Nuclei Detection and Segmentation of Histopathological Images Using a Feature Pyramidal Network Variant of a Mask R-CNN
Abstract
1. Introduction
- SIS-based approach vs. DIS-based approach;
- Limitation of SIS-based approach: use of traditional post-processing algorithms;
- Use of DIS-based approach for nuclei detection: end-to-end trainable and no need for traditional post-processing algorithms to detect nuclei.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Network
2.2. Dataset
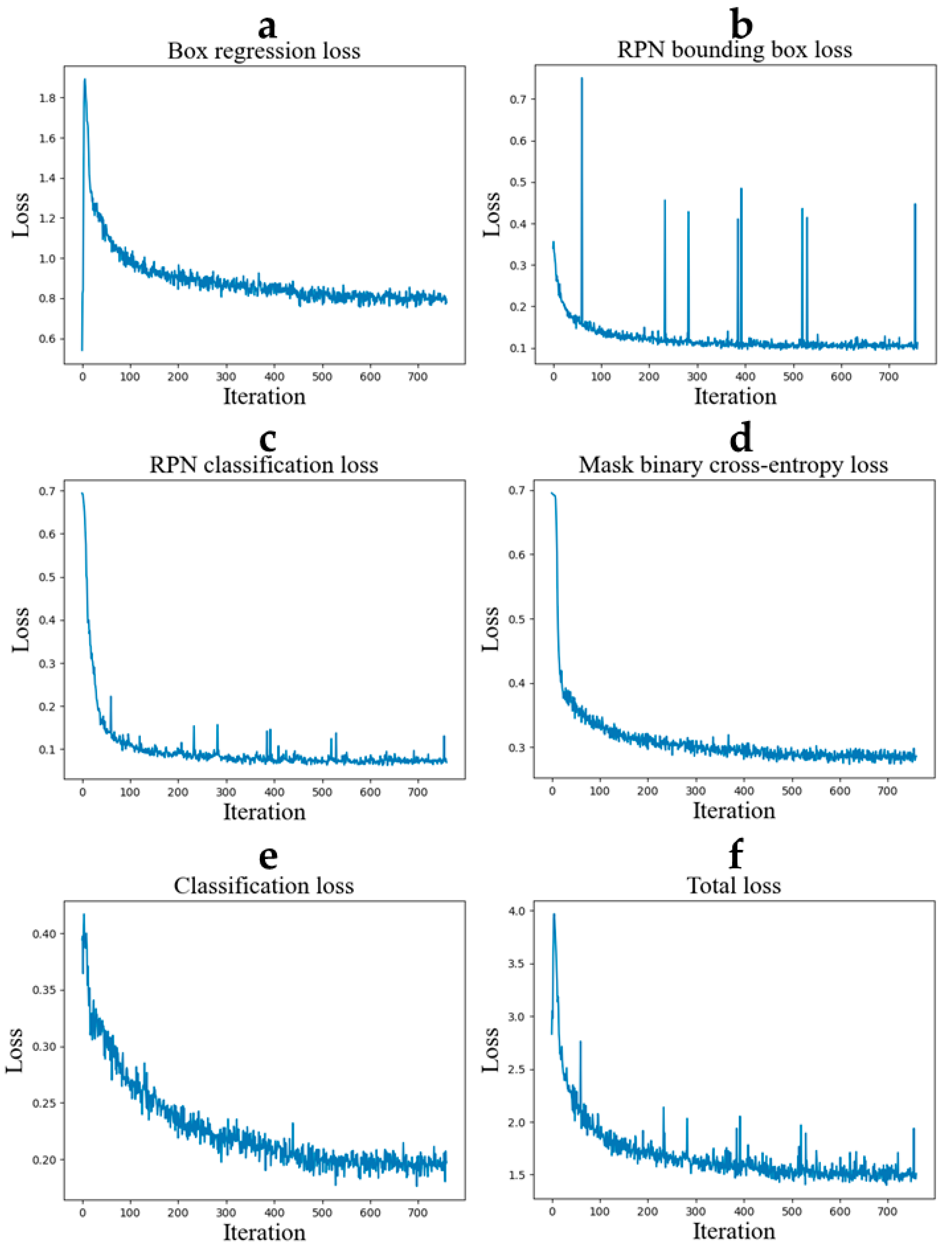
2.3. Training
2.4. Tuning
2.5. Metrics
2.6. Inference
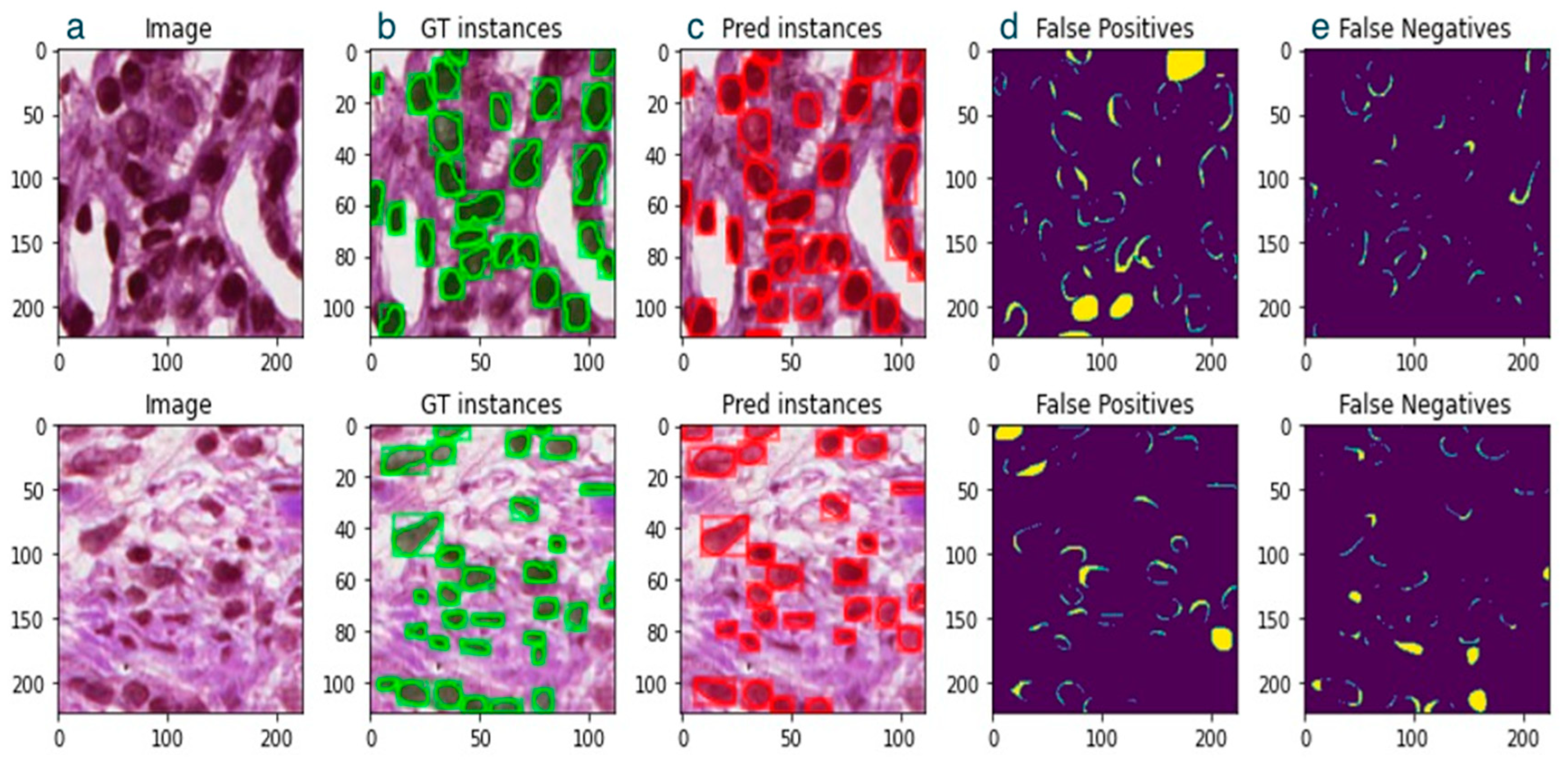
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Fischer, E.G. Nuclear Morphology and the Biology of Cancer Cells. Acta Cytol. 2020, 64, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, P. Cancer nucleus: Morphology and beyond. Diagn. Cytopathol. 2010, 38, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, W.; Chang, E.I.; Fan, Y.; Lai, M.; Xu, Y. Deep learning in digital pathology image analysis: A survey. Front. Med. 2020, 14, 470–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abels, E.; Pantanowitz, L.; Aeffner, F.; Zarella, M.D.; van der Laak, J.; Bui, M.M.; Vemuri, V.N.; Parwani, A.V.; Gibbs, J.; Agosto-Arroyo, E.; et al. Computational pathology definitions, best practices, and recommendations for regulatory guidance: A white paper from the Digital Pathology Association. J. Pathol. 2019, 249, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janowczyk, A.; Madabhushi, A. Deep learning for digital pathology image analysis: A comprehensive tutorial with selected use cases. J. Pathol. Inform. 2016, 7, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, M.; Żejmo, M.; Skobel, M.; Korbicz, J.; Monczak, R. Cell Nuclei Segmentation in Cytological Images Using Convolutional Neural Network and Seeded Watershed Algorithm. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsu, N. A Threshold Selection Method from Gray-Level Histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tom, M.; Ramakrishnan, V.; van Oterendorp, C.; Deserno, T. Automated Detection of Schlemm’s Canal in Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. In Proceedings of the Medical Imaging 2015: Computer-Aided Diagnosis, Orlando, FL, USA, 20 March 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Lateef, F.; Ruichek, Y. Survey on semantic segmentation using deep learning techniques. Neurocomputing 2019, 338, 321–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, A.; Orts, S.; Oprea, S.; Villena Martinez, V.; Rodríguez, J. A Review on Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Semantic Segmentation. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.06857. [Google Scholar]
- Asgari Taghanaki, S.; Abhishek, K.; Cohen, J.P.; Cohen-Adad, J.; Hamarneh, G. Deep semantic segmentation of natural and medical images: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2021, 54, 137–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.W. Adapting mask-rcnn for automatic nucleus segmentation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.00500. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengxia, Z.; Zhenwei, S.; Yuhong, G.; Jieping, Y. Object detection in 20 years: A survey. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.05055. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, P.; Jones, M. Rapid object detection using a boosted cascade of simple features. In Proceedings of the 2001 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, CVPR 2001, Kauai, HI, USA, 8–14 December 2001; p. I. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.-Q.; Zheng, P.; Xu, S.-T.; Wu, X. Object Detection With Deep Learning: A Review. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2019, 30, 3212–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Ouyang, W.; Wang, X.; Fieguth, P.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Pietikäinen, M. Deep Learning for Generic Object Detection: A Survey. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2020, 128, 261–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, D.; Han, Y.; Wang, B.; Guan, T.; Gu, H.; Wei, W. Review of object instance segmentation based on deep learning. J. Electron. Imaging 2022, 31, 041205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, K.W.; Fu, C.; Ho, D.J.; Lee, S.; Han, S.; Salama, P.; Delp, E.J. DeepSynth: Three-dimensional nuclear segmentation of biological images using neural networks trained with synthetic data. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 18295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.-A.; Liao, C.-T.; Raybould, R.; Talabani, B.; Grigorieva, I.; Szomolay, B.; Bowen, T.; Andrews, R.; Taylor, P.R.; Fraser, D. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing identifies new classes of proximal tubular epithelial cells in kidney fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 32, 2501–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morabito, S.; Miyoshi, E.; Michael, N.; Shahin, S.; Martini, A.C.; Head, E.; Silva, J.; Leavy, K.; Perez-Rosendahl, M.; Swarup, V. Single-nucleus chromatin accessibility and transcriptomic characterization of Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.; Epstein, D.; Rajpoot, N. Dense steerable filter cnns for exploiting rotational symmetry in histology images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 4124–4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Qi, X.; Yu, L.; Dou, Q.; Qin, J.; Heng, P.-A. DCAN: Deep contour-aware networks for object instance segmentation from histology images. Med. Image Anal. 2017, 36, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Gkioxari, G.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R. Mask r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2961–2969. [Google Scholar]
- Paperswithcode. Multi-Tissue Nucleus Segmentation on Kumar. Available online: https://paperswithcode.com/sota/multi-tissue-nucleus-segmentation-on-kumar (accessed on 15 March 2023).
