A Multimodal Neurophysiological Approach to Evaluate Educational Contents in Terms of Cognitive Processes and Engagement
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Experimental Protocol
- Task “Educational video”: A popular science video (6 min 49 s) incorporating short video clips, infographics, and practical examples (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3MUstQxdi34, accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Task “Academic video”: A traditional lecture-style video (7 min 17 s) featuring PowerPoint slides and a voice-over narration (https://www.youtube.com/watch?app=desktop&v=eV4ufhg7W6c, accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Task “Text reading”: An encyclopedic text excerpt, designed to be read within approximately 7 min (https://it.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bluetooth, accessed on 5 May 2024).
2.3. Neurophysiological Data Collection and Processing
2.3.1. Electroencephalography (EEG)
2.3.2. Photoplethysmography (PPG)
2.3.3. Electrodermal Activity (EDA)
2.4. Subjective and Behavioral Data Collection
- The simplicity with which they could comprehend the disseminated information.
- The facility with which they could internalize the content.
- The capacity to sustain attention during the entirety of the task.
- The degree of interest elicited by the employed narrative modality.
- The extent of engagement is provoked by the narrative approach.
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
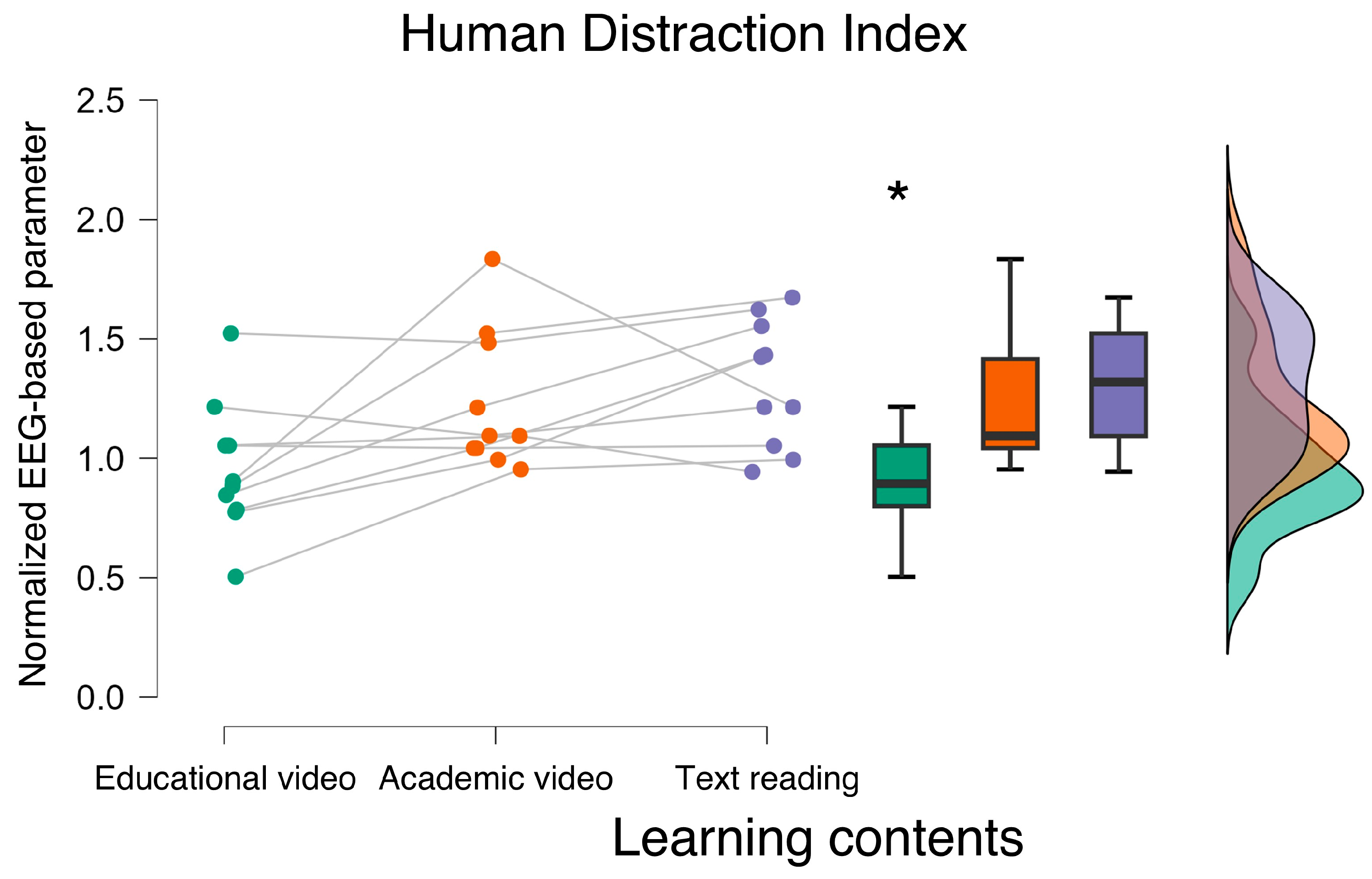
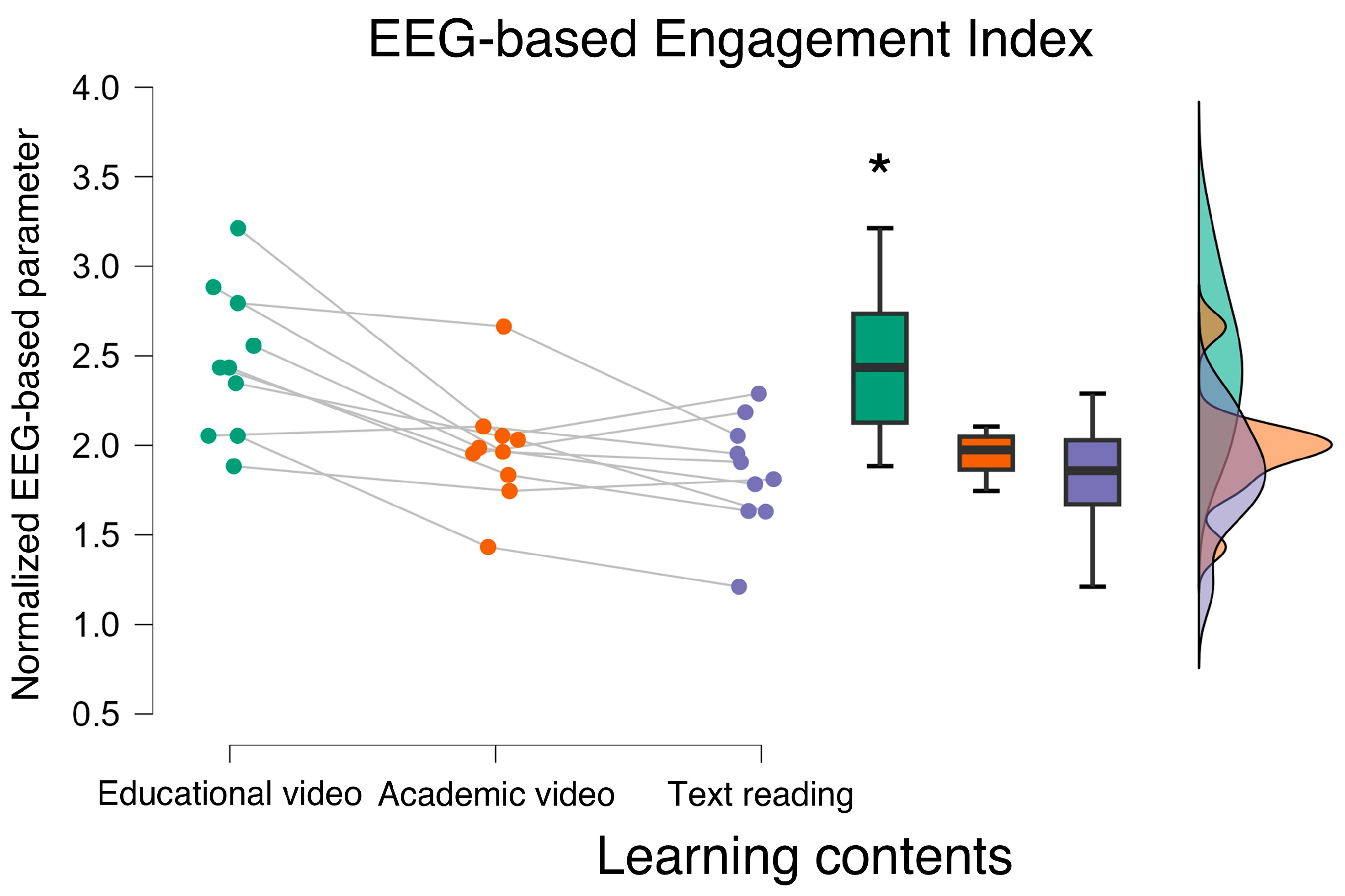
3.1. Neurophysiological Results
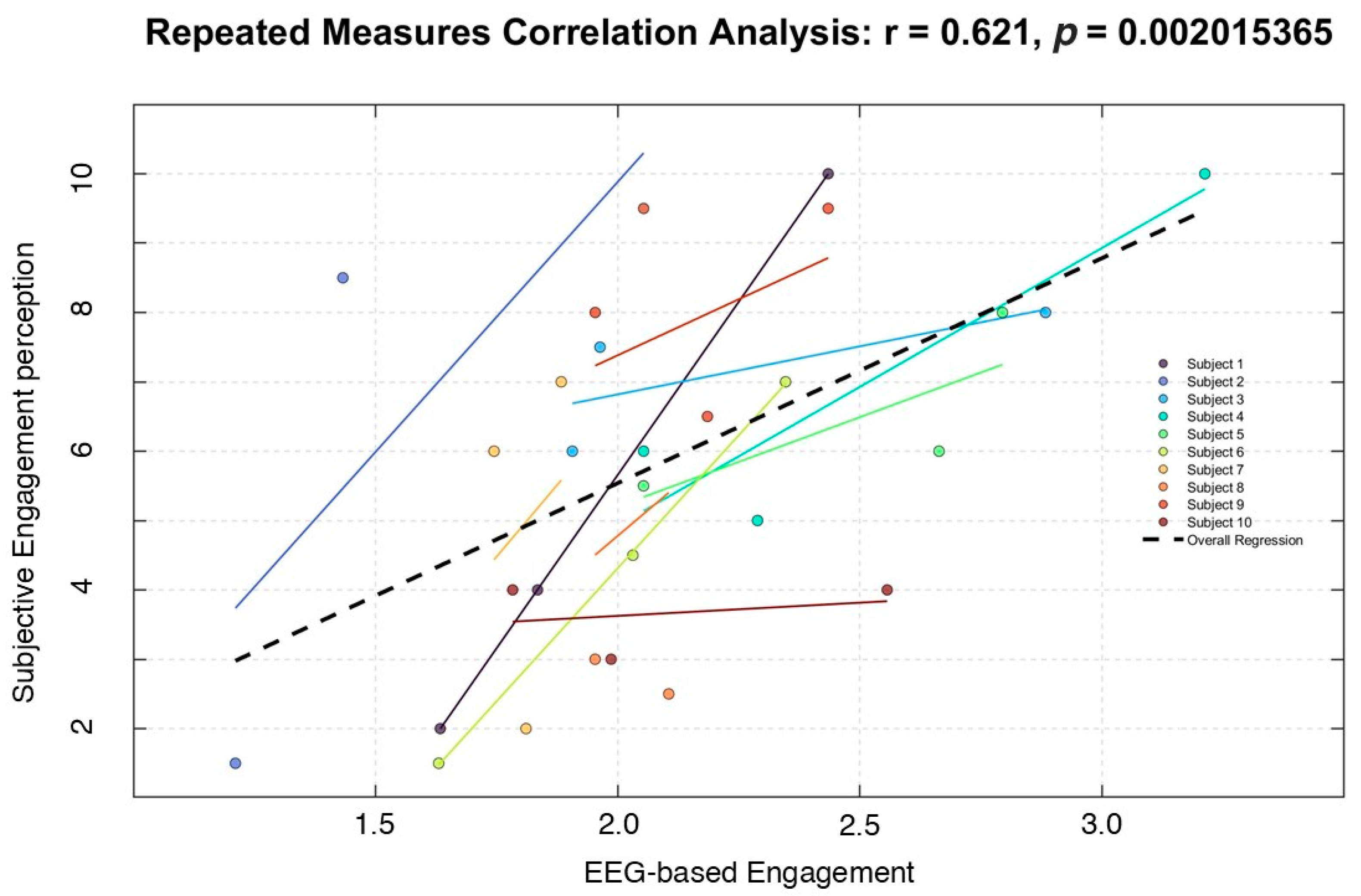
3.2. Correlation Analysis
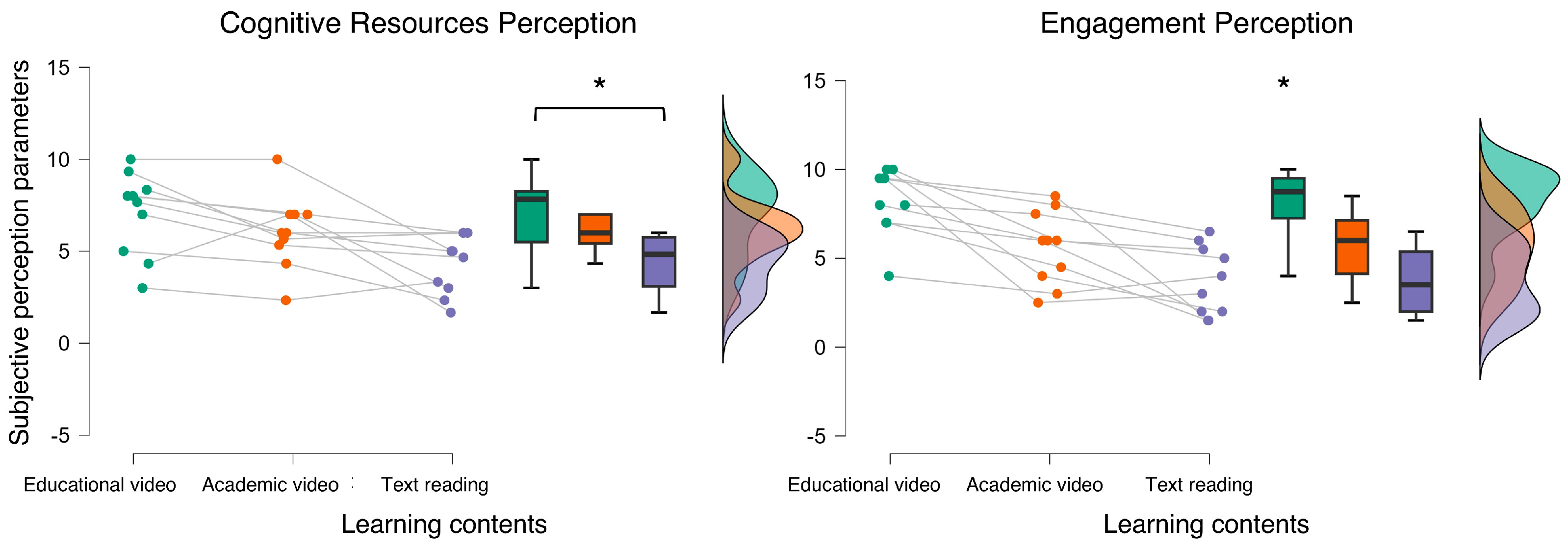
3.3. Subjective Results
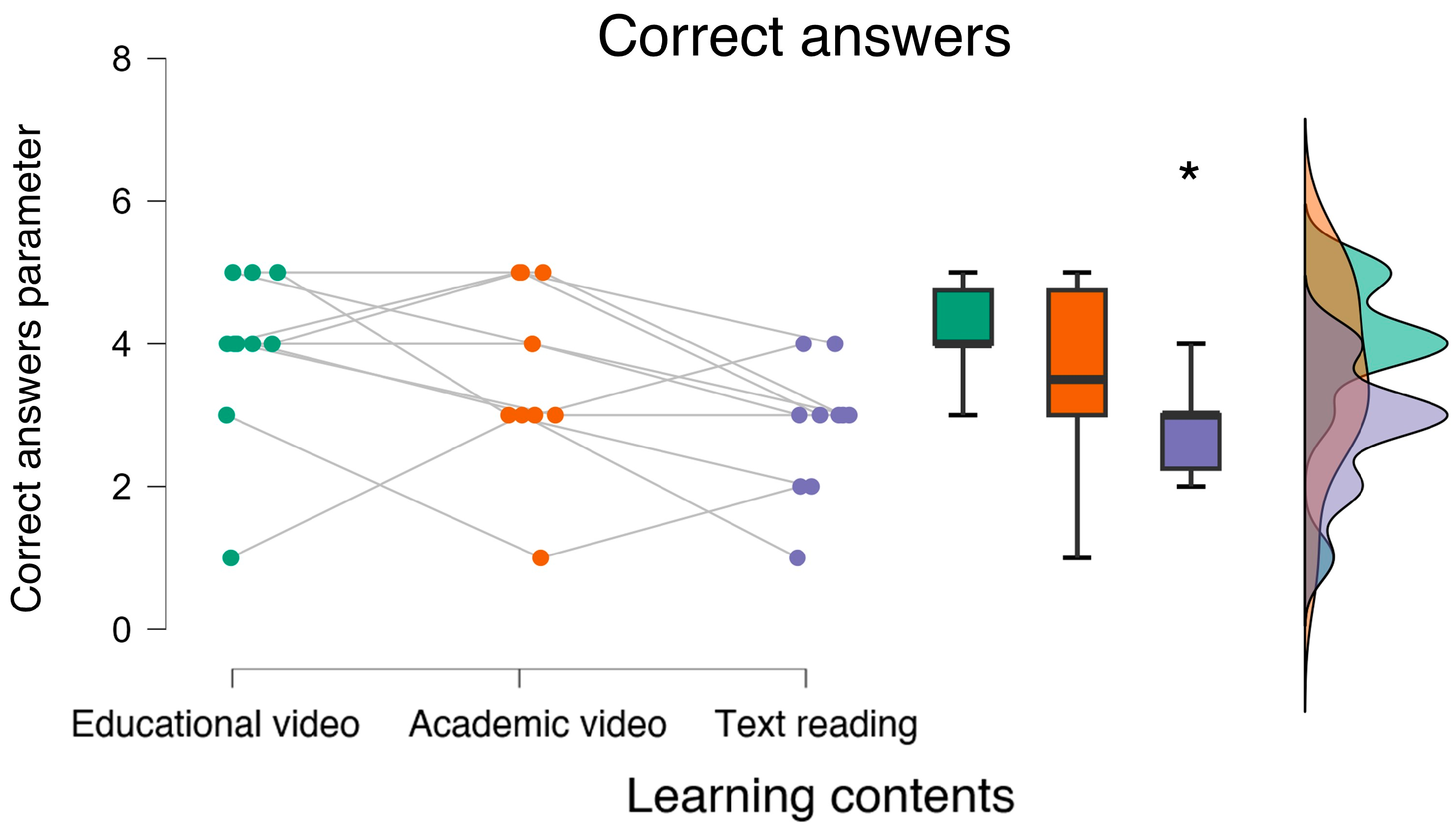
3.4. Behavioral Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Future Trends
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Byrnes, J.P.; Vu, L.T. Educational neuroscience: Definitional, methodological, and interpretive issues. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Cogn. Sci. 2015, 6, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darvishi, A.; Khosravi, H.; Sadiq, S.; Weber, B. Neurophysiological Measurements in Higher Education: A Systematic Literature Review. Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2021, 32, 413–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, C.M.; Murray, M.M.; Lantz, G.; Gonzalez, S.; Spinelli, L.; De Peralta, R.G. EEG source imaging. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2004, 115, 2195–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protzak, J.; Gramann, K. Investigating established EEG parameter during real-world driving. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EEG Correlates of Task Engagement and Mental Workload in Vigilance, Learning, and Memory Tasks—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17547324/ (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Di Flumeri, G.; Ronca, V.; Giorgi, A.; Vozzi, A.; Aricò, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Zeng, H.; Dai, G.; Kong, W.; Babiloni, F.; et al. EEG-Based Index for Timely Detecting User’s Drowsiness Occurrence in Automotive Applications. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 866118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Borghini, G.; Aricò, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Lanzi, P.; Pozzi, S.; Vignali, V.; Lantieri, C.; Bichicchi, A.; Simone, A.; et al. EEG-based mental workload neurometric to evaluate the impact of different traffic and road conditions in real driving settings. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Jung, T.-P. A collaborative brain-computer interface for improving human performance. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, L. Study of EEG characteristics while solving scientific problems with different mental effort. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 23783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Oh, Y.; Kounios, J.; Beeman, M. Dynamics of hidden brain states when people solve verbal puzzles. NeuroImage 2022, 255, 119202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Duc, N.T.; Choi, M.; Lee, B. EEG microstate features according to performance on a mental arithmetic task. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varao-Sousa, T.L.; Kingstone, A. Memory for Lectures: How Lecture Format Impacts the Learning Experience. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wammes, J.D.; Boucher, P.O.; Seli, P.; Cheyne, J.A.; Smilek, D. Mind wandering during lectures I: Changes in rates across an entire semester. Sch. Teach. Learn. Psychol. 