User Perspectives and Psychophysiological Manifestations of Fatigue with Trunk Orthosis for Dystrophinopathy Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
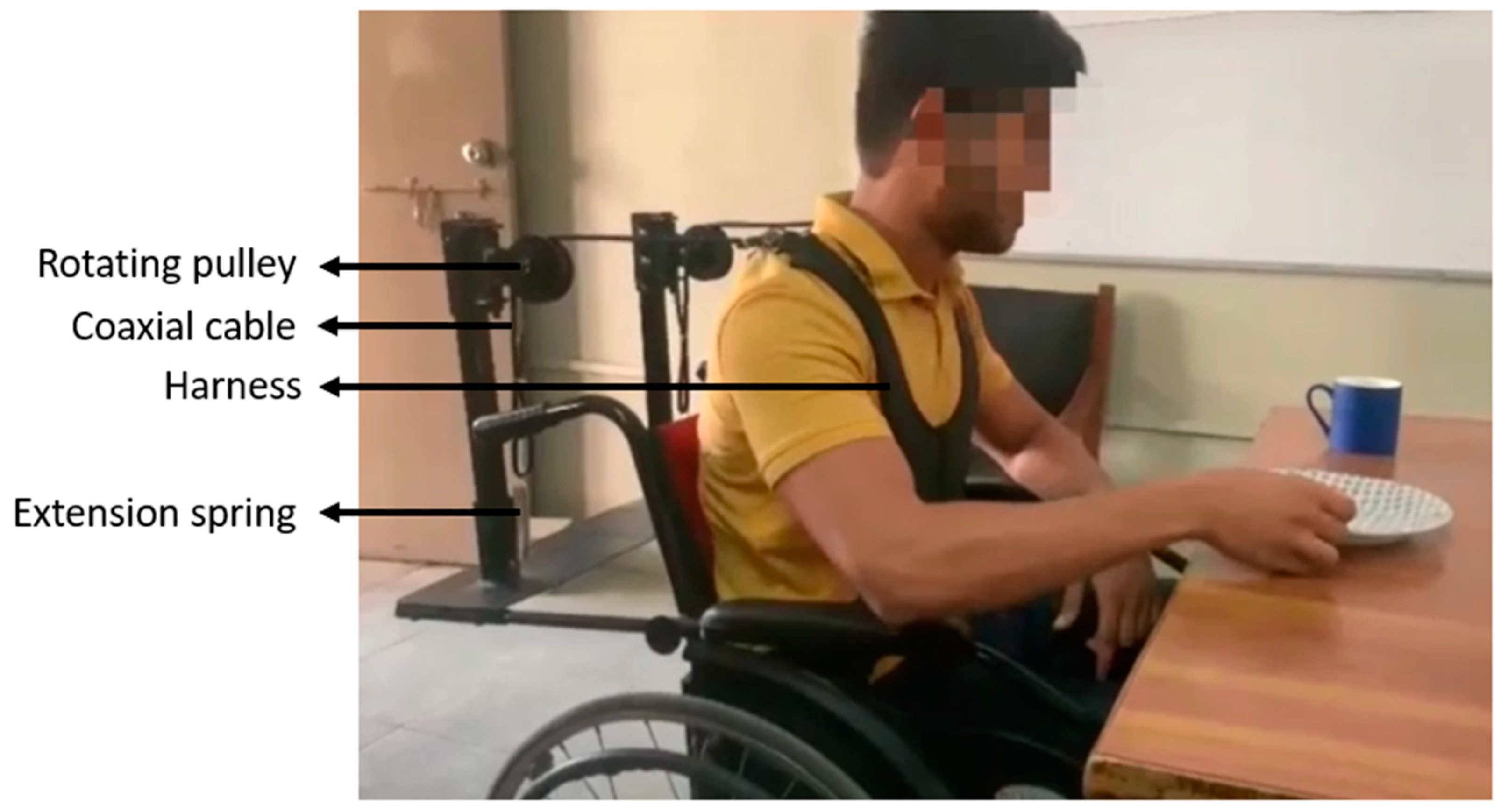
2. Materials and Methods
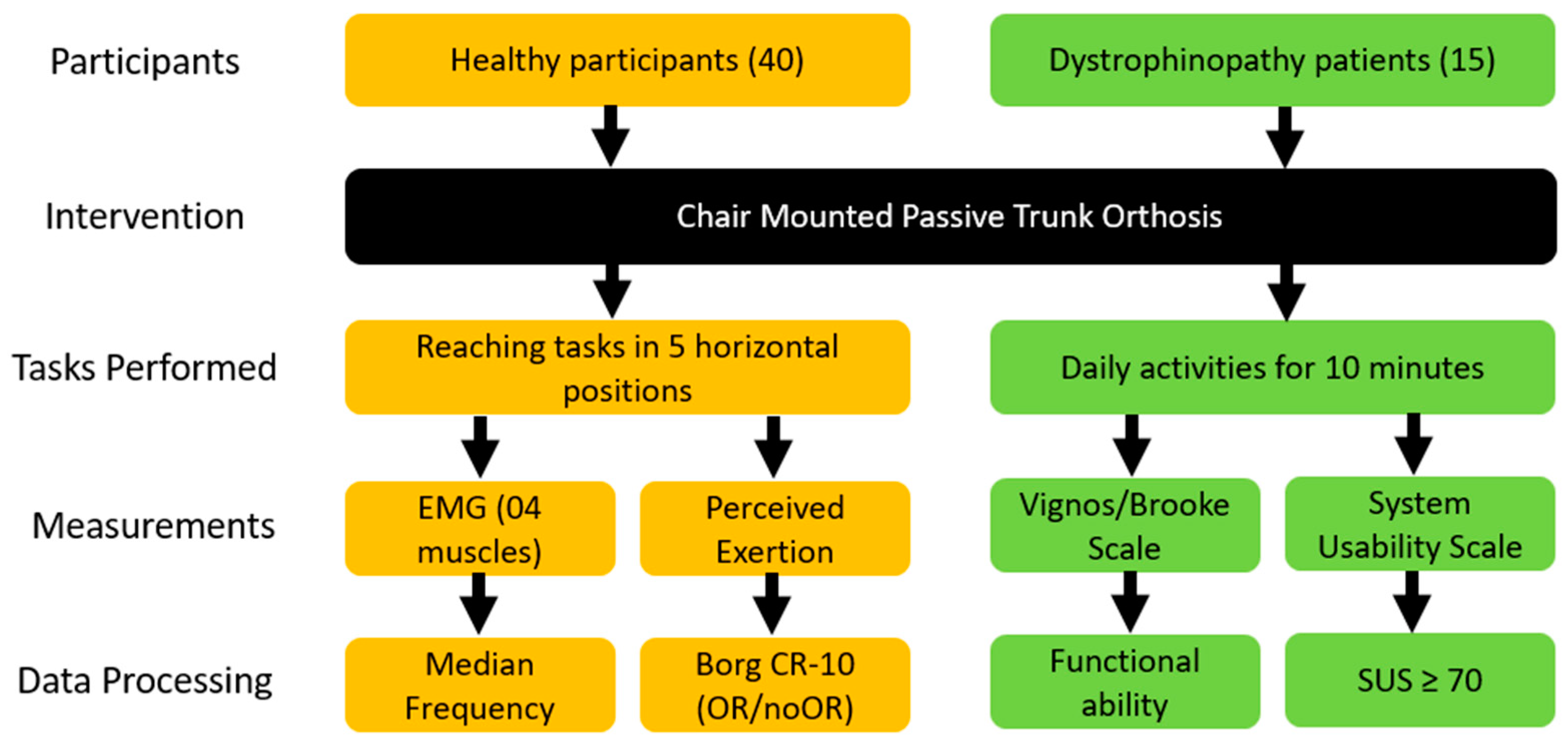
2.1. Participants
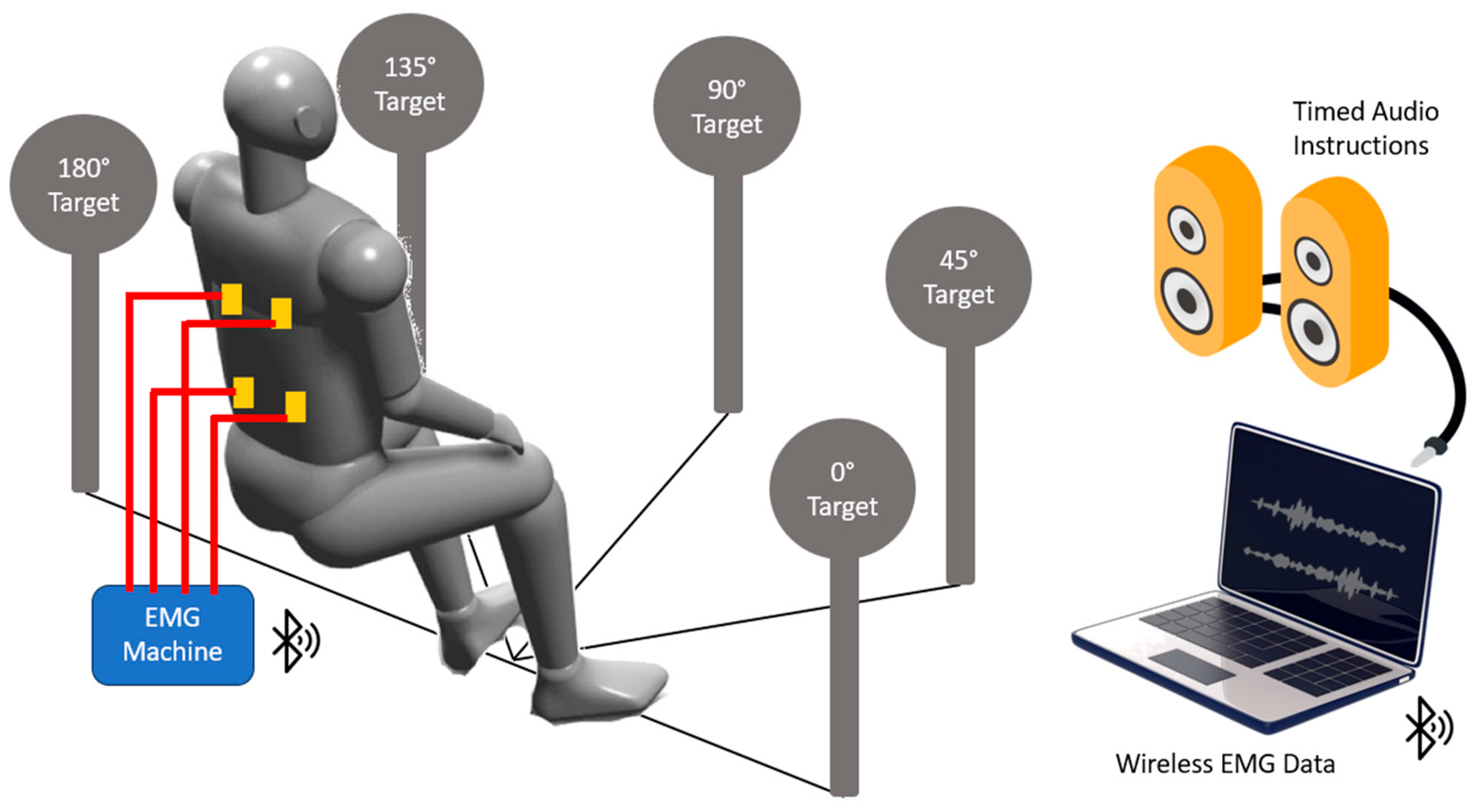
2.2. Experimental Procedure
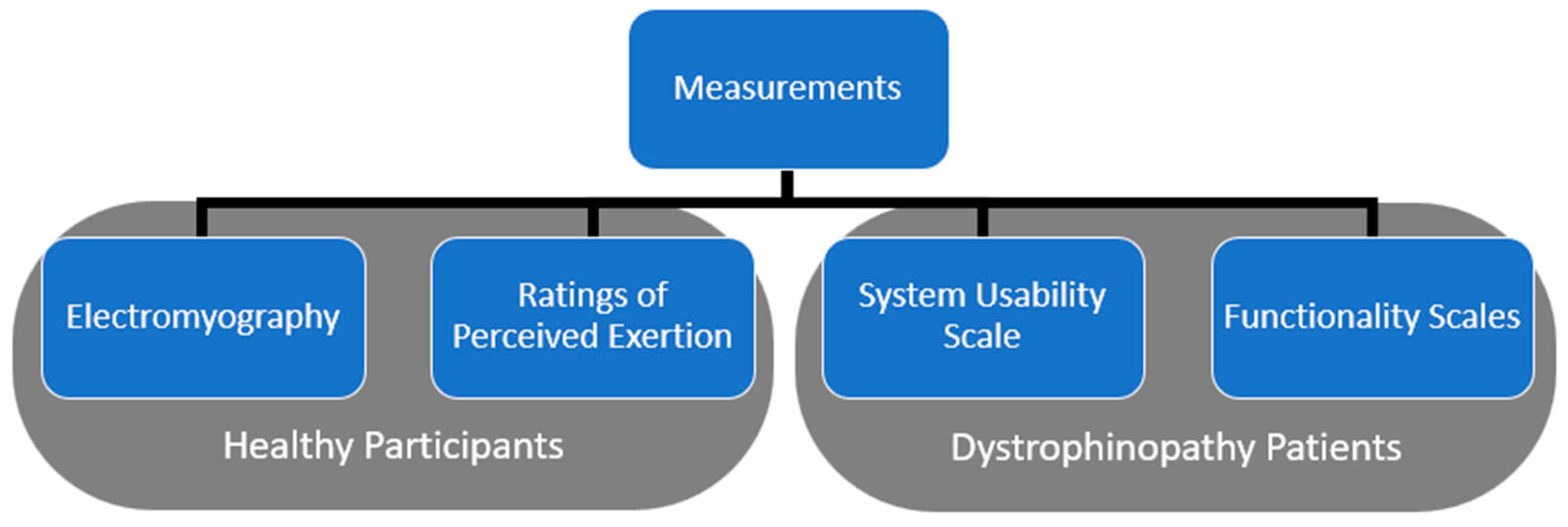
2.3. Data Measurement
2.3.1. Electromyography
2.3.2. Perceived Exertion
2.3.3. Functionality Scales
2.3.4. Usability
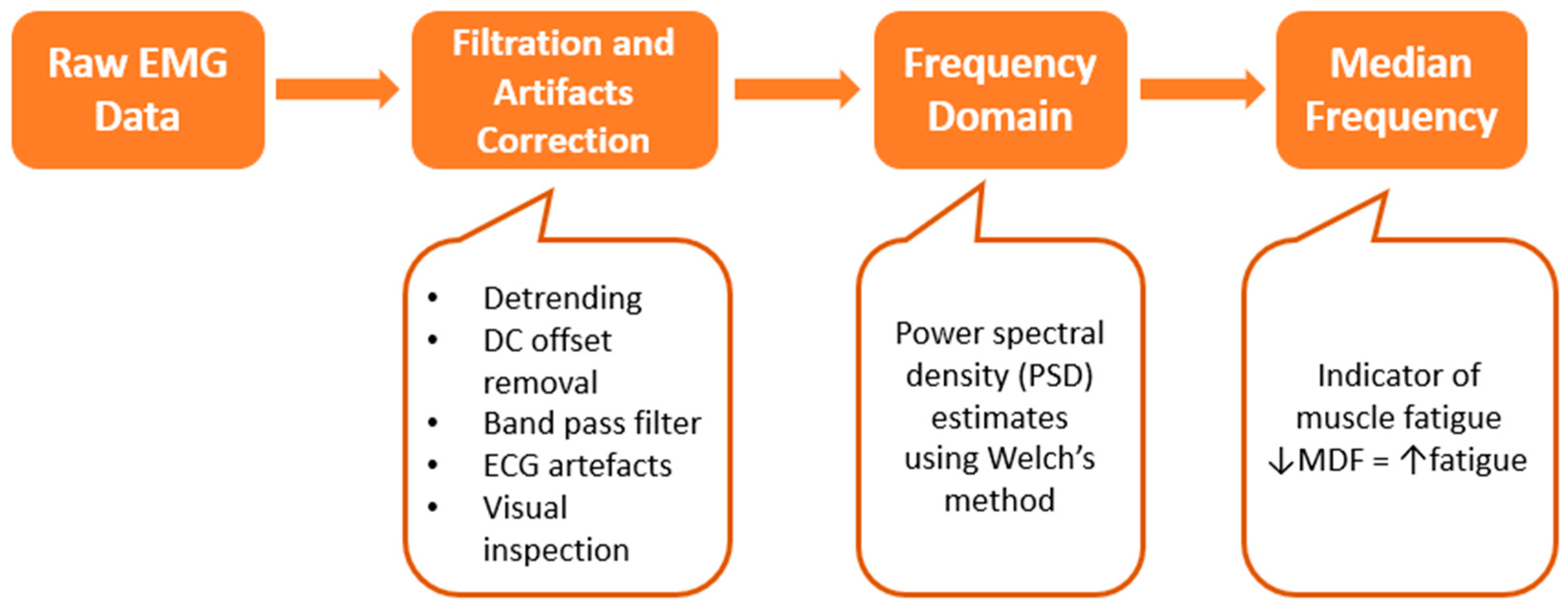
2.4. Data Processing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
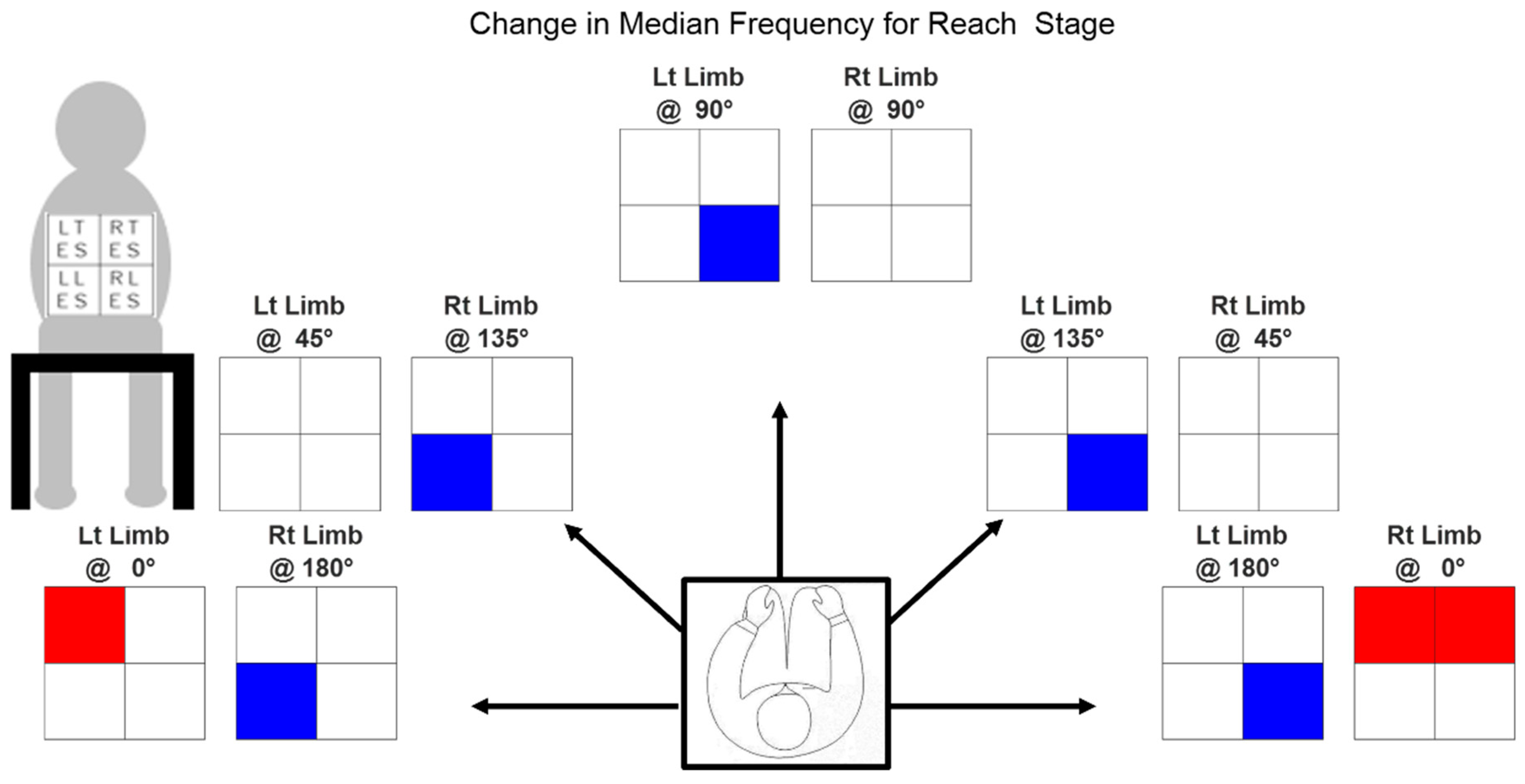
3.1. Variance in Median Frequency
3.2. Ratings of Perceived Exertion
3.3. Usability Ratings by Patients
4. Discussion
4.1. Manifestations of Fatigue
4.2. Perspectives of Patients
4.3. Suggestions for CMPTO Usage
4.4. Limitations and Recommendations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crisafulli, S.; Sultana, J.; Fontana, A.; Salvo, F.; Messina, S.; Messina, S.; Trifirò, G. Global Epidemiology of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2020, 15, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Matsumura, T.; Ogata, K.; Mori-Yoshimura, M.; Takeshita, E.; Kimura, K.; Kawashima, T.; Tomo, Y.; Arahata, H.; Miyazaki, D.; et al. Natural History of Becker Muscular Dystrophy: A Multicenter Study of 225 Patients. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2023, 10, 2360–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercuri, E.; Bönnemann, C.G.; Muntoni, F. Muscular Dystrophies. Lancet 2019, 394, 2025–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, D.; Goemans, N.; Takeda, S.; Mercuri, E.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.R.; Mynhier, M.A.; Miller, R.G. Muscular Fatigue in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Neurology 1995, 45, 306–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beenakker, E.A.C.; Maurits, N.M.; Fock, J.M.; Brouwer, O.F.; van der Hoeven, J.H. Functional Ability and Muscle Force in Healthy Children and Ambulant Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patients. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2005, 9, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlini, L.; Cecconi, I.; Parmeggiani, A.; Cordelli, D.M.; Dormi, A. Quadriceps Muscle Strength in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Effect of Corticosteroid Treatment. Acta Myol. 2020, 39, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambon, A.A.; Ayyar Gupta, V.; Ridout, D.; Manzur, A.Y.; Baranello, G.; Trucco, F.; Muntoni, F.; Tirupath, S.; Douglas, M.; McFetridge, J.; et al. Peak Functional Ability and Age at Loss of Ambulation in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2022, 64, 979–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttley, L.; Carlton, J.; Woods, H.B.; Brazier, J. A Review of Quality of Life Themes in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy for Patients and Carers. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2018, 16, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.S.; Hnaini, M.M.; ElAloul, B.; Zapata, E.; Campbell, C. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Fatigue Trajectories. Neuropediatrics 2024, 55, 042–048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.J.; Qin, Z.; Wang, P.Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X. Muscle Fatigue: General Understanding and Treatment. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granata, K.P.; Gottipati, P. Fatigue Influences the Dynamic Stability of the Torso. Ergonomics 2008, 51, 1258–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Speechley, K.N.; Zou, G.; Campbell, C. Factors Associated with Health-Related Quality of Life in Children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Child Neurol. 2016, 31, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, A.; Alkan, H.; Firat, T.; Karaduman, A.A.; Yilmaz, Ö.T. How Do Physical Capacity, Fatigue and Performance Differ in Children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Compared with Their Healthy Peers? Neurosci. J. 2018, 23, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aloul, B.; Speechley, K.N.; Wei, Y.; Wilk, P.; Campbell, C. Fatigue in Young People with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2020, 62, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka-Ninagawa, N.; Goto, M.; Ikeda, R.; Sakurai, H. Muscular Dystrophy and Rehabilitation Interventions with Regenerative Treatment. Curr. Phys. Med. Rehabil. Rep. 2020, 8, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, M.M.H.P.; Horstik, J.; Klap, P.; de Groot, I.J.M. Feasibility and Effectiveness of a Novel Dynamic Arm Support in Persons with Spinal Muscular Atrophy and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longatelli, V.; Antonietti, A.; Biffi, E.; Diella, E.; D’Angelo, M.G.; Rossini, M.; Molteni, F.; Bocciolone, M.; Pedrocchi, A.; Gandolla, M. User-Centred Assistive SystEm for Arm Functions in NeUromuscuLar Subjects (USEFUL): A Randomized Controlled Study. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, A.; Callaway, L.; Randall, M.; Ryan, M. Mobile Arm Supports in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Pilot Study of User Experience and Outcomes. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2021, 16, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, G.; Sun, Y.; Lin, K.; Zhou, Z.; Cai, J. Application of Surface Electromyography in Exercise Fatigue: A Review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 893275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta-Piccoli, M.; Cescon, C.; D’antona, G. Evaluation of Performance Fatigability through Surface EMG in Health and Muscle Disease: State of the Art. Arab. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2021, 28, 20–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merletti, R.; Knaflitz, M.; De Luca, C.J. Myoelectric Manifestations of Fatigue in Voluntary and Electrically Elicited Contractions. J. Appl. Physiol. 1990, 69, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fegni Ndam, E.O.; Goubault, É.; Moyen-Sylvestre, B.; Côté, J.N.; Bouffard, J.; Maso, F.D. What Are the Best Indicators of Myoelectric Manifestation of Fatigue? medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardozo, A.C.; Gonçalves, M.; Dolan, P. Back Extensor Muscle Fatigue at Submaximal Workloads Assessed Using Frequency Banding of the Electromyographic Signal. Clin. Biomech. 