Emulating Hyperspectral and Narrow-Band Imaging for Deep-Learning-Driven Gastrointestinal Disorder Detection in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Spectrum Aided Vision Enhancer
2.3. Model Architecture
2.3.1. Inception-Net V3
2.3.2. MobileNetV2
2.3.3. MobileNetV3
2.3.4. AlexNet
3. Results
3.1. MobileNetV2
3.2. MobileNetV3
3.3. Inception-Net V3
3.4. AlexNet
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richard, M.L.; Sokol, H. The gut mycobiota: Insights into analysis, environmental interactions and role in gastrointestinal diseases. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.; Abnet, C.C.; Neale, R.E.; Vignat, J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global burden of 5 major types of gastrointestinal cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 335–349.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, C.; Bai, C.; Brown, T.D.; Hood, L.E.; Tian, Q. Human gut microbiota and gastrointestinal cancer. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 16, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, K.J.; Cormier, R.T.; Scott, P.M. Role of ion channels in gastrointestinal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Xu, G.; Li, C.; He, L.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z.; Jing, B.; Deng, Y.; Jin, Y.; Li, Y. Real-time artificial intelligence for detection of upper gastrointestinal cancer by endoscopy: A multicentre, case-control, diagnostic study. Lancet Oncol. 2019, 20, 1645–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Necula, L.; Matei, L.; Dragu, D.; Neagu, A.I.; Mambet, C.; Nedeianu, S.; Bleotu, C.; Diaconu, C.C.; Chivu-Economescu, M. Recent advances in gastric cancer early diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Shi, L.; He, X.; Luo, Y. Gastrointestinal cancers in China, the USA, and Europe. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2021, 9, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, D.; Madni, T.M.; Janjua, U.I.; Anwar, F.; Kakakhail, A. An automatic gastric polyp detection technique using deep learning. Int. J. Imaging Syst. Technol. 2023, 33, 866–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Ramai, D.; Tringali, A. Novel classification of gastric polyps: The good, the bad and the ugly. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 3640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanth, P.; Inadomi, J.M. Screening and prevention of colorectal cancer. Bmj 2021, 374, n1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashida, H. Endoscopic diagnosis of sessile serrated polyp: A systematic review. Dig. Endosc. 