Abstract
Lake ice models are a vital tool for studying the response of ice-covered lakes to changing climates throughout the world. The Canadian Lake Ice Model (CLIMo) is a one-dimensional freshwater ice cover model that simulates Arctic and sub-Arctic lake ice cover well. Modelling ice cover in temperate regions has presented challenges due to the differences in ice composition between northern and temperate region lake ice. This study presents a comparison of measured and modelled ice regimes, with a focus on refining CLIMo for temperate regions. The study sites include two temperate region lakes (MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake, Central Ontario) and two High Arctic lakes (Resolute Lake and Small Lake, Nunavut) where climate and ice cover information have been recorded over three seasons. The ice cover simulations were validated with a combination of time lapse imagery, field measurements of snow depth, snow density, ice thickness and albedo data, and historical ice records from the Canadian Ice Database (for Resolute Lake). Simulations of High Arctic lake ice cover show good agreement with previous studies for ice-on and ice-off dates (MAE 6 to 8 days). Unadjusted simulations for the temperate region lakes show good ice-on timing, but an under-representation of ice thickness, and earlier complete ice-off timing (~3 to 5 weeks). Field measurements were used to adjust the albedo values used in CLIMo, which resulted in improvements to both simulated ice thickness (~3 cm MAE compared to manual measurements), and ice-off timing, within 0 to 7 days (2 days MAE) of observations. These findings suggest regionally specific measurements of albedo can improve the accuracy of lake ice simulations, which further our knowledge of the response of temperate and High Arctic lake ice regimes to climate conditions.
Keywords:
lake ice; modelling; albedo; snow; arctic; temperate region; ice thickness; observation data 1. Introduction
Globally, the greatest spatial distribution of freshwater lakes is between 45 and 75° N [1] with most of these lakes experiencing some level of ice cover throughout the year. Reported trends in lake ice cover have shown shifts towards shorter ice-covered seasons, with the rates of change depending on the time span examined, e.g., [2]. Long-term trends of Northern Hemisphere lakes project the number of lakes transitioning from annual ice cover to intermittent winter ice cover will increase exponentially with climate warming [3]. Regional water and energy balances will likely experience changes as a result of this decreasing ice cover; through changes to the exchange of moisture and gas fluxes (e.g., increased evaporation), as well as to ecosystems (e.g., earlier lake stratification, warmer summer surface temperatures and increased aquatic productivity) and socio-economic changes (e.g., reduced winter recreation and transportation) [2,4,5,6,7,8,9]. These changes and their impacts vary spatially, due to latitudinal differences in ice types and how they respond to climate. With northern latitudes warming at a more rapid rate than southern latitudes [10], the latitudinal response of lake ice becomes even more pertinent.
The dominant controls on ice phenology (ice-off, ice-on, duration) are lake size, air temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and the radiation balance [4,11]. After formation, ice thickens as a result of conductive heat loss from the warmer water below through the ice/snow cover to the atmosphere, leading to the formation of black ice [11]. On-ice snow accumulation can both modify the thickness through insulating properties and contribute to thickening from flooded snow or slush refreezing into the ice sheet as white ice [4,11]. Additionally, in temperate regions ice thickening through white ice growth has been observed to occur through multiple mid-winter freeze/thaw events [12]. The albedo of the ice and any overlying snow plays a large role in the ice-off process, as ice melt initiation is affected by albedo, and where the main drivers of ice melt are solar radiation and air temperature. Albedo is a surface property describing the ratio of outgoing to incoming solar radiation [13]. Lake ice albedo is primarily affected by snow cover, ice type (e.g., black ice and white ice) and ice thickness but can also be affected by the presence of impurities, cloud cover, air temperature and solar zenith angle [11]. The light scattering properties of white ice are different than black ice due to the tightly packed air bubbles, which result in a higher albedo [11,14]. Both snow cover and white ice delay ice-off due to the higher albedo compared to the lower albedo of black ice [11,14], however, when snow-free conditions exist on the ice or moisture is present in the white ice, albedo begins to decrease, and melt occurs. Once snow and ice melt occur, albedo values drop to between 0.7 and 0.25, which results in more energy available for melt and creates a positive feedback loop that accelerates the melt process [11,15,16,17,18]. Studies of lake ice albedo indicate that values can range from 0.10 to 0.85 [15,16,17,18,19,20]. In addition, the albedo measured for snow on ice covered lakes ranges between 0.5 and 0.95 [14,17,18,19]. These studies indicate that lake ice (and overlying snow) albedo values vary temporally and spatially which makes the parameterization of albedo in modelling applications difficult [11,21], highlighting the need to better understand and improve the representation of albedo for ice regimes within lake ice models.
Physically based models can be used to simulate ice phenology, thickness and to examine the sensitivity of these factors to climate change, e.g., [22,23,24]. A primary advantage to modelling over other techniques for examining lake ice, such as using satellite-based data, is the ability to simulate the ice thickness; a component not yet readily detectable from space-based imagery. Satellite-based imagery, particularly from the active microwave bands, is extremely useful for examining ice phenology, and when cloud-free conditions occur, visible imagery also plays an important role in ice phenology detection and modelling validation. Since spatio-temporal resolution and data availability limitations can present challenges for obtaining the level of detail needed for examining ice cover changes on smaller lakes, physically based models provide an excellent alternative, either on their own or in combination with space-based data, e.g., [14,20,22]. The Canadian Lake Ice Model (CLIMo) is a well-used, well-tested, physically based model, that has provided many useful simulations of Arctic and sub-Arctic lake ice cover using local weather station data, e.g., [13,22,25,26,27,28,29]. This model uses a thermodynamic approach to determine ice formation, growth and decay, where these processes are controlled by an energy surplus or deficit [4]. However, CLIMo differs from other thermodynamic models through its parameterization of snow conductivity and surface albedo [13]. The albedo parameterization in CLIMo is dependent on surface type (ice, snow, or open water), whether the surface temperature is above or below freezing, and the thickness of the ice [13]. Currently, albedo is parametrized following Maykut [30] for cold conditions and uses observation data from High Arctic lake ice [15] for melting conditions. These observations were obtained from Small Lake, NU, where the typical ice conditions exceed two metres with a very small amount (<1– 7%, [31]) of white ice formed at the top of the ice column (white ice was measured at <4% of the total ice thickness [12,31]). In the temperate regions, however, typical ice conditions do not exceed 1 m and have a much higher amount of white ice. For example, in the Haliburton region of Central Ontario, maximum white ice percentages ranged from 25 to 73% of the ice column between 2016 and 2019 ([12], updated to 2019). Initial model simulations for this region using CLIMo found that ice-off dates were too early, as the large amount of white ice was not accounted for [32], indicating that the current parameterization of surface albedo in CLIMo is not suitable for temperate lake ice. Recent modelling work for temperate region lakes has focused primarily on climate change, evaporation and lake temperature, e.g., [3,9,33,34], while few studies have focused on simulating ice phenology and thickness on small or medium sized lakes, e.g., [34,35,36]. This research compares ice cover simulations from High Arctic and temperate region lakes to illustrate the latitudinal differences in lake ice properties and presents refinements to CLIMo to better simulate ice thickness and ice-off timing in the temperate region. The specific objectives of this research were to (1) show the effectiveness of CLIMo for simulating the ice cover regimes of a small (<1 km2) and a medium (1–100 km2) sized High Arctic lakes and (2) investigate and improve the ability of CLIMo to simulate temperate region ice covers using two medium sized lakes in Central Ontario. Understanding the latitudinal differences in lake ice processes, types, and the interactions of climate and lake ice is important for improving climate and lake ice modelling accuracy—which is an essential precursor to providing more robust modelling results of predicted changes.
