Mendelian Randomization and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Important Roles for CEBPB and CX3CR1 in Osteoarthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
2.2. Weighted Gene Coexpression Network Construction Analysis (WGCNA)
2.3. Differential Expression Analysis
2.4. Identification of Candidate Genes
2.5. Identification of Potential Biomarkers, Establishment of Nomogram, and Expression Validation
2.6. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.7. MR Analysis
2.8. Network Construction
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
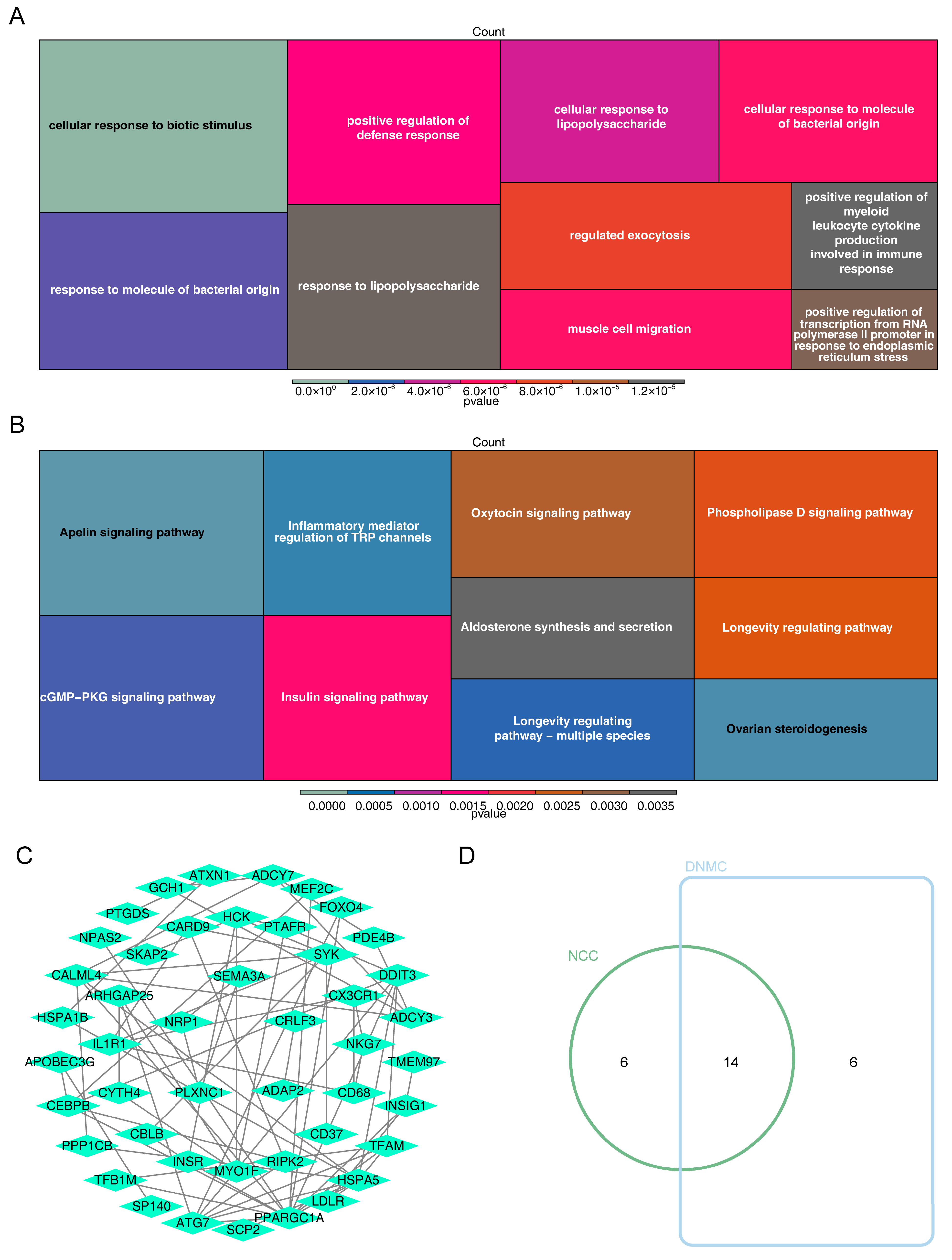
3.1. Recognition of DE-CRGs
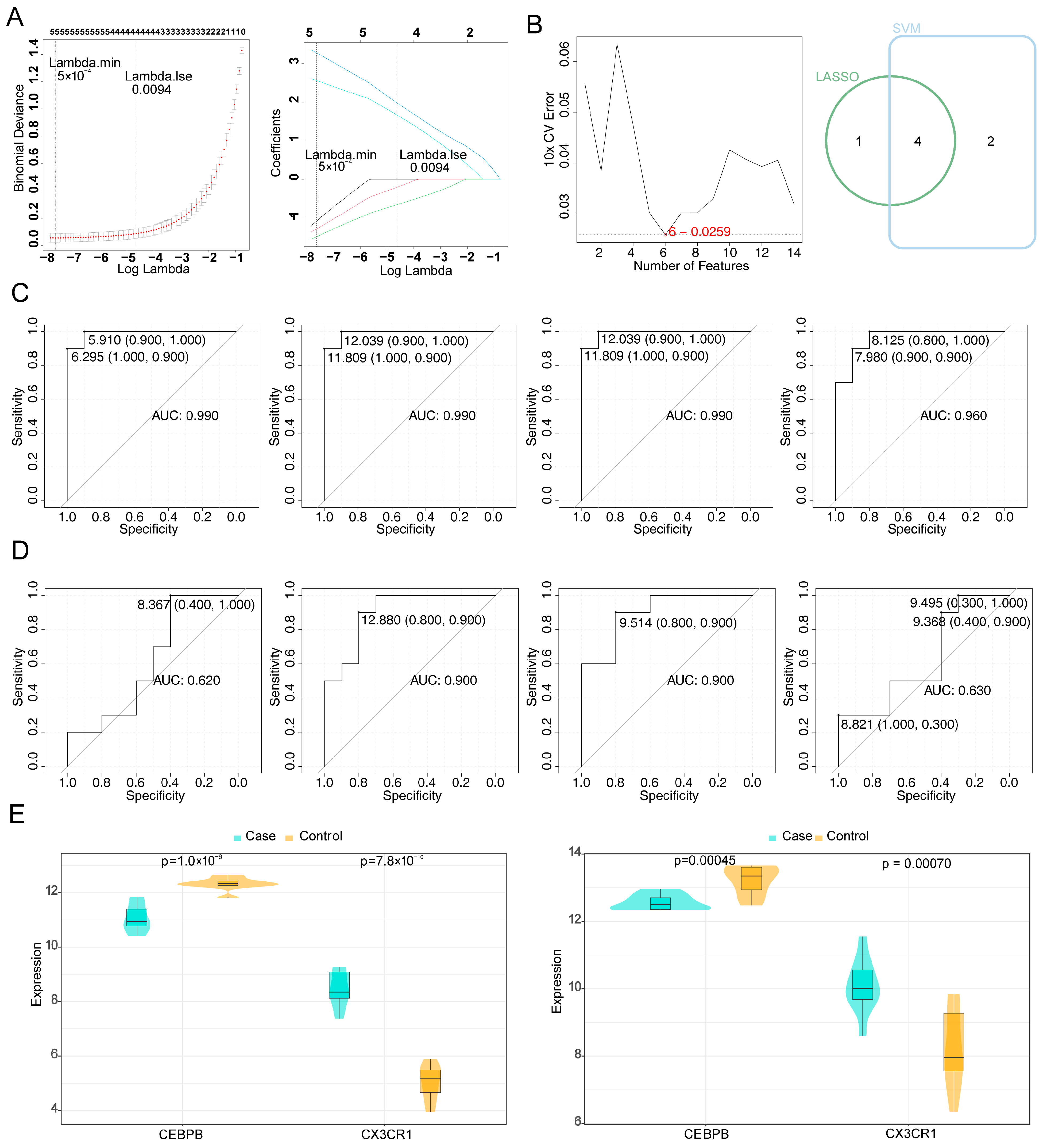
3.2. CEBPB and CX3CR1 Were Identified as Potential Biomarkers
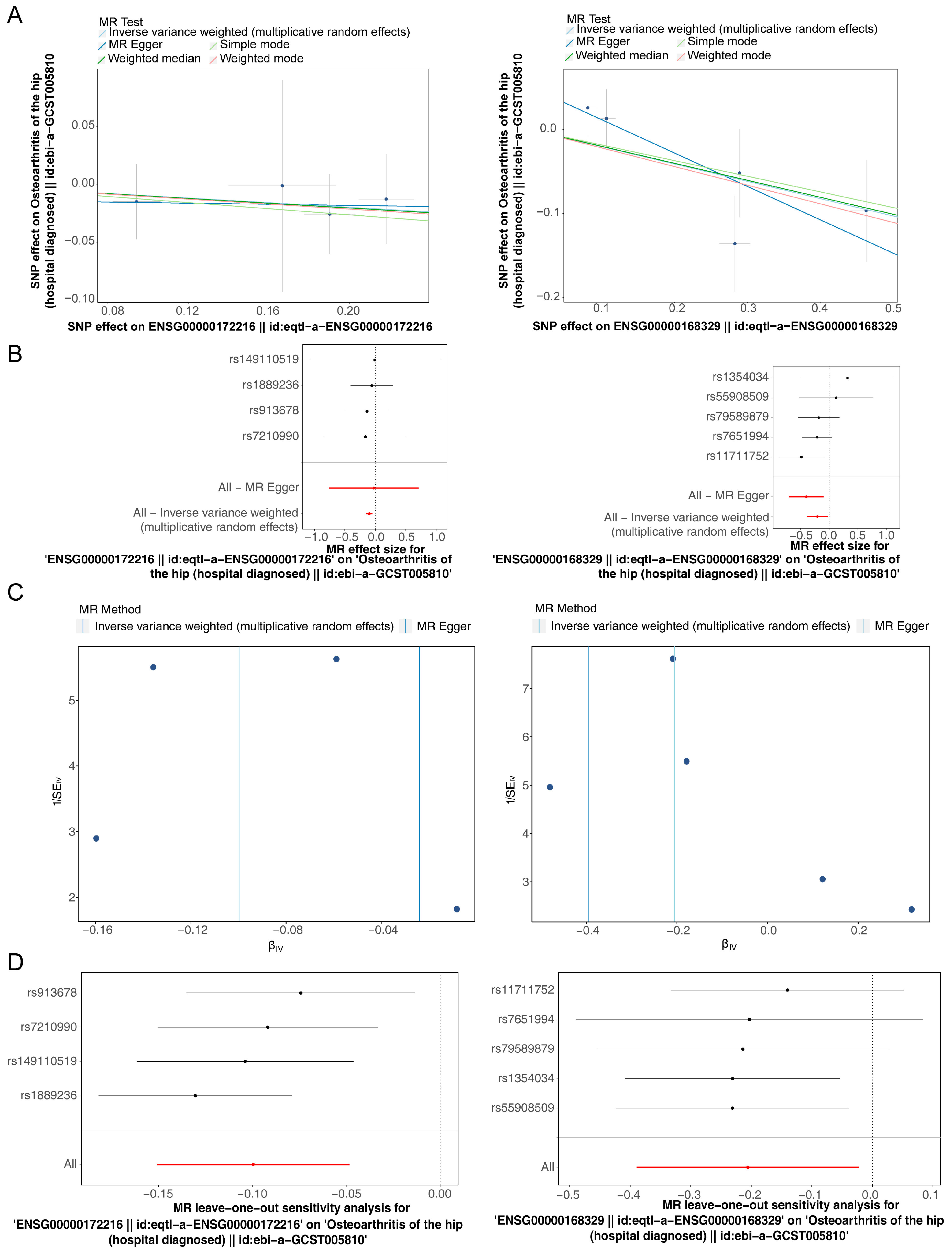
3.3. CEBPB and CX3CR1 Were Causally Associated with OA
3.4. Complex Interactions Between Potential Biomarkers
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Barr, A.J.; Cicuttini, F.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Cooper, C.; Goldring, M.B.; Goldring, S.R.; Jones, G.; Teichtahl, A.J.; Pelletier, J.P. Osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y. Osteoarthritis year in review 2021: Biology. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2022, 30, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minnig, M.C.C.; Golightly, Y.M.; Nelson, A.E. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: Literature update 2022–2023. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2024, 36, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perruccio, A.V.; Young, J.J.; Wilfong, J.M.; Denise Power, J.; Canizares, M.; Badley, E.M. Osteoarthritis year in review 2023: Epidemiology & therapy. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2024, 32, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolasinski, S.L.; Neogi, T.; Hochberg, M.C.; Oatis, C.; Guyatt, G.; Block, J.; Callahan, L.; Copenhaver, C.; Dodge, C.; Felson, D.; et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip, and Knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2020, 72, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whittaker, J.L.; Truong, L.K.; Dhiman, K.; Beck, C. Osteoarthritis year in review 2020: Rehabilitation and outcomes. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2021, 29, 190–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A.; Thudium, C.S.; Bay-Jensen, A.C.; Maleitzke, T.; Geissler, S.; Duda, G.N.; Winkler, T. Biomarkers for osteoarthritis: Current status and future prospects. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 37, 101852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, F.E. Osteoarthritis biomarkers: Year in review. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2018, 26, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luster, A.D. Chemokines--chemotactic cytokines that mediate inflammation. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 436–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Nibbs, R.J.B. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2944–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.; Jia, L.; Wang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, A.; Liu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. CC chemokines family in fibrosis and aging: From mechanisms to therapy. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakogiannis, C.; Sachse, M.; Stamatelopoulos, K.; Stellos, K. Platelet-derived chemokines in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Cytokine 2019, 122, 154157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chu, S.F.; Liu, D.D.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, L.L.; Zhou, X.; Chen, N.H. Chemokines play complex roles in cerebral ischemia. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 112, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markl, F.; Huynh, D.; Endres, S.; Kobold, S. Utilizing chemokines in cancer immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 2022, 8, 670–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakotoarivelo, V.; Variya, B.; Langlois, M.F.; Ramanathan, S. Chemokines in human obesity. Cytokine 2020, 127, 154953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, J.W.; Sokol, C.L.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines and chemokine receptors: Positioning cells for host defense and immunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 32, 659–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Vithran, D.T.A.; Kwabena, B.R.; Xiao, W.; Li, Y. CC chemokines and receptors in osteoarthritis: New insights and potential targets. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 25, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birney, E. Mendelian Randomization. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2022, 12, a041302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekula, P.; Del Greco, M.F.; Pattaro, C.; Kottgen, A. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, W.W.; Cai, Y.S.; Cao, C.; Zhang, F.R.; Zeng, Q.; Liu, D.Y.; Wang, N.; Qu, X.C.; Chen, X.D.; Deng, H.W.; et al. Mendelian randomization and transcriptome analysis identified immune-related biomarkers for osteoarthritis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1334479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Q.; Chao, P.; Zhang, L.; Xu, L.; Cui, X.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Wusiman, M.; Jiang, H.; Lu, C. Single-cell RNA and transcriptome sequencing profiles identify immune-associated key genes in the development of diabetic kidney disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1030198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, M.E.; Phipson, B.; Wu, D.; Hu, Y.; Law, C.W.; Shi, W.; Smyth, G.K. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zhengn, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. OMICS 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Xu, H.C.; Shi, Y.C.; Deng, L.; Chen, X.Y. Potential Molecular Mechanisms of Plantain in the Treatment of Gout and Hyperuricemia Based on Network Pharmacology. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 2020, 3023127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Lu, F.G.; Yin, Y.N. Applying logistic LASSO regression for the diagnosis of atypical Crohn’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 113400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Zhao, Y.M.; Canes, A.; Steinberg, D.; Lyashevska, O.; Collab, A.B.-D.C.T. Predictive analytics with gradient boosting in clinical medicine. Ann. Transl. Med. 2019, 7, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Gao, W.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y.W.; Qi, Z.C.; Li, T. Ferroptosis and Autophagy-Related Genes in the Pathogenesis of Ischemic Cardiomyopathy. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 906753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, M.C. plotROC: A Tool for Plotting ROC Curves. J. Stat. Softw. 2017, 79, 2231–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orifjon, S.; Jammatov, J.; Sousa, C.; Barros, R.; Vasconcelos, O.; Rodrigues, P. Translation and Adaptation of the Adult Developmental Coordination Disorder/Dyspraxia Checklist (ADC) into Asian Uzbekistan. Sports 2023, 11, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Burgess, S. Mendelian randomization with invalid instruments: Effect estimation and bias detection through Egger regression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 44, 512–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, S.; Scott, R.A.; Timpson, N.J.; Davey Smith, G.; Thompson, S.G.; Consortium, E.-I. Using published data in Mendelian randomization: A blueprint for efficient identification of causal risk factors. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2015, 30, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davey Smith, G.; Bowden, J. Robust inference in summary data Mendelian randomization via the zero modal pleiotropy assumption. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu-Bryan, R.; Terkeltaub, R. Emerging regulators of the inflammatory process in osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, H.; Lepus, C.M.; Wang, Q.; Wong, H.H.; Lingampalli, N.; Oliviero, F.; Punzi, L.; Giori, N.J.; Goodman, S.B.; Chu, C.R.; et al. CCL2/CCR2, but not CCL5/CCR5, mediates monocyte recruitment, inflammation and cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Gu, M.; Xu, X.; Wen, X.; Yang, G.; Li, L.; Sheng, P.; Meng, F. CCL3/CCR1 mediates CD14(+)CD16(-) circulating monocyte recruitment in knee osteoarthritis progression. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2020, 28, 613–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, S.; Obeidat, A.M.; Wokosin, D.L.; Ren, D.; Miller, R.J.; Malfait, A.M.; Miller, R.E. The role of intra-articular neuronal CCR2 receptors in knee joint pain associated with experimental osteoarthritis in mice. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdrighi, N.; Vago, J.P.; Blom, A.B.; van de Loo, F.A.J.; Blaney Davidson, E.N. Innate Immunity at the Core of Sex Differences in Osteoarthritic Pain? Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 881500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterken, B.A.; Ackermann, T.; Muller, C.; Zuidhof, H.R.; Kortman, G.; Hernandez-Segura, A.; Broekhuis, M.; Spierings, D.; Guryev, V.; Calkhoven, C.F. C/EBPbeta isoform-specific regulation of migration and invasion in triple-negative breast cancer cells. NPJ Breast Cancer 2022, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X.; Yu, S.P.; Ye, K.X.; Wang, J.Z.; Ye, K.; Wang, X.C. C/EBPbeta is a key transcription factor for APOE and preferentially mediates ApoE4 expression in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2021, 26, 6002–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper-Knock, J.; Green, C.; Altschuler, G.; Wei, W.; Bury, J.J.; Heath, P.R.; Wyles, M.; Gelsthorpe, C.; Highley, J.R.; Lorente-Pons, A.; et al. A data-driven approach links microglia to pathology and prognosis in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2017, 5, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, M.; Ji, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Deng, C.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, W.; Shen, Y.; et al. Identification of Regulatory Factors and Prognostic Markers in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Li, B.; Yin, Z.; Peng, P.; Cao, J.; Xie, W.; Liu, L.; Cao, F.; Zhang, B. Multi-omics characterization of macrophage polarization-related features in osteoarthritis based on a machine learning computational framework. Heliyon 2024, 10, e30335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J.; Dai, T.; Zhu, W.; Wang, T.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. Unveiling the ageing-related genes in diagnosing osteoarthritis with metabolic syndrome by integrated bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2025, 53, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shi, W.; Wu, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.; Yin, G.; Xie, X.; Bi, S.; et al. TMF inhibits extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the C/EBPbeta/ADAMTS5 signaling pathway in osteoarthritis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 174, 116501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wu, L.; Yin, G.; Xie, X.; Kong, W.; Zhou, J.; Liu, S. C/EBPβ: The structure, regulation, and its roles in inflammation-related diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, E.; Pistoia, V.; Corcione, A. Role of fractalkine/CX3CL1 and its receptor in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and malignant diseases with emphasis on B cell malignancies. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 480941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.W.; Ye, Y.L.; Wang, G.W.; Ye, Y.G. Fractalkine (CX3CL1): A biomarker reflecting symptomatic severity in patients with knee osteoarthritis. J. Investig. Med. 2015, 63, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culemann, S.; Gruneboom, A.; Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; Weidner, D.; Lammle, K.F.; Rothe, T.; Quintana, J.A.; Kirchner, P.; Krljanac, B.; Eberhardt, M.; et al. Locally renewing resident synovial macrophages provide a protective barrier for the joint. Nature 2019, 572, 670–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aharon-Yariv, A.; Wang, Y.; Ahmed, A.; Delgado-Olguin, P. Integrated small RNA, mRNA and protein omics reveal a miRNA network orchestrating metabolic maturation of the developing human heart. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wei, S.; Fan, Y.; Jiang, S. Bioinformatic-based Identification of Genes Associated with Aortic Valve Stenosis. Heart Surg. Forum 2022, 25, E069–E078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Tai, Y.; Zhao, H.; Fu, B.; Zhang, T.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, Y.; et al. Downregulation of miR-33a-5p in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Possible Mechanism for Chemotherapy Resistance. Med. Sci. Monit. 2017, 23, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- De Silva, K.; Demmer, R.T.; Jonsson, D.; Mousa, A.; Forbes, A.; Enticott, J. A data-driven biocomputing pipeline with meta-analysis on high throughput transcriptomics to identify genome-wide miRNA markers associated with type 2 diabetes. Heliyon 2022, 8, e08886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cao, N. Uncovering potential differentially expressed miRNAs and targeted mRNAs in myocardial infarction based on integrating analysis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2020, 22, 4383–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, M.; Okuzaki, D.; Yamauchi, A.; Ishikawa, S.; Nomura, Y.; Nishimura, A.; Motoike, Y.; Koshikawa, M.; Hitachi, K.; Tsuchida, K.; et al. Circulating miR-20b-5p and miR-330-3p are novel biomarkers for progression of atrial fibrillation: Intracardiac/extracardiac plasma sample analysis by small RNA sequencing. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Dong, X.; Zhan, Y.; Ma, S.; Liu, C.; Gao, Y. Expression profile of microRNAs in patients with decompensated cirrhosis by small RNA deep sequencing. Clin. Biochem. 2024, 123, 110705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, R.; Dong, X.; Gong, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, M.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Yang, S.; et al. hsa-miR-106b-5p participates in the development of chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension via targeting matrix metalloproteinase 2. Pulm. Circ. 2020, 10, 2045894020928300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Xue, Y.; Zheng, S.; Cai, L. Hsa-let-7c-5p, hsa-miR-130b-3p, and hsa-miR-142-3p as Novel miRNA Biomarkers for Melanoma Progression. Genet. Res. 2022, 2022, 5671562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Fang, H.; Xu, N. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 is transcriptionally activated by JUND and contributes to osteoarthritis progression via targeting the miR-423-5p/KDM5C axis. Life Sci. 2020, 258, 118095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Song, Q.; Yang, Z.; Wang, L.; Meng, Q. Identification of aging-related biomarkers and immune infiltration characteristics in osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis and machine learning. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1168780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Deng, L.; Zou, K.; Tian, Y.; Tang, X. ATF3 Modulates the Proliferation, Migration, and Apoptosis of Synovial Fibroblasts after Arthroscopy by Promoting RGS1 Transcription. Curr. Mol. Med. 2023, 23, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Liu, J. Identification and Molecular Mechanisms Study of Genes Associated with Osteoarthritis: A Comprehensive Bioinformatic Study of Cartilage and Synovium. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2022, 32, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Gong, N. Identification and verification of ferroptosis-related genes in the synovial tissue of osteoarthritis using bioinformatics analysis. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 992044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fan, Y.; Liu, S. ATF3 as a potential diagnostic marker of early-stage osteoarthritis and its correlation with immune infiltration through bioinformatics analysis. Bone Jt. Res. 2022, 11, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Fang, J.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, G.; Zou, Y.; Hu, S.; Zheng, Y.; Fang, H.; et al. TCF12 regulates the TGF-beta/Smad2/3 signaling pathway to accelerate the progression of osteoarthritis by targeting CXCR4. J. Orthop. Transl. 2024, 44, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poursamimi, J.; Shariati-Sarabi, Z.; Tavakkol-Afshari, J.; Mohammadi, M. A Significant Increase in the Gene Expression of GATA-3 Following the Treatment of Osteoarthritis Patients with Crocin. Iran. J. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2022, 21, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.N.P.; Yadav, U.S.; Azad, K.; Goswami, P.; Kinare, V.; Bandyopadhyay, A. NFIA and GATA3 are crucial regulators of embryonic articular cartilage differentiation. Development 2018, 145, dev156554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xiao, S.; Li, F.; Fang, K.; Wen, J.; Gong, H. Max interacting protein 1 induces IL-17-producing T helper/regulatory T imbalance in osteoarthritis by upregulating tectonic family member 2. Tissue Cell 2022, 78, 101906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragni, E.; Piccolo, S.; Papait, A.; De Luca, P.; Taiana, M.; Grieco, G.; Silini, A.R.; Parolini, O.; de Girolamo, L. Stable Housekeeping Genes in Bone Marrow, Adipose Tissue, and Amniotic Membrane-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Orthopedic Regenerative Medicine Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amarnani, A.A.; Poladian, K.R.; Marciano, B.E.; Daub, J.R.; Williams, S.G.; Livinski, A.A.; Hsu, A.P.; Palmer, C.L.; Kenney, C.M.; Avila, D.N.; et al. A Panoply of Rheumatological Manifestations in Patients with GATA2 Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yuan, S.; Niu, X.; Kelleher, R.; Sheridan, H. ESR1 dysfunction triggers neuroinflammation as a critical upstream causative factor of the Alzheimer’s disease process. Aging 2022, 14, 8595–8614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.M.; Li, H.L.; Shi, L.H.; Chen, X.P.; Luo, J.; Zhang, Z.L. The pharmacogenomics of valproic acid. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Jia, M.; Pan, H.; Chen, J. Excited State Kinetics of Benzo[a]pyrene Is Affected by Oxygen and DNA. Molecules 2023, 28, 5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Gene | id.Exposure | id.Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Method | nsnp | b | se | pval | p_no | Level Test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SKAP2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000005020 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000005020 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000005020 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 12 | −0.06355 | 0.029 | 0.028 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.964302 |
| ANK1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000029534 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000029534 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000029534 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.28875 | 0.06493 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.604415 |
| TFB1M | eqtl-a-ENSG00000029639 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000029639 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000029639 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.22194 | 0.051988 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.787497 |
| HSPA5 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000044574 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000044574 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000044574 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | 0.156907 | 0.04502 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.953288 |
| ASB1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000065802 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000065802 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000065802 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.095562 | 0.048124 | 0.047 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.476947 |
| SEMA3A | eqtl-a-ENSG00000075213 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000075213 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000075213 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.27709 | 0.017105 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.986775 |
| SP140 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000079263 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000079263 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000079263 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.17196 | 0.086501 | 0.047 | MR Egger | 0.840832 |
| EPB41L2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000079819 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000079819 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000079819 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.121946 | 0.046439 | 0.009 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.62119 |
| MEF2C | eqtl-a-ENSG00000081189 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000081189 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000081189 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.13635 | 0.069189 | 0.049 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.38673 |
| OVGP1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000085465 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000085465 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000085465 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.09836 | 0.03839 | 0.01 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.725835 |
| NRP1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000099250 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000099250 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000099250 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 6 | −0.12929 | 0.037849 | 0.001 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.866044 |
| CYTH4 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000100055 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000100055 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000100055 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.17078 | 0.079644 | 0.032 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.716136 |
| SYNGR1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000100321 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000100321 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000100321 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.06284 | 0.029177 | 0.031 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.531044 |
| KIAA0930 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000100364 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000100364 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000100364 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.14508 | 0.027017 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.75393 |
| HCK | eqtl-a-ENSG00000101336 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000101336 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000101336 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.07236 | 0.013991 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.902966 |
| FNDC3A | eqtl-a-ENSG00000102531 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000102531 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000102531 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.09655 | 0.029565 | 0.001 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.745019 |
| NOMO3 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000103226 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000103226 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000103226 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.11221 | 0.029073 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.709799 |