2016, 2, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz, D.A.; Tucker, C.S. Assessing Students’ Emotional States: An Approach to Identify Lectures That Provide an Enhanced Learning Experience. In Proceedings of the ASME Design Engineering Technical Conference, Buffalo, NY, USA, 17–20 August 2014; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazher, M.; Aziz, A.A.; Malik, A.S.; Amin, H.U. An EEG-Based Cognitive Load Assessment in Multimedia Learning Using Feature Extraction and Partial Directed Coherence. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 14819–14829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-M.; Sun, Y.-C. Assessing the effects of different multimedia materials on emotions and learning performance for visual and verbal style learners. Comput. Educ. 2012, 59, 1273–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; Giorgi, A.; Germano, D.; Ronca, V.; Vozzi, A.; Borghini, G.; Tamborra, L.; Simonetti, I.; Capotorto, R.; Ferrara, S.; et al. A Neuroergonomic Approach Fostered by Wearable EEG for the Multimodal Assessment of Drivers Trainees. Sensors 2023, 23, 8389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutlu-Bayraktar, D.; Ozel, P.; Altindis, F.; Yilmaz, B. Split-attention effects in multimedia learning environments: Eye-tracking and EEG analysis. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2022, 81, 8259–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, A.; Faye, I.; Mumtaz, W.; Malik, A.S.; Sato, H. EEG in classroom: EMD features to detect situational interest of students during learning. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2018, 78, 16261–16281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, F.; Ali, A.; Soomro, T.A.; Marouf, M.; Bilal, M.; Chowdhry, B.S. Electroencephalogram (EEG) Signals for Modern Educational Research. In Innovative Education Technologies for 21st Century Teaching and Learning; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2021; pp. 149–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, I.; Tamborra, L.; Giorgi, A.; Ronca, V.; Vozzi, A.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Sciaraffa, N.; Trettel, A.; Babiloni, F.; et al. Neurophysiological Evaluation of Students’ Experience during Remote and Face-to-Face Lessons: A Case Study at Driving School. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Hou, K.; Shi, J.; Gao, W. A comprehensive review of research on indoor cognitive performance using electroencephalogram technology. Build. Environ. 2024, 257, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuvaraj, R.; Chadha, S.; Prince, A.A.; Murugappan, M.; Bin Islam, S.; Sumon, S.I.; Chowdhury, M.E.H. A Machine Learning Framework for Classroom EEG Recording Classification: Unveiling Learning-Style Patterns. Algorithms 2024, 17, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas, J. Is learning styles-based instruction effective? A comprehensive analysis of recent research on learning styles. Theory Res. Educ. 2015, 13, 308–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Bhatia, S.; Kaushik, K.; Ahuja, N.J.; Nayyar, A.; Masud, M. Blended Learning Tools and Practices: A Comprehensive Analysis. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 85151–85197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, V.; Brambati, F.; Napoletano, L.; Marx, C.; Trösterer, S.; Vozzi, A.; Aricò, P.; Giorgi, A.; Capotorto, R.; Borghini, G.; et al. A Novel EEG-Based Assessment of Distraction in Simulated Driving under Different Road and Traffic Conditions. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apicella, A.; Arpaia, P.; Frosolone, M.; Improta, G.; Moccaldi, N.; Pollastro, A. EEG-based measurement system for monitoring student engagement in learning 4.0. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, L.; Lee, H.; Becke, E.; Trenado, C.; Abad-Hernando, S.; Sperling, M.; Vidaurre, D.; Wald-Fuhrmann, M.; Richardson, D.C.; Ward, J.A.; et al. Delta-Band Inter-Brain Synchrony Reflects Collective Audience Engagement with Live Dance Performances. Available online: https://osf.io/uz573 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Sciaraffa, N.; Di Flumeri, G.; Germano, D.; Giorgi, A.; Di Florio, A.; Borghini, G.; Vozzi, A.; Ronca, V.; Babiloni, F.; Aricò, P. Evaluation of a New Lightweight EEG Technology for Translational Applications of Passive Brain-Computer Interfaces. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 901387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronca, V.; Di Flumeri, G.; Giorgi, A.; Vozzi, A.; Capotorto, R.; Germano, D.; Sciaraffa, N.