Periodontitis and Metabolic Syndrome: Statistical and Machine Learning Analytics of a Nationwide Study
Abstract
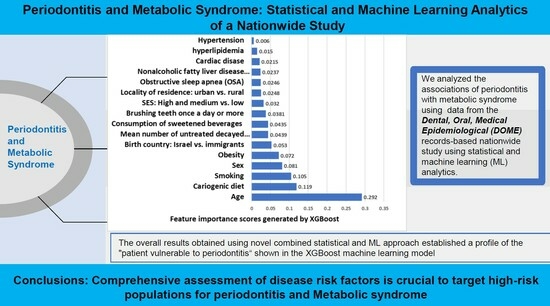
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Data Source
2.2. Ethical Clearance
2.3. Study Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Variables’ Definitions
2.4.1. The Dependent Variable: Periodontitis
2.4.2. Independent Variables
Sociodemographic Variables
- Age in years;
- Sex (men/women);
- Education: Educational attainment categorized as high school and below, technical college, or academic;
- Locality of Residence: Classification into urban Jewish, urban non-Jewish, or rural areas;
- Socioeconomic Status (SES): Socioeconomic status as derived from the Israeli Ministry of the Interior records, categorized as low (1st–4th), medium (5th–7th), or high (8th–10th) deciles;
- Birth countries: North America, Eastern Europe, Western Europe, Ethiopia, Africa, Asia, South America, and Israel.
Health Behaviors
Definition of Medical Diagnoses and Auxiliary Test Results
2.5. Analytical Approach
2.5.1. Statistical Analyses
2.5.2. Machine Learning (ML) Models
3. Results
- Technical (odds ratios (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) = 2.035 (1.107–1.317)) and academic education (OR = 1.208 (1.107–1.317)) compared to high school education;
- High (OR = 1.277 (1.102–1.480)) and medium (OR = 1.254 (1.084–1.452)) SES compared to low SES;
- Rural (OR = 2.017 (1.479–2.751)) and urban non-Jewish (OR = 1.117 (1.032–1.210)) compared to urban Jewish localities;
- African birth country (OR = 1.648 (1.066–2.546)) compared to native Israelis;
- Current smoker status (OR = 1.682 (1.531–1.849));
- Brushing teeth at least once a day (OR = 3.182 (2.940–3.443));
- Cariogenic diet consumption (OR = 1.966 (1.860–2.078));
- Sweetened beverage consumption (OR = 1.632 (1.544–1.725));
- Age (OR = 1.035 (1.032–1.039)).
| Parameter | Variable | Periodontitis No. (%) | Without Periodontitis No. (%) | p Value | OR (95% Confidence Interval) # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | Men | 4190 (74.4) | 38,322 (73.9) | 0.384 * | 1.028 (0.966–1.095) |
| Women | 1440 (25.6) | 13,544 (26.1) | 1 | ||
| Educational level | High school | 4306 (76.6) | 43,111 (83.2) | <0.001 ^ | 1 |
| Technicians | 664 (11.8) | 3267 (6.3) | 2.035 (1.107–1.317) | ||
| Academic | 653 (11.6) | 5414 (10.5) | 1.208 (1.107–1.317) | ||
| Socioeconomic status (SES) | Low | 209 (3.8) | 2414 (4.7) | 0.005 ^ | 1 |
| Medium | 3017 (54.3) | 27,785 (54.2) | 1.254 (1.084–1.452) | ||
| High | 2333 (42.0) | 21, 098 (41.1) | 1.277 (1.102–1.480) | ||
| Residency location | Urban Jewish | 4772 (85.0) | 44,792 (86.7) | <0.001 ^ | 1 |
| Urban non-Jewish | 790 (14.1) | 6637 (12.8) | 1.117 (1.032–1.210) | ||
| Rural | 49 (0.9) | 228 (0.4) | 2.017 (1.479–2.751) | ||
| Birth country | Western Europe | 494 (8.8) | 4293 (8.3) | 0.006 ^ | 1.066 (0.976–1.176) |
| Eastern Europe | 81 (1.4) | 738 (1.4) | 1.017 (0.807–1.282) | ||
| Asia | 29 (0.5) | 199 (0.4) | 1.351 (0.914–1.966) | ||
| Ethiopia | 104 (1.8) | 884 (1.7) | 1.090 (0.888–1.399) | ||
| Africa | 24 (0.4) | 135 (0.3) | 1.648 (1.066–2.546) | ||
| North America | 81 (1.4) | 1050 (2.0) | 0.715 (0.596–0.898) | ||
| South America | 49 (0.9) | 378 (0.7) | 1.201 (0.891–1.620) | ||
| Israel | 4767 (84.7) | 44,178 (85. 2) | 1 | ||
| Current smoker status | No | 5071 (90.1) | 48,676 (93.8) | <0.001 * | 1 |
| Yes | 559 (9.9) | 3190 (6.2) | 1.682 (1.531–1.849) | ||
| Brushing teeth once a day or more | No | 752 (13.4) | 17,068 (32.9) | <0.001 * | 1 |
| Yes | 4878 (86.6) | 34,798 (67.1) | 3.182 (2.940–3.443) | ||
| Cariogenic diet consumption | No | 2534 (45.0) | 31,987 (67.1) | <0.001 * | 1 |
| Yes | 3096 (55.0) | 19,879 (38.3) | 1.966 (1.860–2.078) | ||
| Sweetened drink consumption | No | 2165 (46.4) | 30,394 (58.6) | <0.001 * | 1 |
| Yes | 3015 (53.6) | 21,472 (41.4) | 1.632 (1.544–1.725) | ||
| Parameter | Mean ± SD | p value | OR (95% Confidence Interval) ^^ | ||