| RIPK2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000104312 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000104312 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000104312 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.14312 | 0.034984 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.825168 |
| CD37 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000104894 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000104894 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000104894 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.12521 | 0.048795 | 0.01 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.440039 |
| NKG7 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000105374 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000105374 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000105374 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.179132 | 0.057999 | 0.002 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.874258 |
| ZKSCAN1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000106261 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000106261 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000106261 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.04586 | 0.009649 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.916197 |
| TNFSF8 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000106952 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000106952 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000106952 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.1412 | 0.037591 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.70572 |
| PTGDS | eqtl-a-ENSG00000107317 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000107317 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000107317 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.234073 | 0.059862 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.564796 |
| TFAM | eqtl-a-ENSG00000108064 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000108064 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000108064 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 7 | 0.066743 | 0.029934 | 0.026 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.473236 |
| TMEM97 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000109084 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000109084 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000109084 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 6 | −0.06877 | 0.026808 | 0.01 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.829951 |
| PPARGC1A | eqtl-a-ENSG00000109819 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000109819 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000109819 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.042277 | 0.006439 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.929293 |
| PANX1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000110218 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000110218 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000110218 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.08089 | 0.035894 | 0.024 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.501225 |
| SLC22A18 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000110628 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000110628 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000110628 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.040591 | 0.020205 | 0.045 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.787391 |
| CBLB | eqtl-a-ENSG00000114423 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000114423 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000114423 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.062925 | 0.028786 | 0.029 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.754687 |
| TP53I3 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000115129 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000115129 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000115129 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.052781 | 0.01687 | 0.002 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.79608 |
| IL1R1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000115594 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000115594 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000115594 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.13532 | 0.026544 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.906106 |
| SCP2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000116171 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000116171 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000116171 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | 0.084015 | 0.036215 | 0.02 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.53642 |
| ITGB1BP1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000119185 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000119185 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000119185 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.12499 | 0.061858 | 0.043 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.697252 |
| ADCY7 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000121281 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000121281 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000121281 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.080449 | 0.00958 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.90424 |
| NQO2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000124588 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000124588 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000124588 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 6 | 0.103165 | 0.036288 | 0.004 | MR Egger | 0.421145 |
| ATXN1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000124788 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000124788 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000124788 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.083781 | 0.038075 | 0.028 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.697622 |