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Aricò, P. o-CLEAN: A novel multi-stage algorithm for the ocular artifacts’ correction from EEG data in out-of-the-lab applications. J. Neural Eng. 2024, 21, 056023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An open source toolbox for analysis of single-trial EEG dynamics including independent component analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. EEG alpha and theta oscillations reflect cognitive and memory performance: A review and analysis. Brain Res. Rev. 1999, 29, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauseng, P.; Klimesch, W.; Schabus, M.; Doppelmayr, M. Fronto-parietal EEG coherence in theta and upper alpha reflect central executive functions of working memory. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2005, 57, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchiato, G.; Babiloni, F.; Astolfi, L.; Toppi, J.; Cherubino, P.; Dai, J.; Kong, W.; Wei, D. Enhance of theta EEG spectral activity related to the memorization of commercial advertisings in Chinese and Italian subjects. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Informatics (BMEI), Shanghai, China, 15–17 October 2011; Volume 3, pp. 1491–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klimesch, W. Alpha-band oscillations, attention, and controlled access to stored information. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2012, 16, 606–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiloni, F. Mental Workload Monitoring: New Perspectives from Neuroscience. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Borghini, G.; Ronca, V.; Vozzi, A.; Aricò, P.; Di Flumeri, G.; Babiloni, F. Monitoring performance of professional and occupational operators. In Handbook of Clinical Neurology; Elsevier B.V.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 168, pp. 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, M.S.; Brookhuis, K.A.; Wickens, C.D.; Hancock, P.A. State of science: Mental workload in ergonomics. Ergonomics 2015, 58, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arns, M.; Conners, C.K.; Kraemer, H.C. A Decade of EEG Theta/Beta Ratio Research in ADHD: A Meta-Analysis. J. Atten. Disord. 2013, 17, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, H.; Busch, K.; Studer, P.; Erbe, K.; Moll, G.H.; Kratz, O. EEG spectral analysis of attention in ADHD: Implications for neurofeedback training? Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Qiu, S.; He, H. Time-Distributed Attention Network for EEG-Based Motor Imagery Decoding From the Same Limb. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabilitation Eng. 2022, 30, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillas-Romero, A.; Tortella-Feliu, M.; Bornas, X.; Putman, P. Spontaneous EEG theta/beta ratio and delta–beta coupling in relation to attentional network functioning and self-reported attentional control. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 15, 598–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Flumeri, G.; De Crescenzio, F.; Berberian, B.; Ohneiser, O.; Kramer, J.; Aricò, P.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Bagassi, S.; Piastra, S. Brain–Computer Interface-Based Adaptive Automation to Prevent Out-Of-The-Loop Phenomenon in Air Traffic Controllers Dealing With Highly Automated Systems. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kumada, T. Relationship between workload and mind-wandering in simulated driving. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smallwood, J. Mind wandering and attention. In The Handbook of Attention; Boston Review: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 233–255. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Tompkins, W.J. A Real-Time QRS Detection Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1985, 32, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramshur, J. Design, Evaluation, and Application of Heart Rate Variability Analysis Software (HRVAS). Electronic Theses and Dissertations. July 2010. Available online: https://digitalcommons.memphis.edu/etd/83 (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Benedek, M.; Kaernbach, C. Decomposition of skin conductance data by means of nonnegative deconvolution. Psychophysiology 2010, 47, 647–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassab, S.E.; El-Baz, A.; Hassan, N.; Hamdy, H.; Mamede, S.; Schmidt, H.G. Construct validity of a questionnaire for measuring student engagement in problem-based learning tutorials. BMC Med. Educ. 2023, 23, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, P.; Coates, H.; Mcinnis, C.; James, R. The Development of an Extended Course Experience Questionnaire. Qual. High. Educ. 2003, 9, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Estrada, E.; Villaseñor, J.A.; Acosta-Pech, R. Shapiro-Wilk test for multivariate skew-normality. Comput. Stat. 2022, 37, 1985–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakdash, J.Z.; Marusich, L.R. Repeated measures correlation. Front. Psychol. 