Abstract
On the one hand, Sinkhole Flooding (SF) is an essential hydrological process to recharge karst aquifer in arid to dry sub-humid regions. On the other hand, the increase of rain extremes is one of the major consequences of global warming, together with the expansion of drylands. Thus, appropriate runoff regulation in endorheic karst basins in order to reduce the risk of flooding and improve the quantity and quality of the water drained by sinkholes will be more and more crucial. With these premises, a systematic review of SF cases study was performed by using Web of Science (WoS) engine to infer the hydrological properties for modeling the water management in regions actually or potentially affected by water scarcity. Hydrological models are essential to manage the consequences of climate change on karst water resource, however the review shows that providing the tools necessary for reliable modeling is still challenging. Finally, due to the intrinsic vulnerability of the karst aquifers, pollution reduction and wastewater recycling policy will play a key role in the next decades.
1. Introduction
Sinkholes are the most diagnostic landforms of karst terrain and are produced as results of different endogenous and exogenous geological processes [1]. Such a term become initially popular in North America among geologist and engineers, and subsequently has supplanted the Slav term “doline”, widely used in Europe from the eighteenth century [2]. However, either sinkholes or dolines can be described as closed depressions which allow surface waters to be drained underground. In such a view, they act as “infiltration points”. Other terms (swallow hole, swallet, ponor, sinking stream) are also used in literature. As regards the rainwater runoff, sinkholes are drainage convergence points of different sized basins (named endorheic or closed basins) and allow no surficial outflow to rivers or seas. Sinkhole Flooding (SF)s were comprehensively conceptualized and classified by Crawford almost forty years ago [3].
In arid to dry sub-humid regions, SF is a process essential to recharge karst aquifers, but difficult to manage [4,5,6,7,8]. Climate change and population growth are continuously increasing human pressure on water resources and thus, it is appropriate to investigate how accumulated scientific knowledge about SF can support sustainable management in conditions of water depletion. Nevertheless, defining the issue it deals with as the “land degradation in arid, semi-arid, and dry sub-humid areas resulting from various factors”, the United Nation Convention to Combat Desertification has brought together, for research purposes, the lands actually or potentially affected by water scarcity [9]. Before addressing the question of SF, some definitions and basic features must be given.
Arid to dry sub-humid lands are defined as regions with Aridity Index (AI, i.e., the ratio between precipitation and potential evapotranspiration) less than 0.65 [10,11,12]. They cover almost 50% of Earth’s surface, including several karst areas (see e.g., [6,13,14]). The streams are usually ephemeral while floods are not frequent events in karst catchments; however, especially in endorheic basins, the inundations can be highly damaging to people, infrastructures and water resources, both superficial and underground [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. Despite a wide variety of local geomorphological features, the karst areas are usually characterized by a dual underground runoff drainage, through the swallow holes (infiltration points or, simply, sinkholes) and the networks of dissolution-enlarged fractures inside the superficial layer of the rock masses (diffuse, epikarstic infiltration), respectively [8,23,24].
It must be also considered that, since the ancient civilizations, hydraulic works have frequently altered the hydrology of the karst catchments, thereby changing both the infiltration pathways and the floodplain features. The sinkholes have historically served for runoff regulation, stormwater discharge, and wastewater disposal. A further function, the intentional (managed) groundwater recharge, was added in recent times [1,6,25,26]. As a whole, karst aquifers currently supply a quarter of the global population with water. They are highly sensitive to changes in recharge patterns because they combine a high transmissivity with a low specific yield, thus their correct use is vital to ensure the water availability for years to come [27,28].
Despite SFs being essential for groundwater balance, they are still difficult to foresee and manage [29,30]. They occur as consequences of extreme precipitation when: (1) the rate of stormwater flow exceeds the discharge capacity of the sinkhole (SF type 1); (2) the underground karst system is unable to drain the entire stormwater flow (SF type 2); (3) the groundwater level rapidly rise especially because of the diffuse infiltration (SF type 3) [3,31] (Figure 1).
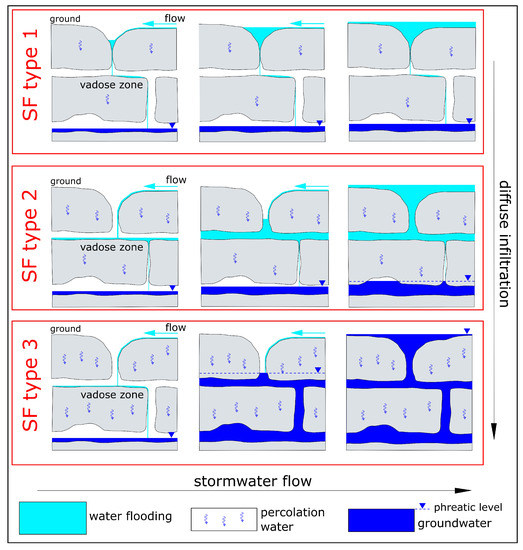
Figure 1.
Simplified scheme of SF types. It is not representative of the whole complexity of the phenomenon and simply considers change in width of the karst shafts. The increase in diffuse infiltration from SF type 1 to SF type 3 is a generic trend.
Together with the expansion of drylands, the increase of rain extremes is one of the major consequences of the changes in climate pattern and hydrological cycle due to the global warming [10,12,32,33,34]. With these premises, a systematic review of documented cases of SF occurred in arid to dry sub-humid areas was performed to infer the hydrological properties useful for the upcoming water management plans. Since model development requires time-series data, particular attention was given to observational studies [17,35,36,37].
2. Climate Change Effects on Sinkhole Flooding
Worldwide evidences suggest a recent net decline in endorheic basin water storage for regions with arid and semi-arid climates [38,39,40,41]. Climate change is one of the concurrent causes together with climate variability and direct human activities. Nevertheless, more than half of the total dryland expansion during the last six decades was occurred in semi-arid regions. Semi-arid areas replaced sub-humid areas especially in Africa, Europe, Asia, and eastern Australia, while they replaced arid areas mainly in both the American continents as well as western Australia [42]. However, the transition from sub-humid (and even humid) to semi-arid conditions also affected different areas of North and South America, thus increasing the uncertainties on the meteorological effects of climate change.
Multi-decadal average aquifer recharge is described as a major limiting factor for the sustainable use of water resources because it determines the amount of groundwater that may be withdrawn without irreversible depletion. By using global precipitation data sets, Doll and Fiedler [43] found the smaller values of average per-capita renewable groundwater resources especially in arid to semi-arid regions. Therefore, effective water management plans need to be developed in these regions, with the aim of maximizing the aquifer recharge during intense and prolonged rainfall.
