Association between Elastic Modulus of Foot Soft Tissues and Gait Characteristics in Young Individuals with Flatfoot
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval and Clinical Registration
2.2. Participants Recruitment
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Diagnosed with flatfoot, and the diagnosis of flatfoot was confirmed by the same experienced surgeon from the Department of Foot and Ankle Surgery;
- (2)
- Age 16–30 years old (each gender was permitted);
- (3)
- No walking disorder;
- (4)
- No language disorder.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Suffering from other orthopedic or neurological diseases, such as osteoarthritis of the knee;
- (2)
- Suffering from severe osteoporosis or limited joint mobility;
- (3)
- Suffering from previous stroke;
- (4)
- Suffering from cognitive dysfunction;
- (5)
- Suffering from lower extremity fracture or surgery of the lower extremity within 10 years;
- (6)
- Suffering from malignant neoplastic disease either currently or within the previous 10 years (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer).
2.2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Paticipants with Normal Foot Arches
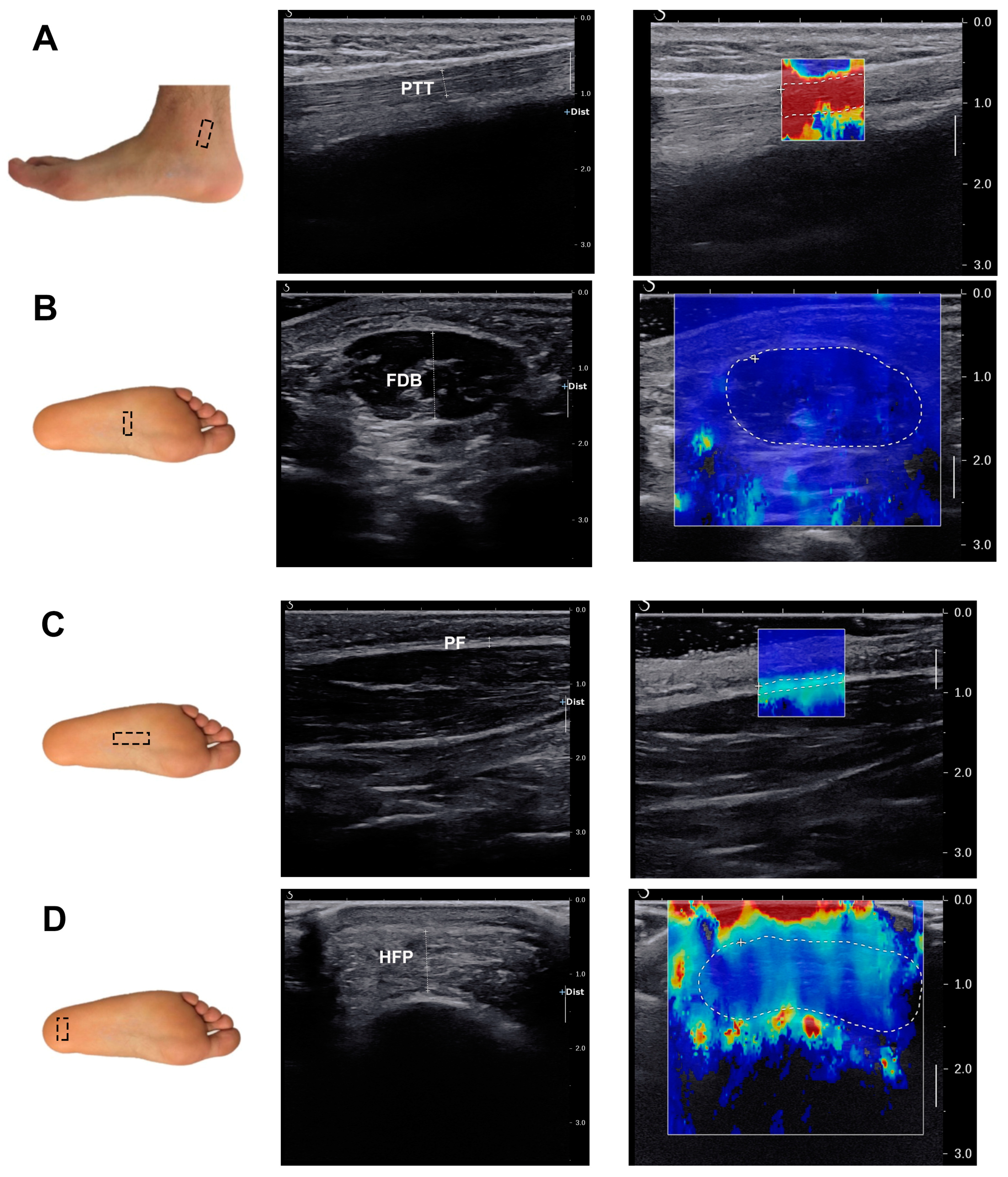
2.3. Ultrasound Data Acquisition
2.3.1. Data Acquisition Process
2.3.2. Ultrasound Parameters
2.4. Gait Data Acquisition
2.4.1. Data Acquisition Process
2.4.2. Data Processing
2.4.3. Gait Parameters
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of Participants
3.2. Reliability of Elastic Modulus Measurements
3.3. Thickness of Soft Tissues
3.4. Elastic Modulus of Soft Tissues
3.5. Gait Data
3.5.1. Spatiotemporal Parameters
3.5.2. Kinematics
3.5.3. Kinetics
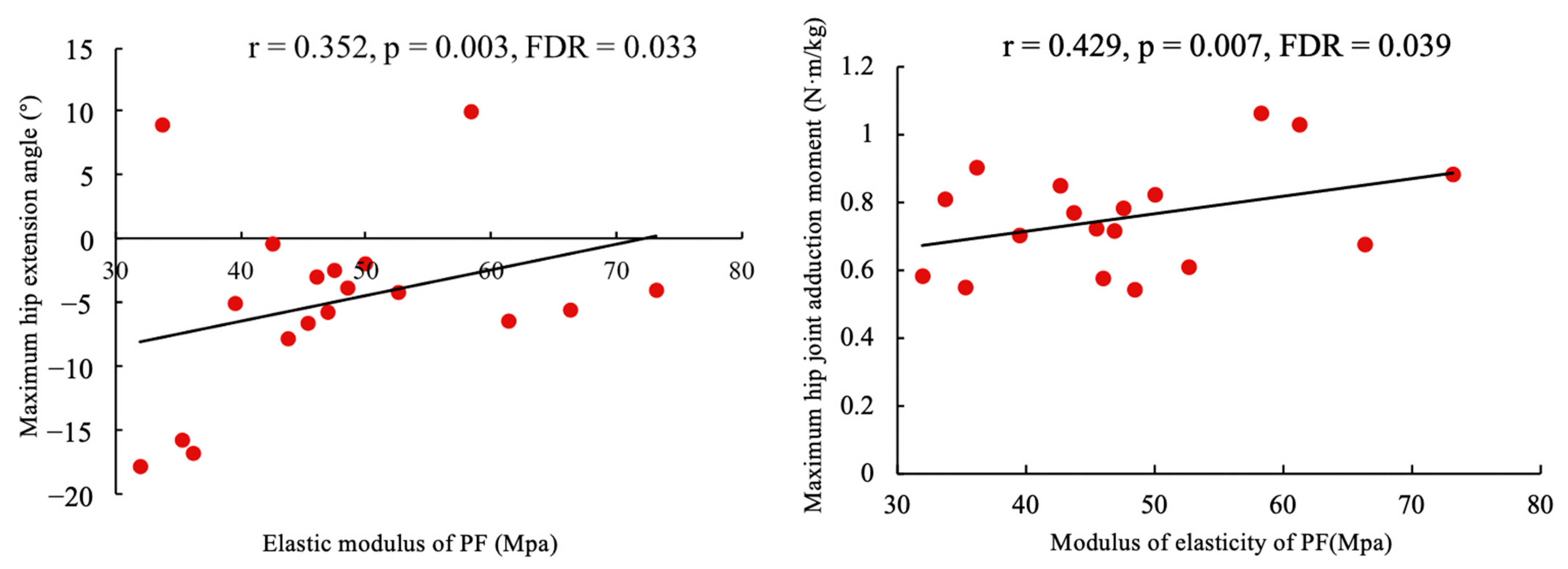
3.6. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aenumulapalli, A.; Kulkarni, M.M.; Gandotra, A.R. Prevalence of Flexible Flat Foot in Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, AC17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Shah, P.; Ravaliya, S.; Patel, M. Relationship of Anterior Knee Pain and Flat Foot: A Cross-Sectional Study. Int. J. Health Sci. Res. 2021, 11, 86–92. [Google Scholar]
- Vittore, D.; Patella, V.; Petrera, M.; Caizzi, G.; Ranieri, M.; Putignano, P.; Spinarelli, A. Extensor Deficiency: First Cause of Childhood Flexible Flat Foot. Orthopedics 2009, 32, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastias, G.F.; Dalmau-Pastor, M.; Astudillo, C.; Pellegrini, M.J. Spring Ligament Instability. Foot Ankle Clin. 2018, 23, 659–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karasick, D.; Schweitzer, M.E. Tear of the Posterior Tibial Tendon Causing Asymmetric Flatfoot: Radiologic Findings. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 1993, 161, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakoutikhah, H.; Madenci, E.; Latt, L.D. A Computational Model of Force within the Ligaments and Tendons in Progressive Collapsing Foot Deformity. J. Orthop. Res. 2023, 41, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walters, J.L.; Mendicino, S.S. The Flexible Adult Flatfoot: Anatomy and Pathomechanics. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2014, 31, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinger, P.; Murley, G.S.; Barton, C.J.; Cotchett, M.P.; McSweeney, S.R.; Menz, H.B. A Comparison of Foot Kinematics in People with Normal- and Flat-Arched Feet Using the Oxford Foot Model. Gait Posture 2010, 32, 519–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toullec, E. Adult Flatfoot. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, S11–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothari, A.; Dixon, P.C.; Stebbins, J.; Zavatsky, A.B.; Theologis, T. Are Flexible Flat Feet Associated with Proximal Joint Problems in Children? Gait Posture 2016, 45, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravaggi, P.; Rogati, G.; Leardini, A.; Bevoni, R.; Girolami, M.; Berti, L. Clinical and Multi-Segment Kinematic Analysis of a Modified Grice Arthrodesis to Correct Type II Adult-Acquired Flat-Foot. Gait Posture 2023, 100, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godoy-Santos, A.L.; Schmidt, E.L.; Chaparro, F. What Are the Updates on Epidemiology of Progressive Collapsing Foot Deformity? Foot Ankle Clin. 2021, 26, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taş, S.; Ünlüer, N.Ö.; Korkusuz, F. Morphological and Mechanical Properties of Plantar Fascia and Intrinsic Foot Muscles in Individuals with and without Flat Foot. J. Orthop. Surg. 2018, 26, 2309499018802482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angin, S.; Crofts, G.; Mickle, K.J.; Nester, C.J. Ultrasound Evaluation of Foot Muscles and Plantar Fascia in Pes Planus. Gait Posture 2014, 40, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanev, D.; Moustakas, K. Stiffness Modulation of Redundant Musculoskeletal Systems. J. Biomech. 2019, 85, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monte, A.; Zignoli, A. Muscle and Tendon Stiffness and Belly Gearing Positively Correlate with Rate of Torque Development during Explosive Fixed End Contractions. J. Biomech. 2021, 114, 110110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, W.-L.; Chan, C.-H.; Lam, C.-H.; Lee, C.