| Age | Without periodontitis | 22.4 ± 6.5 | <0.001 ** | 1 | |
| Periodontitis | 24.3 ± 8.3 | 1.035 (1.032–1.039) | |||
| Mean number of untreated decayed teeth | Without periodontitis | 2.22 ± 2.85 | <0.001** | 1 | |
| Periodontitis | 2.00 ± 2.75 | 0.972 (0.961–0.982) | |||
| Parameter | Variable | Periodontitis No.% (%) | Without Periodontitis No. (%) | p Value * | OR (95% Confidence Interval) ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypertension | No | 5413 (96.1) | 50,435 (97.2) | <0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 217 (3.9) | 1431 (2.8) | 1.413 (1.222–1.634) | ||
| Diabetes type 2 | No | 5591 (99.3) | 51,702 (99.7) | <0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 39 (0.7) | 164 (0.3) | 2.199 (1.549–3.121) | ||
| Hyperlipidemia | No | 5558 (98.7) | 51,427 (99.2) | 0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 72 (1. 3) | 439 (0.8) | 1.518 (1.181–1.950) | ||
| Obesity | No | 5044 (89.6) | 48,414 (93.3) | <0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 586 (10.4) | 3452 (6.7) | 1.629 (1.486–1.787) | ||
| Cardiac disease | No | 5380 (95.6) | 50,297 (97.0) | <0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 250 (4.4) | 1569 (3.0) | 1.490 (1.300–1.707) | ||
| Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) | No | 5579 (99.1) | 51,730 (99.7) | <0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 51 (0.9) | 136 (0.3) | 3.477 (2.517–4.803) | ||
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | No | 5514 (97.9) | 51,424 (99.1) | <0.001 | 1 |
| Yes | 116 (2.1) | 442 (0.9) | 2.448 (1.991–3.008) | ||
| Parameter | N | Study group | Mean ± SD | p value ^ | OR (95% confidence interval) ^^ |
| Body mass index (BMI) kg/m2 | 24,596 | Without periodontitis | 24.36 ± 4.41 | 0.00009 | 1 |
| 2880 | Periodontitis | 24.70 ± 4.39 | 1.017 (1.009–1.026) | ||
| Cholesterol (mg/dL) | 11,481 | Without periodontitis | 176.65 ± 35.73 | 0.012 | 1 |
| 1646 | Periodontitis | 179.02 ± 36.53 | 1.002 (1.001–1.003) | ||
| High-density lipoprotein (HDL) (mg/dL) | 11,481 | Without periodontitis | 47.95 ± 11.62 | 0.006 | 1 |
| 1646 | Periodontitis | 47.11 ± 11.24 | 0.994 (0.989–0.998) | ||
| Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) | 7479 | Without periodontitis | 108.92 ± 30.70 | 0.048 | 1 |
| 1106 | Periodontitis | 110.87 ± 30.92 | 1.002 (1.000–1.004) | ||
| Non-HDL cholesterol (mg/dL) | 6842 | Without periodontitis | 130.77 ± 35.05 | 0.007 | 1 |
| 1103 | Periodontitis | 133.79 ± 35.56 | 1.002 (1.001–1.004) | ||
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 11,484 | Without periodontitis | 106.47 ± 64.74 | 0.017 | 1 |
| 1646 | Periodontitis | 110.55 ± 67.45 | 1.001 (1.000–1.002) | ||
| Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) (mg/dL) | 11,461 | Without periodontitis | 20.96 ± 11.30 | 0.013 | 1 |
| 1644 | Periodontitis | 21.71 ± 11.90 | 1.006 (1.001–1.010) | ||
| Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) (%) | 847 | Without periodontitis | 5.42 ± 0.98 | 0.63 | 1 |
| 158 | Periodontitis | 5.47 ± 1.11 | 1.040 (0.884–1.223) | ||
| Oral glucose tolerance test-T0 (mg/dL) | 312 | Without periodontitis | 89.90 ± 20.12 | 0.017 | 1 |
| 51 | Periodontitis | 97.90 ± 31.18 | 1.012 (1.001–1.023) | ||
| Oral glucose tolerance test-T60 (mg/dL) | 438 | Without periodontitis | 133.02 ± 44.13 | 0.008 | 1 |
| 60 | Periodontitis | 151.70 ± 87.62 | 1.005 (1.001–1.010) | ||
| Oral glucose tolerance test-T120 (mg/dL) | 119 | Without periodontitis | 105.24 ± 38.21 | 0.040 | 1 |