2011, 26, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, R.A.; Nizamis, K.; Koopman, B.F.J.M.; Herder, J.L.; Sartori, M.; Plettenburg, D.H. A Case Study with Symbihand: An SEMG-Controlled Electrohydraulic Hand Orthosis for Individuals with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumoto, Y.; Miyama, T. Alleviation of Masticatory Disturbance with an Occlusal Splint in a Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patient. Spec. Care Dent. 2021, 41, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godwin, A.A.; Stevenson, J.M.; Agnew, M.J.; Twiddy, A.L.; Abdoli-Eramaki, M.; Lotz, C.A. Testing the Efficacy of an Ergonomic Lifting Aid at Diminishing Muscular Fatigue in Women over a Prolonged Period of Lifting. Int. J. Ind. Ergon. 2009, 39, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamers, E.P.; Soltys, J.C.; Scherpereel, K.L.; Yang, A.J.; Zelik, K.E. Low-Profile Elastic Exosuit Reduces Back Muscle Fatigue. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, C.A.; Agnew, M.J.; Godwin, A.A.; Stevenson, J.M. The Effect of an On-Body Personal Lift Assist Device (PLAD) on Fatigue during a Repetitive Lifting Task. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2009, 19, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, L.H.C.; de Groot, I.J.M.; Geurts, A.C.H. Trunk Involvement in Performing Upper Extremity Activities While Seated in Neurological Patients with a Flaccid Trunk—A Review. Gait Posture 2018, 62, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.O.; De Souza, L.H. Clinical Features of Children and Adults with a Muscular Dystrophy Using Powered Indoor/Outdoor Wheelchairs: Disease Features, Comorbidities and Complications of Disability. Disabil. Rehabil. 2018, 40, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergsma, A.; Lobo-Prat, J.; Vroom, E.; Furlong, P.; Herder, J.L.; Corrigan, M.; de Groot, I.; Faisal, A.; Goemans, N.; Han, J.; et al. 1st Workshop on Upper-Extremity Assistive Technology for People with Duchenne: State of the Art, Emerging Avenues, and Challenges. April 27th 2015, London, United Kingdom. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2016, 26, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, J.; Morrow, M.; Michael, S. Wheelchair Postural Support for Young People with Progressive Neuromuscular Disorders. Int. J. Ther. Rehabil. 