-M.; Ying, M. Sonographic Evaluation of the Effect of Long-Term Exercise on Achilles Tendon Stiffness Using Shear Wave Elastography. J. Sci. Med. Sport 2016, 19, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taljanovic, M.S.; Gimber, L.H.; Becker, G.W.; Latt, L.D.; Klauser, A.S.; Melville, D.M.; Gao, L.; Witte, R.S. Shear-Wave Elastography: Basic Physics and Musculoskeletal Applications. Radiographics 2017, 37, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Hirota, K.; Otsuki, R.; Onodera, J.; Kodesho, T.; Taniguchi, K. Morphological and Mechanical Characteristics of the Intrinsic and Extrinsic Foot Muscles under Loading in Individuals with Flat Feet. Gait Posture 2024, 108, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taş, S.; Aktaş, A.; Tüfek, M.T. Passive Mechanical Properties of Extrinsic Foot Muscles and Achilles Tendon in Adults with and without Pes Planus. J. Biomech. 2022, 133, 110961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Wu, J.; Chang, F.; Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Ren, L. Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Plantar Fascia in Flexible Flatfoot: A Noninvasive In Vivo Study. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 727940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buldt, A.K.; Levinger, P.; Murley, G.S.; Menz, H.B.; Nester, C.J.; Landorf, K.B. Foot Posture Is Associated with Kinematics of the Foot during Gait: A Comparison of Normal, Planus and Cavus Feet. Gait Posture 2015, 42, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrnes, S.K.; Wearing, S.; Böhm, H.; Dussa, C.U.; Horstmann, T. Effects of Idiopathic Flatfoot Deformity on Knee Adduction Moments during Walking. Gait Posture 2021, 84, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynn, S.K.; Reid, S.M.; Costigan, P.A. The Influence of Gait Pattern on Signs of Knee Osteoarthritis in Older Adults over a 5–11 Year Follow-up Period: A Case Study Analysis. Knee 2007, 14, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Gu, D. Biomechanical Differences before and after Arthroscopic Partial Meniscectomy in Patients with Semilunar and Discoid Lateral Meniscus Injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 2793–2804. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bell, A.L.; Brand, R.A.; Pedersen, D.R. Prediction of Hip Joint Centre Location from External Landmarks. Hum. Mov. Sci. 1989, 8, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.H. Biostatistics 104: Correlational Analysis. Singap. Med. J. 2003, 44, 614–619. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The Measurement of Observer Agreement for Categorical Data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Cha, S.; Choi, J.E.; Jeon, M.; Choi, J.Y.; Yang, S.