2019, 31, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, H.; Naeem, A.; Sadeghi-Niaraki, A.; Naqvi, R.A.; Lee, S.-W. Multi-classification deep learning models for detection of ulcerative colitis, polyps, and dyed-lifted polyps using wireless capsule endoscopy images. Complex Intell. Syst. 2024, 10, 2477–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, Y. A comprehensive analysis of deep learning-based approaches for the prediction of gastrointestinal diseases using multi-class endoscopy images. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 2023, 30, 4499–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmoud Al-Adhaileh, M.; Mohammed Senan, E.; Alsaade, F.W.; Aldhyani, T.H.H.; Alsharif, N.; Abdullah Alqarni, A.; Uddin, M.I.; Alzahrani, M.Y.; Alzain, E.D.; Jadhav, M.E. Deep learning algorithms for detection and classification of gastrointestinal diseases. Complexity 2021, 2021, 6170416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogan, T.; Cogan, M.; Tamil, L. MAPGI: Accurate identification of anatomical landmarks and diseased tissue in gastrointestinal tract using deep learning. Comput. Biol. Med. 2019, 111, 103351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muir, A.; Falk, G.W. Eosinophilic esophagitis: A review. JAMA 2021, 326, 1310–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biedermann, L.; Straumann, A. Mechanisms and clinical management of eosinophilic oesophagitis: An overview. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, Y.; Al-Kaabi, A.; Shaheen, N.J.; Chak, A.; Blum, A.; Souza, R.F.; Di Pietro, M.; Iyer, P.G.; Pech, O.; Fitzgerald, R.C. Barrett oesophagus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.F.; Spechler, S.J. Mechanisms and pathophysiology of Barrett oesophagus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 19, 605–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebigbo, A.; Mendel, R.; Probst, A.; Manzeneder, J.; de Souza, L.A., Jr.; Papa, J.P.; Palm, C.; Messmann, H. Computer-aided diagnosis using deep learning in the evaluation of early oesophageal adenocarcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 1143–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quante, M.; Wang, T.C.; Bass, A.J. Adenocarcinoma of the oesophagus: Is it gastric cancer? Gut 2023, 72, 1027–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gros, B.; Kaplan, G.G. Ulcerative colitis in adults: A review. JAMA 2023, 330, 951–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neurath, M.F.; Leppkes, M. Resolution of ulcerative colitis. In Proceedings of the Seminars in Immunopathology, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–23 October 2019; pp. 