Abstract
The advent of satellite rainfall products can provide a solution to the scarcity of observed rainfall data. The present study aims to evaluate the performance of high spatial-temporal resolution satellite rainfall products (SRPs) and rain gauge data in hydrological modelling and flood inundation mapping. Four SRPs, Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) - Early, - Late (IMERG-E, IMERG-L), Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation-Near Real Time (GSMaP-NRT), and Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks- Cloud Classification System (PERSIANN-CCS) and rain gauge data were used as the primary input to a hydrological model, Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) and the simulated flood level and runoff were compared with the observed data using statistical metrics. GSMaP showed the best performance in simulating hourly runoff with the lowest relative bias (RB) and the highest Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) of 4.9% and 0.79, respectively. Meanwhile, the rain gauge data was able to produce runoff with −12.2% and 0.71 for RB and NSE, respectively. The other three SRPs showed acceptable results in daily discharge simulation (NSE value between 0.42 and 0.49, and RB value between −23.3% and −31.2%). The generated flood map also agreed with the published information. In general, the SRPs, particularly the GSMaP, showed their ability to support rapid flood forecasting required for early warning of floods.
1. Introduction
Flood is the most damaging natural disaster in Malaysia causing massive economic destruction with an average annual loss of approximately 1.271 million USD based on EM-DAT database [1]. Heavy rain during the northeastern monsoon (November to January) affect the states of Kelantan, Terengganu, and Pahang in the eastern coast of Peninsular Malaysia. Series of heavy rainfall episodes often causes severe floods in the region. The destructive flood of Kelantan in December 2014 caused an estimated loss of about 2.8 billion ringgit (685 million USD) with 151,072 victims and ten deaths [2]. This extreme inundation event called the Kelantan Big Yellow Flood because of heavy mud content in the floodwater. Based on the recorded rainfall data, [3] found about 1598.8 mm and 386.6 mm rainfall at Gunung Gagau station and Brook station respectively in 7 days. Many upstream stations experienced rainfall events with average recurrence interval (ARI) near or above 100 years and several stations experienced rainfalls with ARI over 500 years. The extreme rainfall cause this unprecedented flood event in Kelantan [3].
The traditional way of modelling floods relies primarily on the availability of rainfall data recorded in a basin obtained from a network of rain gauges. This crucial data plays a significant role in both hydrological modelling and flood inundation mapping. However, rain gauging stations in Malaysia are somewhat scarce, particularly in remote areas [4,5]. Remote sensing technology has advantages in producing spatially distributed rainfall estimation. The satellite rainfall products can provide rainfall information at a specific spatial and temporal resolution of areal coverage [6,7]. Furthermore, the dataset offers near-real-time rainfall, which can be another source of rainfall data, especially in a data scare or ungauged basin [8,9]. Several examples of satellite-based rainfall data are Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA) [10], Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) [11], PERSIANN-Cloud Classification System (PERSIANN-CCS) [12], and Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) [13]. The Satellite Rainfall Products (SRPs) have become indispensable data for hydrologists and water resources scientists. The evaluation of satellite rainfall products as inputs to hydrological models for flood simulation has been conducted in various locations around the world [14,15,16,17,18]. However, studies related to the reliability of such data in Malaysia is very limited [19,20,21,22,23]. For example, [20] assessed the reliability of three GPM products for streamflow simulation and showed their acceptable performance in term of NSE (~0.5), R2 (~0.6), and RB (~ −30%). Other SRPs products (particularly near-real-time), such as GSMaP-NRT and PERSIANN-CCS used in the present study, have not yet been evaluated in Malaysia yet. Moreover, no study has been conducted in Malaysia so far to estimate the amount of errors at different locations due to different SRPs [9,24,25].
The typical flood modelling consists two parts: (i) rainfall-runoff modelling, and (ii) hydraulic simulation [26,27,28]. The authors of [29] coupled two models from Hydrologic Engineering Center (HEC) of which HEC-HMS output is used as input to HEC-RAS for flood mapping using Geographical Information System (GIS) and remote sensing data. Such coupling controlled by upstream boundary conditions, i.e., discharge or water level [29] and less useful in emergency situations. It led to the development of a commercial integrated one-dimensional and two-dimensional (1D2D) model, e.g., SOBEK, MIKE Flood, and Flood Modeller. However, these models are impracticable for areas greater than 1000 km2 when the required resolution is less than 10 m, as the calculation time may be considerably long [30]. The authors of [31] developed a rainfall-runoff–inundation (RRI) model, integrating the rainfall-runoff simulation and the hydrodynamic model. The advantage of the RRI model can simulate flooding and estimate river flow at downstream floodplains and upstream mountain areas simultaneously, modelling flood inundation at multiple basins [32].
Several studies have been carried out by integrating SRPs and RRI model for flood mapping [31,33,34,35,36,37]. The results of the simulations in these studies have a good agreement with the observed hydrological data and satellite-derived flood map extent. The effects of land use and climate change on flood behavior were also investigated using the RRI model [38,39]. None of these studies, however, used Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) data in the RRI model.
Decision-making process over any disaster, especially flood requires up-to-date information on the current situations of the affected areas. The use of remote sensing to delineate flood map are promising [40,41,42,43]. Despite that, clouds are always the main problem for optical-based satellite systems to capture images [44,45], especially during the rainy season while flooding is happening [46,47]. Microwave satellites can overcome this problem as its signal can penetrate cloud and light to moderate rain [42,48], but limited available microwave satellites prevent near-real-time flood mapping [42,48]. Nevertheless, these satellite-based flood inundation mappings are significant for emergency response [49,50] and the use of remote sensing technology in the disaster emergency is increasing [51]. Moreover, an inadequate network of rain gauges at basin impede in hydrological modelling particularly when the gauging stations are destroyed due to the high velocity of floodwater or debris [52,53]. Flood monitoring during the rainy season is very challenging in the tropical region. Flood modelling based on the spatially distributed, multi-temporal rainfall data (SRPs) could be the best option to demonstrate the current situation of floods. Against these, the present paper aims to assess the performance of high spatial-temporal satellite rainfall products in RRI model for runoff simulation and flood inundation mapping.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Study Area
The study area is located in the Kelantan River Basin in the Northern part of Peninsular Malaysia (Figure 1). This area experiences two monsoon seasons, Southwest Monsoon (April to August) and Northeast Monsoon (October to January). Rainfall intensity of the Northeast Monsoon (1530 mm/year) is higher than the Southwest Monsoon (993 mm/year) [54]. High rainfall during Northeast monsoon often causes prolonged flooding [55]. According to [54], the northeast zone on peninsular Malaysia, i.e., Kelantan, Terengganu and Pahang has the highest annual rainfall of 2940 mm/year. The total area of the Kelantan River basin catchment is approximately 13,135 km2, with the highest point of 2083 m above the mean sea level. The main tributary in this area is Galas River and Lebir River.