- Kumar, N.; Verma, R.; Sharma, S.; Bhargava, S.; Vahadane, A.; Sethi, A. A dataset and a technique for generalized nuclear segmentation for computational pathology. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2017, 36, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohta, S.; Suganuma, H.; Tanaka, Y. MRL: Learning to mix with attention and convolutions. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2208.13975. [Google Scholar]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.04597v1. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, S.; Vu, Q.D.; Raza, S.E.A.; Kwak, J.T.; Rajpoot, N. XY network for nuclear segmentation in multi-tissue histology images. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.06499. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Hosang, J.; Benenson, R.; Schiele, B. Learning non-maximum suppression. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 4507–4515. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Kirillov, A.; Massa, F.; Lo, W.-Y.; Girshick, R. Detectron2. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2 (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Deng, J.; Dong, W.; Socher, R.; Li, L.-J.; Li, K.; Fei-Fei, L. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Bottou, L. Stochastic learning. In Advanced Lectures on Machine Learning: ML Summer Schools 2003, Canberra, Australia, February 2–14, 2003, Tübingen, Germany, August 4–16, 2003, Revised Lectures; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 146–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Girshick, R. Fast r-cnn. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Goyal, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Dollár, P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 2980–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Bucher, M.; Herbin, S.; Jurie, F. Hard negative mining for metric learning based zero-shot classification. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2016 Workshops, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 8–10 October 2016; pp. 524–531. [Google Scholar]
- Sorensen, T.A. A method of establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species content and its application to analyses of the vegetation on Danish commons. Biol. Skar. 1948, 5, 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Weiler, M.; Hamprecht, F.A.; Storath, M. Learning steerable filters for rotation equivariant cnns. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 849–858. [Google Scholar]
- Hafiz, A.M.; Bhat, G.M. A survey on instance segmentation: State of the art. Int. J. Multimed. Inf. Retr. 2020, 9, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Coppola, L.; Cianflone, A.; Grimaldi, A.M.; Incoronato, M.; Bevilacqua, P.; Messina, F.; Baselice, S.; Soricelli, A.; Mirabelli, P.; Salvatore, M. Biobanking in health care: Evolution and future directions. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochhausen, M.; Whorton, J.M.; Zayas, C.E.; Kimbrell, M.P.; Bost, S.J.; Singh, N.; Brochhausen, C.; Sexton, K.W.; Blobel, B. Assessing the Need for Semantic Data Integration for Surgical Biobanks-A Knowledge Representation Perspective. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

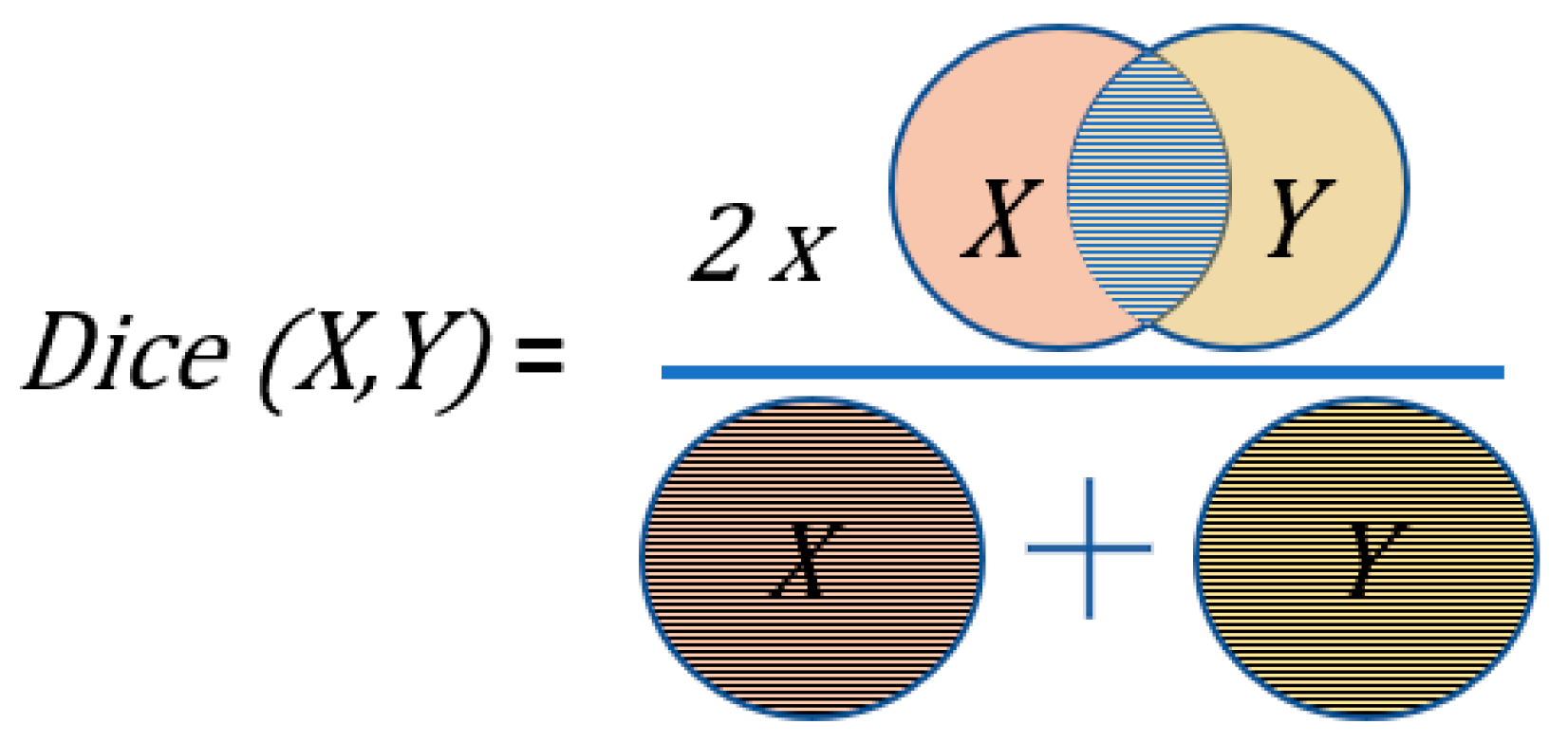

