De-Epithelization of the Human Amniotic Membrane Using a System Involving Ozonated Water and Ultrasound
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Type and Ethical Aspects
2.2. Sample Collection
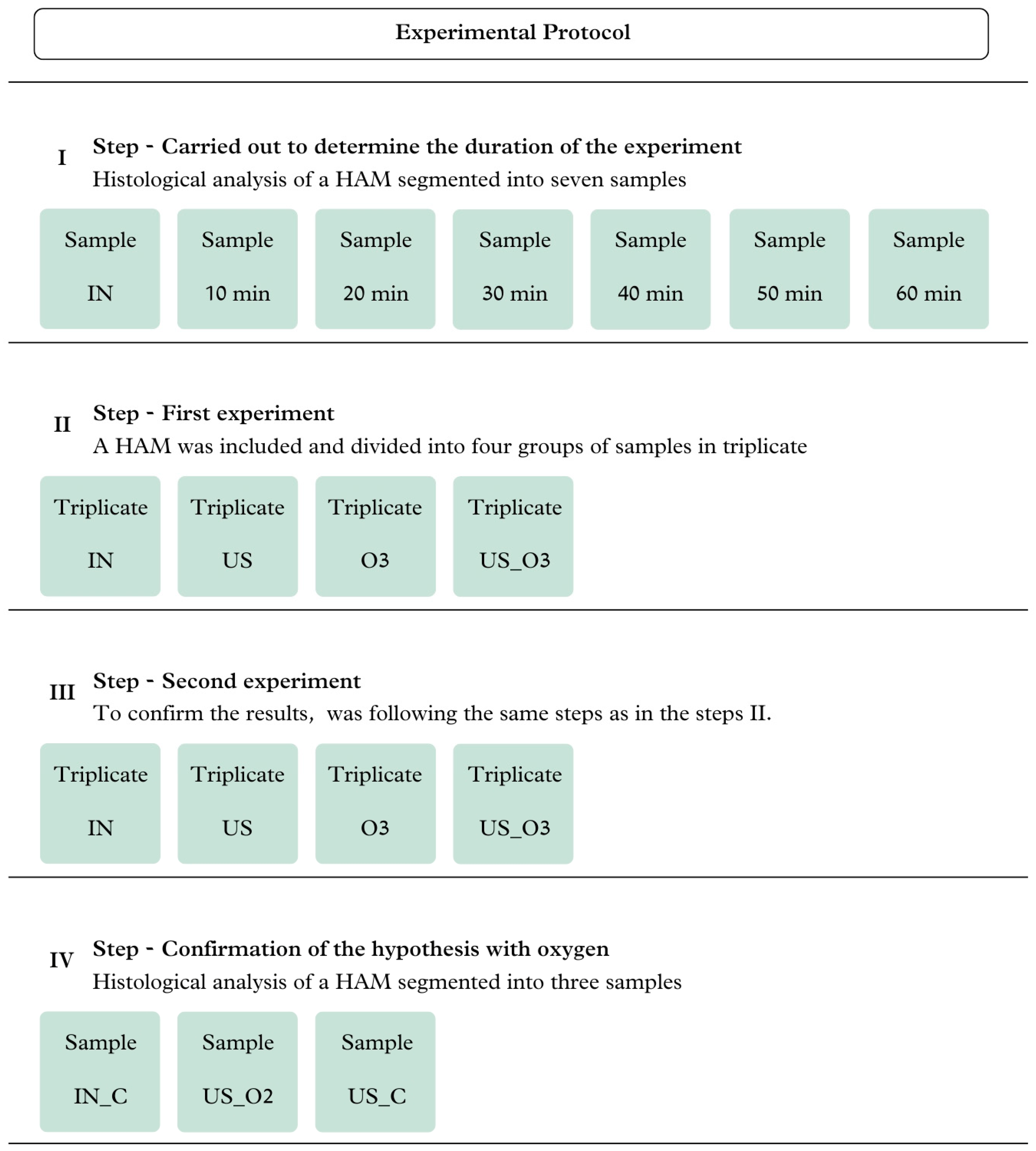
2.3. Experimental Procedure
2.4. Analysis