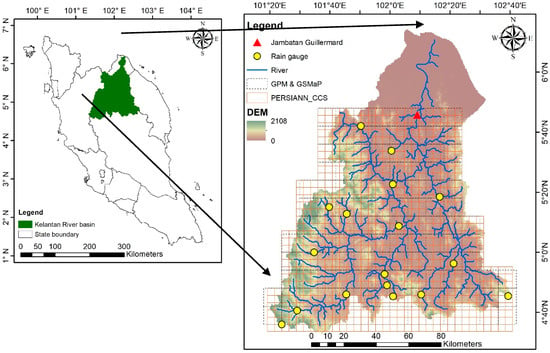
Figure 1.
Distribution of rain gauges and Jambatan Guillermard river flow measuring station in Kelantan River basin and the resolution (Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) and Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) with 0.1°; Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks-Cloud Classification System (PERSIANN-CCS) with 0.04°) and coverage of different satellite rainfall products.
The recent destructive flood in December 2014 in Kelantan state was mainly due to intense rainfall from 14 to 19 December 2014 with rivers exceeding the critical level by 17 December [2]. Furthermore, the GPM data is available from March 2014. The simulation was conducted from 1 December 2014 to 1 January 2015, during which the warm-up period was from 1 December to 14 December. The warm-up period is the time for which the model is run before simulation of the desired runoff event.
2.2. Data Sources
2.2.1. Rain Rauge and Streamflow Data
Hourly observation river discharge (m3/s) and water level (m) data at Jambatan Guillermard station were used as a reference data to assess the simulated discharge and water level produced by the SRP-driven RRI model. To evaluate the applicability of SRP, 17-meteorological stations were used to execute the RRI model. These datasets provided by the Department of Irrigation and Drainage (DID), Malaysia. The geographical distribution of meteorological stations and the hydrological stations is shown in Figure 1. Both hourly hydrological data and meteorological data from 2014 to 2015 were used.
2.2.2. River Geometry
Detailed information of river geometry is not available. Therefore, a conventional rectangle geometry was assumed [56]. The river depth (D) and width (W) are estimated using the following equations:
where A is the upstream contributing area (km2). In this study, a total of five cross-section data provided by DID spreading over the Kelantan River basin. Subsequently, the geometry parameters, CW = 2.49, SW = 0.533, CD = 13.82 and SD = 0.0446, are obtained.
2.2.3. Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
The USGS HydroSHED DEM data was used in this study [57], which is derived from Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) data. The HydroSHED is a hydrologically conditioned DEM, and therefore, suitable for hydrological applications. A 15 arcsec (approximately 450 m) spatial resolution DEM was used. The DEM-derived flow direction (DIR) and flow accumulation (ACC) were also used in RRI model. The USGS HydroSHED is available at https://hydrosheds.cr.usgs.gov/. The DEM, DIR and ACC data were stored into ASCII format is the required format by the RRI model.
2.2.4. Land Cover and Soil Map
The Global Land Cover by National Mapping Organizations (GLCNMO) was used in this study. The data were prepared by using MODIS data with remote sensing technology [58,59]. The GLCNMO version 2 having a spatial resolution of 15 arcsec was used. Soil data of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nation’s global dataset with approximately 9 km [60] was used. Both the land cover and soil type data were used in RRI model.
2.2.5. Satellite Rainfall Products
All near-real-time (NRT) high spatial-temporal satellite rainfall products were evaluated in the present study, i.e., GPM (IMERG_E, IMERG_L), PERSIANN-CCS, and GSMaP-NRT, for flood simulation. The characteristics of these SRPs are given in Table 1. Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) provides three different levels of products for public download. The use of GPM product in this study is Level-3 gridded product; it blended all passive satellite microwave rainfall estimates, i.e., Integrated Multisatellite Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) [61]. The spatiotemporal resolution of IMERG is 0.1° × 0.1° every 30 min, which is near-real-time product. IMERG’s primary enhancement are the mixture of high spatial-temporal resolutions, the near-global coverage, and the high quality by using active instruments to support the use of passive instruments. IMERG has three levels gridded products: IMERG-E (Early Run) and IMERG-L (Late Run) are near-real-time product with a latency of 4 h and 12 h, respectively, and IMERG-F (Final Run) is a research product with a latency of 2.5 months. GPM data can be found online (https://pmm.nasa.gov/data-access/downloads/gpm).

Table 1.
Characteristics of satellite rainfall products used in the present study.
The PERSIANN-CCS algorithm extracts local and regional cloud characteristics using infrared (IR) cloud images to estimate finer scale rainfall distribution (0.04° × 0.04° and 30 min). The algorithm involves four steps, (1) segmentation of IR cloud images into different cloud patches using incremental temperature threshold technique, (2) extraction of cloud characteristics, i.e., geometry, texture, and coldness; (3) classification of cloud patches using self-organizing feature map (SOFM) algorithm; and (4) estimation of rain rate by establishing Tb - R relationship to various cloud patches [62]. This study also revealed that nonlinear approaches successfully identify different Tb − R function for each cloud patches rather than the threshold and linear approach. The product of PERSIANN-CCS is available online (https://chrsdata.eng.uci.edu/).
The GSMaP project is sponsored by JST-CREST and is promoted by the JAXA Precipitation Measuring Mission (PMM) Science Team [13,63,64,65]. The GSMaP algorithm blends TRMM estimates and other satellites to produce high resolution globally precipitation products (0.1° × 0.1° and 1 h). GSMaP provides eight levels of products with different latencies, which are realtime (GSMaP_NRT), realtime_gauge (GSMaP_Gauge_NRT), now (GSMaP_NOW), standard (GSMaP_MVK), standard_gauge (GSMaP_Gauge), reanalysis (GSMaP_RNL), reanalysis_gague (GSMaP_Gauge_RNL) and riken_nowcast (GSMaP_RNC). GSMaP data is available online (https://sharaku.eorc.jaxa.jp/GSMaP/).
