Abstract
Wavelet transform, wavelet spectra, and coherence are popular tools for studying fluctuations in time series in the form of a bidimensional time and scale representation. We discuss two aspects of wavelet analysis—namely the significance and stochastic/deterministic character of the wavelet spectra. Real-time series of discharge, sodium, and sulfate concentrations in the alpine Rhône River, Switzerland, are used to illustrate these issues. First, the consequences of using an arbitrary stochastic process (usually, AR (1)) instead of the best-fitted general ARMA process in the evaluation of the significance of wavelet spectra are analyzed. Using a general ARMA instead of AR (1) decreases the significance level of the differences in wavelet power spectra (WPS) of ARMA and AR (1) compared to the WPS of the time series in all cases studied and points to a possible systematic overestimation of significance in many published studies. Besides, the significance of particular patches in the spectra is affected by multiple testing. A (conservative) way to circumvent this problem, using global wavelet spectra and global coherence spectra, is evaluated. Finally, we discuss the issue of causality and investigated it in the three measured time series mentioned above. Even if the use of the best fitted ARMA pointed to no deterministic features being present in the corrected series studied (i.e., stochastic processes are dominant in the three data series), coherence spectra between variables allowed to reveal cause-effect relationships between two “coherent” variables and/or the existence of a common effect on both variables. Therefore, such type of analysis provides a useful tool to better understand data causal relationships.
1. Introduction
When studying time series, it is usual to perform a spectral (frequency) analysis (e.g., Fourier transform) alongside the time analysis. As many time series resulting from natural phenomena are periodic or quasi-periodic, such frequency analysis gives the fundamental oscillations of the phenomenon under study. The Fourier transform, however, is only applicable to stationary time series data. When power at different frequencies changes with time, results of spectra calculations can be misleading [1]. As natural time series data are not stationary (e.g., climatic time series such as NAO and ENSO indexes, which do show (quasi) periodicities, but with changing periods and strengths), other methods should be used to study those series’ in the frequency domain. The most frequently applied, and probably the best of such methods, is wavelet analysis (wavelet transform and wavelet spectrum), which gives a two-dimensional description of the time series (both in time and in scale–frequency). Two types of wavelet analyses exist, discrete and continuous; only the second will be used here.
Wavelets are used in many fields where time series data are a central subject of study from economics to climatology, astronomy, physiology, physics, geology, etc. In environmental sciences and, particularly, hydrology, many authors calculate continuous wavelet power spectra (WPSs) and wavelet coherence spectra (WCSs), most often applied to discharges [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]. Nitrate and other nutrient concentrations have also been widely treated [10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18]. Reviews exist on hydrology applications of wavelets [19] and hybrid wavelet-artificial intelligence models in hydrology [20]. Several free software packages are available [21,22,23,24].
As is the case in other statistical questions (e.g., temporal trends), knowing when a feature of a WPS or WCS of a time series is significant, and deducing from it the existence of a causal deterministic effect, is not straightforward. In the case of wavelet analysis, three aspects need to be considered: (i) the choice of the reference stochastic process; (ii) the problems derived from multiple testing; (iii) causality itself. These three research questions are the object of this study and are discussed below.
Torrence and Compo [21] were the first to develop significance tests for WPSs and WCSs. Any definition of statistical significance implies a comparison with a stochastic model. The usual way to define significance in a wavelet spectrum is to compare the actual spectrum of the time series with the spectrum of the stochastic AR (1) process (“red noise”) that best fits the original time series [3,4,5,6,9,10,21,22,23,25,26,27]. If a particular point (t, s-scale) in the spectrum is outside, say, 95% of the distribution of spectral power obtained from AR (1), it is admitted that a particular deterministic cause(s) is (are) in play alongside the stochastic random process at this (95%) significance level. Significance in WCSs can be defined in the same way, that is, adjusting an AR (1) process to each of the two series we are comparing, obtaining a distribution of coherences at each point by using pairs of realizations of both processes, and then comparing the coherence of the two-original series’ with the distribution of coherence at each point. This is the method used in three of the four software packages cited above. The reason for choosing AR (1) as a reference is that many geochemical processes can be represented by that type of process [21]. What happens, however, if a series can be better fitted by a stochastic process different from AR (1)? [28,29]. To our knowledge, this possibility has only been taken into consideration by Aguiar-Conraria & Soares [24]. They have made available software based on an ARMA (p,q) process type but they neither comment on nor compare it with the usual AR (1) choice. Val et al. [18] mention the use of ARMA for significance estimation but they do not give any further details either.
Some authors use white noise (AR (0)) instead of red noise as the reference process to estimate significance, but again with little or no justification [8,13,30,31,32,33].