2017, 8, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivan, M.; Vaknin, S.; Peleg, N.; Ackerman, R.; Horowitz-Kraus, T. Higher theta-beta ratio during screen-based vs. printed paper is related to lower attention in children: An EEG study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0283863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabès, A.; Klencklen, G.; Ruggeri, P.; Antonietti, J.-P.; Lavenex, P.B.; Lavenex, P. Age-Related Differences in Resting-State EEG and Allocentric Spatial Working Memory Performance. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 704362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, V.; Di Flumeri, G.; Vozzi, A.; Giorgi, A.; Arico, P.; Sciaraffa, N.; Babiloni, F.; Borghini, G. Validation of an EEG-based Neurometric for online monitoring and detection of mental drowsiness while driving. In Proceedings of the 2022 44th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine & Biology Society (EMBC), Glasgow, UK, 11–15 July 2022; Volume 2022, pp. 3714–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, V.; Martinez-Levy, A.C.; Vozzi, A.; Giorgi, A.; Aricò, P.; Capotorto, R.; Borghini, G.; Babiloni, F.; Di Flumeri, G. Wearable Technologies for Electrodermal and Cardiac Activity Measurements: A Comparison between Fitbit Sense, Empatica E4 and Shimmer GSR3+. Sensors 2023, 23, 5847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capotorto, R.; Ronca, V.; Sciaraffa, N.; Borghini, G.; Di Flumeri, G.; Mezzadri, L.; Vozzi, A.; Giorgi, A.; Germano, D.; Babiloni, F.; et al. Cooperation objective evaluation in aviation: Validation and comparison of two novel approaches in simulated environment. Front. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1409322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronca, V.; Uflaz, E.; Turan, O.; Bantan, H.; MacKinnon, S.N.; Lommi, A.; Pozzi, S.; Kurt, R.E.; Arslan, O.; Kurt, Y.B.; et al. Neurophysiological Assessment of An Innovative Maritime Safety System in Terms of Ship Operators’ Mental Workload, Stress, and Attention in the Full Mission Bridge Simulator. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, S.; Pokhrel, S.R. Analysis, Modeling and Design of Personalized Digital Learning Environment. arXiv 2024. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.10476v1 (accessed on 5 May 2024).