2.4.1. FT-IR Analysis
2.4.2. Histological Analysis
2.4.3. SEM-FEG Analysis
3. Results
3.1. O3 Concentration Curve Dissolved in Water
3.2. FT-IR Analysis
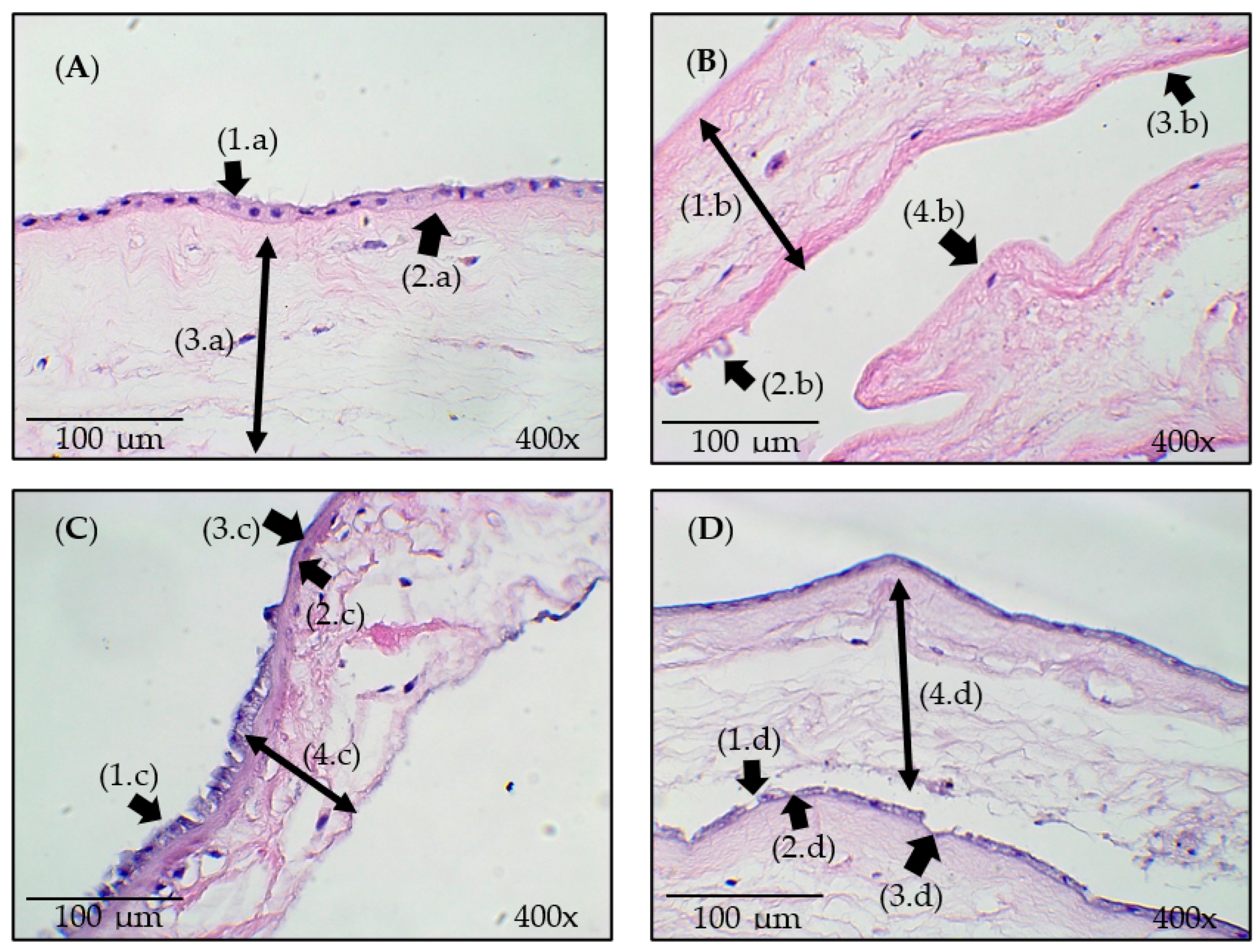
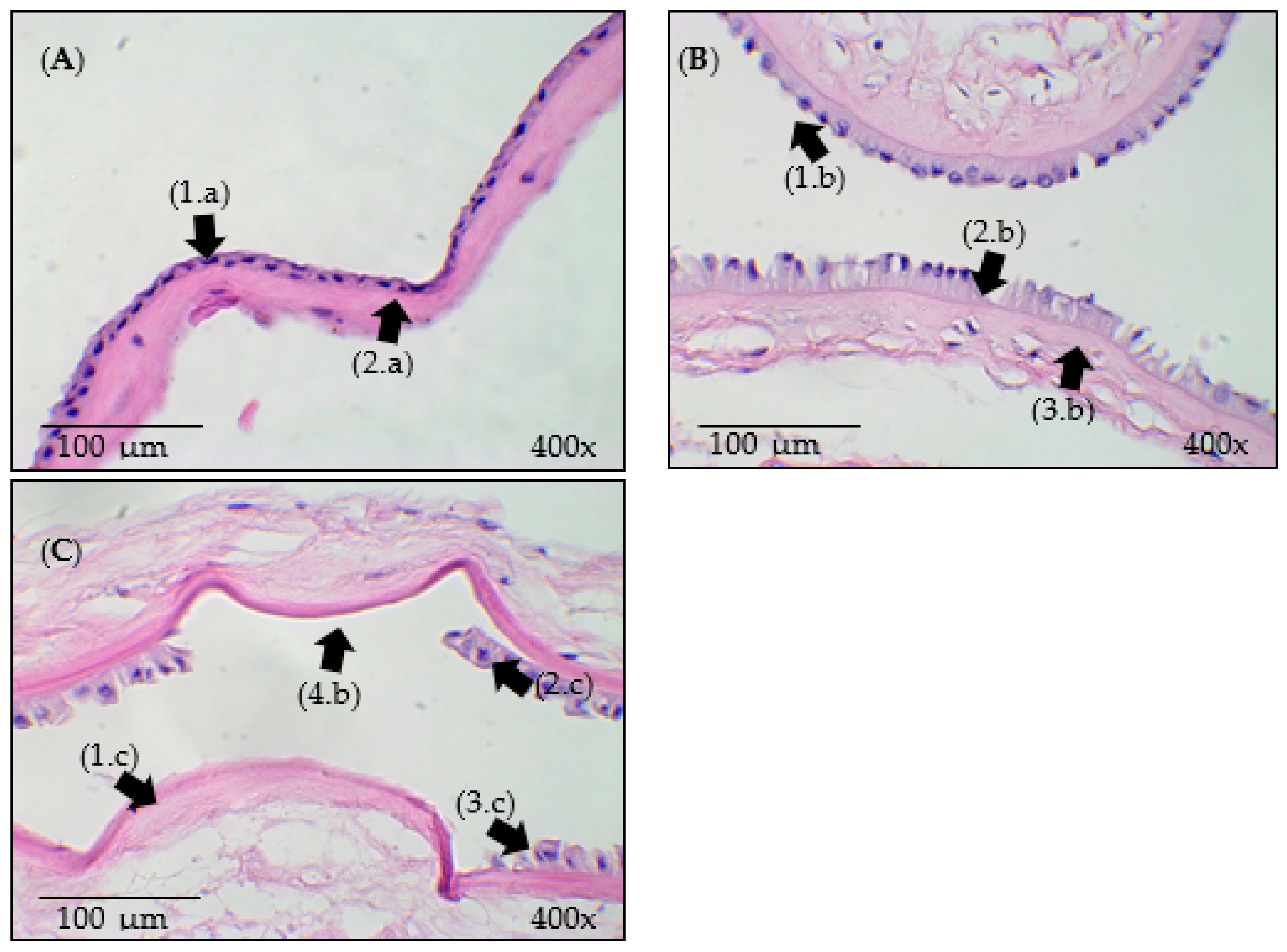
3.3. Histological Analysis
