Optical Transmission in Single-Layer Brain Tissues under Different Optical Source Types: Modelling and Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
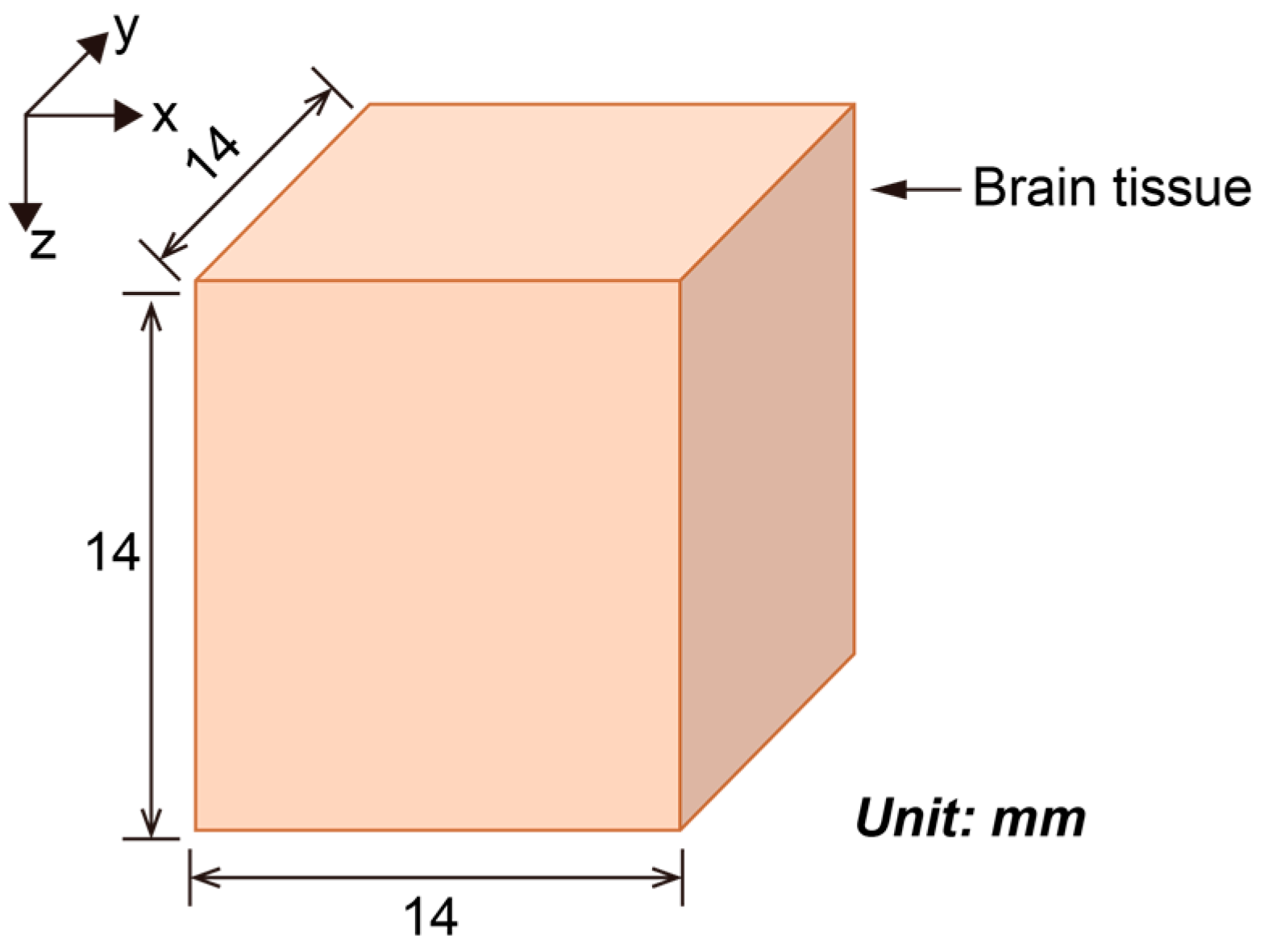
2.1. Simplified Brain Model
2.2. Optical Simulation Method
2.3. Various Types of Optical Sources
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Data Preprocessing
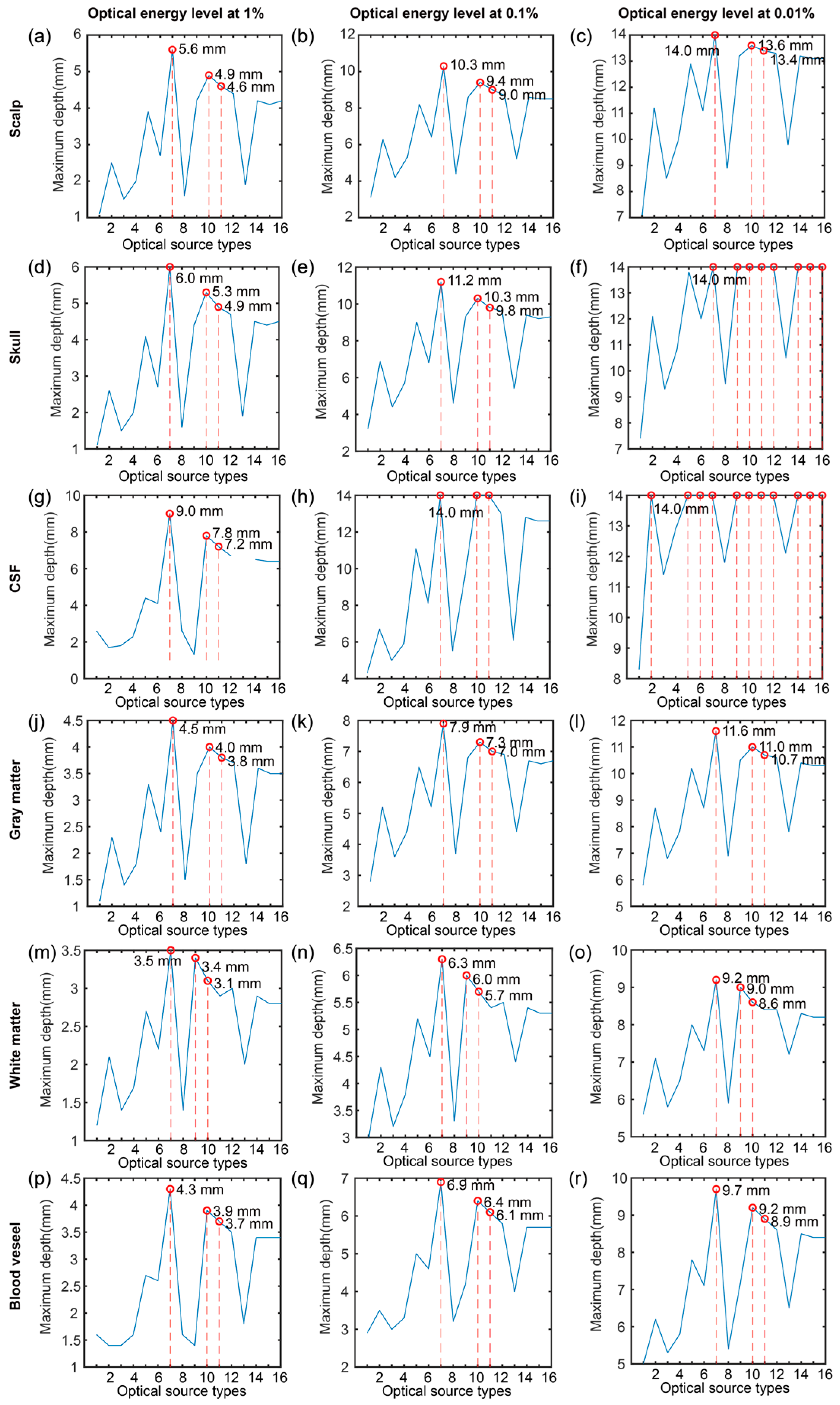
2.4.2. Propagating Depth Evaluation
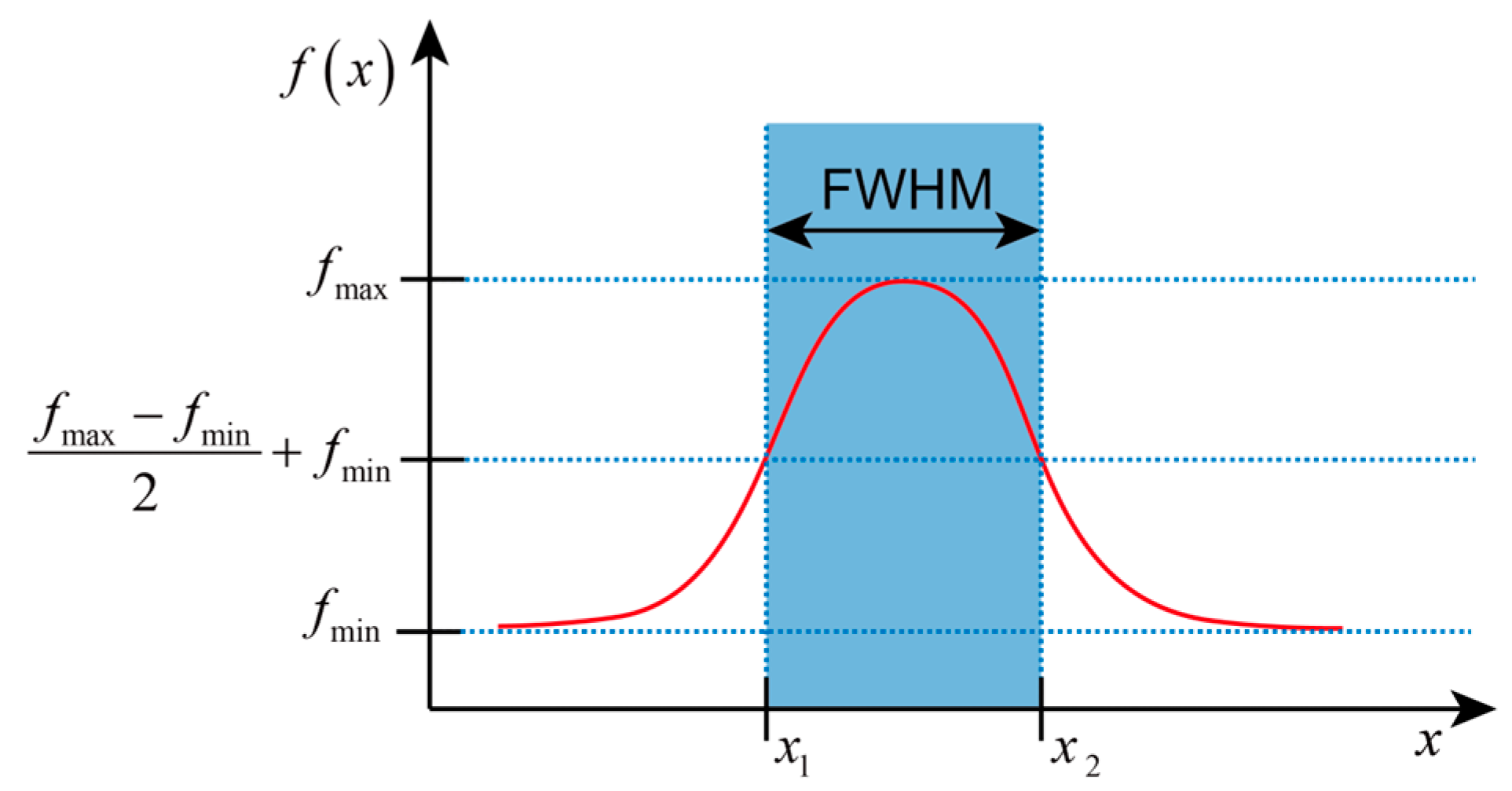
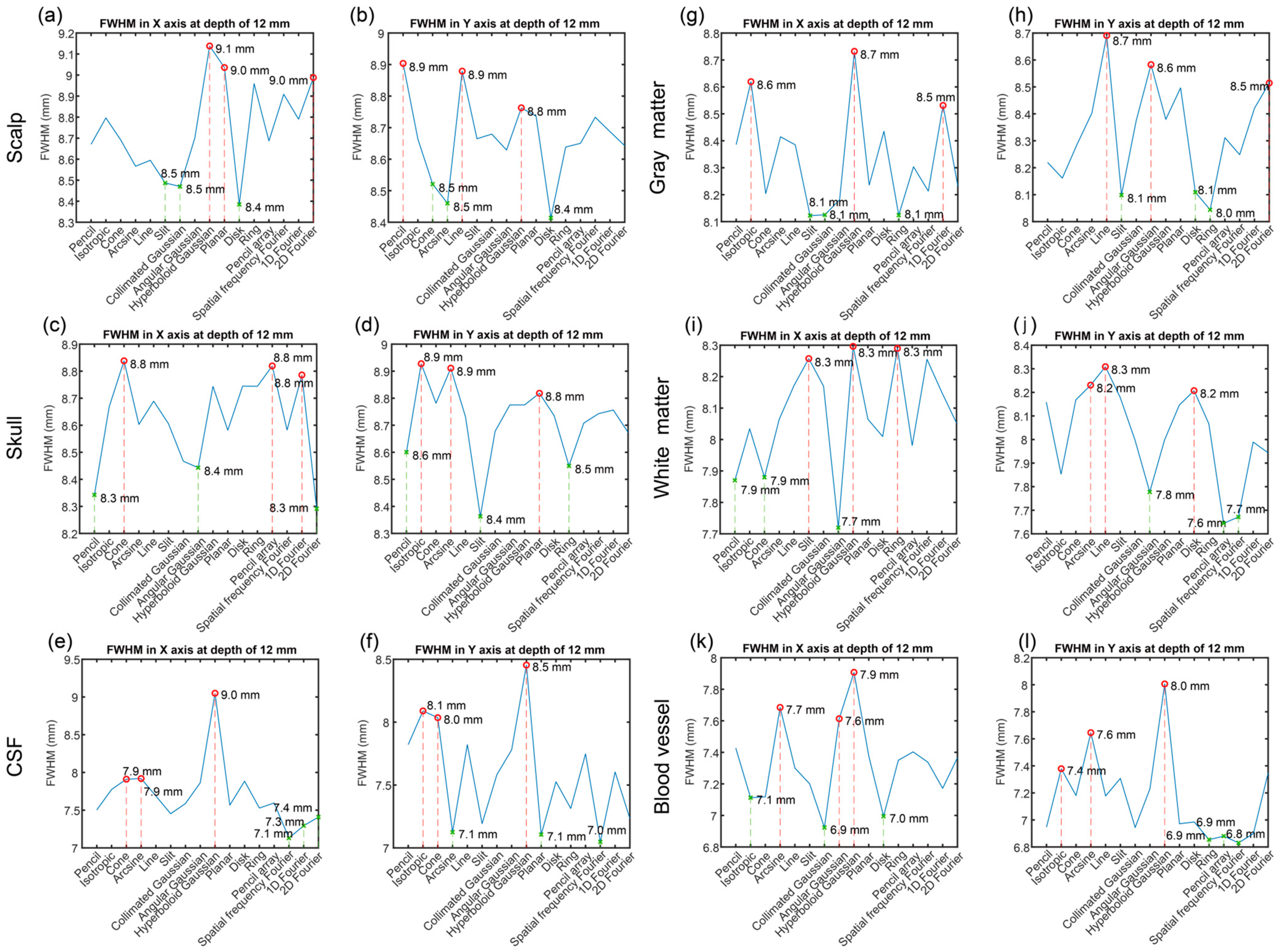
2.4.3. Optical Field Width Evaluation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Distribution in Different Planes
3.2. Optical Propagation in Vertical Direction
3.3. Optical Distribution in Horizontal Directions
3.4. Optical Source Types under Different Conditions
3.5. Discussion with Multi-Layer Brain Model
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Insel, T.R.; Landis, S.C.; Collins, F.S. The NIH BRAIN Initiative. Science 2013, 340, 687–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.H.; Xia, F.; Sawan, M. Photoacoustic imaging for monitoring of stroke diseases: A review. Photoacoustics 2021, 23, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic brain imaging: From microscopic to macroscopic scales. Neurophotonics 2014, 1, 011003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krol, A.; Thittai, A.K. Simulation of photoacoustic tomography (PAT) system in COMSOL and comparison of two popular reconstruction techniques. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2017: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging, Orlando, FL, USA, 11–16 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sivasubramanian, K.; Periyasamy, V.; Wen, K.K.; Pramanik, M. Optimizing light delivery through fiber bundle in