Bottom Sediment Characteristics of a Tropical Lake: Lake Tana, Ethiopia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
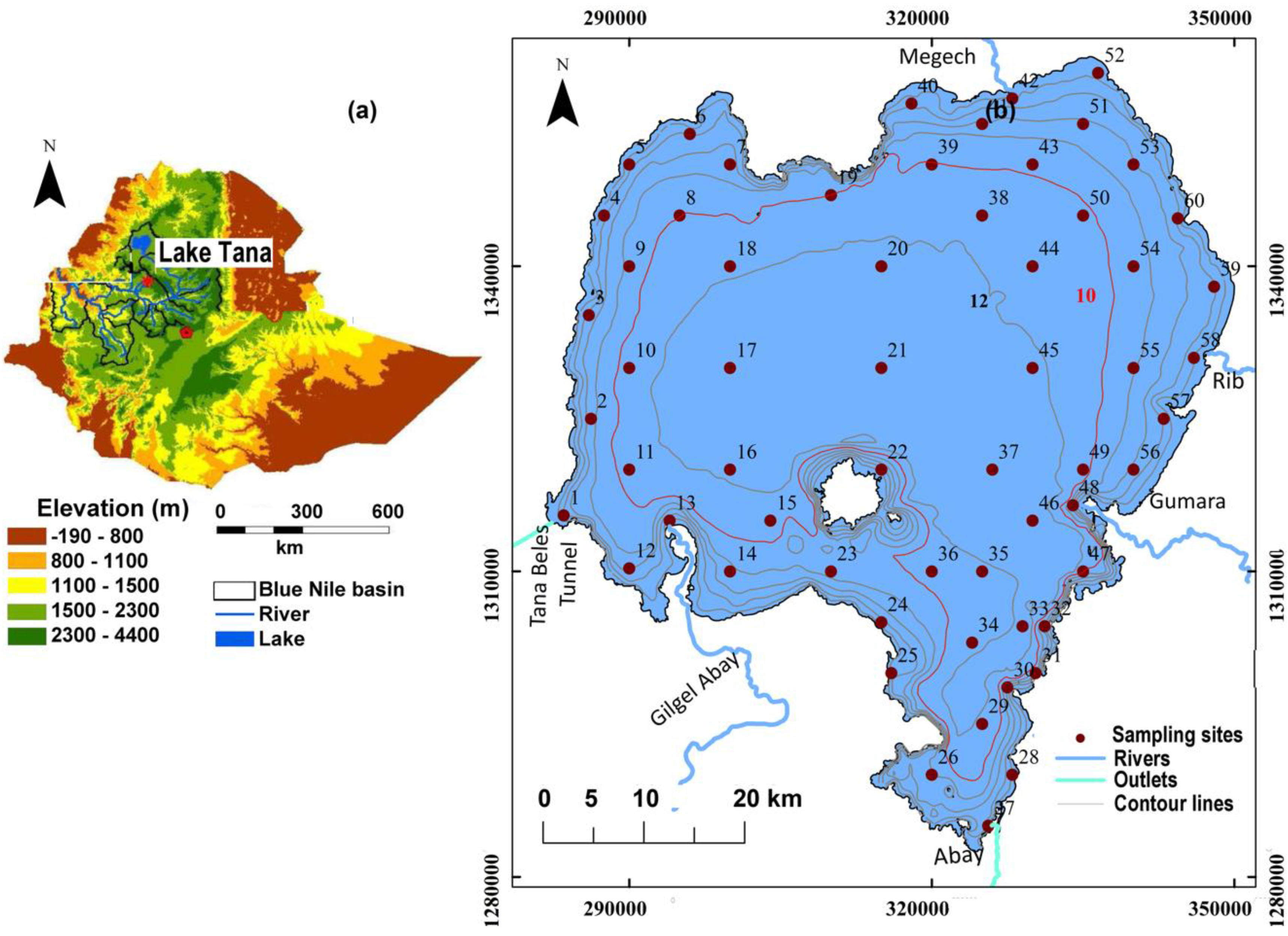
2.1. Study Area
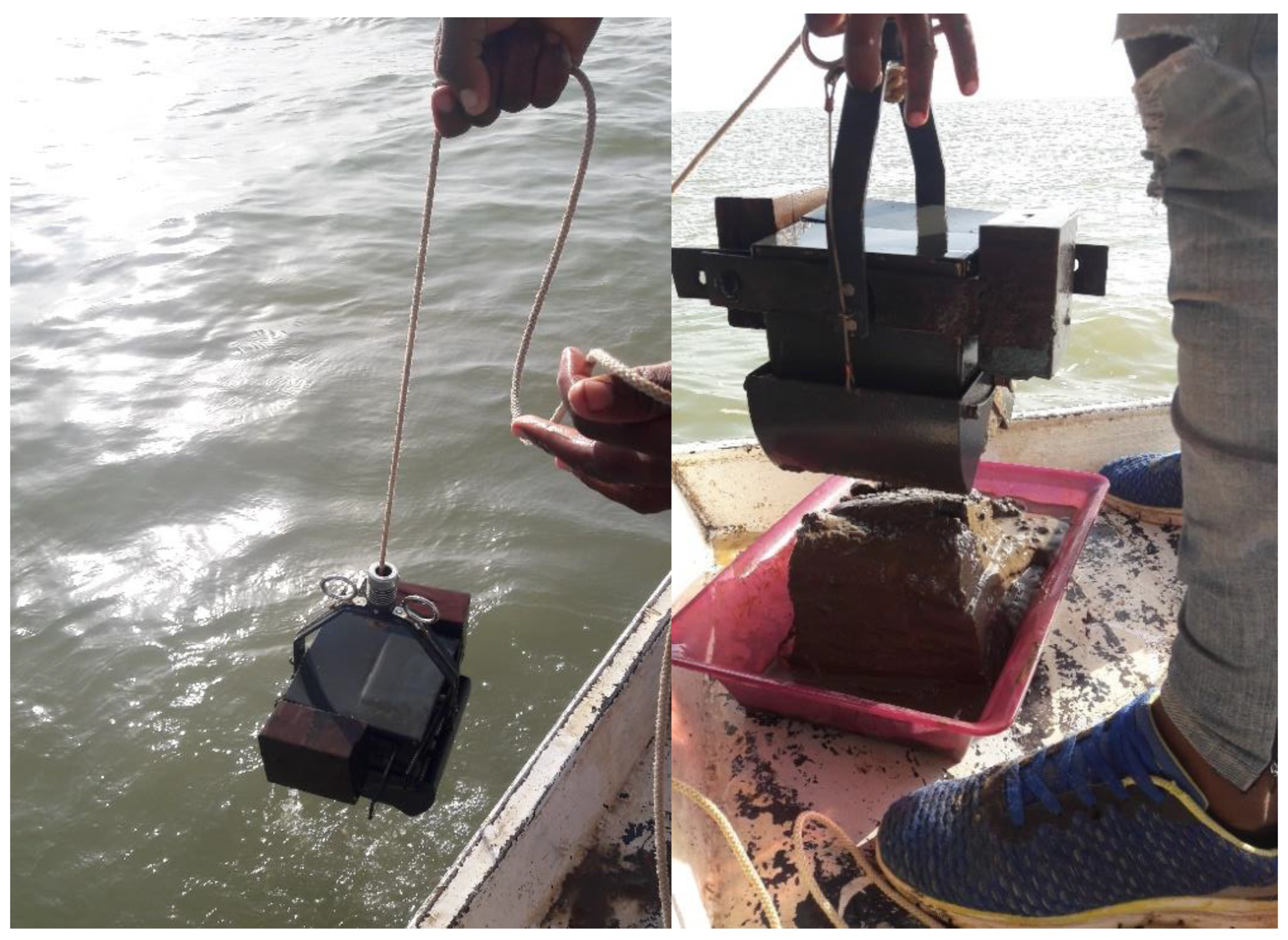
2.2. Bottom Sediment Sampling
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.4. Interpolation
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
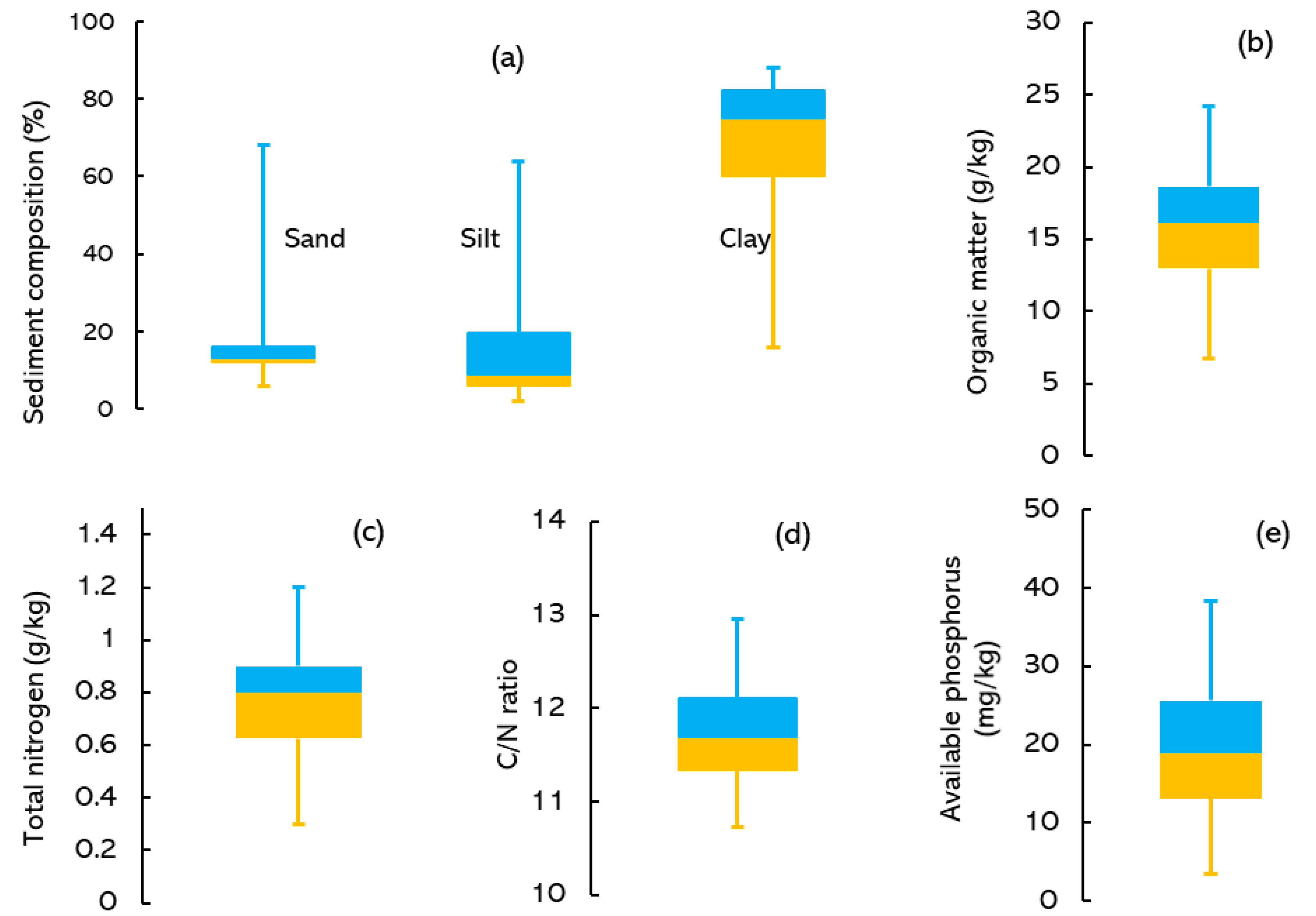
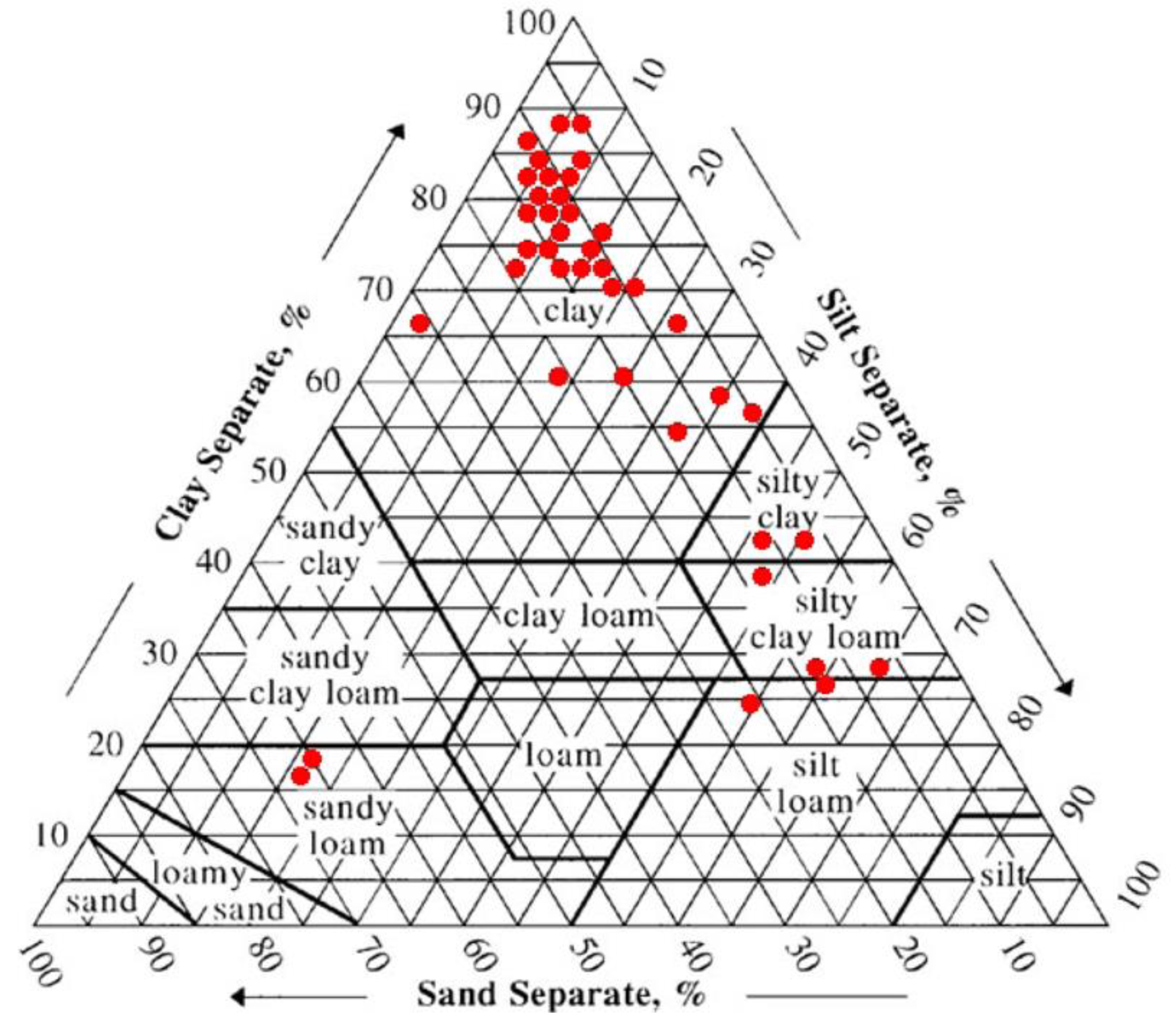
3.1. Bottom Sediment Characteristics of Lake Tana
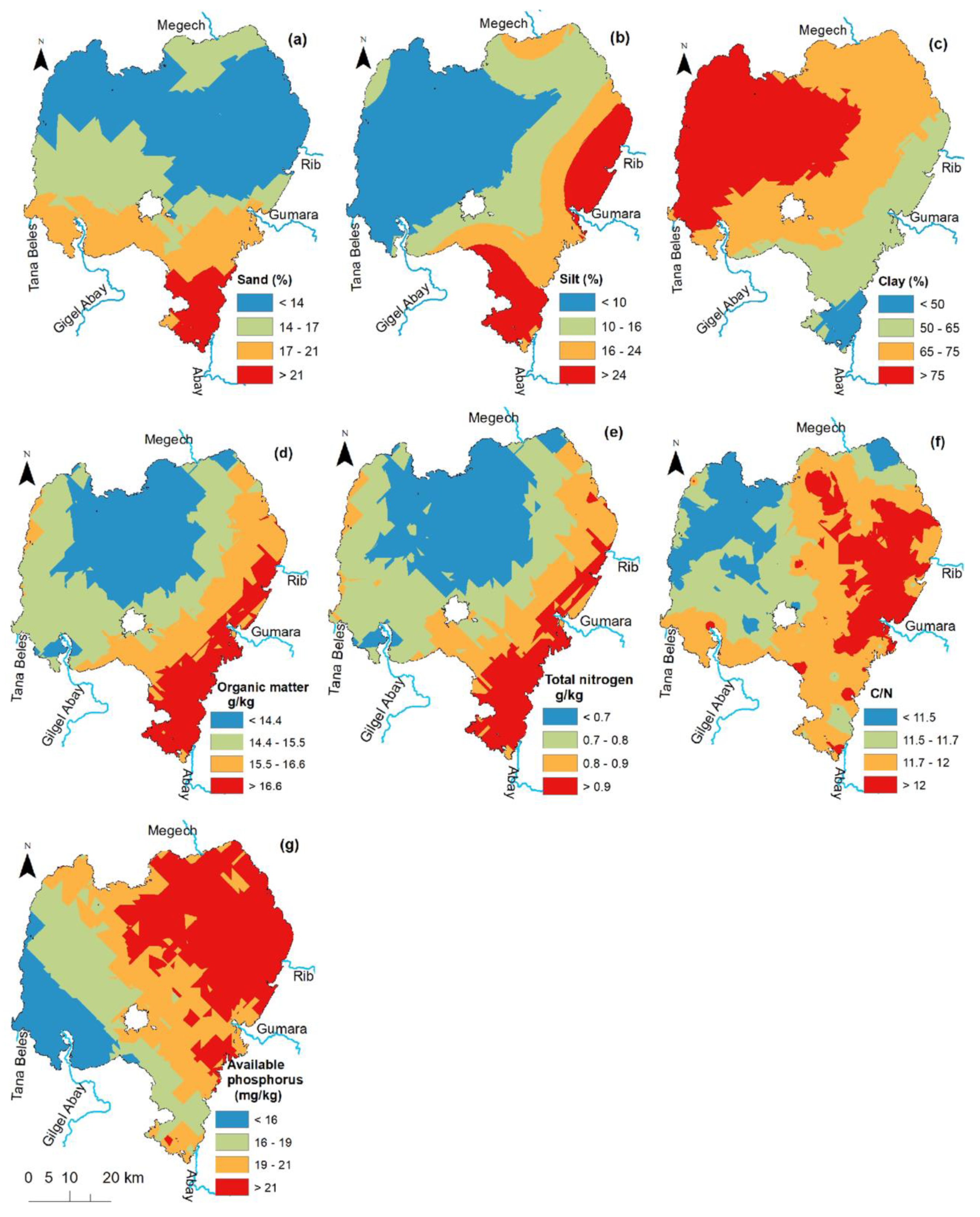
3.2. Spatial Distribution
3.3. Correlation
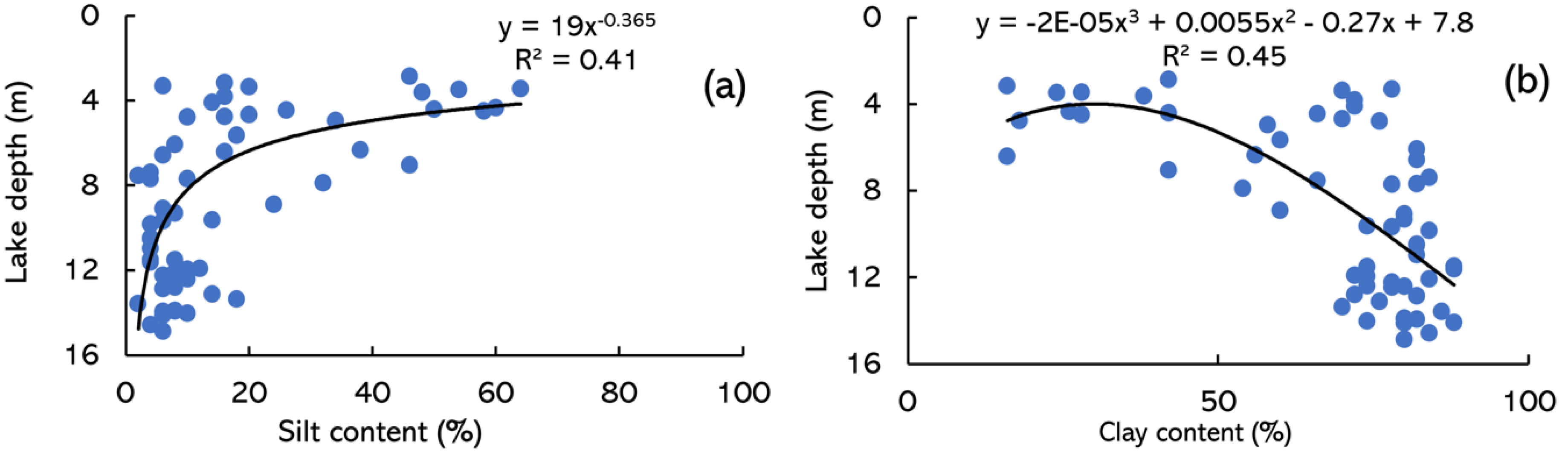
3.4. Relationship with Lake Depth
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Sit. No | X | Y | Sand (%) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | OM g kg−1 | TN g kg−1 | OC g kg−1 | C/N | Av. P mg kg−1 | Dept. (m) | Texture Class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 283000 | 1315000 | 10 | 82 | 8 | 12.1 | 0.6 | 7 | 11.7 | 9.5 | 6.1 | Silty loam |
| 2 | 286200 | 1325000 | 12 | 78 | 10 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 7.8 | 11.1 | 15.4 | 7.7 | Heavy clay |
| 3 | 286000 | 1335200 | 14 | 76 | 10 | 18.2 | 0.9 | 10.6 | 11.7 | 8.6 | 4.8 | Heavy clay |
| 4 | 287500 | 1345000 | 10 | 70 | 20 | 19.5 | 1.0 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 12 | 4.7 | Heavy clay |
| 5 | 290000 | 1350000 | 10 | 70 | 20 | 14.8 | 0.7 | 8.6 | 12.3 | 12 | 3.4 | Heavy clay |
| 6 | 296000 | 1353000 | 16 | 78 | 6 | 17.5 | 0.9 | 10.2 | 11.3 | 6.9 | 3.3 | Heavy clay |
| 7 | 300000 | 1350000 | 14 | 82 | 4 | 11.4 | 0.6 | 6.6 | 11 | 17.1 | 7.7 | Heavy clay |