| 23 | Periodontitis | 123.39 ± 45.01 | 1.010 (1.000–1.010) |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papapanou, P.N.; Sanz, M.; Buduneli, N.; Dietrich, T.; Feres, M.; Fine, D.H.; Flemmig, T.F.; Garcia, R.; Giannobile, W.V.; Graziani, F.; et al. Periodontitis: Consensus report of workgroup 2 of the 2017 World Workshop on the Classification of Periodontal and Peri-Implant Diseases and Conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S173–S182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.X.; Zhong, Y.J.; Dong, Q.Q.; Wong, H.M.; Wen, Y.F. Global, regional, and national burden of severe periodontitis, 1990-2019: An analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Jepsen, S.; Jin, L.; Otomo-Corgel, J. Impact of the global burden of periodontal diseases on health, nutrition and wellbeing of mankind: A call for global action. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azzolino, D.; Passarelli, P.C.; De Angelis, P.; Piccirillo, G.B.; D’Addona, A.; Cesari, M. Poor Oral Health as a Determinant of Malnutrition and Sarcopenia. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.D.; Papapanou, P.N.; Philips, K.H.; Offenbacher, S. Periodontal Medicine: 100 Years of Progress. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, J.R.; Martins, C.C.; Faria, S.F.S.; Carvalho, A.P.; Pereira, A.G.; Costa, F.O.; Cota, L.O.M. Association between components of metabolic syndrome and periodontitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral. Investig. 2022, 26, 5557–5574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, K.G.; Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Cleeman, J.I.; Donato, K.A.; Fruchart, J.C.; James, W.P.; Loria, C.M.; Smith, S.C., Jr.; et al. Harmonizing the metabolic syndrome: A joint interim statement of the International Diabetes Federation Task Force on Epidemiology and Prevention; National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; American Heart Association; World Heart Federation; International Atherosclerosis Society; and International Association for the Study of Obesity. Circulation 2009, 120, 1640–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Kang, J. Relationship between obstructive sleep apnea, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome: A nationwide population-based survey. Endocr. J. 2023, 70, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropeano, A.; Corica, D.; Li Pomi, A.; Pepe, G.; Morabito, L.A.; Curatola, S.L.; Casto, C.; Aversa, T.; Wasniewska, M. The metabolic syndrome in pediatrics: Do we have a reliable definition? A systematic review. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 185, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecoro, G.; Annunziata, M.; Iuorio, M.T.; Nastri, L.; Guida, L. Periodontitis, Low-Grade Inflammation and Systemic Health: A Scoping Review. Medicina 2020, 56, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preshaw, P.M.; Alba, A.L.; Herrera, D.; Jepsen, S.; Konstantinidis, A.; Makrilakis, K.; Taylor, R. Periodontitis and diabetes: A two-way relationship. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizenbud, I.; Wilensky, A.; Almoznino, G. Periodontal Disease and Its Association with Metabolic Syndrome-A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, P.; Rezaei Esfahrood, Z.; Foroughi, M. Paraoxonase-1, a novel link between periodontitis and ischemic heart disease: A case-control study. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendran, N.; Shenoy, S.; Kodangala, S.; Raghavendra Vamsi, A.; Kamath, V. Assessment of myocardial strain in hypertensive patients with periodontitis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2023, 60, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khudan, R.; Krynytska, I.; Marushchak, M.; Korda, M. Influence of chronic hyperhomocysteinemia on the features of bone metabolism in the case of lipopolysaccharide-induced periodontitis. Dent. Med. Probl. 2022, 59, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montero, E.; Molina, A.; Carasol, M.; Fernandez-Meseguer, A.; Calvo-Bonacho, E.; Teresa Garcia-Margallo, M.; Sanz, M.; Herrera, D. The association between metabolic syndrome and periodontitis in Spain: Results from the WORALTH (Workers’ ORAL healTH) Study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2021, 48, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotin, J.; Walther, C.; Wenzel, U.; Zyriax, B.C.; Borof, K.; Schnabel, R.B.; Seedorf, U.; Jagodzinski, A.; Heydecke, G.; Lamprecht, R.; et al. Association between periodontitis and metabolic syndrome in the Hamburg City Health Study. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Choi, C.H.; Chung, K.H. No Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Periodontitis in Korean Postmenopausal Women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 11110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario-Dos-Santos, H.L.; Miranda, S.S.; Gomes-Filho, I.S.; Cruz, S.S.D.; Figueiredo, A.; Souza, E.S.; Hintz, A.M.; Loomer, P.M.; Passos-Soares, J.S. Periodontitis severity relationship with metabolic syndrome: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Oral. Dis. 2023, 29, 2512–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheiham, A.; Watt, R.G. The common risk factor approach: A rational basis for promoting oral health. Community Dent. Oral. Epidemiol. 2000, 28, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Assuli, O.; Bar, O.; Geva, G.; Siri, S.; Tzur, D.; Almoznino, G. Body Mass Index and Caries: Machine Learning and Statistical Analytics of the Dental, Oral, Medical Epidemiological (DOME) Nationwide Big Data Study. Metabolites 2022, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Riela, P.M.; Iannella, G.; Lechien, J.R.; La Mantia, I.; De Vincentiis, M.; Cammaroto, G.; Calvo-Henriquez, C.; Di Luca, M.; Chiesa Estomba, C.; et al. Machine Learning Identification of Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity through the Patient Clinical Features: A Retrospective Study. Life 2023, 13, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimpi, N.; McRoy, S.; Zhao, H.; Wu, M.; Acharya, A. Development of a periodontitis risk assessment model for primary care providers in an interdisciplinary setting. Technol. Health Care 2020, 28, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.S.; Su, C.; Tellez, M.; Albandar, J.M.; Rao, R.; Iyer, V.; Shi, E.; Wu, H. Developing and testing a prediction model for periodontal disease using machine learning and big electronic dental record data. Front. Artif. Intell. 2022, 5, 979525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, H.M.; Koroukian, S.M.; Stange, K.; Schiltz, N.K.; Bissada, N.F. Identifying Factors Associated with Periodontal Disease Using Machine Learning. J. Int. Soc. Prev. Community Dent. 2022, 12, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wu, J.; Mao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Huang, G.F.; Petritis, B.; Huang, R.P. Developing a periodontal disease antibody array for the prediction of severe periodontal disease using machine learning classifiers. J. Periodontol. 2020, 91, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertas, K.; Pence, I.; Cesmeli, M.S.; Ay, Z.Y. Determination of the stage and grade of periodontitis according to the current classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions (2018) using machine learning algorithms. J. Periodontal. Implant Sci 2023, 53, 38–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almoznino, G.; Kedem, R.; Turgeman, R.; Bader, T.; Yavnai, N.; Zur, D.; Shay, B. The Dental, Oral, Medical Epidemiological (DOME) Study: Protocol and Study Methods. Methods Inf. Med. 2020, 59, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, D.; Wilensky, A.; Zur, D.; Almoznino, G. The Triangle of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Periodontitis: Analysis of the Dental, Oral, Medical and Epidemiological (DOME) Records-Based Nationwide Research. Metabolites 2022, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ytzhaik, N.; Zur, D.; Goldstein, C.; Almoznino, G. Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Metabolic Dysfunction, and Periodontitis—Machine Learning and Statistical Analyses of the Dental, Oral, Medical Epidemiological (DOME) Big Data Study. Metabolites 2023, 13, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Academy of Periodontology. 1999 International International Workshop for a Classification of Periodontal Diseases and Conditions. Papers. Oak Brook, Illinois, October 30–November 2, 1999. Ann. Periodontol. 1999, 4, 1–112. [Google Scholar]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-Learn: Machine Learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, J. Greedy function approximation: A gradient boosting machine. Ann. Stat. 2001, 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. In Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, San Francisco, CA, USA, 13–17 August 2016; pp. 785–794. [Google Scholar]