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Wallner, B.; Björ, O.; Andreasson, A.; Vieth, M.; Schmidt, P.T.; Hellström, P.M.; Forsberg, A.; Talley, N.J.; Agreus, L. Z-line alterations and gastroesophageal reflux: An endoscopic population-based prospective cohort study. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 54, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fati, S.M.; Senan, E.M.; Azar, A.T. Hybrid and deep learning approach for early diagnosis of lower gastrointestinal diseases. Sensors 2022, 22, 4079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Q.; Deng, R.; Pan, Y.; Liu, R.; Chen, Y.; Gong, G.; Zou, J.; Yang, H.; Han, D. Robotic wireless capsule endoscopy: Recent advances and upcoming technologies. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soffer, S.; Klang, E.; Shimon, O.; Nachmias, N.; Eliakim, R.; Ben-Horin, S.; Kopylov, U.; Barash, Y. Deep learning for wireless capsule endoscopy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 831–839.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehedi, I.M.; Rao, K.P.; Alotaibi, F.M.; Alkanfery, H.M. Intelligent wireless capsule endoscopy for the diagnosis of gastrointestinal diseases. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Chun, H.J. Capsule endoscopy: Pitfalls and approaches to overcome. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagao, S.; Tsuji, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Minatsuki, C.; Niimi, K.; Yamashita, H.; Yamamichi, N.; Seto, Y.; Tada, T. Highly accurate artificial intelligence systems to predict the invasion depth of gastric cancer: Efficacy of conventional white-light imaging, nonmagnifying narrow-band imaging, and indigo-carmine dye contrast imaging. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2020, 92, 866–873.