| 8 | 295000 | 1345000 | 14 | 82 | 4 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 22.3 | 10.5 | Heavy clay |
| 9 | 290000 | 1340000 | 16 | 78 | 6 | 17.5 | 0.9 | 10.2 | 11.3 | 27.4 | 9.7 | Heavy clay |
| 10 | 290000 | 1330000 | 8 | 88 | 4 | 14.1 | 0.7 | 8.2 | 11.7 | 10.3 | 11.6 | Heavy clay |
| 11 | 290000 | 1320000 | 8 | 88 | 4 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 7.8 | 11.5 | Heavy clay |
| 12 | 290000 | 1310300 | 12 | 82 | 6 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 21.4 | 6.6 | Heavy clay |
| 13 | 294000 | 1315000 | 68 | 16 | 16 | 10.8 | 0.5 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 8.6 | 3.2 | Sandy loam |
| 14 | 300000 | 1310000 | 14 | 80 | 6 | 20.2 | 1.0 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 7.8 | 9.1 | Heavy clay |
| 15 | 304000 | 1315000 | 16 | 78 | 6 | 9.4 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 10.9 | 14.6 | 12.2 | Heavy clay |
| 16 | 300000 | 1320000 | 12 | 86 | 2 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 8.6 | 13.6 | Heavy clay |
| 17 | 300000 | 1330000 | 6 | 88 | 6 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 7.8 | 11.1 | 18.9 | 14.1 | Heavy clay |
| 18 | 335000 | 1354000 | 12 | 84 | 4 | 9.4 | 0.5 | 5.5 | 10.9 | 25.7 | 7.5 | Heavy clay |
| 19 | 310000 | 1347000 | 14 | 82 | 4 | 7.4 | 0.4 | 4.3 | 10.7 | 25.7 | 11 | Heavy clay |
| 20 | 315000 | 1340000 | 12 | 80 | 8 | 8.1 | 0.4 | 4.7 | 11.7 | 34.2 | 13.9 | Heavy clay |
| 21 | 315000 | 1330000 | 14 | 80 | 6 | 10.8 | 0.5 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 25.7 | 14.9 | Heavy clay |
| 22 | 315000 | 1320000 | 12 | 80 | 8 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 7.8 | 11.1 | 20.6 | 13.9 | Heavy clay |