In principle, once the most suitable stochastic model is selected, it is possible to apply a significance test at each (time, scale) point of the WPS to look for deterministic effects. In practice, however, some problems related to significance in WPS remain unresolved, namely the multiple testing problem (false positives or error I). For instance, if WPS were the result of a purely stochastic process, 5% of the points would still present a spectral power higher than the 95% significance limit and would appear as significant. We do not know how to differentiate those false positives, which are caused merely by chance, from genuine peaks due to a deterministic cause. Besides, the power in a WPS point is correlated with powers in nearby points because wavelet transform is the result of a convolution between mother wavelet and time series values [30,34] and false positives appear as significant patches, not merely points. Maraun et al. [23] developed an areal significance method that eliminates many, but not all, of these false positives, but at the price of increasing error II (false negatives), i.e., not considering as significant those points that are so.
In this study, we explore the consequences of failing to use the most suitable stochastic process when assessing WPS and WCS significance through the evaluation of real-time series of discharge, sodium, and sulfate in the alpine catchment of Rhône River in Switzerland. Then, we use global wavelet spectra (GWSs) as a way of treating the multiple testing problem. Finally, the related question of deterministic effects (causality) on those time series is also addressed by studying the global coherence spectra (GCSs).
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Data
Data used in this study comes from the Swiss NADUF programme. Switzerland has a network of hydrological stations, belonging to the Swiss National River Monitoring and Survey Programme (NADUF), which holds a long series of many physical and chemical parameters. The discharge data used in this study (1074 evenly spaced points) are two-week averages of discharges measured every 10 min at the hydrological station in Porte du Scex, Rhône River, Switzerland, during the period 1974–2015.
Sodium and sulfate concentration data are two-week, discharge-weighted averages at the same sampling point as discharges in the same period, 1974–2015, and with the same two-week periods. There are 1052 sodium and 1049 sulfate data points. The few missing points have been interpolated using the interp1 function of Matlab, which uses the piecewise cubic Hermite interpolation method. For additional details on the NADUF data series, see [35,36].
2.2. Data Pre-Treatment and Reference Stochastic Processes Calculation
Before utilization, time series are detrended and standardized, as in Koscielny-Bunde et al. [37], to eliminate short-term (seasonality) and long-term (trend) fluctuations. This is necessary to make the time series as stationary as possible for the application of the methods to fit an ARMA model.
The trend is estimated with the non-parametric Mann–Kendall method and Sen’s slopes are calculated as explained in [38]. Residual values XRt are obtained by subtracting trend straight line from the series Xt instead of just the mean value as in [37]:
a and b being the Y-intercept and the Sen’s slope, respectively, and t the time.
XRt = Xt − (a − b t)
To eliminate seasonality, the mean value Xmean of each month is subtracted from each residual belonging to that month, and, to minimize possible seasonal variations of the variance, this difference is normalized by the variance of the given month in the entire series, σ2, obtaining the corrected (detrended and deseasonalized) time series XRCt:
XRCt = (XRt − Xmean)/σ2
To get the best fitting ARMA process, we use the ARMASA toolbox for Matlab, developed by Broersen [39,40] and De Waele [29]. ARMASA can generate time series as realizations of a given ARMA model as well as to select the optimal ARMA model (a stochastic process) corresponding to a given time series. This procedure allows the assessment of the accuracy of the estimated model, the computation of the autocorrelation function, and the power spectra of the series. The ARMAsel algorithm calculates automatically the type and order of the stochastic process for the structures AR (p), MA (q), and ARMA (r, r − 1).
AR (1) processes have also been fitted to time series using the “aryule” built-in function of Matlab, which estimates the AR coefficient by the Yule-Walker approximation. 1000 realizations of each process are calculated and an autocorrelation function (ACF) is calculated for each realization. The ACFs of the original time series (transformed as explained above) are then compared to the ACFs obtained with AR (1) and the optimal ARMA. Confidence limits of 95% have been constructed for each process and each time lag by calculating distances from autocorrelations (ACs) of realizations to mean AC values at each lag in standard deviation units, using the non-parametric procedure explained by Wilcox [41].
2.3. Wavelet Analysis
An extensive literature exists for a comprehensive explanation of wavelet transform and related topics (wavelet spectra and wavelet coherence). Outstanding examples of accessible tutorials with geophysical and climatic applications are found in the literature ([1,21,30]). Aguiar-Conraria and Soares [24] give a nice introduction to the wavelet topic even though it applies to economics. A brief overview is given below.
The basic idea of wavelet analysis is to apply a band-pass filter (called “wavelet”) to a time series. This filter has the particularity of being of variable temporal and frequency width. At each scale, a wavelet with an extension in time defined by the scale is used. The wavelet is displaced in time and, at each time point t of the series, the convolution of the wavelet with the value of the series calculated:
where n′ is the index of the time series x, n is a localized time index of the normalized wavelet ψ (ψ* is the complex conjugate), s is the scale, t the time, and N the number of points of the time series. The wavelet function at each scale is normalized to have unit energy as:
where ψ is the normalized and ψ0 the original wavelet function.
