Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives
Abstract
1. Introduction
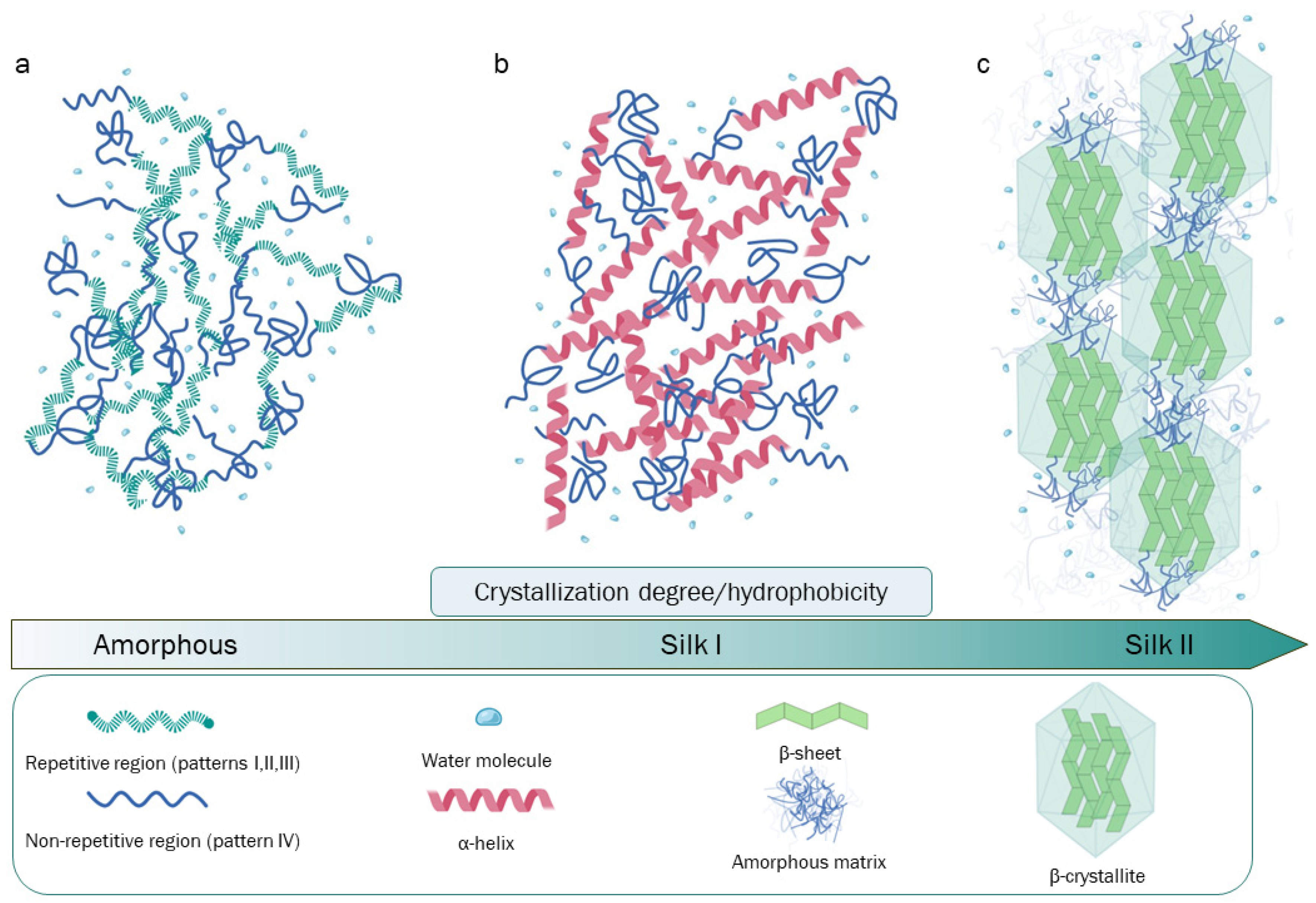
2. The Composition and Structure of Silk Fibroin
3. Silk Fibroin Processing
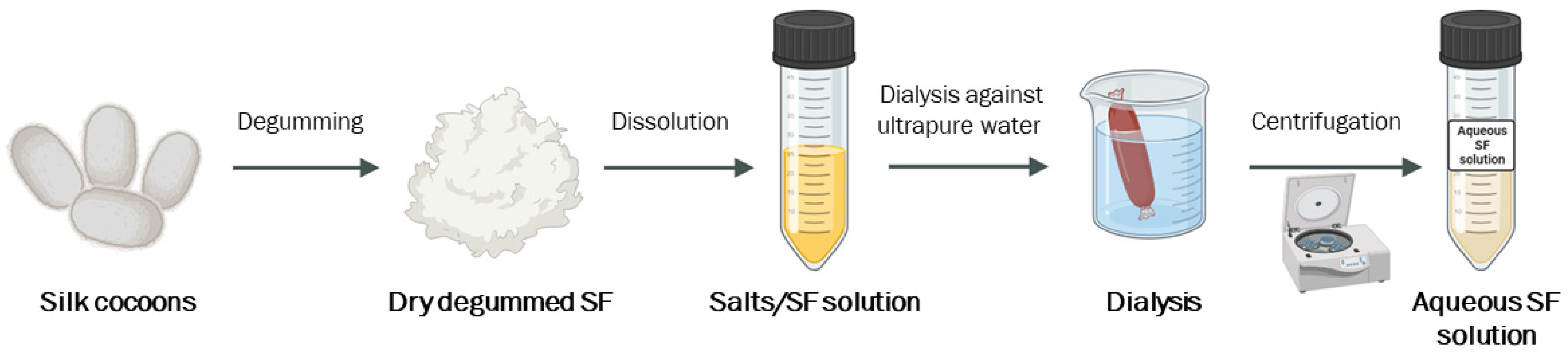
3.1. Aqueous Silk Fibroin Solution Production
3.2. Aqueous Silk Fibroin Regeneration
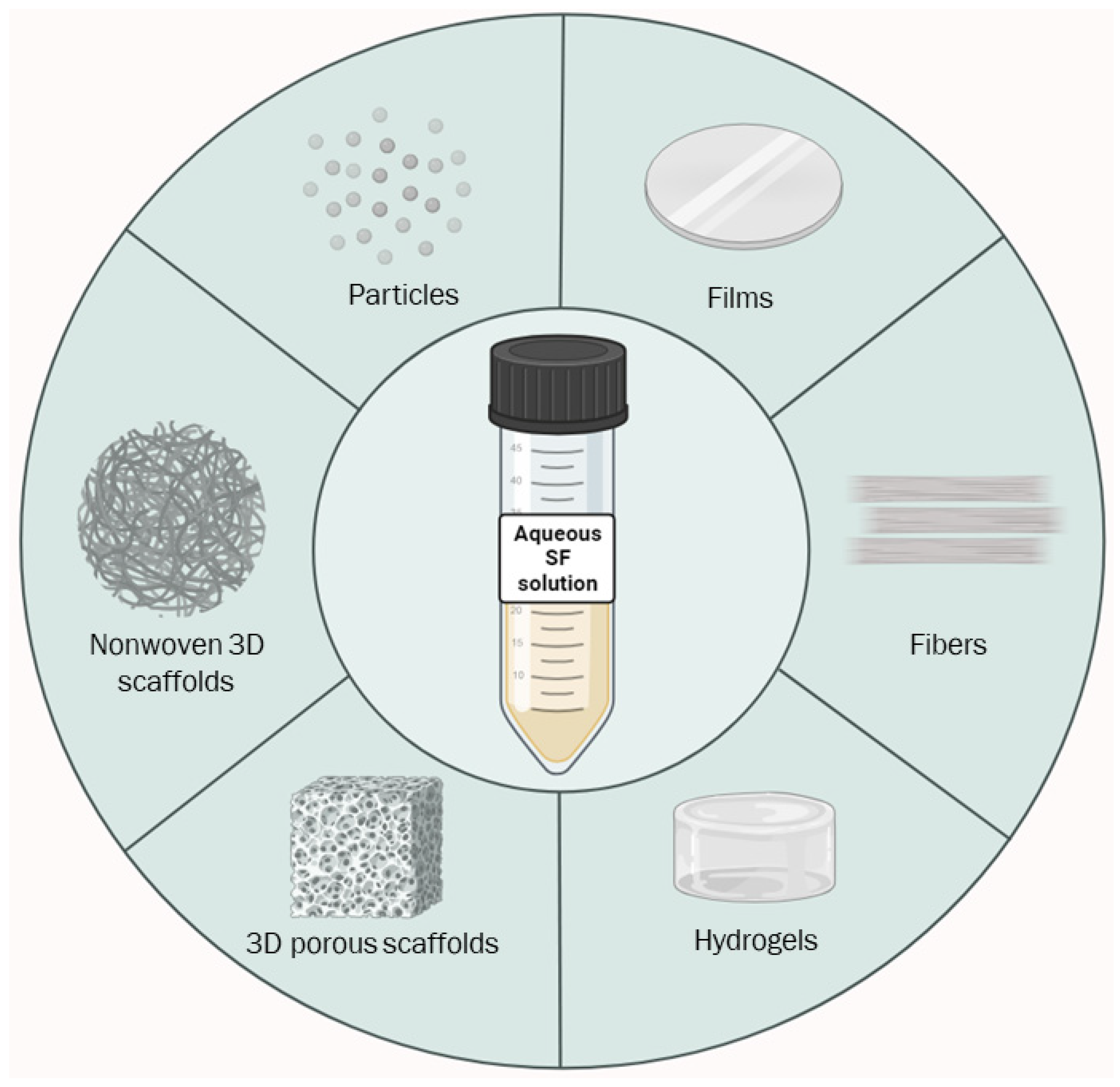
4. Silk Fibroin-Based Materials
4.1. Films
4.2. Fibers
4.3. Hydrogels
4.4. Three-Dimensional Porous Scaffolds and Non-Woven 3D Scaffolds
4.5. Particles
4.6. Silk Fibroin Composites
5. The Biocompatibility of Silk Fibroin-Based Materials
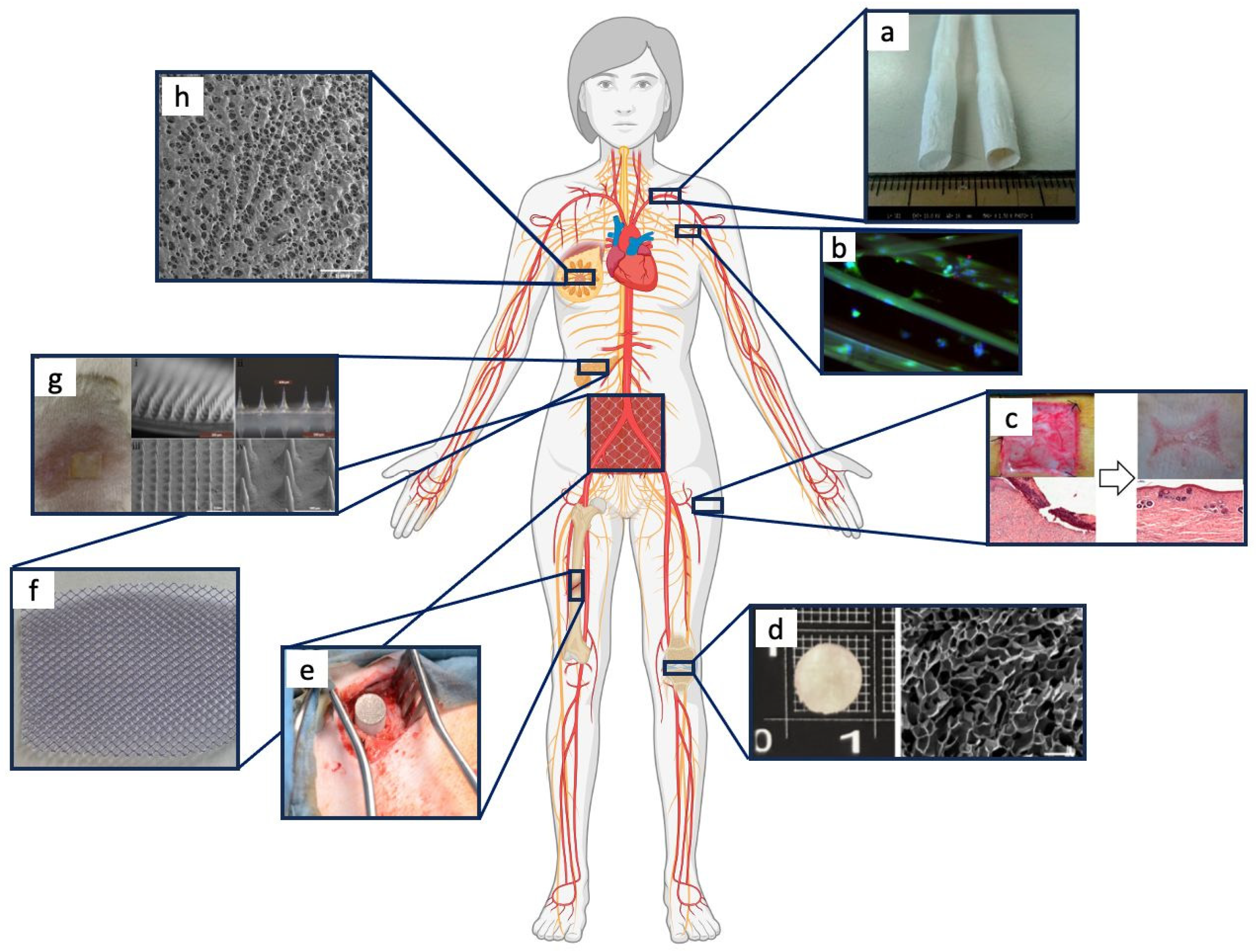
6. The Applications of Silk Fibroin-Based Materials for Tissue Regeneration
6.1. Bone Tissue Regeneration
6.2. Cartilage Tissue Regeneration
6.3. Cardiovascular System Regeneration
6.4. Skin Tissue Regeneration
6.5. Neural Tissue Regeneration
6.6. Pancreatic Tissue Regeneration
6.7. Other Biomedical Applications
6.7.1. Breast Implants
6.7.2. Hernia and Abdominal Wall Defect Treatment
6.7.3. Suture
7. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, W.; Gregory, D.A.; Tomeh, M.A.; Zhao, X. Molecular Sciences Silk Fibroin as a Functional Biomaterial for Tissue Engineering. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlman, H.; Keränen, P.; Paakinaho, K.; Linden, J.; Hannula, M.; Manninen, I.K.; Hyttinen, J.; Manninen, M.; Laitinen-Vapaavuori, O. Novel Osteoconductive β-Tricalcium Phosphate/Poly(L-Lactide-Co-e-Caprolactone) Scaffold for Bone Regeneration: A Study in a Rabbit Calvarial Defect. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2018, 29, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Cao, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Wang, N.; Yao, Z.; Dai, Y.; Xie, X.; Zhang, P.; et al. Porous Composite Scaffold Incorporating Osteogenic Phytomolecule Icariin for Promoting Skeletal Regeneration in Challenging Osteonecrotic Bone in Rabbits. Biomaterials 2018, 153, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Kim, J.S.; Oh, E.J.; Kim, T.J.; Kim, H.M.; Shim, J.H.; Yoon, W.S.; Huh, J.B.; Moon, S.H.; Kang, S.S.; et al. Effects of Three-Dimensionally Printed Polycaprolactone/β-Tricalcium Phosphate Scaffold on Osteogenic Differentiation of Adipose Tissue- and Bone Marrow-Derived Stem Cells. Arch. Craniofac. Surg. 2018, 19, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, J.; Mu, X.; Pramanick, A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Ghosh, S. Recent Advances in Bioprinting Using Silk Protein-Based Bioinks. Biomaterials 2022, 287, 121672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucciarelli, A.; Motta, A. Use of Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin in Tissue Engineering: From Cocoons to Medical Devices, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 139, 212982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craig, C.L. Evolution of arthropod silks. Annu. Rev. Èntomol. 1997, 42, 231–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saad, M.; El-Samad, L.M.; Gomaa, R.A.; Augustyniak, M.; Hassan, M.A. A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advances in Silk Sericin: Extraction Approaches, Structure, Biochemical Characterization, and Biomedical Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 250, 126067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutherland, T.D.; Young, J.H.; Weisman, S.; Hayashi, C.Y.; Merritt, D.J. Insect Silk: One Name, Many Materials. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2010, 55, 171–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vepari, C.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 991–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péreź-Rigueiro, J.; Viney, C.; Llorca, J.; Elices, M. Silkworm Silk as an Engineering Material. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 70, 2439–2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, D.; Bayley, H.; Birge, R.R.; Hench, L.L.; Mann, S.; Ratner, B.D.; Ringsdorf, H.; Schoen Brigham And Women’s Hospital; Tirrell, D.A.; Urry, D.W.; et al. Bioengineering of Materials Series Editor Editorial Advisory Board Forthcoming Books in the Series; Birkhäuser: Boston, MA, USA, 1997; ISBN 978-1-4612-4094-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmathulla, V.K. Management of Climatic Factors for Successful Silkworm (Bombyx Mori L.) Crop and Higher Silk Production: A Review. Psyche 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, E.C.; Rayor, L.S. Maternal Care and Subsocial Behaviour in Spiders. Biol. Rev. 2014, 89, 427–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, T.; Li, X.; Hu, X.; Huang, W.; Yuan, W.; Lin, Z. Artificial Superstrong Silkworm Silk Surpasses Natural Spider Silks. Matter 2022, 5, 4396–4406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Dong, Q.; Yu, Y.; Niu, B.; Ji, D.; Li, M.; Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Tan, A. Mass Spider Silk Production through Targeted Gene Replacement in Bombyx Mori. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 8757–8762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.; Moghimi, F.; Arami, M.; Mazaheri, F. Silk Degumming Using Microwave Irradiation as an Environmentally Surface Modification Method. Fibers Polym. 2010, 11, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, G.; Mossotti, R.; Innocenti, R. Degumming of Silk Fabric with Several Proteases. J. Biotechnol. 2003, 106, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockwood, D.N.; Preda, R.C.; Yücel, T.; Wang, X.; Lovett, M.L.; Kaplan, D.L. Materials Fabrication from Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin. Nat. Protoc. 2011, 6, 1612–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajzler, V.; Arif, S.; Min, K.; Kim, S.; Nekvindova, P. All-Polymer Silk-Fibroin Optical Planar Waveguides. Opt. Mater. 2021, 114, 110932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, J.; Hassan, B.; Liang, Y.; Ganesan, K.; Rajasekharan, R.; Evans, R.; Egan, G.; Kavehei, O.; Li, J.; Chana, G.; et al. A Silk Fibroin Bio-Transient Solution Processable Memristor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.U.D.; Gautam, S.P.; Qadrie, Z.L.; Gangadharappa, H.V. Silk Fibroin as a Natural Polymeric Based Bio-Material for Tissue Engineering and Drug Delivery Systems-A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 2145–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, H.W.; Ju, J.E.; Shin, M.; Holland, C.; Lee, K.H. Sericin Promotes Fibroin Silk i Stabilization Across a Phase-Separation. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaille, J.J.; Garel, A.; Prudhomme, J.C. The expression of five middle silk gland specific genes is territorially regulated during the larval development of Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. 1989, 19, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, M.; Trivedy, K.; Nirmal Kumar, S. The Silk Proteins, Sericin and Fibroin in Silkworm, Bombyx Mori Linn—A Review. Casp. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 5, 63–76. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, F.; Porter, D.; Vollrath, F. Structure and Physical Properties of Silkworm Cocoons. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 2299–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, R.I.; Brancalhão, R.M.C.; Ribeiro, L.D.F.C.; Natali, M.R.M. Silkworm Sericin: Properties and Biomedical Applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, T.; Okushita, K.; Williamson, M.P. Analysis of the Structure of Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin by NMR. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Tanaka, K.; Arisaka, F.; Kimura, S.; Ohtomo, K.; Mizuno, S. Silk Fibroin of Bombyx Mori Is Secreted, Assembling a High Molecular Mass Elementary Unit Consisting of H-Chain, L-Chain, and P25, with a 6:6:1 Molar Ratio. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 40517–40528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Inoue, S.; Mizuno, S. Hydrophobic interaction of P25, containing Asn-linked oligosaccharide chains, with the H-L complex of silk fibroin produced by Bombyx mori. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1999, 29, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Kajiyama, N.; Ishikura, K.; Waga, S.; Kikuchi, A.; Ohtomo, K.; Takagi, T.; Mizuno, S. Determination of the site of disulfide linkage between heavy and light chains of silk fibroin produced by Bombyx mori. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzym. 1999, 1432, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.-Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Medina, N.; Zivanovic, Y.; Esnault, C.; Yang, T.; Jacquet, M.; Janin, J.; Duguet, M.; Perasso, R.; et al. Fine Organization of Bombyx Mori Fibroin Heavy Chain Gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 2413–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foo, C.W.P.; Bini, E.; Hensman, J.; Knight, D.P.; Lewis, R.V.; Kaplan, D.L. Role of PH and Charge on Silk Protein Assembly in Insects and Spiders. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process 2006, 82, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.Z.; Confalonieri, F.; Jacquet, M.; Perasso, R.; Li, Z.G.; Janin, J. Silk Fibroin: Structural Implications of a Remarkable Amino Acid Sequence. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Genet. 2001, 44, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, B.; Cesari, F.C. The Chemical Structure and the crystalline structures of Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin. Biochimie 1979, 61, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.E.; Corey, R.B.; Pauling, L. An Investigation of the Structure of Silk Fibroin. Biochimica Biophysica Acta 1955, 16, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi’, K.; Kikuchi’, Y.; Takagi’, T.; Kikuchi’, A.; Oyama’, F.; Shimural, K.; Mizuno’s, S. Primary Structure of the Silk Fibroin Light Chain Determined by CDNA Sequencing and Peptide Analysis. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 210, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, T.; Ohgo, K.; Komatsu, K.; Kanenari, M.; Okuyama, K. Refinement of Repeated β-Turn Structure for Silk I Conformation of Bombyx Mori Silk Fibroin Using13C Solid-State NMR and X-Ray Diffraction Methods. Macromolecules 2005, 38, 7397–7403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, N.; Yang, Z.; Liu, X.Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, H.Y. Structural Origin of the Strain-Hardening of Spider Silk. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.T.; Huang, Q.L.; Yang, Z.; Lin, N.; Xu, G.; Liu, X.Y. Crystal Networks in Silk Fibrous Materials: From Hierarchical Structure to Ultra Performance. Small 2014, 11, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D. Conformational Transitions Model Silk Peptides. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 2690–2701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, A.; Lindsay, A.; Abedian, B.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Fibroin Solution Properties Related to Assembly and Structure. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 1006–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cebe, P.; Partlow, B.P.; Kaplan, D.L.; Wurm, A.; Zhuravlev, E.; Schick, C. Silk I and Silk II Studied by Fast Scanning Calorimetry. Acta Biomater. 2017, 55, 323–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valluzzi, R.; Gido, S.P.; Muller, W.; Kaplan, D.L. Orientation of silk III at the air-water interface. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1999, 24, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Wu, L.; Huang, J.; Guo, C. Tensile Behavior and Morphology of Differently Degummed Silkworm (Bombyx Mori) Cocoon Silk Fibres. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöltje, M.; Kölbel, A.; Aibibu, D.; Cherif, C. A Fast and Reliable Process to Fabricate Regenerated Silk Fibroin Solution from Degummed Silk in 4 Hours. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, L.S.; Hu, X.; Gallego, J.; Georgakoudi, I.; Omenetto, F.G.; Schmidt, D.; Kaplan, D.L. Effect of Processing on Silk-Based Biomaterials: Reproducibility and Biocompatibility. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2011, 99B, 89–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashina, E.S.; Bochek, A.M.; Novoselov, N.P.; Kirichenko, D.A. Structure and Solubility of Natural Silk Fibroin. Russ. J. Appl. Chem. 2006, 79, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, H.; Nakao, H.; Takasu, Y.; Tsubouchi, K. Preparation of undegraded native molecular fibroin solution from silkworm cocoons. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2001, 14, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajisawa, A. Dissolution of Silk Fibroin with Calciumchloride/Ethanol Aqueous Solution. J. Sericultural Sci. Jpn. 1997, 67, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, J.H.; Lee, K.G.; Kweon, H.Y.; Woo, S.O.; Han, S.M.; Kim, S.S.; Demura, M. Fractionation of a Silk Fibroin Hydrolysate and Its Protective Function of Hydrogen Peroxide Toxicity. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Shmelev, K.; Sun, L.; Gil, E.S.; Park, S.H.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Regulation of Silk Material Structure by Temperature-Controlled Water Vapor Annealing. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Q.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Kluge, J.A.; Lu, S.; Cebe, P.; Kaplan, D.L. Water-Insoluble Silk Films with Silk I Structure. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 1380–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Fan, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, S.; You, R. Freezing-Induced Silk I Crystallization of Silk Fibroin. CrystEngComm 2020, 22, 3884–3890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaewpirom, S.; Boonsang, S. Influence of Alcohol Treatments on Properties of Silk-Fibroin-Based Films for Highly Optically Transparent Coating Applications. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15913–15923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reizabal, A.; Gonçalves, R.; Fidalgo-Marijuan, A.; Costa, C.M.; Pérez, L.; Vilas, J.L.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Tailoring Silk Fibroin Separator Membranes Pore Size for Improving Performance of Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 598, 117678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.D.; Kaplan, D.L. Strategies for Improving the Physiological Relevance of Human Engineered Tissues. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klabukov, I.; Tenchurin, T.; Shepelev, A.; Baranovskii, D.; Mamagulashvili, V.; Dyuzheva, T.; Krasilnikova, O.; Balyasin, M.; Lyundup, A.; Krasheninnikov, M.; et al. Biomechanical Behaviors and Degradation Properties of Multilayered Polymer Scaffolds: The Phase Space Method for Bile Duct Design and Bioengineering. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reizabal, A.; Costa, C.M.; Pérez-Álvarez, L.; Vilas-Vilela, J.L.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Silk Fibroin as Sustainable Advanced Material: Material Properties and Characteristics, Processing, and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2022, 33, 2210764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, A.; Fambri, L.; Migliaresi, C. Regenerated Silk Fibroin Films: Thermal and Dynamic Mechanical Analysis. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2002, 203, 1658–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Gunawidjaja, R.; Lin, Y.H.; Gupta, M.K.; Kaplan, D.L.; Naik, R.R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Mechanical Properties of Robust Ultrathin Silk Fibroin Films. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2007, 17, 2229–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Wang, Y.; Guo, C.; Li, Y.; Ling, S.; Huang, W.; Cebe, P.; Hsu, H.H.; De Ferrari, F.; Jiang, X.; et al. 3D Printing of Silk Protein Structures by Aqueous Solvent-Directed Molecular Assembly. Macromol. Biosci. 2020, 20, 1900191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Marelli, B.; Yang, M.; An, B.; Onses, M.S.; Rogers, J.A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Inkjet Printing of Regenerated Silk Fibroin: From Printable Forms to Printable Functions. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 4273–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benfenati, V.; Toffanin, S.; Chieco, C.; Sagnella, A.; Di Virgilio, N.; Posati, T.; Varchi, G.; Natali, M.; Ruani, G.; Muccini, M.; et al. Silk Fibroin Based Technology for Industrial Biomanufacturing. In Factories of the Future: The Italian Flagship Initiative; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaramillo-Quiceno, N.; Álvarez-López, C.; Restrepo-Osorio, A. Structural and Thermal Properties of Silk Fibroin Films Obtained from Cocoon and Waste Silk Fibers as Raw Materials. Procedia Eng. 2017, 200, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinowski, C.; He, F.