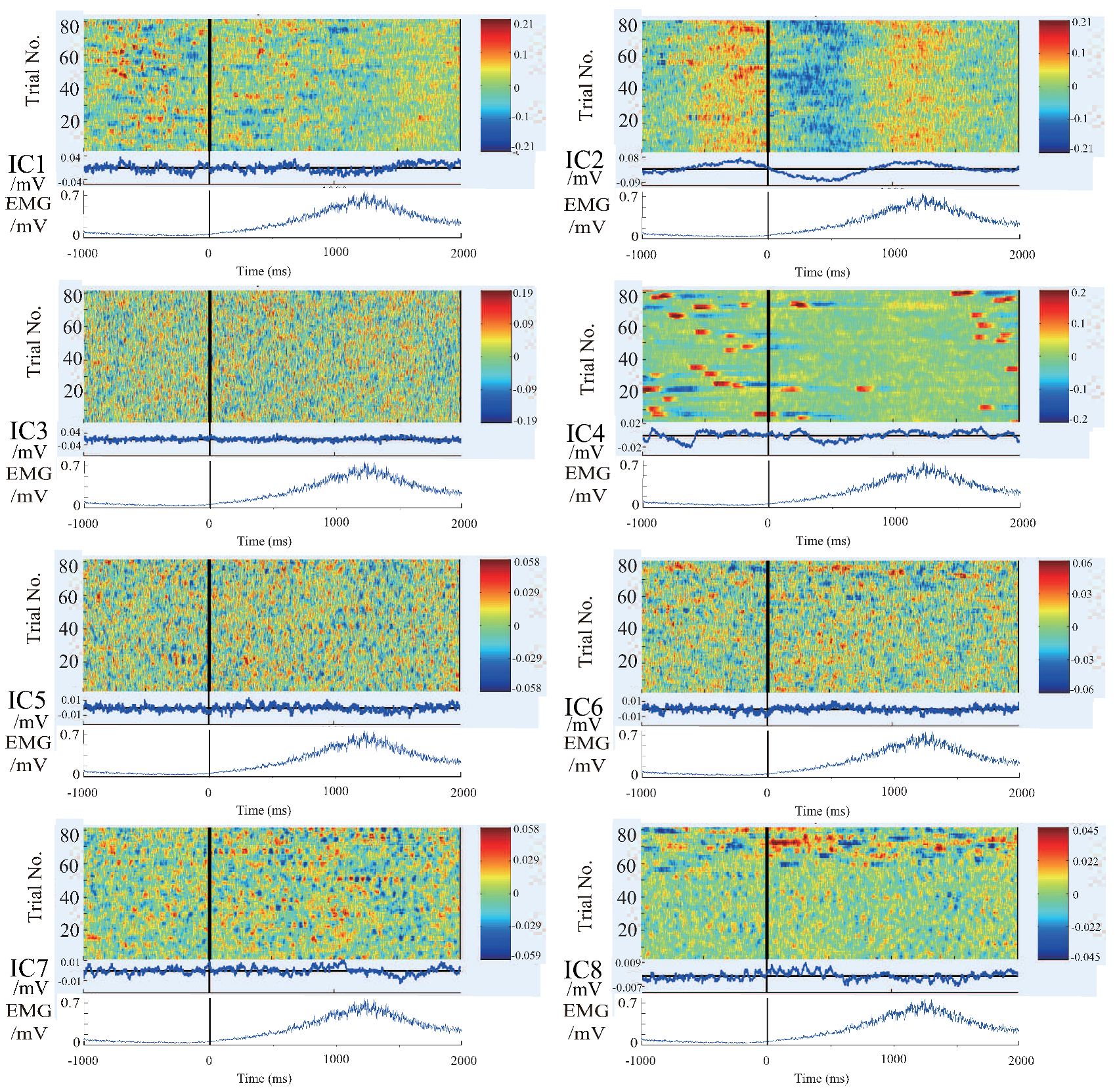
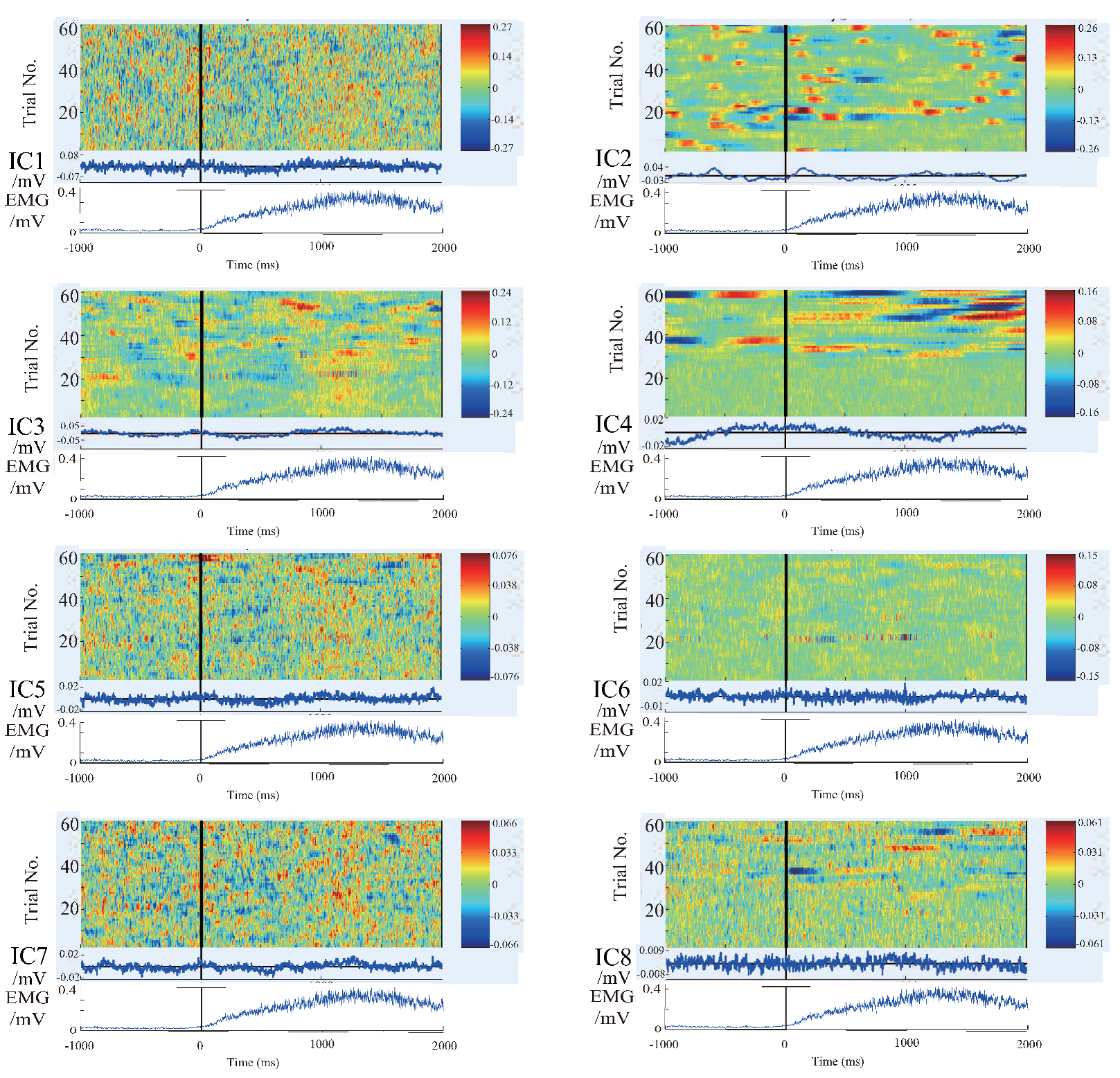
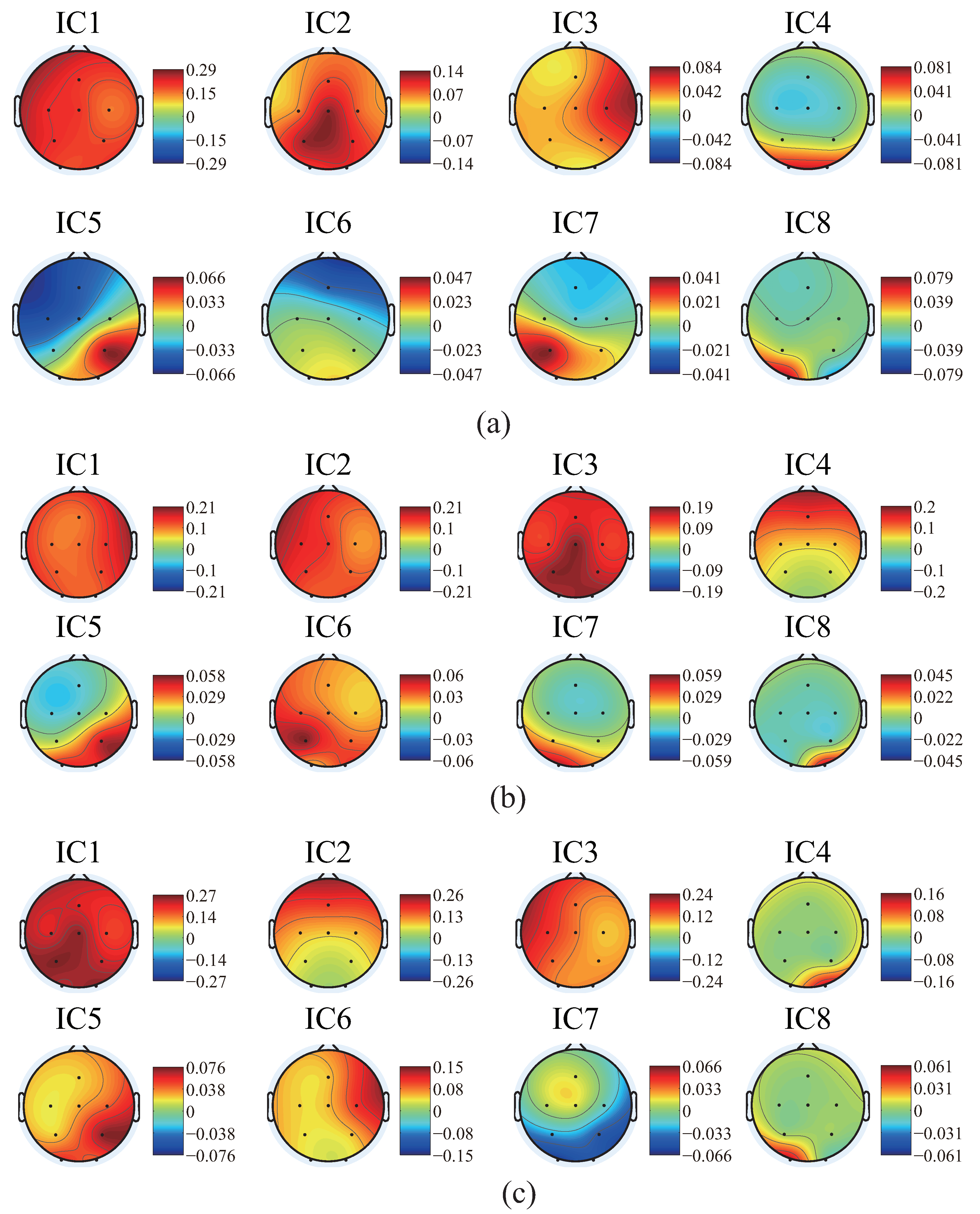
4. Results
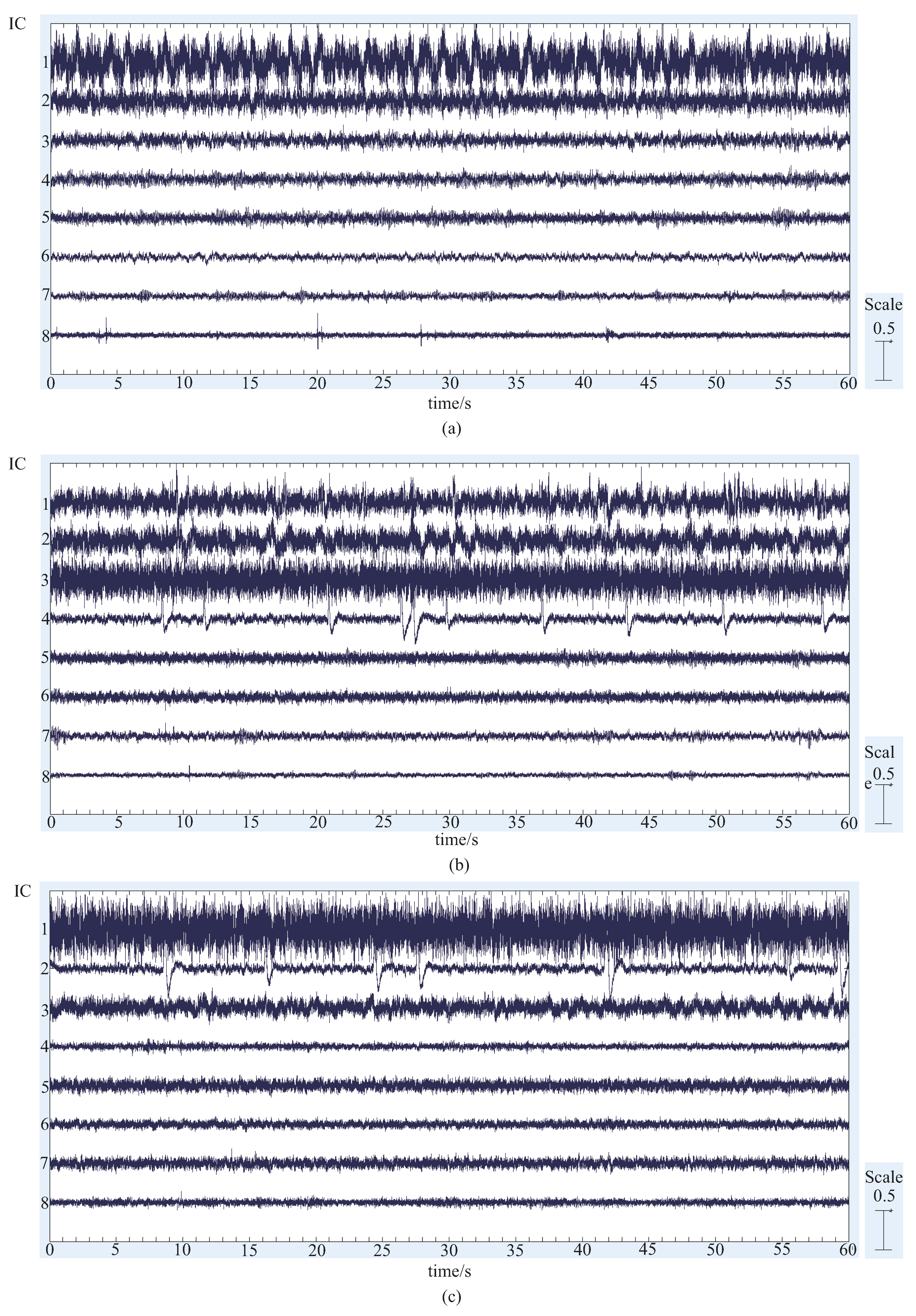
4.1. Results and Discussion of ICA and Components Presumption
- The similar components are considered as the most likely motion-related component, in other words, a characteristic component of the EEG signals during the motion performing.
- Intermittent pulse components, which are considered as the noise introduced by eye-blinking or eye movement.
- The components with small amplitudes and no obvious changes, which are considered as the background EEG signals.
- And other tiny noise components.
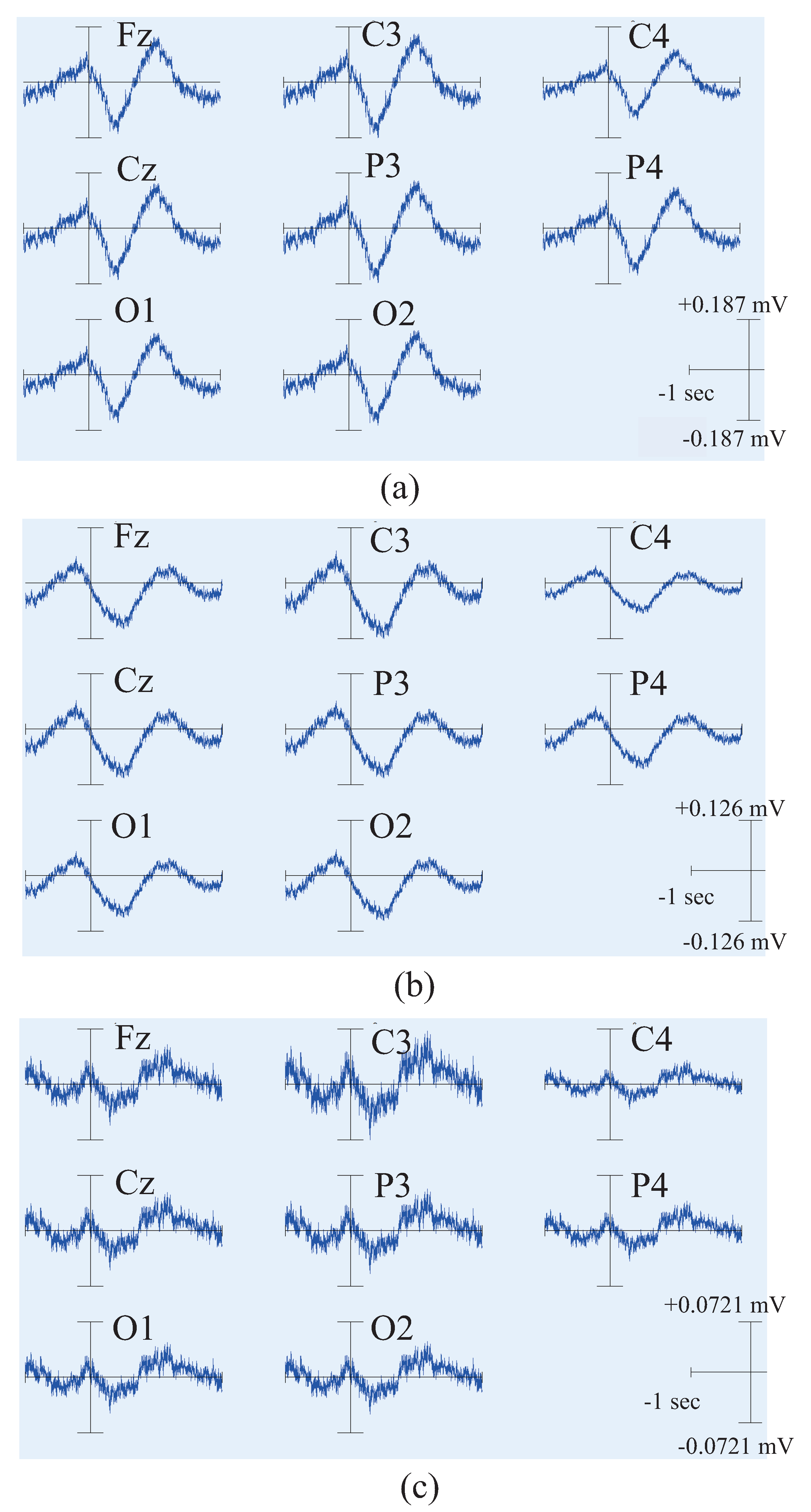
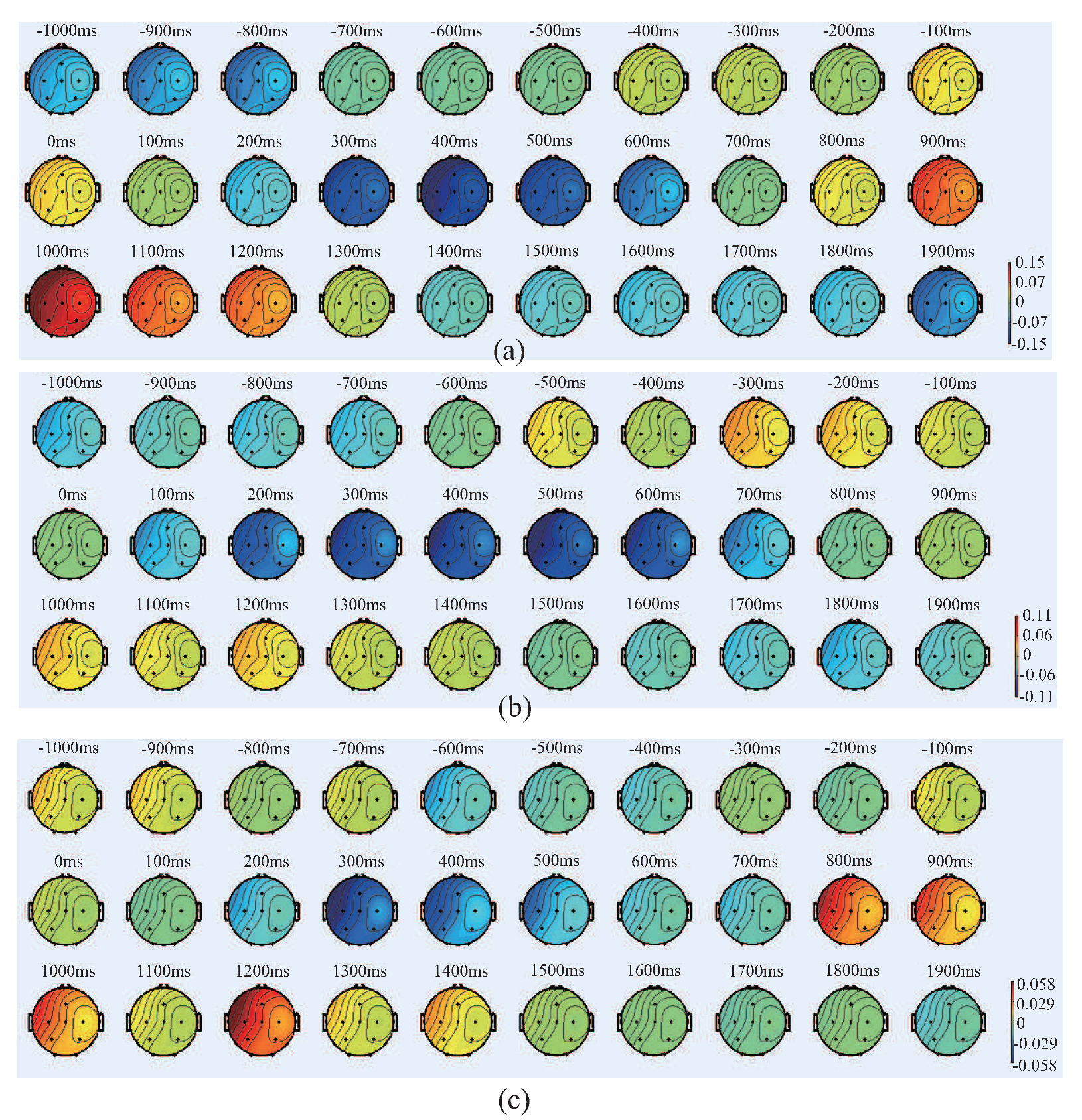
4.2. Results and Discussion of Feature’S Average
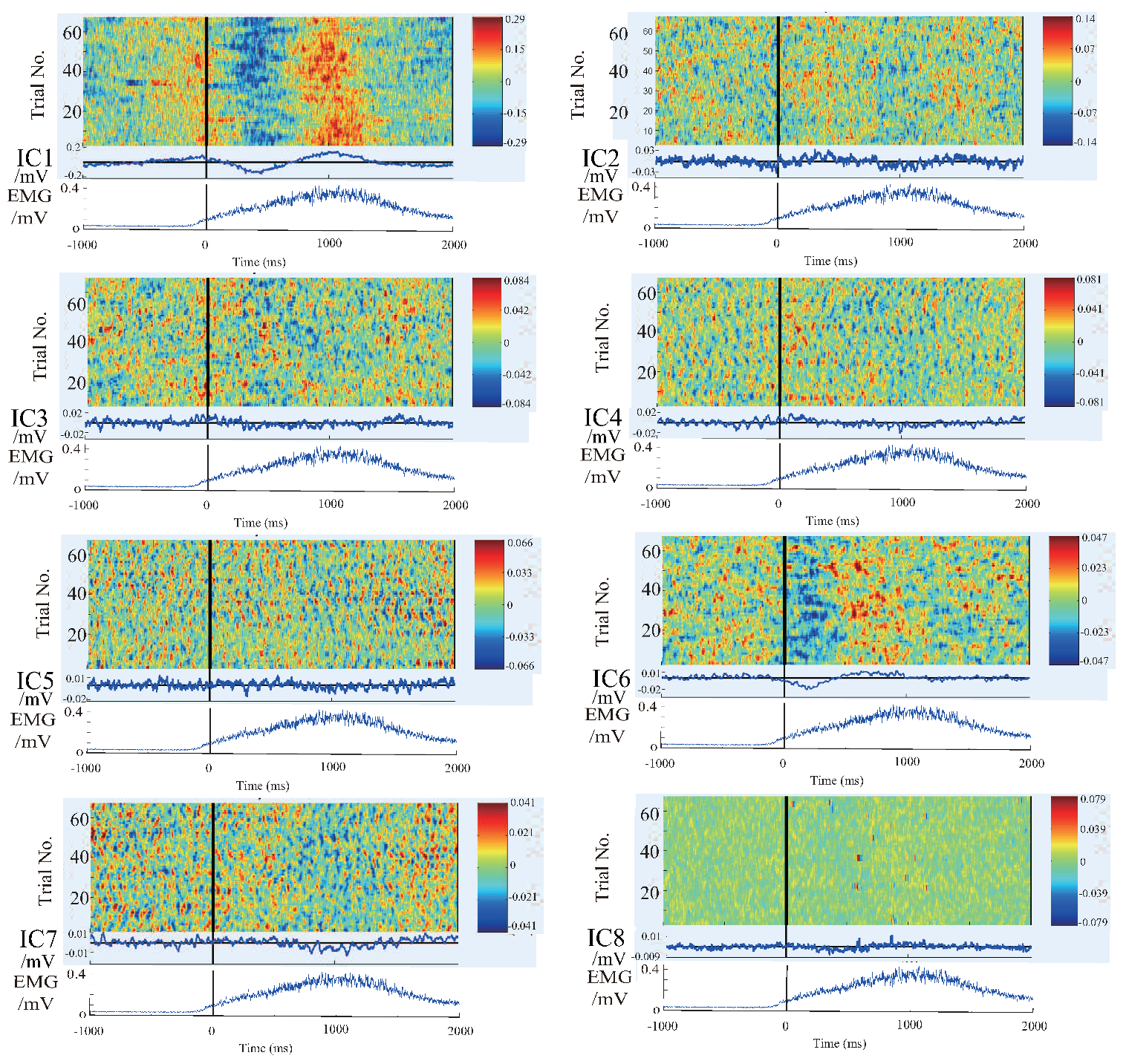
4.3. Results and Discussion of the Relationship Between EEG Signal and EMG Signal