photoacoustic imaging with clinical ultrasound system: Monte Carlo simulation and experimental validation. J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 22, 041008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Teng, A.; Chen, H.; Wei, J.; Song, L. Finite Element Simulation of the Interaction between Pulsed Laser and Mouse Brain. In Proceedings of the Optics Frontier: The 4th Optics Young Scientist Summit (OYSS 2020), Ningbo, China, 28 February 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, H.; Rebling, J.; Razansky, D. Prediction and near-field observation of skull-guided acoustic waves. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada, H.; Rebling, J.; Razansky, D. Observation of skull-guided acoustic waves in a water-immersed murine skull using optoacoustic excitation. In Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 28 January–2 February 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Estrada, H.; Rebling, J.; Turner, J.; Razansky, D. Broadband acoustic properties of a murine skull. Phys. Med. Biol. 2016, 61, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.; Yuan, X.; Lin, L.; Isla, J.; Garrett, D.; Wang, L.V. Transcranial photoacoustic computed tomography based on a layered back-projection method. Photoacoustics 2020, 20, 100213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Wang, R.; Yu, X.; Wei, J.; Song, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chen, W.; Wang, P.; Qiu, J.; et al. Analysis of the influence of skull on photon transmission based on Monte Carlo method. In Proceedings of the 24th National Laser Conference & Fifteenth National Conference on Laser Technology and Optoelectronics, Shanghai, China, 17–20 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Song, X.; Wang, R.; Wei, J.; Song, L. Simulation