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, I.; Hatchett, D.W.; Zhai, S.; Zhao, H. Nanopatterned Silk Fibroin Films with High Transparency and High Haze for Optical Applications. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 40792–40799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amsden, J.J.; Domachuk, P.; Gopinath, A.; White, R.D.; Negro, L.D.; Kaplan, D.L.; Omenetto, F.G. Rapid Nanoimprinting of Silk Fibroin Films for Biophotonic Applications. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 1746–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asha, S.; Sangappa, Y.; Ganesh, S. Tuning the Refractive Index and Optical Band Gap of Silk Fibroin Films by Electron Irradiation. J. Spectrosc. 2015, 2015, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, C.M.; Purwar, R.; Kannaujia, R.; Sharma, D. Flexible Silk Fibroin Films for Wound Dressing. Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1020–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Liu, Q.; Liu, S.; Wu, R.; Ma, L. Silk Fibroin Based Conductive Film for Multifunctional Sensing and Energy Harvesting. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2022, 4, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Bailey, K.; Wang, S.; Feng, X. Silk Fibroin Films for Potential Applications in Controlled Release. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 116, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, R.; Li, G.; Kaplan, D.L.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, X. Generation of Nano-Pores in Silk Fibroin Films Using Silk Nanoparticles for Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Biomacromolecules 2021, 22, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, R.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, C.; Han, B. Green Chemistry Fabrication of Durable Antimicrobial Peptide-Immobilized Silk Fibroin Films for Accelerated Full-Thickness Wound Healing. Mater. Today Chem. 2023, 29, 101468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, B.D.; Omenetto, F.; Chui, K.; Kaplan, D.L. Processing Methods to Control Silk Fibroin Film Biomaterial Features. J. Mater. Sci. 2008, 43, 6967–6985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, C.; Numata, K.; Rnjak-Kovacina, J.; Seib, F.P. The Biomedical Use of Silk: Past, Present, Future. Adv. Health Mater. 2018, 8, e1800465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, M.E.; Lefèvre, T.; Beaulieu, L.; Asakura, T.; Pézolet, M. Study of Protein Conformation and Orientation in Silkworm and Spider Silk Fibers Using Raman Microspectroscopy. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Hu, F.; Wu, R.; Xu, Z.; Shao, G.; Yu, R.; Liu, X.Y. New Silk Road: From Mesoscopic Reconstruction/Functionalization to Flexible Meso-Electronics/Photonics Based on Cocoon Silk Materials. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagiotti, M.; Bassani, G.A.; Chiarini, A.; Vincoli, V.T.; Dal Prà, I.; Cosentino, C.; Alessandrino, A.; Taddei, P.; Freddi, G. Electrospun Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Tissue Regeneration: Chemical, Structural, and Toxicological Implications of the Formic Acid-Silk Fibroin Interaction. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 833157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.M.; Lee, G.; Kim, S.H.; Nam, Y.S.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. Electrospinning of Silk Fibroin Nanofibers and Its Effect on the Adhesion and Spreading of Normal Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts in Vitro. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frydrych, M.; Greenhalgh, A.; Vollrath, F. Artificial Spinning of Natural Silk Threads. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wöltje, M.; Isenberg, K.L.; Cherif, C.; Aibibu, D. Continuous Wet Spinning of Regenerated Silk Fibers from Spinning Dopes Containing 4% Fibroin Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, H.; Hu, X. Studies on the Post-Treatment of the Dry-Spun Fibers from Regenerated Silk Fibroin Solution: Post-Treatment Agent and Method. Mater. Des. 2012, 36, 816–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, L.; Shao, H.; Qin, K.; Hu, X.; Xia, X. Recombinant Spider Silk from Aqueous Solutions via a Bio-Inspired Microfluidic Chip. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Z.; Yuan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Fabrication of High Performance Silk Fibroin Fibers: Via Stable Jet Electrospinning for Potential Use in Anisotropic Tissue Regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 3934–3945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Kluge, J.A.; Leisk, G.G.; Kaplan, D.L. Sonication-Induced Gelation of Silk Fibroin for Cell Encapsulation. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1054–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, B.P. Recent Developments in Tough Hydrogels for Biomedical Applications. Gels 2018, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.Q. Processing Silk Hydrogel and Its Applications in Biomedical Materials. Biotechnol. Prog. 2015, 31, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Zuo, B. Functional Silk Fibroin Hydrogels: Preparation, Properties and Applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 9, 1238–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, U.J.; Park, J.; Li, C.; Jin, H.J.; Valluzzi, R.; Kaplan, D.L. Structure and Properties of Silk Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yin, Z.; Wu, F.; Fu, H.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Orientational Behaviors of Silk Fibroin Hydrogels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenkova, N.; Osama, I.; Seib, F.P.; Carswell, H.V.O. In Vivo Evaluation of Engineered Self-Assembling Silk Fibroin Hydrogels after Intracerebral Injection in a Rat Stroke Model. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Song, D.; Zhang, X.; Ding, Z.; Kong, X.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk-Graphene Hybrid Hydrogels with Multiple Cues to Induce Nerve Cell Behavior. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 613–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yan, S.; Qu, J.; Li, M.; Ye, D.; You, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D. Soft Freezing-Induced Self-Assembly of Silk Fibroin for Tunable Gelation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 117, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Yu, H.; Sun, M.; Li, Z.; Zhao, F.; Ao, Y.; Chen, H. Investigation on the Structure and Mechanical Properties of Highly Tunable Elastomeric Silk Fibroin Hydrogels Cross-Linked by Î3-Ray Radiation. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lin, K.; Zhao, C.; Wang, X. Silk Fibroin Scaffolds: A Promising Candidate for Bone Regeneration. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1054379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Wang, K.; Mei, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, W.; An, D.; Xiao, N.; Zhao, Q.; Kong, D.; et al. Fabrication of Highly Interconnected Porous Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Potential Use as Vascular Grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2014–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarov, R.; Jin, H.J.; Kaplan, D.L. Porous 3-D Scaffolds from Regenerated Silk Fibroin. Biomacromolecules 2004, 5, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniglio, D.; Bonani, W.; Migliaresi, C.; Motta, A. Silk Fibroin Porous Scaffolds by N2O Foaming. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2018, 29, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, N.; Fan, Q.; Yan, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, D.; You, R. Silk Fibroin Scaffolds with Stable Silk I Crystal and Tunable Properties. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 248, 125910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, C.; Ma, X.; Li, Y. Optimization of Macroporous 3-D Silk Fibroin Scaffolds by Salt-Leaching Procedure in Organic Solvent-Free Conditions. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, C.; Lu, S.; Wu, Z.; Yan, H. Study on Porous Silk Fibroin Materials: 3. Influence of Repeated Freeze-Thawing on the Structure and Properties of Porous Silk Fibroin Materials. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2002, 13, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitropoulos, A.N.; Burpo, F.J.; Nguyen, C.K.; Nagelli, E.A.; Ryu, M.Y.; Wang, J.; Sims, R.K.; Woronowicz, K.; Wickiser, J.K. Noble Metal Composite Porous Silk Fibroin Aerogel Fibers. Materials 2019, 12, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, H.; Montes, S.; Hayati-Roodbari, N.; Putz, F.; Huesing, N. Compressible, Thermally Insulating, and Fire Retardant Aerogels through Self-Assembling Silk Fibroin Biopolymers Inside a Silica Structure-An Approach towards 3D Printing of Aerogels. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 22718–22730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yetiskin, B.; Okay, O. High-Strength Silk Fibroin Scaffolds with Anisotropic Mechanical Properties. Polymer 2017, 112, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutmacher, D.W. Scaffolds in tissue engineering bone and cartilage. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 2529–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.H.; Wang, L.; Dai, H.L.; Wang, X.Y.; Li, J.S.; Zhao, Z. Fabrication, Characterization, and in Vitro Evaluation of Biomimetic Silk Fibroin Porous Scaffolds via Supercritical CO2 Technology. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2019, 150, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, B.; Guo, Y.; Dong, K. Development of Silk Fibroin-sodium Alginate Scaffold Loaded Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Hemostasis and Cell Adhesion. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 211, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadisi, Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Walsh, T.; Dehghan, M.M.; Farzad-Mohajeri, S.; Gholami, H.; Diyanoush, A.; Pagan, E.; Akbari, M. In Vitro and in Vivo Evaluation of Silk Fibroin-Hardystonite-Gentamicin Nanofibrous Scaffold for Tissue Engineering Applications. Polym. Test. 2020, 91, 106698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Fan, C.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. 3D-Printed Scaffolds of Biomineralized Hydroxyapatite Nanocomposite on Silk Fibroin for Improving Bone Regeneration. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 467–468, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shome, A.; Moses, J.C.; Rather, A.M.; Mandal, B.B.; Manna, U. Unconventional and Facile Fabrication of Chemically Reactive Silk Fibroin Sponges for Environmental Remediation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 24258–24271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, G. Silk Fibroin Microfiber and Nanofiber Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering and Regeneration. In Silk Biomaterials for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 157–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Baughman, C.B.; Kaplan, D.L. In Vitro Evaluation of Electrospun Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Vascular Cell Growth. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2217–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasoju, N.; Bhonde, R.R.; Bora, U. Fabrication of a Novel Micro-Nano Fibrous Nonwoven Scaffold with Antheraea Assama Silk Fibroin for Use in Tissue Engineering. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 2466–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pra, I.; Chiarini, A.; Boschi, A.; Freddi, G.; Armato, U. Novel Dermo-Epidermal Equivalents on Silk Fibroin-Based Acid-Crosslinked Three-Dimensional Nonwoven with Prospective Applications in Human Engineering/Regeneration/Repair. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2006, 8, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balan, K.K.; Sundaramoorthy, S. Hydroentangled Nonwoven Eri Silk Fibroin Scaffold for Tissue Engineering Applications. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 48, 1291–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Tavanai, H.; Moradi, A.R. Production of Fibroin Nanopowder through Electrospraying. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2011, 13, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Shen, W.D.; Xiang, R.L.; Zhuge, L.J.; Gao, W.J.; Wang, W.B. Formation of Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles in Water-Miscible Organic Solvent and Their Characterization. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2007, 9, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammel, A.S.; Hu, X.; Park, S.H.; Kaplan, D.L.; Scheibel, T.R. Controlling Silk Fibroin Particle Features for Drug Delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4583–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myung, S.J.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, Y.; Chen, P.; Jin, H.-J. Fluorescent silk fibroin nanoparticles prepared using a reverse microemulsion. Macromol. Res. 2008, 16, 604–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Yang, H.; Xu, W. Effective Removal of Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using Ultrafine Silk Fibroin Powder. Adv. Powder Technol. 2014, 25, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Yadav, S.C. Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery Systems. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 75, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, J.; Chung, Y.I.; Kim, Y.H.; Tae, G.; Kundu, S.C. Silk Fibroin Nanoparticles for Cellular Uptake and Control Release. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 388, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, M. Bin Silk Fibroin-Based Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 4880–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, D.T.; Tiyaboonchai, W. Fibroin Nanoparticles: A Promising Drug Delivery System. Drug Deliv. 2020, 27, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, N.; Lei, R.; Xu, J.; Kundu, S.C.; Cai, Y.; Yao, J.; Ni, Q. Fabricated Porous Silk Fibroin Particles for PH-Responsive Drug Delivery and Targeting of Tumor Cells. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3319–3330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subbiah, R.; Veerapandian, M.; Yun, K.S. Nanoparticles: Functionalization and Multifunctional Applications in Biomedical Sciences. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4559–4577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naserzadeh, P.; Mortazavi, S.A.; Ashtari, K.; Salimi, A.; Farokhi, M.; Pourahmad, J. Evaluation of the Toxicity Effects of Silk Fibroin on Human Lymphocytes and Monocytes. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2018, 32, 22056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Guo, C.; Yang, Q.; Li, C.; Zhao, P.; Xia, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Protein Composites from Silkworm Cocoons as Versatile Biomaterials. Acta Biomater. 2021, 121, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Han, Y.; Cheng, H. Biomedical Applications of Chitosan/Silk Fibroin Composites: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 240, 124407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharjee, P.; Ahearne, M. Fabrication and Biocompatibility of Electroconductive Silk Fibroin/Pedot: Pss Composites for Corneal Epithelial Regeneration. Polymers 2020, 12, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganuma, K.; Matsuda, H.; Asakura, T. Characterization of Polyurethane and a Silk Fibroin-Polyurethane Composite Fiber Studied with NMR Spectroscopies. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Ibe, Y.; Jono, T.; Tanaka, R.; Naito, A.; Asakura, T. Characterization of a Water-Dispersed Biodegradable Polyurethane-Silk Composite Sponge Using13c Solid-State Nuclear Magnetic Resonance as Coating Material for Silk Vascular Grafts with Small Diameters. Molecules 2021, 26, 4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, W. Physical Characteristics and Properties of Waterborne Polyurethane Materials Reinforced with Silk Fibroin Powder. J. Polym. Sci. B Polym. Phys. 2010, 48, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, L.D.; Cheng, Y.; Teng, C.P.; Khin, Y.W.; Loh, X.J.; Tee, S.Y.; Low, M.; Ye, E.; Yu, H.D.; Zhang, Y.W.; et al. Structures, Mechanical Properties and Applications of Silk Fibroin Materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2015, 46, 86–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, A.; Smeets, R.; Gosau, M.; Friedrich, R.E.; Fuest, S.; Behbahani, M.; Barbeck, M.; Rutkowski, R.; Burg, S.; Kluwe, L.; et al. Production and Characterization of Porous Fibroin Scaffolds for Regenerative Medical Application. Vivo 2019, 33, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katti, M.V.; Sami-Subbu, R.; Ranjekar, P.K.; Gupta, V.S. Amino Acid Repeat Patterns in Protein Sequences: Their Diversity and Structural-functional Implications. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 1203–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yigit, S.; Hallaj, N.S.; Sugarman, J.L.; Chong, L.C.; Roman, S.E.; Abu-Taleb, L.M.; Goodman, R.E.; Johnson, P.E.; Behrens, A.M. Toxicological Assessment and Food Allergy of Silk Fibroin Derived from Bombyx Mori Cocoons. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kundu, B.; Rajkhowa, R.; Kundu, S.C.; Wang, X. Silk Fibroin Biomaterials for Tissue Regenerations. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 65, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ode Boni, B.O.; Bakadia, B.M.; Osi, A.R.; Shi, Z.; Chen, H.; Gauthier, M.; Yang, G. Immune Response to Silk Sericin–Fibroin Composites: Potential Immunogenic Elements and Alternatives for Immunomodulation. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 22, 2100292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal Pra, I.; Freddi, G.; Minic, J.; Chiarini, A.; Armato, U. De Novo Engineering of Reticular Connective Tissue in Vivo by Silk Fibroin Nonwoven Materials. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 1987–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.P.; Huang, K.C.; Bai, M.Y. Silk Fibroin Protein-Based Nonwoven Mats Incorporating Baicalein Chinese Herbal Extract: Preparation, Characterizations, and in Vivo Evaluation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenkova, N.; Maitz, M.F.; Böhme, G.; Alhadrami, H.A.; Jiffri, E.H.; Totten, J.D.; Werner, C.; Carswell, H.V.O.; Seib, F.P. The Innate Immune Response of Self-Assembling Silk Fibroin Hydrogels. Biomater. Sci. 2021, 9, 7194–7204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Gui, X.; Ran, J.; Xu, G.; Zhao, H.; Zeng, M.; Ji, J.; et al. Silk Fibroin Biomaterial Shows Safe and Effective Wound Healing in Animal Models and a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2017, 6, 1700121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Cao, C.; Ma, X.; Hu, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, C. In Vitro and in Vivo Degradation Behavior of Aqueous-Derived Electrospun Silk Fibroin Scaffolds. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1679–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Redmond, S.L.; Papadimitriou, J.M.; Teh, B.M.; Yan, S.; Wang, Y.; Atlas, M.D.; Marano, R.J.; Zheng, M.; Dilley, R.J. The Biocompatibility of Silk Fibroin and Acellular Collagen Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering in the Ear. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 9, 015015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Liu, H.; Toh, S.L.; Goh, J.C.H. Anterior Cruciate Ligament Regeneration Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Silk Scaffold in Large Animal Model. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4967–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Wei, D.; Huang, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Y. 3D Printing of Mesoporous Bioactive Glass/Silk Fibroin Composite Scaffolds for Bone Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 103, 109731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundmark, K.; Westermark, G.T.; Olsé, A.; Westermark, P. Protein fibrils in nature can enhance amyloid protein A amyloidosis in mice: Cross-seeding as a disease mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 6098–6102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukawaki, S.; Murakami, T.; Suzuki, K.; Nakazawa, Y. Studies on the Potential Risk of Amyloidosis from Exposure to Silk Fibroin. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 11, 065010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuluaga-Vélez, A.; Quintero-Martinez, A.; Orozco, L.M.; Sepúlveda-Arias, J.C. Silk Fibroin Nanocomposites as Tissue Engineering Scaffolds–A Systematic Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 141, 111924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Domínguez, C.; Lozano-Picazo, P.; Álvarez-López, A.; Garrote-Junco, J.; Panetsos, F.; Guinea, G.V.; Elices, M.; Rojo, F.J.; González-Nieto, D.; Colchero, L.; et al. Axonal Guidance Using Biofunctionalized Straining Flow Spinning Regenerated Silk Fibroin Fibers as Scaffold. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.P.; Nguyen, Q.V.; Nguyen, V.H.; Le, T.H.; Huynh, V.Q.N.; Vo, D.V.N.; Trinh, Q.T.; Kim, S.Y.; Van Le, Q. Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polymers 2019, 11, 1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wu, N.; Zeng, J.; Liang, Z.; Qi, Z.; Jiang, H.; Chen, H.; Liu, X. Chondrogenic Differentiation of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cells Induced by Decellularized Cartilage Matrix/Silk Fibroin Secondary Crosslinking Hydrogel Scaffolds with a Three-Dimensional Microstructure. Polymers 2023, 15, 1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovati, A.B.; Lopa, S.; Bottagisio, M.; Talò, G.; Canciani, E.; Dellavia, C.; Alessandrino, A.; Biagiotti, M.; Freddi, G.; Segatti, F.; et al. Peptide-Enriched Silk Fibroin Sponge and Trabecular Titanium Composites to Enhance Bone Ingrowth of Prosthetic Implants in an Ovine Model of Bone Gaps. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 563203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, G.; Jiang, F.; Jia, T.; Qi, Z.; Xing, T.; Kundu, S.C.; Lu, S. Glucose-Responsive Silk Fibroin Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery of Insulin. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzi, M.C.; Marcolin, C.; Draghi, L.; Farè, S. 2D and 3D 2D and 3D Electrospun Silk Fibroin Gelatin Coatings to Improve Scaffold Performances in Cardiovascular Applications. Mater. Proc. 2020, 2, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, R.; Fuentes-Chandía, M.; Ai, J.; Habibi Roudkenar, M.; Reza Mahboubian, A.; Rad Malekshahi, M.; Nasser Ostad, S. A Thermo-Sensitive Hydrogel Composed of Methylcellulose/Hyaluronic Acid/Silk Fibrin as a Biomimetic Extracellular Matrix to Simulate Breast Cancer Malignancy. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 176, 111421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, D.W.; Dumanian, G.A. Bone Biology and Physiology: Part I. the Fundamentals. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 1314–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshpande, R.; Shukla, S.; Sayyad, R.; Salunke, S.; Nisal, A.; Venugopalan, P. Silk Fibroin and Ceramic Scaffolds: Comparative in Vitro Studies for Bone Regeneration. Bioeng. Transl. Med. 2021, 6, 10221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, T.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Chen, C.; Liu, F. The Incorporation of β-Tricalcium Phosphate Nanoparticles within Silk Fibroin Composite Scaffolds for Enhanced Bone Regeneration: An in Vitro and in Vivo Study. J. Biomater. Appl. 2022, 36, 1567–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Sequential and Sustained Release of SDF-1 and BMP-2 from Silk Fibroin-Nanohydroxyapatite Scaffold for the Enhancement of Bone Regeneration. Biomaterials 2016, 106, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Wang, T.; Yang, C.; Darvell, B.W.; Wu, J.; Lin, K.; Chang, J.; Pan, H.; Lu, W.W. Alkaline Biodegradable Implants for Osteoporotic Bone Defects—Importance of Microenvironment PH. Osteoporos. Int. 2016, 27, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vimalraj, S. Alkaline Phosphatase: Structure, Expression and Its Function in Bone Mineralization. Gene 2020, 754, 144855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; Meng, Z.; Wu, Q.; Zeng, D.; Guo, Z.; Yao, J.; Bian, Y.; Gu, Y.; Cheng, S.; Peng, L.; et al. Biomimetic and Osteogenic 3D Silk Fibroin Composite Scaffolds with Nano MgO and Mineralized Hydroxyapatite for Bone Regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. 