2. Study Areas
2.1. Study Area: High Arctic
Small Lake and Resolute Lake (Figure 1a–c) are located on Cornwallis Island in Nunavut, Canada. Small Lake (74°45′ N, 95°05′ W) has a surface area of 0.2 km2 [37] and a maximum depth of ~10 m and mean depth of 4 m [15]. Ice-off and ice-on, recorded by digital cameras from 2016–2018, occurred late July to early August and early September to late September, respectively. Maximum ice thickness in 1980 and 1981 was 2.42 m ± 0.1 m and 2.37 m ± 0.1 m, respectively [31] and in May 2016 it was measured at ~1.88 m with the ice type being composed of almost entirely black ice [38].
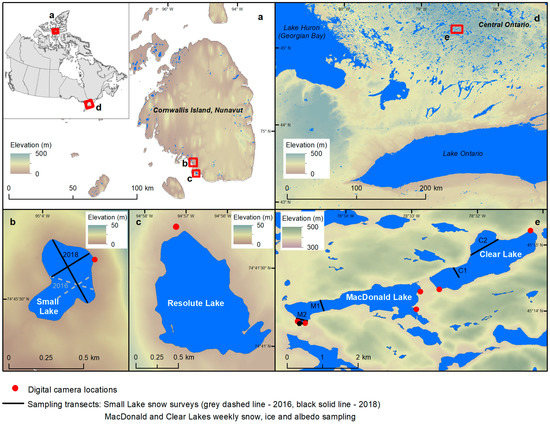
Figure 1.
Location of field sites in Canada: High Arctic field sites (a) with zoom in (b) Small Lake and (c) Resolute Lake, Cornwallis Island, Nunavut; temperate field sites (d) with zoom in (e) MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake, Ontario. MacDonald Lake Automated Weather Station noted with Black circle at M2; Shallow Water Ice Profiler (SWIP) is also located at M2. Base map and lake boundaries © [44] and Canadian digital elevation model © [45].
Resolute Lake (74°43′ N, 94°57′ W) has a surface area of 1.27 km2 and a maximum depth of 22.5 m [39] (mean depth not available, assumed to be ~10 m). Historical ice date records between 1961 and 1986 for Resolute Lake are recorded in the Canadian Ice Database (CID) [40], where ice-off and ice-on occurred late July to late August and early September to early October, respectively. Mean maximum ice thickness measured in June between 1970 and 1982 was ~2.13 m [40]. Recently, thickness was measured on May 19, 2019 and ranged from 2.1 to 2.4 m (data collected by Resolute community members).
The location of the Resolute Bay weather station (74°43′ N, 94°58′ W) is ~4.9 km south-east of Small Lake and ~3 km north of Resolute Lake. The mean climatology (1981–2010) [41] indicates subfreezing temperatures last for 9 months (from September to May) with a mean winter temperature of −31.5 °C and a mean summer temperature of 2.3 °C. Mean snowfall is 111.2 cm; with a mean end of May snow depth of 17 cm [41] (used to represent end-of-season snow). However, the representativeness of weather station snowfall to snow accumulation in High Arctic basins has been shown to be under-represented by 130–300% [42,43]. End of season snow surveys on Small Lake (Table 1) completed 22 May 2016 and 16 May 2018 measured mean snow depth on the lake at 17 cm and 11 cm, respectively. In 1980 and 1981, snow surveys were completed throughout June, with the central part of the lake mean snow depth measuring 0.1 m or less and the mean snow depth at edges of the lake measuring 1.5 m or less [31].

Table 1.
End of season snow survey mean (standard deviation; SD) of snow depth (cm) and density (kg m3) for Small Lake, NU.
2.2. Study Area: Temperate
The temperate study lakes, MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake, are located within the Haliburton Forest and Wild Life Reserve Ltd. (45.12° N, 78.07° W) in Central Ontario, Canada (Figure 1d,e). Haliburton County is located at the southern end of the Precambrian shield, in the Ontario Shield ecoregion, and is defined by a temperate climate and dominated by mixed and deciduous forests [46,47]. MacDonald Lake has a surface area of 1.56 km2 and a maximum depth of 39.6 m (mean depth 12.2 m) while the surface area of Clear Lake is 1.8 km2 with a maximum depth of 42.7 m (mean depth 15.2 m) [48].
The mean climatology records (1981–2010) [37] from the nearby Town of Haliburton, Ontario (45.03° N, 78.53° W; 22 km south of the study lakes) show sub-freezing temperatures last for 4 months (December to March) with a mean winter temperature of −5.0 °C and a mean summer temperature of 16.6 °C. The mean annual snowfall is 279.6 cm with a mean end of March snow depth of 16 cm [41]. On-ice mean snow depth and density for MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake were collected over three field seasons (2016, 2017, and 2018; Table 2) and showed considerable variability throughout all three field seasons. The mean snow depth on the lakes in 2016 was 14 cm; in 2017 it was 12 cm; and in 2018 it was 7 cm. The range of snow densities (Table 2) provided from the Canadian Snow CD [49] indicate mean snow densities of 259 kg m−3. In comparison, mean field snow densities were 206 kg m−3, 337 kg m−3, 328 kg m−3 in 2016, 2017 and 2018, respectively.

Table 2.
Average bi-weekly snow density (kg m3) from the Canadian Snow CD and weekly average (standard deviation; SD) of on-ice sampled snow depth (cm) and snow density (kg m−3) for 2015–2016, 2016–2017, and 2017–2018 for MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake.
3. Data and Methodology
3.1. Terminology
Assessing and comparing simulations to observations of ice cover can be challenging due to the differing definitions used, this paper will follow definitions determined by [22]. The date when simulations form a permanent/complete ice cover for the season is defined as simulated ice-on, with the first day of simulated open water defined as simulated ice-off. The observed ice-on/off date is defined as the first day when ice/open water is detected above the ice thickness sensor. The camera imagery is subjective since visual assessment and interpretation of ice conditions are impacted by light availability and weather conditions; however, images can be used to identify the freeze-up period, which is defined as the time between when the ice is initially visible in the camera view (freeze-onset) until the formation of solid ice cover (complete ice-on). Surface ice decay can also be identified with camera imagery and is defined by the time when any ice in the camera view is visibly beginning to melt (snow free, wet/slushy surface). The break-up period is defined as the date between the first appearance of open water and when water is completely free of ice (complete ice-off). Dates extracted from the CID represent complete freeze over (ice-on) and when the water body is clear of ice (ice-off) [40].
3.2. Data Collection
3.2.1. High Arctic
Intense data collection is not logistically possible for the High Arctic lakes, however in situ measurements of snow depth and density were measured through end-of-season snow survey’s [50] on Small Lake for 20 May 2016, and 16 May 2018. Sampling transects ranged from 200 to 700 m, snow depth was measured every 10 m along each transect, with density measurements taken at the start, mid-point and end of each transect. To monitor ice conditions and snow redistribution −40 °C-rated outdoor digital trail cameras (RECONYX PC800 HyperFire Covert) were installed at each lake. One camera was installed at Small Lake prior to ice-off in May 2016 and a second was installed prior to ice-on at Resolute Lake (Figure 1) in August 2017. The cameras are in locations selected to maximize field of view of the lake and to allow for accessibility; they capture daily imagery at mid-day to maximize daylight conditions later in the season. No camera imagery was collected for ice-off at Small Lake in 2017 due to a camera power issue. To extend the ice cover record for Resolute Lake, available ice-on and ice-off dates were obtained from the CID from 1960 to 1985. Finally, the mean snow density for May, extracted from the Canadian Snow Database CD [49] (which contains gridded snow density normals between 1960 and 1990), for the region is 303 kg m−3, while the measured on-ice snow density from the snow surveys was 357 kg m−3 in 2016 and 308 kg m−3 in 2018; slightly higher than on land, as on-ice snow densities are typically higher by ~20% [51]. In addition, 1 km Moderate Resolution Imagining Spectroradiometer (MODIS) corrected reflectance (true colour) images from Worldview were used to visually estimate ice-on and ice-off dates between 2000 and 2017 when no observed ice dates are available. Detailed albedo values for the ice on this lake were measured by [15] and these values form the basis of the melt parameterization currently used in CLIMo [13].