| 23 | 310000 | 1310000 | 12 | 74 | 14 | 18.2 | 0.9 | 10.6 | 11.7 | 18.9 | 9.6 | Heavy clay |
| 24 | 315000 | 1305000 | 14 | 28 | 58 | 10.8 | 0.5 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 4.5 | Silty clay loam |
| 25 | 316000 | 1300000 | 14 | 26 | 60 | 24.2 | 0.12 | 14 | 11.7 | 18.9 | 4.4 | Silty loam |
| 26 | 320000 | 1290000 | 16 | 60 | 24 | 18.2 | 0.9 | 10.6 | 11.7 | 18 | 8.9 | Clay |
| 27 | 325600 | 1285000 | 66 | 18 | 16 | 14.8 | 0.7 | 8.6 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 4.8 | Sandy loam |
| 28 | 328000 | 1290000 | 14 | 38 | 48 | 23.5 | 1.2 | 13.6 | 11.4 | 12.9 | 3.6 | Silty clay loam |
| 29 | 325000 | 1295000 | 14 | 78 | 8 | 17.5 | 0.9 | 10.2 | 11.3 | 27.4 | 12.5 | Heavy clay |
| 30 | 327500 | 1298600 | 6 | 56 | 38 | 8.7 | 0.4 | 5 | 12.6 | 38.5 | 6.3 | Clay |
| 31 | 330300 | 1300000 | 68 | 16 | 16 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 18 | 6.4 | Sandy loam |
| 32 | 331200 | 1304600 | 22 | 60 | 18 | 22.9 | 1.1 | 13.3 | 12.1 | 17.1 | 5.7 | Clay |
| 33 | 329000 | 1304600 | 16 | 74 | 10 | 14.1 | 0.7 | 8.2 | 11.7 | 6.1 | 14 | Heavy clay |
| 34 | 324000 | 1303000 | 16 | 74 | 10 | 19.5 | 1.0 | 11.3 | 11.3 | 28.2 | 12.4 | Heavy clay |
| 35 | 325000 | 1310000 | 20 | 72 | 8 | 18.8 | 0.9 | 10.9 | 12.1 | 16.3 | 12.8 | Heavy clay |
| 36 | 320000 | 1310000 | 16 | 74 | 10 | 18.2 | 0.9 | 10.6 | 11.7 | 24.8 | 12 | Heavy clay |
| 37 | 326000 | 1320000 | 14 | 80 | 6 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 24 | 14.1 | Heavy clay |
| 38 | 325000 | 1345000 | 12 | 80 | 8 | 18.8 | 0.9 | 10.9 | 12.1 | 6.9 | 12.4 | Heavy clay |