| DOCK4 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000128512 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000128512 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000128512 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.37826 | 0.147865 | 0.011 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.638297 |
| KLHDC10 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000128607 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000128607 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000128607 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.07208 | 0.035492 | 0.042 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.607087 |
| CALML4 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000129007 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000129007 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000129007 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.02755 | 0.010673 | 0.01 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.837662 |
| CD68 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000129226 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000129226 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000129226 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.26171 | 0.015244 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.893517 |
| CDO1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000129596 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000129596 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000129596 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | 0.072609 | 0.006502 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.927536 |
| LDLR | eqtl-a-ENSG00000130164 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000130164 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000130164 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 8 | 0.20067 | 0.04522 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.682704 |
| GCH1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000131979 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000131979 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000131979 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.10284 | 0.032484 | 0.002 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.68823 |
| EGLN1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000135766 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000135766 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000135766 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.1614 | 0.065631 | 0.014 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.562518 |
| PLXNC1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000136040 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000136040 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000136040 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.17868 | 0.072646 | 0.014 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.727798 |
| C7orf25 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000136197 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000136197 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000136197 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 8 | −0.1108 | 0.044746 | 0.013 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.44153 |
| IFI44 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000137965 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000137965 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000137965 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 7 | 0.179405 | 0.050254 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.827067 |
| ADCY3 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000138031 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000138031 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000138031 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.21249 | 0.101604 | 0.036 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.586261 |
| RAB15 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000139998 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000139998 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000139998 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.25442 | 0.080683 | 0.002 | MR Egger | 0.948296 |
| MFGE8 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000140545 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000140545 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000140545 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.093175 | 0.044274 | 0.035 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.800747 |
| MYO1F | eqtl-a-ENSG00000142347 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000142347 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000142347 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.350313 | 0.089257 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.64159 |
| HNMT | eqtl-a-ENSG00000150540 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000150540 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000150540 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.07073 | 0.00656 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.979268 |
| ING1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000153487 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000153487 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000153487 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.02985 | 0.008805 | 0.001 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.96251 |
| ARHGAP25 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000163219 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000163219 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000163219 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.162316 | 0.026159 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.823096 |
| TGFBR2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000163513 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000163513 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000163513 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.15754 | 0.070785 | 0.026 | MR Egger | 0.477357 |