Climate model projections for the 21st century indicate the following general responses about the rainfall characteristics: decrease of the light precipitations and in wet spell length, increase of the intensity of extremes, and increase in the number of dry days [32,44]. Whether such weather changes will affect endorheic karst basins belonging to arid to sub-humid regions, a reduction in annual average soil moisture and an increase in severe flood events are easily predictable [28,45]. However, precipitation events occurring during wet seasons and with soil moisture close to saturation will determine larger runoff and water flood volumes. Thus, taking on constant values of discharge capacity, the sinkhole infiltration will increase in volume and time. In regions affected by water scarcity, management aimed to improve the quantity and quality of the water drained underground by sinkholes will be essential. Nevertheless, to establish how karst aquifers may be affected by climate change and elaborate model management plans, the duality of the infiltration flow in karst terrain (punctual versus diffuse infiltration) must be properly taken into account [46,47,48].
3. Methods
The systematic review of literature differs from the typical narrative review by the effort to establish a clear, not subjective and replicable procedure for the studies identification. Initially developed in Medical and Healthcare Sciences, systematic reviews gained increasing popularity in Earth and Environmental Sciences through the last decade.
In the present work, the systematic review was conducted according to [49,50,51,52]. It aimed to the comprehensive identification and appraisal of the studies relevant for the pursued subject. Web of Science (WoS) was chosen as bibliographic data source for the screening process [53,54,55]. The identification of the studies was implemented in all WoS databases. A limitation of the adopted procedure is that it only includes items written in English. Moreover, a temporal period was not specified. The screening process has consisted of three stages. In the first one, WoS engine search was used as the primary platform for “title/abstract/author keywords/Keywords Plus”. The abstract screening was performed in Stage 2 and the full-text articles assessment for eligibility in Stage 3 (Figure 2). Careful exclusion procedures were adopted in Stages 2 and 3.
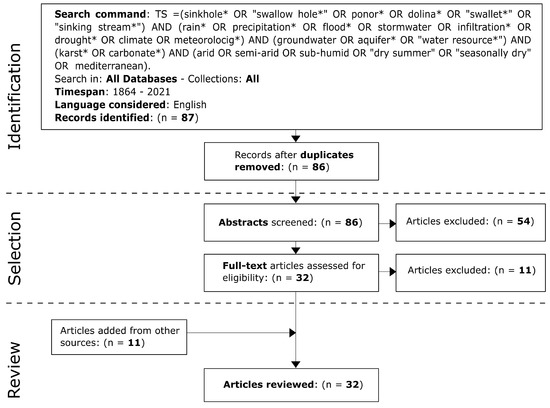
Figure 2.
Flow diagram explaining the screening process (see [49,52]).
4. Results
WoS engine allowed the identification of 87 records, only one of which was excluded as duplicate (Figure 2). The selection of Stage 2 has determined the exclusion of 54 articles for being apparently irrelevant to the review purpose and belonging to different subject areas (i.e., ecology, hydrobiology, geomorphology, sinkhole occurrence, regional hydrogeology, karst hydrochemistry, baseflow estimation, particles transport, paleoclimate, civil engineering, pollution impact, vulnerability assessment, rainfall chemistry, mathematical model). Despite the positive evaluation of the abstracts, eleven out of thirty-two articles were then excluded by the full-text assessment of the Stage 3 (Appendix A). These exclusions were caused by the irrelevance of the article on the sinkhole flooding process, or because the article deals with cases of humid regions (Table A1). Eleven articles identified by other sources (examination of the bibliography of the selected articles; personal literature knowledge; use of common search engines) have been added for the review analysis. Finally, a total of 32 articles were reviewed.
Two articles were published in the late 1990s, twelve in the past decade, and eighteen in the 2020s. It therefore appears that there has been growing attention from scholars. Many articles concern basins belonging to the Mediterranean area (Figure 3). More in detail, they are relative to North Africa [56], Iberian Peninsula [16], south Continental Europe [57,58,59,60], Italian Peninsula [19,21,45,61,62,63], Balkan Peninsula [64,65,66,67], and Anatolian Peninsula [68,69]. Some articles examine cases of the Middle East: three located near the Mediterranean coast [20,36,70], and three near the coast of the Persian Gulf [71,72,73]. Australia [48,74], China [18,75], and North America [76,77] are featured with two articles each. Finally, one article was identified for both South America [22] and India [78]. The results of the screening process show some little redundancies. In fact, the papers [58,59] deal with the Fontaine de Nimes Basin (France), and the papers [19,63] with the Asso Torrent Basin (Italy). They slightly bias the prevalence of cases studied in the Mediterranean area.
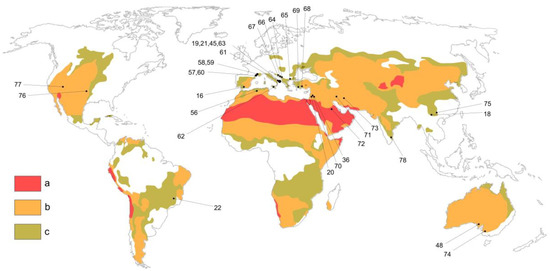
Figure 3.
Location of reviewed cases study (see References numbering). Climatic regions map based on the Aridity Index in according to United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) [79], modified after [80,81]. Areas: a, hyper arid; b, from arid to semi-arid; c, dry sub-humid.
“Aquifer recharge” is the main objective for ten articles (third column of Table 1), while for the others it is “flood management” (twelve articles) or “contamination risk” (six). Four articles address “multiple objectives”. Twenty-two studies state the type(s) of examined SF or provide information for such classification.

Table 1.
Summary of reviewed studies. * = Added from other sources; und. = undetermined type; Cont. = Continental; Cent. = Central.
Looking for appropriate practices suggested by the authors for water management in karst endorheic areas, the first apparent feature is the frequent recourse to the use of hydrological models [16,20,21,22,36,45,58,59,60,63,66,70,71,72,77]. It must be pointed out that the authors usually do not cite Crawford [3] but provide useful indicators for classifying the SFs they studied. In the reviewed literature, the articles dealing with flood events series are rather limited in number, and even about the sinkhole discharge capacity the numerical quantification are very few. Instead, more attention is given to the description, also in quantitative terms, of the aquifer recharge. A number of the screened articles listed in Table 1, especially among those published in the last six years, finally mention the occurrence of SF in relation to changing climate conditions [18,19,21,22,63,67,68,69,70,78]. However, no one investigates the phenomenon in such a perspective. Given the above, the main topics identified by the literature examination are summarized below (types of sinkhole flooding, Section 4.1; flood events series, Section 4.2; sinkhole discharge capacity, Section 4.3, aquifer recharge process, Section 4.4; water resource planning, Section 4.5). The relationship among the topics is schematized in Figure 4.
