Coronal Alignment Does Not Adequately Predict Femoral Rotation Axes in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Application of a 3D Image-Based Robotic-Assisted Arthroplasty Platform
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
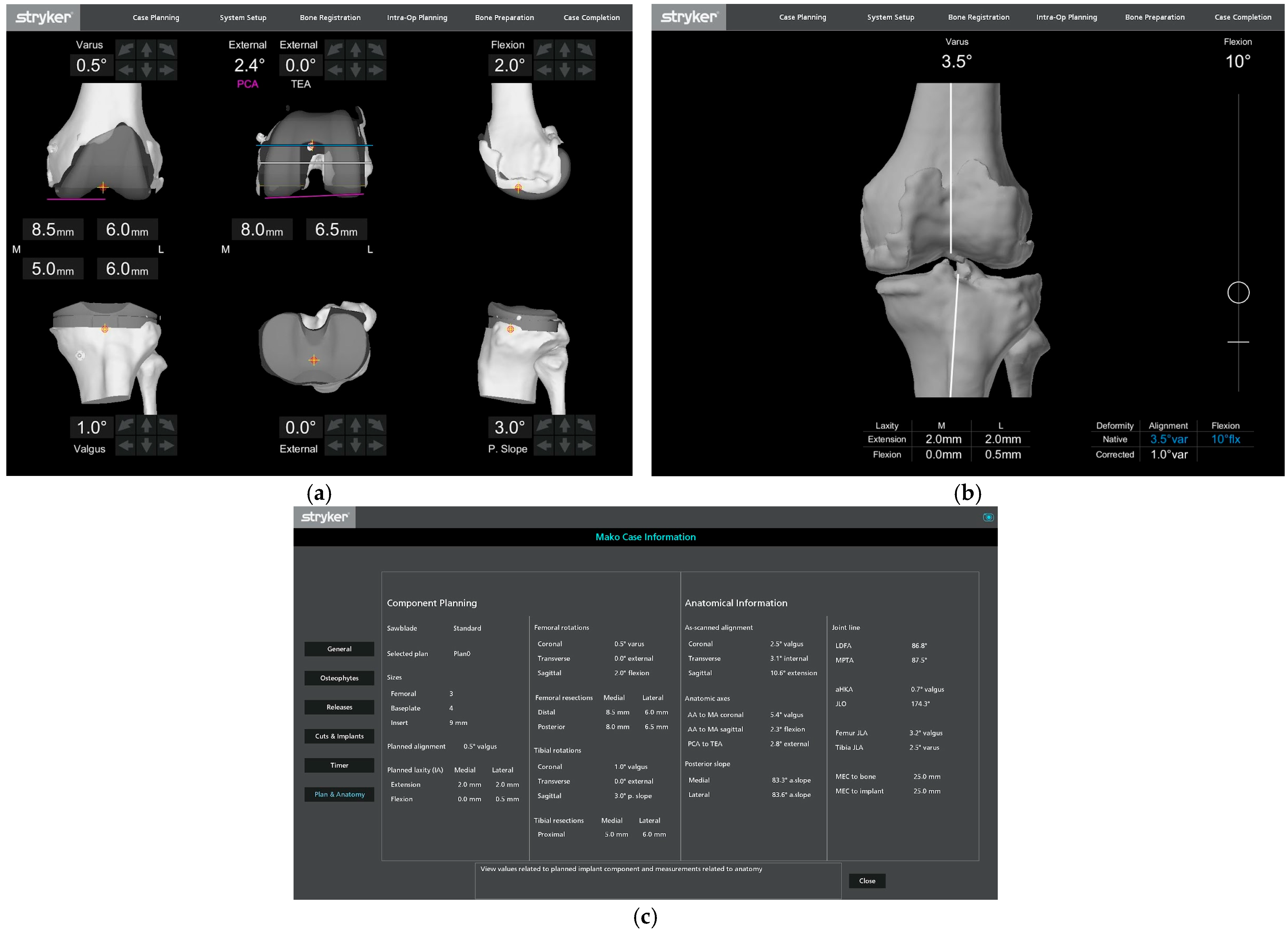
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Data Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Femoral Rotation Morphology
3.2. Overall Corona Limb Alignment
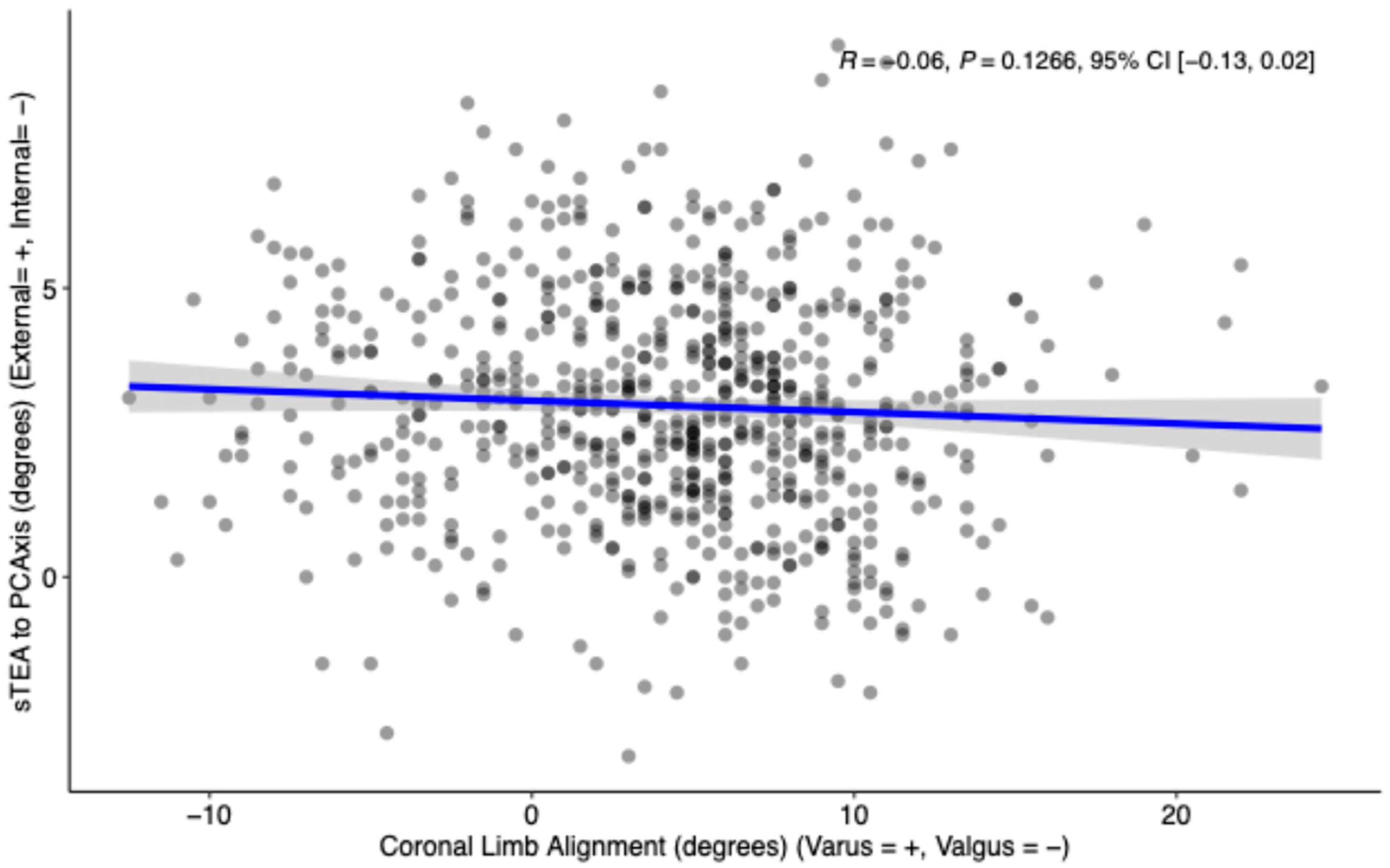
3.3. Coronal Limb Alignment vs. Femoral Rotation Morphology
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daines, B.K.; Dennis, D.A. Gap balancing vs. measured resection technique in total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2014, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaipel, M.; Gergely, I.; Sinz, K.; Neumann, C.; Sinz, G. Femoral rotation in ligament balanced knee arthroplasty: A prospective clinical study. J. Arthroplast. 2013, 28, 1103–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, R.B.; Draper, C.E.; Fredericson, M.; Powers, C.M. Femur Rotation and Patellofemoral Joint Kinematics: A Weight-Bearing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2010, 40, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlinden, C.; Uvin, P.; Labey, L.; Luyckx, J.P.; Bellemans, J.; Vandenneucker, H. The influence of malrotation of the femoral component in total knee replacement on the mechanics of patellofemoral contact during gait: AN IN VITRO BIOMECHANICAL STUDY. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2010, 92-B, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Akagi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Tamura, J.; Nakamura, T. In Vivo Three-Dimensional Knee Kinematics Using a Biplanar Image-Matching Technique. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 388, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, T.R.; Pfeifle, A.L. Chapter 69—Patellofemoral Disorders. In Orthopaedic Physical Therapy Secrets, 3rd ed.; Placzek, J.D., Boyce, D.A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poilvache, P.L.; Insall, J.N.; Scuderi, G.R.; Font-Rodriguez, D.E. Rotational landmarks and sizing of the distal femur in total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1996, 331, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.S.; Connors-Ehlert, R.; LiArno, S.; Geller, J.A.; Cooper, H.J.; Shah, R.P. Accuracy of Reference Axes for Femoral Component Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Computed Tomography-Based Study of 2,128 Femora. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2019, 101, e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, E.A.; Fox, M.G.; Blankenbaker, D.G.; French, C.N.; Frick, M.A.; Hanna, T.N.; Jawetz, S.T.; Onks, C.; Said, N.; Stensby, J.D.; et al. ACR Appropriateness Criteria® Imaging After Total Knee Arthroplasty: 2023 Update. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. JACR 2023, 20, S433–S454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.D. Femoral and tibial component rotation in total knee arthroplasty: Methods and consequences. Bone Jt. J. 2013, 95-B (Suppl. A), 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, D.A.; Komistek, R.D.; Kim, R.H.; Sharma, A. Gap balancing versus measured resection technique for total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskin, R.S. Flexion space configuration in total knee arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 1995, 10, 657–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Roth, J.D.; Howell, S.M.; Hull, M.L. How Frequently Do Four Methods for Mechanically Aligning a Total Knee Arthroplasty Cause Collateral Ligament Imbalance and Change Alignment from Normal in White Patients? AAOS Exhibit Selection. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2014, 96, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Howell, S.M.; Hull, M.L. Simulation of total knee arthroplasty in 5° or 7° valgus: A study of gap imbalances and changes in limb and knee alignments from native. J. Orthop. Res. Off. Publ. Orthop. Res. Soc. 2016, 35, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akagi, M.; Yamashita, E.; Nakagawa, T.; Asano, T.; Nakamura, T. Relationship between frontal knee alignment and reference axes in the distal femur. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 388, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, T.; Zambianchi, F.; Catani, F.; Bellemans, J.; Victor, J. Coronal alignment is a predictor of the rotational geometry of the distal femur in the osteo-arthritic knee. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. Off. J. ESSKA 2012, 21, 2331–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyse, T.J.; Chong, L.R.; Davis, J.; Boettner, F.; Haas, S.B.; Potter, H.G. MRI analysis for rotation of total knee components. Knee 2012, 19, 571–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Liu, L.M.; Luo, J.M.; Ma, C.; Feng, Q.; Yang, L.; Guo, L. Could surgical transepicondylar axis be identified accurately in preoperative 3D planning for total knee arthroplasty? A reproducibility study based on 3D-CT. Arthroplasty 2022, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, E.-K.; Seon, J.-K.; Yim, J.-H.; Netravali, N.A.; Bargar, W.L. Robotic-assisted TKA reduces postoperative alignment outliers and improves gap balance compared to conventional TKA. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aglietti, P.; Sensi, L.; Cuomo, P.; Ciardullo, A. Rotational Position of Femoral and Tibial Components in TKA Using the Femoral Transepicondylar Axis. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 2751–2755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Ayeni, F.E.; Sorial, R. Impact of change in coronal plane alignment of knee (CPAK) classification on outcomes of robotic-assisted TKA. Arthroplasty 2024, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschini, V.; Nodzo, S.R.; Della Valle, A.G. Femoral Component Rotation in Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Comparison Between Transepicondylar Axis and Posterior Condylar Line Referencing. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 2917–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrack, R.L.; Schrader, T.; Bertot, A.J.; Wolfe, M.W.; Myers, L. Component rotation and anterior knee pain after total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 392, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matassi, F.; Pettinari, F.; Frasconà, F.; Innocenti, M.; Civinini, R. Coronal alignment in total knee arthroplasty: A review. J. Orthop. Traumatol. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Orthop. Traumatol. 2023, 24, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, F.M.; Insall, J.N.; Scuderi, G.R. The posterior condylar angle in osteoarthritic knees. J. Arthroplast. 1998, 13, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | n = 695 |
|---|---|
| Age at Surgery | |
| Mean (SD) | 67.7 (9.3) |
| Median (IQR) | 68.0 (13.0) |
| Range | 27–94 |
| Sex | |
| Female | 486 (69.9%) |