- Arbabshirani, M.R.; Fornwalt, B.K.; Mongelluzzo, G.J.; Suever, J.D.; Geise, B.D.; Patel, A.A.; Moore, G.J. Advanced machine learning in action: Identification of intracranial hemorrhage on computed tomography scans of the head with clinical workflow integration. NPJ Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, M.; Lu, X.S.; Yao, C. Weighted Gini index feature selection method for imbalanced data. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Zhuhai, China, 27–29 March 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.; Lu, G.; Cai, G.; Xu, D.; Xu, J.; Li, F.; Zhang, L. Feature Selection of Power Quality Disturbance Signals with an Entropy-Importance-Based Random Forest. Entropy 2016, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Berdine, G. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Southwest Respir. Crit. Care Chron. 2017, 5, 34–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Oral Disorders Collaborators; Bernabe, E.; Marcenes, W.; Hernandez, C.R.; Bailey, J.; Abreu, L.G.; Alipour, V.; Amini, S.; Arabloo, J.; Arefi, Z.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Levels and Trends in Burden of Oral Conditions from 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonetti, M.S.; Greenwell, H.; Kornman, K.S. Staging and grading of periodontitis: Framework and proposal of a new classification and case definition. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. S1), S159–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baima, G.; Romandini, M.; Citterio, F.; Romano, F.; Aimetti, M. Periodontitis and Accelerated Biological Aging: A Geroscience Approach. J. Dent. Res. 2022, 101, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walther, C.; Spinler, K.; Borof, K.; Kofahl, C.; Heydecke, G.; Seedorf, U.; Beikler, T.; Terschuren, C.; Hajek, A.; Aarabi, G. Evidence from the Hamburg City Health Study—Association between education and periodontitis. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiau, H.J.; Reynolds, M.A. Sex differences in destructive periodontal disease: Exploring the biologic basis. J. Periodontol. 2010, 81, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, M.S.; Su, S.; Crespo, C.J.; Hung, M. Men and Oral Health: A Review of Sex and Gender Differences. Am. J. Mens Health 2021, 15, 15579883211016361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falcon-Flores, J.A.; Jimenez-Corona, M.E.; Rangel-Nieto, I.; Moreno-Altamirano, L.; Borges-Yanez, S.A.; Vazquez-Duran, M.; Jimenez-Corona, A. Social determinants of health for moderate and severe periodontal disease in rural and urban populations. Community Dent. Health 2023, 40, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewon, L.A.; Parvinen, T.H.; Sinisalo, T.V.; Larmas, M.A.; Alanen, P.J. Dental status of adults with and without periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 1988, 59, 595–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merchant, A.T. Periodontitis and dental caries occur together. J. Evid.-Based Dent. Pract. 2012, 12, 18–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniaci, A.; Ferlito, S.; Lechien, J.R.; Di Luca, M.; Iannella, G.; Cammaroto, G.; Cannavicci, A.; Pollicina, I.; Stilo, G.; Di Mauro, P.; et al. Anxiety, depression and sleepiness in OSA patients treated with barbed reposition pharyngoplasty: A prospective study. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2022, 279, 4189–4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.D.; Chen, M.X.; Chen, G.P.; Lin, X.J.; Huang, J.F.; Zeng, A.M.; Huang, Y.P.; Lin, Q.C. Association between obstructive sleep apnea and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in pediatric patients: A meta-analysis. Pediatr. Obes. 2021, 16, e12718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Gong, Y.; Chu, T.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Deng, H.; Hu, R.; Wang, Y. Mendelian randomization highlights the causal association of obesity with periodontal diseases. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2022, 49, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y. A systematic comparison of machine learning algorithms to develop and validate prediction model to predict heart failure risk in middle-aged and elderly patients with periodontitis (NHANES 2009 to 2014). Medicine 2023, 102, e34878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Corrected p Value | i | p Value Level for FDR | Number of Comparisons | Crit | BH Test Result | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) | 0.63 | 28 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.05 | Not Significant |
| Sex | 0.384 | 27 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.048214 | Not Significant |
| Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) | 0.048 | 26 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.046429 | Not Significant |
| Oral glucose tolerance test-120 | 0.04 | 25 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.044643 | Significant |
| Oral glucose tolerance test-T0 | 0.017 | 24 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.042857 | Significant |
| Triglycerides | 0.017 | 23 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.041071 | Significant |
| Very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) | 0.013 | 22 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.039286 | Significant |
| Cholesterol | 0.012 | 21 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.0375 | Significant |
| Oral glucose tolerance test-T60 | 0.008 | 20 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.035714 | Significant |
| Non-HDL cholesterol | 0.007 | 19 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.033929 | Significant |
| HDL | 0.006 | 18 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.032143 | Significant |
| Birth country | 0.006 | 17 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.030357 | Significant |
| Socioeconomic status (SES) | 0.005 | 16 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.028571 | Significant |
| Body mass index (BMI) kg/m2 | 0.00009 | 15 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.026786 | Significant |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | 0 | 14 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.025 | Significant |
| Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) | 0 | 13 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.023214 | Significant |
| Cardiac disease | 0 | 12 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.021429 | Significant |
| Obesity | 0 | 11 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.019643 | Significant |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0 | 10 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.017857 | Significant |
| Diabetes type 2 | 0 | 9 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.016071 | Significant |
| Hypertension | 0 | 8 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.014286 | Significant |
| Mean number of untreated decayed teeth | 0 | 7 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.0125 | Significant |
| Cariogenic diet consumption | 0 | 6 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.010714 | Significant |
| Brushing teeth once a day or more | 0 | 5 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.008929 | Significant |
| Current smoker status | 0 | 4 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.007143 | Significant |