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gopura, R.A.R.C.; Kiguchi, K.; Li, Y. SUEFUL-7: A 7DOF upper-limb exoskeleton robot with muscle-model- oriented EMG-based control. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 10–15 October 2009; pp. 1126–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Mito, G.; Kawamoto, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Sankai, Y. Intention-Based Walking Support for Paraplegia Patient with Robot Suit HAL. Climbing Walk. Robots 2010, 383–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Rosen, J.; Li, X. PID admittance control for an upper limb exoskeleton. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 29 June–1 July 2011; pp. 1124–1129. [Google Scholar]
- Lenzi, T.; de Rossi, S.M.M.; Vitiello, N.; Carrozza, M.C. Proportional EMG control for upper-limb powered exoskeletons. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 628–631. [Google Scholar]
- Rocon, E.; Belda-Lois, J.M.; Ruiz, A.F.; Manto, M.; Moreno, J.C.; Pons, J.L. Design and validation of a rehabilitation robotic exoskeleton for tremor assessment and suppression. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2007, 15, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, T.; Murakami, T. Power-Assist Control of Pushing Task by Repulsive Compliance Control in Electric Wheelchair. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 59, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Li, Z.; Su, C.Y.; Xue, A. Development and Learning Control of a Human Limb With a Rehabilitation Exoskeleton. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 3776–3785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. An EMG-based control for an upper-limb power-assist exoskeleton robot. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybern.) 2012, 42, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, T.M.; Heetderks, W.J.; Trejo, L.J.; Rymer, W.Z.; Weinrich, M.; Moore, M.M.; Kübler, A.; Dobkin, B.H.; Birbaumer, N.; Donchin, E.; et al. Brain-computer interface technology: A Review of the Second International Meeting. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2003, 11, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kübler, A.; Kotchoubey, B.; Kaiser, J.; Wolpaw, J.R.; Birbaumer, N. Brain-computer communication: Unlocking the locked in. Psychol. Bull. 2001, 127, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schomer, D.L.; da Silva, F.L. EEG-Based Brain-Computer Interfaces. In Niedermeyer’s Electroencephalography: Basic Principles, Clinical Applications, and Related Fields, 6th ed.; Series 57; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2010; Chapter 9; Volume 1, pp. 1227–1236. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura, N.; DaSalla, C.S.; Hanakawa, T.; Sato, M.; Koike, Y. Reconstruction of Muscle activities from EEG cortical currents estimated. IEICE Tech. Rep. 2011, 111, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Paek, A.Y.; Brown, J.D.; Gillespie, R.B.; O’Malley, M.K.; Shewokis, P.A.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Reconstructing surface EMG from scalp EEGs during myoelectric control of a closed looped prosthetic device. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 5602–5605. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, C.; Okada, Y.; Yoshioka, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Yu, H.; Yan, Y.; Duan, F. Power Augmentation of Upper Extremity by Using Agonist Electromyography Signals Only for Extended Admittance Control. IEEJ J. Ind. Appl. 2013, 3, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizuka, T.; Masuda, T.; Kiryu, T.; Sadoyama, T. Practical Usage of Surface Electromyogram (Biomechanism Library), 1st ed.; Tokyo Denki University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2006. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- de Munck, J.C. A linear discretization of the volume conductor boundary integral equation using analytically integrated elements. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1992, 39, 986–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, J.; Aoki, N. Equivalent dipole sources localization using cortical dipole layer imaging and independent component analysis. Int. J. Bioelectromagn. 2008, 10, 100–110. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, A.J.; Sejnowski, T.J. An information-maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Comput. 