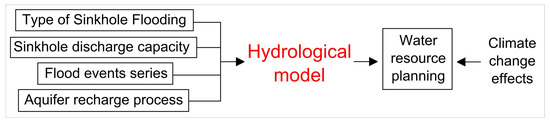
Figure 4.
Relationship diagram among the topics identified by the review.
4.1. Types of Sinkhole Flooding
Half of the 32 reviewed studies address the SF type 1, while among the remaining studies the SF type 2 (six articles) prevail. Only two cases were confidently ascribed to the SF type 3. Finally, in four studies the attribution is uncertain or SF is the result of two concurrent causes (Table 1).
The ascription to the SF type 1 implies the knowledge of the discharge capacity of the sinkhole or, at least, of its underground shape and dimensions [4,8]. Despite the lack of data on the underground karst system, Herczeg et al. [74] provided pioneer field observation on the basic hydrological features of the Pretty Gully Sinkhole (Gambier Basin, Southern Australia), thus giving sufficient elements for the definition of SF type occurred in a dryland context (Figure 3). Dar et al. [78] focused on the speleological features of the area they studied (Cuddapah Basin, Southern India), carrying out hydrological insight about the aquifer recharge. However, such a study did not collect sufficient clues to define the type of SF (Table 1). Estimating the aquifer recharge for the small endorheic As Sulb Basin (located in the hyper arid As Summan Plateau, Saudi Arabia, Middle East), Schulz et al. [72] documented by camera monitoring the occurrence of SF type 1. Where the sinkhole is a dissolution doline covered by residual soil, the issue to define the SF type does not arise as it is of the first type (see e.g., [22]).
The ascription to the second type of SF requires accurate knowledge about the development of the underground karst system, previously achieved mainly by speleological exploration and mapping [5,61]. Dealing with an extreme flood occurred within a flat karst depression (Polje of Cetinje, Montenegro, south-west of Balkan Peninsula), and the inability of the cave system to drain the stormwater flow was identified as the main cause by Mijatovic (1988) [64]. Some later authors have come to the same conclusion [57,60,62,65,69]. Other authors have considered SF type 2 as a concurrent cause together with type 1 or type 3 [36,58,67] (see Table 1). The case described by Liguori and Manno [62] (Platani Basin, Italian Peninsula) is quite unique in the context of this review, dealing with sinkholes induced by quarrying and then flooded because of the water filling excavation tunnels. Drilling data and speleological surveys in the southern slope of the Falakro Mountain (Greece, Balkan Peninsula) reveal the decrease of the width of karst conduits with depth, and allow to attribute to type 2 the SF studied by [65]. The recurrent SF affecting the Gokova Graben (Anatolian Peninsula) must be attribute to the type 2 as a result of the spectral analyses on the precipitation and spring discharge time series carried out by [69].
The type 3 is apparently the least common of SF. In fact, only two of the thirty-one reviewed studies attribute the flooding to the quick rise of the groundwater level [16,48]. Both these studies support such an attribution by means of aquifer monitoring. For a few other studied cases, type 3 is tentatively referred to as concurrent cause in possible conjunction with type 2 (Table 1).
4.2. Flood Events Series
Several essential features arose from the full-text assessment on SF series reported in literature. A three years series of floods is analysed by Bailly et al. [60] as regards the swallow hole named Puits de l’aven, which is placed within the karst basin of Coulazou River (France, South Continental Europe) (see also [57]). The thirteen events occurred from 2004 to 2007 were used by the authors to show that exchanges between surface water and groundwater during flood events are characterized by inversion of direction, in strict dependence of the hydraulic gradient changes. The observational approach used in the study, which made use of various instruments such as rain gauges, discharge gauging stations, and monitoring wells, was decisive for the obtained findings.
Guo et al. [18,75] monitored the recurrent floods affecting karst depressions placed within the sub-humid and seasonally drought-prone Fengshan County (Guangxi) and Guangnan County (Yunnan), South China. Floods were found to last up to four months during the rainy season, in stark contrast with the extreme drought conditions of the dry season. Moreover, several processes of sinkhole clogging (see e.g., [7,63,82]) were detected.
The flood history of some endorheic catchments was scrutinized in the reviewed literature. Parise [61] found more than twenty flood events struck the karst basin of Castellana-Grotte (Italian Peninsula) throughout the last three centuries. It is one of the longest known series of events. Hydraulic works aimed to improve the discharge capacity of a cluster of swallow holes started in 1865. They consisted of increasing the entrance section of the sinkholes and excavating a connecting tunnel. Although designed to mitigate the damage caused by flooding, such works have also increased the recharge of the regional karst aquifer.
A thirty-year series of floods affected the extensively engineered Asso Torrent Basin (Italian Peninsula) is analyzed by Apollonio et al. [63] with the aim of understanding to what extent clogging processes in sinkholes from microbial growth had affected the increase in recorded floods. By using rain gauges data, basin runoff model, and evaluation of contaminant loads from sewage treatment plants, the authors showed the occurrence of floods even in the absence of clogging processes, which still had a small impact on the hydrological disorder in the studied case. Instead, the main detected problem is the low discharge capacity of the swallow holes.
4.3. Sinkhole Discharge Capacity
The discharge capacity is a basic parameter in the relation between SF and aquifer recharge. However, it is rarely quantified or at least estimated in the literature studies [19,63]. Such a result confirms the concern of Field [83], which likely first observed the “little attention” by the authors for this subject and provided mathematical models to simulate drainage through flooded sinkhole.
The discharge capacity is a simple direct function of the water level in the sinkhole when flow in the underground karst system is not under pressure. Exceeding a threshold value of the sinkhole water level, the flow comes under pressure and the discharge capacity becomes dependent on the difference in head hydraulic between the sinkhole and another measuring point (a spring, as an example) [84]. Despite its good reliability, such an approach requires extensive measures for the computation of a coefficient and thus it is rarely used. However, dealing with sinkholes of simple shapes (cylinder-shaped, cone-shaped, bowl-shaped), simplified mathematical models were developed to estimate the discharge capacity [83].
The above theoretical approaches are not frequently used. [60] performed an analysis on the infiltration rate in the Puits de l’aven sinkhole (see Section 4.2) during recession, using it to estimate the hydraulic conductivity of the karst system rather than to establish the discharge capacity.