| 39 | 320000 | 1350000 | 18 | 74 | 8 | 6.7 | 0.3 | 3.9 | 13 | 17.1 | 11.5 | Heavy clay |
| 40 | 318000 | 1356000 | 14 | 72 | 14 | 14.1 | 0.7 | 8.2 | 11.7 | 31.6 | 4.1 | Heavy clay |
| 41 | 325000 | 1354000 | 14 | 54 | 32 | 20.2 | 1.0 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 14.6 | 7.9 | Clay |
| 42 | 328000 | 1356500 | 12 | 42 | 46 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 14.6 | 2.9 | Clay |
| 43 | 330000 | 1350000 | 14 | 82 | 4 | 16.1 | 0.8 | 9.3 | 11.7 | 27.4 | 10.5 | Heavy clay |
| 44 | 330000 | 1340000 | 12 | 82 | 6 | 21.5 | 1.1 | 12.5 | 11.3 | 32.5 | 12.9 | Heavy clay |
| 45 | 330000 | 1330000 | 12 | 70 | 18 | 12.1 | 0.6 | 7 | 11.7 | 23.1 | 13.4 | Heavy clay |
| 46 | 330000 | 1315000 | 12 | 82 | 6 | 14.8 | 0.7 | 8.6 | 12.3 | 20.6 | 13.9 | Heavy clay |
| 47 | 335000 | 1310000 | 16 | 72 | 12 | 23.5 | 1.2 | 13.6 | 11.4 | 32.5 | 11.9 | Heavy clay |
| 48 | 334000 | 1316500 | 22 | 24 | 54 | 16.8 | 0.8 | 9.7 | 12.2 | 23.1 | 3.5 | Clay loam |
| 49 | 335000 | 1320000 | 10 | 76 | 14 | 10.8 | 0.5 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 13.7 | 13.1 | Heavy clay |
| 49 | 348000 | 1338000 | 8 | 58 | 34 | 22.2 | 1.1 | 12.9 | 11.7 | 29.1 | 5 | Clay |
| 50 | 335000 | 1345000 | 8 | 84 | 8 | 14.8 | 0.7 | 8.6 | 12.3 | 19.7 | 12.1 | Heavy clay |
| 51 | 300000 | 1340000 | 32 | 66 | 2 | 17.5 | 0.9 | 10.2 | 11.3 | 30.8 | 12.8 | Heavy clay |
| 52 | 336500 | 1359000 | 12 | 72 | 16 | 13.4 | 0.7 | 7.8 | 11.1 | 24 | 3.8 | Heavy clay |
| 53 | 340000 | 1350000 | 12 | 84 | 4 | 14.1 | 0.7 | 8.2 | 11.7 | 18.9 | 7.4 | Heavy clay |
| 54 | 340000 | 1340000 | 12 | 84 | 4 | 10.8 | 0.5 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 25.7 | 9.8 | Heavy clay |