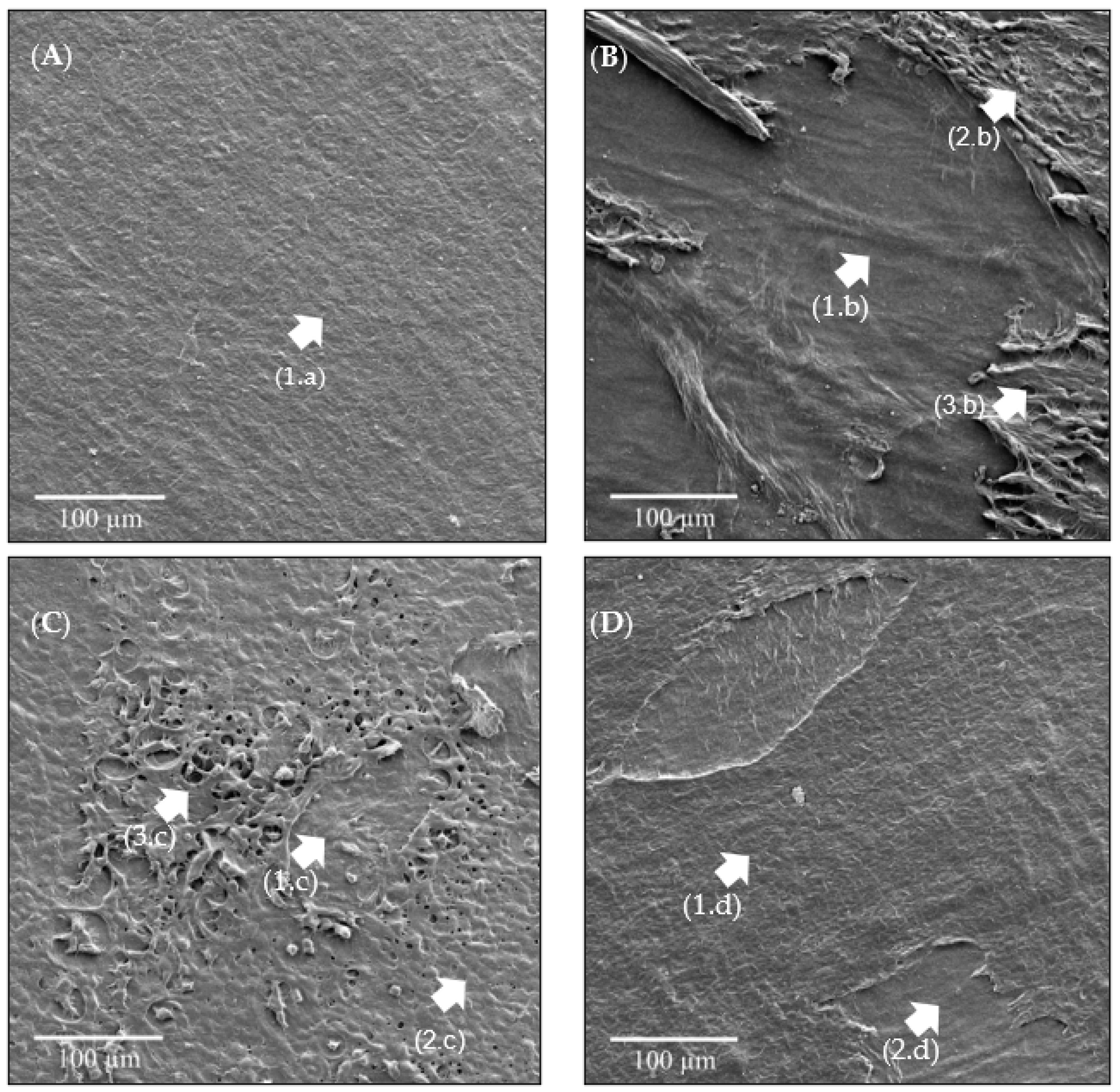
3.4. SEM-FEG Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The FT-IR spectra showed subtle changes, such as slight shifts and intensity changes in the bands, indicating no significant changes in the biochemical properties of the HAM after the experiment.
- Ultrasound had greater effects on de-epithelization, and O3, despite causing similar effects, did not surpass the impact of ultrasound.
- In the case of ozonated water combined with ultrasound, no significant alterations in the structure of the epithelial tissue were observed.