-S. Relation of Flatfoot Severity with Flexibility and Isometric Strength of the Foot and Trunk Extensors in Children. Children 2023, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.W.K.; Kong, P.W. Association between Foot Type and Lower Extremity Injuries: Systematic Literature Review with Meta-Analysis. J. Orthop. Sports Phys. Ther. 2013, 43, 700–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-N.; Chang, C.-W.; Li, C.-T.; Chang, C.-H.; Lin, C.-F. Finite Element Analysis of Plantar Fascia during Walking: A Quasi-Static Simulation. Foot Ankle Int. 2015, 36, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, G.A.; La Fata, P.C. Pathologic Conditions of the Plantar Fascia. Clin. Podiatr. Med. Surg. 2005, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, T.; Koh, M.W.P.; Jor, A.; Hisano, G.; Murata, H.; Ichimura, D.; Hobara, H. Ground Reaction Forces during Double Limb Stances while Walking in Individuals with Unilateral Transfemoral Amputation. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1041060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, K.P.; Brunet, M.E.; Gansneder, B.M.; Shultz, S.J. Effects of Pronated and Supinated Foot Postures on Static and Dynamic Postural Stability. J. Athl. Train. 2005, 40, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gold, M.; Munjal, A.; Varacallo, M. Anatomy, Bony Pelvis and Lower Limb, Hip Joint. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- In, T.-S.; Jung, J.-H.; Kim, M.; Jung, K.-S.; Cho, H.-Y. Effect of Posterior Pelvic Tilt Taping on Pelvic Inclination, Muscle Strength, and Gait Ability in Stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Study. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malige, A.; Chang, H.; Mellor, X.; Talwar, D.; Davidson, R.S. Flexible Flat Foot, Short Tendo-Achilles, and Altered Gait. Cureus 2022, 14, e21983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herchenröder, M.; Wilfling, D.; Steinhäuser, J. Evidence for Foot Orthoses for Adults with Flatfoot: A Systematic Review. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2021, 14, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Age | Gender (Male/Female) | Height (cm) | Body Mass (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal Foot (NF) | 23.16 ± 3.90 | 10/12 | 167.28 ± 8.49 | 66.35 ± 13.30 |
| Flatfoot | 23.60 ± 1.56 | 10/10 | 167.87 ± 7.52 | 63.91 ± 12.70 |
| p-value | 0.600 | 0.768 | 0.819 | 0.558 |
| PTT | FDB | PF | HFP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICC | 0.995 | 0.960 | 0.967 | 0.973 |
| PTT | FDB | PF | HFD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF | 0.304 ± 0.026 | 0.955 ± 0.166 | 0.113 ± 0.012 | 0.846 ± 0.246 |
| Flatfoot | 0.293 ± 0.032 | 0.990 ± 0.206 | 0.115 ± 0.008 | 0.836 ± 0.178 |
| p-value | 0.081 | 0.397 | 0.276 | 0.832 |