The result is a set of coefficients W, depending on s and t, called continuous wavelet transform (CWT). From Equation (3), the WPS is obtained as the square of the modulus of W. Maxima of spectral power are, at each scale, where convolution (correlation) of time series with the wavelet is maximum, i.e., at the times of maximum variability.
For each scale, we can average WPS at every time and obtain an analog of Fourier transform spectrum called the global wavelet spectrum (GWS):
This spectrum shows the time-averaged power of the fluctuations in the series at each temporal period (scale).
Two-time series X and Y can be compared by means of the “cross-wavelet spectrum”. If and are the wavelet transforms at scale s of the series X, Y, the cross wavelet spectrum is defined as:
with a power . WXY gives the correlation between the wavelet transform of each series at each scale s and time ti.
A normalized version of the cross-wavelet spectrum is the “wavelet coherence”, which is defined as the power of cross wavelet spectrum normalized to the two single wavelet spectra of series X and Y [32]:
For an analogy to Equation (5), we can substitute WCSi (s) for |Wn(s)|2 for each scale, and average WCO at every time, and thus obtain a global coherence spectrum (GCS). This spectrum shows the time-averaged coherence of the two series at each temporal period (scale).
Wavelet power spectra (WPSs) are calculated using Torrence and Compo software available at http://paos.colorado.edu/research/wavelets/. Wavelet coherence spectra (WCSs) are calculated using this software and that of Maraun and co-workers available at http://tocsy.agnld.uni-potsdam.de/wavelets/. We have integrated these calculation methods in two Matlab scripts, calculating WPSs and GWSs of discharge, sodium and sulfate, and WCSs and GCSs of discharge-sodium, discharge-sulfate, and sodium-sulfate. We have used as mother wavelet the Morlet wavelet with ω0 = 6. Only values inside the cone of influence have been considered. Distances (in standard error units) to the mean of distributions of spectral power or coherences are calculated, and spectral powers or coherences of the original transformed series are considered significant if they have a distance to the mean larger than the 95% of the distribution [41].
3. Results
Using ARMASA, we have fitted ARMA models to the time series of discharges, sodium, and sulfate two-week concentrations in Porte du Scex (Rhône River, Switzerland). Figure 1 represents both the original and the corrected time series. Sulfate is best fitted with an AR (3) process, although AR (1) gives ACs which are almost all of them inside the confidence limits and are practically identical to those from AR (3). For discharge and sodium, AR (1) gives in several cases (lags) ACs outside the confidence limits. AR (9) is the best-fit process for discharge, and AR (34) for sodium (Figure 2). The case of sodium is atypical, as a pronounced one-year seasonality is present after seasonality elimination. This might be due to the human-dominated sodium inputs to the river, which are highest in winter [35].
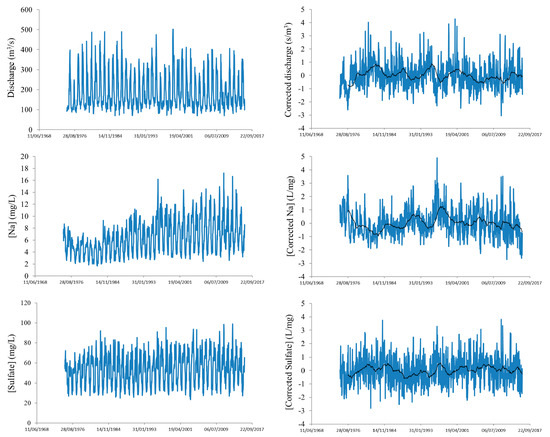
Figure 1.
Original and corrected time series for discharge, sodium, and sulfate. Black lines in the corrected time series plots are moving averages (with a period of 48 two-weeks).
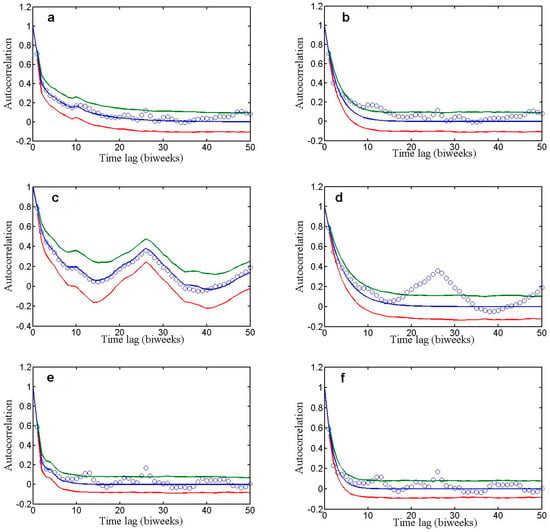
Figure 2.