- Therefore, cavitation caused by the ultrasound promoted the de-epithelization of the HAM, without significant changes to the stroma.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dadkhah Tehrani, F.; Firouzeh, A.; Shabani, I.; Shabani, A. A Review on Modifications of Amniotic Membrane for Biomedical Applications. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 606982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamede, A.C.; Carvalho, M.J.; Abrantes, A.M.; Laranjo, M.; Maia, C.J.; Botelho, M.F. Amniotic membrane: From structure and functions to clinical applications. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 349, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DCunha, A.R.; Jehangir, S.; Rebekah, G.; Thomas, R.J. Human amniotic membrane vs collagen in the treatment of superficial second-degree burns in children. Wounds 2022, 34, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munoz-Torres, J.R.; Martínez-González, S.B.; Lozano-Luján, A.D.; Martínez-Vázquez, M.C.; Velasco-Elizondo, P.; Garza-Veloz, I.; Martinez-Fierro, M.L. Biological properties and surgical applications of the human amniotic membrane. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 10, 1067480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Chen, G.; Han, F.; Jiang, W. Human amniotic membrane graft for refractory macular hole: A single-arm meta-analysis and systematic review. J. Francais Ophtalmol. 2023, 46, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaheb, M.; Kohestani, B.M.; Karrabi, M.; Khosrojerdi, M.; Khajeh, M.; Shahrestanaki, E.; Sahebkar, M. Evaluation of Dried Amniotic Membrane on Wound Healing at Split-Thickness Skin Graft Donor Sites: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-blind Trial. Adv. Skin. Wound Care 2020, 33, 636–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitriani, N.; Wilar, G.; Narsa, A.C.; Mohammed, A.F.A.; Wathoni, N. Application of Amniotic Membrane in Skin Regeneration. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doudi, S.; Barzegar, M.; Taghavi, E.A.; Eini, M.; Ehterami, A.; Stokes, K.; Alexander, J.S.; Salehi, M. Applications of acellular human amniotic membrane in regenerative medicine. Life Sci. 2022, 310, 121032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etchebarne, M.; Fricain, J.-C.; Kerdjoudj, H.; Di Pietro, R.; Wolbank, S.; Gindraux, F.; Fenelon, M. Use of Amniotic Membrane and Its Derived Products for Bone Regeneration: A Systematic Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 661332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanafrooz, Z.; Bakhshandeh, B.; Behnam Abdollahi, S.; Seyedjafari, E. Human amniotic membrane as a multifunctional biomaterial: Recent advances and applications. J. Biomater. Appl. 2023, 37, 1341–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal-Marin, S.; Kern, T.; Hofmann, N.; Pogozhykh, O.; Framme, C.; Börgel, M.; Figueiredo, C.; Glasmacher, B.; Gryshkov, O. Human Amniotic Membrane: A review on tissue engineering, application, and storage. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1198–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzaphlidou, M. Collagen as a model for the study of radiation induced side effects: Use of image processing. Micron 2002, 33, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Protzman, N.M.; John, N.; Kuehn, A.; Long, D.; Sivalenka, R.; Junka, R.A.; Shah, A.U.; Gosiewska, A.; Hariri, R.J.; et al. An in vitro comparison of human corneal epithelial cell activity and inflammatory response on differently designed ocular amniotic membranes and a clinical case study. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2023, 111, 684–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Melo, G.B.; Gomes, J.P.; da Glória, M.A.; Martins, M.C.; Haapalainen, E.F. Avaliação morfológica de diferentes técnicas de desepitelização da membrana amniótica humana. Arq. Bras. Oftalmol. 2007, 70, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Echarte, L.; Grazioli, G.; Pereira, L.; Francia, A.; Pérez, H.; Kuzuian, W.; Vicentino, W.; Pardo, H.; Mombrú, A. Processing methods for human amniotic membrane as scaffold for tissue engineering with mesenchymal stromal human cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2022, 25, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashouri, S.; Hosseini, S.A.; Hoseini, S.J.; Tara, F.; Ebrahimzadeh-Bideskan, A.; Webster, T.J.; Kargozar, S. Decellularization of human amniotic membrane using detergent-free methods: Possibilities in tissue engineering. Tissue Cell 2022, 76, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niknejad, H.; Peirovi, H.; Jorjani, M.; Ahmadiani, A.; Ghanavi, J.; Seifalian, A.M. Properties of the amniotic membrane for potential use in tissue engineering. Eur. Cell Mater. 2008, 15, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awoyama, S.M.; Carvalho, H.C.; Botelho, T.S.; dos Santos, S.I.S.; Palacios, D.A.B.; Henríque, S.S.M.; Zângaro, R.A.; de Lima, C.J.; Fernandes, A.B. Disinfection of Human Amniotic Membrane Using a Hydrodynamic System with Ozonated Water. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2022, 45, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, G.V.; Voblikova, V.A.; Sabitova, L.V.; Tkachenko, I.S.; Tkachenko, S.N.; Lunin, V.V. Ozone Solubility in Water. Mosc. Univ. Chem. Bull. 2015, 70, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayarri, B.; Cruz-Alcalde, A.; López-Vinent, N.; Micó, M.M.; Sans, C. Can ozone inactivate SARS-CoV-2? A review of mechanisms and performance on viruses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 415, 125658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passos, T.M.; da Silva, L.H.M.; Moreira, L.M.; Zângaro, R.A.; Santos, R.S.; Fernandes, F.B.; de Lima, C.J.; Fernandes, A.B. Comparative analysis of ozone and ultrasound effect on the elimination of Giardia spp. cysts from wastewater. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2014, 36, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yadav, A.K.; Ji, B.; Kang, P.; Wei, T. Ozone based inactivation and disinfection in the pandemic time and beyond: Taking forward what has been learned and best practice. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 862, 160711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wu, Q.P.; Zhang, J.M.; Yang, X.H. Effects of ozone on membrane permeability and ultrastructure in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 1006–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albright, M.; Guttenberg, M.A.; Tighe, R.M. Ozone-Induced Models of Airway Hyperreactivity and Epithelial Injury. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2506, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldo, F. Ozone Degradation of Biological Macromolecules: Proteins, Hemoglobin, RNA, and DNA. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2006, 28, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matafonova, G.; Batoev, V. Dual-frequency ultrasound: Strengths and shortcomings to water treatment and disinfection. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wan, H.; Jiang, X.; Peng, C. Piezoelectric Micromachined Ultrasound Transducer Technology: Recent Advances and Applications. Biosensors 2022, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zou, Q.; Qin, D. Enhancing cavitation dynamics and its mechanical effects with dual-frequency ultrasound. Phys. Med. Biol. 2022, 67, 085017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.M.; Abou-Elkacem, L.; Lee, T.; Dahl, J.; Lutz, A.M. Ultrasound and microbubble mediated therapeutic delivery: Underlying mechanisms and future outlook. J. Control. Release 2020, 326, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikesh, M.S.; Yang, X. The effect of ultrasound cavitation on endothelial cells. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 758–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milyudin, E.; Volova, L.T.; Kuchuk, K.E.; Timchenko, E.V.; Timchenko, P.E. Amniotic Membrane Biopolymer for Regenerative Medicine. Polymers 2023, 15, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinzelmann, T.R.D.O.; Carvalho, M.C.D.O.; Azevedo, L.D.L.; Kawata, B.A.; Procópio Alves, L.; Carvalho, H.C.; de Lima, C.J.; Fernandes, A.B. Disinfection of Surgical Instruments Using a Hydrodynamic System with Ozonated Water and Ultrasound: Preliminary Study. Ozone Sci. Eng. 2024, 46, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasil. Ministério da Saúde-Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária. RESOLUÇÃO-RDC Nº 190, DE 18 DE JULHO DE 2003 Determina Normas Técnicas Para o Funcionamento dos Bancos de Sangue de Cordão Umbilical e Placentário. Brasília. 2003. Available online: https://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/saudelegis/anvisa/2003/rdc0190_18_07_2003.html (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Weidinger, A.; Poženel, L.; Wolbank, S.; Banerjee, A. Sub-Regional Differences of the Human Amniotic Membrane and Their Potential Impact on Tissue Regeneration Application. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 613804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sripriya, R.; Kumar, R. Denudation of human amniotic membrane by a novel process and its characterisations for biomedical applications. Prog. Biomater. 2016, 5, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talari, A.C.S.; Martinez, M.A.G.; Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Advances in Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy of biological tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2017, 52, 456–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalu, S.; Roiu, G.; Pop, O.; Heredea, D.A.P.; Costea, T.O.; Costea, C.F. Nano-Scale Modifications of Amniotic Membrane Induced by UV and Antibiotic Treatment: Histological, AFM and FT-IR Spectroscopy Evidence. Materials 2021, 14, 863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roiu, G.; Cavalu, S.; Teusdea, A.; Petricas-Heredea, D.A.; Fratila, O. Assessment of Antibiotic Influence on Structural Modifications of Amniotic Membrane by FT-IR Spectroscopy. Mater. Plast. 2020, 57, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdadolnik, J. Conformation of Bovine Serum Albumin as a Function of Hydration Monitored by Infrared Spectroscopy. Internet J. Vib. Spectrosc. 2002, 6, 6. Available online: https://www.irdg.org/ijvs/ijvs-volume-6-edition-1/conformation-of-bovine-serum-albumin-as-a-function-of-hydration-monitored-by-infrared-spectroscopy (accessed on 10 August 2023).