| Study | Methodology | Performance (Dice Score) | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kumar et al. [27] | Semantic segmentation (CNN) | 76.23% | + Achieved a moderate dice score − Struggled with overlapping nuclei |
| Mohta et al. [28] | MRL-based network architecture (GC-MHVN) | 84.3% | + Improved capacity, generalization, and efficiency − Pointed toward overfitting |
| Ronneberger et al. [29] | U-Net with post-processing | 75.8% | + Very good performance on different biomedical segmentation applications − Relied heavily on post-processing, leading to potential over-segmentation |
| He et al. [25] | Detection-based instance segmentation (Mask R-CNN) | 76% | + Good generalization − Computationally expensive |
| Graham et al. [30] | Hybrid approach (Hover-Net) | 82.6% | + Combined SIS and DIS, showing promise − Required significant computational resources |
| Network | Data Augmentation | Optimizer | Additional Hacks | Dice Score (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mask R-CNN (Standard) [25] | None | SGD | None | 76.0 |
| Mask R-CNN + FPN | None | SGD | None | 81.2 |
| Mask R-CNN + FPN | None | Adam | None | 82.0 |
| Mask R-CNN + FPN | Rotation and Image-blending | Adam | None | 82.6 |
| Mask R-CNN + FPN | Rotation and Image-blending | Adam | OHEM [40] and Focal Loss [39] | 83.1 |
| Type | Network | Dice Score (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Detection-based Instance Segmentation (DIS) Algorithms | Mask R-CNN (ResNet50 + FPN) | 83.1 |
| Mask R-CNN (Standard) [25] | 76.0 | |
| Segmentation-based Instance Segmentation (SIS) Algorithms | GC-MHVN [28] | 84.3 |
| MHVN [28] | 83.0 | |
| DSF-Net [23] | 82.6 | |
| HoverNet [30] | 82.6 | |
| Steerable G-CNN [42] | 81.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ramakrishnan, V.; Artinger, A.; Daza Barragan, L.A.; Daza, J.; Winter, L.; Niedermair, T.; Itzel, T.; Arbelaez, P.; Teufel, A.; Cotarelo, C.L.; et al. Nuclei Detection and Segmentation of Histopathological Images Using a Feature Pyramidal Network Variant of a Mask R-CNN. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100994
Ramakrishnan V, Artinger A, Daza Barragan LA, Daza J, Winter L, Niedermair T, Itzel T, Arbelaez P, Teufel A, Cotarelo CL, et al. Nuclei Detection and Segmentation of Histopathological Images Using a Feature Pyramidal Network Variant of a Mask R-CNN. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(10):994. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100994
Chicago/Turabian StyleRamakrishnan, Vignesh, Annalena Artinger, Laura Alexandra Daza Barragan, Jimmy Daza, Lina Winter, Tanja Niedermair, Timo Itzel, Pablo Arbelaez, Andreas Teufel, Cristina L. Cotarelo, and et al. 2024. "Nuclei Detection and Segmentation of Histopathological Images Using a Feature Pyramidal Network Variant of a Mask R-CNN" Bioengineering 11, no. 10: 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100994
APA StyleRamakrishnan, V., Artinger, A., Daza Barragan, L. A., Daza, J., Winter, L., Niedermair, T., Itzel, T., Arbelaez, P., Teufel, A., Cotarelo, C. L., & Brochhausen, C. (2024). Nuclei Detection and Segmentation of Histopathological Images Using a Feature Pyramidal Network Variant of a Mask R-CNN. Bioengineering, 11(10), 994. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100994