| 55 | 340000 | 1330000 | 12 | 80 | 8 | 12.8 | 0.6 | 7.4 | 12.4 | 3.5 | 9.3 | Heavy clay |
| 56 | 340000 | 1320000 | 12 | 42 | 46 | 16.8 | 0.8 | 9.7 | 12.2 | 26.5 | 7.1 | Clay |
| 57 | 343000 | 1325000 | 8 | 42 | 50 | 21.5 | 1.1 | 12.5 | 11.3 | 18 | 4.4 | Clay |
| 58 | 346000 | 1331000 | 8 | 28 | 64 | 20.2 | 1.0 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 29.9 | 3.4 | Silty clay loam |
| 59 | 348000 | 1338000 | 8 | 58 | 34 | 22.2 | 1.1 | 12.9 | 11.7 | 29.1 | 4.951 | Clay |
| 60 | 344400 | 1344700 | 8 | 66 | 26 | 20.2 | 1.0 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 27.4 | 4.5 | Heavy clay |
References
- Hou, X.; Feng, L.; Duan, H.; Chen, X.; Sun, D.; Shi, K. Fifteen-year monitoring of the turbidity dynamics in large lakes and reservoirs in the middle and lower basin of the yangtze river, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimore, M. Population growth and land degradation. GeoJournal 1993, 31, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Jang, T.I.; Kang, M.S.; Im, S.J.; Park, S.W. Gis-based lake sediment budget estimation taking into consideration land use change in an urbanizing catchment area. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 2155–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.V. Water Quality Assessments: A Guide to the Use of Biota, Sediments, and Water in Environmental Monitoring; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Almada Rojas, G.; Palafox, J.T.P.; Uribe, D.M.; Gaytan, J.M.; Garcia, L.F.C.; Figueroa, J.L.A. Morphological, sediment and soil chemical characteristics of dry tropical shallow reservoirs in the southern mexican heghlands. J. Limnol. 