study of the transmission of photons in mouse brain using Monte Carlo method. In Proceedings of the SPIE Photonex and Vacuum Expo, Online, 5–9 October 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodkalayeh, S.; Lu, X.; Ansari, M.A.; Li, H.; Nasiriavanaki, M. Optimization of Light Illumination for Photoacoustic Computed Tomography of Human Infant Brain. In Proceedings of the SPIE BiOS, San Francisco, CA, USA, 27 January–1 February 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Chai, C.; Zuo, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Shi, J.; Ma, C.; Sawan, M. Monte Carlo-Based Optical Simulation of Optical Distribution in Deep Brain Tissues Using Sixteen Optical Sources. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Gong, H.; Luo, Q. Visualization of light propagation in visible Chinese human head for functional near-infrared spectroscopy. J. Biomed. Opt. 2011, 16, 045001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, C.; Yang, X.; Gao, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, X.; Song, H.; Chen, Y.-H.; Sawan, M. Enhancing Photoacoustic Imaging for Lung Diagnostics and BCI Communication: Simulation of Cavity Structures Artifact Generation and Evaluation of Noise Reduction Techniques. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2024, 12, 1452865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Nina-Paravecino, F.; Kaeli, D.; Fang, Q. Scalable and massively parallel Monte Carlo photon transport simulations for heterogeneous computing platforms. J. Biomed. Opt. 2018, 23, 010504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.V.; Wu, H.-i. Biomedical Optics: Principles and Imaging; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]



| Brain Tissues |
Absorption Coefficient,
μa (1/mm) |
Scattering Coefficient,