3.2.2. Temperate
Building from the [12] study, in situ measurements of ice thickness, ice composition, snow depth, and snow density were recorded weekly when ice conditions permitted for the 2015–2016, 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 field seasons. Four sampling transects (Figure 1) ranging from 50–400 m were established, with two on each study lake; snow depth and snow density were measured following the same protocol as on Small Lake. In addition, manual ice thickness measurements were taken along each transect noting the total ice thickness, and the thickness of black and white ice layers. Ice thickness and layer composition were averaged weekly for each study lake.
Six RECONYX cameras similar to the ones used in the High Arctic were installed on trees around the study lakes. Placement of the cameras was selected based on road accessibility and for maximizing the field of view for capturing the snow and ice conditions of the centres and bays of the lakes on an hourly basis (Figure 1). Continuous ice evolution was monitored using a Shallow Ice Water Profiler (SWIP, ASL Environmental) for the 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 study years, deployed at a depth of ~3 m in MacDonald Lake, within the field of view of the on-shore AWS for data validation purposes. The SWIP was monitoring the ice thickness every 2 min and the data were extracted and processed following the similar protocol outlined previously by others, e.g., [12,22,52,53].
In addition to the snow and ice data collected for the temperate lakes, the surface albedo of the lake ice and on-ice snow were measured on each snow transect (start, middle and end) using a hand-held Solarmeter® Model 10.0 Global Power Meter and averaged for each week (end of the 2018 and throughout the 2019 field campaigns). To obtain the ice albedo, the snow was cleared away from the surface of the ice. During two separate site visits, the ice was snow-free which allowed us to obtain ice surface albedo only (Figure 2; 23 February 2018 and 2 March 2018). In addition to the hand-held measurements during the 2019 field campaign, a Kipp and Zonen CNR4 net radiometer (measuring downward and upward facing solar radiation in the 0.3 to 2.8 µm range every 60 s), was mounted and levelled, extended from a dock 1.2 m above the snow/ice surface on MacDonald Lake (within the 1–2 m above-surface range indicated as ideal by [54]) for a full season of 8 dates. Albedo values were calculated by dividing the total reflected shortwave radiation by the total incoming shortwave radiation during daylight hours.
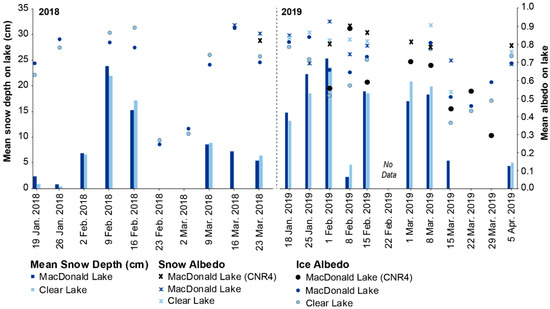
Figure 2.
Point measurements of lake ice albedo (2018 and 2019), on-ice snow albedo (2019), ice and snow albedo from the CNR4 (2019) and mean transect snow depths (2018 and 2019) from MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake.
3.3. Lake Ice Model—For High Latitudes
This section briefly reviews CLIMo as it was originally created for high latitude lakes. A full description of CLIMo can be found in [13], while this abridged description follows our own papers [14,22,27,55]. CLIMo has been adapted from the one-dimensional thermodynamic sea-ice model of [56] which is based on the one-dimensional unsteady heat conduction equation, with penetrating solar radiation, of [57]:
where [13] define the following variables as: (kg m−3) is the density, the specific heat capacity is (J kg −1 K−1), T (K) is the temperature within the ice or snow, t is time (s), z is depth measured positive downward (m) from the upper surface, k (Wm−1 K−1) is the thermal conductivity, Fsw (Wm−2) is the downwelling shortwave radiative energy flux calculated following [58], is the fraction of shortwave flux that penetrates the surface (equal to 0.17 if snow depth is ≤0.01 m and equal to 0 if snow depth >0.1 m), α is the surface albedo and K is the bulk extinction coefficient for penetrating shortwave radiation (m−1).
To determine the net heat flux absorbed at the surface, the surface energy budget is calculated using:
where F0 (Wm−2) is the net downward heat flux absorbed at the surface, ε is the surface emissivity, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant (5.67 × 10−8 Wm −2 K−4), Flw (Wm−2) is the downwelling longwave radiative flux calculated using the formula of [59], Flat (Wm−2) is the latent heat flux and Fsens (Wm−2) is the sensible heat flux both calculated based on [13,60]. A fixed value mixing depth (set for each lake) is used in CLIMo to represent the mixed layer of a lake for an annual cycle, where ice melts completely in the summer [13]. In CLIMo, when ice is present, the mixing depth layer is fixed at the freezing point, otherwise when ice is absent, the mixing layer temperature is computed from the surface energy budget and represents heat storage in the lake [13]. CLIMo does not require site specific calibration as it is driven by the local climate data.
An important component of the surface energy balance calculation used in CLIMo is albedo and it is used to determine ice melt and ice-off dates. As discussed earlier, the surface albedo parameterization in CLIMo considers surface type, surface temperature and ice thickness. The surface albedo parameterization is summarized by [13,14] as:
where α is surface albedo, αow is albedo of open water (0.05), αs is the albedo of snow, αmi is the albedo of melting ice (0.55), αi is the ice albedo, h is the total thickness of the snow and ice layers (kept at five layers for these simulations), hi is ice thickness (m), hmin is minimum ice thickness below which open water is assumed (0.001 m), hs is snow thickness (m), T(0,t) is the temperature within ice or snow at the vertical coordinate 0 at the time t (s), Tm is melting temperature at the surface (273.15 K); c1 (0.1 m), c2 (0.44 m−0.28) and c3 (0.075 m−2) are derived from various field observations of ice thickness and radiative flux, which were documented by [30] for cold ice. Equation (3) uses ice and snow thickness to determine the albedo value, whereas Equations (4) and (5) determine the value of both snow and ice albedo. The strong albedo dependence of young ice on thickness is approximated in Equation (3) and this has been derived from the observations of [61] on the radiation balance over sea ice. The melting ice parameterization is based on Arctic lake ice observations from [15] (at Small Lake), which has a larger proportion of black ice and, therefore, a lower albedo than what would be found at the white ice dominated temperate lakes [12]. A schematic of the simulation process and lake ice model can be found in Figure 3.
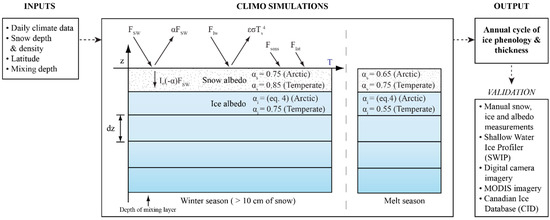
Figure 3.
Illustration of the simulation process outlining the required input data to drive the model, schematic of CLIMo (modified from [13]) during the winter and melt season, including the albedo modifications for CLIMo-Temperate, and the output/validation data (Arctic: CID, digital camera and MODIS imagery; Temperate: manual measurements, SWIP and camera imagery). The mottled layer represents snow, while the blue shaded layers represent ice. The surface energy budget is depicted by the arrows along the top of the winter season (applies to the melt season as well). See Equations (1) through (5). for the explanation of each parameter.
The simulations for Resolute Lake were run from 1958 to 2018 to match the ice record length from the CID (1958–1990) and the digital camera record (2017–2018), whereas the simulations for Small Lake were run from 2016 to 2018 to match the record from the digital camera imagery. The model was driven by daily meteorological data obtained from Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) (Table 3). Improved ice cover simulations are produced when snow density values monitored over the season are used over a fixed average value for the cold season and melt [22]. This approach was followed here, with bi-weekly density obtained from the Canadian Snow CD [49]. The May end-of-season mean on-ice snow density measured May 2016 and 2018 at Small Lake (307 kg m−3) is similar to the late May (15-31 May) value in the Canadian Snow CD (303 kgm−3), which lends confidence to using the historical snow density values for the entire simulation period. Snow redistribution is prominent for Arctic lakes, with highly variable snow depths common across the lake surface, typically with less snow on-ice than is measured on land at local weather stations [42,43,62]. Comparing the end-of-season snow depths measured at the Resolute weather station to Small Lake in 2016 and 2018 on the same days shows that only 65% and 40% of the station snow depth was measured on the ice. Both snow surveys had mean snow depths below the mean annual snow depth of 21 cm with the on-ice snow depths in May 2016 and May 2018 having standard deviations of 11.8 cm and 21.5 cm (respectively); suggesting large snow depth variations across the lake. To represent snow redistribution throughout the season two snow accumulation scenarios were used: 50%, to represent the average amount of snow cover on the ice (and align with previous research for these lakes [27]), and 0% to represent the maximum redistribution possible.