2004, 11, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeters, L.H.C.; Kingma, I.; van Dieën, J.H.; de Groot, I.J.M. Don’t Forget the Trunk in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patients: More Muscle Weakness and Compensation than Expected. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.Z.; Hasan, M.A. Evaluation of a Chair-Mounted Passive Trunk Orthosis: A Pilot Study on Able-Bodied Subjects. Sensors 2021, 21, 8366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.N.; Peeters, L.H.C.; Paalman, M.; Verkerke, G.J.; Kingma, I.; van Dieën, J.H. Development and Evaluation of a Passive Trunk Support System for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Patients. J. NeuroEng. Rehabil. 2018, 15, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verros, S.; Mahmood, N.; Peeters, L.; Lobo-Prat, J.; Bergsma, A.; Hekman, E.; Verkerke, G.J.; Koopman, B. Evaluation of Control Interfaces for Active Trunk Support. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2018, 26, 1965–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Looft, J.M.; Sjoholm, R.; Hansen, A.H.; Fairhurst, S.; Voss, G.; Dellamano, C.A.; Egginton, J.; Olney, C.; Goldish, G. User-Centered Design and Development of a Trunk Control Device for Persons with Spinal Cord Injury: A Pilot Study. J. Spinal Cord Med. 2022, 45, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogura, T.; Itami, T.; Yano, K.; Mori, I.; Kameda, K. An Assistance Device to Help People with Trunk Impairment Maintain Posture. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, London, UK, 17–20 July 2017; pp. 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ophaswongse, C.; Murray, R.C.; Santamaria, V.; Wang, Q.; Agrawal, S.K. Human Evaluation of Wheelchair Robot for Active Postural Support (WRAPS). Robotica 2019, 37, 2032–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, G.; Borg, E. The Borg CR Scales® Folder Methods for Measuring Intensity of Experience; Hässelby, Sweden. 2010. Available online: https://borgperception.se/wp-content/uploads/2019/10/The-Borg-CR-Scales-Folder.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2021).