| CITED2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000164442 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000164442 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000164442 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.152919 | 0.069401 | 0.028 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.57333 |
| GALNT10 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000164574 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000164574 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000164574 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.307127 | 0.086586 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.612881 |
| SYK | eqtl-a-ENSG00000165025 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000165025 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000165025 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.041277 | 0.017723 | 0.02 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.826421 |
| NCF1C | eqtl-a-ENSG00000165178 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000165178 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000165178 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.11162 | 0.025492 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.695435 |
| TRANK1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000168016 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168016 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168016 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.04324 | 0.019382 | 0.026 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.973751 |
| CX3CR1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.20561 | 0.093691 | 0.028 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.22481 |
| RAB31 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000168461 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168461 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168461 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 8 | −0.12515 | 0.06257 | 0.045 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.520829 |
| PTAFR | eqtl-a-ENSG00000169403 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000169403 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000169403 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.269285 | 0.109184 | 0.014 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.535136 |
| NPAS2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000170485 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000170485 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000170485 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.086253 | 0.020196 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.827519 |
| PKIA | eqtl-a-ENSG00000171033 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000171033 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000171033 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 10 | −0.08369 | 0.04137 | 0.043 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.569548 |
| INSR | eqtl-a-ENSG00000171105 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000171105 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000171105 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.429477 | 0.117337 | 0 | MR Egger | 0.686507 |
| CEBPB | eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.09969 | 0.026082 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.851249 |
| DDIT3 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000175197 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000175197 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000175197 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.228411 | 0.040889 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.875236 |
| MRPL48 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000175581 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000175581 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000175581 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.107887 | 0.009995 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.906152 |
| CRLF3 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000176390 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000176390 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000176390 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.075777 | 0.023369 | 0.001 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.743505 |
| ADAP2 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000184060 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000184060 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000184060 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.450766 | 0.217043 | 0.038 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.474219 |
| FOXO4 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000184481 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000184481 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000184481 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | −0.38696 | 0.034977 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.935967 |
| PDE4B | eqtl-a-ENSG00000184588 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000184588 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000184588 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.236931 | 0.041429 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.735599 |
| INSIG1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000186480 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000186480 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000186480 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 7 | 0.111239 | 0.043196 | 0.01 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.611197 |
| FPR3 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000187474 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000187474 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000187474 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 6 | −0.21036 | 0.067108 | 0.002 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.703622 |