Table 3.
Data description for meteorological and snow data used for both study locations. Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) data mainly used for the High Arctic sites and an on-shore Automatic Weather Station (AWS) primarily used for the temperate sites.
3.4. Lake Ice Model—For Temperate Latitudes
This section reviews modifications to CLIMo to better represent the temperate ice cover (with the modified model referred to as CLIMo-Temperate from here on). To achieve this, the albedo values in Equations (4) and (5), based on Small Lake in Resolute, were replaced with measured on-lake snow and ice albedo values from the 2017–2018 and 2018–2019 field seasons from Central Ontario. Pre-melt ice albedo was determined January–March 2019 (excluding 1 February and 8 February due to rain events), where the albedo ranged from 0.71 to 0.84 (Figure 2). Pre-melt ice albedo was set to a constant value of 0.75 (average value) in CLIMo-Temperate, in lieu of non-melt in Equation (4), as testing showed the measured albedo of the temperate region white ice was much higher than the existing parameterization accounted for (Figure 4: CLIMo, short dashed light blue line; Field data, light blue circles). For example, using a range of 5–70 cm ice thickness returns albedos in the range of only ~0.3–0.5 with the existing parameterization for snow-free ice. During the melt period identified by [16] for a temperate lake in Minnesota USA, including the days with fresh snowfalls, the average melt albedo was ~0.5 to 0.6, which is a similar range to our record during the melt season, where our average albedo was 0.56 in 2019 under a mix of melting and snow days (8, 15, 22, 29 March and 5 April, after this point we could not sample on the ice). As the melt parameterization in CLIMo is based on black ice, simulations were run using a fixed albedo of 0.56 in lieu of the melting ice albedo in Equation (4) to represent our ice cover. The existing maximum melt albedo in CLIMo is 0.55 and simulations using our melt albedo value of 0.56 yielded virtually the same simulation results as using the existing maximum melt albedo of 0.55 (same thickness and ice-off timing). Note: the melt season albedo is not the same as the snow-free ice albedo when air temperature is above 0 °C as shown in Figure 4 (αice: snow-free, TA > 0) as the temperature-based categorization in Figure 4 does not capture surface conditions or snowfalls during the melt season. Since the results were similar using 0.55 vs. 0.56, this research kept the existing value of 0.55 in CLIMo-Temperate as our field data consist of only five records; more detailed work should be conducted on melt season albedo in temperate latitudes to build a larger sample size.
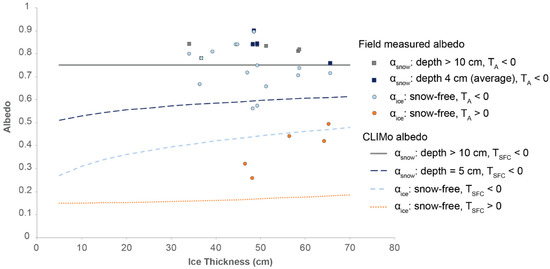
Figure 4.
Comparison of albedo values used in CLIMo and temperate region field data. Field data are separated by air temperature (TA) for visualization, while CLIMo uses surface temperature (TSFC) for the determination of melt/non-melt conditions.
In addition, pre-melt snow albedo in Equation (5) was also adjusted to better capture the influence of more frequent fresh snowfalls that occur in temperate regions than in the Arctic (fresh snow was present during most site visits each field season). When snow accumulation on the ice is thicker than 10 cm, CLIMo uses 0.75 as the snow albedo (Figure 4: solid grey line), this was increased to 0.85 in CLIMo-Temperate (Figure 4: grey squares) based on snow conditions. Average snow albedo was determined from the 2019 field season between January and March 2019 (excluding mid and late March due to substantial slushing on the lakes). Multiple snowfalls occurred through the season, with fresh snow (within 1–3 days) on the ice most weeks. The average snow albedo was 0.82 (ranging from 0.69 to 0.92) and the effects of using the field-based value on the ice simulations were investigated by altering the albedo by ± 0.03, half of the standard deviation. Since the field sampling ceased before the snow and ice season was done, several late season fresh snowfalls were not captured in our data set. Hence, an increase of 1 standard deviation (0.85) yielded better ice-off dates through sensitivity testing.
For snow covers less than 10 cm CLIMo reduces the albedo as in Equation (3) (Figure 4: long dashed dark blue line, 5 cm example). Our field data for shallow snow on the ice suggest the albedo remains as high as deeper snow (Figure 4: blue squares, average 0.83), however our data set only contains four values with snow thinner than 10 cm. We did not investigate altering the melting snow albedo beyond the existing parametrization in CLIMo (set deduction of 0.1 from the non-melt albedo), as only cold snow or slush were present on the ice during the sampling days. Similar to the melting ice albedo, further investigation into the albedo of melting on-ice snow in temperate regions should also be explored as a future research direction.
The model simulations for MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake were driven by daily onshore meteorological data (Table 3) from an AWS, located at the southwestern end of MacDonald Lake (Figure 1d). Cloud cover was obtained for 2015 to 2018 from 1 km MODIS satellite imagery (MOD08_D3: daily mean cloud fraction) as no nearby ECCC stations collect cloud cover information. Snow density was represented by the actual snow conditions on site. While on-lake snow density is typically denser than that measured on land [49], the Canadian Snow CD [49] density values were not representative of current on-lake snow processes (Table 2), so field-measured densities were used in the simulations. Snow redistribution across the lake surface was accounted for by the snow cover scenarios for both MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake, which were simulated by determining the mean snow redistribution percentage (the difference between snow accumulation on shore and the measured on-lake snow depth). The scenarios used for 2015–2016, 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 are 47%, 19%, and 100%, respectively. Additionally, to be able to validate the simulated ice thickness from CLIMo with the SWIP, the mixing depth was set to 3 m for MacDonald Lake and 4 m for Clear Lake (as it is a slightly larger and deeper lake).
3.5. Model Performance
For datasets with more than 20 records, model performance was measured using the Index of Agreement (Ia) in the R package ‘HydroGOF’ (Ia; standardized measure of the degree of model prediction error which varies between 0 and 1, where 1 indicates perfect agreement [63,64]), and statistical errors were measured using Mean Bias Error (MBE; determines the systematic errors that occur and identifies if the values are being over- or under-estimated) and Mean Absolute Error (MAE; an absolute measure of the average magnitude of errors, with 0 indicating no error) in the R package ‘tdr’ [65]. For smaller datasets, only statistical errors could be assessed using MAE.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Model Simulations—High Arctic
Simulations for ice-on at Small Lake correctly captured the observed first presence of ice for 2016 (12 September 2016) and was within 1 day of the observed ice for 2017 (8 September 2017; Figure 5, Table 4 and Table 5). The initial ice cover that formed was subsequently broken-up by wave action (visible in the camera imagery), resulting in the final ice-on date occurring 14 days later in 2016 and 4 days later in 2017. High wind speeds are often recorded in Resolute. CLIMo simulations return thermodynamic ice formation dates, hence the wind driven break-up events in this region were not captured (wind speed is used for the bulk formulae in the surface energy budget determination).
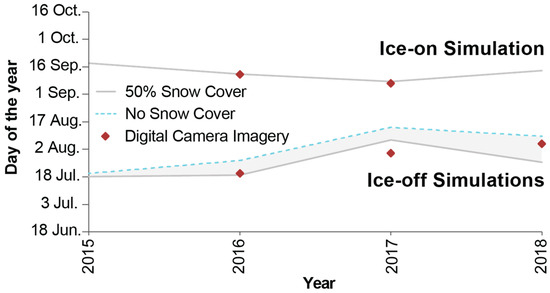
Figure 5.