Autocorrelation functions (ACFs) of the original time series and AR (1) fitted processes and better fitted ARMA processes. In x-axes is the time lag (1 unit = two weeks). Circles are the ACFs of the time series (transformed as explained in the text), the blue line the ACF of the fitted process, and red and green lines the 95% confidence limits of the fitted process ACF. (a) Discharge AR (9), (b) discharge AR (1), (c) sodium AR (34), (d) sodium AR (1), (e) sulfate AR (3), (f) sulfate AR (1).
WPSs have been calculated for all three-time series. Significant areas are clearer at short scales (less than one year) and in scales of 1–2 years in 1998–2005 in discharge and sodium spectra. At 6–8 years, there is a small significant area in 1990–1997. Sulfate shows a feature at 4–6 years around 1996. The big significant area at the beginning of the series and longest scales is not reliable because it is outside the cone of influence (Figure 3).
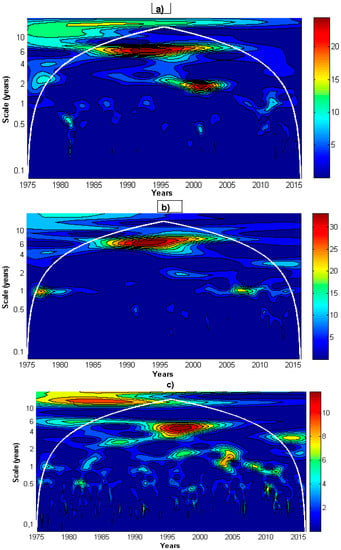
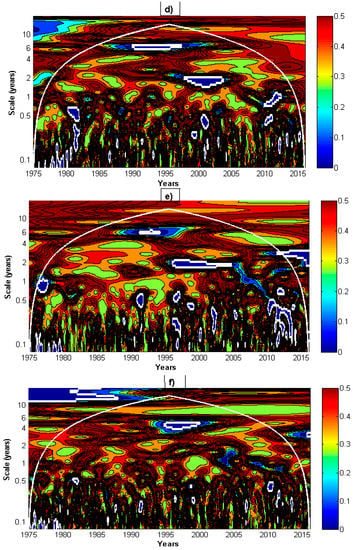
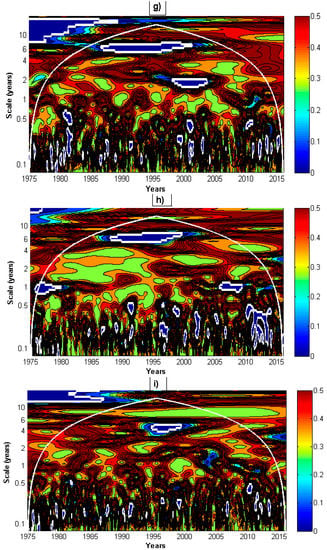
Figure 3.
Wavelet power spectra (WPSs) for (a) discharge, (b) sodium, (c) sulfate and significance levels (p values) of deviations from those WPS of WPS of the best fitted ARMA processes and of WPS of AR (1): Best ARMA significance levels of the deviation for (d) discharge, (e) sodium, (f) sulfate, AR (1) significance levels of the deviation for (g) discharge, (h) sodium, (i) sulfate. Broad white lines correspond to p = 0.05, and the areas inside these lines then contain the points (t,s) with significant differences to WPS of time series. The cone of influence (COI) appears as a thin white line.
Characteristic interannual fluctuations are more visible using GWSs (Figure 4). GWSs of discharge and sodium are similar, with a high peak at about 7 years and a shoulder at about 10 years, but main short-scale peaks differ in both spectra (one year for sodium, two years for discharge). Sulfate shows a very different GWS, with two high peaks at 5 and 13 years.
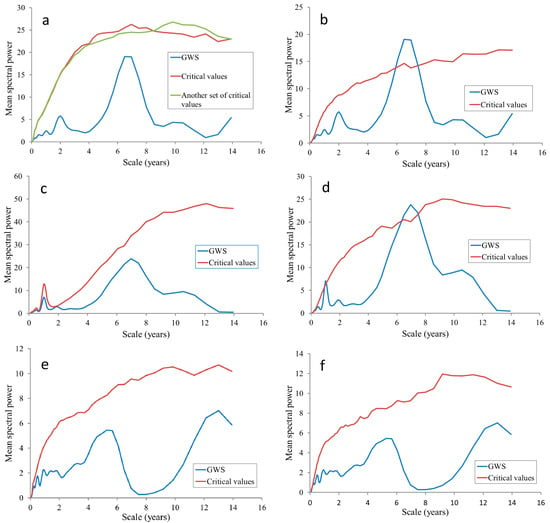
Figure 4.