- Brooke, M.H.; Griggs, R.C.; Mendell, J.R.; Fenichel, G.M.; Shumate, J.B.; Pellegrino, R.J. Clinical Trial in Duchenne Dystrophy. I. The Design of the Protocol. Muscle Nerve 1981, 4, 186–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignos, P.J.; Watkins, M.P. The Effect of Exercise in Muscular Dystrophy. JAMA 1966, 197, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangor, A.; Kortum, P.; Miller, J. Determining What Individual SUS Scores Mean: Adding an Adjective Rating Scale. J. Usability Stud. 2009, 4, 114–123. [Google Scholar]
- Welch, P.D. The Use of Fast Fourier Transform for the Estimation of Power Spectra: A Method Based on Time Averaging over Short, Modified Periodograms. IEEE Trans. Audio Electroacoust. 1967, 15, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Izal, M.; Malanda, A.; Gorostiaga, E.; Izquierdo, M. Electromyographic Models to Assess Muscle Fatigue. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2012, 22, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Montecinos, C.; Bustamante, A.; Candia-González, M.; González-Bravo, C.; Gallardo-Molina, P.; Andersen, L.L.; Calatayud, J. Perceived Physical Exertion Is a Good Indicator of Neuromuscular Fatigue for the Core Muscles. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 2019, 49, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, J.W.D.; O’Driscoll, J.M.; Coleman, D.A.; Wiles, J.D. Validity and Reliability of the ‘Isometric Exercise Scale’ (IES) for Measuring Ratings of Perceived Exertion during Continuous Isometric Exercise. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, G.S.; Stefanetti, R.J.; Blain, A.; Jimenez-Moreno, C.; Errington, L.; Ng, Y.S.; McFarland, R.; Turnbull, D.M.; Newman, J. Measuring the Effects of Exercise in Neuromuscular Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses. Wellcome Open Res. 2020, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siciliano, G.; Chico, L.; Lo Gerfo, A.; Simoncini, C.; Schirinzi, E.; Ricci, G. Exercise-Related Oxidative Stress as Mechanism to Fight Physical Dysfunction in Neuromuscular Disorders. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 527851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sado, N.; Yoshioka, S.; Fukashiro, S. Lumbar Axial Torque Actively Induces Trunk Axial Rotation during Sidestep Cutting Manoeuvre: Insight to Expand the Trunk Control Concept. J. Biomech. 2020, 111, 110003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, D.; Bilodeau, M. Rating of Perceived Exertion (RPE) in Studies of Fatigue-Induced Postural Control Alterations in Healthy Adults: Scoping Review of Quantitative Evidence. Gait Posture 2021, 90, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossi, O.; Lacroix, J.; Compagnat, M.; Daviet, J.C.; Mandigout, S. Perceived Exertion and Energy Expenditure during Physical Activities in Healthy Young People and Older Adults. Folia Med. 2021, 63, 502–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pangalila, R.F.; van den Bos, G.A.; Bartels, B.; Bergen, M.; Stam, H.J.; Roebroeck, M.E. Prevalence of Fatigue, Pain, and Affective Disorders in Adults with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Their Associations with Quality of Life. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2015, 96, 1242–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salters, D.; Scharoun Benson, S.M. Hand Preference for Unimanual and Bimanual Tasks: Evidence from Questionnaires and Preferential Reaching. Laterality 2022, 27, 308–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, K.M.; Frazier, E.C.; Shively, C.M.; Hartman, R.A.; Ulibarri, J.