μs (1/mm) |
Anisotropy Factor,
g |
Refractive Index,
n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scalp | 0.018 | 19.0 | 0.9 | 1.37 |
| Skull | 0.016 | 16.0 | 0.9 | 1.43 |
| Cerebrospinal fluid | 0.004 | 2.4 | 0.9 | 1.33 |
| Gray matter | 0.036 | 22.0 | 0.9 | 1.37 |
| White matter | 0.014 | 91.0 | 0.9 | 1.37 |
| Blood vessel | 0.223 | 50.0 | 0.99 | 1.4 |
| Tissue | Optical Energy of 1% | Optical Energy of 0.1% | Optical Energy of 0.01% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scalp | Collimated Gaussian (5.6 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (10.3 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (14.0 mm) |
| Planar (4.9 mm) | Planar (9.4 mm) | Planar (13.6 mm) | |
| Disk (4.6 mm) | Disk (9.0 mm) | Disk (13.4 mm) | |
| Skull | Collimated Gaussian (6.0 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (11.2 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (14.0 mm) |
| Planar (5.3 mm) | Planar (10.3 mm) | Planar (14.0 mm) | |
| Disk (4.9 mm) | Disk (9.8 mm) | Disk (14.0 mm) | |
| CSF | Collimated Gaussian (9.0 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (11.2 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (14.0 mm) |
| Planar (7.8 mm) | Planar (10.3 mm) | Planar (14.0 mm) | |
| Disk (7.2 mm) | Disk (9.8 mm) | Disk (14.0 mm) | |
| Gray matter | Collimated Gaussian (4.5 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (7.9 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (11.6 mm) |
| Planar (4.0 mm) | Planar (7.3 mm) | Planar (11.0 mm) | |
| Disk (3.8 mm) | Disk (7.0 mm) | Disk (10.7 mm) | |
| White matter | Collimated Gaussian (3.5 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (6.3 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (9.2 mm) |