| Residency location | 0 | 3 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.005357 | Significant |
| Educational level | 0 | 2 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.003571 | Significant |
| Age | 0 | 1 | 0.05 | 28 | 0.001786 | Significant |
| Parameter | Variable | Multivariate Binary Logistic Regression Analysis | Collinearity Statistics Using Linear Regression Analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B | SE | p Value | OR and 95% Confidence Interval | Tolerance | VIF | ||
| (Intercept) | 0.412 | 0.837 | 0.622 | ||||
| Age | 0.040 | 0.003 | <0.001 | 1.040 (1.035–1.046) | 0.504 | 1.986 | |
| Residency location—reference rural | Urban Jewish | −0.930 | 0.230 | <0.001 | 0.395 (0.251–0.620) | 0.989 | 1.011 |
| Urban non-Jewish | −0.816 | 0.233 | <0.001 | 0.442 (0.280–0.698) | 0.982 | 1.019 | |
| Socioeconomic status (SES)—reference high | low | −0.146 | 0.078 | 0.062 | 0.864 (0.741–1.007) | 0.948 | 1.055 |
| Medium | 0.008 | 0.030 | 0.795 | 1.008 (0.949–1.070) | 0.945 | 1.058 | |
| Birth country: reference Israel | Western Europe | 0.051 | 0.052 | 0.330 | 1.052 (0.950–1.166) | 0.864 | 1.158 |
| Eastern Europe | 0.050 | 0.122 | 0.685 | 1.051 (0.827–1.335) | 0.959 | 1.043 | |
| Asia | 0.231 | 0.214 | 0.279 | 1.260 (0.829–1.915) | 0.843 | 1.187 | |
| Ethiopia | 0.168 | 0.110 | 0.127 | 1.183 (0.954–1.468) | 0.971 | 1.030 | |
| Africa | 0.302 | 0.249 | 0.225 | 1.353 (0.830–2.205) | 0.835 | 1.198 | |
| North America | −0.255 | 0.124 | 0.039 | 0.775 (0.608–0.988) | 0.927 | 1.078 | |
| South America | 0.178 | 0.163 | 0.274 | 1.195 (0.868–1.645) | 0.602 | 1.661 | |
| Smoking | 0.163 | 0.059 | 0.006 | 1.176 (1.047–1.322) | 0.756 | 1.322 | |
| Brushing teeth once a day or more | 1.095 | 0.044 | <0.001 | 2.985 (2.739–3.257) | 0.817 | 1.224 | |
| Consumption of a cariogenic diet | 0.502 | 0.037 | <0.001 | 1.652 (1.536–1.776) | 0.609 | 1.643 | |
| Consumption of sweetened beverages | 0.005 | 0.037 | 0.889 | 1.005 (0.934–1.081) | 0.598 | 1.671 | |
| Mean number of untreated decayed teeth | −0.020 | 0.006 | <0.001 | 0.980 (0.970–0.991) | 0.798 | 1.253 | |
| Hypertension | 0.036 | 0.084 | 0.669 | 1.037 (0.879–1.222) | 0.903 | 1.107 | |
| Diabetes type 2 | 0.243 | 0.200 | 0.224 | 1.275 (0.862–1.886) | 0.952 | 1.050 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 0.038 | 0.140 | 0.787 | 1.038 (0.789–1.366) | 0.957 | 1.045 | |
| Obesity | 0.026 | 0.062 | 0.669 | 1.027 (0.909–1.159) | 0/685 | 1.460 | |
| Cardiac disease | 0.048 | 0.078 | 0.538 | 1.049 (0.900–1.222) | 0.928 | 1.077 | |
| Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA ( | 0.784 | 0.178 | <0.001 | 2.188 (1.545–3.105) | 0.973 | 1.028 | |
| Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) | 0.395 | 0.121 | 0.001 | 1.483 (1.171–1.879) | 0.905 | 1.104 | |
| Anemia | 0.014 | 0.055 | 0.802 | 1.014 (0.910–1.128) | 0.886 | 1. 098 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wilensky, A.; Frank, N.; Mizraji, G.; Tzur, D.; Goldstein, C.; Almoznino, G. Periodontitis and Metabolic Syndrome: Statistical and Machine Learning Analytics of a Nationwide Study. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121384
Wilensky A, Frank N, Mizraji G, Tzur D, Goldstein C, Almoznino G. Periodontitis and Metabolic Syndrome: Statistical and Machine Learning Analytics of a Nationwide Study. Bioengineering. 2023; 10(12):1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121384
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilensky, Asaf, Noa Frank, Gabriel Mizraji, Dorit Tzur, Chen Goldstein, and Galit Almoznino. 2023. "Periodontitis and Metabolic Syndrome: Statistical and Machine Learning Analytics of a Nationwide Study" Bioengineering 10, no. 12: 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121384
APA StyleWilensky, A., Frank, N., Mizraji, G., Tzur, D., Goldstein, C., & Almoznino, G. (2023). Periodontitis and Metabolic Syndrome: Statistical and Machine Learning Analytics of a Nationwide Study. Bioengineering, 10(12), 1384. https://doi.org/10.3390/bioengineering10121384