2011, 70, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.L.; Fan, J. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook: Design and Management of Dams, Reservoirs, and Watersheds for Sustainable Use; McGraw Hill Professional: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Danz, N.P.; Niemi, G.J.; Regal, R.R.; Hollenhorst, T.; Johnson, L.B.; Hanowski, J.M.; Axler, R.P.; Ciborowski, J.J.; Hrabik, T.; Brady, V.J. Integrated measures of anthropogenic stress in the us great lakes basin. Environ. Manag. 2007, 39, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L.; Jansson, M. Principles of Lake Sedimentology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1983; Volume 316. [Google Scholar]
- Balamurugan, P.; Vasudevan, S.; Selvaganapathi, R.; Nishikanth, C. Spatial distribution of grain size characteristics and its role in interpreting the sedimentary depositional environment, Kodaikanal Lake, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Earth Sci. Clim. Chang. 2014, 5, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Mclaren, P.; Bowles, D. The effects of sediment transport on grain-size distributions. J. Sediment. Petrol. 1985, 55, 457–470. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, G.; Collins, M. The use of grain size trends in marine sediment dynamics: A review. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2001, 19, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremariam, B. Basin Scale Sedimentary and Water Quality: Responses to External Forcing in Lake Abaya, Southern Ethiopian Rift Valley. 2009. Available online: https://refubium.fu-berlin.de/handle/fub188/6983 (accessed on 19 March 2019).
