Micron-Sized Fe3O4/PCL Biocomposite Scaffolds to Attract Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fe3O4/PCL Scaffolds Preparation
2.2. Degradability of Scaffolds in Simulated Body Fluid
2.3. Mouse Cells Culture
2.4. Cytotoxicity Assay of Fe3O4/PCL Scaffolds
2.5. Animal Experiment
2.6. Histological Assessment
2.7. Real-Time PCR
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
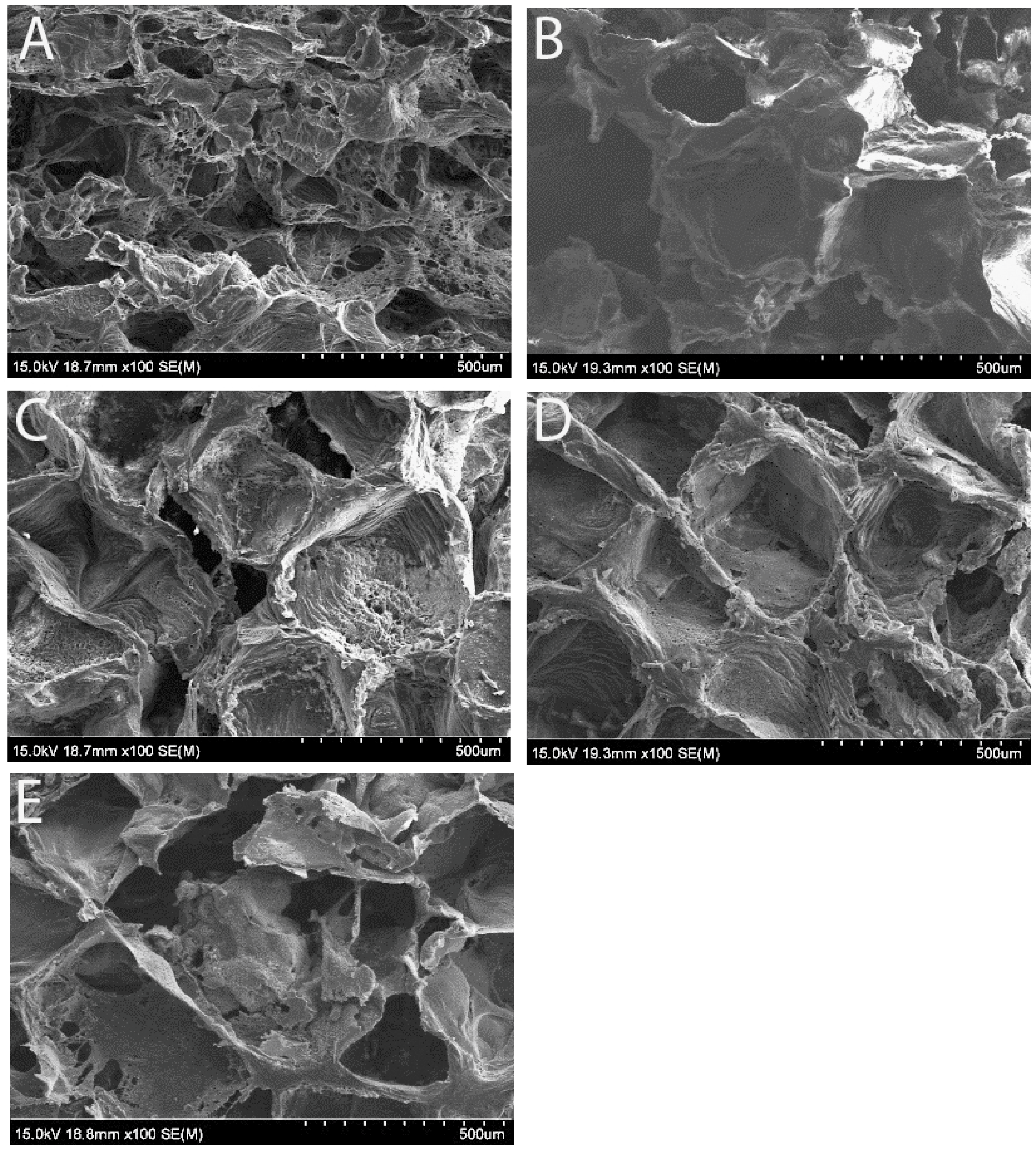
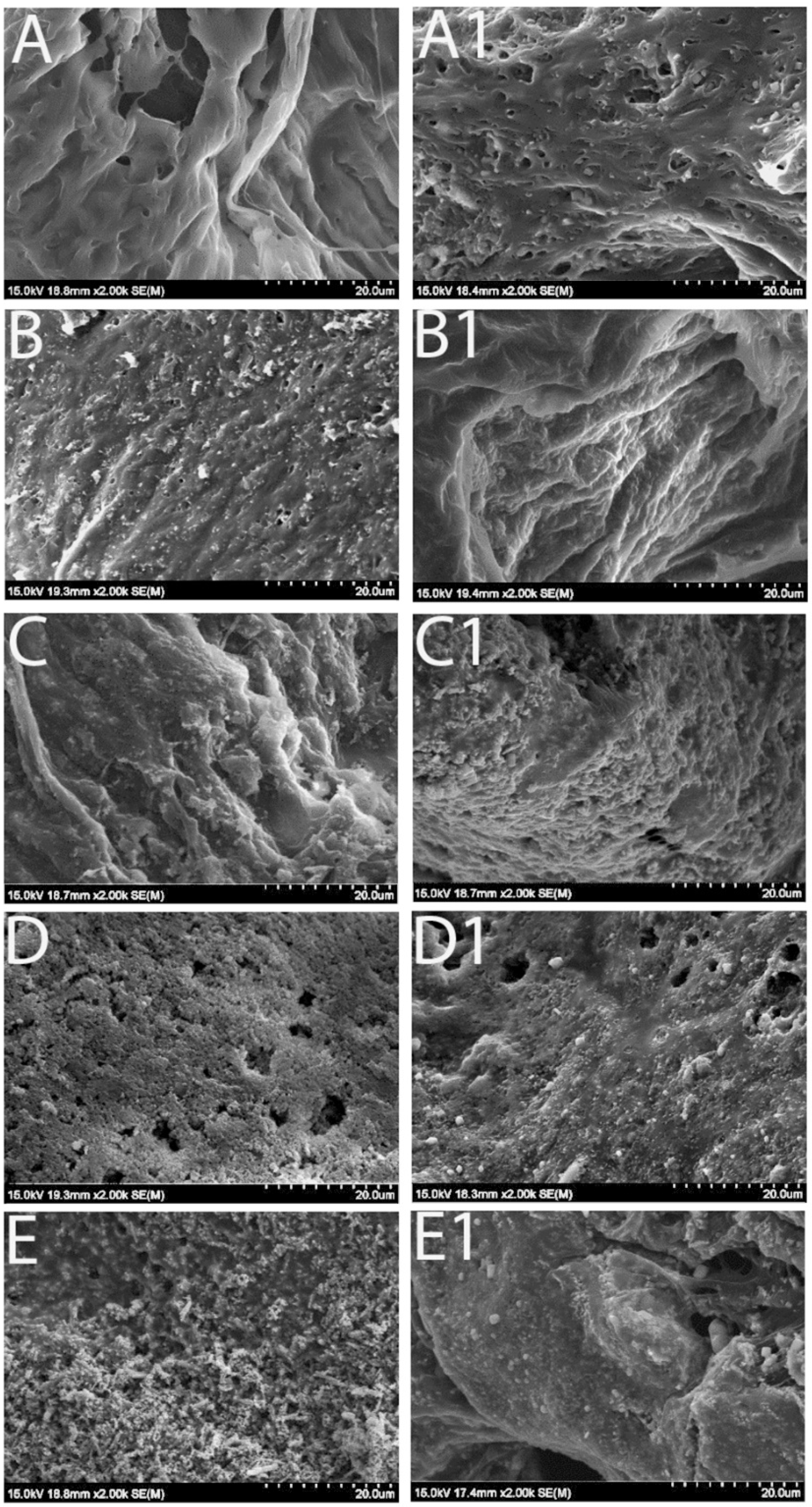
3.1. Scaffold Morphology Under Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
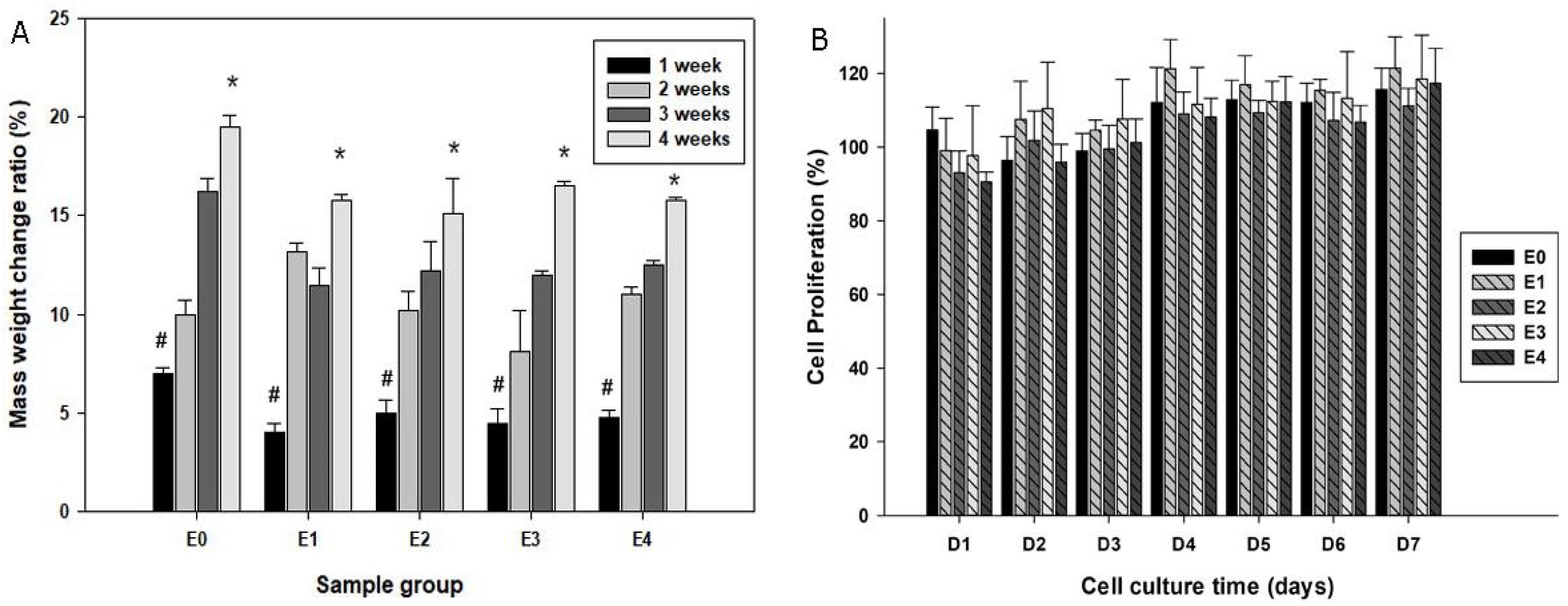
3.2. Degradability of Scaffolds in SBF
3.3. Biocompatibility of the Scaffolds
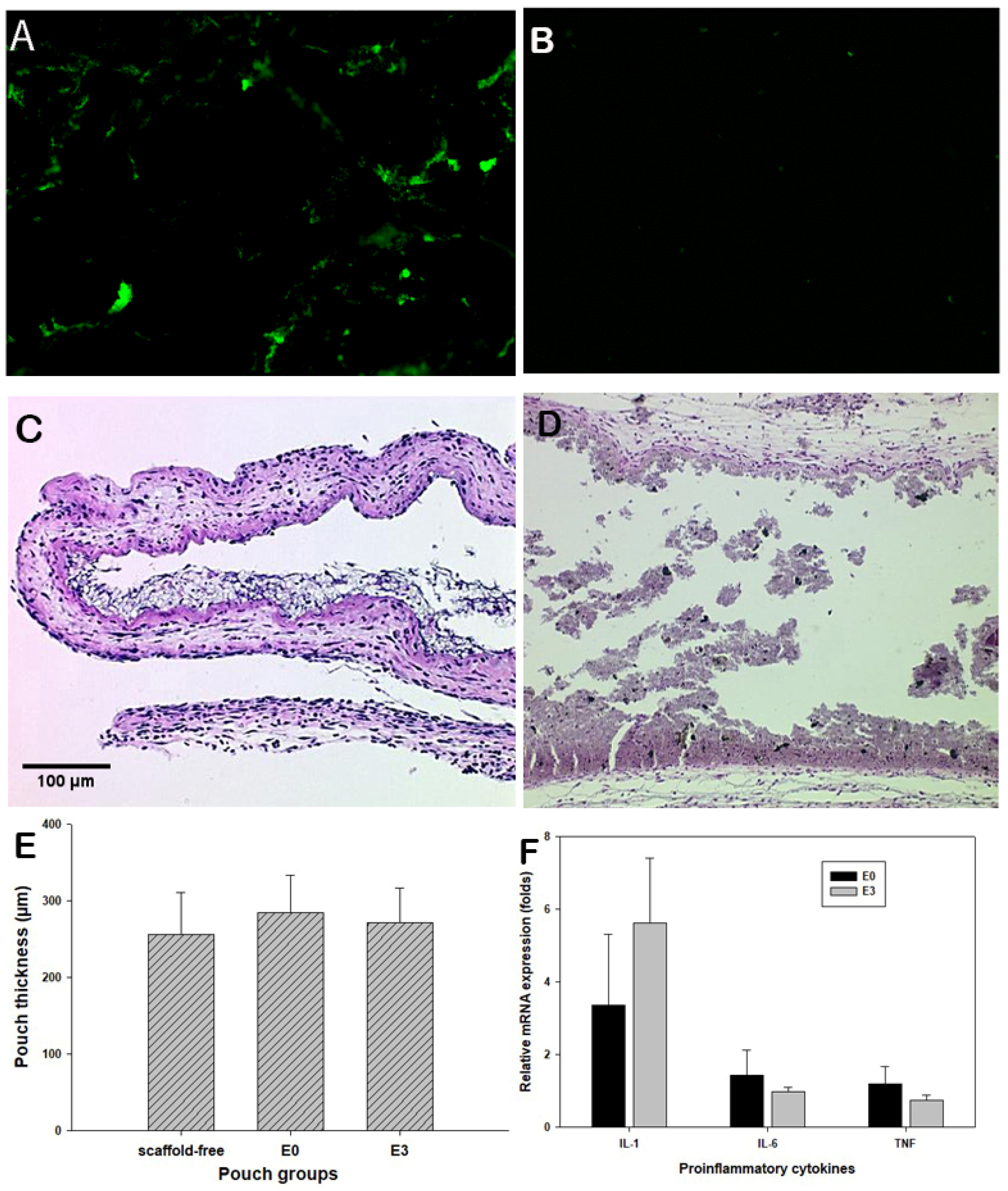
3.4. Murine Air Pouch Model for Targeted Drug Delivery
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCL | polycaprolactone |
| MTDDS | magnetic targeted drug delivery system |
| SBF | simulated body fluid |
| H&E | hematoxylin and eosin staining |
| RT-PCR | reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Jensen, C.; Madsen, D.H.; Hansen, M.; Schmidt, H.; Svane, I.M.; Karsdal, M.A.; Willumsen, N. Non-invasive biomarkers derived from the extracellular matrix associate with response to immune checkpoint blockade (anti-CTLA-4) in metastatic melanoma patients. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolini, L.; Poli, C.; Blanchard, S.; Urban, T.; Croue, A.; Rousselet, M.C.; Le Roux, S.; Labarriere, N.; Jeannin, P.; Hureaux, J. Thoracic and cutaneous sarcoid-like reaction associated with anti-PD-1 therapy: Longitudinal monitoring of PD-1 and PD-L1 expression after stopping treatment. J. Immunother. Cancer 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fan, L.; Xu, H.; Qin, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Wei, J.; Qian, Z.; et al. HSP90AA1 is an unfavorable prognostic factor for hepatocellular carcinoma and contributes to tumorigenesis and chemotherapy resistance. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 50, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanton, C.; Bernard, E.; Abbosh, C.; Andre, F.; Auwerx, J.; Balmain, A.; Bar-Sagi, D.; Bernards, R.; Bullman, S.; DeGregori, J.; et al. Embracing cancer complexity: Hallmarks of systemic disease. Cell 2024, 187, 1589–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, H.; Han, X. Magnetic field triggered drug release from lipid microcapsule containing lipid-coated magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 706, 455–460. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Yu, X.; Qin, W.; Wang, T.; Jia, Z.; Xiao, R.; Qi, C. Preparation and anti-Raji lymphoma efficacy of a novel pH sensitive and magnetic targeting nanoparticles drug delivery system. Bioorganic Chem. 2020, 94, 103375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceylan, M.; Misak, H.E.; Strong, N.; Yang, S.-Y.; Asmatulu, R. Reduced toxicity of protein/magnetic targeted drug delivery system for improved skin cancer treatment in mice model. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2021, 539, 168404. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Huang, T.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L.; Liao, S.; Gong, X.; Bello, M.G.; Zhu, W.; Huang, S.; Zhang, X. Loading curcumin on hyperbranched polymers functionalized Zein via the phenol-yne click reaction as pH-responsive drug delivery system for chemotherapy and photodynamic therapy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 293, 139750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, H.; Deng, J.; Xu, W.; Zhao, C.; Lu, Q.; He, Z.; Sun, B.; Tian, C.; et al. Enabling oral novel Taxanes-based Chemotherapy with Lipophilic prodrug Self-nanoemulsifying drug delivery system. Bioorganic Chem. 2024, 153, 107902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bi, H.