Assessment of Erosion in River Basins: A Distributed Model to Estimate the Sediment Production over Watersheds by a 3-Dimensional LS Factor in RUSLE Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
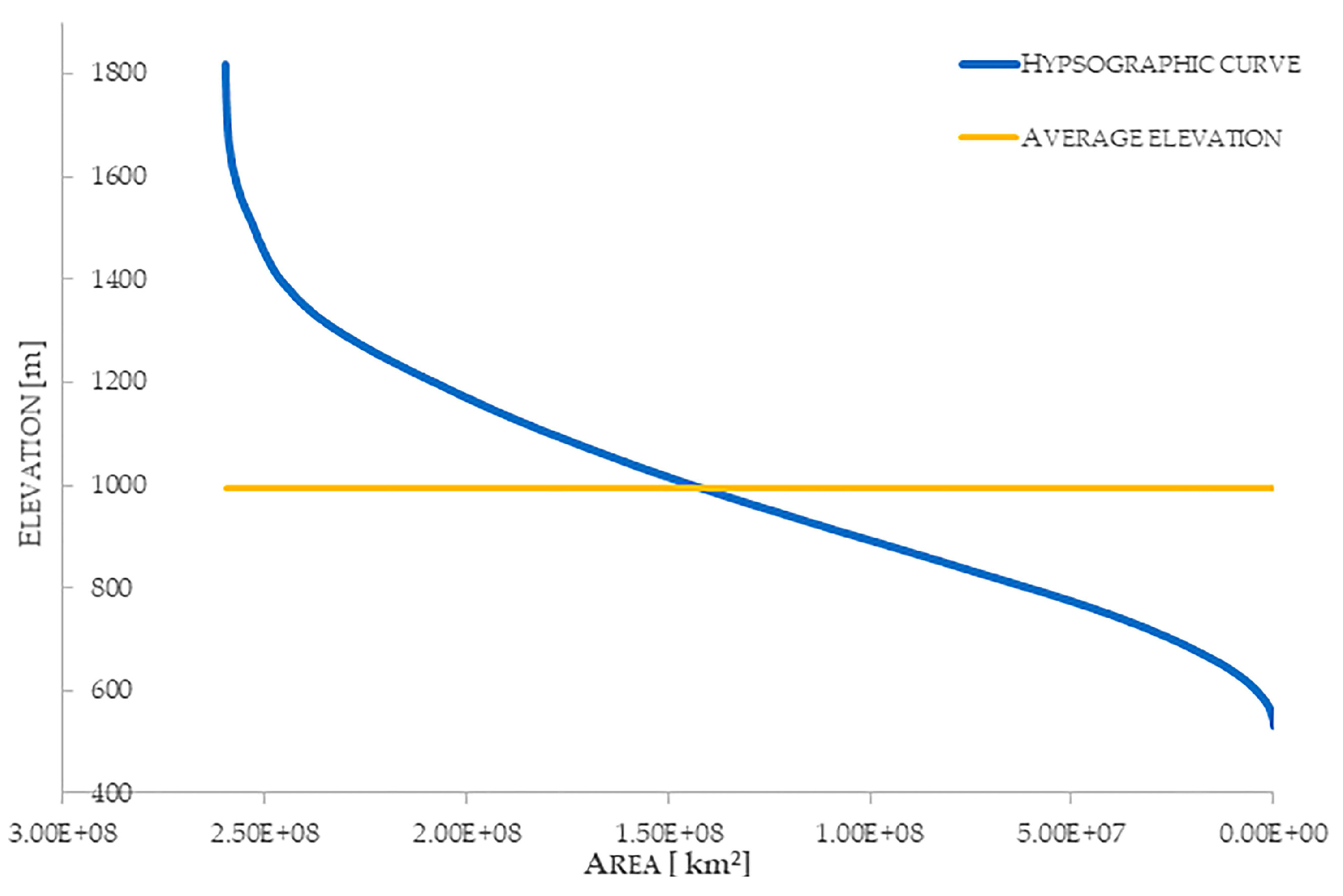
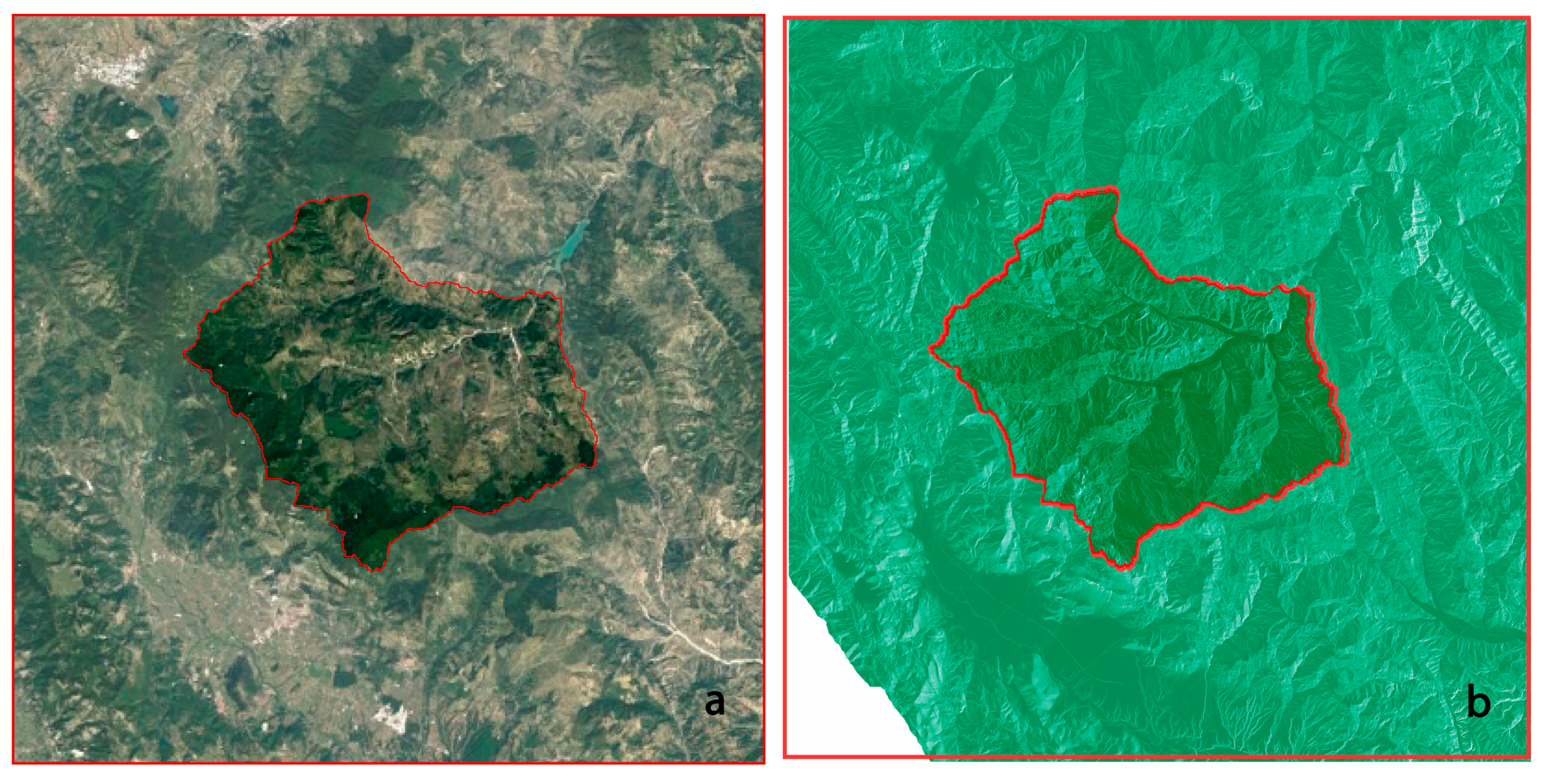
2.1. The Study Area
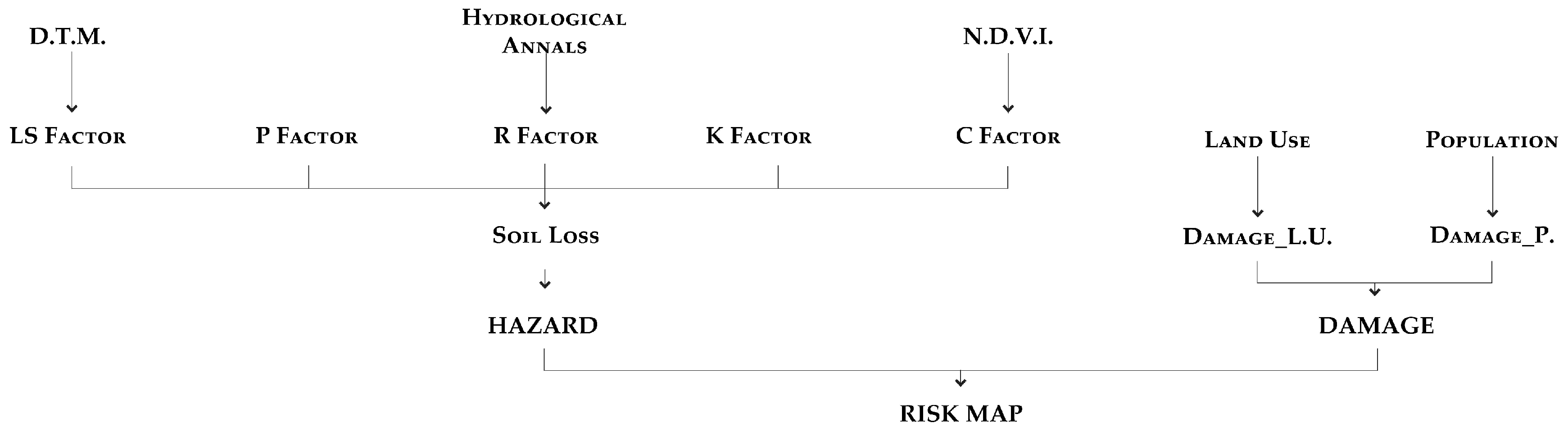
2.2. The RUSLE Approach
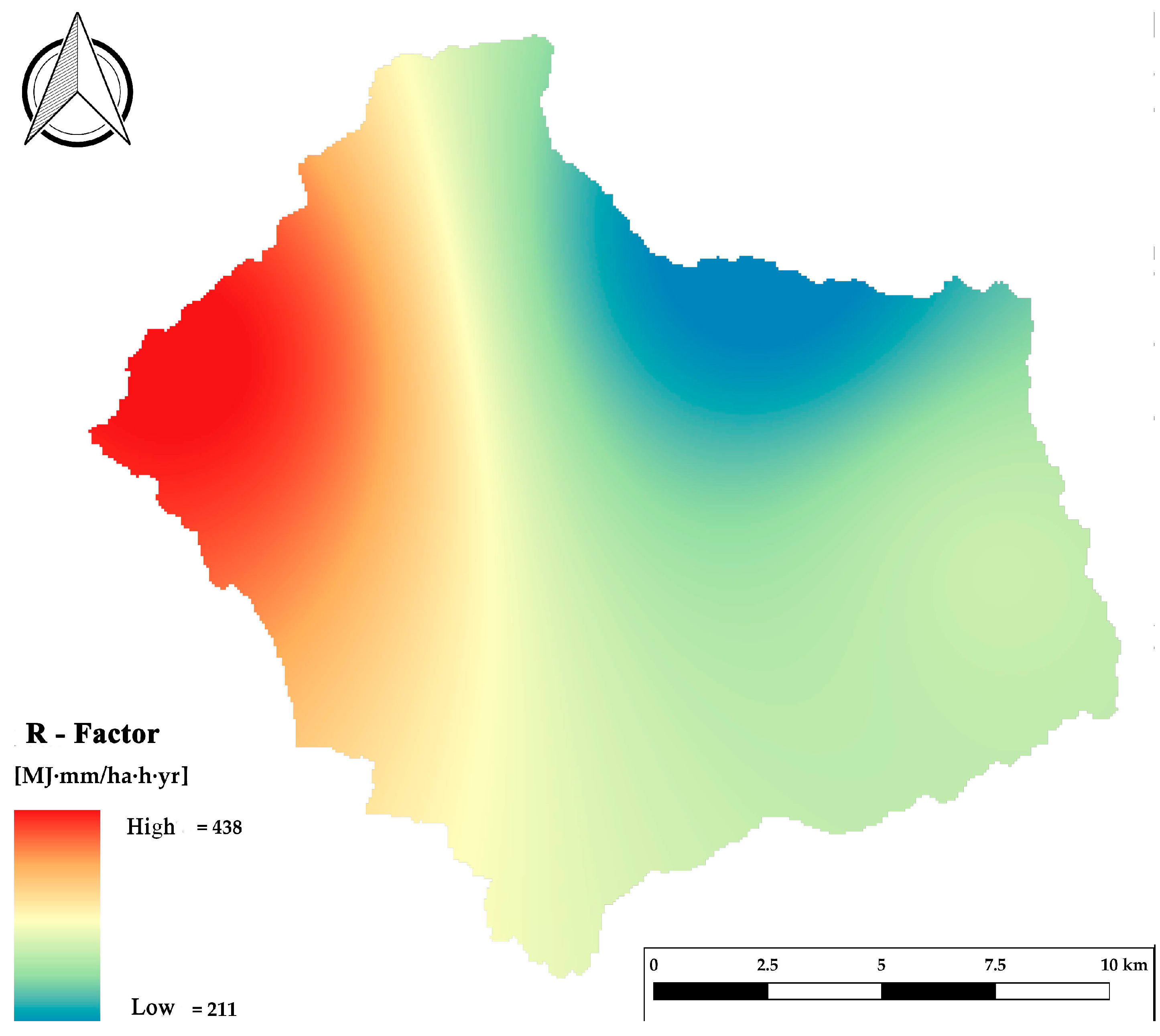
2.2.1. R-Factor
2.2.2. K-Factor
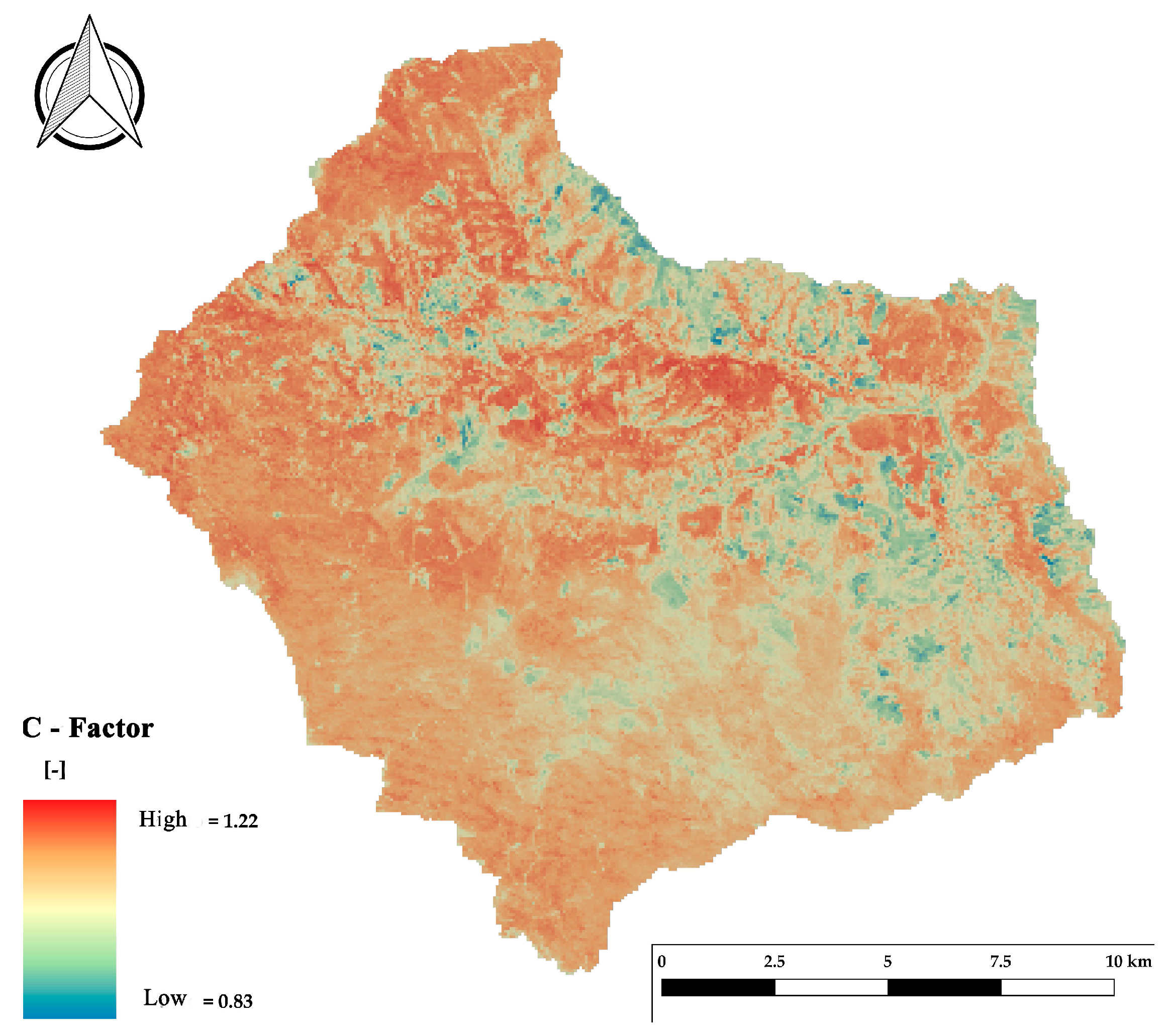
2.2.3. C-Factor
2.2.4. P-Factor
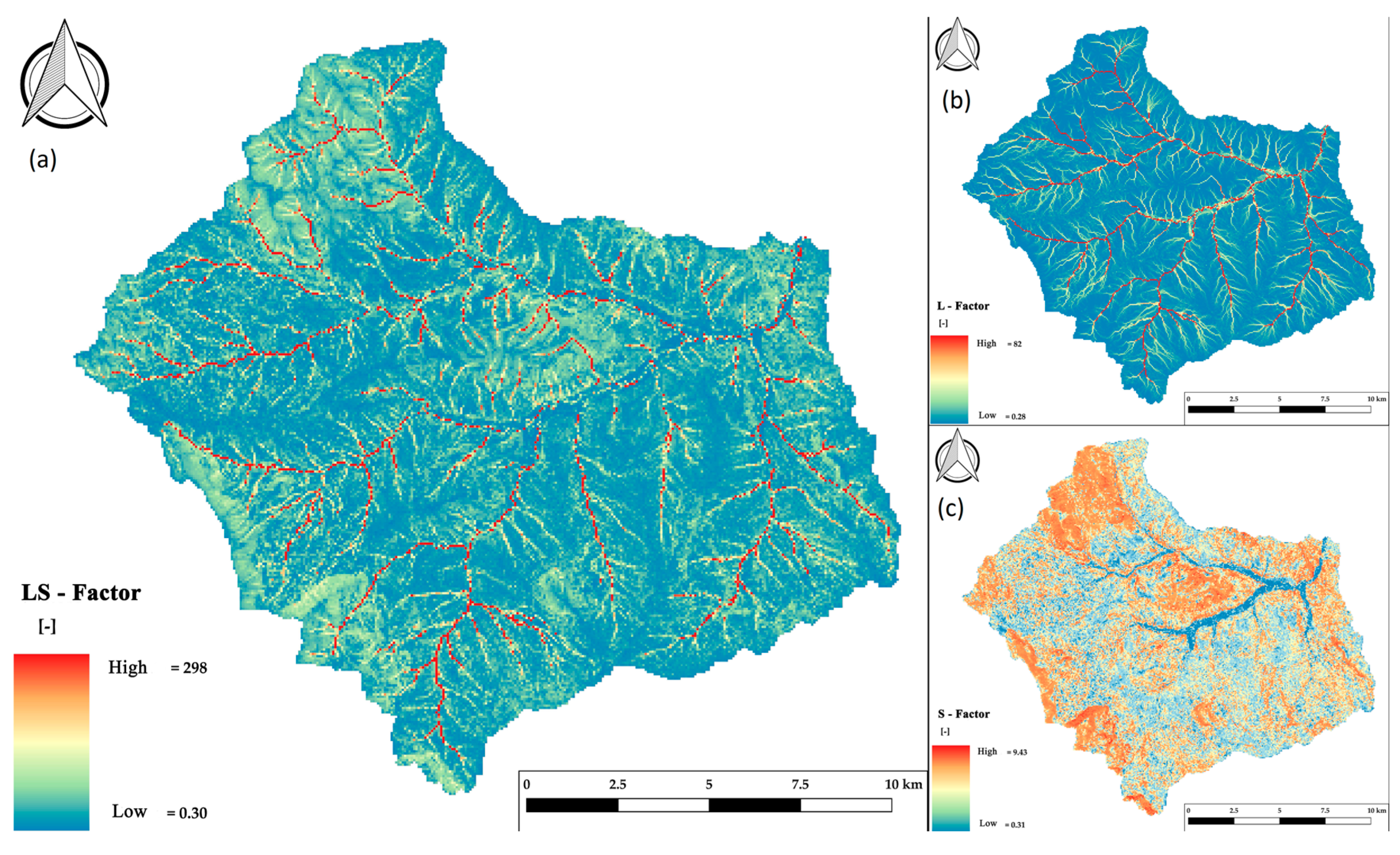
2.2.5. LS-Factor
- for hillsides longer than 4.6 m (15 feet), it is evaluated with a piecewise function:
- for hillsides of less than 4.6 m in length, the following relationship must be used:
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Model Setting and Input Parameters
3.1.1. R-Factor
3.1.2. K-Factor
3.1.3. C-Factor
3.1.4. P-Factor
3.1.5. LS-Factor
L-Subfactor
S-Subfactor
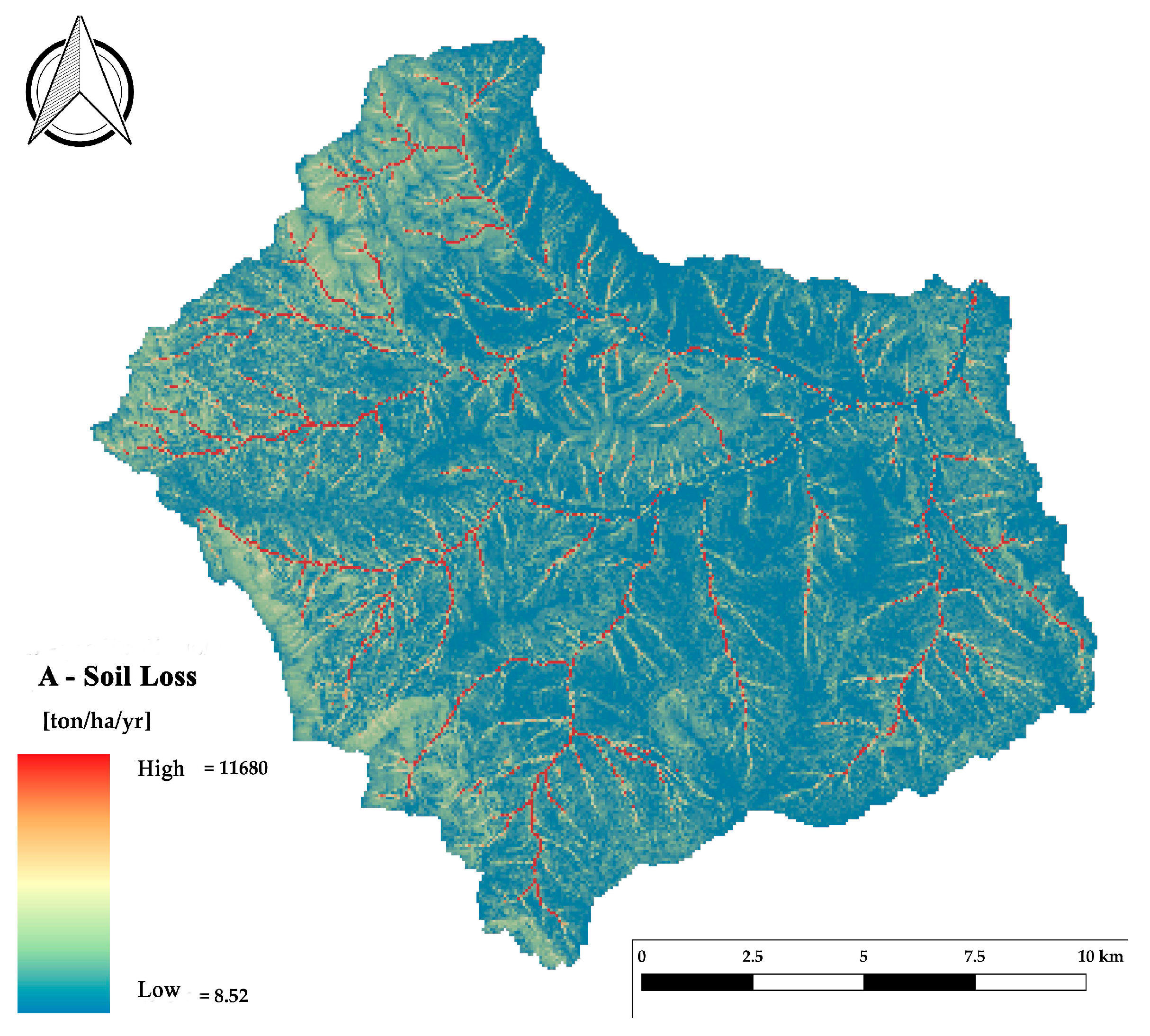
3.1.6. Estimate of Soil Loss
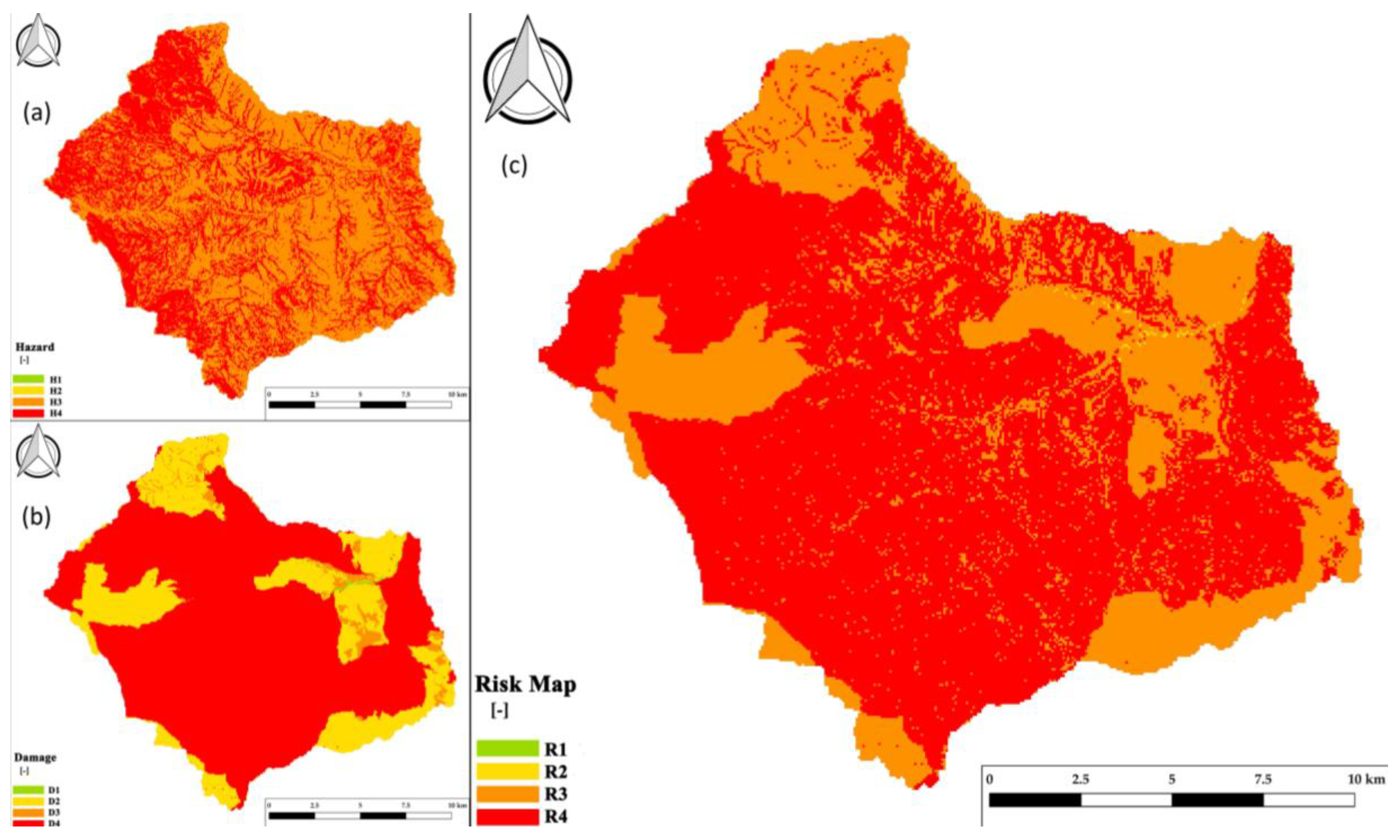
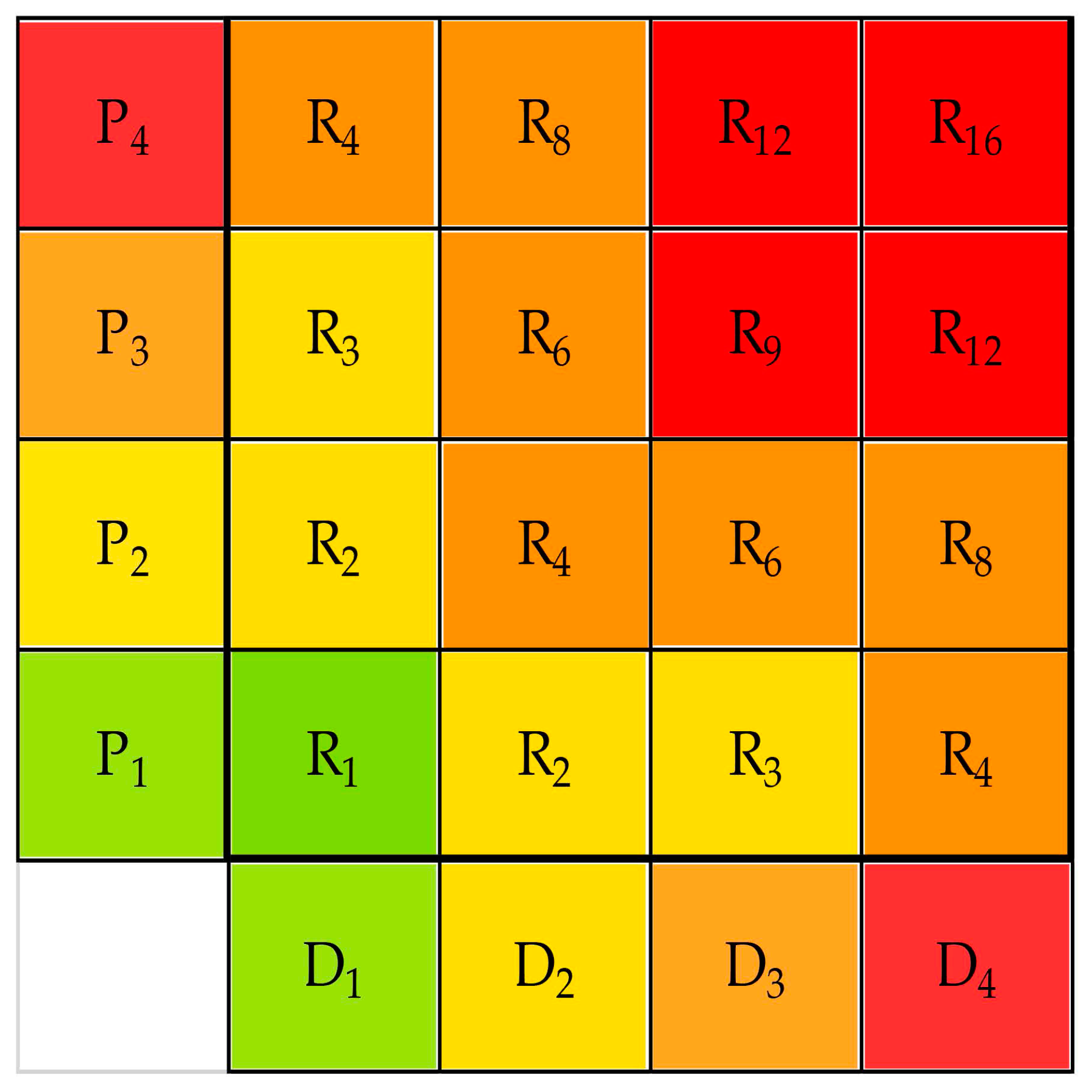
3.2. The Risk Related to Soil Erosion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Jiu, J.; Wu, H.; Sen, L.S. The implication of land-use/land-cover change for the declining soil erosion risk in the Three Gorges Reservoir Region, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.; Ommolbanin, B.; Thomas, P.; Elham, R.S. Modeling the impact of climate change and land use change scenarios on soil erosion at the Minab Dam Watershed. Sustainability 2019, 11, 3353. [Google Scholar]