| Male | 209 (30.1%) |
| Race | |
| White | 365 (52.5%) |
| Black | 102 (14.7%) |
| Asian | 49 (7.1%) |
| Other | 179 (25.8%) |
| Laterality | |
| Left | 358 (51.5%) |
| Right | 337 (48.5%) |
| Procedure Length (Minutes) | |
| Mean (SD) | 106.3 (23.9) |
| Median (IQR) | 102.0 (28.0) |
| Range | 58–234 |
| Body Mass Index | |
| Mean (SD) | 31.6 (5.1) |
| Median (IQR) | 31.3 (7.1) |
| Range | 20–48 |
| American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Score | |
| 1 | 17 (2.4%) |
| 2 | 419 (60.3%) |
| 3 | 258 (37.1%) |
| 4 | 1 (0.1%) |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) | |
| Mean (SD) | 3.6 (2.5) |
| Median (IQR) | 3.0 (3.0) |
| Range | 0–24 |
| Characteristic | n = 695 |
|---|---|
| sTEA to PCAxis (External = +, Internal = −) | |
| Mean (SD) | 3.0 (2.0) |
| Median (IQR) | 2.9 (2.7) |
| Range | −3.1 to 9.2 |
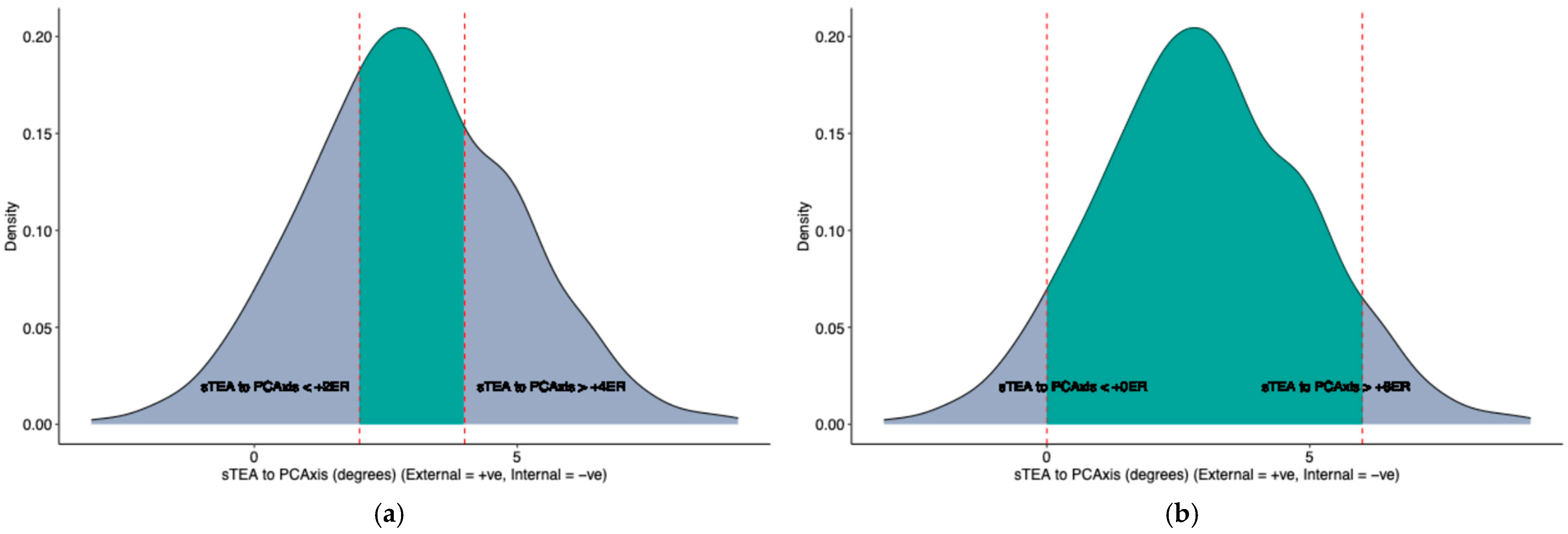
| sTEA to PCAxis between +2 to +4 degrees | 270 (39%) |
| sTEA to PCAxis between +1 to +5 degrees | 466 (67%) |
| sTEA to PCAxis between +0 to +6 degrees | 595 (86%) |
| sTEA to PCAxis > 0 degrees | 647 (93%) |
| sTEA to PCAxis < 0 degrees | 43 (6.2%) |
| Characteristic | n = 695 |
|---|---|
| Coronal Limb Alignment (Varus = +, Valgus = −) | |
| Mean (SD) | 4.3 (5.8) |
| Median (IQR) | 5.0 (7.5) |
| Range | −12.5 to 24.5 |
| Varus Alignment > 2 degrees | 465 (67%) |
| Valgus Alignment > 2 degrees | 101 (15%) |
| Characteristic | Valgus > 2 Degrees, n = 101 1 | Varus > 2 Degrees, n = 465 1 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | <0.001 2 | ||
| Female | 85 (84%) | 302 (65%) | |
| Male | 16 (16%) | 163 (35%) | |
| Age at Surgery | 0.9 3 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 67.4 (10.31) | 67.9 (8.91) | |
| Range | 41, 94 | 39, 90 | |
| Median (IQR) | 67.5 (11.25) | 68.0 (13.00) | |
| Race | 0.6 2 | ||
| White | 50 (50%) | 246 (53%) | |
| Black | 19 (19%) | 63 (14%) | |
| Asian | 6 (5.9%) | 32 (6.9%) | |
| Other | 26 (26%) | 124 (27%) | |
| American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) Score | 0.6 2 | ||
| 1 | 3 (3.0%) | 10 (2.2%) | |
| 2 | 60 (59%) | 279 (60%) | |
| 3 | 38 (38%) | 175 (38%) | |
| 4 | 0 (0%) | 1 (0.2%) | |
| Body Mass Index | 0.004 3 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 30.1 (5.39) | 31.8 (4.91) | |
| Range | 20, 46 | 20, 48 | |