- Ferenczy, P.A.v.H.; de Souza, L.B. Comparação dos meios de preparação e preservação de membrana amniótica humana para uso no tratamento de doenças da superfície ocular. Rev. Bras. Oftalmol. 2020, 79, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzi Plepis, A.M.; Goissis, G.; Das-Gupta, D.K. Dielectric and pyroelectric characterization of anionic and native collagen. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Tauseef, H.; Ainuddin, J.A.; Zafar, M.; Khan, I.; Salim, A.; Mirza, M.R.; Mohiuddin, O.A. Assessment of the proteome profile of decellularized human amniotic membrane and its biocompatibility with umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A. 2024, 112, 1041–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daniele, E.; Ferrari, B.; Rassu, N.; Ben-Nun, J.; Bosio, L.; Barbaro, V.; Ferrari, S.; Ponzin, D. Comparison of human amniotic membrane decellularisation approaches for hESC-derived RPE cells culture. BMJ Open Ophthalmol. 2022, 7, e000981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, T.S.; Kawata, B.A.; Awoyama, S.M.; Marrafa, P.A.L.I.; Carvalho, H.C.; de Lima, C.J.; Fernandes, A.B. Sterilization of Human Amniotic Membrane Using an Ozone Hydrodynamic System. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 52, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Li, Z.; Xiao, J.; Su, M.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, C.; Pan, Y.; et al. Tunable Fluid-Type Metasurface for Wide-Angle and Multifrequency Water-Air Acoustic Transmission. Research 2021, 2021, 9757943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

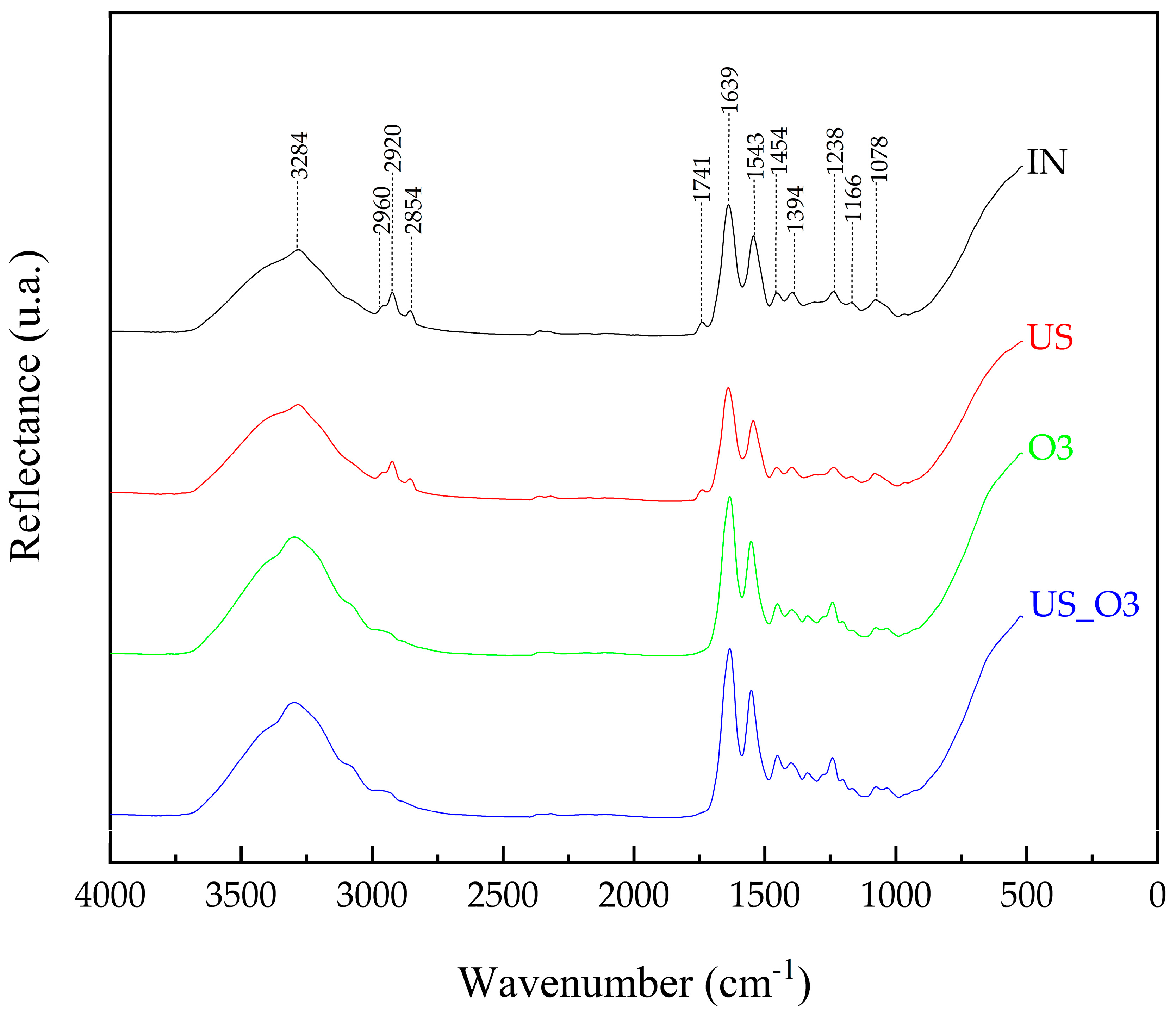
| Functional Group | ω (cm−1) | Assignments | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amide A | 3284 | ν NH | [35,36] |
| Lipids, DNA and proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids | 2960 | νa CH3 | [36,37] |
| 2960 | νa CH3 | [36,37] | |
| Lipids | 2854 | νs CH2 | [36] |
| Fat and lipid | 1741 | ν C=O | [36] |
| Amide I | 1639 | ν C=O | [36,38] |
