Orthodontic Bracket Removal and Enamel Roughness: Comparing the Effects of Sapphire and Metallic Brackets in an In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection and Ethical Approval
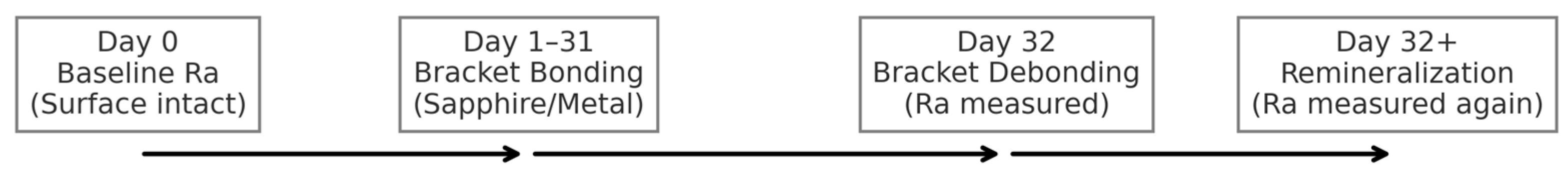
2.2. Experimental Design and Workflow
- Stage 1 (Day 0): Baseline assessment of the intact enamel surface.
- Stage 2 (Day 32): Assessment immediately after bracket debonding.
- Stage 3 (Day 32+): Final assessment following a 10-day remineralization protocol.
2.3. Sample Size Determination
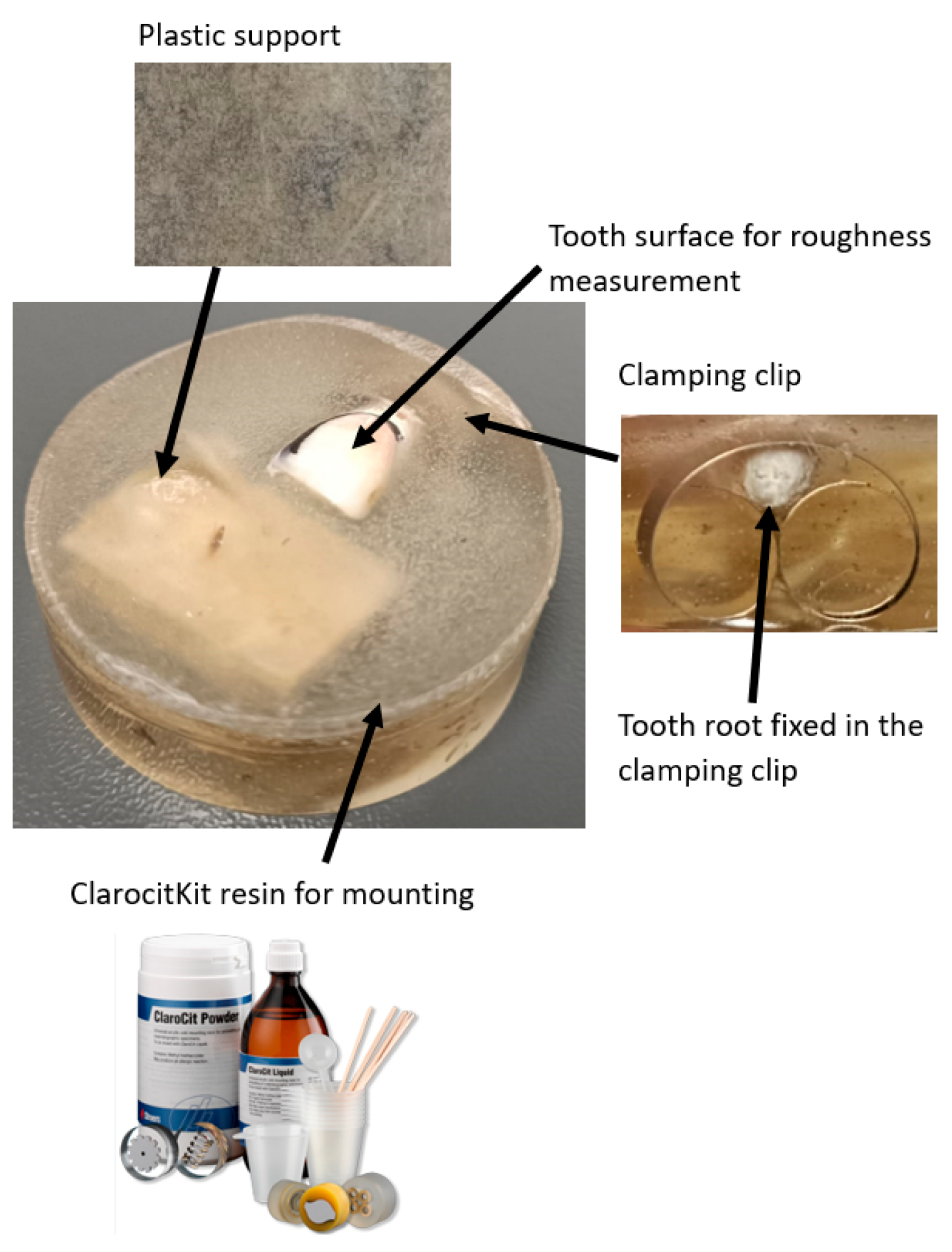
2.4. Tooth Preparation and Disinfection
2.5. Experimental Group Allocation
- Group A: Teeth with sapphire brackets applied (n = 100).
- Group B: Teeth with metallic brackets applied (n = 100).