-Y.; Li, H.; Mao, X.-M.; Liang, Y.-Q. Synthesis, characterization, and sustained release property of Fe3O4@(enrofloxacin-layered double hydroxides) nanocomposite. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 886–891. [Google Scholar]
- Maheswari, P.U.; Muthappa, R.; Bindhya, K.P.; Begum, K.M.S. Evaluation of folic acid functionalized BSA-CaFe2O4 nanohybrid carrier for the controlled delivery of natural cytotoxic drugs hesperidin and eugenol. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102105. [Google Scholar]
- Sattarahmady, N.; Azarpira, N.; Hosseinpour, A.; Heli, H.; Zare, T. Albumin coated arginine-capped magnetite nanoparticles as a paclitaxel vehicle: Physicochemical characterizations and in vitro evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2016, 36, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Hou, Y. Magnetic Micro/nanorobots in Cancer Theranostics: From Designed Fabrication to Diverse Applications. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 7444–7481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Z.; Wen, W.; Guo, Z.; Song, X.-Z.; Zheng, K.; Xu, X.; Qi, X.; Tan, Z. SiO2-coated magnetic nano-Fe3O4 photosensitizer for synergistic tumour-targeted chemo-photothermal therapy. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 195, 111274. [Google Scholar]
- Gonbadi, P.; Jalal, R.; Akhlaghinia, B.; Ghasemzadeh, M.S. Tannic acid-modified magnetic hydrotalcite-based MgAl nanoparticles for the in vitro targeted delivery of doxorubicin to the estrogen receptor-overexpressing colorectal cancer cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 68, 103026. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xu, M.; Zhang, J.; Dong, W. Magnetic field-driven drug release from modified iron oxide-integrated polysaccharide hydrogel. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 108, 558–567. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Q.; Tan, Z.; Zheng, D.; Qiu, X. pH-responsive magnetic Fe3O4/carboxymethyl chitosan/aminated lignosulfonate nanoparticles with uniform size for targeted drug loading. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 225, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, L.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, R.; Yang, G. Superparamagnetic chitosan nanocomplexes for colorectal tumor-targeted delivery of irinotecan. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 584, 119394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedin, F.; Anwar, M.R.; Asmatulu, R.; Yang, S.Y. Albumin-based micro-composite drug carriers with dual chemo-agents for targeted breast cancer treatment. J. Biomater. Appl. 2015, 30, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misak, H.E.; Asmatulu, R.; Gopu, J.S.; Man, K.P.; Zacharias, N.M.; Wooley, P.H.; Yang, S.Y. Albumin-based nanocomposite spheres for advanced drug delivery systems. Biotechnol. J. 2014, 9, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wamocha, H.L.; Misak, H.E.; Song, Z.; Chu, H.Y.; Chen, Y.Y.; Asmatulu, R.; Yang, S.Y.; Ho, J.C. Cytotoxicity of release products from magnetic nanocomposites in targeted drug delivery. J. Biomater. Appl. 2013, 27, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kweon, H.; Yoo, M.K.; Park, I.K.; Kim, T.H.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, H.S.; Oh, J.S.; Akaike, T.; Cho, C.S. A novel degradable polycaprolactone networks for tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Matthew, H.W.; Wooley, P.H.; Yang, S.Y. Effect of porosity and pore size on microstructures and mechanical properties of poly-epsilon-caprolactone- hydroxyapatite composites. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2008, 86, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Miyaji, F.; Kokubo, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Soga, N.; Nakamura, T. Apatite formation on silica gel in simulated body fluid: Effects of structural modification with solvent-exchange. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1998, 9, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Wooley, P.H.; Yang, S.-Y. Biocompatibility of Poly-ε-caprolactone-hydroxyapatite composite on mouse bone marrow-derived osteoblasts and endothelial cells. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2009, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Asmatulu, R.; Zhu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, S.Y. Synthesis and Properties of Magnetic Fe3O4/PCL Porous Biocomposite Scaffolds with Different Sizes and Quantities of Fe3O4 Particles. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wooley, P.H.; Morren, R.; Andary, J.; Sud, S.; Yang, S.Y.; Mayton, L.; Markel, D.; Sieving, A.; Nasser, S. Inflammatory responses to orthopaedic biomaterials in the murine air pouch. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Jia, T.; Gong, W.; Ning, B.; Wooley, P.H.; Yang, S.Y. Macrophage Polarization in IL-10 Treatment of Particle-Induced Inflammation and Osteolysis. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.Y.; Wu, B.; Mayton, L.; Mukherjee, P.; Robbins, P.D.; Evans, C.H.; Wooley, P.H. Protective effects of IL-1Ra or vIL-10 gene transfer on a murine model of wear debris-induced osteolysis. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z.; Jia, J.; Zhu, J.; Miao, X.; Yan, B. Initiation of targeted nanodrug delivery in vivo by a multifunctional magnetic implant. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 20771–20778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Kubican, S.E.; Yi, Z.; Tong, S. Advances in magnetic nanoparticles for molecular medicine. Chem. Commun. 2025, 61, 3093–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, J.; Zhai, M.; Zhang, Y.; Bian, J.; Wu, J. Biocompatible Fe3O4/chitosan scaffolds with high magnetism. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 128, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.J.; Meredith, C.; Johnson, C.; Galis, Z.S. The effect of scaffold degradation rate on three-dimensional cell growth and angiogenesis. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 5735–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Scaffold ID | Fe3O4 (w/w, %) | PCL (w/w, %) |
|---|---|---|
| E0 | 0 | 100 |
| E1 | 5 | 95 |
| E2 | 10 | 90 |
| E3 | 20 | 80 |
| E4 | 40 | 60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ge, J.; Drees, R.; Wang, A.; Zhu, B.; Yang, S.-Y. Micron-Sized Fe3O4/PCL Biocomposite Scaffolds to Attract Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040371
Ge J, Drees R, Wang A, Zhu B, Yang S-Y. Micron-Sized Fe3O4/PCL Biocomposite Scaffolds to Attract Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(4):371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040371
Chicago/Turabian StyleGe, Jianhua, Riley Drees, Aoran Wang, Bo Zhu, and Shang-You Yang. 2025. "Micron-Sized Fe3O4/PCL Biocomposite Scaffolds to Attract Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery" Bioengineering 12, no. 4: 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040371
APA StyleGe, J., Drees, R., Wang, A., Zhu, B., & Yang, S.-Y. (2025). Micron-Sized Fe3O4/PCL Biocomposite Scaffolds to Attract Magnetic Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Bioengineering, 12(4), 371. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12040371