| Hyperboloid Gaussian (3.4 mm) | Hyperboloid Gaussian (6.0 mm) | Hyperboloid Gaussian (9.0 mm) | |
| Planar (3.1 mm) | Planar (5.7 mm) | Planar (8.6 mm) | |
| Blood vessel | Collimated Gaussian (4.3 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (6.9 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (9.7 mm) |
| Planar (3.9 mm) | Planar (6.4 mm) | Planar (9.2 mm) | |
| Disk (3.7 mm) | Disk (6.1 mm) | Disk (8.9 mm) |
| Tissue | Optical Source Types with Maximum Value | Optical Source Types with Minimum Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FWHM of Energy in the X Axis | FWHM of Energy in the Y Axis | FWHM of Energy in the X Axis | FWHM of Energy in the Y Axis | |
| Scalp | Hyperboloid Gaussian (9.1 mm) | Pencil (8.9 mm) | Disk (8.4 mm) | Disk (8.4 mm) |
| Planar (9.0 mm) | Line (8.9 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (8.5 mm) | Arcsine (8.5 mm) | |
| 2D Fourier (9.0 mm) | Hyperboloid Gaussian (8.8 mm) | Slit (8.5 mm) | Cone (8.5 mm) | |
| Skull | Cone (8.8 mm) | Isotropic (8.8 mm) | 2D Fourier (8.3 mm) | Slit (8.4 mm) |
| Pencil (8.8 mm) | Arcsine (8.9 mm) | Pencil (8.3 mm) | Ring (8.5 mm) | |
| 2D Fourier (8.8 mm) | Planar (8.8 mm) | Angular Gaussian (8.4 mm) | Pencil (8.6 mm) | |
| CSF | Hyperboloid Gaussian (9.0 mm) | Hyperboloid Gaussian (8.5 mm) | Spatial frequency Fourier (7.1 mm) | Spatial frequency Fourier (7.0 mm) |
| Arcsine (7.9 mm) | Isotropic (8.1 mm) | 1D Fourier (7.3 mm) | Planar (7.1 mm) | |
| Cone (7.9 mm) | Cone (8.0 mm) | 2D Fourier (7.4 mm) | Arcsine (7.1 mm) | |
| Gray matter | Hyperboloid Gaussian (8.7 mm) | Line (8.7 mm) | Slit (8.1 mm) | Ring (8.0 mm) |
| Arcsine (8.6 mm) | Angular Gaussian (8.6 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (8.1 mm) | Slit (8.1 mm) | |
| 1D Fourier (8.5 mm) | 2D Fourier (8.5 mm) | Ring (8.1 mm) | Disk (8.1 mm) | |