2.6. Bracket Bonding and Photopolymerization
2.7. Debracketing Procedure and Post-Treatment Analysis
2.8. Remineralization Protocol
2.9. Instrumentation
- -
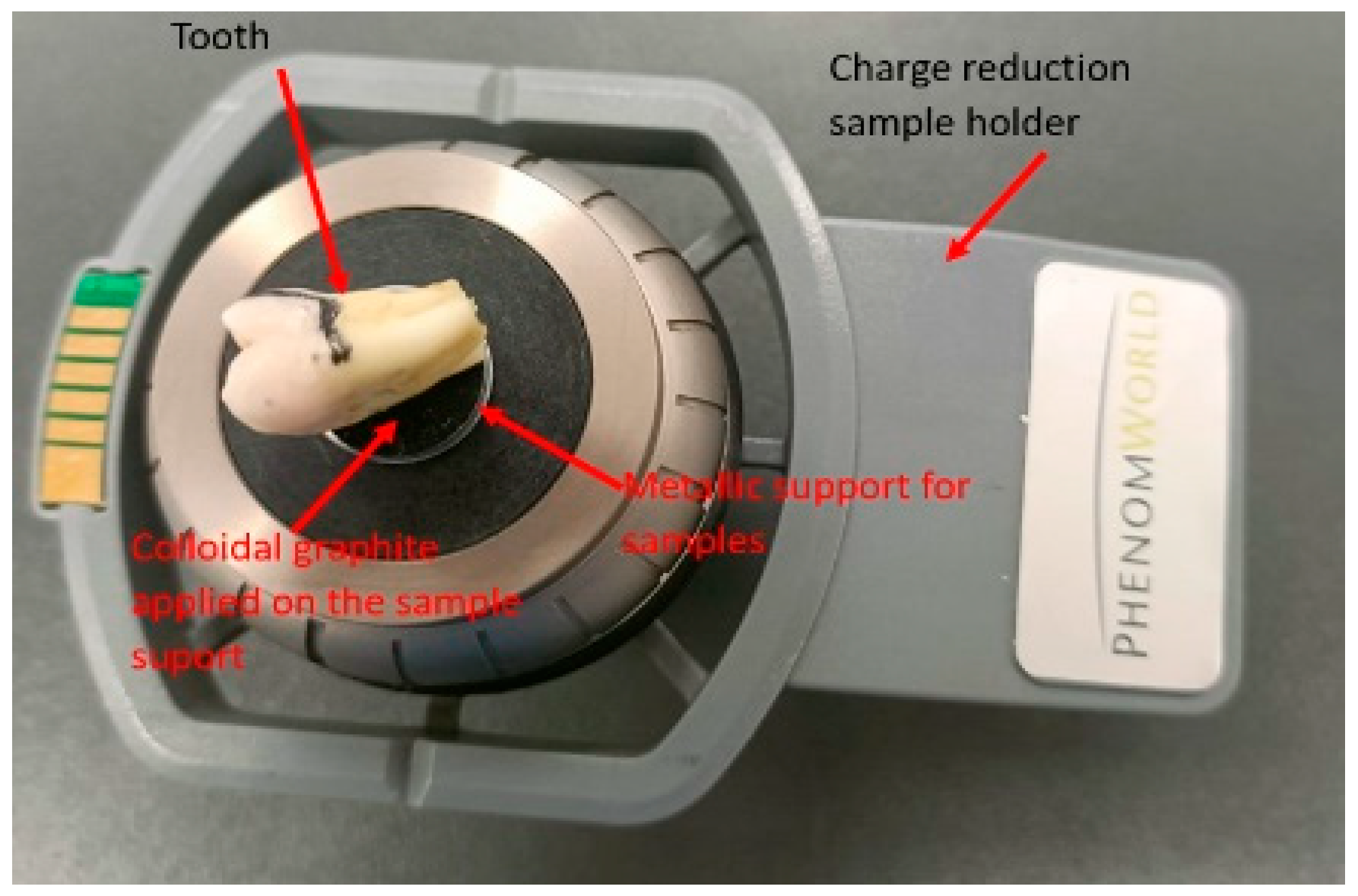
- Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): A Phenom Pure ProX scanning electron microscope (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), equipped with a backscattered electron detector, was used for qualitative and morphological analysis of the enamel surface. The instrument was operated at an accelerating voltage of 15 keV, and images were captured at magnifications of ×1000 and ×2000.
- -