Rough evaluations of the total discharge capacity for clusters of sinkholes located within karst depressions are present in the reviewed literature. They could be carefully obtained by subtracting the other losses (diffuse infiltration, outflow stream discharge, evaporation) from the water volume change of the flooded area occurred during a fixed time interval. However, simplifications are usually used because the involved quantities are not available or easy to calculate. Investigating the 22 km2 Zafarraya Basin (Spain, Iberian Peninsula), Lopez-Chicano et al. [16] calculated a value of 3.5 m3/s. Dasic et al. [67] instead found a value of 160 m3/s for the 37.5 km2 Gatacko Polje (Herzegovina, Balkan Peninsula). The difference of two orders of magnitude may seem unexpected, considering that the basins have roughly similar areas. However, it falls within the variability of the karst systems and highlights the need to carry out detailed hydrological investigation on each of them to obtain solid bases for the management [1].
4.4. Aquifer Recharge Process
Aquifer recharge in karst basins usually involves two different processes—the diffuse (epikarstic) infiltration and the localized (through the sinkholes) infiltration, respectively. The amount of the two contributions in the aquifer recharge and the evolution of the processes over time are characteristic of each karst basin. Nevertheless, the initial soil moisture (i.e., before the onset of precipitation) can significantly affect the partition among diffuse and localized infiltration [17,30,35,70,74].
Braga et al. [22] found a value of recharge around the 10% of the yearly rainfall for the semi-arid Rio Verde Grande Catchment (Minas Gerais, South-East Brazil). Considering the annual rainfall height and the basin surface, a large amount of water runoff is lost in a region subjected to severe water stress. However, the hydrogeological features of the sinkholes of the basin (dissolution doline covered by residual soil) do not seem to allow an increase in water infiltration without the execution of drainage wells.
Djidi et al. [56] described the mixing process of stormwater infiltrated through sinkholes with deep hydrothermal water in the Saida Plateau (Algeria, North Africa) by means of geochemistry and isotope analysis. In such a basin, speleological explorations have detected some swallow holes reaching the aquifer, while the authors found a direct correlation between sinkhole infiltration and spring discharge. Finally, because hydrothermal water may have unfit characteristics for human consumption or irrigation, a careful strategy is required for the management of this type of resource which will become even more important with global warming.
As the management of the karst aquifer recharge becomes more and more crucial, the correct design of hydraulic engineering works becomes increasingly essential. In arid to dry sub-humid regions, large volumes of water flood can be lost due to evapotranspiration. Looking for a solution to this problem, Leventeli et al. [76] proposed the construction of “engineered sinkhole” at a small catchment basin located in South Oklahoma (Central North America) and characterized by prolonged dry summers. Learning from nature, the structure is meant to simulate a natural swallow hole with control on the sediment filtering and the photodegratation (i.e., the combined actions of oxidation and hydrolysis processes) of the water pollutants to avoid clogging phenomena.
In the next decades, a major challenge will be quantifying the change in aquifers recharge due to the variation in precipitation frequency and amount. As deducted by the literature, for this scope, the use of reliable models will play a role of reference [70,72].
4.5. Water Resource Planning
In the karst basins drained by sinkholes, the upcoming water management plans will require an overview of all aspects of flooding in a framework of the local impact of global warming. Firstly, the aquifer recharge enhancement will have to be conciliated with the reduction of flooding risk [45,68]. Different management strategies are suggested in the examined literature, from the construction of several small-sized rainwater harvesting systems to reduce the runoff toward the swallow holes [63] to the building of centralized infrastructures to transfer elsewhere large quantities of flooding water for usage in hydropower production, irrigation, or water supply [67].
To face the reduction of water availability in wide rural areas alternatively affected by flooding and drought problems and threatened by desertification, [18] suggested both large new hydraulic works and systematic cleaning of karst conduits from clogging material. According to these authors, for future sustainable development, detailed hydrological investigation should be done to define the anthropic and natural impacts on karst aquifer. For proper management, if one part of the literature supports the request for detailed field studies, another part calls for use of recent advances in remote sensing. Following the second view, Jones et al. [77] applied a modified version of the COP method (originally developed by [85]) to the semi-arid Kaibab Plateau (Arizona, West North America, Figure 3). To identify the “sinkhole density”, the authors use high-definition LIDAR-derived digital elevation model and automated GIS techniques. As a result, out of more than 257,000 depressions, almost 7000 were identified as true sinkholes over an investigated surface of about 2500 km2.
In arid to dry sub-humid regions, the Hortonian runoff concept [86] should be carefully considered in modelling for water management [87,88,89]. Thus, according to Iacobellis et al. [45], the soil moisture condition before the rainfall event must be quantified together with the sinkhole discharge capacity. The latter is used, in the model proposed by these authors, to calculate the “storage capacity”, i.e., the maximum volume of water that can be stored in a sinkhole before the flooding of the surrounding area. Moreover, the rainfall input should be provided by means of the “intensity duration frequency curve” for a given return period.
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Over the last two decades, a worldwide decline in water storage for sub-continental sized endorheic regions has been detected [39,41]. At catchment scale, several studies highlighted this phenomenon in many karst basins (see e.g., [90,91,92,93]). In arid to dry sub-humid regions, aquifer recharge through sinkholes is a discontinuous process that occurs as a result of flooding or intense runoff [65,72,74]. If wet soil moisture condition precedes the rainfall event, extensive runoff is triggered and contributes to large SF with considerable water accumulation [30,45]. Where SF occurs in karst areas threatened by water scarcity, pollutant free water accumulated on the surface should be discharged into the aquifer rather than evaporate to the atmosphere. The main influencing factors of such a process are: duration and intensity of the rain, discharge capacity of the swallow holes, average soil moisture, and mean air temperature [22,35,70].
Based on the climate model projections for the 21st century (Section 2), in the regions actually or potentially affected by water scarcity, the stress on karst water sources is likely to significantly grow over the next decades [32,44]. However, given the current uncertainties, a very difficult question to address is how much potential changes in temperature and precipitation will affect water availability in karst regions [9,42,47].
The need to correctly regulate the runoff in endorheic karst basins in order to reduce the risk of SF type 1 (i.e., the most recurrent type of SF according to the reviewed studies, see Section 4.1) and, at the same time, improve the quantity and quality of the water drained by the sinkholes is crucial anyway [19,21,76]. In the reviewed literature, several case studies suggest some basic guidelines. Cleaning of sinkholes to avoid clogging phenomena, maintenance of the tributary channels, and increase of use of draining pavements over the basin surfaces are the most recurrent solutions (see e.g., [16,63,75]). However, as deduced from the full-text analysis, ordinary and low-cost interventions are not sufficient to guarantee proper drainage in several karst areas. In these last cases, the solution generally consists of hydraulic works with the creation of centralized infrastructures [18,64,67,75].