3. Methodology
Figure 2 show the flowchart of the present study. The overall methodology is divided into three phases, i.e., input data (blue blox), two-dimensional hydrodynamic modelling using SRPs (purple box) and evaluation of the results (red box). All SRP data and rain gauge data were separately used runoff modeling and flood inundation mapping.
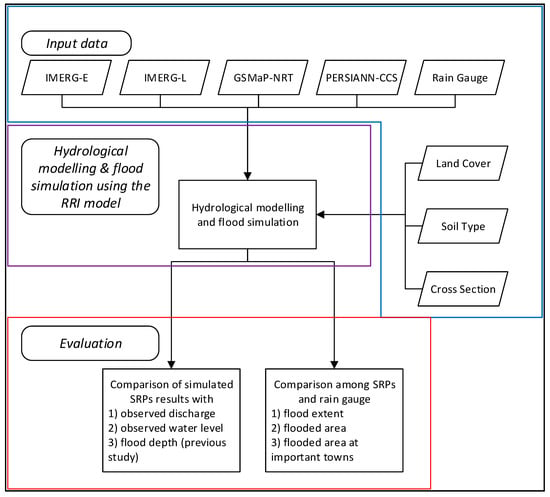
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the methodology used in the present study.
3.1. RRI Model
The RRI is a 2D fully distributed hydrological model that simulates rainfall-runoff and flood level simultaneously (Figure 3) [31,34]. At a pixel is river channel, this model presumes slope and river are at same pixel cell. 2D and 1D diffusive equations are used to calculate the flow on the slope pixel and the flow in a channel, respectively. This model simulates lateral subsurface flow, vertical infiltration flow and surface flow for describing the processes of rainfall-runoff-inundation. The lateral subsurface flow consists of saturated subsurface and surface flow. The Green-Ampt equation is responsible for vertical infiltration flow. The flow interaction of river channel and land is estimated based on different overflowing formula. The RRI model is a standalone product and its output, i.e., discharge, water level, and inundation can be displayed easily. In addition, the maximum flood inundation can be saved into ASCII format for further analysis, such as flood hazard mapping or identification of elements-at-risk, using GIS platform with additional data.
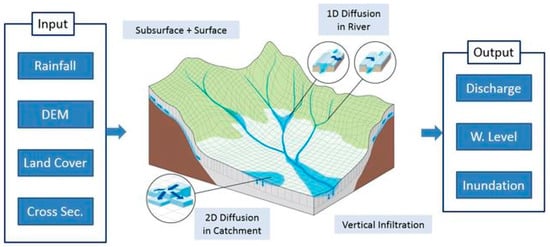
Figure 3.
Schematic diagram of Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) Model.
The required input data to drive RRI model is shown in Figure 3. The characteristics of the data are explained in Section 2.2. The prepare the data are explained in details in RRI user manual [56].
3.2. Evaluation Methods
The accuracy of RRI model simulation based on hourly rain gauge data were evaluated using four statistical metrics, root means square error (RMSE), relative bias (RB), correlation coefficient (r), and Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) [66]. The relative bias estimates the systematic bias of modelled runoff in percentage (%). Meanwhile, the Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency is used for assessing the goodness of fit of the hydrologic model; the more accurate RRI model will have NSE value close to 1.
where Qs and Qo are simulated discharge and observed discharge, respectively; and are average observed discharge and average simulated discharge, respectively, n is the total number of measurement, and i is the index of data.
The second evaluation method is the rainfall pattern analysis comparing SRPs and rain gauge data. Such assessment provides an understanding of the sensitivity of rainfall estimate to flood events. Therefore, all the rainfall data from each estimate (SRPs at all pixels and 17 meteorological stations) were average and plotted into a bar graph. All these rainfall data located at upstream of Kelantan River Basin. Figure 4 shows the average daily rainfall of different rainfall estimates from 15 December 2014 to 1 January 2015.
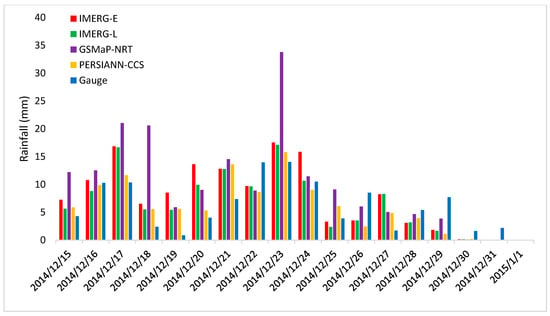
Figure 4.
Comparison of averaged upstream daily rainfall of different rainfall estimates.
Mann-Whitney (MW) test, a nonparametric test of hypothesis was used to determine whether two samples are likely to derive from the same population (i.e., that the two populations have the same shape). The null hypothesis is that there is no difference between the distributions of the data samples. This test was used to determine if averaged rainfall estimates at upstream of Kelantan River basin between SRPs and rain gauge were statistically significant, that is, there is a distinct difference between SRPs-generated and rain gauge-generated value of NSE and r. If the null hypothesis is rejected, then value of NSE and r for SRP-forced streamflow simulation is smaller than rain gauge simulation.
4. Results and Discussion
Floods in Malaysia is a regular natural disaster, especially during monsoon seasons which is characterized by heavy and regular rainfall between October and March every year. In December 2014, an unprecedented flood event took place in the state of Kelantan. The present study attempts to use RRI model to simulate the flood events in 2014. A simple comparison of average rainfall was conducted between the SRPs and the rain gauge (Figure 4). The four satellite rainfall products were simulated at an hourly basis and compared using observed discharge data from Jambatan Guillermard station. Figure 5 and Figure 6 show the hydrographs for all satellite rainfall products with observed data in term of discharge and water level, respectively.
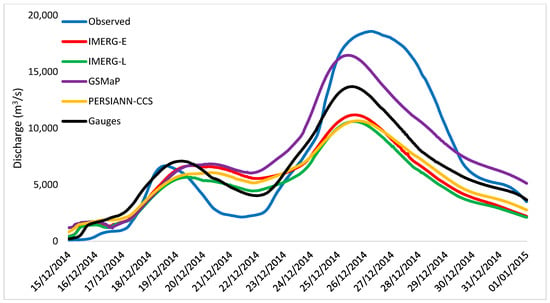
Figure 5.
Comparison of hydrograph of observed discharge and simulated discharges.