| Median (IQR) | 30.3 (7.58) | 31.5 (7.04) | |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) | 0.5 3 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 3.5 (2.37) | 3.7 (2.63) | |
| Range | 0, 11 | 0, 24 | |
| Median (IQR) | 3.0 (3.00) | 3.0 (3.00) | |
| Laterality | 0.2 2 | ||
| Left | 46 (46%) | 249 (54%) | |
| Right | 55 (54%) | 216 (46%) | |
| sTEA to PCAxis (External = +, Internal = −) | 0.7 3 | ||
| Mean (SD) | 2.9 (1.90) | 2.8 (1.99) | |
| Range | −3, 7 | −3, 9 | |
| Median (IQR) | 3.0 (2.80) | 2.8 (2.60) | |
| sTEA to PCAxis between +2 to +4 degrees | 37 (37%) | 179 (38%) | 0.8 2 |
| sTEA to PCAxis between +1 to +5 degrees | 70 (69%) | 312 (67%) | 0.7 2 |
| sTEA to PCAxis > 0 degrees | 96 (95%) | 427 (92%) | 0.3 |
| sTEA to PCAxis < 0 degrees | 4 (4.0%) | 34 (7.3%) | 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anil, U.; Di Gangi, C.; Anderson, L.; Lin, C.C.; Hepinstall, M.; Meftah, M.; Arshi, A. Coronal Alignment Does Not Adequately Predict Femoral Rotation Axes in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Application of a 3D Image-Based Robotic-Assisted Arthroplasty Platform. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070727
Anil U, Di Gangi C, Anderson L, Lin CC, Hepinstall M, Meftah M, Arshi A. Coronal Alignment Does Not Adequately Predict Femoral Rotation Axes in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Application of a 3D Image-Based Robotic-Assisted Arthroplasty Platform. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(7):727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070727
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnil, Utkarsh, Catherine Di Gangi, Lachlan Anderson, Charles C. Lin, Matthew Hepinstall, Morteza Meftah, and Armin Arshi. 2025. "Coronal Alignment Does Not Adequately Predict Femoral Rotation Axes in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Application of a 3D Image-Based Robotic-Assisted Arthroplasty Platform" Bioengineering 12, no. 7: 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070727
APA StyleAnil, U., Di Gangi, C., Anderson, L., Lin, C. C., Hepinstall, M., Meftah, M., & Arshi, A. (2025). Coronal Alignment Does Not Adequately Predict Femoral Rotation Axes in Total Knee Arthroplasty: Application of a 3D Image-Based Robotic-Assisted Arthroplasty Platform. Bioengineering, 12(7), 727. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12070727