Global wavelet spectra (GWSs) with best fitted ARMA and AR (1) for discharge, sodium, and sulfate. y-axes represent spectral power for the time series at each scale and x-axes scales (in years). (a) discharge, AR (9); (b) discharge, AR (1); (c) sodium, AR (34); (d) sodium, AR (1); (e) sulfate, AR (3); (f) sulfate, AR (1).
The main fluctuations of discharge and sodium are significant when referred to an AR (1) process but none is significant when the best fitting ARMA processes are used as reference (Figure 4). Regarding sulfate, the two peaks are not significantly different from the GWSs of the two stochastic processes AR (1) and AR (3). The significant areas in some time periods do not give a ‘global’ significance in the whole time period (limited by the cone of influence).
WCSs of discharge and sodium, discharge and sulfate, and sulfate-sodium have been calculated (Figure 5) from the wavelet coherence spectra (Figure 6). Discharge and sodium are particularly strongly coherent at scales of more than four years, but significant global coherence exists between both variables at practically every scale. Sulfate and discharge are coherent at scales smaller than four years (except around one year), with three peaks at 1.6, 2.5, and 3.7 years. In this case, and contrary to the sodium, there is no coincidence with the main peaks in GWSs of sulfate and discharge.
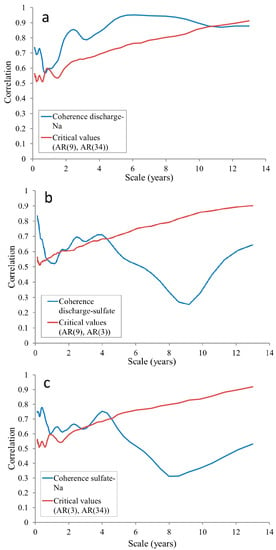
Figure 5.
Global coherences and wavelet coherence spectra (WCSs) for (a) discharge-sodium, (b) discharge-sulfate, and (c) sulfate-sodium. y-axes represent coherences (between 0 and 1) and x-axes scales (in years).
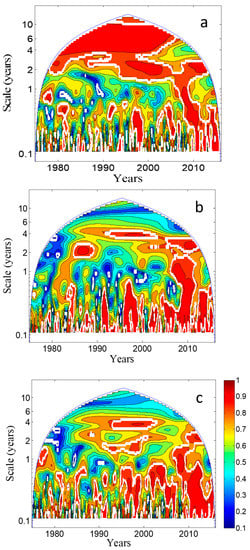
Figure 6.
Wavelet coherence spectra. Axes as in WPS spectra. Only coherences inside the cone of influence (COI) are represented by a color scale. The white line limits 95% significant areas. (a) Discharge-sodium; (b) discharge-sulfate; (c) sulfate-sodium.
Using the original two-week averaged data of discharge and concentrations, we have plotted the c-Q relationships of discharge and sodium and sulfate. In both cases, a strong relationship with discharge is clearly observed, stronger in the case of sodium (Figure 7).
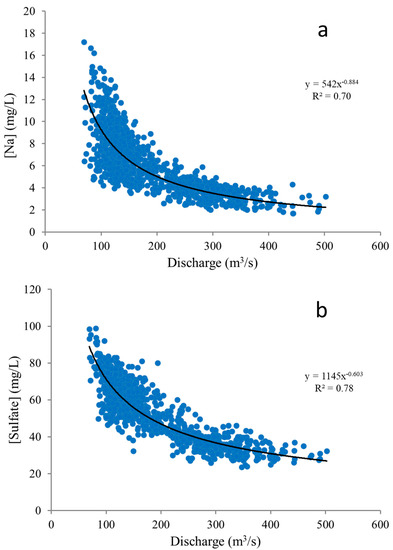
Figure 7.
(a) Sodium and (b) sulfate concentration-discharge relationships.
Sulfate and sodium show a global coherence spectrum similar to that of discharge-sulfate, with significant coherence at <4 years and no coherence at longer time scales.
4. Discussion
4.1. Choice of the Reference Stochastic Process
Our results clearly show that very different conclusions concerning significance can be obtained in wavelet analysis depending on the stochastic process chosen to derive that significance. Moreover, using more realistic ARMA processes instead of AR (1) gives less significant results in all the systems tested. Thus, using AR (1) instead of, for instance, the best-fitted ARMA is not irrelevant because using AR (1) leads to consider as significant features that are not significant if an ARMA process is employed instead. We suggest that an optimal ARMA, and not an AR (1), should be used when estimating significances in wavelet and wavelet coherence spectra.