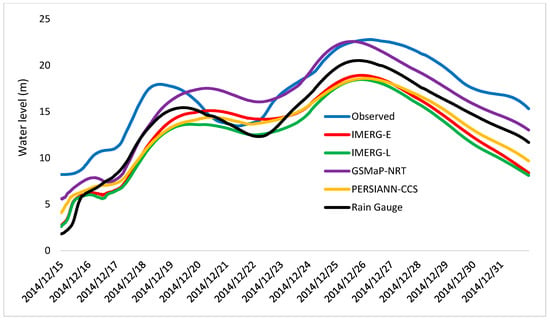
Figure 6.
Comparison of hydrograph of observed water level and simulated water levels.
Based on the hydrographs, all simulated runoff produced by each SRP has a similar pattern. It was also noticed that all SRPs captured the peak discharge and water level one day in advance, which are consistent with the observed data. However, only the peak discharge and water level produced by GSMaP-NRT was relatively close to the observed data. The peak discharge and water level produced by the GSMaP-NRT were 16,461 m3/s and 22.1 m, respectively, compared to 18,576 m3/s and 22.8 m, respectively, estimated using observed data. This means that GSMaP-NRT was successful in capturing the areal peak rainfall from 21 to 24 December, which other SRPs and rain gauge stations could not do (see Figure 4).
The performance of hourly simulated runoff hydrograph was evaluated using the performance statistics (see Table 2). GSMaP-NRT showed a performance very close to that obtained using observed data, with the lowest RMSE of 2674.7 m3/s and the highest r of 0.83. It overestimated the mean runoff only by 4.9% and provided the best predictive runoff with highest NSE of 0.79. The p-value of Mann-Whitney test suggested that there was no significant difference in term of NSE and r when using GSMaP-NRT data as compared to observed rainfall data. The RMSE using the rain gauge data was 3177.8 m3/s which was slightly higher than GSMaP-NRT. Both NSE and r of rain gauge were above 0.7, which indicates that rain gauge data also performs well. Similar performance was observed for other SRP products, i.e., IMERG-E, IMERG-L, and PERSIANN-CCS. However, the simulated runoff was significantly underestimated compared to the observed runoff by all those products. The RMSE, NSE and r of those products were almost the same. Although r was above 0.7, NSE was lower than 0.5, which according to [67] indicates that these three SRPs produced acceptable results.

Table 2.
Statistical performance of satellite rainfall products in simulating river flow.
The hourly simulations made using the GSMaP-NRT generally produced very satisfying results, while the remaining SRPs and even gauge data yielded acceptable results, (Table 2). Such satisfying results had also reported in [31,33]. It is unanticipated, in particular, the GSMaP-NRT data, as studies found that GSMaP had a significant discrepancy with observed data in rainfall estimation [68,69,70] and runoff simulation [71]. In Malaysia, rainfall estimates using SRPs have been carried out in several studies [19,20,72]. It has been reported that all SRPs are able to produce good results in estimating annual and monthly precipitation. However, the SRPs showed poor performance in simulating daily rainfall. The authors of [72] also found that by applying bias correction on SRPs, the error discrepancy and correlation between TRMM and rain gauge can be reduced by 18.38% and up to 16.28% respectively. Improving the accuracy of SRPs by considering bias correction is of great importance to ensure their applicability for daily and/or hourly application in hydrological and water resources modelling. For a better understanding of its usability for rainfall estimates at different spatial and temporal scales, a comprehensive evaluation of GSMaP-NRT should remain relevant in the future.
The authors of [73] conducted a hydro-meteorological evaluation over Kelantan river basin for a period between 2014 and 2016 using three GPM (IMERG-E, -L, -F) products using the SWAT model. The study simulated the flood event discharge in December 2014 and discovered that IMERG-E and IMERG-L data had produced good streamflow estimates with NSE and r values of 0.43–0.51 and 0.61–0.62, respectively. The findings of the present study are in line with their findings. Even though the RRI model is still under development [56], the results showed that the model is suitable to support hydrological simulation. However, the simulated flood inundation extent should be validated by an existing flood map produced by a related agency or satellite-derived flood extent map.
The spatial extent of maximum flood inundation in the downstream area from 15 December 2014 to 1 January 2015 is illustrated using the calibrated RRI model with SRPs and the gauged data in Figure 7. The figure shows that although the study area is relatively flat, the flooding differences were noticeable. Figure 8 shows the comparison of flooded area derived from SRPs and rain gauge. GSMaP-NRT data produced the most extensive coverage of the flooded area with 2856.1 km2. However, the flooded area created by the GSMaP-NRT was 2 to 3 times larger compared to that produced by other SRPs and rain gauge data. The generated flood map also showed that Tanah Merah had the worst flood situation. According to [74], Tanah Merah is one of the worst affected areas, together with Kuala Krai and Gua Musang. A comparison of flood depth in different towns in the downstream area also conducted, and the results are shown in Figure 9 and Table 3. Tanah Merah showed the highest flood depth of 5.9 m followed by Pasir Mas (3 m), Kadok (2.5 m), Wakaf Bunut (2.4 m), Peringat (1 m), and Kota Bharu (0.8 m). This study only carried out a simple flood depth assessment without validation with the ground truth data. However, flood depth record was available at Pangkalan Krai Jetty from the previous study by Yahaya et al. (2015) which was used to verify the simulated flood depth obtained from SRPs and rain gauge. The results showed that the GSMaP produced the closest flood depth with 1.4 m difference, and the difference in flood depths estimated other products was between 3.8 m and 6.4 m (Table 4).
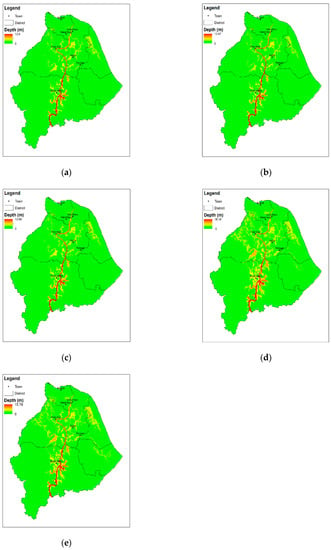
Figure 7.
Distribution of maximum flood inundation depth at downstream from 15 December 2014 to 1 January 2015, calculated by the calibrated Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation (RRI) model; (a) Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Information using Artificial Neural Networks- Cloud Classification System (PERSIANN-CCS) (b) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals-Late (IMERG-L) (c) Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals-Early (IMERG-E) (d) Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation GSMaP (e) Gauge.