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kang, J.D.; Donaldson, W.F. Assessing Range of Motion to Evaluate the Adverse Effects of Ill-Fitting Cervical Orthoses. Spine J. 2009, 9, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadasivan, A.; Warrier, M.; Polavarapu, K.; Preethish-Kumar, V.; Nair, M.; Keerthipriya, M.; Vengalil, S.; Sagar, J.; Kishore, T.; Nalini, A.; et al. Palliative Care in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Study on Parents’ Understanding. Indian J. Palliat. Care 2021, 27, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliverti, A.; LoMauro, A.; D’Angelo, M.G.; Aliverti, A. Assessment and Management of Respiratory Function in Patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Current and Emerging Options. Ther. Clin. Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 1475–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkarakittichoke, N.; Waongenngarm, P.; Janwantanakul, P. Effects of Postural Shifting Frequency on Perceived Musculoskeletal Discomfort during 1-Hour Sitting in Office Workers. J. Manip. Physiol. Ther. 2023, 46, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cup, E.H.; Pieterse, A.J.; ten Broek-Pastoor, J.M.; Munneke, M.; van Engelen, B.G.; Hendricks, H.T.; van der Wilt, G.J.; Oostendorp, R.A. Exercise Therapy and Other Types of Physical Therapy for Patients with Neuromuscular Diseases: A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2007, 88, 1452–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Tsukada, A.; Ohura, T. Surveying Therapists on Seating Approaches for Patients with Muscular Dystrophy in Japan. Healthcare 2021, 9, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H. Early Introduction of Power Mobility Devices for Children with Fukuyama Congenital Muscular Dystrophy and Its Psychological Impact on Caregivers: A Case Report. Pediatr. Rep. 2023, 15, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoabli, G.; Mathieu, P.A.; Aubin, C.-É. Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Erector Spinae Muscles in Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Implication for Scoliotic Deformities. Scoliosis 2008, 3, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preuss, R.A.; Grenier, S.G.; McGill, S.M. Postural Control of the Lumbar Spine in Unstable Sitting. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2005, 86, 2309–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A.Z.; Siddique, S.S.; Mujib, M.D.; Hasan, M.A.; Alokaily, A.O.; Tahira, T. Sensor Fusion and Machine Learning for Seated Movement Detection with Trunk Orthosis. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 41676–41687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Rao, A.Z.; Ejaz, O.; Raees, F.; Mujib, M.D.; Hamad, M.; Athar, M.; Qazi, S.A. Emergence of Neurofeedback Technology and Quantitative EEG in Pakistan. In International Trends in Neurofeedback; The Foundation for Neurofeedback and Neuromodulation Research: Hendersonville, NC, USA, 2023; Volume 1, pp. 216–234. [Google Scholar]
- Shahid, H.; Hasan, M.A.; Ejaz, O.; Khan, H.R.; Idrees, M.; Ashraf, M.; Aftab, S.; Qazi, S.A. The Severity of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress: Recommendations from Joint Work of Research Center and Psychology Clinics in COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 839542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.A.; Shahid, H.; Qazi, S.A.; Ejaz, O.; Mujib, M.D.; Vuckovic, A. Underpinning the Neurological Source of Executive Function Following Cross Hemispheric TDCS Stimulation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2023, 185, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujib, M.D.; Rao, A.Z.; Hasan, M.A.; Ikhlaq, A.; Buzdar, S.A.; Qazi, S.A. Frontal Cortex Cooling and Modulation of Brain Frequencies Using a Wearable Peltier Device. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2023, 652, 414641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujib, M.D.; Hasan, M.A.; Qazi, S.A.; Vuckovic, A. Understanding the Neurological Mechanism Involved in Enhanced Memory Recall Task Following Binaural Beat: A Pilot Study. Exp. Brain Res. 2021, 239, 2741–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alokaily, A.O.; Alqabbani, A.F.; Aleid, A.; Alhussaini, K. Toward Accessible Hearing Care: The Development of a Versatile Arabic Word-in-Noise Screening Tool: A Pilot Study. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 12459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