- Sujatha, E.R.; Sridhar, V. Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a small mountainous watershed using RUSLE: A case-study of the Palar Sub Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India. Water 2018, 10, 1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldemariam, G.W.; Iguala, A.D.; Tekalign, S.; Reddy, R.U. Spatial modeling of soil erosion risk and its implication for conservation planning: The case of the Gobele Watershed, East Hararghe Zone, Ethiopia. Land 2018, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, H.H. Elements of Soil Conservation; McGraw-Hill Book Company Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Cencetti, C.; De Rosa, P.; Fredduzzi, A.; Marchesini, I. Erosione dei suoli e GRASS GIS: Esempi di applicazione. Geomat. Workb. 2005, 5, 16. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Molino, B.; Viparelli, R.; Caramuscio, P. A methodological approach for estimating turbidity in a river. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, C.; de Rigo, D.; Dewitte, O.; Poesen, J.; Panagos, P. Modelling soil erosion at European scale: Towards harmonization and reproducibility. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Van Liedekerke, M.; Jones, A.; Montanarella, L. European Soil Data Centre: Response to European policy support and public data requirements. Land Use Policy 2012, 29, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terranova, O.; Antronico, L.; Coscarelli, R.; Iaquinta, P. Soil erosion risk scenarios in the Mediterranean environment using RUSLE and GIS: An application model for Calabria (southern Italy). Geomorphology 2009, 112, 228–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, H.L. The Nature and Controlling Variables of the Water Erosion Process. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1937, 1, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zingg, A.W. Degree and length of land slope as it affects soil loss in runoff. Agric. Eng. 1940, 21, 59–64. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.D. Interpretation of soil conservation data for field use. Agric. Eng. 1941, 22, 173–175. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting soil erosion by water: A guide to conservation planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE). In Agricultural Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, A.; Himanshu, S.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Physically based soil erosion and sediment yield models revisited. Catena 2016, 147, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Nearing, M.A. Handbook of Erosion Modelling; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Capolongo, D.; Diodato, N.; Mannaerts, C.M.; Piccarreta, M.; Strobl, R.O. Analyzing temporal changes in climate erosivity using a simplified rainfall erosivity model in Basilicata (southern Italy). J. Hydrol. 2008, 356, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. A Rainfall Erosion Index for a Universal Soil-Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1959, 23, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V.; Saleh, A.; Jaynes, D.B.; Arnold, J. Predicting water, sediment and NO 3-N loads under scenarios of land-use and management practices in a flat watershed. Water Air Soil Poll. 2004, 154, 271–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaplot, V. Impact of spatial input data resolution on hydrological and erosion modeling: Recommendations from a global assessment. Phys. Chem. Earth 2014, 67, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting rainfall erosion losses—A guide to conservation planning. In Agricultural Handbook; United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Williams, J.R. Sediment-yield prediction with Universal Equation using runoff energy factor. In Present and Prospective Technology for Predicting Sediment Yields and Sources; Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. RUSLE: Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation, Soil and Water Conservation Society. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Mitasova, H.; Hofierka, J.; Zlocha, M.; Iverson, L.R. Modelling topographic potential for erosion and deposition using GIS. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1996, 10, 629–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnell, P.I.A.; Risse, L.M. USLE-M: Empirical Modeling Rainfall Erosion through Runoff and Sediment Concentration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A.; Romkens, M.J.M.; Norton, L.D.; Stott, D.E.; Rhoton, F.E.; Laflen, J.M.; Flanagan, D.C.; Alonso, C.V.; Binger, R.L.; Dabney, S.M.; et al. Measurements and models of soil loss rates. Science 2000, 290, 1300–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoli, R. Modeling Erosion Risk Using the RUSLE Equation. In QGIS and Applications in Water and Risks; Baghdadi, N., Mallet, C., Zribi, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Beskow, S.; Mello, C.R.; Norton, L.D.; Curi, N.; Viola, M.R.; Avanzi, J.C. Soil