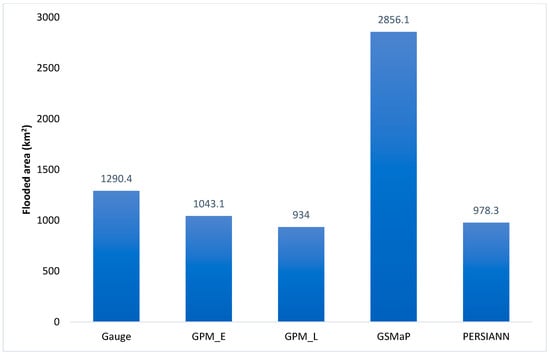
Figure 8.
Comparison of flooded area at downstream derived using hydrological model using different satellite precipitation products and rain gauge data.
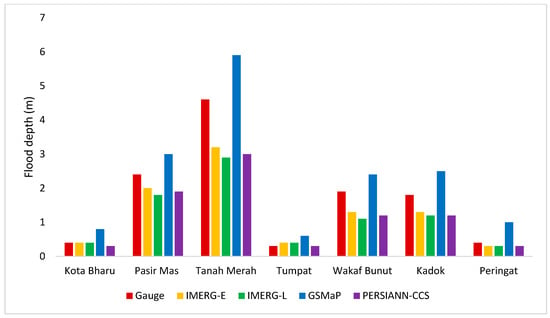
Figure 9.
Comparison of flood depth at different towns estimated using different satellite precipitation products and rain gauge data in a hydrological model.

Table 3.
Comparison of flood depth at different towns using hydrological model using different satellite precipitation products and rain gauge data.

Table 4.
Comparison of estimated flood depth to reference flood depth using the hydrological model using different satellite precipitation products and rain gauge data.
Figure 4 shows the areal average rainfall in the upstream area. The GSMaP-NRT was successful in capturing a few prominent peaks of rainfall which was not captured by the rain gauges. It shows that the existing rain gauges network is not capable of recording high spatial and temporal resolution rainfall information. To fully understand the rainfall-runoff response, it is necessary to install more and well-distributed rain gauge stations in the area. The conventional designing of a rain gauge network is divided into two types: haphazard manner and quantitative approach [75]. The former method is independent of rain gauge data, whereas the latter approach dependent on rain gauge data. The drawback of the latter approach is the insufficient number of rain gauges used to design the rain gauge network. Such methods are, therefore, challenging to implement and difficult to achieve an optimal outcome. So far only [75] successfully carried out a framework for the design of rain gauge network based on an integration of principal component analysis (PCA) (obtain optimum rain gauge density) and variable selection criteria (identify rain gauge location) using a ground radar rainfall dataset. Satellite rainfall products are also suitable as such dataset can provide a considerable amount of local rainfall patterns.
In this paper, four SRPs (IMERG-E, IMERG-L, GSMaP-NRT, and PERSIANN-CCS) were used as forcing data to drive the RRI model for hydrological modelling and flood inundation mapping. Also, the performance of SRPs in hourly discharge estimation for extreme flood event was analyzed. Near-real-time satellite rainfall products are an indispensable source of data for emergency response. Thus, the need for such reliable data is essential for the rescue and assessment of flood damages. This research provided a guidance for prediction of extreme flood events using SRPs data to yield more precise hydrologic and flood simulation.
The present study focuses on the emergency phase of the disaster management cycle. Therefore, a simple comparison between SRPs and rain gauge on extreme rainfall event was carried out (Figure 4). According to [3], the December 2014 flood event had two phases. The first phase was during 15–19 December, while the second phase was from 20 to 24 December. Generally, all the satellite rainfall products were found capable in capturing these two phases. However, GSMaP-NRT was able to record two extreme peak rainfalls on 17 and 23 December 2014. The daily amount of rainfalls on those two days were twofold relative to other SRPs and the rain gauge estimation.
The performance of satellite rainfall products on discharge simulation is evaluated by comparing the simulated and observed discharge and water level hydrographs (Figure 5 and Figure 6). In addition to the visual comparison, the performance evaluation of each SRP is assessed using the statistical approach with a hypothesis testing to validate the significance of the result (Table 2). Overall, all SRPs-derived hydrographs are matched to the observed hydrography. Based on Table 2, GSMaP-NRT had the best hydrological performance but overestimated runoff, which was consistent with the findings by [76]. While the rest of the SRPs had an acceptable underestimated runoff. According to [77], the underestimation in discharge simulation due to the underestimated rainfall estimates. Similar findings are also reported in [17,73,78,79]. Therefore, we could conclude that GSMaP-NRT has a positive bias in this extreme event. The overestimation discharge driven GSMaP-NRT due to the re-evaporation of rainfall [80]. However, IMERG and PERSIANN-CCS underestimate rainfall may due to warm-rainfall process associated with orographic uplift caused by the onshore flow toward the mountain [81] and poor detection of light rainfall event at high elevation area [82,83,84]. In addition, a statistical hypothesis test, the Mann-Whitney test to confirm the performance of GSMaP-NRT product in discharge simulation as good as rain gauge data. Therefore, the GSMaP-NRT data was shown to produce more accurate discharge simulation for the extreme flood event.
In fact, NRT products do not take gauge-correction into account [80]. More studies on the bias correction of satellite rainfall products are conducted [72,85,86,87]. In addition to enhancing the reliability of rainfall estimates, the streamflow simulation model has also improved [83,85]. Various bias correction methods have been adopted to reduce the bias of SRPs, such as bias factor [85,88], modified bias factor [86], principal components [89], probability approach [90] and cumulative distribution function [87]. However, the corrected-SRPs still showed some bias in rainfall estimates, which is due to topography effects, extreme event, and climate event [83,87,90,91]. According to [92], there is a relation between soil moisture and rainfall. Due to satellite-based soil moisture products has reached a promising level in term of accuracy [93], for example, [94,95]. Therefore, improvement in the accuracy of satellite rainfall estimates using soil moisture products are widely conducted [93,96,97,98]. Consideration of these factors into rainfall estimates may help algorithm developers to improve their products for better regional application use.