- A TR200 roughness tester (Salu Tron Messtechnik GmbH, Frechen, Germany) was used for quantitative topographical analysis. The instrument was calibrated to measure the surface roughness parameters Ra (arithmetic mean deviation) and Rz (average height of irregularities) with a precision of ±0.01 μm.
2.10. Comparative Roughness Measurement Using TR200 Profilometer
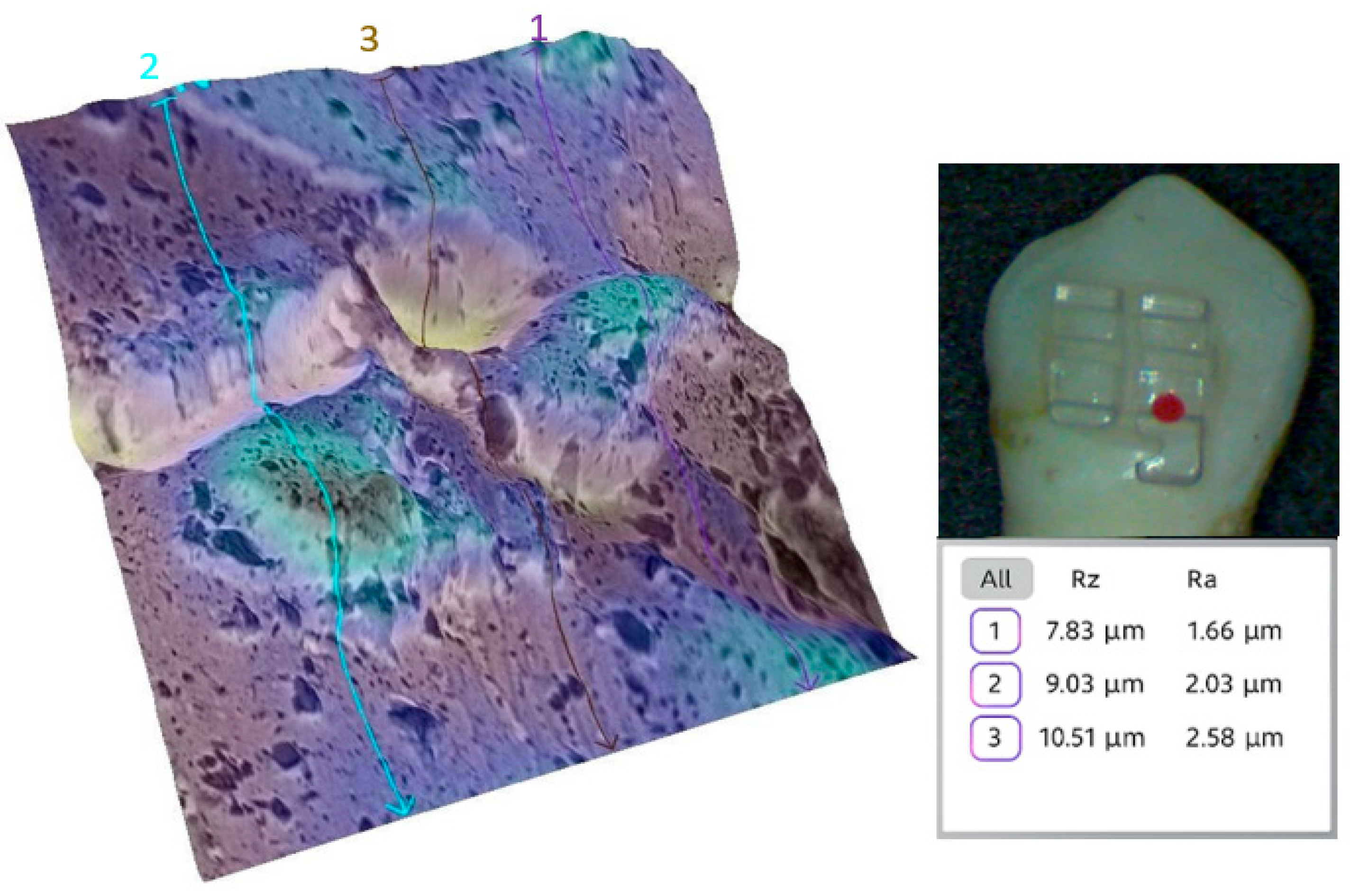
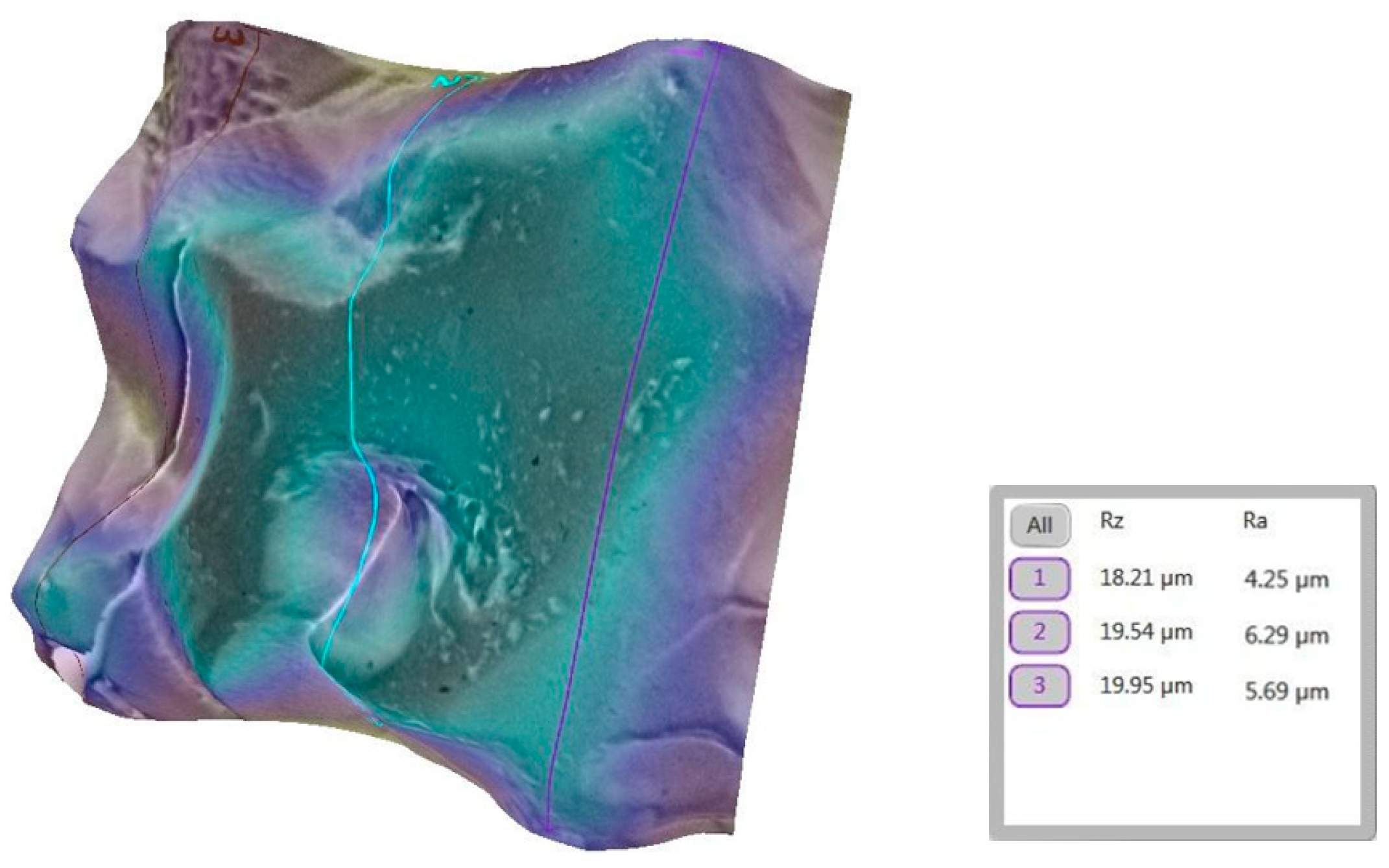
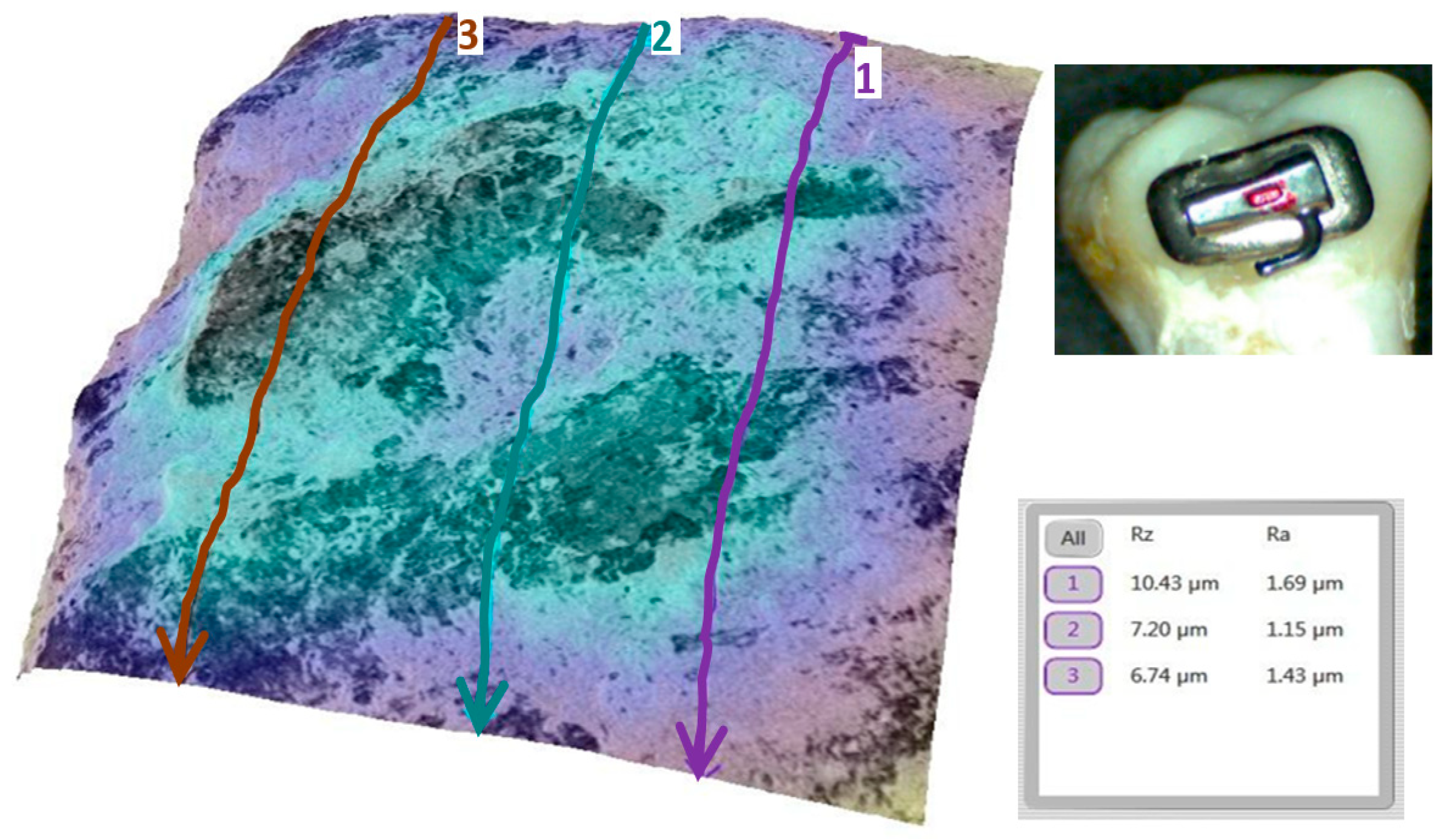
2.11. Surface Selection and Preparation for SEM Analysis
2.12. SEM Imaging and 3D Roughness Reconstruction
2.13. Surface Roughness Analysis
2.14. Statistical Analysis
- -
- Group A1: Contains the experimental data for 100 teeth before the bonding of sapphire brackets.