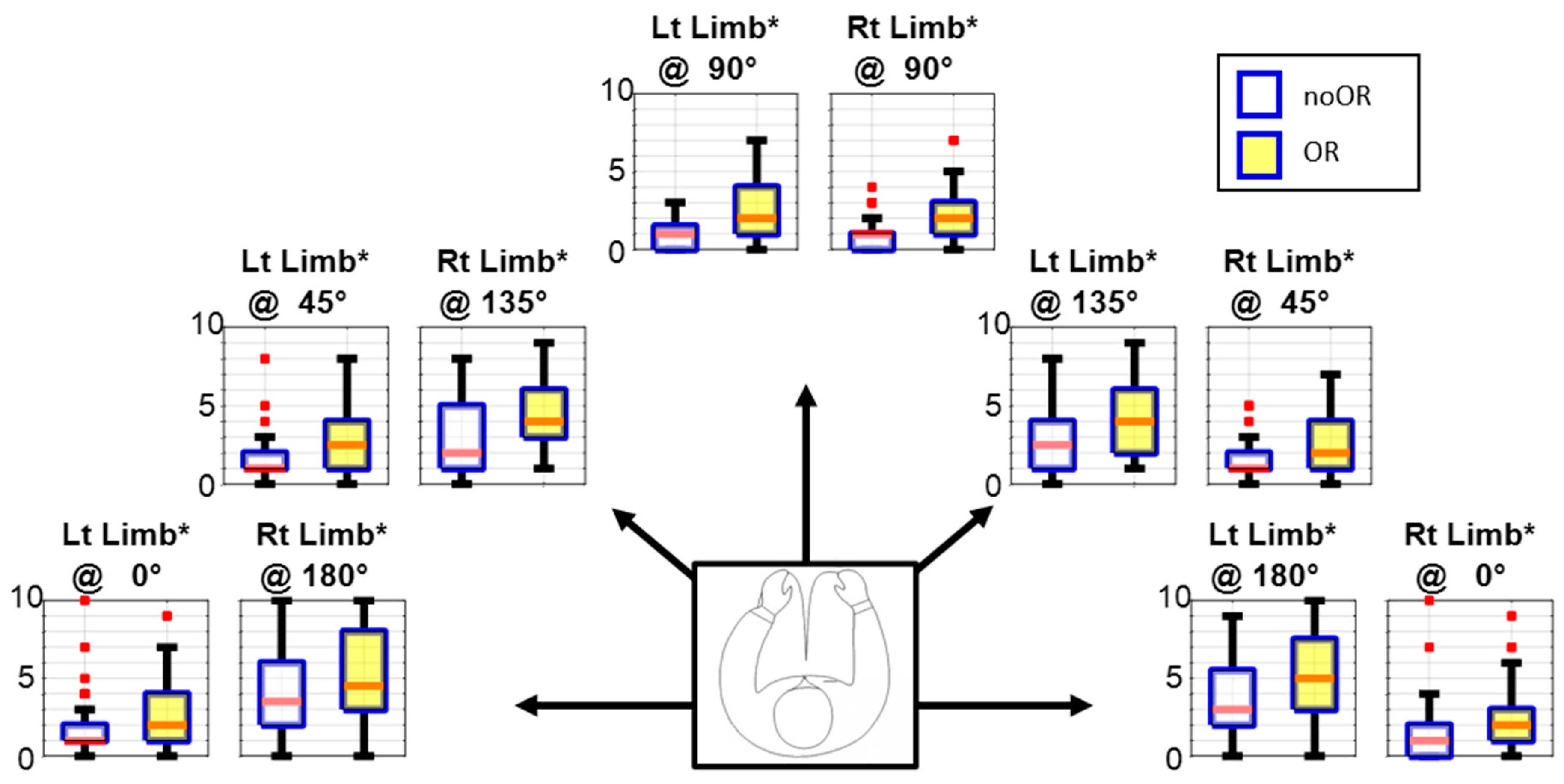
| Source | df | F | p | η2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Task Orientation | 4 | 8.33 | <0.001 | 0.009 |
| Limb Used | 1 | 5.57 | 0.110 | 0.002 |
| Muscle | 3 | 39.01 | <0.001 | 0.031 |
| Orthosis | 1 | 7.33 | 0.048 | 0.002 |
| Task Orientation × Limb Used | 4 | 4.42 | 0.015 | 0.005 |
| Task Orientation × Muscle | 12 | 17.65 | <0.001 | 0.055 |
| Task Orientation × Orthosis | 4 | 0.11 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| Limb Used × Muscle | 3 | 3.14 | 0.122 | 0.003 |
| Limb Used × Orthosis | 1 | 0.30 | 1.000 | 0.000 |
| Muscle × Orthosis | 3 | 4.85 | 0.020 | 0.004 |
| Task Orientation × Limb Used × Muscle | 12 | 5.39 | <0.001 | 0.017 |
| Task Orientation × Limb Used × Orthosis | 4 | 3.91 | 0.029 | 0.004 |
| Task Orientation × Muscle × Orthosis | 12 | 1.60 | 0.336 | 0.005 |
| Limb Used × Muscle × Orthosis | 3 | 5.62 | 0.008 | 0.005 |
| Task Orientation × Limb Used × Muscle × Orthosis | 12 | 0.62 | 1.000 | 0.002 |
| Muscle Orientation | RTES | LTES | RLES | LLES | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Limb Used | Rt | 0° | 2.279 | 3.326 | −0.133 | 1.564 |
| 45° | 0.854 | −0.553 | −3.013 | 2.209 | ||
| 90° | −0.443 | −2.142 | −0.109 | −1.947 | ||
| 135° | 2.516 | −1.874 | −2.020 | −10.860 | ||
| 180° | 0.476 | −1.705 | 0.153 | −10.405 | ||
| Lt | 0° | 1.325 | 3.170 | −0.670 | 1.458 | |
| 45° | 1.455 | 0.715 | −2.982 | 2.747 | ||
| 90° | −1.400 | 0.417 | −5.327 | −3.584 | ||
| 135° | 1.067 | −0.765 | −13.333 | 1.857 | ||
| 180° | −2.502 | −0.971 | −16.714 | 1.222 | ||
| Subject | Age | Dystrophy | Brooke | Vignos | SUS Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 06 | Duchenne | 2 | 7 | 70.0 |
| S2 | 14 | Duchenne | 5 | 9 | 97.5 |
| S3 | 14 | Duchenne | 6 | 10 | 90.0 |
| S4 | 15 | Duchenne | 5 | 9 | 92.5 |
| S5 | 18 | Becker | 4 | 9 | – |
| S6 | 19 | Duchenne | 5 | 9 | – |
| S7 | 21 | Becker | 4 | 9 | – |
| S8 | 23 | Becker | 4 | 9 | 87.5 |
| S9 | 27 | Duchenne | 5 | 9 | – |
| S10 | 28 | Becker | 5 | 9 | 80.0 |
| S11 | 29 | Becker | 5 | 9 | – |
| S12 | 30 | Becker | 5 | 9 | – |
| S13 | 40 | Becker | 5 | 9 | 82.5 |
| S14 | 43 | Becker | 5 | 9 | 75.0 |
| S15 | 47 | Becker | 5 | 9 | – |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rao, A.Z.; Danish Mujib, M.; Abul Hasan, M.; Alokaily, A.O.; Tahira, T.; Qazi, S.A. User Perspectives and Psychophysiological Manifestations of Fatigue with Trunk Orthosis for Dystrophinopathy Patients. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080780
Rao AZ, Danish Mujib M, Abul Hasan M, Alokaily AO, Tahira T, Qazi SA. User Perspectives and Psychophysiological Manifestations of Fatigue with Trunk Orthosis for Dystrophinopathy Patients. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(8):780. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080780
Chicago/Turabian StyleRao, Ahmad Zahid, Muhammad Danish Mujib, Muhammad Abul Hasan, Ahmad O. Alokaily, Tayyaba Tahira, and Saad Ahmed Qazi. 2024. "User Perspectives and Psychophysiological Manifestations of Fatigue with Trunk Orthosis for Dystrophinopathy Patients" Bioengineering 11, no. 8: 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080780
APA StyleRao, A. Z., Danish Mujib, M., Abul Hasan, M., Alokaily, A. O., Tahira, T., & Qazi, S. A. (2024). User Perspectives and Psychophysiological Manifestations of Fatigue with Trunk Orthosis for Dystrophinopathy Patients. Bioengineering, 11(8), 780. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11080780