Simulated ice-on and ice-off dates between 2015 and 2018 for Small Lake, NU compared with the observed ice-on and ice-off dates from the digital camera imagery 2016–2018.

Table 4.
Comparison between simulated complete ice-on and ice-off dates and those observed between 2016 and 2018.

Table 5.
Validation (Mean Absolute Error; MAE) results of simulated ice-on and ice-off dates compared to the first observed complete ice cover date and ice-off date from the digital camera at Small Lake, NU between 2016 and 2018.
Ice-off simulations are heavily dependent on snow cover and a range of dates are framed by the two simulations. Simulations for 2016 showed ice-off on 19 and 27 July for 50% snow and no snow respectively, with observations indicating ice free conditions by 21 July. Ice-off was simulated slightly later than observations in 2017, 8 and 15 August, with observed ice-free conditions by 1 August. The 2018 ice-off simulations indicated ice-free on 27 July and 10 August, with the observed ice-free conditions occurring 6 August. Open water can be observed in the camera imagery near the lake edges in mid-June as snowmelt runoff pools on the ice at the shore, forming a moat, and initiating near-shore melt. However, large floating ice pans can persist until late July or early August; on Small Lake the floating ice pans melted, and open water conditions coincide well with simulated ice-off. For the three ice-off seasons simulated, the average error was 6 days (50% snow cover) and 8 days (no snow cover).
Resolute Lake (Figure 6) also shows good agreement between observed and simulated complete ice-on dates (Table 6), with an Ia of 0.65 for 50% snow cover and 0.79 for no snow, a MBE of -3 and -4 days, respectively, which indicates a slight underprediction (earlier complete ice-on), and a MAE of 6 days for both snow cover simulations. Overall, the observed complete ice-on dates from the CID are modelled within 0 to 17 days of the observed complete ice-on dates, 0 to 7 days of the estimated MODIS imagery, and the camera imagery from 2017–2018 depicts complete ice-on within in 2 to 3 days of the simulated complete freeze-over. The MODIS imagery dates tend to slightly overestimate ice-on due to extensive cloud cover which obscures the ice processes, but the annual variability is in line with the model simulations.
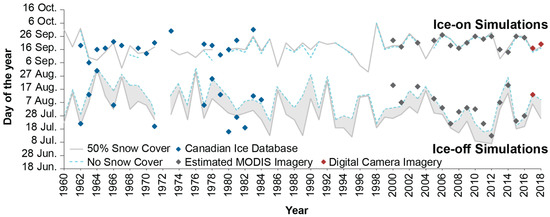
Figure 6.
Comparison between simulated ice-on and ice-off dates and those observed from the CID (1961–1986) and digital camera (2017–2018) for Resolute Lake, NU. Note, no ice-off (and therefore no ice-on) was simulated for 1972 with either scenario. Estimated ice-on and ice-off dates from MODIS imagery (2000–2018) are added for visual comparison but are not included in subsequent statistics as cloud cover results in substantial uncertainty.

Table 6.
Validation results (Ia = Index of agreement, MAE = mean absolute error, MBE = mean bias error) of simulated complete ice-on and ice-off dates to the observed complete ice-on and ice-off dates from the CID from 1962 to 1994 and the observed date of first complete ice cover and ice-off from the digital camera at Resolute Lake, NU from 2017 to 2018.
The simulated ice-off dates for Resolute Lake using the 50% snow cover scenario are within 1–15 days of observations and within 26 days for the no snow scenario. The digital camera imagery in 2017 shows matching ice-off dates with the 50% scenario, while the no snow scenario, which would have grown thicker ice with no insulating snow overtop, simulates ice-off 7 days later. The estimated dates from the MODIS imagery are within 0 to 25 days and predominantly later than the simulations, which is not unexpected as extensive cloud cover in the region can persist for consecutive days, obscuring the view, and preventing the exact ice off date from being determined. Despite some years with large differences between the simulations and the observations, the results show a good year-to-year fit with an Ia of 0.75 for 50% snow cover and 0.77 for no snow cover scenarios. The ice-off for the 50% snow cover and no snow cover scenarios indicate an MBE of -2 days and 7 days, respectively, and a MAE of 8 days for both scenarios (Table 6). These results show that the simulations vary between underprediction and overprediction, which is likely linked to annual snow cover variability, and the occasional presence of residual ice pans. Resolute Lake is larger and deeper than Small Lake and can experience floating ice pans that remain later into the summer than on Small Lake, or in some cases persist through the summer and freeze into the new ice that forms in the fall. While ice pans were observed in both 2016 and 2017, records from the CID do not indicate the presence of residual ice pans which could lead to some discrepancy between the recorded ice-off dates and the simulations.
Using an average value of 50% snow cover to represent the long-term snow redistribution aims to represent a suitable amount of snow redistribution over the last 60 years. Using the snow survey data from the two available seasons (Table 1) on Small Lake can highlight the redistribution as evidenced through the large standard deviation recorded, particularly 2018 (11 cm mean, 21.5 cm SD). The range of on-ice snow depths (0–154 cm) indicates snow free in some regions and in other regions depth exceeding 100% of the on-land values in other down-wind (2018 only) and near-shore regions. The uncertainties in the snow conditions of a given year attributed to redistribution are difficult to capture using one snow cover scenario and can result in the range of ice-off dates between snow cover scenarios.
Overall, the results of the simulations of ice-on and ice-off for both lakes, show agreement with previous studies from high latitude lakes where these studies simulated ice-on from 0 to 15 days and 1 to 10 days for ice-off, with the range affected by the snow cover scenarios [13,25,27,66]. Thickness simulations are not presented for these lakes as validation data is not available; the CID does contain some maximum thickness values; however, the database does not indicate the date of when the measurement was taken.
4.2. Model Simulations—Temperate
Ice thickness and phenology were initially simulated using the unadjusted CLIMo for MacDonald Lake and Clear Lake using the snow depth differences (percentage of on-shore compared to on-lake snow depth) determined for each study year (Table 2) and the measured snow density (field density). The simulations are compared to observations for each year at two transects on each lake and provided in Figure 7 (red line). Ice-on for MacDonald Lake was simulated well for the three seasons with an overall MAE of 2 day compared to the camera imagery and 3 days compared to the SWIP (Table 7). Ice-on at Clear Lake was also simulated, with an MAE of 2 days for the 3 seasons (Table 8).
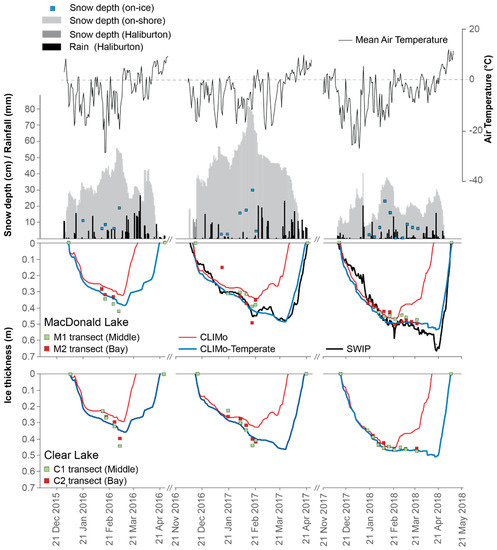
Figure 7.
MacDonald and Clear Lake model runs for three consecutive seasons showing the high latitude CLIMo (red line) and CLIMo-Temperate (dark blue line), compared to the Shallow Water Ice Profiler (SWIP, black line), and manual auger measurements (M-1: MacDonald Lake transect, middle of lake; M-2: MacDonald Lake, over the SWIP; C-1: Clear Lake, middle of Lake and C-2: Clear Lake, sheltered bay). Also included, on-shore and on-ice snow depths from the AWS, or nearby Haliburton weather station when the AWS was not available; daily rainfall from Haliburton; and daily mean air temperature from the AWS.