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Shen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sang, J.; Ding, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Jin, C. Convolutional neural network for the diagnosis of early gastric cancer based on magnifying narrow band imaging. Gastric Cancer 2020, 23, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummins, G.; Cox, B.F.; Ciuti, G.; Anbarasan, T.; Desmulliez, M.P.; Cochran, S.; Steele, R.; Plevris, J.N.; Koulaouzidis, A. Gastrointestinal diagnosis using non-white light imaging capsule endoscopy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 429–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurita, T. Principal component analysis (PCA). In Computer Vision: A Reference Guide; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 1013–1016. [Google Scholar]
- Greenacre, M.; Groenen, P.J.; Hastie, T.; d’Enza, A.I.; Markos, A.; Tuzhilina, E. Principal component analysis. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-P.; Karmakar, R.; Mukundan, A.; Tsao, Y.-M.; Sung, T.-C.; Lu, C.-L.; Wang, H.-C. Spectrum aided vision enhancer enhances mucosal visualization by hyperspectral imaging in capsule endoscopy. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 22243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, D.; Smedsrud, P.H.; Riegler, M.A.; Halvorsen, P.; De Lange, T.; Johansen, D.; Johansen, H.D. Kvasir-seg: A segmented polyp dataset. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, Thessaloniki, Greece, 8–11 January 2019; pp. 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Smedsrud, P.H.; Thambawita, V.; Hicks, S.A.; Gjestang, H.; Nedrejord, O.O.; Næss, E.; Borgli, H.; Jha, D.; Berstad, T.J.D.; Eskeland, S.L. Kvasir-Capsule, a video capsule endoscopy dataset. Sci. Data 2021, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamath, V.; Kurian, C.P.; Padiyar, U.S. Development of bayesian neural network model to predict the correlated color temperature using digital camera and Macbeth ColorChecker chart. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 55499–55507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G. Mobilenets: Efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.04861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, F.; Hassan, M.M.; Hasan, M.; Zaman, S.; Bairagi, A.K.; El-Shafai, W.; Fouad, H.; Chun, Y.C. GastroNet: Gastrointestinal polyp and abnormal feature detection and classification with deep learning approach. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 97605–97624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, W.; Chen, L.C.; Tan, M.; Chu, G.; Vasudevan, V.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Alom, M.Z.; Taha, T.M.; Yakopcic, C.; Westberg, S.; Sidike, P.; Nasrin, M.S.; Van Esesn, B.C.; Awwal, A.A.S.; Asari, V.K. The history began from alexnet: A comprehensive survey on deep learning approaches. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.01164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Mikami, T.; Sakuraba, H.; Fukuda, S. Anatomical classification of upper gastrointestinal organs under various image capture conditions using AlexNet. Comput. Biol. Med. 2020, 124, 103950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabi, B.S.; Selmy, A.S.; Mohamed, W.A. Improving the diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases using a modified AlexNet. In Proceedings of the 2024 34th International Conference on Computer Theory and Applications (ICCTA), Alexandria, Egypt, 14–16 December 2024; pp. 46–53. [Google Scholar]
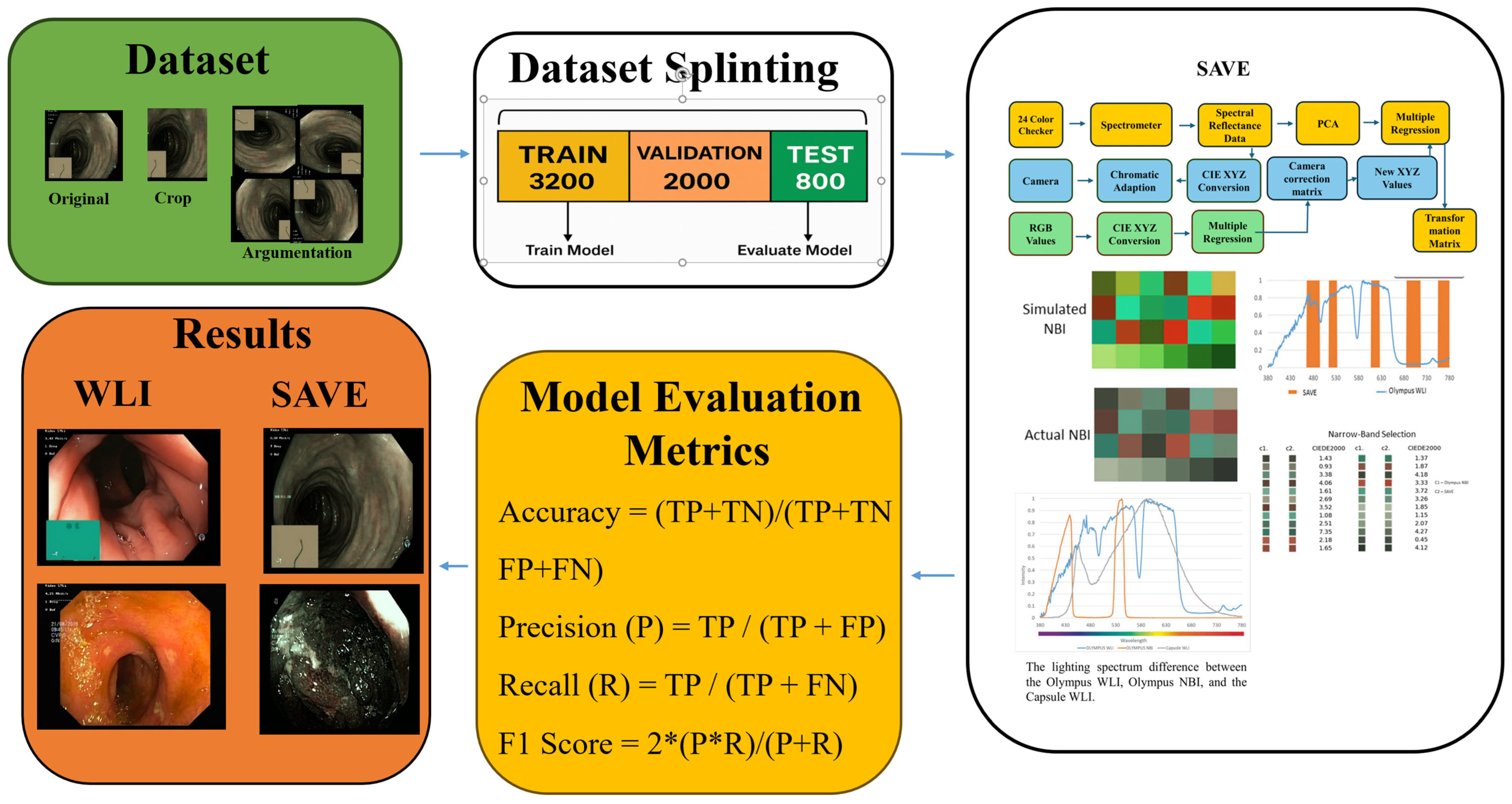
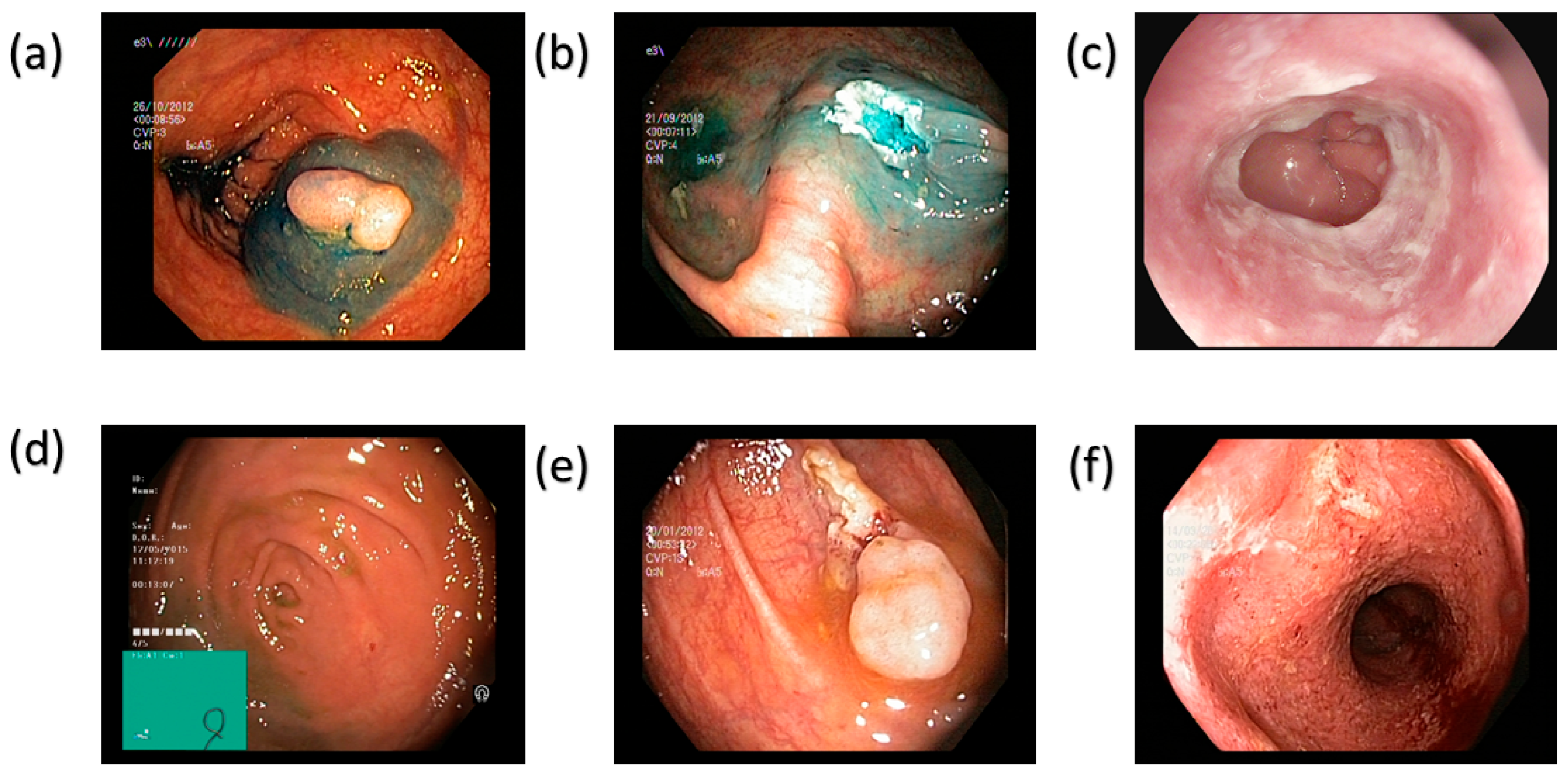
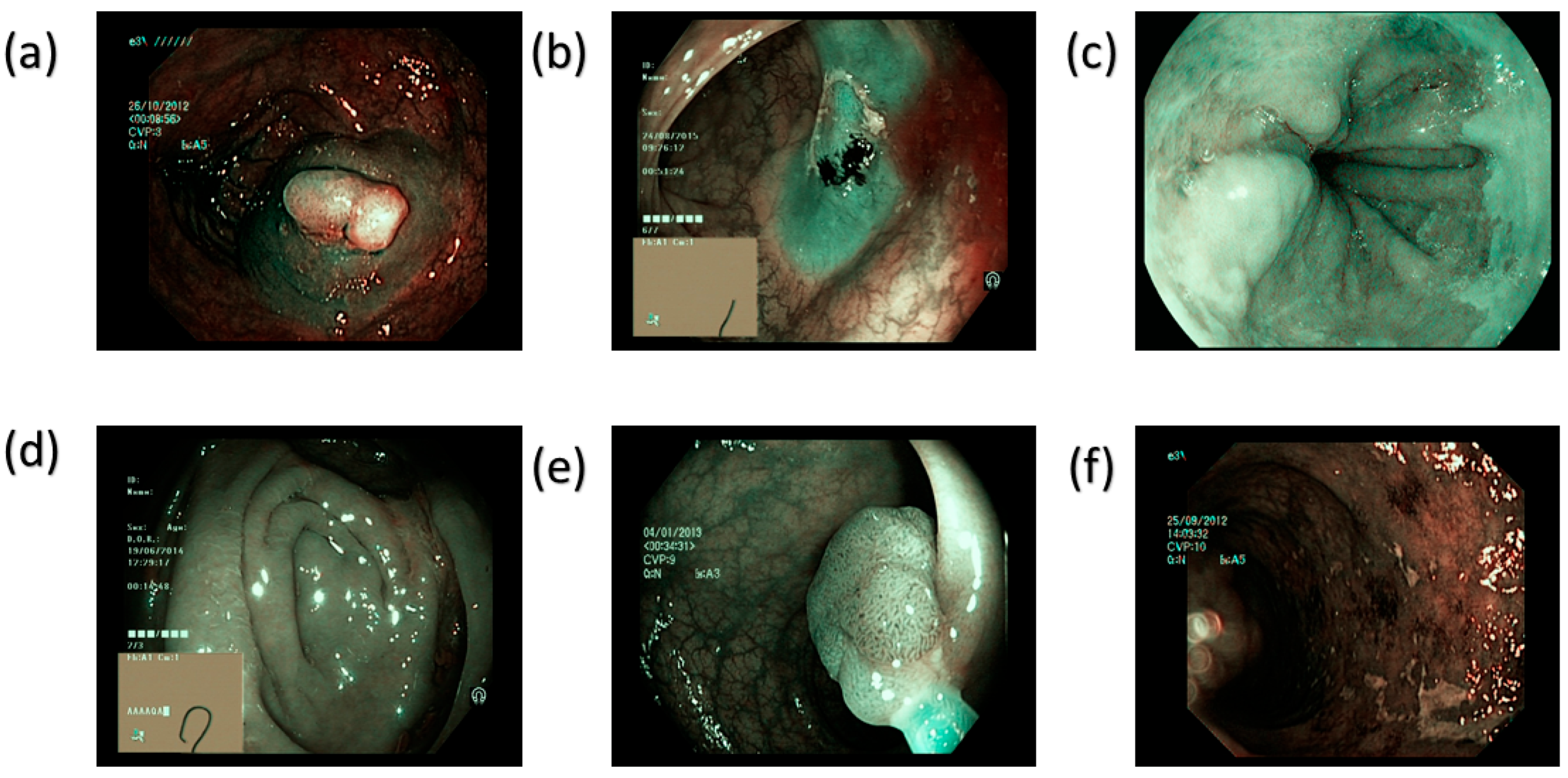
| Class Name | Train | Validation | Test | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dyed Lifted Polyps | 637 | 182 | 93 | 912 |
| Normal Z-line | 582 | 166 | 85 | 833 |
| Dyed Resection Margins | 366 | 104 | 55 | 525 |
| Normal Pylorus | 569 | 162 | 83 | 814 |
| Normal Cecum | 682 | 195 | 99 | 976 |
| Polyps | 696 | 199 | 100 | 995 |
| Ulcerative Colitis | 307 | 87 | 45 | 439 |
| Esophagitis | 696 | 199 | 101 | 996 |
| Total | 4535 | 1294 | 661 | 6490 |
| Type | Classes | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLI | Normal (Merged) | 91% | 93% | 92% | 90% |
| Polyps | 88% | 89% | 89% | ||
| Dyed-Lifted Polyps | 91% | 90% | 91% | ||
| Esophagitis | 86% | 82% | 84% | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | 88% | 93% | 90% | ||
| Dyed-Resection Margins | 94% | 87% | 91% | ||
| SAVE | Normal (Merged) | 91% | 92% | 92% | 90% |
| Polyps | 94% | 97% | 96% | ||
| Dyed-Lifted Polyps | 91% | 90% | 91% | ||
| Esophagitis | 86% | 82% | 84% | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | 88% | 93% | 90% | ||
| Dyed-Resection Margins | 94% | 87% | 91% |
| Type | Classes | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLI | Normal | 98% | 100% | 99% | 92% |
| Ulcer | 98% | 72% | 83% | ||
| Polyps | 80% | 97% | 87% | ||
| Esophagitis | 98% | 100% | 99% | ||
| SAVE | Normal | 97% | 100% | 98% | 95% |
| Ulcer | 89% | 96% | 93% | ||
| Polyps | 97% | 85% | 91% | ||
| Esophagitis | 99% | 100% | 99% |
| Type | Classes | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLI | Dyed-Lifted Polyps | 90% | 77% | 83% | 89% |
| Dyed-Resection Margins | 77% | 85% | 81% | ||