To properly manage karst aquifers, the recharge contribution coming from sinkholes compared to diffuse infiltration must be known. This also takes into account that the two supplies change over time according to meteorological conditions. For such a issue, Herczeg et al. [74] use a simple mass balance of the two respective end-members previously identified by both Cl− and deuterium concentrations. For the aquifer of the about 1000 km2 Gambier Basin, these authors found less than 10% of point recharge contribution, which coincides with the area covered by the sinkholes adjusted for a theoretical influence radius of 200 m. While this data is valid specifically for the aforementioned case study, the method could be effectively used in other karst basins (eventually by means of different chemical and isotopic parameters as appropriate) with analogous environmental conditions (better in cases where flood events series is known, see Section 4.2). Small groundwater recharge contributions through swallow holes are inferred from other reviewed studies also [45,67]. However, there are karst areas where point recharge is apparently dominant, such as the 40 km2 As Sulb Basin (belonging to the arid As Summan Plateau [72]) or the 500 km2 southern slope of the Falakro Mountain (belonging to the sub-humid Aggitis Basin [65]).
The variability in hydraulic behavior between the mentioned karst areas underlines how much detailed studies on karst hydrology are essential for the aquifer recharge management [19,36]. However, due probably to the complex in situ measurements, sinkhole discharge capacity is often overlooked in studies (Section 4.3). It must also be considered that the reviewed articles deal with cases related to only a part of the karst areas potentially affected by the issue herein discussed. In arid to dry sub-humid regions, there are in fact a number of karst basins with few or no hydrological knowledge about flooding processes [1,47], which cannot be identified with search engine inquiries. This is, as an example, the case of the seasonally water deficient Rio Sao Miguel Catchment (South East Brazil) [94], a sub-basin of the Rio Sao Francisco Basin (as the Rio Verde Grande Catchment, previously mentioned in Section 4.4).
The management of karst aquifer recharge is now mandatory in several anthropized areas (see e.g., [36,63]). Currently, the volume of managed aquifer recharge at global scale is estimated at 10 km3/year, while its rate of expansion is 100 km3/year [26]. This quantity is relatively small compared to the 4600 km3/year of the global water demand for all uses [95]. However, karst aquifers are a basic source of drinking water supply to about a quarter of the world population living in densely populated areas [1,47]. Thus, the need to properly manage the underground drainage of natural runoff and treated wastewater should considerably increase in karst areas. The actual spreading of aquifer recharge facilities will be the result of the understanding of their capabilities and constraints, the effective risk management, and the economic advantages in comparison with alternatives [96].
Due to the consequences of climate change and the intrinsic vulnerability of the karst aquifers, pollution reduction and wastewater recycling policy will play a key role in the next decades [19,26,36,46,97]. Therefore, treated wastewater facilities will have to avoid fast direct aquifer recharge (through sinkholes or injection wells) in favour of slow and delayed diffuse infiltration [98]. Soil covered epikarst should be preferentially used in wastewater recharge because of its natural treatment processes, such as contaminant adsorption and spread of the injected effluent.
Finally, it must be stressed that hydrological models are essential to manage climate change effects on karst water resources [46,47]. To perform reliable simulations for karst endorheic catchments, the input parameters must be calibrated on appropriate knowledge about the main hydraulic features, such as type of SF, sinkhole discharge capacity, and aquifer recharge process. Moreover, flood series events should be reconstructed in order to evaluate the simulations [60,63]. The review of the pertinent literature has however shown that providing the tools necessary for reliable modeling is still challenging, starting from the reliable definition of the SF type that could require specific skills such as speleological exploration and mapping [5,61,65,78]. Nevertheless, even the calculation of the sinkhole discharge capacity is still poorly performed [19,83]. Again, the flood events series, which are essential for models validation, were not of specific interest to the authors except for a few cases studies [60,61,63]. However, in the years to come, the management of the water resources in karst endorheic basins will require more in-depth knowledge.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
| Author (s) and Year | Main Objective | Exclusion Cause |
|---|---|---|
| Nebbache et al. (2001) [99] | particles transport | in humid region |
| Massei et al. (2003) [100] | particles transport | in humid region |
| Alberic (2004) [101] | river backflooding | in humid region |
| Celico et al. (2004) [102] | contamination risk | no SF process |
| Aquilina et al. (2006) [103] | epikarst hydrology | no SF process |
| Massei et al. (2006) [104] | particles transport | in humid region |
| Milanovic (2007) [105] | regional hydrogeology | no SF process |
| Jardani et al. (2007) [106] | sinkhole occurrence | in humid region |
| Fournier et al. (2008) [107] | particles transport | no SF process |
| Polemio et al. (2009) [108] | vulnerability assessment | no SF process |
| Guillaume et al. (2020) [109] | vulnerability assessment | no SF process |
The above listed articles have been excluded by the review due to two causes (see third column of Table A1). They deal with karst areas with no water scarcity (humid regions) or in which no SF processes are described.