1995, 7, 1129–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehara, Y. User’s Digital Signal Processing; Tokyo Denki University Press: Tokyo, Japan, 2006; pp. 28–32. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar]
- Lew, E.; Chavarriaga, R.; Silvoni, S.; Millán, J.D.R. Detection of self-paced reaching movement intention from EEG signals. Front. Neuroeng. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, S.W.; Guan, C.; Ang, K.K.; Phua, K.S.; Wang, C.; Zhao, L.; Teo, W.P.; Chew, E. Motor imagery BCI for upper limb stroke rehabilitation: An evaluation of the EEG recordings using coherence analysis. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-H.; Chavarriaga, R.; Millán, J.D.R.; Lee, S.-W. Three-dimensional upper limb movement decoding from EEG signals. In Proceedings of the 2013 International Winter Workshop on Brain-Computer Interface (BCI), Gangwo, Korea, 18–20 February 2013; pp. 109–111. [Google Scholar]
- Caracillo, R.C.; Castro, M.C.F. Classification of executed upper limb movements by means of EEG. In Proceedings of the 2013 ISSNIP Biosignals and Biorobotics Conference: Biosignals and Robotics for Better and Safer Living (BRC), Rio de Janerio, Brazil,, 18–20 February 2013; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Beuchat, N.J.; Chavarriaga, R.; Degallier, S.; Millán, J.D.R. Offline decoding of upper limb muscle synergies from EEG slow cortical potentials. Conf. Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 3594–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Number of Averaging | Improvement of SNR | |
|---|---|---|
| M (times) | (times) | (dB) |
| 10 | 3.2 | 10.0 |
| 50 | 7.1 | 17.0 |
| 60 | 7.7 | 17.8 |
| 70 | 8.4 | 18.4 |
| 80 | 8.9 | 19.0 |
| 90 | 9.5 | 19.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liang, H.; Zhu, C.; Iwata, Y.; Maedono, S.; Mochita, M.; Liu, C.; Ueda, N.; Li, P.; Yu, H.; Yan, Y.; et al. Feature Extraction of Shoulder Joint’s Voluntary Flexion-Extension Movement Based on Electroencephalography Signals for Power Assistance. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6010002
Liang H, Zhu C, Iwata Y, Maedono S, Mochita M, Liu C, Ueda N, Li P, Yu H, Yan Y, et al. Feature Extraction of Shoulder Joint’s Voluntary Flexion-Extension Movement Based on Electroencephalography Signals for Power Assistance. Bioengineering. 2019; 6(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiang, Hongbo, Chi Zhu, Yu Iwata, Shota Maedono, Mika Mochita, Chang Liu, Naoya Ueda, Peirang Li, Haoyong Yu, Yuling Yan, and et al. 2019. "Feature Extraction of Shoulder Joint’s Voluntary Flexion-Extension Movement Based on Electroencephalography Signals for Power Assistance" Bioengineering 6, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6010002
APA StyleLiang, H., Zhu, C., Iwata, Y., Maedono, S., Mochita, M., Liu, C., Ueda, N., Li, P., Yu, H., Yan, Y., & Duan, F. (2019). Feature Extraction of Shoulder Joint’s Voluntary Flexion-Extension Movement Based on Electroencephalography Signals for Power Assistance. Bioengineering, 6(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering6010002