| CARD9 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000187796 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000187796 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000187796 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 6 | −0.07716 | 0.030194 | 0.011 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.481819 |
| ATG7 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000197548 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000197548 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000197548 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.17177 | 0.070871 | 0.015 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.522111 |
| CCDC69 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000198624 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000198624 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000198624 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 3 | 0.20586 | 0.060369 | 0.001 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.863129 |
| HSPA1B | eqtl-a-ENSG00000204388 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000204388 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000204388 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.18574 | 0.048195 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.737545 |
| PPP1CB | eqtl-a-ENSG00000213639 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000213639 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000213639 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | 0.140212 | 0.064686 | 0.03 | MR Egger | 0.264393 |
| ANG | eqtl-a-ENSG00000214274 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000214274 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000214274 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 9 | −0.09934 | 0.050357 | 0.049 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.457848 |
| APOBEC3G | eqtl-a-ENSG00000239713 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000239713 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000239713 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 6 | −0.11315 | 0.026796 | 0 | MR Egger weighted median | 0.767311 |
| id.Exposure | id.Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Method | nsnp | b | se | pval | lo_ci | up_ci | or | or_lci95 | or_uci95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | MR Egger | 4 | −0.0239 | 0.3751 | 0.9551 | −0.75897 | 0.711265 | 0.9764 | 0.468148 | 2.036566 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 4 | −0.0997 | 0.0261 | 0.0001 | −0.15081 | −0.04857 | 0.9051 | 0.860009 | 0.952588 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | Weighted median | 4 | −0.1027 | 0.1244 | 0.4089 | −0.34642 | 0.141037 | 0.9024 | 0.707218 | 1.151467 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | Simple mode | 4 | −0.1323 | 0.167 | 0.486 | −0.45961 | 0.194957 | 0.8761 | 0.631528 | 1.215259 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | Weighted mode | 4 | −0.1075 | 0.1456 | 0.5138 | −0.39285 | 0.177832 | 0.8981 | 0.675133 | 1.194625 |
| id.Exposure | id.Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Method | nsnp | b | se | pval | lo_ci | up_ci | or | or_lci95 | or_uci95 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | MR Egger | 5 | −0.396 | 0.153 | 0.0812 | −0.6959 | −0.09612 | 0.673 | 0.498624 | 0.908354 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | Inverse-variance weighted (multiplicative random effects) | 5 | −0.2056 | 0.0937 | 0.0282 | −0.38925 | −0.02198 | 0.8141 | 0.677567 | 0.978261 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | Weighted median | 5 | −0.2015 | 0.1042 | 0.0531 | −0.4058 | 0.002726 | 0.8175 | 0.666446 | 1.002729 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | Simple mode | 5 | −0.1856 | 0.1347 | 0.2405 | −0.44964 | 0.078536 | 0.8306 | 0.637857 | 1.081703 |
| eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | Weighted mode | 5 | −0.221 | 0.1248 | 0.1512 | −0.46556 | 0.023509 | 0.8017 | 0.627786 | 1.023788 |
| Gene | id.Exposure | id.Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Method | Q | Q_df | Q_pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPB | eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | MR Egger | 0.1051 | 2 | 0.9488 |
| CEBPB | eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | Inverse-variance weighted | 0.1503 | 3 | 0.9852 |
| CX3CR1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | MR Egger | 2.1718 | 3 | 0.5375 |
| CX3CR1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | Inverse-variance weighted | 4.4956 | 4 | 0.3431 |
| Gene | id.Exposure | id.Outcome | Outcome | Exposure | Egger_Intercept | se | pval |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPB | eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000172216 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000172216 | −0.0135 | 0.0636 | 0.8512 |
| CX3CR1 | eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | ebi-a-GCST005810 | Osteoarthritis of the hip (hospital-diagnosed) || id:ebi-a-GCST005810 | ENSG00000168329 || id:eqtl-a-ENSG00000168329 | 0.051 | 0.0335 | 0.2248 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, H.; Gan, X.; He, J.; He, C. Mendelian Randomization and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Important Roles for CEBPB and CX3CR1 in Osteoarthritis. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090930
Gao H, Gan X, He J, He C. Mendelian Randomization and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Important Roles for CEBPB and CX3CR1 in Osteoarthritis. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(9):930. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090930
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Hui, Xinling Gan, Jing He, and Chengqi He. 2025. "Mendelian Randomization and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Important Roles for CEBPB and CX3CR1 in Osteoarthritis" Bioengineering 12, no. 9: 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090930
APA StyleGao, H., Gan, X., He, J., & He, C. (2025). Mendelian Randomization and Transcriptome Analyses Reveal Important Roles for CEBPB and CX3CR1 in Osteoarthritis. Bioengineering, 12(9), 930. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12090930