- -
- Group A2: Contains the experimental data for 100 teeth after the debonding of sapphire brackets.
- -
- Group A3: Contains the experimental data for 100 teeth after the debonding of sapphire brackets and the application of the remineralization treatment.
- -
- Group B1: Contains the experimental data for 100 teeth before the bonding of metallic brackets.
- -
- Group B2: Contains the experimental data for 100 teeth after the debonding of metallic brackets.
- -
- Group B3: Contains the experimental data for 100 teeth after the debonding of metallic brackets and the application of the remineralization treatment.
3. Results
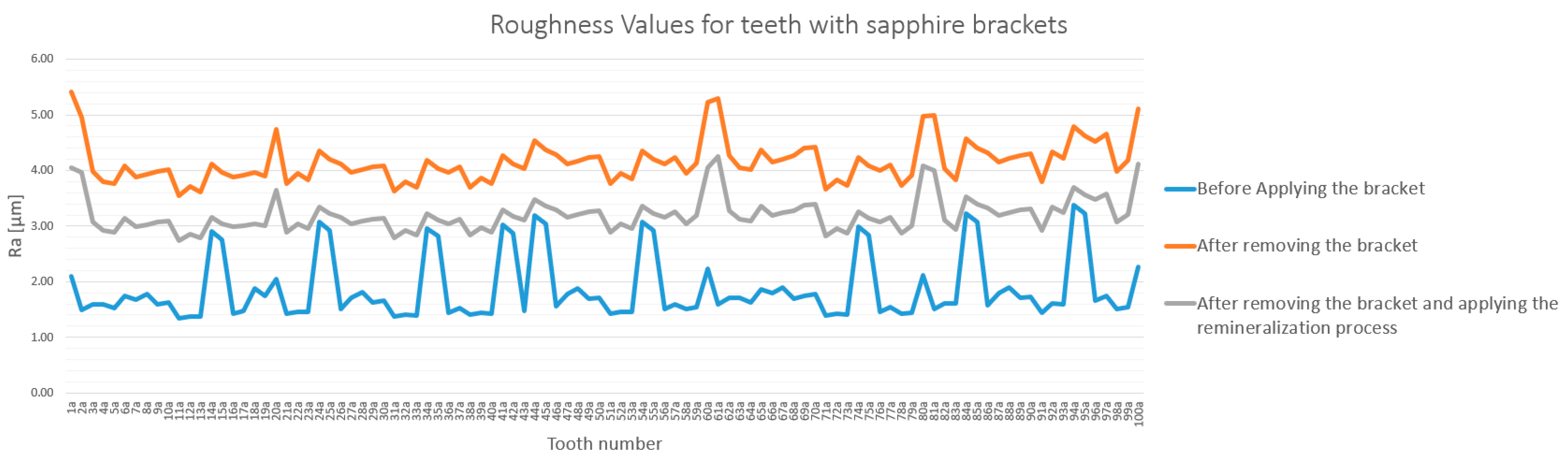
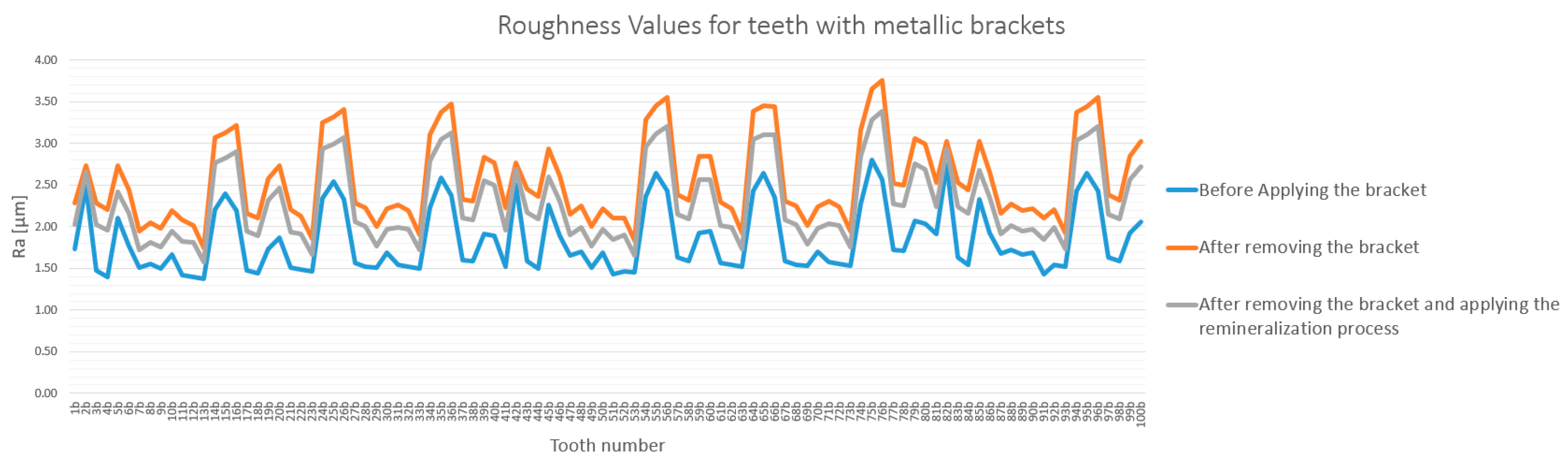
3.1. General Analysis of Enamel Surface Roughness
3.2. Qualitative and Cross-Validation Analysis
3.3. Method Cross-Validation with TR200 Profilometer
3.4. Detailed Statistical Confirmation
- Both bracket types significantly increased enamel roughness.
- Sapphire brackets caused a statistically significant higher increase in roughness than metallic brackets did.
- Remineralization significantly reduced roughness in both groups, but failed to restore the enamel to its original state.