| White matter | Hyperboloid Gaussian (8.3 mm) | Line (8.3 mm) | Angular Gaussian (7.7 mm) | Ring (7.6 mm) |
| Ring (8.3 mm) | Arcsine (8.2 mm) | Isotropic (7.9 mm) | Spatial frequency Fourier (7.7 mm) | |
| Slit (8.3 mm) | Disk (8.2 mm) | Cone (7.9 mm) | Angular Gaussian (7.8 mm) | |
| Blood vessel | Hyperboloid Gaussian (7.9 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (8.0 mm) | Collimated Gaussian (6.9 mm) | Spatial frequency Fourier (6.8 mm) |
| Arcsine (7.7 mm) | Arcsine (7.6 mm) | Disk (7.0 mm) | Ring (6.9 mm) | |
| Angular Gaussian (7.6 mm) | Isotropic (7.4 mm) | Isotropic (7.1 mm) | Pencil array (6.9 mm) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, X.; Chai, C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Sawan, M. Optical Transmission in Single-Layer Brain Tissues under Different Optical Source Types: Modelling and Simulation. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090916
Yang X, Chai C, Chen Y-H, Sawan M. Optical Transmission in Single-Layer Brain Tissues under Different Optical Source Types: Modelling and Simulation. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(9):916. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090916
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Xi, Chengpeng Chai, Yun-Hsuan Chen, and Mohamad Sawan. 2024. "Optical Transmission in Single-Layer Brain Tissues under Different Optical Source Types: Modelling and Simulation" Bioengineering 11, no. 9: 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090916
APA StyleYang, X., Chai, C., Chen, Y.-H., & Sawan, M. (2024). Optical Transmission in Single-Layer Brain Tissues under Different Optical Source Types: Modelling and Simulation. Bioengineering, 11(9), 916. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11090916