4.2. How to Tackle the Multiple Testing Problem
As discussed in the introduction, the multiple testing problem has to be considered when dealing with significances [30,34]. The use of GWS and GWC spectra offers a way of overcoming these problems. Both spectra are obtained from the WPS and the WCS respectively by averaging spectral power at each scale over the entire time interval of the time series. When the GWS (or the GWC) is bigger (at a value of scale) than the critical value obtained with the reference stochastic process, we accept that it is an indication of the existence of a deterministic effect on the time series at this scale. The disadvantage of this procedure is that we lose the information about the time evolution of the fluctuations of the series, which is one of the main features of wavelet analysis, but the information on the series fluctuation at different time scales is preserved. By using averaging to discover significant features in the wavelet spectra, we are also taking a conservative approach, as possibly significant areas (t, s) in the WPS or GWC spectra could result in a non-significant average in the GWS or WCS spectra.
Another alternative to estimate significance levels could be to construct resamplings from the original time series with bootstrap. Aguiar-Conraria and Soares [24] offer this alternative in their software. However, the bootstrap can be used to construct confidence limits but not to assess the probability of a deterministic cause. For this, a distribution of WPSs or WCSs corresponding to the H0 (null) hypothesis (purely stochastic effect) must be constructed, and, therefore, a reference stochastic process is necessary.
4.3. Further Insight into Causality
Significance, as defined above, is a pretty clear and unambiguous concept. Causality is a more complex issue. The most widely used treatment of the cause-effect relationship between two-time series is the “Granger causality”, first exposed by that author in 1969 [42,43]. An analysis of that concept of causality and other more recent developments can be found in Eichler [44]. Two main characteristics of causality are accepted in those approaches: (a) temporal precedence: causes precede their effects, and (b) physical influence: manipulation of the cause changes the effects [44].
An interesting topic is how it is possible to obtain evidence of deterministic causality acting on a time series without using the methods mentioned above. We have implicitly considered that a significant (x %) departure of the best stochastic ARMA model which describes the time series indicates deterministic causality at this (x %) significance level. Strictly speaking, the significance test just falsifies (or not) the H0 hypothesis (that is, H0 = “an ARMA process “explains” the time series”), but the lack of a good “ARMA explanation” does not guarantee a deterministic explanation because other stochastic processes (for example, long-term memory processes type ARFIMA [45]) could be in play. Deterministic nonstationary effects on discharge and sodium time series are acting in the catchment (i.e., anthropogenic inputs of sodium salts [35] and changes in discharge variability caused by dam building in the Alpine Rhône tributaries [46]). Those effects, which are not completely taken into account by the detrending and deseasonalizing of the time series, could be the origin of the non-stochastic features in the WPSs. An investigation on the particular causes of deviations from stochastic behavior as, for example, the possible non-stationarity of corrected time series, is outside the scope of this study.
As a result, we accept that the rejection of the ARMA explanation can be a useful indication of a deterministic factor acting on the time series; i.e., statistical significance is an indication (not a firm proof) of non-stochastic causality. This is the, often implicit, assumption made by many authors when looking for causes of the observed time series (for example, wavelet analysis of series of temperature or climate proxies, as river discharge [4] to identify climate change fingerprints). To decide whether a cause-effect relationship is acting on the time series, we need to analyze the correlation between the time series in question and the suspected cause, that is, the cross-correlation and the coherence spectrum of the two series.
Looking at our results, WPSs of discharge and sodium and sulfate concentrations show that spectral power is not significant at the 95% level at most times and scales, Thus, stochastic processes are dominant in the three-time series. Moreover, GWSs of the series are not above the significance limit at any time scale, reinforcing this conclusion.
However, coherence spectra have an interesting property that might provide a useful tool better to identify deterministic causality relationships in the data: coherence spectra magnify the coincidences of spectral power of the series, as it is patent in our results of discharge-sodium and discharge-sulfate coherence spectra. The existence of significant areas in the WCSs provides evidence of the existence of a deterministic cause-effect relationship (i.e., if they show a significant coherence, both series may be independent but, in this case, they should still have a common deterministic cause). Consider, for instance, discharge and sodium concentrations in the Porte du Scex catchment. Taken in isolation, both series WPSs are mostly stochastic (Figure 3 and Figure 4) but the coherence spectrum is strongly significant practically at each scale (Figure 5). Obviously, we cannot go further and conclude that there is a causal relationship without additional knowledge on the variables related but, at the same time, it is clear that a deterministic effect of discharge on sodium is present. In fact, a strong dilution effect is observed when we plot the original sodium series against discharge, which means that a strong relationship between sodium and discharge exists at this temporal scale (two weeks) (Figure 7). This effect also exists in the case of sulfate, and the coherence spectrum and the global coherence discharge-sulfate are significant at scales of less than four years, but, contrary to the case of sodium, no significant coherence exists at longer time scales. Sulfate and sodium show a similar global coherence compared to discharge and sulfate, which suggest a common deterministic cause, most probably discharge.