The authors of [31] noted that the simulation of the RRI model entails certain uncertainties, such as model parameters (hydraulic conductivity, Manning’s roughness, soil type, and river geometry) and topographic data. The authors of [34] found that the RRI model is also responsive to rainfall data in which 1% rise in rainfall results in a 2.3% and 4.2% increase in runoff and flood inundation, respectively. Furthermore, [99] assessed the sensitivity of the RRI model using different DEM dataset and DEM smoothing techniques. They showed that the RRI model is greatly sensitive to Manning’s roughness coefficient values for flood plains, followed by the dataset of DEM, and the soil depth. Monte Carlo simulation is one of the methods to evaluate uncertainty in rainfall-runoff simulation and inundation simulation [31]. Therefore, [33] conducted a large-scale rainfall-runoff-inundation modelling with consideration of parameter calibration using Monte Carlo simulation. They found that that river geometry is the most sensitive parameter in the RRI model. All these uncertainties can contribute to the simulated discharge errors (Table 2) and flood depth difference (Table 4). Although GSMaP-NRT yielded the best results as compared to other SRPs, it still underestimated flood depth (Table 4). This underestimation is mainly caused by the resolution of DEM used in this study was too coarse, i.e., 450 m. High resolution data is necessary in order to enhance the results [33].
5. Conclusions
Four datasets of SRPs (PERSIANN-CCS, IMERG-E, IMERG-L, and GSMaP-NRT) were used in the RRI model to assess their relative performance in simulating flood inundation in Kelantan river basin. This study showed that GSMaP-NRT can produce reliable flood inundation model using RRI. However, the other SRPs (PERSIANN-CCS, IMERG-E, and IMERG-L) shall be considered after bias adjustment for simulating discharge and the extent of flood inundation. Further works are still required to validate the flood inundation map produced by RRI model with available flood map or the flood extent derived from remote sensing imagery. The findings of the present study might support related agencies or departments in issuing early flood warnings and predicting flood situations, particularly in areas where hydrometeorological stations are sparse, or satellite images are not available.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: T.H.T. and M.Z.A.R.; Investigation: I.U.K.; Methodology: S.H. and M.N.H.; Software: T.H.T.; Validation: S.H. and M.N.H.; Visualization: I.U.K.; Writing—original draft: T.H.T.; Writing—review & editing: M.Z.A.R.
Funding
This study was funded by Universiti Teknologi Malaysia under grant (GUP: Q.J130000.2527.17H76)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thanks to the Department of Irrigation Drainage, Malaysia and all satellite rainfall products developers (GPM, PERSIANN, GSMaP) for providing the data in this study. Also, the authors thank Takahiro Sayama for making the RRI model as a public domain model. Authors greatly appreciate the constructive comments and suggestions from the anonymous reviewers. Lastly, thanks to Shamsuddin Shahid for proofreading the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
- Shaluf, I.M.; Ahmadun, F.l.-R. Disaster types in Malaysia: An overview. Disaster Prev. Manag. 2006, 15, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, N.S.; Lim, C.-S.; Jamaluddin, U.A.; Pereira, J.J. The December 2014 Flood in Kelantan: A Post-Event Perspective. War. Geol. 2015, 41, 54–57. [Google Scholar]
- Alias, N.E.; Mohamad, H.; Chin, W.Y.; Yusop, Z. Rainfall analysis of the Kelantan big yellow flood 2014. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, S.; Abustan, I. Estimating the Clark Instantaneous Unit Hydrograph Parameters for Selected Gauged Catchments in The West Coast of Peninsular Malaysia. ASEAN Eng. J. Part C. 2011, 13, 126–141. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, M.; Mah, Y.S.; Putuhena, F.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Selaman, O.S. TRMM Satellite Algorithm Estimates to Represent the Spatial Distribution of Rainstorms. MATEC Web Conf. 2017, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I. Evaluation of remote-sensing-based rainfall products through predictive capability in hydrological runoff modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, H.T.; Ishidaira, H.; Shaowei, N. Evaluation of the use of global satellite–gauge and satellite-only precipitation products in stream flow simulations. Appl. Water Sci. 2019, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Sun, W.; Yang, G.; Zhang, D. Hydrological Analysis Using Satellite Remote Sensing Big Data and CREST Model. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 9006–9016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Soe, K.M.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Applications of TRMM- and GPM-Era Multiple-Satellite Precipitation Products for Flood Simulations at Sub-Daily Scales in a Sparsely Gauged Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Nelkin, E.J.; Wolff, D.B.; Adler, R.F.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E.F. The TRMM Multisatellite Precipitation Analysis (TMPA): Quasi-Global, Multiyear, Combined-Sensor Precipitation Estimates at Fine Scales. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skofronick-Jackson, G.; Petersen, W.A.; Berg, W.; Kidd, C.; Stocker, E.F.; Kirschbaum, D.B.; Kakar, R.; Braun, S.A.; Huffman, G.J.; Iguchi, T.; et al. The Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission for Science and Society. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 98, 1679–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.L.; Gupta, H.V.; Gao, X.; Sorooshian, S. Estimation of physical variables from multichannel remotely sensed imagery using a neural network: Application to rainfall estimation. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 1605–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, K.i.; Ushio, T.; Iguchi, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iwanami, K. The global satellite mapping of precipitation (GSMaP) project. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Seoul, Koera, 29 July 2005; pp. 3414–3416. [Google Scholar]
- Bajracharya, S.R.; Shrestha, M.S.; Shrestha, A.B. Assessment of high-resolution satellite rainfall estimation products in a streamflow model for flood prediction in the Bagmati basin, Nepal. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casse, C.; Gosset, M.; Peugeot, C.; Pedinotti, V.; Boone, A.; Tanimoun, B.A.; Decharme, B. Potential of satellite rainfall products to predict Niger River flood events in Niamey. Atmos. Res. 2015, 163, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, A.; Rahman, S.; Hossain, F.; Yarborough, L.; Bagtzoglou, A.C.; Easson, G. Satellite-based Flood Modeling Using TRMM-based Rainfall Products. Sensors 2007, 7, 3416–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolopoulos, E.I.; Anagnostou, E.N.; Borga, M. Using High-Resolution Satellite Rainfall Products to Simulate a Major Flash Flood Event in Northern Italy. J. Hydrometeorol. 2013, 14, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeriano, O.C.S.; Koike, T.; Yang, D.; Nyunt, C.T.; Van Khanh, D.; Chau, N.L. Flood simulation using different sources of rainfall in the Huong River, Vietnam. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2009, 54, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Ibrahim, A.; Duan, Z.; Cracknell, A.; Chaplot, V. Evaluation of Six High-Resolution Satellite and Ground-Based Precipitation Products over Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.L.; Santo, H. Comparison of GPM IMERG, TMPA 3B42 and PERSIANN-CDR satellite precipitation products over Malaysia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 202, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varikoden, H.; Samah, A.A.; Babu, C.A. Spatial and temporal characteristics of rain intensity in the peninsular Malaysia using TRMM rain rate. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semire, F.A.; Mohd-Mokhtar, R.; Ismail, W.; Mohamad, N.; Mandeep, J.S. Ground validation of space-borne satellite rainfall products in Malaysia. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 50, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soo, E.Z.X.; Jaafar, W.Z.W.; Lai, S.H.; Islam, T.; Srivastava, P. Evaluation of satellite precipitation products for extreme flood events: Case study in Peninsular Malaysia. J. Water Clim. Chang. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ma, J.; Yang, G.; Li, W. Statistical and Hydrological Evaluations of Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products over Fujiang River Basin in Humid Southeast China. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajracharya, S.R.; Palash, W.; Shrestha, M.S.; Khadgi, V.R.; Duo, C.; Das, P.J.; Dorji, C. Systematic Evaluation of Satellite-Based Rainfall Products over the Brahmaputra Basin for Hydrological Applications. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alho, P.; Aaltonen, J. Comparing a 1D hydraulic model with a 2D hydraulic model for the simulation of extreme glacial outburst floods. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 1537–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnifait, L.; Delrieu, G.; Lay, M.L.; Boudevillain, B.; Masson, A.; Belleudy, P.; Gaume, E.; Saulnier, G.-M. Distributed hydrologic and hydraulic modelling with radar rainfall input: Reconstruction of the 8–9 September 2002 catastrophic flood event in the Gard region, France. Adv. Water Resour. 2009, 32, 1077–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.; Thorstensen, A.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.; AghaKouchak, A.; Sanders, B.; Koren, V.; Cui, Z.; Smith, M. A high resolution coupled hydrologic–hydraulic model (HiResFlood-UCI) for flash flood modeling. J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zin, W.W.; Kawasaki, A.; Takeuchi, W.; San, Z.M.L.T.; Htun, K.Z.; Aye, T.H.; Win, S. Flood Hazard Assessment of Bago River Basin, Myanmar. J. Disaster Res. 2018, 13, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, J.; Jakeman, A.J.; Vaze, J.; Croke, B.F.W.; Dutta, D.; Kim, S. Flood inundation modelling: A review of methods, recent advances and uncertainty analysis. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 90, 201–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T.; Ozawa, G.; Kawakami, T.; Nabesaka, S.; Fukami, K. Rainfall–runoff–inundation analysis of the 2010 Pakistan flood in the Kabul River basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2012, 57, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Amarnath, G. Applications of Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates in Flood Inundation Modeling—A Case Study in Mundeni Aru River Basin, Sri Lanka. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastiti, K.D.; An, H.; Kim, Y.; Jung, K. Large-scale rainfall–runoff–inundation modeling for upper Citarum River watershed, Indonesia. Environ. Earth Sci. 2018, 77, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T.; Tatebe, Y.; Iwami, Y.; Tanaka, S. Hydrologic sensitivity of flood runoff and inundation: 2011 Thailand floods in the Chao Phraya River basin. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Try, S.; Lee, G.; Yu, W.; Oeurng, C.; Jang, C. Large-Scale Flood-Inundation Modeling in the Mekong River Basin. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushiyama, T.; Sayama, T.; Tatebe, Y.; Fujioka, S.; Fukami, K. Numerical Simulation of 2010 Pakistan Flood in the Kabul River Basin by Using Lagged Ensemble Rainfall Forecasting. J. Hydrometeorol. 2014, 15, 193–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Amarnath, G. Application of a flood inundation model to analyze the potential impacts of a flood control plan in Mundeni Aru river basin, Sri Lanka. Nat. Hazards 2018, 91, 491–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barasa, B.N.; Perera, E.D.P. Analysis of land use change impacts on flash flood occurrences in the Sosiani River basin Kenya. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2018, 16, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwami, Y.; Hasegawa, A.; Miyamoto, M.; Kudo, S.; Yamazaki, Y.; Ushiyama, T.; Koike, T. Comparative study on climate change impact on precipitation and floods in Asian river basins. Hydrol. Res. Lett. 2017, 11, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greifeneder, F.; Wagner, W.; Sabel, D.; Naeimi, V. Suitability of SAR imagery for automatic flood mapping in the Lower Mekong Basin. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2014, 35, 2857–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Yu, X.; Liu, R.; Huang, C. Sub-pixel flood inundation mapping from multispectral remotely sensed images based on discrete particle swarm optimization. ISPRS J. Photogramm Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.J.P.; Moller, D.K. Microwave remote sensing of flood inundation. Phys. Chem. Earthparts A/B/C 2015, 83–84, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Twele, A.; Cao, W.; Plank, S.; Martinis, S. Sentinel-1-based flood mapping: A fully automated processing chain. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2016, 37, 2990–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-H.; Tsai, P.-H.; Lai, K.-H.; Chen, J.-Y. Cloud removal from multitemporal satellite images using information cloning. IEEE Trans Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laborde, H.; Douzal, V.; Ruiz Piña, H.A.; Morand, S.; Cornu, J.-F. Landsat-8 cloud-free observations in wet tropical areas: A case study in South East Asia. Remote Sens. Lett. 2017, 8, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, K.N.; Chishtie, F.; Anderson, E.R.; Saah, D.; Griffin, R.E. On the merging of optical and SAR satellite imagery for surface water mapping applications. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, K.; Matin, M.A.; Meyer, F.J. Operational Flood Mapping Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-1 SAR Images: A Case Study from Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Wang, D.; Mao, K.; Anagnostou, E.; Hong, Y. Inundation Extent Mapping by Synthetic Aperture Radar: A Review. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumann, G.J.-P.; Brakenridge, G.R.; Kettner, A.J.; Kashif, R.; Niebuhr, E. Assisting Flood Disaster Response with Earth Observation Data and Products: A Critical Assessment. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, G.; de Boissezon, H.; Hosford, S.; Pasco, X.; Montfort, B.; Ranera, F. The evolution of Earth Observation satellites in Europe and its impact on the performance of emergency response services. ACTA Astronaut. 