- Van Schoors, R.; Elen, J.; Raes, A.; Vanbecelaere, S.; Depaepe, F. The Charm or Chasm of Digital Personalized Learning in Education: Teachers’ Reported Use, Perceptions and Expectations. TechTrends 2023, 67, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Technologies and Tools for Creating Adaptive E-Learning Content. Математика и инфoрматика 2020, 63, 382–390.
- Apoki, U.C.; Al-Chalabi, H.K.M.; Crisan, G.C. From Digital Learning Resources to Adaptive Learning Objects: An Overview. Commun. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 1126, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subject | Mean Artifact (%) |
|---|---|
| Participant 1 | 5.88 |
| Participant 2 | 6.93 |
| Participant 3 | 7.41 |
| Participant 4 | 6.89 |
| Participant 5 | 7.71 |
| Participant 6 | 6.22 |
| Participant 7 | 7.09 |
| Participant 8 | 6.57 |
| Participant 9 | 7.81 |
| Participant 10 | 6.02 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronca, V.; Aricò, P.; Tamborra, L.; Biagi, A.; Di Flumeri, G. A Multimodal Neurophysiological Approach to Evaluate Educational Contents in Terms of Cognitive Processes and Engagement. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060597
Ronca V, Aricò P, Tamborra L, Biagi A, Di Flumeri G. A Multimodal Neurophysiological Approach to Evaluate Educational Contents in Terms of Cognitive Processes and Engagement. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(6):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060597
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonca, Vincenzo, Pietro Aricò, Luca Tamborra, Antonia Biagi, and Gianluca Di Flumeri. 2025. "A Multimodal Neurophysiological Approach to Evaluate Educational Contents in Terms of Cognitive Processes and Engagement" Bioengineering 12, no. 6: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060597
APA StyleRonca, V., Aricò, P., Tamborra, L., Biagi, A., & Di Flumeri, G. (2025). A Multimodal Neurophysiological Approach to Evaluate Educational Contents in Terms of Cognitive Processes and Engagement. Bioengineering, 12(6), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12060597