erosion prediction in the Grande River Basin, Brazil using distributed modeling. Catena 2009, 79, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvem, A.; Topaloglu, F.; Uygyr, V. Estimating spatial distribution of soil loss over Seyhan River Basin in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2009, 336, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Cai, C.F.; Ding, S.W.; Wang, T.W.; Chow, T.L. Soil conservation planning at the small watershed level using RUSLE with GIS: A case study in the Three Gorge Area of China. Catena 2004, 55, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Q.; Li, R.; Liu, Q.; Moore, D.; He, P.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. Extension of a GIS procedure for calculating the RUSLE equation LS factor. Comput. Geosci. 2013, 52, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carone, M.T.; Greco, M.; Molino, B. A sediment-filter ecosystem for reservoir rehabilitation. Ecol. Eng. 2006, 26, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Molino, A.J.; Molino, B.; Scorpio, V. Reservoir rehabilitation: The new methodological approach of Economic Environmental Defence. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Covelli, C.; Molino, A.; Pannone, M.; Ciccaglione, M.; Molino, B. Long-Term Management Policies of Reservoirs: Possible Re-Use of Dredged Sediments for Coastal Nourishment. Water 2018, 11, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, B.; Viparelli, R.; De Vincenzo, A. Effects of river network works and soil conservation measures on reservoir siltation. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2007, 22, 273. [Google Scholar]