These observations suggest that a stochastic variable (e.g., discharge) can exert a deterministic effect on another stochastic variable (e.g., sodium concentration), and this is revealed in the coherence spectrum. Therefore, a significant area of coherence does not guarantee a deterministic feature in the wavelet spectra of the two series separately but does imply a deterministic relationship of sodium with discharge. Thus, WCS spectra reveal cause-effect relationships between “coherent” variables and/or the existence of a common effect on both variables [22]. Strictly speaking, two coherent time series (that is, with coherence above the ARMA coherence) are deterministically “associated”, that is, we do not know which series is the cause and which is the effect, and we do not know if the association is caused by a third series which has a deterministic influence in both original series. In our case, the knowledge of the physical system (concentrations and discharges) allows us to identify cause and effect. Granger’s or Eichler’s methods should be used in the case of complicated or not obvious cause-effects are apparent.
5. Conclusions
Wavelet analysis is a powerful tool or studying fluctuations in time series largely used in hydrology and environmental sciences. However, the application of this type of analysis often neglects the consequences of the blind use of reference stochastic processes as AR (1) and white noise. Our results show that this might have led to the widespread overestimation of the existence of statistically significant effects in published studies. Concerning the multiple testing problem, we suggest using the global wavelet and coherence spectra to avoid the “false positives” associated with considering a random feature significant at the price of losing the time-resolved spectral power determination characteristic of wavelets. This is obviously not really a satisfactory method [23,30]. A better understanding of the caveats of significance assessment opens the possibility of extending the use of coherence spectra to the identification of cause-effect relationships between “coherent” variables as it was the case in our discharge, sodium, and sulfate datasets.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.R.-M. and M.F.; methodology, J.C.R.-M.; software, J.C.R.-M.; data curation, J.C.R.-M.; writing—original draft preparation, J.C.R.-M. and M.F.; writing—review and editing, J.C.R.-M. and M.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. The work has not received financial support from our affiliation organizations (CSIC and University of Geneva), other than the regular salary we get from them.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Lau, K.-M.; Weng, H. Climate signal detection using wavelet transform: How to make a time series Sing. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantelhardt, J.W.; Rybski, D.; Zschiegner, S.A.; Braun, P.; Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Livina, V.; Havline, S.; Bunde, A. Multifractality of river runoff and precipitation: Comparison of fluctuation analysis and wavelet methods. Physica A 2003, 330, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Oscillations in land surface hydrological cycle. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2006, 242, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Wavelet analysis of the annual discharge records of the world’s largest rivers. Adv. Water Resour. 2008, 31, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labat, D. Cross wavelet analyses of annual continental freshwater discharge and selected climate indices. J. Hydrol. 2010, 385, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefli, B.; Maraun, D.; Holschneider, M. What drives high flow events in the Swiss Alps? Recent developments in wavelet spectral analysis and their application to hydrology. Adv. Water Resour. 2007, 30, 2511–2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaefli, B.; Zehe, E. Hydrological model performance and parameter estimation in the wavelet-domain. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1921–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, L.; Laignel, B.; Massei, N.; Munier, S.; Becker, M.; Turki, I.; Coynel, A.; Cazenave, A. Hydrological variability of major French rivers over recent decades, assessed from gauging station and GRACE observations. Hydrolog. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1844–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.A.; Schmidt, J.C.; Topping, D.J. Application of wavelet analysis for monitoring the hydrologic effects of dam operation: Glen Canyon dam and the Colorado River at Lees Ferry, Arizona. River Res. Appl. 2005, 21, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keener, V.W.; Feyereisen, G.W.; Lall, U.; Jones, J.W.; Bosch, D.D.; Lowrance, R. El-Niño/Southern Oscillation (ENSO) influences on monthly NO3 load and concentration, stream flow and precipitation in the Little River Watershed, Tifton, Georgia (GA). J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, J.; Hatvania, I.G.; Korponai, J.; Kovács, I.S. Morlet wavelet and autocorrelation analysis of long-term data series of the Kis-Balaton water protection system (KBWPS). Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, K.; Thompson, S.E.; Harman, C.J.; Basu, N.B.; Rao, P.S.C.; Sivapalan, M.; Packman, A.I.; Kalita, P.K. Spatiotemporal scaling of hydrological and agrochemical export dynamics in a tile-drained Midwestern watershed. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W00J02. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koirala, S.R.; Gentry, R.W.; Mulholland, P.J.; Perfect, E.; Schwartz, J.S.; Sayler, G.S. Persistence of hydrologic variables and reactive stream solute concentrations in an east Tennessee watershed. J. Hydrol. 2011, 401, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco-Villoria, M.; Hoey, T.; Fischbacher-Smith, D. Temporal investigation of flow variability in Scottish rivers using wavelet analysis. J. Environ. Stat. 2012, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Mengistu, S.G.; Creed, I.F.; Kulperger, R.J.; Quick, C.G. Russian nesting dolls effect—Using wavelet analysis to reveal non-stationary and nested stationary signals in water yield from catchments on a northern forested landscape. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, S.G.; Quick, C.G.; Creed, F.I. Nutrient export from catchments on forested landscapes reveals complex nonstationary and stationary climate signals. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 3863–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, B.; Mohanty, B.P.; McGuire, J.T.; Cozzarelli, I.M. Temporal dynamics of biogeochemical processes at the Norman Landfill site. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 6909–6926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Val, J.; Pino, R.; Navarro, E.; Chinarro, D. Addressing the local aspects of global change impacts on stream metabolism using frequency analysis tools. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 798–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Y.-F. A review on the applications of wavelet transform in hydrology time series analysis. Atmos. Res. 2013, 122, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, V.; Andalib, G.; Dąbrowska, D. Conjunction of wavelet transform and SOM-mutual information data pre-processing approach for AI-based Multi-Station nitrate modeling of watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2017, 548, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Proc. Geoph. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D.; Kurths, J.; Holschneider, M. Nonstationary Gaussian processes in wavelet domain: Synthesis, estimation and significance testing. Phys. Rev. E 2007, 75, 016707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar-Conraria, L.; Soares, M.J. The continuous wavelet transform: Moving beyond uni- and bivariate analysis. J. Econ. Surv. 2014, 28, 344–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.K. Spectral-temporal characterization of riverflow variability in England and Wales for the period 1865–2002. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, G.P.; Marques, W.C. Long-term temporal variability of the freshwater discharge and water levels at Patos Lagoon, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Int. J. Geoph. 2012, 459497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajwa-Kuligiewicz, A.; Bialik, R.J.; Rowiński, P.M. Wavelet characteristics of hydrological and dissolved oxygen time series in a Lowland River. Acta Geophys. 2016, 64, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broersen, P.M.T. Facts and fiction in spectral analysis. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2000, 49, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Waele, S. Automatic Inference from Finite Time Observations of Stationary Stochastic Signals. Ph.D. Thesis, Delft Technical University, Delft, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Maraun, D.; Kurths, J. Cross wavelet analysis. Significance testing and pitfalls. Nonlinear Process. Geoph. 2004, 11, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z. Significance tests for the wavelet power and the wavelet power spectrum. Ann. Geophys. 2007, 25, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Z. Significance tests for the wavelet cross spectrum and wavelet linear coherence. Ann. Geophys. 2008, 26, 3819–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.A.K.; Walden, A.T. A Statistical Study of Temporally Smoothed Wavelet Coherence. IEEE Trans. Signal Proces. 2010, 58, 2964–2973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maraun, D. What Can We Learn from Climate Data? Methods for Fluctuation, Time/Scale and Phase Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Zobrist, J.; Schoenenberger, U.; Figura, S.; Hug, S.J. Long-term trends in Swiss rivers sampled continuously over 39 years reflect changes in geochemical processes and pollution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16788–16809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botter, M.; Burlando, P.; Fatichi, S. Anthropogenic and catchment characteristic signatures in the water quality of Swiss rivers: A quantitative assessment. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 1885–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koscielny-Bunde, E.; Kantelhardt, J.W.; Braund, P.; Bunde, A.; Havlin, S. Long-term persistence and multifractality of river runoff records: Detrended fluctuation studies. J. Hydrol. 2006, 322, 120–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Murillo, J.C.; Zobrist, J.; Filella, M. Temporal trends in organic carbon content in the main Swiss rivers, 1974–2010. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 206–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broersen, P.M.T. Automatic spectral analysis with time series models. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2002, 51, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broersen, P.M.T. Automatic Autocorrelation and Spectral Analysis; Springer: London, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox, R. Statistical Modeling and Decision Science: Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing, 3rd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2012; pp. 471–532. [Google Scholar]
- Granger, C.W.J. Investigating causal relations by econometric models and cross-spectral methods. Econometrica 1969, 37, 424–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granger, C.W.J. Testing for causality. A personal viewpoint. J. Econ. Dyn. Control 1980, 2, 329–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, M. Causal inference in time series analysis. In Causality: Statistical Perspectives and Applications; Berzuini, C., Dawid, P., Bernardinelli, L., Eds.; Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2013; pp. 327–354. [Google Scholar]
- Beran, J.; Feng, Y.; Ghosh, S.; Kulik, R. Long Memory Processes. Probabilistic Properties and Statistical Methods; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Loizeau, J.-L.; Dominik, J. Evolution of the Upper Rhone River discharge and suspended sediment load during the last 80 years and some implications for Lake Geneva. Aquatic Sci. 2000, 62, 54–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).