Table 7.
Observed and simulated ice-on and off dates for MacDonald Lake.

Table 8.
Observed and simulated ice-on and off dates for Clear Lake.
Ice thickness is underpredicted (Figure 7, Table 9) for both MacDonald and Clear Lake during 2015–2016, 2016–2017 and 2017–2018. Ice thickness for MacDonald Lake in comparison to the SWIP (Table 10) is 12.0 cm and 15.8 cm for 2016–2017 and 2017–2018, respectively. In comparison to the observed thickness, MacDonald Lake has a mean MAE of 5.4 cm and Clear Lake has a mean MAE of 5.5 cm for the entire study period (2016–2018). Spatial variability is evident when comparing the manual measurements to the simulations and the SWIP, highlighting the thickness variability across the lakes. The overall error was within 6 cm to the manual measurements; however, the end of season thickness was not included in the manual measurements (e.g., Figure 7, manual measurements ceased before maximum thickness) and the large discrepancy in the thickness values becomes evident when compared with the SWIP (Figure 7, Table 10). Furthermore, ice-off simulations were very poor (Table 7 and Table 8) ranging from 3 to 5 weeks too early (overall MAE of 26 days), clearly showing both ice thickness and ice-off dates are not representative of these temperate lake sites.

Table 9.
Observed thickness versus modelled thickness MAE in cm for study lakes M-1: MacDonald Lake transect, middle of lake; M-2: MacDonald Lake, over the SWIP; C-1: Clear Lake, middle of Lake and C-2: Clear Lake, sheltered bay.

Table 10.
Model performance and error statistics for observed (SWIP) compared to simulated ice thickness for MacDonald Lake.
The white ice formed in the temperate region presents a challenge within CLIMo with regards to adequately simulating thickness throughout the ice-covered season, since the model does not currently include the contributions of midwinter rain or meltwater refreeze on the ice. The current black ice (Arctic-based) parameterization also contributed to underpredicting ice-off dates because the expected black ice (versus the actual white ice) has a lower albedo, which results in a more rapid melt once underway. Therefore, to adequately represent ice thickness and melt simulations in the temperate region with CLIMo, the albedo needs to be represented using field data from temperate lakes.
4.3. Improved Model Simulations—CLIMo-Temperate
Initially, changes were only made to the albedo of the ice during melt to explore the relationship between the white ice and the melt rate and ice-off timing. While the results improved, this adjustment did not fully address the underprediction of thickness and ice-off timing. Therefore, further simulations were run using an adjusted albedo parameterization of both snow and ice (Figure 7; dark blue line, Figure 8), with the ice albedo being the dominant driver of the improvements. These results were compared to the original unadjusted simulations.
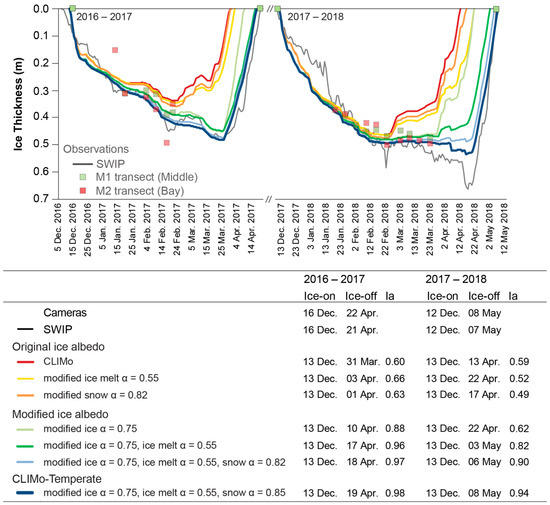
Figure 8.
Simulations for MacDonald Lake showing the interim model results through the albedo adjustments, superimposed on Figure 7, for 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 seasons, including the ice-on, ice-off dates and Ia values (compared to the Shallow Water Profiler, SWIP, thickness).
Table 7, Table 8, Table 9 and Table 10 highlight the substantial improvement to the model fit for the two temperate lakes. Ice-on dates show little to no change, as snow and ice albedo do not factor into the fall freeze conditions until ice is present on the lake (though, freeze timing can be affected through melt timing from the previous summer, as is the case for MacDonald Lake in fall 2017 when ice formed 1 day sooner). For MacDonald Lake, ice-off improved greatly from a MAE of 22 (SWIP) and 26 (digital camera) days to 2 and 3 days, with Clear Lake improving from 26 (digital camera) to 2 days as well (Table 7 and Table 8). 2015–2016 showed the greatest difference from observations for ice-off (with simulations 5 and 7 days earlier than observed ice-off), likely due to the large late-season snowfalls that occurred after ice melt had begun (Figure 7); with no field observations during this time, it is possible that more than 47% of the late season snow stayed on the ice and hence is under represented in the model input data.
Simulated thickness compared to the transect data improved substantially, with overall MAE values ranging from 2.6 to 3.1 cm across both lakes (Table 9). Some variation between the modelled and the measured ice thickness is to be expected, as it would be attributed to spatial variability across the lake (from on-ice snow or bathometry variations), which would not be captured by the 1-D model. CLIMo-Temperate simulations for 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 show a marked improvement for ice thickness compared to the SWIP data, with the Ia increasing to 0.98 and 0.96, MAE decreasing to 3 and 5 cm, and virtually no MBE at −0.2 and 0 (Table 10) in 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 respectively, with the end of season thickness now represented more accurately. The under-representation of ice thickness in the 2017–2018 simulations at the end of season is attributed to the snow conditions at the on-shore AWS during a snow event 14–15 April underrepresenting the total snowfall. The Haliburton ECCC station recorded 24 cm of snow, while the AWS recorded only 9 cm of snow during this event. A model simulation using the ECCC snow data in place of the AWS snow data does capture most of the ice thickness increase during this time (not shown), however the shoreline position and prevailing wind conditions at our AWS likely resulted in substantial redistribution during the snow event, limiting the overall accumulation under the snow sensor. Additionally, the end of season cumulative rainfall for the month of March (69 mm) and runoff from the 11.4 km2 catchment, may have further contributed to the increase in observed ice growth monitored in 2018 by the SWIP when the weight of the wet snow depressed the ice cover. However, after this brief thickening, the melt rate and timing were very similar between the simulations and the SWIP.
The unadjusted model results indicate earlier ice-off dates, which we attribute to the lower albedo of black ice parameterized in the model, and hence does not account for the delay in ice melt attributed to the predominantly white ice. This supports the work by [67] which states that snow-ice (white ice) slows the ice thinning rate during the early melt season. By utilizing field-based parameterization values of ice and snow albedos in the adjusted simulations, ice decay and ice-off timing are substantially delayed in the ice-cover season, resulting in much better representation of temperate region ice.
Comparing our results to previous temperate lake ice phenology simulations using freshwater lake numerical models (e.g., F-Lake, Hosteler, Minlake, Simple Ice Model, General Lake Model) shows improvements. Previous research simulated ice-on and ice-off with substantial deviations between the four models used and the observed ice cover dates (A different statistical measure of fit was used, rather than difference of days) [34], while other studies simulated ice-on within 6 to 8 days [35,36]; CLIMo was within 2 days for both ice-on and ice-off. Ice thickness was previously simulated within 2 cm using an ice-cover and water-temperature model [35], which yielded similar thickness results to CLIMo. However, [34] found that simulated ice thickness results were over-estimated for their study lake.