- Molino, B.; De Vincenzo, A.; Ferone, C.; Messina, F.; Colangelo, F.; Cioffi, R. Recycling of clay sediments for geopolymer binder production. A new perspective for reservoir management in the framework of Italian legislation: The Occhito reservoir case study. Materials 2014, 7, 5603–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molino, B.; Savastano, V. Approccio distribuito per la stima dell’erosione idrica superficiale di un bacino idrografico, Il processo di interrimento degli invasi: Genesi, effetti ed interventi per la tutela dell’ambiente. Collana Stud. Ric. Dell’autorità Bacino Della Basilicata 2004, 4, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Onori, F.; De Bonis, P.; Grauso, S. Soil erosion prediction at the basin scale using the revised universal soil loss equation (RUSLE) in a catchment of Sicily (southern Italy). Environ. Geol. 2006, 50, 1129–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, X. Research progress on the watershed sediment delivery ratio. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.; Freimund, J. Using monthly precipitation data to estimate the Rfactor in the Revised USLE. J. Hydrol. 1994, 157, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Asaro, F. Valutazione dell’indice di erosività relativo a singoli eventi erosivi. Riv. Ing. Agrar. 1994, XXV, 83–96. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
- Rouse, J.W., Jr.; Haas, R.H.; Schell, J.A.; Deering, D.W. Monitoring the Vernal Advancement of Retrogradation of Natural Vegetation; NASA/GSFC: Greenbelt, MD, USA, 1974; Volume III, p. 371.