References
- Ford, D.C.; Williams, P.W. Karst Hydrogeology and Geomorphology, 1st ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2007; pp. 103–208. [Google Scholar]
- Parise, M. Chapter 110—Sinkholes. In Encyclopedia of Caves, 3rd ed.; White, W.B., Culver, D.C., Pipan, T., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 934–942. [Google Scholar]
- Crawford, N. Sinkhole flooding associated with urban development upon karst terrain: Bowling Green, Kentucky. In Sinkholes: Their Geology, Engineering and Environmental Impact. The Proceedings, First Multidisciplinary Conference on Sinkholes; Beck, B.F., Ed.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; pp. 283–292. [Google Scholar]
- Kemmerly, P. The need for recognition and implementation of a sinkhole-floodplain hazard designation in urban karst terrains. Environ. Geol. 1981, 3, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currens, J.C.; Graham, D.R. Flooding of sinking Creek, Garretts Spring karst drainage basin, Jessamine and Woodford counties, Kentucky, USA. Environ. Geol. 1993, 22, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gams, I.; Nicod, J.; Julian, M.; Anthony, E.; Sauro, U. Environmental change and human impacts on the Mediterranean karsts of France, Italy and dinaric region. Catena Suppl. 1993, 25, 59–98. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, E.A. Land use change and sinkhole flooding in Cookeville, Tennessee. Southeast Geogr. 2006, 46, 35–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W. Drainage and flooding in karst terraines. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, J.F.; Stafford Smith, D.M.; Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Mortimore, M. Global desertification: Building a science for dryland development. Science 2007, 316, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Fu, Q. Expansion of global drylands under a warming climate. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 10081–10094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Vogt, J.; Naumann, G.; Carrao, H.; Barbosa, P. Towards identifying areas at climatological risk of desertification using the Köppen–Geiger classification and FAO aridity index. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 2210–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Gao, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, D.; Yu, H.; Chen, X. Accelerated dryland expansion regulates future variability in dryland gross primary production. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, W.B.; Culver, D.C.; Herman, J.S.; Kane, T.C.; Mylroie, J.E. Karst Lands—The dissolution of carbonate rock produces unique landscapes and poses significant hydrological and environmental concerns. Am. Sci. 1995, 83, 450–459. [Google Scholar]
- Gillieson, D.; Thurgate, M. Karst and agriculture in Australia. Int. J. Speleol. 1999, 28, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmett, A.J.; Telfer, A.L. Influence of karst hydrology on water quality management in southeast South Australia. Environ. Geol. 1994, 23, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Chicano, M.; Calvache, M.L.; Martin-Rosales, W.; Gisbert, J. Conditioning factors in flooding of karstic poljes—The case of the Zafarraya polje (South Spain). Catena 2002, 49, 331–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doglioni, A.; Simeone, V.; Giustolisi, O. The activation of ephemeral streams in karst catchments of semi-arid regions. Catena 2012, 99, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jiang, G.; Yuan, D.; Polk, J.S. Evolution of major environmental geological problems in karst areas of Southwestern China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 2427–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Rose, M.; Fidelibus, C. Water resource management in karstic catchments: The case of the Asso Torrent basin (Southern Italy). Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 75, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dvory, N.Z.; Ronen, A.; Livshitz, Y.; Adar, E.; Kuznetsov, M.; Yakirevich, A. Quantification of Groundwater Recharge from an Ephemeral Stream into a Mountainous Karst Aquifer. Water 2018, 10, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masciopinto, C.; De Giglio, O.; Scrascia, M.; Fortunato, F.; La Rosa, G.; Suffredini, E.; Pazzani, C.; Prato, R.; Montagna, M.T. Human health risk assessment for the occurrence of enteric viruses in drinking water from wells: Role of flood runoff injections. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 666, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, L.T.P.; Velasquez, L.N.M.; Fleming, P.M. Groundwater recharge through the dolines in the semi-arid climate in Minas Gerais State, Brazil. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohrt, J.; Ries, F.; Sauter, M.; Lange, J. Significance of preferential flow at the rock soil interface in a semi-arid karst environment. Catena 2014, 123, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fidelibus, M.D.; Balacco, G.; Gioia, A.; Iacobellis, V.; Spilotro, G. Mass transport triggered by heavy rainfall: The role of endorheic basins and epikarst in a regional karst aquifer. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 394–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royster, D.L. Use of sinkholes for drainage. Transp. Res. Rec. 1984, 978, 18–25. [Google Scholar]
- Dillon, P.; Stuyfz, P.; Grischek, T.; Lluria, M.; Pyne, R.D.; Jain, R.C.; Bear, J.; Schwarz, J.; Wang, W.; Fernez, E.; et al. Sixty years of global progress in managed aquifer recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younger, P.L.; Teutsch, G.; Custodio, E.; Elliot, T.; Manzano, M.; Sauter, M. Assessments of the sensitivity to climate change of flow and natural water quality in four major carbonate aquifers of Europe. Geol. Soc. Spec. Publ. 2002, 193, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Rose, M.; Fidelibus, C.; Martano, P. Assessment of Specific Yield in Karstified Fractured Rock through the Water-Budget Method. Geosciences 2018, 8, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, P.; Maréchal, J.C.; Ladouche, B. Karst flash-flood forecasting in the city of Nîmes (southern France). Eng. Geol. 2013, 164, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delle Rose, M.; Martano, P.; Fidelibus, C. The Recent Floods in the Asso Torrent Basin (Apulia, Italy): An Investigation to Improve the Stormwater Management. Water 2020, 12, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O.; Ljubenkov, I.; Roje-Bonacci, T. Karst flash floods: An example from the Dinaric karst (Croatia). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2006, 6, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trenberth, K.E.; Dai, A.; Rasmussen, R.M.; Parsons, D.B. The Changing Character of Precipitation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2003, 84, 1205–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, L.P.; Soden, B.J. Atmospheric Warming and the Amplification of Precipitation Extremes. Science 2008, 321, 1481–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Im, E.S.; Coppola, E.; Diffenbaugh, N.S.; Gao, X.J.; Mariotti, L.; Shi, Y. Higher Hydroclimatic Intensity with Global Warming. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 5309–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ries, F.; Lange, J.; Schmidt, S.; Puhlmann, H.; Sauter, M. Recharge estimation and soil moisture. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 1439–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanke, J.; Liesch, T.; Goeppert, N.; Klinger, J.; Gassen, N.; Goldscheider, N. Contamination risk and drinking water protection for a large-scale managed aquifer recharge site in a semi-arid karst region, Jordan. Hydrogeol. J. 2017, 25, 1795–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebreen, H.; Wohnlich, S.; Wisotzky, F.; Banning, A.; Niedermayr, A.; Ghanem, M. Recharge estimation in semi-arid karst catchments: Central West Bank, Palestine. Grundwasser 2018, 23, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, Z. Climate change and water storage variability over an arid endorheic region. J. Hydrol. 2015, 529, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Song, C.; Reager, J.T.; Yao, F.