- Shah, R.A.; Achyuthan, H.; Puthan-Veettil, R.S.; Derwaish, U.; Rafiq, M. Sediment distribution pattern and environmental implications of physico-chemical characteristics of the Akkulam-Veli Lake, South India. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwamburi, J. Spatial variations in sedimentary organic matter in surficial lake sediments of nyanza gulf (lake victoria, kenya) after invasion of water hyacinth. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2016, 21, 94–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraj, R.; Achyuthan, H. Distribution of sediments and organic matter source: Berijam lake, tamil nadu. J. Geol. Soc. India 2015, 86, 620–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lone, A.M.; Shah, R.A.; Achyuthan, H.; Rafiq, M. Source identification of organic matter using c/n ratio in freshwater lakes of Kashmir Valley, Western Himalaya, India. Himal. Geol. 2018, 39, 101–114. [Google Scholar]
- Hamidi, S.A.; Hosseiny, H.; Ekhtari, N.; Khazaei, B. Using modis remote sensing data for mapping the spatio-temporal variability of water quality and river turbid plume. J. Coast. Conserv. 2017, 21, 939–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fish, G.R.; Andrew, I.A. Nitrogen and phosphorus in the sediments of lake rotorua. N. Z. J. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1980, 14, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liang, T. Distribution characteristics of phosphorus in the sediments and overlying water of Poyang lake. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crane, J.L. Ambient sediment quality conditions in minnesota lakes, USA: Effects of watershed parameters and aquatic health implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 607–608, 1320–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheesman, R.E. Lake Tana & the Blue Nile: An Abyssinian Quest; Frankcas and Company Ltd.: London, UK, 1936. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, H.M.; Bryant, C.L.; Huws, D.G.; Lamb, H.F. Generating long chronologies for lacustrine sediments using luminescence dating: A 250,000 year record from lake tana, ethiopia. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2018, 202, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, H.F.; Bates, C.R.; Bryant, C.L.; Davies, S.J.; Huws, D.G.; Marshall, M.H.; Roberts, H.M.; Toland, H. 150,000-year palaeoclimate record from northern ethiopia supports early, multiple dispersals of modern humans from Africa. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, M.; Nyssen, J.; Moges, M.M.; Enku, T.; Zimale, F.A.; Tilahun, S.A.; Adgo, E.; Steenhuis, T.S. Long-term landscape changes in the lake tana basin as evidenced by delta development and floodplain aggradation in ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1820–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondie, A.; Mengistu, S.; Vijverberg, J.; Dejen, E. Seasonal variation in primary production of a large high altitude tropical lake (lake tana, ethiopia): Effects of nutrient availability and water transparency. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, M.L.; Geset, M.; Mosa, H.M.; Zemale, F.A.; Moges, M.A.; Giri, S.K.; Tillahun, S.A.; Melesse, A.M.; Ayana, E.K.; Steenhuis, T.S. Spatial and temporal trends of recent dissolved phosphorus concentrations in lake tana and its four main tributaries. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1742–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijverberg, J.; Sibbing, F.A.; Dejen, E. Lake Tana: Source of the Blue Nile, in The Nile; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 163–192. [Google Scholar]
- Dejen, E.; Anteneh, W.; Vijverberg, J. The decline of the lake tana (ethiopia) fisheries: Causes and possible solutions. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dersseh, M.G.; Kibret, A.A.; Tilahun, S.A.; Worqlul, A.W.; Moges, M.A.; Dagnew, D.C.; Abebe, W.B.; Melesse, A.M. Potential of water hyacinth infestation on lake tana, ethiopia: A prediction using a gis-based multi-criteria technique. Water 2019, 11, 1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshu, G.; Byamukama, D.; Manafi, M.; Kirschner, A.K.; Farnleitner, A.H. A pilot study on anthropogenic faecal pollution impact in bahir dar gulf of lake tana, northern ethiopia. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2010, 10, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshu, G.; Koelmans, A.; de Klein, J. Water Quality of Lake Tana Basin, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. A Review of Available Data, in Social and Ecological System Dynamics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 127–141. [Google Scholar]
- Anteneh, W.; Dereje, T.; Addisalem, A.; Abebaw, Z.; Befta, T. Water Hyacinth Coverage Survey Report on Lake Tana; Bahir Dar University: Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wondie, A. Dynamics of the Major Phytoplankton and Zooplankton Communities and Their Role in the Food Web of Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Ph.D. Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2006; 162p. [Google Scholar]
- Ligdi, E.E.; El Kahloun, M.; Meire, P. Ecohydrological status of lake tana—A shallow highland lake in the blue nile (abbay) basin in ethiopia. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2010, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondim, Y.K.; Mosa, H.M. Spatial variation of sediment physicochemical characteristics of lake tana, ethiopia. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 5, 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Ewnetu, D.A. Determination of Surface Water Quality Status and Identifying Potential Pollution Sources of Lake Tana: Particular Emphasis on the Lake Boundary of Bahirdar City, Amhara Region, North West Ethiopia. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kaba, E. Validation of Altimetry Lake Level Data and Its Application in Water Resources Management. Master’s Thesis, ITC, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zimale, F.A.; Moges, M.A.; Alemu, M.L.; Ayana, E.K.; Demissie, S.S.; Tilahun, S.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. Budgeting suspended sediment fluxes in tropical monsoonal watersheds with limited data: The lake tana basin. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2018, 66, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemma, H.; Admasu, T.; Dessie, M.; Fentie, D.; Deckers, J.; Frankl, A.; Poesen, J.; Adgo, E.; Nyssen, J. Revisiting lake sediment budgets: How the calculation of lake lifetime is strongly data and method dependent. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2018, 43, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppe, L.; Frankl, A.; Poesen, J.; Admasu, T.; Dessie, M.; Adgo, E.; Deckers, J.; Nyssen, J. Geomorphology of the lake tana basin, ethiopia. J. Maps 2013, 9, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, M. Ecosystem services and tourism potential in lake tana peninsula: Ethiopia review. J. Tour. Hosp. 2017, 6, 2167-0269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worku, M. Lake tana as biosphere reserve: Review. J. Tour. Hosp. 2017, 6, 2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awulachew, S.B.; McCartney, M.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Ahmed, A.A. A Review of Hydrology, Sediment and Water Resource Use in the Blue Nile Basin; IWMI: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009; Volume 131. [Google Scholar]