| Amide II | 1543 | sc NH/ν C-N | [36,37,38] |
| Lipids | 1454 | sc CH2 | [36] |
| Proteins | 1394 | wag CH3 | [36] |
| Amide III | 1238 | ν C-N/sc N-H/ν C-C/sc C=O | [35,37,39] |
| Collagen (type I) | 1166 | ν C-O | [36] |
| Nucleic acids, glycolipids, and phospholipids | 1078 | ν PO2 | [36] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, F.D.R.P.; Kawata, B.A.; Oliveira Heinzelmann, T.R.d.; Belfort, M.G.S.; Crispim de Oliveira Carvalho, M.; Móbille Awoyama, S.; Gomes de Oliveira Neto, J.; José de Lima, C.; Barrinha Fernandes, A. De-Epithelization of the Human Amniotic Membrane Using a System Involving Ozonated Water and Ultrasound. Bioengineering 2024, 11, 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100987
Santos FDRP, Kawata BA, Oliveira Heinzelmann TRd, Belfort MGS, Crispim de Oliveira Carvalho M, Móbille Awoyama S, Gomes de Oliveira Neto J, José de Lima C, Barrinha Fernandes A. De-Epithelization of the Human Amniotic Membrane Using a System Involving Ozonated Water and Ultrasound. Bioengineering. 2024; 11(10):987. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100987
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Francisco Dimitre Rodrigo Pereira, Bianca Akemi Kawata, Tatiana Regina de Oliveira Heinzelmann, Marcia Guelma Santos Belfort, Maycon Crispim de Oliveira Carvalho, Sílvia Móbille Awoyama, João Gomes de Oliveira Neto, Carlos José de Lima, and Adriana Barrinha Fernandes. 2024. "De-Epithelization of the Human Amniotic Membrane Using a System Involving Ozonated Water and Ultrasound" Bioengineering 11, no. 10: 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100987
APA StyleSantos, F. D. R. P., Kawata, B. A., Oliveira Heinzelmann, T. R. d., Belfort, M. G. S., Crispim de Oliveira Carvalho, M., Móbille Awoyama, S., Gomes de Oliveira Neto, J., José de Lima, C., & Barrinha Fernandes, A. (2024). De-Epithelization of the Human Amniotic Membrane Using a System Involving Ozonated Water and Ultrasound. Bioengineering, 11(10), 987. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering11100987