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Sheng, Y.; MacDonald, G.M.; Brun, F.; Schmied, H.M.; Marston, R.A.; et al. Recent global decline in endorheic basin water storages. Nature Geosci. 2018, 11, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapiyev, V.; Samarkhanov, K.; Tulegenova, N.; Jumassultanova, S.; Verhoef, A.; Saidaliyeva, Z.; Umirov, N.; Sagintayev, Z.; Namazbayeva, A. Estimation of water storage changes in small endorheic lakes in Northern Kazakhstan. J. Arid. Environ. 2019, 160, 42–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Pokhrel, Y.; Hugonnet, R.; Wada, Y.; Cáceres, D.; Müller, S.H.; Song, C.; Berthier, E.; et al. Divergent causes of terrestrial water storage decline between drylands and humid regions globally. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL095035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Ji, M.; Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Ran, J. Global semi-arid climate change over last 60 years. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 46, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doll, P.; Fiedler, K. Global-scale modeling of groundwater recharge. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 863–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Raffaele, F.; Coppola, E. The response of precipitation characteristics to global warming for climate projections. Earth Syst. Dynam. 2019, 10, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobellis, V.; Castorani, A.; Di Santo, A.R.; Gioia, A. Rationale for flood prediction in karst endorheic areas. J. Arid. Environ. 2015, 112, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butscher, C.; Huggenberger, P. Modeling the temporal variability of karst groundwater vulnerability with implications for climate change. Environ Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1665–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Goldscheider, N.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J.; Weiler, M. Karst water resources in a changing world: Review of hydrological modeling approaches. Rev. Geophys. 2014, 52, 218–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaratne, N. Characteristics of point recharge in karst aquifers. Water 2014, 6, 2782–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Biomed. J. 2009, 339, b2535. [Google Scholar]
- Evaristo, J.; McDonnell, J.J. A role for meta-analysis in hydrology. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3588–3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengist, W.; Soromessa, T.; Legese, G. Method for conducting systematic literature review and meta-analysis for environmental science research. MethodsX 2020, 7, 100777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Biomed. J. 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Rollins, J.; Yan, E. Web of Science use in published research and review papers 1997–2017: A selective, dynamic, cross-domain, content-based analysis. Scientometrics 2018, 115, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birkle, C.; Pendlebury, D.A.; Schnell, J.; Adams, J. Web of Science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2020, 1, 363–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, M.; van Eck, N.J.; Waltman, L. Large-scale comparison of bibliographic data sources: Scopus, Web of Science, Dimensions, Crossref, and Microsoft Academic. Quant. Sci. Stud. 2021, 2, 20–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijdi, K.; Bakalowicz, M.; Benali, A.M. Mixed, classical and hydrothermal karstification in a carbonate aquifer Hydrogeological consequences. The case of the Saida aquifer system, Algeria. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2008, 340, 462–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batiot-Guilhe, C.; Seidel, J.L.; Jourde, H.; Hebrard, O.; Bailly-Comte, V. Seasonal variations of CO2 and 222Rn in a mediterranean sinkhole—Spring (Causse d’Aumelas, SE France). Int. J. Speleol. 2007, 36, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, J.C.; Ladouche, B.; Dorfliger, N. Karst flash flooding in a Mediterranean karst, the example of Fontaine de Nîmes. Eng. Geol. 2008, 99, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marechal, J.C.; Ladouche, B.; Dorfliger, N. Analyse hydrogéologique de la contribution de l’eau souterraine à la crue éclair des 6 et 8 septembre 2005 à Nîmes. Houille Blanche 2009, 95, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bailly-Comte, V.; Jourde, H.; Pistre, S. Conceptualization and classification of groundwater–surface water hydrodynamic interactions in karst watersheds: Case of the karst watershed of the Coulazou River (Southern France). J. Hydrol. 2009, 376, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, M. Flood history in the karst environment of Castellana Grotte (Apulia, southern Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2003, 3, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liguori, V.; Manno, G. Environmental hazard and water quality: The River Platani basin. In Environmental Health Risk IV; Brebbia, C.A., Ed.; Wessex Institute of Technology: Southampton, UK, 2007; pp. 147–159. [Google Scholar]
- Apollonio, C.; Delle Rose, M.; Fidelibus, C.; Orlanducci, L.; Spasiano, D. Water management problems in a karst flood-prone endorheic basin. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijatovic, B.F. Catastrophic flood in the Polje of Cetinje in February 1986, a typical example of the environmental impact of karst. Environ. Geol. Water. Sci. 1988, 12, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novel, J.P.; Dimadi, A.; Zervopoulou, A.; Bakalowicz, M. The Aggitis karst system, Eastern Macedonia, Greece: Hydrologic functioning and development of the karst structure. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ljubenkov, I. Multicriteria flood mitigation in the Imotsko-Bekijsko Polje (Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina). J. Water Land Dev. 2015, 26, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasic, C.; Vasic, L. Flood protection and water utilization of karst poljes: Example of Gatačko Polje, Eastern Herzegovina. Environ. Earth Sci. 2020, 79, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demiroglu, M. Classification of karst springs for flash-flood-prone areas in western Turkey. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 16, 1473–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagır, C.; Kurtulus, B.; Razack, M. Hydrodynamic characterization of Mugla Karst Aquifer using correlation and spectral analyses on the rainfall and springs water-level time series. Water 2020, 12, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, M.; Peach, C.; Robins, N.; Hughes, A. Using a distributed recharge model to quantify recharge processes in a semi-arid karst catchment: An example from Wadi Natuf, West Bank. Water 2019, 11, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassery, H.R.; Alijani, F.; Mirzaei, L. Environmental characterization of a karst polje: An example from Izeh polje, southwest Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, S.; de Rooij, G.H.; Michelsen, N.; Rausch, R.; Siebert, C.; Schüth, C.; Al-Saud, M.; Merz, R. Estimating groundwater recharge for an arid karst system using a combined approach of time-lapse camera monitoring and water balance modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 30, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soldo, B.; Mahmoudi Sivand, S.; Afrasiabian, A.; Đurin, B. Effect of Sinkholes on Groundwater Resources in Arid and Semi-Arid Karst Area in Abarkooh, Iran. Environments 2020, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herczeg, A.L.; Leaney, F.W.J.; Stadter, M.F.; Allan, G.L.; Fifield, L.K. Chemical and isotopic indicators of point-source recharge to a karst aquifer, South Australia. J. Hydrol. 1997, 192, 271–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Jiang, G. Problems of Flood and Drought in a Typical Peak Cluster Depression Karst Area (SW China). In Advances in Research in Karst Media; Andreo, B., Carrasco, F., Duran, J.J., LaMoreaux, J.W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Leventeli, Y.; Halihan, T.; Dailey, M.; Hurt, K.; Kellogg, W. Design for an “engineered sinkhole” to improve, recharge and reduce evapotranspiration in an upstream flood control structure. In Sustainable Irrigation Management, Technologies and Policies III; Brebbia, C.A., Ed.; Wessex Institute of Technology: Southampton, UK, 2010; pp. 