| PTT | FDB | PF | HFD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NF | 208.04 ± 30.374 | 13.002 ± 1.774 | 40.709 ± 9.742 | 18.821 ± 4.145 |
| Flatfoot | 197.56 ± 30.914 | 12.333 ± 2.515 | 46.730 ± 12.394 | 18.112 ± 3.978 |
| p-value | 0.117 | 0.165 | 0.011 * | 0.421 |
| NF | Flatfoot | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed (m/s) | 1.153 ± 0.080 | 1.184 ± 0.194 | 0.346 |
| Stride width (m) | 0.114 ± 0.026 | 0.118 ± 0.020 | 0.373 |
| Step length (m) | 0.618 ± 0.043 | 0.639 ± 0.064 | 0.084 |
| Gait cycle (s) | 0.536 ± 0.029 | 0.546 ± 0.046 | 0.255 |
| Cadence (steps/min) | 112.338 ± 6.084 | 110.806 ± 9.748 | 0.396 |
| Stance phase (%) | 0.619 ± 0.036 | 0.640 ± 0.065 | 0.073 |
| Swing phase (%) | 0.456 ± 0.028 | 0.456 ± 0.032 | 0.905 |
| Double-stance phase (%) | 0.083 ± 0.014 | 0.092 ± 0.022 | 0.005 * |
| Joint | Movement | Parameter | NF | Flatfoot | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle | Dorsi | Maximum dorsal | 15.923 ± 2.713 | 15.869 ± 2.834 | 0.930 |
| Maximum plantar flexion | −13.903 ± 6.044 | −15.061 ± 6.377 | 0.400 | ||
| range of motion | 29.826 ± 4.807 | 30.93 ± 5.528 | 0.340 | ||
| Foot Progression Angle | Maximum toe-in | −7.925 ± 4.970 | −9.198 ± 7.451 | 0.371 | |
| Maximum toe-out | −23.238 ± 5.536 | −23.689 ± 7.924 | 0.768 | ||
| range of motion | 15.313 ± 3.916 | 14.491 ± 4.594 | 0.388 | ||
| Knee | Flexion | Maximum flexion | 66.397 ± 5.997 | 66.561 ± 5.240 | 0.895 |
| Maximum extension | 4.414 ± 4.126 | 4.786 ± 5.155 | 0.722 | ||
| range of motion | 61.983 ± 5.002 | 61.775 ± 2.935 | 0.817 | ||
| Adduction | Maximum adduction | 6.992 ± 4.488 | 6.375 ± 4.967 | 0.558 | |
| Maximum abduction | −5.225 ± 4.793 | −5.074 ± 3.359 | 0.869 | ||
| range of motion | 12.217 ± 4.050 | 11.45 ± 3.808 | 0.379 | ||
| Rotation | Maximum internal rotation | −0.131 ± 5.981 | 1.238 ± 4.848 | 0.256 | |
| Maximum external rotation | −17.6 ± 6.340 | −15.631 ± 5.596 | 0.139 | ||
| range of motion | 17.469 ± 5.714 | 16.869 ± 3.425 | 0.562 | ||
| Hip | Flexion | Maximum flexion | 38.112 ± 8.991 | 35.331 ± 7.496 | 0.131 |
| Maximum extension | 0.479 ± 10.313 | −4.149 ± 7.502 | 0.002 * | ||
| range of motion | 37.633 ± 4.774 | 39.48 ± 4.760 | 0.084 | ||
| Adduction | Maximum adduction | 7.230 ± 3.850 | 7.018 ± 3.410 | 0.792 | |
| Maximum abduction | −5.995 ± 3.462 | −6.403 ± 3.560 | 0.601 | ||
| range of motion | 13.224 ± 3.240 | 13.42 ± 3.433 | 0.792 | ||
| Rotation | Maximum internal rotation | 6.922 ± 11.023 | 6.185 ± 9.952 | 0.750 | |
| Maximum external rotation | −6.445 ± 10.166 | −7.043 ± 8.508 | 0.773 | ||
| range of motion | 13.368 ± 3.960 | 13.228 ± 3.489 | 0.866 | ||
| Pelvis | Tilt | Maximum anterior tilt | 14.744 ± 7.530 | 11.057 ± 5.289 | 0.012 |