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparisons with Other Studies
4.2. Methodological Considerations
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Strengths and Contributions of Study
4.5. Study Significance and Scope
4.6. Clinical Significance of Surface Roughness Changes
4.7. Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Beniash, E.; Stifler, C.A.; Sun, C.-Y.; Jung, G.S.; Qin, Z.; Buehler, M.J.; Gilbert, P.U.P.A. The hidden structure of human enamel. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacruz, R.S.; Habelitz, J.T.; Paine, M.L. Dental Enamel Formation and Implications for Oral Health and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 939–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjos, M.; Barroso, R.C.; Pérez, C.A.; Braz, D.; Moreira, S.; Dias, K.R.H.C.; Lopes, R.T. Elemental mapping of teeth using micro-XRF and micro-CT. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. At. 2004, 213, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Veis, A. Enamel formation and implications for regenerative dentistry. Front. Dent. Med. 2023, 4, 117. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, G.M.; Abouauf, E.A.; AbuBakr, N.; Dörfer, C.E.; El-Sayed, K.F. Tissue engineering approaches for enamel, dentin, and pulp regeneration: An update. Stem Cells Int. 2020, 2020, 5734539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iplinsky, N.T.; Gandini Junior, L.G.; Gandini, A.S.; Bagatini, A.T.; Oliveira, P.H.J.; Silva, P.C.H.; Santos-Pinto, A. Radiographic evaluation of enamel thickness of pemanent teeth: Relevance and applicability. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2024, 29, e242422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasam, V.; Rangarajan, H.; Easwaran, H.N.; Muthu, M.S. Proximal enamel thickness of the permanent teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2021, 160, 793–804.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado-Álvarez, M.; Muñoz-Soto, E.; Torres-Rosas, R.; Lauritano, D.; Strietzel, F.P.; Petrucci, A.; Piras, F. Effects of Interproximal Enamel Reduction on the Periodontium: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6831. [Google Scholar]
- Livas, C.; Jongsma, A.C.; Ren, Y. Enamel reduction Techniques in Orthodontics: A Literature Review. Open Dent. L 2013, 7, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekharan, D.; Sourabh, C.; Katepogu Praveen, D. Enamel surface roughness evaluation after bracket debonding: Comparision between light cure and self cure adhesive resin 3-Dimesional profilometric study. Indian J. Res. 2022, 33, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Křivková, T.; Tichý, A.; Tycová, H.; Kučera, J. The Influence of Various Adhesive Systems and Polishing Methods on Enamel Surface Roughness after Debonding of Orthodontic Brackets: A Three-Dimensional In Vitro Evaluation. Materials 2023, 16, 5107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øgaard, B.; Fjeld, M. The enamel surface and bonding in orthodontics. Semin. Orthod. 2010, 16, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thawaba, A.A.; Albelasy, N.F.; Elsherbini, A.M.; Hafez, A.M. Evaluation of enamel roughness after orthodontic debonding and clean-up procedures using zirconia, tungsten carbide, and white stone burs: An in vitro study. BMC Oral. Health 2023, 23, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, M.R.; Kazemi, P.; Shirkhani, A.M. Comparison of Enamel Surface Roughness after Orthodontic Brackets Debonding and Surface Polishing with Restorative and Orthodontic Composites. Res. J. Pharm. Technol. 2024, 17, 734–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øgaard, B.; Brantley, W.A.; Eliades, T. Oral Microbiological Changes, Long-Term Enamel Alterations Due to Decalcification and Caries Prophylactic Aspects. In Orthodontic Materials: Scientific and Clinical Aspects; Thieme: Stuttgart, Germany, 2001; p. 127. [Google Scholar]