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, N.A.; Hansen, J.; Springer, A.E.; Valle, C.; Tobin, B.W. Modeling intrinsic vulnerability of complex karst aquifers: Modifying the COP method to account for sinkhole density and fault location. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 2857–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, F.A.; Perrin, J.; Riotte, J.; Gebauer, H.D.; Narayana, A.C.; Ahmed, S. Karstification in the Cuddapah Sedimentary Basin, southern India: Implications for groundwater resources. Acta Carsologica 2011, 40, 457–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorensen, L. A Spatial Analysis Approach to the Global Delineation of Dryland Areas of Relevance to the CBD Programme of Work on Dry and Subhumid Lands, 1st ed.; UNEP-WCMC: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 9–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; McVicar, T.; Yang, D. An Analytical Solution for the Impact of Vegetation Changes on Hydrological Partitioning Within the Budyko Framework. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, R.; Moriyama, T. Recent Trends of Annual Aridity Indices and Classification of Arid Regions with Satellite-Based Aridity Indices. Remote Sens. Earth Sys. Sci. 2019, 2, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogden, A.E. Investigation of sinkhole flooding problems in Knoxville, Tennessee. In Karst Geohazards: Engineering and Environmental Problems in Karst Terrane; Beck, B.F., Ed.; A.A. Balkema: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; pp. 291–296. [Google Scholar]
- Field, M.S. Simulating drainage from a flooded sinkhole. Acta Carsologica 2010, 39, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonacci, O. Karst Hydrology with Special Reference to the Dinaric Karst; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1987; p. 184. [Google Scholar]
- Vías, J.M.; Andreo, B.; Perles, J.M.; Carrasco, F.; Vadillo, I. Proposed method for groundwater vulnerability mapping in carbonate (karstic) aquifers: The COP method. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 912–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horton, R.E. The role of infiltration in the hydrologic cycle. Trans. Am. Geophys. Union. 1933, 14, 446–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallart, F.; Amaxidis, Y.; Botti, P.; Canè, G.; Castillo, V.; Chapman, P.; Froebrich, J.; García-Pintado, J.; Latron, J.; Llorensictja-Csic, P.; et al. Investigating hydrological regimes and processes in a set of catchments with temporary waters in Mediterranean Europe. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwenzi, W.; Nyamadzawo, G. Hydrological Impacts of Urbanization and Urban Roof Water Harvesting in Water-limited Catchments: A Review. Environ. Process. 2014, 1, 573–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunkel, A.; Shadeed, S.; Hartmann, A.; Wagener, T.; Lange, J. Model signatures and aridity indices enhance the accuracy of water balance estimations in a data-scarce Eastern Mediterranean catchment. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2015, 4, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, D.; Shen, Y.; Sun, A.; Hong, Y.; Longuevergne, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Chen, L. Drought and flood monitoring for a large karst plateau in Southwest China using extended GRACE data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 155, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, H.; Feng, J.; Lu, T.; Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Shi, M. Dynamic evolution of karst water levels and its controlling and influencing factors in Northern China: A case study in the Dawu water source area. Carbonates Evaporites 2020, 35, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthelin, R.; Rinderer, M.; Andreo, B.; Baker, A.; Kilian, D.; Leonhardt, G.; Lotz, A.; Lichtenwoehrer, K.; Mudarra, M.; Padilla, I.Y.; et al. A soil moisture monitoring network to characterize karstic recharge and evapotranspiration at five representative sites across the globe. Geosci. Instrum. Method. Data Syst. 2020, 9, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Flores, G.; Gutiérrez-Aguirre, M.A.; Cervantes-Martínez, A.; Marín-Celestino, A.E. Historical analysis of a karst aquifer: Recharge, water extraction, and consumption dynamics on a tourist island (Cozumel, Mexico). Int. J. Limnol. 2021, 57, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucon, T.N.; Costa, A.T.; Galvao, P.; Leite, M.G.P.; Madeira, T.; Nogueira, L.B. Recharge sources and hydraulic communication of karst aquifer, São Miguel watershed, MG, Brazil. J. S. Am. Earth Sci. 2020, 100, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boretti, A.; Rosa, L. Reassessing the projections of the World Water Development Report. NPJ Clean Water 2019, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.; Hasnain, S. Factors affecting the costs of managed aquifer recharge schemes. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2018, 4, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, B.G.; Griffin, D.W.; Davis, J.H. Groundwater quality impacts from the land application of treated municipal wastewater in a large karstic spring basin: Chemical and microbiological indicators. Sci. Total. Environ. 2009, 407, 2872–2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daher, W.; Pistre, S.; Kneppers, A.; Bakalowicz, M.; Najem, W. Karst and artificial recharge, theoretical and practical problems: A preliminary approach to artificial recharge assessment. J. Hydrol. 2011, 408, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebbache, S.; Feeny, V.; Poudevigne, I.; Alard, D. Turbidity and nitrate transfer in karstic aquifers in rural areas: The Brionne Basin case-study. J. Environ. Manag. 2001, 62, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, N.; Wang, H.Q.; Dupont, J.P.; Rodet, J.; Laignel, B. Assessment of direct transfer and resuspension of particles during turbid floods at a karstic spring. J. Hydrol. 2003, 275, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberic, P. River backflooding into a karst resurgence (Loiret, France). J. Hydrol. 2004, 286, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celico, F.; Musilli, I.; Naclerio, G. The impacts of pasture- and manure-spreading on microbial groundwater quality in carbonate aquifers. Envirom. Geol. 2004, 46, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aquilina, L.; Ladouche, B.; Dorfliger, N. Water storage and transfer in the epikarst of karstic systems during high flow periods. J. Hydrol. 2006, 327, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massei, N.; Dupont, J.P.; Mahler, B.J.; Laignel, B.; Fournier, M.; Valdes, D.; Ogier, S. Investigating transport properties and turbidity dynamics of a karst aquifer using correlation, spectral, and wavelet analyses. J. Hydrol. 2006, 329, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanovic, S. Hydrogeological characteristics of some deep siphonal springs in Serbia and Montenegro karst. Environ. Geol. 2007, 51, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardani, A.; Revil, A.; Santos, F.; Fauchard, C.; Dupont, J.P. Detection of preferential infiltration pathways in sinkholes using joint inversion of self-potential and EM-34 conductivity data. Geophys. Prospect. 2007, 55, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, M.; Massei, B.; Mahler, J.; Bakalowicz, M.; Dupont, J.P. Application of multivariate analysis to suspended matter particle size distribution in a karst aquifer. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 2337–2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polemio, M.; Casarano, D.; Limoni, P.P. Karstic aquifer vulnerability assessment methods and results at a test site (Apulia, southern Italy). Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 1461–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, L.; Peyraube, N.; Lastennet, R.; Denis, A.; Sabidussi, J.; Fournier, M.; Viennet, D.; Gon, J.; Villanueva, J.D. Tracing water perturbation using NO3, doc, particles size determination, and bacteria: A method development for karst aquifer water quality hazard assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138512. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).