| Minimum anterior tilt | 12.032 ± 7.656 | 7.540 ± 5.156 | 0.002 * | ||
| range of motion | 2.712 ± 0.622 | 3.517 ± 1.069 | <0.001 * | ||
| Obliquity | Maximum elevation | 3.938 ± 2.495 | 3.555 ± 2.204 | 0.463 | |
| Maximum depression | −4.051 ± 2.519 | −3.578 ± 2.213 | 0.369 | ||
| range of motion | 7.989 ± 2.861 | 7.134 ± 1.923 | 0.113 | ||
| Rotation | Maximum internal rotation | 7.198 ± 2.994 | 7.34 ± 3.534 | 0.845 | |
| Maximum external rotation | −6.194 ± 3.226 | −7.082 ± 3.205 | 0.216 | ||
| range of motion | 13.392 ± 4.228 | 14.422 ± 4.386 | 0.283 |
| Joint | Movement | NF | Flatfoot | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ankle | Maximum dorsal | 1.367 ± 0.122 | 1.496 ± 0.179 | 0.324 |
| Maximum plantar flexion | −0.161 ± 0.080 | −0.181 ± 0.100 | 0.320 | |
| Knee | Maximum flexion | 0.709 ± 0.185 | 0.729 ± 0.207 | 0.277 |
| Maximum extension | −0.285 ± 0.046 | −0.264 ± 0.099 | 0.221 | |
| Maximum adduction | 0.402 ± 0.125 | 0.436 ± 0.225 | 0.325 | |
| Maximum abduction | −0.116 ± 0.044 | −0.092 ± 0.079 | 0.106 | |
| Hip | Maximum flexion | 0.618 ± 0.157 | 0.659 ± 0.188 | 0.318 |
| Maximum extension | −0.650 ± 0.140 | −0.700 ± 0.340 | 0.570 | |
| Maximum adduction | 0.770 ± 0.080 | 0.880 ± 0.080 | 0.002 * | |
| Maximum abduction | −0.180 ± 0.050 | −0.160 ± 0.120 | 0.640 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiao, X.; Hu, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Acquah, M.E.E.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Gan, Y.; Gu, D. Association between Elastic Modulus of Foot Soft Tissues and Gait Characteristics in Young Individuals with Flatfoot. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070728
Jiao X, Hu T, Li Y, Wang B, Acquah MEE, Wang Z, Chen Q, Gan Y, Gu D. Association between Elastic Modulus of Foot Soft Tissues and Gait Characteristics in Young Individuals with Flatfoot. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(7):728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070728
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiao, Xin, Tianyi Hu, Yongjin Li, Binbin Wang, Mirabel Ewura Esi Acquah, Zengguang Wang, Qianqian Chen, Yaokai Gan, and Dongyun Gu. 2024. "Association between Elastic Modulus of Foot Soft Tissues and Gait Characteristics in Young Individuals with Flatfoot" Bioengineering 11, no. 7: 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070728
APA StyleJiao, X., Hu, T., Li, Y., Wang, B., Acquah, M. E. E., Wang, Z., Chen, Q., Gan, Y., & Gu, D. (2024). Association between Elastic Modulus of Foot Soft Tissues and Gait Characteristics in Young Individuals with Flatfoot. Bioengineering, 11(7), 728. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11070728