- Song, H.; Liu, Z.; Zou, Z. Biomimetic Construction of the Enamel-like Hierarchical Structure. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2023, 39, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Den Besten, P.K.; Diekwisch, T.G.H. Editorial: Tooth enamel research: Enamel 10 and beyond. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1323504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolone, G.; Mandurino, M.; Baldani, S.; Paolone, M.G.; Goracci, C.; Scolavino, S.; Gherlone, E.; Cantatore, G.; Gastaldi, G. Quantitative Volumetric Enamel Loss after Orthodontic Debracketing/Debonding and Clean-Up Procedures: A Systematic Review. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thys, D.G.; Pizzolatti Martins, F.R.; Cardinal, L.; Ribeiro, G.L.U. In vitro enamel surface roughness analysis of 4 methods for removal of remaining orthodontic adhesive after bracket debonding. Angle Orthod. 2023, 93, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsigialou, N.; Sifakakis, I.; Zinelis, S.; Papageorgiou, S.N.; Eliades, T. Manual and mechanical stripping-induced enamel waviness, roughness and elemental composition in vivo. Eur. J. Orthod. 2023, 45, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafopoulou, S.; Zafeiriadis, A.A.; Tsolakis, A.I. Enamel Defects During Orthodontic Treatment. Balk. J. Dent. Medicine 2018, 22, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shutkla, C.; Singh, G.; Jain, U.; Swamy, K. Comparison of Mean Shear Bond Strenght of Light Cure, Self Cure, Self-Cure Composite Resins, Self-Etching and Moisture-Insensitive primers: An in Vitro Study. J. Ind. Orthod. Soc. 2012, 46, 254–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasser, L.A.; Saeid, A.W. Effect of early orthodontic force in shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets bonded with different adhesive systems. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2010, 138, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.-Z.; Lai, E.H.-H.; Chang, J.Z.-C.; Chen, H.-J.; Chang, F.H.-F.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-P. Effect of simulated debracketing on enamel damage. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2012, 111, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollen, C.M.; Lambrechts, P.; Quirynen, M. Comparison of surface roughness of oral hard materials to the threshold surface roughness for bacterial plaque retention: A review of the literature. Dent. Mater. 1997, 13, 258–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tărâță, M.; Georgescu, D.; Badea, P.; Ovidiu, A.D.; Șerbănescu, M.S.; Cătălin, M.N. Medical Informatics and Biostatistics; University Medical Publishing House Craiova: Craiova, Romania, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Zawawi, R.N.; Almosa, N.A. Assessment of enamel surface roughness and hardness with metal and ceramic orthodontic brackets using different etching and adhesive systems: An in vitro study. Saudi Dent. J. 2023, 35, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent-Bugnas, S.; Borsa, L.; Gruss, A.; Lupi, L. prioritization of predisposing factors of gingival hyperplasia during orthodontic treatment: The role of amount of biofilm. BMC Oral. Health 2021, 21, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 21920-2:2022; Geometrical Product Specifications (GPS)—Surface Texture: Profile—Part 2: Terms, Definitions and Surface Texture Parameters. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Ahrari, F.; Akbari, M.; Akbari, J. Enamel Surface Roughness after Debonding of Orthodontic Brackets and Various Clean-Up Techniques. J. Dent. 2013, 10, 82–93. [Google Scholar]
- Hamdi, K.; Elsebaai, A.; Abdelshafi, M.A.; Hamama, H.H. Remineralization and anti-demineralization effect of orthodontic adhesives on enamel surrounding orthodontic brackets: A systematic review of in vitro studies. BMC Oral. Health 2024, 24, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolokitha, O.-E. Role of Third Molars in Orthodontics: A Review. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Sigiliao, L.C.; Marquezan, M.; Elias, C.N.; Ruellas, A.C.; Sant’Anna, E.F. Efficiency of different for enamel clean-up after bracket debonding: An in vitro study. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2015, 20, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almosa, N.A.; Alqasir, A.M.; Aldekhayyil, M.A.; Aljelayel, A.; Aldosari, M.A. Enamel demineralization around two different orthodontic bracket adhesive systems: An in vivo study. Saudi Dent. J. 2019, 31, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidor, M.M.; Felix, R.P.; Marchioro, E.M.; Hahn, L. Enamel surface evaluation after bracket debnding and different resin removal methods. Dental. Press. J. Orthod. 2015, 20, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorn, B.; Masucci, C.; Ceinos, R.; Charavet, C. Orthodontic debonding and enamel surface integrity. A systematic review of the literature. Orthod. Fr. 2024, 95, 261–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kakaboura, A.; Fragouli, M.; Rahiotis, C.; Silikas, N. Evaluation of surface characteristics of dental composites using profilometry, scanning electron, atomic force microscopy and gloss-meter. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2007, 18, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karan, S.; Kircelli, B.H.; Tasdelen, B. Enamel surface rough ness after debonding. Angle. Orthod. 2010, 80, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohebi, S.; Shafiee, H.A.; Ameli, N. Evaluation of enamel surface roughness after orthodontic bracket debonding with atomic force microscopy. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, G.M.; Al-Dabagh, D.J.N. Assessment of Enamel Surface after Debonding of Different Types of Esthetic Brackets (An In Vitro Study). J. Baghdad Coll. Dent. 2024, 36, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugsompian, K.; Tansalarak, R.; Piyapattamin, T. Comparison of the enamel surface roughness from different polishing methods: Scanning electron microscopy and atomic force microscopy investigation. Eur. J. Orthod. 2020, 14, 299–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albuquerque, G.D.S.; Filho, M.V.; Lucato, A.S.; Boeck, E.M.; Degan, V.; Kuramae, M. Evaluation of enamel roughness after ceramic bracket debonding and clean-up with different methods. Braz. J. Oral. Sci. 2010, 9, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Caixeta, R.V.; Berger, S.B.; Lopes, M.B.; Paloco, E.A.C.; Faria, E.M.; Contreras, E.F.R.; Gonini, A.; Guiraldo, R.D. Evaluation of enamel roughness after the removal of brackets bonded with different materials: In vivo study, Braz. Dent. J. 2021, 32, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, H.; Ahrari, F.; Mohamadipour, H. The effect of different surface treatments of demineralised enamel on microleak age under metal orthodontic brackets. Prog. Orthod. 2013, 14, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares Tenorio, K.C.; Neupmann Feres, M.F.; Tanaka, C.J.; Augusto, M.K.M.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Pereira da Silva, H.D.; Arana-Chavez, V.E.; Roscoe, M.G. In vitro evaluation of enamel surface roughness and morphology after orthodontic debonding: Traditional cleanup systems versus polymer bur. Int. Orthod. 2020, 18, 546–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, L.A.; Valdrighi, H.C.; Vedovello Filho, M.; Correr, A.B. Effect of adhesive remnant removal enamel topography after bracket debonding. Dent. Press. J. Orthod. 2014, 19, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrescu, S.M.S.; Țuculină, J.M.; Osiac, E.; Camen, A.; Sălan, A.I.; Mărășescu, F.I.; Nicola, A.G.; Bechir, E.S.; Dascălu, I.T. Use of coherence tomography in orthodontic. Exp. Ther. Medicine 2021, 22, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özer, T.; Bașaran, G.; Devecioğlu, K. Surface roughness of the restored enamel after orthodontic treatment. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthopedics 2010, 137, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinzan-Vercelino, C.R.M.; Souza Costa, A.C.; Gurgel, A.; Salvatore Freitas, K.M. Comparison of enamel surface roughness and color alteration after bracket debonding and polishing with 2 systems: A split-mouth clinical trial. AJO-DO 2021, 160, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megh, S.; Rao, V.V.; Minor Babu, M.S.; Satyam, M.; Pallepati, A.; Mythraiye, R.; Paravada, C. An In-vitro Comparison of the Shear Bond Strength of Three Different Composite Materials with Three Different Etchants for the Bonding of Orthodontic Brackets. Cureus 2019, 11, e4944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. GPower 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aref, Y.; Al-Jureisi, A.; El-Oqlah, A.; Duree, M. A review of the available methods for sterilization of extracted human teeth. Int. J. Dent. 2021, 2021, 6645395. [Google Scholar]
- Mullan, F.; Austin, R.S.; Parkinson, C.R.; Hasan, A.; Bartlett, D.W. Measurement of surface roughness changes of unpolished and polished enamel following erosion. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.-M.; Abutayyem, H. Future of Orthodontics—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis on Technological Advancements. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1462. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Izze, F.O.; Al-Ali, M.A.; Al-Shara, S.M.; El-Masry, M.A.; Zaca, O. Surface Roughness of Different Bulk-Fill Composite Restorative Materials after Polishing: An In Vitro Study. Polymers 2023, 15, 2450. [Google Scholar]