5. Summary and Conclusions
The results demonstrate the relationship between snow and ice composition on the simulation of lake ice formation, growth, and decay of both High Arctic and temperate region lake ice using the Canadian Lake Ice Model. The High Arctic sites show good agreement to ice phenology dates, with a MAE of 6 days for ice-on and 8 days for ice-off for both snow cover scenarios (thickness could not be assessed since it was not recorded). Initial CLIMo simulations of two temperate lakes indicated ice-on MAE dates of 2 to 3 days and 26 days for ice-off. Ice thickness on MacDonald Lake showed a MAE of up to 16 cm compared to the SWIP. The initial results highlighted issues with the representation of the melt period within the model for temperate regions where more white ice is present [12]. Adjustments to CLIMo used field measured albedo values for snow and ice on temperate lakes and provided dramatically improved simulations of ice thickness and ice-off dates. The simulations using CLIMo-Temperate had a MAE within 1 to 2 days for ice-on and a MAE of 2 to 3 days for ice-off. Simulated ice thickness over the 2016–2017 and 2017–2018 seasons improved from Ia of 0.61 to 0.98 and 0.58 to 0.96 respectively and was within 5 cm of the SWIP (MAE). Ice thickness compared to observations for all three seasons had a MAE of 3 cm. The albedo of temperate region snow and ice were all increased to better represent the frequent fresh snowfalls and large amounts of white ice that are found in the temperate region. The higher albedo values reflect more incoming radiation, which reduces the absorption of solar radiation into the ice cover and delays the simulated melt onset by approximately 1 month which produces much more realistic results for this region. Overall, this research found that the surface albedo is critical to represent correctly at temperate latitudes because of the impacts ice thickness, the timing of melt onset, and the final ice-off dates. However, further investigation should also be completed regarding the effects of ice thickness on albedo, especially in regions where white ice is dominant. It is important to understand how ice characteristics and cover are changing in temperate latitudes, since freshwater lake abundance is highest within these latitudes [1] and temperature projections suggest the number of lakes transitioning from annual to intermittent winter ice cover will increase exponentially with climate warming [3]. The ability to model lake ice cover with greater accuracy, including the correct representation of the ice column, is a large stride towards a better understanding the feedbacks between lake ice to climate, in the years to come.
Author Contributions
A.L.R. and L.C.B. designed the study, S.S.A. and A.L.R. carried out the principal field component with guidance and supervision from L.C.B., A.L.R. and S.S.A. were involved in data curation and formal analysis including running preliminary model simulations for the High Arctic and Temperate study site, respectively. A.L.R. modified the model code using in-situ field data for the adjusted Temperate lake simulations. A.L.R. prepared the primary manuscript with contributions from all co-authors. L.C.B. and A.L.R. were also responsible for visualization of data for publication. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Canada Foundation for Innovation/Ontario Research Funds (Brown), Grant/Award 34864; NSERC Discovery Grant (Brown), Grant/Award Number: 5316; UTM Department of Geography Graduate Expansion Funds (Robinson/Ariano); Northern Scientific Training Program (NSTP) (Robinson, 2017, 2018; Ariano, 2016); Haliburton Forest and Wild Life Reserve Ltd. (in kind) and Polar Continental Shelf Program (PCSP) (logistical support, in kind).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author. The Environment and Climate Change Canada datasets are available publicly on the cited websites.
Acknowledgments
This project was funded by an NSERC Discovery Grant (Brown), CFI/ORF (Brown), UTM Department of Geography Graduate Expansion Funds (Robinson/Ariano), Northern Scientific Training Program (Robinson/Ariano) and the Polar Continental Shelf Program (Brown). We would like to thank Haliburton Forest and Wild Life Reserve Ltd. for their in-kind support and overall assistance with this project. We would also like to thank Kathy Young, Scott Lamoureux, Laura Thomson, Anna Pienkowski-Furze, Dana Stephenson, Debbie Iqaluk, Sean Yokoyama, Evan Thompson, Justin Murfitt, Alicia Dauginis, William Sturch and the Qarmartalik School for field assistance. We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their helpful feedback that led to an improved manuscript, as well as an anonymous reviewer from an earlier version of this manuscript for their helpful suggestions to clarify the methodology section. We also appreciate the assistance/advice from ASL Environmental and Mike Brady (Environment and Climate Change Canada).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Verpoorter, C.; Kutser, T.; Seekell, D.A.; Tranvik, L.J. A global inventory of lakes based on high-resolution satellite imagery. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 6396–6402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, B.J.; Magnuson, J.J.; Jensen, O.P.; Card, V.M.; Hodgkins, G.; Korhonen, J.; Granin, N.G. Extreme events, trends, and variability in Northern Hemisphere lake-ice phenology (1855–2005). Clim. Chang. 2012, 112, 299–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Blagrave, K.; Magnuson, J.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Oliver, S.; Batt, R.D.; Magee, M.R.; Straile, D.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A.; Winslow, L.; et al. Widespread loss of lake ice around the Northern Hemisphere in a warming world. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2019, 9, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. The response and role of ice cover in lake-climate interactions. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2010, 34, 671–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, C.D.; Jones, B.M.; Liljedahl, A.K.; Hinkel, K.M.; Welker, J.A. Depth, ice thickness, and ice-out timing cause divergent hydrologic responses among Arctic lakes. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 9379–9401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Bernier, M.; Gauthier, Y.; Kouraev, A. Remote Sensing of lake and river ice. In Remote Sensing of the Cryosphere; Tedesco, M., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 273–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, K.; Michelutti, N.; Sugar, M.; Douglas, M.S.V.; Smol, J.P. Ice-cover is the principal driver of ecological change in High Arctic lakes and ponds. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampton, S.E.; Galloway, A.W.; Powers, S.M.; Ozersky, T.; Woo, K.H.; Batt, R.D.; Labou, S.G.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Lottig, N.R.; et al. Ecology under lake ice. Ecol. Lett. 2017, 20, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewitt, B.A.; Lopez, L.S.; Gaibisels, K.M.; Murdoch, A.; Higgins, S.N.; Magnuson, J.J.; Paterson, A.M.; Rusak, J.A.; Yao, H.; Sharma, S. Historical trends, drivers, and future projections of ice phenology in small North Temperate Lakes in the Laurentian Great Lakes Region. Water 2018, 10, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMAP. Snow, Water, Ice and Permafrost in the Arctic (SWIPA) 2017; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme (AMAP): Oslo, Norway, 2017; p. xiv 269. ISBN 978-82-7971-101-8. [Google Scholar]
- Leppäranta, M. Freezing of Lakes and the Evolution of their Ice Cover; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; pp. 84–265. ISBN 978-3-642-29080-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ariano, S.S.; Brown, L.C. Ice processes on medium-sized north-temperate lakes. Hydrol. Process. 2019, 33, 2434–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duguay, C.R.; Flato, G.M.; Jeffries, M.O.; Ménard, P.; Morris, K.; Rouse, W.R. Ice-cover variability on shallow lakes at high latitudes: Model simulations and observations. Hydrol. Process. 2003, 17, 3465–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svacina, N.A.; Duguay, C.R.; Brown, L.C. Modelled and satellite-derived surface albedo of lake ice—Part I: Evaluation of the albedo parameterization scheme of the Canadian Lake Ice Model. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4550–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, R.; Woo, M.K. Decay of a High Arctic lake-ice cover: Observations and modelling. J. Glaciol. 1994, 40, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneman, H.E.; Stefan, H.G. Albedo models for snow and ice on a freshwater lake. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1999, 29, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakkila, J.; Leppäranta, M.; Kawamura, T.; Shirasawa, K.; Salonen, K. Radiation transfer and heat budget during the ice season in Lake Pääjärvi, Finland. Aquat. Ecol. 2009, 43, 681–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdorovennova, G.; Palshin, N.; Efremova, T.; Zdorovennov, R.; Gavrilenko, G.; Volkov, S.; Bogdanov, S.; Terzhevik, A. Albedo of a small ice-covered boreal lake: Daily, meso-scale and interannual variability on the background of regional climate. Geosci. J. 2018, 8, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semmler, T.; Cheng, B.; Yang, Y.; Rontu, L. Snow and ice on Bear Lake (Alaska) sensitivity experiments with two lake ice models. Tellus A 2012, 64, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svacina, N.A.; Duguay, C.R.; King, J.M.L. Modelled and satellite-derived surface albedo of lake ice—Part II: Evaluation of MODIS albedo products. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4562–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, J.; Lyu, S.