- Van der Knijff, J.; Jones, R.; Montanarella, L. Soil Erosion Risk: Assessment in Europe. In ISPRA: European Soil Bureau; Joint Research Centre: Ispra, Italy, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Mutchler, C.K.; Meyer, L.D. Revised Slope Length Factor for the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Trans. ASAE 1989, 32, 1571–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferro, V.; Porto, P.; Yu, B. A comparative study of rainfall erosivity estimation for southern Italy and southeastern Australia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1999, 44, 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendicino, G.; Sole, A. Stima distribuita dell’erosione idrica lungo i versanti di un bacino sotteso da un invaso artificiale. In Proceedings of the Atti del XXVI Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche, Catania, Italy, 9–12 September 1998. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Landsat 8 Satellite of NASA. 2017. Available online: https://www.nasa.gov/content/landsat-8-instruments (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- LULC of Basilicata Region. 2013. Available online: http://rsdi.regione.basilicata.it/ (accessed on 18 March 2019).
- Lazzari, M.; Gioia, D.; Piccarreta, M.; Danese, M.; Lanorte, A. Sediment yield and erosion rate estimation in the mountain catchments of the Camastra artificial reservoir (Southern Italy): A comparison between different empirical methods. Catena 2015, 127, 323–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, L.; Teodoro, A.C.; Gonçalves, J.A.; Soares, D.; Cunha, M. Assessing soil erosion risk using RUSLE through a GIS open source desktop and web application. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; Rosewell, C.J. Technical notes: A robust estimator of the R-factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans. ASAE 1996, 39, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.H.; Huang, X.D.; Ai, L.; Fang, N.F.; Wu, G.L. Quantitative analysis of factors controlling sediment yield inmountainous watersheds. Geomorphology 2014, 226, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canuti, P.; Casagli, N. Fenomeni Franosi e Centri Abitati. In Proceedings of the Conference of Bologna 1994 (CNR–GNDCI–Emilia-Romagna), Bologna, Italy, 27 May 1994; p. 66. (In Italian). [Google Scholar]
- Benchettouh, A.; Kouri, L.; Jebari, S. Spatial estimation of soil erosion risk using RUSLE/GIS techniques and practices conservation suggested for reducing soil erosion in Wadi Mina watershed (northwest, Algeria). Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattarai, R.; Dutta, D. Estimation of Soil Erosion and Sediment Yield Using GIS at Catchment Scale. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 1635–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, A.; Karaburun, A. Estimation of soil erosion using R in a GIS framework: A case study in the Buyukcekmece Lake watershed, northwest Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2012, 66, 903–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaubi, I.; Chaabani, A.; Mammou, A.B.; Hamza, M.H. A GIS-based soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) (Lebna watershed, Cap Bon, Tunisia). Nat. Hazards 2017, 86, 219–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haregeweyn, N.; Tsunekawa, A.; Poesen, J.; Tsubo, M.; Meshesha, D.T.; Fenta, A.A.; Nyssen, J.; Adgo, E. Comprehensive assessment of soil erosion risk for better land use planning in river basins: Case study of the Upper Blue Nile River. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 574, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Li, G.; Valladares, G.S.; Batistella, M. Mapping soil erosion risk in Rondonia, Brazilian Amazonia: Using RUSLE, remote sensing and GIS. Land Degrad. Dev. 2004, 15, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moses, A. GIS-RUSLE Interphase Modelling of Soil Erosion Hazard and Estimation of Sediment Yield for River Nzoia Basin in Kenya. J. Remote Sens. GIS 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Panda, R.K. Grid-cell based assessment of soil erosion potential for identification of critical erosion prone areas using USLE, GIS and remote sensing: A case study in the Kapgari watershed, India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weifeng, Z.; Bingfang, W.U. Assessment of soil erosion and sediment delivery ratio using remote sensing and GIS: A case study of upstream Chaobai River catchment, north China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2008, 23, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winchell, M.F.; Jackson, S.H.; Wadley, A.M.; Srinivasan, R. Extension and validation of a geographic information system-based method for calculating the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation length-slope factor for erosion risk assessments in large watersheds. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2008, 63, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan, Y.; Zregat, D.; Anbar, A. Assessing farmers’ perception of soil erosion risk in Northern Jordan. J. Environ. Prot. 2015, 6, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
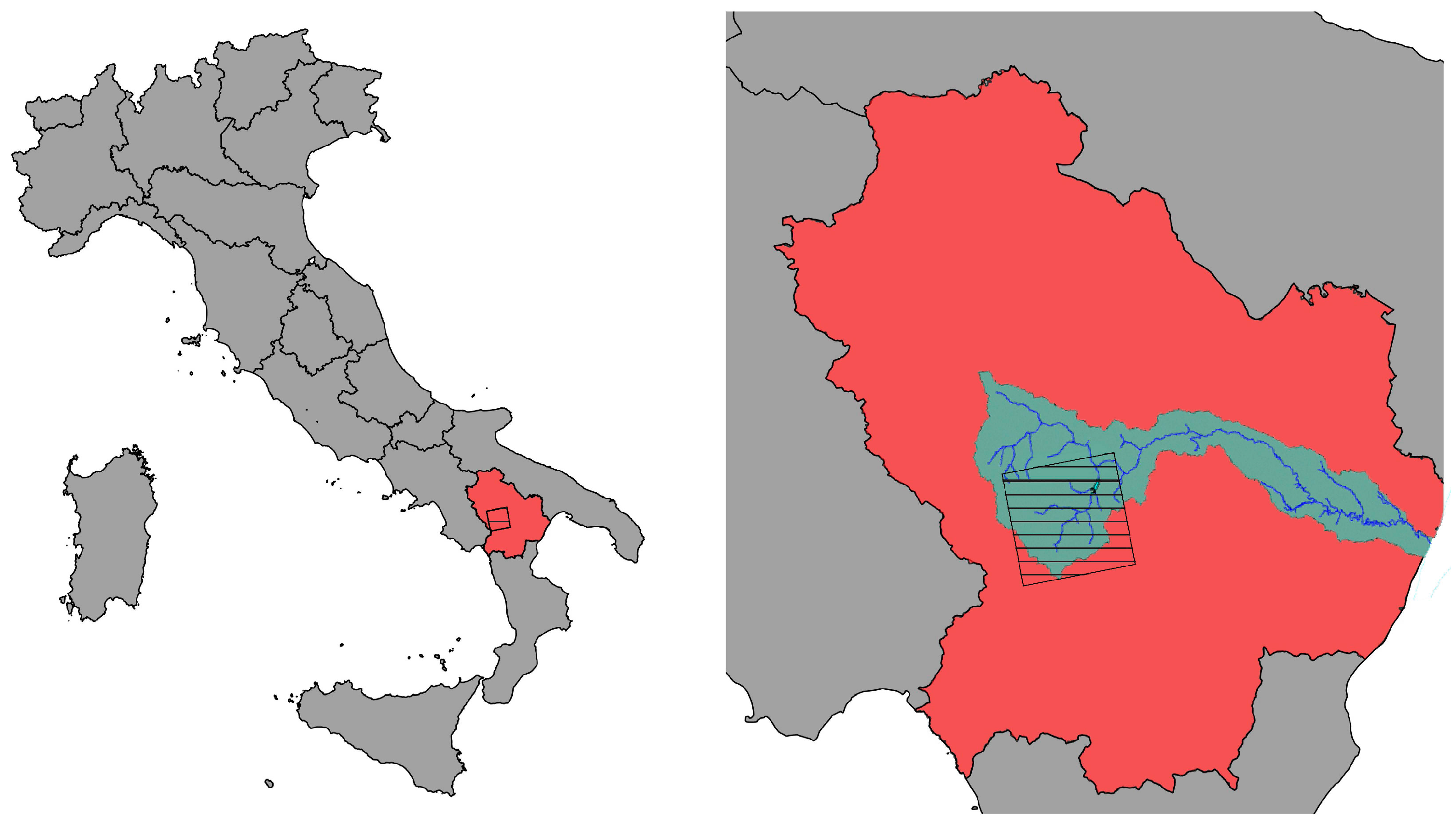
| N-W | 15° 39′ 30,1204″ E | 40° 38′ 41,5553″ N |
| N-E | 16° 06′ 48,2343″ E | 40° 38′ 41,5553″ N |
| S-E | 16° 06′ 48,2343″ E | 40° 17′ 19,9166″ N |
| S-W | 15° 39′ 30,1204″ E | 40° 17′ 19,9166″ N |
| Abriola | ||||||||||||
| Year | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. |
| 2014/15 | 69.8 | 48.4 | 75.0 | 45.4 | 193.9 | 203.6 | 219.5 | 112.5 | 55.9 | 99.6 | 20.5 | 63.1 |
| 2015/16 | 64.3 | 217.2 | 84.0 | 11.2 | 124.5 | 137.7 | 244.6 | 68.7 | 134.0 | 28.9 | 83.0 | 36.6 |
| 2016/17 | 104.4 | 133.3 | 139.6 | 20.4 | 149.0 | 47.8 | 105.2 | 46.2 | 42.0 | 12.6 | 11.5 | 2.8 |
| 2017/18 | 133.2 | 61.4 | 192.8 | 166.7 | 147.0 | 226.2 | 237.6 | 62.3 | 166.6 | 96.0 | 40.8 | 130.5 |
| Anzi | ||||||||||||
| year | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. |
| 2015/16 | 25.8 | 116.2 | 32.0 | 1.4 | 117.9 | 79.8 | 77.7 | 8.4 | 15.8 | 33.4 | 179.2 | 53.2 |
| 2016/17 | 117.9 | 79.8 | 77.7 | 8.4 | 54.2 | 27.0 | 44.8 | 18.2 | 33.5 | 13.2 | 11.7 | 11.9 |
| 2017/18 | 40.0 | 33.7 | 109.5 | 33.4 | 43.6 | 91.0 | 61.6 | 39.4 | 127.9 | 29.4 | 7.5 | 130.5 |
| Laurenzana | ||||||||||||
| year | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | Jan. | Feb. | Mar. | Apr. | May | June | July | Aug. |
| 2014/15 | 71.2 | 39.2 | 72.2 | 56.6 | 173.6 | 177.2 | 117.8 | 43.4 | 43.8 | 42.0 | 4.6 | 104.8 |
| 2015/16 | 42.8 | 141.0 | 37.6 | 1.4 | 23.2 | 67.4 | 236.6 | 37.8 | 76.0 | 49.6 | 62.2 | 78.2 |
| 2016/17 | 80.6 | 76.4 | 112.0 | 18.6 | 127.8 | 41.0 | 64.2 | 18.2 | 43.4 | 35.8 | 19.8 | 13.6 |
| 2017/18 | 60.6 | 25.2 | 154.4 | 70.0 | 50.8 | 180.8 | 156.8 | 58.0 | 142.2 | 49.8 | 3.8 | 59.0 |
| Not Null Cells | 68,436 |
| Minimum value | 8.52 |
| Maximum value | 11,680 |
| Range | 11,671.4 |
| Average | 71.4 |
| Standard deviation | 168.9 |
| Variance | 28,555.8 |
| Variance Coeffcient | 236.70% |
| Sum | 4,885,374.9 |
| Authors | (t yr−1) |
|---|---|
| Lazzari et al. | 1,677,378 |
| Present study | 1,853,981 |
| Year | Inflow (106 m3) | Yield (106 m3) |
|---|---|---|
| 1967 | 35.172 | 0 |
| 1988 | 28.712 | 7 |
| 1993 | 21.754 | 6.958 |
| 1995 | 20.776 | 0.978 |
| 1997 | 21.120 | 0.656 |
| 2005 | 19.421 | 0.699 |
| 2017 | 18.418 | 1.003 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Covelli, C.; Cimorelli, L.; Pagliuca, D.N.; Molino, B.; Pianese, D. Assessment of Erosion in River Basins: A Distributed Model to Estimate the Sediment Production over Watersheds by a 3-Dimensional LS Factor in RUSLE Model. Hydrology 2020, 7, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010013
Covelli C, Cimorelli L, Pagliuca DN, Molino B, Pianese D. Assessment of Erosion in River Basins: A Distributed Model to Estimate the Sediment Production over Watersheds by a 3-Dimensional LS Factor in RUSLE Model. Hydrology. 2020; 7(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleCovelli, Carmine, Luigi Cimorelli, Danila Nicole Pagliuca, Bruno Molino, and Domenico Pianese. 2020. "Assessment of Erosion in River Basins: A Distributed Model to Estimate the Sediment Production over Watersheds by a 3-Dimensional LS Factor in RUSLE Model" Hydrology 7, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010013
APA StyleCovelli, C., Cimorelli, L., Pagliuca, D. N., Molino, B., & Pianese, D. (2020). Assessment of Erosion in River Basins: A Distributed Model to Estimate the Sediment Production over Watersheds by a 3-Dimensional LS Factor in RUSLE Model. Hydrology, 7(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology7010013