- Wosenie, M.D.; Verhoest, N.; Pauwels, V.; Negatu, T.A.; Poesen, J.; Adgo, E.; Deckers, J.; Nyssen, J. Analyzing runoff processes through conceptual hydrological modeling in the upper blue nile basin, ethiopia. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 5149–5167. [Google Scholar]
- Zegeye, A.D.; Langendoen, E.J.; Stoof, C.R.; Tilahun, S.A.; Dagnew, D.C.; Zimale, F.A.; Guzman, C.D.; Yitaferu, B.; Steenhuis, T.S. Morphological dynamics of gully systems in the subhumid ethiopian highlands: The debre mawi watershed. Soil 2016, 2, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taffese, T.; Tilahun, S.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. Phosphorus modeling, in lake tana basin, ethiopia. J. Environ. Hum. 2014, 2, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, M.A.; Schmitter, P.; Tilahun, S.A.; Ayana, E.K.; Ketema, A.A.; Nigussie, T.E.; Steenhuis, T.S. Water quality assessment by measuring and using landsat 7 etm+ images for the current and previous trend perspective: Lake tana ethiopia. J. Water Resour. Protect. 2017, 9, 1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ekman, S. Neue apparate zur qualitativen und quantitativen erforschung der bodenfauna der seen. Int. Rev. Gesamten Hydrobiol. Hydrogr. 1911, 3, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewis, J.; Freitas, F. Physical and Chemical Methods of Soil and Water Analysis; FAO Soils Bulletin: Rome, Italy, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Garc a-Gaines, R.A.; Frankenstein, S. Uscs and the Usda Soil Classification System: Development of a Mapping Scheme; Engineer Research And Development Center Hanover Nh Cold Regions Research: Hanover, NH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, G.; Craze, B.; Stone, M.; Crouch, R. Guidelines for Analytical Laboratory Safety; Department of Conservation & Land Management: Hanover, NH, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Hyne, N.J. The distribution and source of organic matter in reservoir sediments. Environ. Geol. 1978, 2, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, K.; Hoef, J.M.V.; Krivoruchko, K.; Lucas, N. Using Arcgis Geostatistical Analyst; ESRI: Redlands, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 380. [Google Scholar]
- Blais, J.M.; Kalff, J. The influence of lake morphometry on sediment focusing. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1995, 40, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, M.; Nyssen, J.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Moges, M.M.; Tilahun, S.A.; Enku, T.; Adgo, E. Morphological changes of gumara river channel over 50 years, upper blue nile basin, ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2015, 525, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dargahi, B.; Setegn, S.G. Combined 3d hydrodynamic and watershed modelling of lake tana, ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2011, 398, 44–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, L.M.; Hecky, R.E.; Muggide, R.; Dixon, D.G.; Ramlal, P.S. Variation and distribution of total mercury in water, sediment and soil from northern lake victoria, east africa. Biogeochemistry 2003, 65, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, G.S.; Katz, B.J.; Scholz, C.A.; Swart, P.K. Organic Sedimentation in Modern Lacustrine Systems: A Case Study from Lake Malawi, East Africa. Paying Attention to Mudrocks: Priceless; Geological Society of America: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 19–47. [Google Scholar]
- Soreghan, M.J.; Cohen, A.S. Textural and compositional variability across littoral segments of lake tanganyika: The effect of asymmetric basin structure on sedimentation in large rift lakes. AAPG Bull. Am. Assoc. Pet. Geol. 1996, 80, 382–409. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Y.; Brown, E.T.; Crowe, S.A.; Katsev, S. Sediment geochemistry and contributions to carbon and nutrient cycling in a deep meromictic tropical lake: Lake malawi (east africa). J. Great Lakes Res. 2018, 44, 1221–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olando, G.; Olaka, L.A.; Okinda, P.O.; Abuom, P. Heavy metals in surface sediments of lake naivasha, kenya: Spatial distribution, source identification and ecological risk assessment. SN Appl. Sci. 2020, 2, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, P.P.; Allan, J.A. The Nile: Sharing a Scarce Resource; Howell, P.P., Allan, J.A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; p. 426. ISBN 0521450403. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, R.A.; Achyuthan, H.; Lone, A.M.; Ramanibai, R. Diatoms, spatial distribution and physicochemical characteristics of the wular lake sediments, kashmir valley, jammu and kashmir. J. Geol. Soc. India 2017, 90, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, P. Sedimentation of organic and inorganic particulate material in lindaaspollene, a stratified, land-locked fjord in western norway. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Oldend. 1983, 13, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyers, P.A. Preservation of elemental and isotopic source identification of sedimentary organic-matter. Chem. Geol. 1994, 114, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, M.A.; Tilahun, S.A.; Ayana, E.K.; Moges, M.M.; Gabye, N.; Giri, S.; Steenhuis, T.S. Non-point source pollution of dissolved phosphorus in the ethiopian highlands: The awramba watershed near lake tana. Clean Soil Air Water 2016, 44, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sand (%) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | OM (g/kg) | TN (g/kg) | C/N Ratio | Av.P (mg/kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sand (%) | 1 | ||||||
| Clay (%) | −0.581 | 1 | |||||
| Silt (%) | −0.049 | −0.784 | 1 | ||||
| OM (g/kg) | −0.051 | −0.244 | 0.338 | 1 | |||
| TN (g/kg) | −0.071 | −0.206 | 0.307 | 0.993 | 1 | ||
| C/N | 0.175 | −0.265 | 0.192 | −0.199 | −0.307 | 1 | |
| Av.P (mg/kg) | −0.137 | 0.026 | 0.072 | 0.013 | 0.036 | −0.146 | 1 |
| Depth (m) | −0.192 | 0.621 | −0.615 | −0.237 | −0.223 | −0.048 | 0.140 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kebedew, M.G.; Tilahun, S.A.; Zimale, F.A.; Steenhuis, T.S. Bottom Sediment Characteristics of a Tropical Lake: Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Hydrology 2020, 7, 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010018
Kebedew MG, Tilahun SA, Zimale FA, Steenhuis TS. Bottom Sediment Characteristics of a Tropical Lake: Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Hydrology. 2020; 7(1):18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010018
Chicago/Turabian StyleKebedew, Mebrahtom G., Seifu A. Tilahun, Fasikaw A. Zimale, and Tammo S. Steenhuis. 2020. "Bottom Sediment Characteristics of a Tropical Lake: Lake Tana, Ethiopia" Hydrology 7, no. 1: 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010018
APA StyleKebedew, M. G., Tilahun, S. A., Zimale, F. A., & Steenhuis, T. S. (2020). Bottom Sediment Characteristics of a Tropical Lake: Lake Tana, Ethiopia. Hydrology, 7(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010018