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Su, D. An investigation of the ice surface albedo and its influence on the High-Altitude lakes of the Tibetan Plateau. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. A comparison of simulated and measured lake ice thickness using a Shallow Water Ice Profiler. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 2932–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Leppäranta, M.; Cheng, B.; Li, Z. Numerical modelling of snow and ice thicknesses in Lake Vanajavesi, Finland. Tellus A 2012, 64, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, B.; Vihma, T.; Rontu, L.; Kontu, A.; Kheyrollah Pour, H.; Duguay, C.; Pulliainen, J. Evolution of snow and ice temperature, thickness and energy balance in Lake Orajärvi, northern Finland. Tellus A 2014, 66, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ménard, P.; Duguay, C.R.; Flato, G.M.; Rouse, W.R. Simulation of ice phenology on a large lake in the Mackenzie River Basin (1960–2000). In Proceedings of the 59th Eastern Snow Conference, Stowe, VT, USA, 5–7 June 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, K.; Jeffries, M.; Duguay, C.R. Model simulation of the effects of climate variability and change on lake ice in central Alaska, USA. Ann. Glaciol. 2005, 40, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.C.; Duguay, C.R. The fate of lake ice in the North American Arctic. Cryosphere 2011, 5, 869–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kheyrollah Pour, H.; Duguay, C.R.; Martynov, A.; Brown, L.C. Simulation of surface temperature and ice cover of large northern lakes with 1-D models: A comparison with MODIS satellite data and in situ measurements. Tellus A 2012, 64, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surdu, C.M.; Duguay, C.R.; Brown, L.C.; Fernández Prieto, D. Response of ice cover on shallow lakes of the North Slope of Alaska to contemporary climate conditions (1950–2011): Radar remote-sensing and numerical modeling data analysis. Cryosphere 2014, 8, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maykut, G.A. Large-scale heat exchange and ice production in the Central Arctic. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1982, 87, 7971–7984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heron, R. Decay of a High Arctic Lake Ice Cover. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Biology, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Ariano, S.S. An Investigation of Temperate Region Lake Ice in Central Ontario. Master’s Thesis, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, K.; Griffis, T.J.; Baker, J.M.; Bolstad, P.V.; Erickson, M.D.; Lee, X.; Wood, J.D.; Hu, C.; Nieber, J.L. Evaporation from a temperate closed-basin lake and its impact on present, past, and future water level. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Samal, N.R.; Joehnk, K.D.; Fang, X.; Bruce, L.C.; Pierson, D.C.; Rusak, J.A.; James, A. Comparing ice and temperature simulations by four dynamic lake models in Harp Lake: Past performance and future predictions. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4587–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, H.G.; Fang, X. Simulated climate change effects on ice and snow covers on lakes in a temperate region. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 1997, 25, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martynov, A.; Sushama, L.; Laprise, R. Simulation of temperate freezing lakes by one-dimensional lake models: Performance assessment for interactive coupling with regional climate models. Boreal Environ. Res. 2010, 15, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.K. Permafrost Hydrology; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 305–344. ISBN 978-3-642-23462-0. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.C. (University of Toronto, Canada). Personal communication, 2016.
- Lescord, G.L.; Kidd, K.A.; Kirk, J.L.; O’Driscoll, N.J.; Wang, X.; Muir, D.C.G. Factors affecting biotic mercury concentrations and biomagnification through lake food webs in the Canadian high Arctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 509, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenormand, F.; Duguay, C.R.; Gauthier, R. Development of a historical ice database for the study of climate change in Canada. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 3707–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC). Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Available online: https://climate.weather.gc.ca/climate_normals/ (accessed on 6 March 2017).
- Woo, M.K.; Heron, R.; Marsh, P.; Steer, P. Comparison of weather station snowfall with winter snow accumulation in high arctic basins. Atmos. Ocean 1983, 21, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Woo, M.K. Representativeness of local snow data for large scale hydrologic investigations. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1977–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statistics Canada. Available online: https://www12.statcan.gc.ca/census-recensement/2011/geo/bound-limit/bound-limit-2016-eng.cfm (accessed on 27 September 2016).
- Natural Resources Canada. Available online: https://open.canada.ca/data/en/dataset/7f245e4d-76c2-4caa-951a-45d1d2051333 (accessed on 3 March 2018).
- Crins, W.J.; Gray, P.A.; Uhlig, P.W.C.; Wester, M.C. The Ecosystems of Ontario, Part 1: Ecozones and Ecoregions; Ministry of Natural Resources: Peterborough, ON, Canada, 2009; pp. 40–42. [Google Scholar]
- Hadley, K.R.; Paterson, A.M.; Hall, R.I.; Smol, J.P. Effects of multiple stressors on lakes in south-central Ontario: 15 years of change in lakewater chemistry and sedimentary diatom assemblages. Aquat. Sci. 2013, 75, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haliburton Forest; Wild Life Reserve. Haliburton Forest 4th Edition Fishing Guide; Haliburton Forest and Wild Life Reserve Ltd.: Haliburton, ON, Canada, 2012; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- MSC (Meteorological Service of Canada). Canadian Snow Data CD-ROM: Daily Snow Depth and Snow Water Equivalent. Climate Processes and Earth Observation Division; MSC: Downsview, ON, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M. A Guide for Ground Based Measurement of the Arctic Snow Cover; Climate Resolution Branch, Atmosphere, Environment Service: Downsview, ON, Canada, 1997; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Sturm, M.; Liston, G.E. The snow cover on lakes of the Arctic Coastal Plain of Alaska U.S.A. J. Glaciol. 2003, 49, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melling, H.; Johnston, P.H.; Riedel, D.A. Measurements of the underside topography of sea ice by moored subsea sonar. J. Atmos. Ocean Tech. 1995, 12, 589–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marko, J.R.; Fissel, D.B.; Jasek, M. Recent developments in ice and water column profiling technology. In Proceedings of the 18th IAHR symposium on river ice, Sapporo, Japan, 28 August–1 September 2006; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- WMO (World Meteorological Organization). Guide to Meteorological Instruments and Methods of Observation, 2018th ed.; WMO-No 8; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 246–297. ISBN 978-92-63-10008-5. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, G.E.; Duguay, C.R.; Brown, L.C.; King, J.; Atwood, D.; Kasurak, A. Freshwater lake ice thickness derived using X- and Ku-band FMCW scatterometers in the Hudson Bay Lowlands Near Churchill, Manitoba. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2015, 120, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flato, G.M.; Brown, R.D. Variability and climate sensitivity of landfast Arctic sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. 1996, 101, 25767–25777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maykut, G.A.; Untersteiner, N. Some results from a time-dependent thermodynamic model of sea ice. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1971, 76, 1550–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shine, K.P. Parameterization of the shortwave flux over high albedo surfaces as a function of cloud thickness and surface albedo. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 1984, 110, 747–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maykut, G.A.; Church, P.E. Radiation climate of Barrow, Alaska, 1962–1966. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1973, 12, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, E.E.; Curry, J.A. An intermediate one-dimensional thermodynamic sea ice model for investigating ice–atmosphere interactions. J. Geophys. Res. 1993, 98, 10085–10109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, G. Radiation flux investigation. In Arctic Ice Dynamics Joint Experiment (AIDJEX) Bulletin; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1972; Volume 14, pp. 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, M.K.; Young, K.L. Modeling arctic snow distribution and melt at the 1 km grid scale. Nord. Hydrol. 2004, 35, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willmott, C.J. On the validation of models. Phys. Geogr. 1981, 2, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Bigirarini, M. hydroGOF: Goodness-of-Fit Functions for Comparison of Simulated and Observed Hydrological Time Series. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/hydroGOF/ (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Lamigueiro, O.P. tdr:Target Diagram Package. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/tdr/index.html (accessed on 1 October 2019).
- Jeffries, M.O.; Morris, K.; Duguay, C.R. Lake ice growth and decay in central Alaska, USA: Observations and computer simulations compared. Ann. Glaciol. 2005, 40, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashton, G.D. River and Lake Ice Engineering; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).