2020, 11, 2041731420967791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Pathak, J.L.; Liang, D.; Zhong, N.; Guan, H.; Wan, M.; Miao, G.; Li, Z.; Ge, L. Fabrication and Characterization of Strontium-Hydroxyapatite/Silk Fibroin Biocomposite Nanospheres for Bone-Tissue Engineering Applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 366–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, M.; Fernandes, M.H.; Beppu, M.M.; Monteiro, F.J.; Ferraz, M.P. Silk Fibroin/Nanohydroxyapatite Hydrogels for Promoted Bioactivity and Osteoblastic Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow Stromal Cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 89, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Chen, X.; Jiang, X.; Fu, G. Silk Fibroin Hydrogel Membranes Prepared by a Sequential Cross-Linking Strategy for Guided Bone Regeneration. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2023, 147, 106133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbs, D.M.R.; Black, C.R.M.; Dawson, J.I.; Oreffo, R.O.C. A Review of Hydrogel Use in Fracture Healing and Bone Regeneration. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2016, 10, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, M.; Khaleel, A.; Karam, S.M.; Al-Marzouqi, A.H.; ur Rehman, I.; Mohsin, S. Bacterial Inhibition and Osteogenic Potentials of Sr/Zn Co-Doped Nano-Hydroxyapatite-PLGA Composite Scaffold for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications. Polymers 2023, 15, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, X.; Libera, M. Reducing Bacterial Colonization of 3-D Nanofiber Cell Scaffolds by Hierarchical Assembly of Microgels and an Antimicrobial Peptide. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2013, 2, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, M.; Ferraz, M.P.; Monteiro, F.J.; Fernandes, M.H.; Beppu, M.M.; Mantione, D.; Sardon, H. Antibacterial Silk Fibroin/Nanohydroxyapatite Hydrogels with Silver and Gold Nanoparticles for Bone Regeneration. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, V.P.; da Silva Morais, A.; Maia, F.R.; Canadas, R.F.; Costa, J.B.; Oliveira, A.L.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reis, R.L. Combinatory Approach for Developing Silk Fibroin Scaffolds for Cartilage Regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018, 72, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Sun, M.; Hu, X.; Ren, B.; Cheng, J.; Li, C.; Duan, X.; Fu, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, H.; et al. Structurally and Functionally Optimized Silk-Fibroin–Gelatin Scaffold Using 3D Printing to Repair Cartilage Injury In Vitro and In Vivo. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Cui, J.; Wu, S.; Geng, Z.; Su, J. Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Cartilage/ Osteochondral Repair. Theranostics 2022, 12, 5103–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, Q.; Cheng, N.; Tao, X.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Q. Collagen/Silk Fibroin Composite Scaffold Incorporated with PLGA Microsphere for Cartilage Repair. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 61, 705–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Bella, E.; Lee, C.S.D.; Migliaresi, C.; Pelcastre, L.; Schwartz, Z.; Boyan, B.D.; Motta, A. The Synergistic Effects of 3-D Porous Silk Fibroin Matrix Scaffold Properties and Hydrodynamic Environment in Cartilage Tissue Regeneration. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 4672–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharafat-Vaziri, A.; Khorasani, S.; Darzi, M.; Saffarian, Z.; Alizadeh, Z.; Tahmasebi, M.N.; Kazemnejad, S. Safety and Efficacy of Engineered Tissue Composed of Silk Fibroin/Collagen and Autologous Chondrocytes in Two Patients with Cartilage Defects: A Pilot Clinical Trial Study. Knee 2020, 27, 1300–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Fu, X.; Wang, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, L.; Qiao, S.; An, J.; Xia, T. Self-Assemble Silk Fibroin Microcapsules for Cartilage Regeneration through Gene Delivery and Immune Regulation. Small 2023, 19, 2302799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.K.; In Kim, J.; Sim, B.R.; Khang, G. Bioengineered Porous Composite Curcumin/Silk Scaffolds for Cartilage Regeneration. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari Foroushani, P.; Rahmani, E.; Alemzadeh, I.; Vossoughi, M.; Pourmadadi, M.; Rahdar, A.; Díez-Pascual, A.M. Curcumin Sustained Release with a Hybrid Chitosan-Silk Fibroin Nanofiber Containing Silver Nanoparticles as a Novel Highly Efficient Antibacterial Wound Dressing. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naserzadeh, P.; Mortazavi, A.; Ashtari, K.; Seydi, E.; Pourahmad, J. Evaluation of the Toxicity Effects of Silk Fibroin on Isolated Fibroblast and Huvec Cells. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 134–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kiritani, S.; Kaneko, J.; Ito, D.; Morito, M.; Ishizawa, T.; Akamatsu, N.; Tanaka, M.; Iida, T.; Tanaka, T.; Tanaka, R.; et al. Silk Fibroin Vascular Graft: A Promising Tissue-Engineered Scaffold Material for Abdominal Venous System Replacement. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valsecchi, E.; Biagiotti, M.; Alessandrino, A.; Gastaldi, D.; Vena, P.; Freddi, G. Silk Vascular Grafts with Optimized Mechanical Properties for the Repair and Regeneration of Small Caliber Blood Vessels. Materials 2022, 15, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, L.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Guo, J.; Ren, X.; Xia, S.; Zhang, W.; Feng, Y. Biofunctionalized Electrospun PCL-PIBMD/SF Vascular Grafts with PEG and Cell-Adhesive Peptides for Endothelialization. Macromol. Biosci. 2019, 19, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, Y.; Sahin, M.G.; Kok, F.N. Application Potential of Three-Dimensional Silk Fibroin Scaffold Using Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Cardiac Regeneration. J. Biomater. Appl. 2021, 36, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Pan, W.; Tan, G. Silk Fibroin Combined with Electrospinning as a Promising Strategy for Tissue Regeneration. Macromol. Biosci. 2022, 23, e2200380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patra, C.; Talukdar, S.; Novoyatleva, T.; Velagala, S.R.; Mühlfeld, C.; Kundu, B.; Kundu, S.C.; Engel, F.B. Silk Protein Fibroin from Antheraea Mylitta for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 2673–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, N.H.; Yang, M.C.; Chung, T.W.; Chen, J.Y.; Chou, N.K.; Wang, S.S. Cardiac Repair Achieved by Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells/Silk Fibroin/Hyaluronic Acid Patches in a Rat of Myocardial Infarction Model. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 5541–5551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, H.M.; Hussein, K.H.; Sayed, M.M.; El-Aassar, M.R.; Mohamed, I.M.A.; Kwak, H.H.; Woo, H.M.; Abdal-hay, A. Development of Biocompatible Tri-Layered Nanofibers Patches with Endothelial Cells for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 129, 109630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, N.H.; Yang, M.C.; Chung, T.W.; Chou, N.K.; Wang, S.S. Cardiac Repair Using Chitosan-Hyaluronan/Silk Fibroin Patches in a Rat Heart Model with Myocardial Infarction. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Xiao, D.; Su, H.; Chen, Z.; Wang, B.; Feng, X.; Mao, Z.; Sui, X. Highly Stretchable Porous Regenerated Silk Fibroin Film for Enhanced Wound Healing. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, Y.; Ruan, L.; Jiang, G.; Nie, L.; Shavandi, A.; Sun, Y.; Xu, J.; Shao, X.; Zhu, J. Regenerated Silk Fibroin and Alginate Composite Hydrogel Dressings Loaded with Curcumin Nanoparticles for Bacterial-Infected Wound Closure. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 149, 213405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.; Ding, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lu, X.; Lu, Q.; Kaplan, D.L. Anisotropic Biomimetic Silk Scaffolds for Improved Cell Migration and Healing of Skin Wounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 44314–44323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, G.; Chen, Y.; Mao, C.; Yang, M. Polydopamine-Coated Antheraea Pernyi (A. Pernyi) Silk Fibroin Films Promote Cell Adhesion and Wound Healing in Skin Tissue Repair. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 34736–34743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, D.; Lohe, T.U.; Samudrala, P.K.; Mandal, B.B. In Situ Forming Injectable Silk Fibroin Hydrogel Promotes Skin Regeneration in Full Thickness Burn Wounds. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, e1801092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.M.; Chae, T.; Sheikh, F.A.; Ju, H.W.; Moon, B.M.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.R.; Park, C.H. Three Dimensional Poly(ε-Caprolactone) and Silk Fibroin Nanocomposite Fibrous Matrix for Artificial Dermis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, R.D.; Kimmerling, E.P.; Cairns, D.M.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk as a Biomaterial to Support Long-Term Three-Dimensional Tissue Cultures. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 21861–21868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keirouz, A.; Zakharova, M.; Kwon, J.; Robert, C.; Koutsos, V.; Callanan, A.; Chen, X.; Fortunato, G.; Radacsi, N. High-Throughput Production of Silk Fibroin-Based Electrospun Fibers as Biomaterial for Skin Tissue Engineering Applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Armato, U.; Freddi, G.; Chiarini, A.; Dal Prà, I. Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Co-Cultured on Silk Fibroin Scaffolds Exosomally Overrelease Angiogenic and Growth Factors. Cells 2023, 12, 1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boni, R.; Ali, A.; Giteru, S.G.; Shavandi, A.; Clarkson, A.N. Silk Fibroin Nanoscaffolds for Neural Tissue Engineering. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2020, 31, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phamornnak, C.; Han, B.; Spencer, B.F.; Ashton, M.D.; Blanford, C.F.; Hardy, J.G.; Blaker, J.J.; Cartmell, S.H. Instructive Electroactive Electrospun Silk Fibroin-Based Biomaterials for Peripheral Nerve Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 141, 213094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Jia, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Chai, Y. Silk Fibroin Enhances Peripheral Nerve Regeneration by Improving Vascularization within Nerve Conduits. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 2070–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saremi, J.; Khanmohammadi, M.; Azami, M.; Ai, J.; Yousefi-Ahmadipour, A.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S. Tissue-Engineered Nerve Graft Using Silk-Fibroin/Polycaprolactone Fibrous Mats Decorated with Bioactive Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2021, 109, 1588–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chei, S.; Oh, H.J.; Lee, K.; Jin, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, B.Y. Dietary Silk Peptide Inhibits LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Modulating Toll-like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Signaling. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, H.-S.; Kang, Y.K.; Shin, Y.K.; Lee, H.J.; Yu, J.-I.; Lee, K.G.; Yeo, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Sohn, D.-S.; Kim, K.Y.; et al. The Role of BF-7 on Neuroprotection and Enhancement of Cognitive Function. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2004, 8, 173–179. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.-K.; Nam, S.-H.; Sohn, H.-O.; Lee, D.-W. Inhibitory Effect of Silkworm-Extract(SE) on Monoamine Oxidase Activity in Vitro and in Vivo. Entomol. Res. 2005, 35, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-K.; Oh, H.-S.; Cho, Y.-H.; Kim, Y.-J.; Han, Y.-G.; Nam, S.-H. Effects of a Silkworm Extract on Dopamine and Monoamine Oxidase-B Activity in an MPTP-Induced Parkinsons Disease Model. Lab. Anim. Res. 2010, 26, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, A.B.; Sadigh-Eteghad, S.; Torbati, M.; Fazljou, S.M.B.; Vatandoust, S.M.; Golzari, S.E.J.; Farajdokht, F.; Mahmoudi, J. Identification and Applications of Neuroactive Silk Proteins: A Narrative Review. J. Appl. Biomed. 2019, 17, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.K.; Park, D.; Lee, S.H.; Choi, Y.J.; Bae, D.K.; Yang, Y.H.; Yang, G.; Kim, Y.B.; Yeon, S.; Lim, W.T.; et al. Tyrosine-Fortified Silk Amino Acids Improve Physical Function of Parkinson’S Disease Rats. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2011, 20, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Qiu, H.; Niu, W.; Li, X.; Qian, J. A Hyaluronic Acid/Silk Fibroin/Poly-Dopamine-Coated Biomimetic Hydrogel Scaffold with Incorporated Neurotrophin-3 for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Acta Biomater. 2023, 167, 219–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Dai, C.; Liu, X.; Dai, L.; Li, R.; Ma, K.; Xu, H.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, Z.; He, T.; et al. Implantation of Regenerative Complexes in Traumatic Brain Injury Canine Models Enhances the Reconstruction of Neural Networks and Motor Function Recovery. Theranostics 2020, 11, 768–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Rong, L.; Bao, Q.Z. Electrospun Silk Fibroin Nanofiber Tubes for Peripheral Nerve Regeneration. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010 4th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering (iCBBE), Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Guedan-Duran, A.; Jemni-Damer, N.; Orueta-Zenarruzabeitia, I.; Guinea, G.V.; Perez-Rigueiro, J.; Gonzalez-Nieto, D.; Panetsos, F. Biomimetic Approaches for Separated Regeneration of Sensory and Motor Fibers in Amputee People: Necessary Conditions for Functional Integration of Sensory–Motor Prostheses With the Peripheral Nerves. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 584823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojnordi, M.N.; Ebrahimi-Barough, S.; Vojoudi, E.; Hamidabadi, H.G. Silk Nanofibrous Electrospun Scaffold Enhances Differentiation of Embryonic Stem like Cells Derived from Testis in to Mature Neuron. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2018, 106, 2662–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, F.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Gu, X. Biocompatibility Evaluation of Silk Fibroin with Peripheral Nerve Tissues and Cells in Vitro. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyung Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, M.; Jeong, Y.; Lee, S. Exosome-Coated Silk Fibroin 3D-Scaffold for Inducing Osteogenic Differentiation of Bone Marrow Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 406, 127080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhang, K.; Mao, H.Q.; Yang, Y. Application of Conductive PPy/SF Composite Scaffold and Electrical Stimulation for Neural Tissue Engineering. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tufan, Y.; Öztatlı, H.; Garipcan, B.; Ercan, B. Development of Electrically Conductive Porous Silk Fibroin/Carbon Nanofiber Scaffolds. Biomed. Mater. 2021, 16, 025027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmler, L.; Naghilou, A.; Millesi, F.; Wolf, S.; Mann, A.; Stadlmayr, S.; Mero, S.; Ploszczanski, L.; Greutter, L.; Woehrer, A.; et al. Silk-in-Silk Nerve Guidance Conduits Enhance Regeneration in a Rat Sciatic Nerve Injury Model. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2023, 12, e2203237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, B.; Lee, Y.K.; Lee, S.; Chun, J.M.; Suh, J.G.; Park, J.H. Silk Fibroin Promotes the Regeneration of Pancreatic β-Cells in the C57BL/KsJ-Leprdb/DbMouse. Molecules 2020, 25, 3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, X.; Ma, R.; Yang, X.; Ke, T.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Kong, D.; Li, C. A Macroporous Heparin-Releasing Silk Fibroin Scaffold Improves Islet Transplantation Outcome by Promoting Islet Revascularisation and Survival. Acta Biomater. 2017, 59, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama-Iwatsuki, K.; Yamanaka, T.; Negishi, J.; Teshima, J.; Tamada, Y.; Hirabayashi, M.; Hochi, S. Transplantation of Rat Pancreatic Islets Vitrified-Warmed on the Nylon Mesh Device and the Silk Fibroin Sponge Disc. Islets 2020, 12, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, T.; Nakayama-Iwatsuki, K.; Fujimoto, S.; Hirono, N.; Negishi, J.; Tamada, Y.; Hirabayashi, M.; Hochi, S. All-in-One Silk Fibroin Sponge as the Vitrification Cryodevice of Rat Pancreatic Islets and the VEGF-Embedded Scaffold for Subrenal Transplantation. Transpl. Proc. 2021, 53, 1744–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Kim, B.; Nam, H.; Suh, J.G. Improving Glycemic Control in Model Mice with Type 2 Diabetes by Increasing Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity Using Silk Fibroin Hydrolysate (SFH). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wan, J.; Jin, P.; Lv, Q. Multifunctional Silk Fibroin Methacryloyl Microneedle for Diabetic Wound Healing. Small 2022, 18, e2203064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhai, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Weng, J.; Li, J.; Chen, X. An Antibacterial and Proangiogenic Double-Layer Drug-Loaded Microneedle Patch for Accelerating Diabetic Wound Healing. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 11, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matough, F.A.; Budin, S.B.; Hamid, Z.A.; Alwahaibi, N.; Mohamed, J. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Diabetic Complications. Sultan Qaboos Univ. Med. J. 2012, 12, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, E.; Rosendahl, J.; Solberg, A.; Ståhlberg, A.; Håkansson, J.; Chinga-Carrasco, G. Polysaccharides and Structural Proteins as Components in Three-Dimensional Scaffolds for Breast Cancer Tissue Models: A Review. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrabi, A.; Mousazadeh, S.; Mollafilabi, A.; Nafissi, N.; Milan, P.B. Synthesis and Characterization of a Silk Fibroin/Placenta Matrix Hydrogel for Breast Reconstruction. Life Sci. 2023, 334, 122236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yucel, T.; Lovett, M.L.; Giangregorio, R.; Coonahan, E.; Kaplan, D.L. Silk Fibroin Rods for Sustained Delivery of Breast Cancer Therapeutics. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 8613–8620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, C.; Gupta, T.; Jadi, P.K.; Moses, J.C.; Mandal, B.B. Injectable Anti-Cancer Drug Loaded Silk-Based Hydrogel for the Prevention of Cancer Recurrence and Post-Lumpectomy Tissue Regeneration Aiding Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Therapy. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 145, 213224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Cao, Q.; Xia, Y.; Cui, C.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Combination of Biodegradable Hydrogel and Antioxidant Bioadhesive for Treatment of Breast Cancer Recurrence and Radiation Skin Injury. Bioact. Mater. 2024, 31, 408–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radinekiyan, F.; Eivazzadeh-Keihan, R.; Naimi-Jamal, M.R.; Aliabadi, H.A.M.; Bani, M.S.; Shojaei, S.; Maleki, A. Design and Fabrication of a Magnetic Nanobiocomposite Based on Flaxseed Mucilage Hydrogel and Silk Fibroin for Biomedical and In-Vitro Hyperthermia Applications. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Torres, G.; Valdés-Madrigal, M.A.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R.; Baltiérrez-Hoyos, R.; De la Cruz-Burelo, E.D.; Román-Doval, R.; Valencia-Lazcano, A.A. Effect of Silk Fibroin on Cell Viability in Electrospun Scaffolds of Polyethylene Oxide. Polymers 2019, 11, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia–Lazcano, A.A.; Román–Doval, R.; De La Cruz–Burelo, E.; Millán–Casarrubias, E.J.; Rodríguez–Ortega, A. Enhancing Surface Properties of Breast Implants by Using Electrospun Silk Fibroin. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2018, 106, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Jiang, D.; Xie, S.; Zeng, M.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.; Ouyang, H.; Zou, X. Promotion of Hernia Repair with High-Strength, Flexible, and Bioresorbable Silk Fibroin Mesh in a Large Abdominal Hernia Model. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemens, M.W.; Downey, S.; Agullo, F.; Lehfeldt, M.R.; Kind, G.M.; Palladino, H.; Marshall, D.; Jewell, M.L.; Mathur, A.B.; Bengtson, B.P.; et al. Clinical Application of a Silk Fibroin Protein Biologic Scaffold for Abdominal Wall Fascial Reinforcement. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2014, 2, e246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, F.; Cao, W.; Cao, C.; Li, B.; Shi, X.; Gao, C. Construction and Properties of the Silk Fibroin and Polypropylene Composite Biological Mesh for Abdominal Incisional Hernia Repair. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 949917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbaba, S.; Atila, D.; Keskin, D.; Tezcaner, T.; Tezcaner, A. Multilayer Fibroin/Chitosan Oligosaccharide Lactate and Pullulan Immunomodulatory Patch for Treatment of Hernia and Prevention of Intraperitoneal Adhesion. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 265, 118066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konar, S.; Guha, R.; Kundu, B.; Nandi, S.; Ghosh, T.K.; Kundu, S.C.; Konar, A.; Hazra, S. Silk Fibroin Hydrogel as Physical Barrier for Prevention of Post Hernia Adhesion. Hernia 2017, 21, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobin, A.S.; Butler, C.E.; Mathur, A.B. Repair and Regeneration of the Abdominal Wall Musculofascial Defect Using Silk Fibroin-Chitosan Blend. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 3383–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, R.L.; Waldman, B.; Hein, D.W. A Review of Sutures and Suturing Techniques. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1992, 18, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillai, C.K.S.; Sharma, C.P. Review Paper: Absorbable Polymeric Surgical Sutures: Chemistry, Production, Properties, Biodegradability, and Performance. J. Biomater. Appl. 2010, 25, 291–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, D.; Choudhury, A.J.; Chutia, J.; Pal, A.R.; Khan, M.; Choudhury, M.; Pathak, P.; Das, G.; Patil, D.S. Development of Advanced Antimicrobial and Sterilized Plasma Polypropylene Grafted MUGA (Antheraea Assama) Silk as Suture Biomaterial. Biopolymers 2014, 101, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banche, G.; Roana, J.; Mandras, N.; Amasio, M.; Gallesio, C.; Allizond, V.; Angeretti, A.; Tullio, V.; Cuffini, A.M. Microbial Adherence on Various Intraoral Suture Materials in Patients Undergoing Dental Surgery. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 65, 1503–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Wang, B. Biodegradation of Silk Biomaterials. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naleway, S.E.; Lear, W.; Kruzic, J.J.; Maughan, C.B. Mechanical Properties of Suture Materials in General and Cutaneous Surgery. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2015, 103, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Hou, D.; Tang, X.; Wang, L. Quantitative Physical and Handling Characteristics of Novel Antibacterial Braided Silk Suture Materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2015, 50, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, G.; Mao, Y.; Chen, L.; Peng, Y.; Tao, T.H. Biomimicking Antibacterial Opto-Electro Sensing Sutures Made of Regenerated Silk Proteins. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, e2004733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, A.R.; Pirraco, R.; Fernandes, E.M.; Rodrigues, F.; Leonor, I.B.; Kaplan, D.L.; Reis, R.L. Untangling the Biological and Inflammatory Behavior of Silk-like Sutures In Vivo. Biomaterials 2022, 290, 121829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Giorgio, G.; Matera, B.; Vurro, D.; Manfredi, E.; Galstyan, V.; Tarabella, G.; Ghezzi, B.; D’Angelo, P. Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020167
De Giorgio G, Matera B, Vurro D, Manfredi E, Galstyan V, Tarabella G, Ghezzi B, D’Angelo P. Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(2):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020167
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Giorgio, Giuseppe, Biagio Matera, Davide Vurro, Edoardo Manfredi, Vardan Galstyan, Giuseppe Tarabella, Benedetta Ghezzi, and Pasquale D’Angelo. 2024. "Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives" Bioengineering 11, no. 2: 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020167
APA StyleDe Giorgio, G., Matera, B., Vurro, D., Manfredi, E., Galstyan, V., Tarabella, G., Ghezzi, B., & D’Angelo, P. (2024). Silk Fibroin Materials: Biomedical Applications and Perspectives. Bioengineering, 11(2), 167. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11020167