| Esophagitis | 77% | 78% | 78% | ||
| Normal (Merged) | 91% | 92% | 92% | ||
| Polyps | 81% | 87% | 84% | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | 85% | 73% | 79% | ||
| SAVE | Dyed-Lifted Polyps | 79% | 81% | 80% | 86% |
| Dyed-Resection Margins | 76% | 64% | 69% | ||
| Esophagitis | 78% | 71% | 75% | ||
| Normal (Merged) | 90% | 89% | 89% | ||
| Polyps | 84% | 84% | 84% | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | 83% | 76% | 79% |
| Type | Classes | Precision | Recall | F1-Score | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WLI | Normal (Merged) | 86% | 90% | 88% | 81% |
| Polyps | 78% | 80% | 79% | ||
| Dyed-Lifted Polyps | 79% | 69% | 73% | ||
| Esophagitis | 77% | 75% | 76% | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | 79% | 71% | 75% | ||
| Dyed-Resection Margins | 70% | 73% | 71% | ||
| SAVE | Normal (Merged) | 89% | 90% | 89% | 84% |
| Polyps | 88% | 92% | 90% | ||
| Dyed-Lifted Polyps | 91% | 91% | 91% | ||
| Esophagitis | 80% | 78% | 79% | ||
| Ulcerative Colitis | 88% | 82% | 85% | ||
| Dyed-Resection Margins | 90% | 85% | 88% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, C.-K.; Lee, K.-H.; Karmakar, R.; Mukundan, A.; Gade, P.C.; Gupta, D.; Su, C.-C.; Chen, T.-H.; Ko, C.-Y.; Wang, H.-C. Emulating Hyperspectral and Narrow-Band Imaging for Deep-Learning-Driven Gastrointestinal Disorder Detection in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090953
Chou C-K, Lee K-H, Karmakar R, Mukundan A, Gade PC, Gupta D, Su C-C, Chen T-H, Ko C-Y, Wang H-C. Emulating Hyperspectral and Narrow-Band Imaging for Deep-Learning-Driven Gastrointestinal Disorder Detection in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090953
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Chu-Kuang, Kun-Hua Lee, Riya Karmakar, Arvind Mukundan, Pratham Chandraskhar Gade, Devansh Gupta, Chang-Chao Su, Tsung-Hsien Chen, Chou-Yuan Ko, and Hsiang-Chen Wang. 2025. "Emulating Hyperspectral and Narrow-Band Imaging for Deep-Learning-Driven Gastrointestinal Disorder Detection in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090953
APA StyleChou, C.-K., Lee, K.-H., Karmakar, R., Mukundan, A., Gade, P. C., Gupta, D., Su, C.-C., Chen, T.-H., Ko, C.-Y., & Wang, H.-C. (2025). Emulating Hyperspectral and Narrow-Band Imaging for Deep-Learning-Driven Gastrointestinal Disorder Detection in Wireless Capsule Endoscopy. Bioengineering, 12(9), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090953