- Tărâţă, D.F.; Miriţoiu, C.M. Tehnici Avansate de Investigare a Materialelor; Sitech: Craiova, Romania, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Alipour Shoari, S.; Sadrolashrafi, S.V.; Sohrabi, A.; Afrouzian, R.; Ebrahimi, P.; Kouhsoltani, M.; Soltani, M.K. Estimating Mandibular Growth Stage Based on Cervical Vertebral Maturation Using Artificial Intelligence. Prog. Orthod. 2024, 25, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopal, R.; Padmanabhan, S.; Gnanamani, J. A Comparison of Shear Bond Strength and Debonding Characteristics of Conventional, MoistureInsensitive, and Self-etching Primers In Vitro. Angle Orthodontist. 2004, 74, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ekhlassi, S.; English, D.J.; Ontiveros, J.C.; Powers, J.M.; Bussa, H.I.; Frey, G.N.; Colville, C.D.; Ellis, R.K. Bond strength comparison of color-change adhesives for orthodontic bonding using a self-etching primer. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dent. 2011, 3, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, A.S.; Alves, L.S.; Zenkner, J.E.D.A.; Zanatta, F.B.; Maltz, M. Gingival enlargement in orthodontics patients: Effect of treatment duration. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 152, 477–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratten, J.; Wilson, M. Antimicrobial susceptibility and composition of microcosm dental plaques grown on enamel surfaces with different surface finishes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 86, 584–590. [Google Scholar]
- Aljamhan, A.; Habib, S.R.; Alsarhan, M.A.; Al Zahrani, B.; Al Otaibi, H.; Al Sunaidi, N. Effect of Finishing and Polishing on The Surface Roughness of Bulk Fill Composites. Open Dent. J. 2021, 15, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Feng, G.; Hu, B.; Tian, H.; Kuang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Song, J. Comparison of flash-free and conventional bonding systems: A systematic review and meta-analysis. The Angle Orthodontist. 2022, 92, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


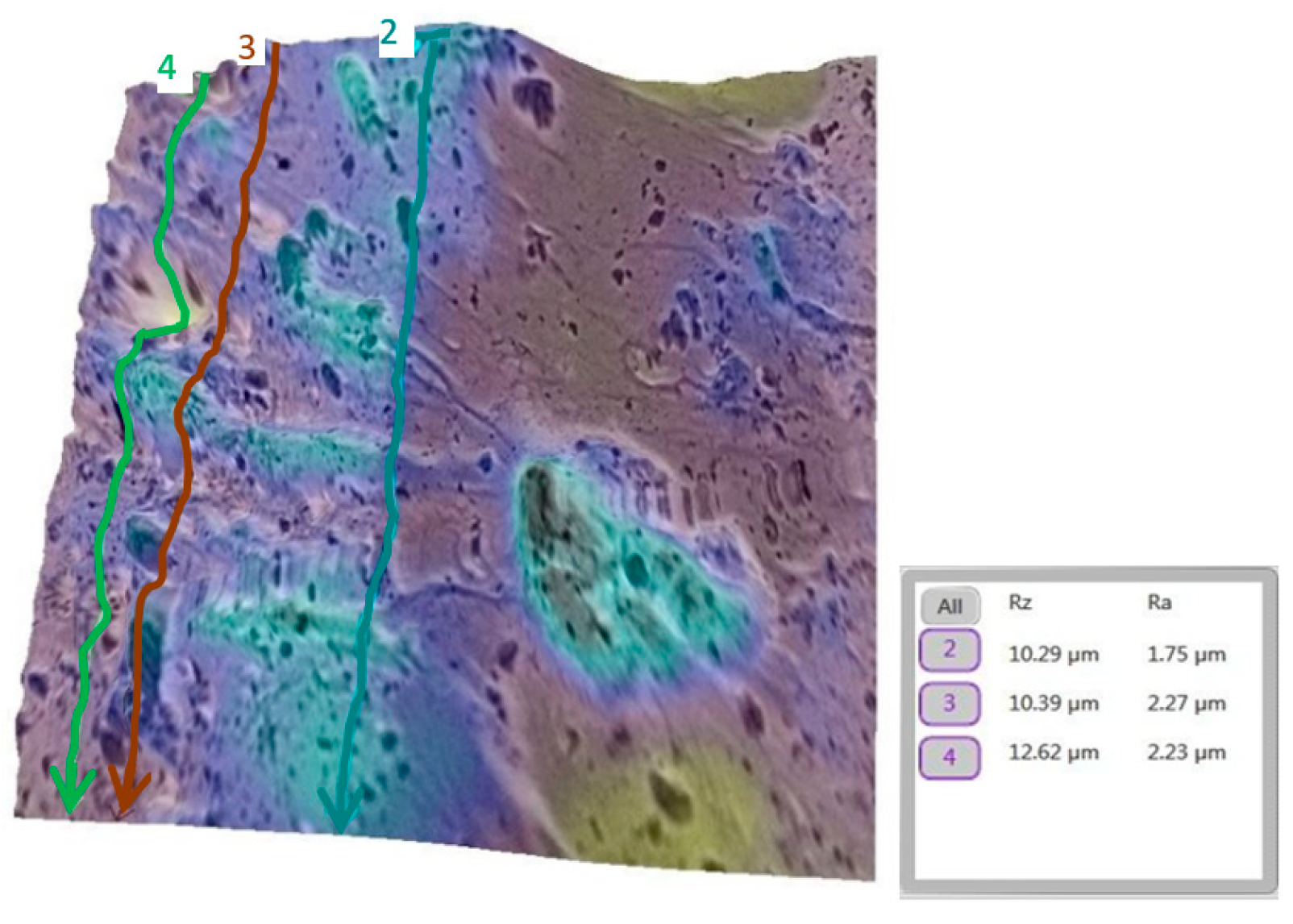
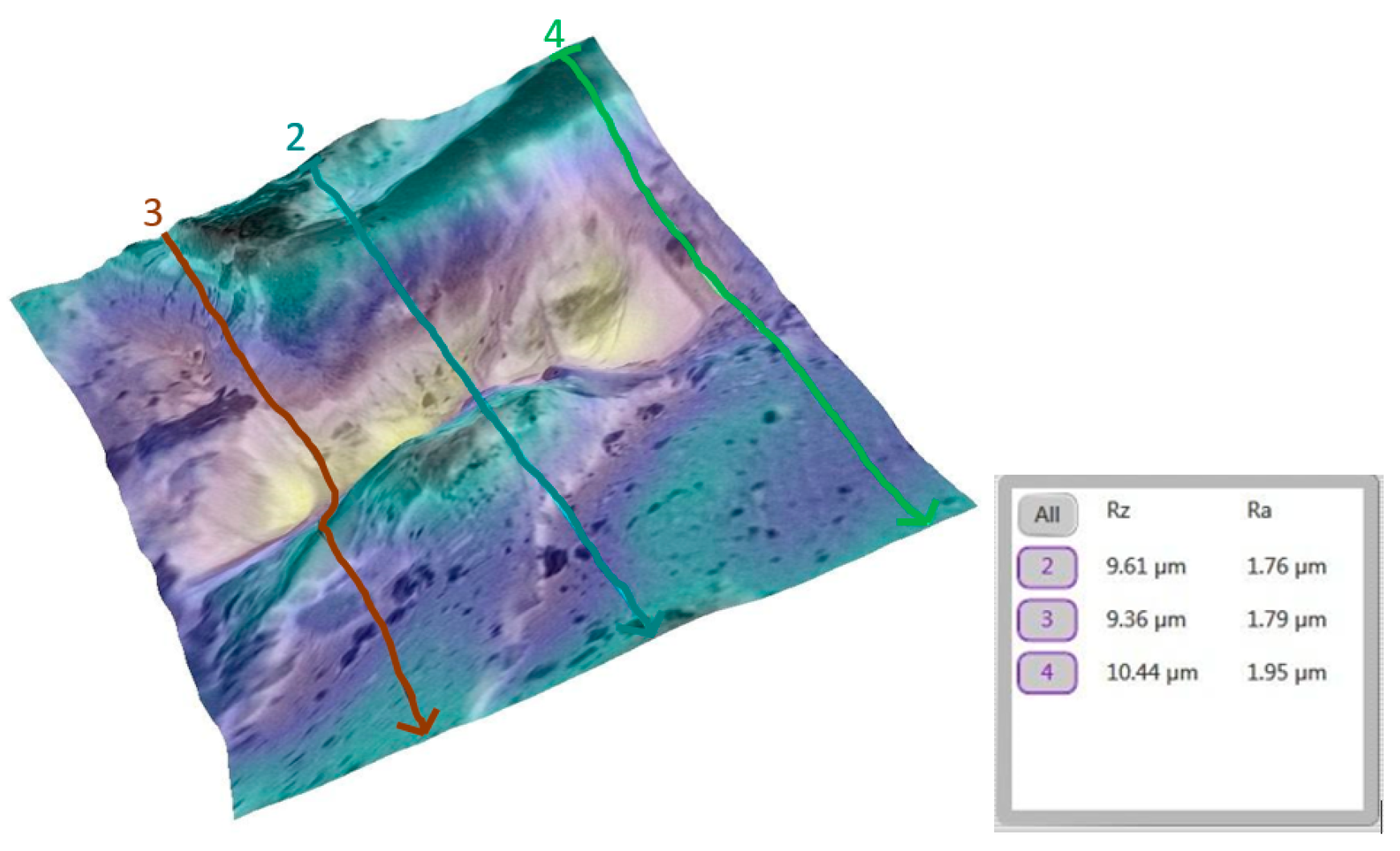
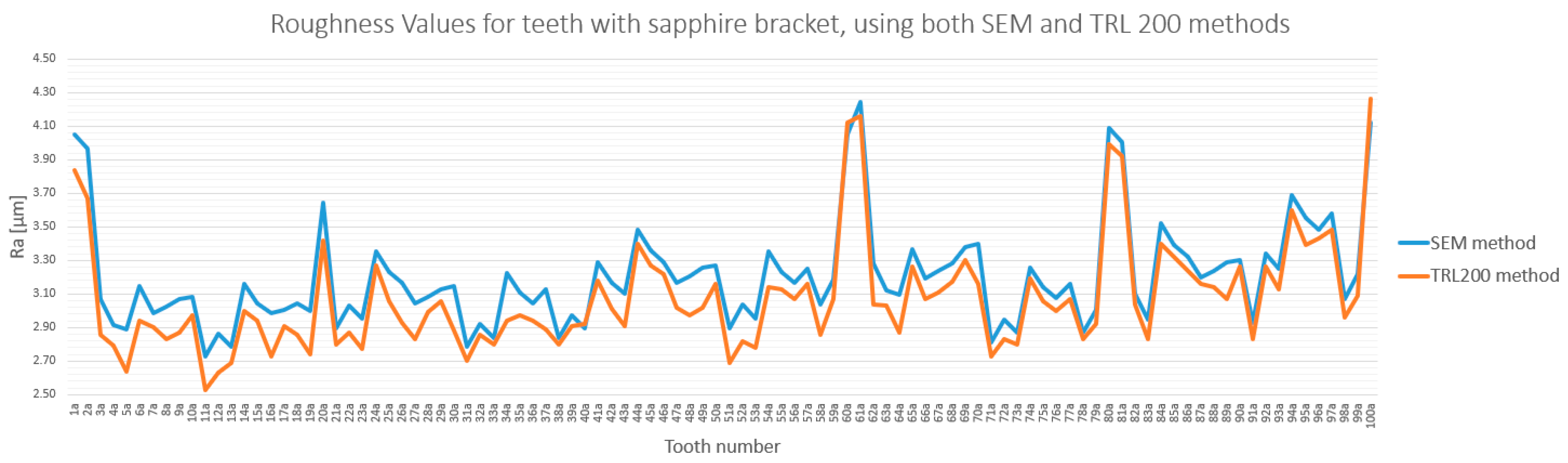
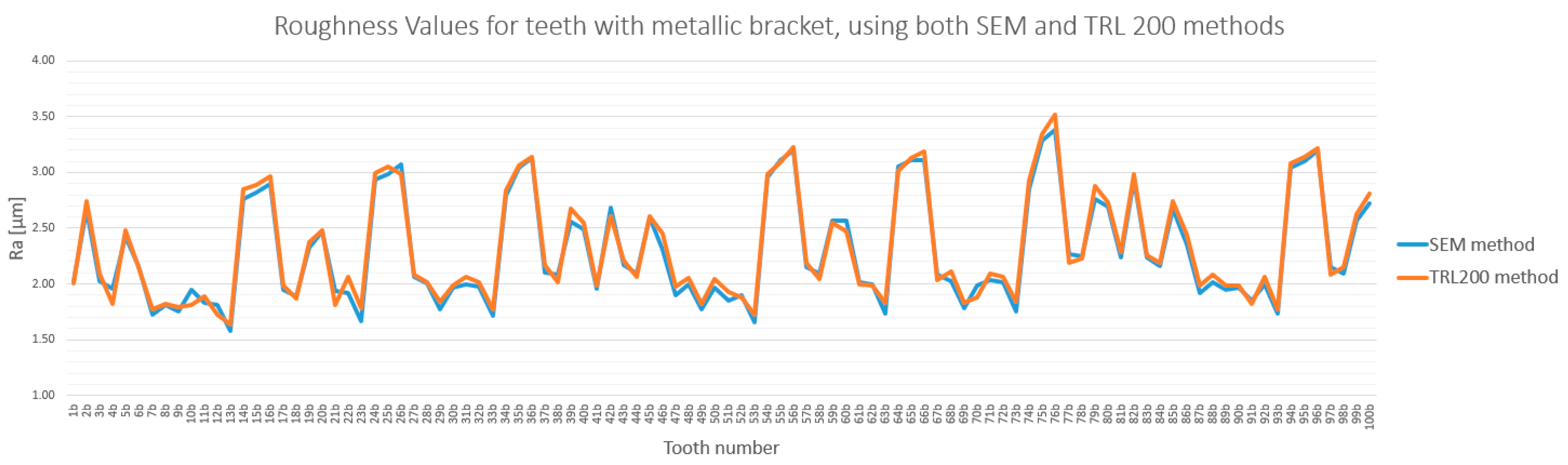
| Comparison | Description | Mean Difference (µm) | Statistically Significant (p < 0.0033) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A1 vs. A2 | Sapphire: Baseline vs. Post-debonding | 2.278 | Yes |
| A2 vs. A3 | Sapphire: Post-debonding vs. Post-remineralization | 0.950 | Yes |
| A2 vs. B2 | Sapphire vs. Metallic (Post-debonding) | 1.585 | Yes |
| A3 vs. B3 | Sapphire vs. Metallic (Post-remineralization) | 0.898 | Yes |
| B1 vs. B2 | Metallic: Baseline vs. Post-debonding | 0.713 | Yes |
| B2 vs. B3 | Metallic: Post-debonding vs. Post-remineralization | 0.262 | Yes |
| Group | Mean Ra (µm) | SD | n | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 | 1.8665 | 0.5747 | 100 | 1.754 | 1.979 |
| A2 | 4.1441 | 0.3622 | 100 | 4.073 | 4.215 |
| A3 | 3.1946 | 0.2971 | 100 | 3.136 | 3.253 |
| B1 | 1.8453 | 0.3977 | 100 | 1.768 | 1.922 |
| B2 | 2.5586 | 0.5161 | 100 | 2.457 | 2.660 |
| B3 | 2.2962 | 0.4771 | 100 | 2.203 | 2.390 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Licsăndroiu, C.B.; Țuculină, M.J.; Bugălă, A.S.; Mărășescu, P.C.; Mărășescu, F.I.; Nicola, A.G.; Cumpătă, C.N.; Mirițoiu, C.M.; Gheorghe, O.I.; Bezna, M.C.; et al. Orthodontic Bracket Removal and Enamel Roughness: Comparing the Effects of Sapphire and Metallic Brackets in an In Vitro Study. Bioengineering 2025, 12, 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101041
Licsăndroiu CB, Țuculină MJ, Bugălă AS, Mărășescu PC, Mărășescu FI, Nicola AG, Cumpătă CN, Mirițoiu CM, Gheorghe OI, Bezna MC, et al. Orthodontic Bracket Removal and Enamel Roughness: Comparing the Effects of Sapphire and Metallic Brackets in an In Vitro Study. Bioengineering. 2025; 12(10):1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101041
Chicago/Turabian StyleLicsăndroiu, Cosmin Bogdan, Mihaela Jana Țuculină, Adelina Smaranda Bugălă, Petre Costin Mărășescu, Felicia Ileana Mărășescu, Andreea Gabriela Nicola, Cristian Niky Cumpătă, Cosmin Mihai Mirițoiu, Ovidiu Ioan Gheorghe, Maria Cristina Bezna, and et al. 2025. "Orthodontic Bracket Removal and Enamel Roughness: Comparing the Effects of Sapphire and Metallic Brackets in an In Vitro Study" Bioengineering 12, no. 10: 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101041
APA StyleLicsăndroiu, C. B., Țuculină, M. J., Bugălă, A. S., Mărășescu, P. C., Mărășescu, F. I., Nicola, A. G., Cumpătă, C. N., Mirițoiu, C. M., Gheorghe, O. I., Bezna, M. C., Licsăndroiu, E. V., & Dascălu, I. T. (2025). Orthodontic Bracket Removal and Enamel Roughness: Comparing the Effects of Sapphire and Metallic Brackets in an In Vitro Study. Bioengineering, 12(10), 1041. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering12101041