2016, 127, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, S.; Giulio-Tonolo, F.; Lyons, J.; Kučera, J.; Jones, B.; Schneiderhan, T.; Platzeck, G.; Kaku, K.; Hazarika, M.K.; Czaran, L.; et al. Global trends in satellite-based emergency mapping. Science 2016, 353, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Meteorological Organization. Manual on Stream Gauging, Volume 1–Fieldwork; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- BrÁZdil, R.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Benito, G. Historical hydrology for studying flood risk in Europe. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 739–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.L.; Liew, J.; Yusop, Z.; Ismail, T.; Venneker, R.; Uhlenbrook, S. Rainfall Characteristics and Regionalization in Peninsular Malaysia Based on a High Resolution Gridded Data Set. Water 2016, 8, 500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, N.W.; Parker, D.J. Response to dynamic flood hazard factors in peninsular Malaysia. Geogr. J. 1996, 162, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayama, T. Rainfall-Runoff-Inundation Model User’s Manual; Disaster Prevention Research Institute (DPRI), Kyoto University: Kyoto, Japan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lehner, B.; Verdin, K.; Jarvis, A. New Global Hydrography Derived From Spaceborne Elevation Data. Eos. Trans. Agu. 2008, 89, 93–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, R.; Hoan, N.T.; Kobayashi, T.; Alsaaideh, B.; Tana, G.; Phong, D.X. Production of global land cover data-GLCNMO2008. J. Geogr. Geol. 2014, 6, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, R.; Uriyangqai, B.; Al-Bilbisi, H.; Ghar, M.A.; Tsend-Ayush, J.; Kobayashi, T.; Kasimu, A.; Hoan, N.T.; Shalaby, A.; Alsaaideh, B. Production of global land cover data–GLCNMO. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2011, 4, 22–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, G.; Nachtergaele, F.; Prieler, S.; Van Velthuizen, H.; Verelst, L.; Wiberg, D. Global Agro-Ecological Zones Assessment for Agriculture (GAEZ 2008); IIASA, Laxenburg, Austria and FAO: Rome, Italy, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.; Joyce, R.; Xie, P.; Yoo, S.-H. NASA global precipitation measurement (GPM) integrated multi-satellite retrievals for GPM (IMERG). 2015; p. 30. Available online: https://pmm.nasa.gov/sites/default/files/document_files/IMERG_ATBD_V4.5.pdf (accessed on 6 November 2019).
- Hong, Y.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Gao, X. Precipitation Estimation from Remotely Sensed Imagery Using an Artificial Neural Network Cloud Classification System. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 1834–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aonashi, K.; Awaka, J.; Hirose, M.; Kozu, T.; Kubota, T.; Liu, G.; Shige, S.; Kida, S.; Seto, S.; Takahashi, N.; et al. GSMaP Passive Microwave Precipitation Retrieval Algorithm: Algorithm Description and Validation. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. Ii 2009, 87A, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Hashizume, H.; Aonashi, K.; Takahashi, N.; Seto, S.; Hirose, M.; Takayabu, Y.N.; Ushio, T.; Nakagawa, K.; et al. Global Precipitation Map Using Satellite-Borne Microwave Radiometers by the GSMaP Project: Production and Validation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 2259–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ushio, T.; Sasashige, K.; Kubota, T.; Shige, S.; Okamoto, K.i.; Aonashi, K.; Inoue, T.; Takahashi, N.; Iguchi, T.; Kachi, M.; et al. A Kalman Filter Approach to the Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) from Combined Passive Microwave and Infrared Radiometric Data. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. Ser. Ii. 2009, 87A, 137–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, J.; Sutcliffe, J. River forcasting using conceptual models, 1. A discussion of principles. J. Hydrol. 1970, 10, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriasi, D.N.; Arnold, J.G.; Van Liew, M.W.; Bingner, R.L.; Harmel, R.D.; Veith, T.L. Model Evaluation Guidelines for Systematic Quantification of Accuracy in Watershed Simulations. Trans. Asabe 2007, 50, 885–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awange, J.L.; Ferreira, V.G.; Forootan, E.; Andam-Akorful, S.A.; Agutu, N.O.; He, X.F. Uncertainties in remotely sensed precipitation data over Africa. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 303–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, N.; Pradhanang, S.; Lakhankar, T.; Jha, A. Evaluating satellite products for precipitation estimation in mountain regions: A case study for Nepal. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 4107–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satgé, F.; Xavier, A.; Pillco Zolá, R.; Hussain, Y.; Timouk, F.; Garnier, J.; Bonnet, M.-P. Comparative Assessments of the Latest GPM Mission’s Spatially Enhanced Satellite Rainfall Products over the Main Bolivian Watersheds. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakoksung, K.; Takagi, M. Effect of satellite based rainfall products on river basin responses of runoff simulation on flood event. Model Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Zad, S.; Zulkafli, Z.; Muharram, F. Satellite Rainfall (TRMM 3B42-V7) Performance Assessment and Adjustment over Pahang River Basin, Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Samat, N.; Chan, N.; Roy, R. Hydro-Meteorological Assessment of Three GPM Satellite Precipitation Products in the Kelantan River Basin, Malaysia. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhi, A.M.; Rohasliney, H.; Zarul, H. Fish composition and diversity in Perak, Galas and Kelantan rivers (Malaysia) after the major flood of 2014. Transylv. Rev. Syst. Ecol. Res. 2017, 19, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dai, Q.; Bray, M.; Zhuo, L.; Islam, T.; Han, D. A Scheme for Rain Gauge Network Design Based on Remotely Sensed Rainfall Measurements. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 363–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; Viarre, J.; Quantin, G.; Alcoba, M. Evaluation of several rainfall products used for hydrological applications over West Africa using two high-resolution gauge networks. QJRMS 2013, 139, 923–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M. Evaluation of satellite rainfall products through hydrologic simulation in a fully distributed hydrologic model. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, X. Assessing Hydrological Modelling Driven by Different Precipitation Datasets via the SMAP Soil Moisture Product and Gauged Streamflow Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Zhang, L.; Win, K.W.W.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y. Assessment of GPM and TRMM Multi-Satellite Precipitation Products in Streamflow Simulations in a Data-Sparse Mountainous Watershed in Myanmar. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCollum, J.R.; Gruber, A.; Ba, M.B. Discrepancy between Gauges and Satellite Estimates of Rainfall in Equatorial Africa. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 666–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinku, T.; Ruiz, F.; Connor, S.J.; Ceccato, P. Validation and Intercomparison of Satellite Rainfall Estimates over Colombia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Gochis, D.; Cheng, J.-t.; Hsu, K.-l.; Sorooshian, S. Evaluation of PERSIANN-CCS Rainfall Measurement Using the NAME Event Rain Gauge Network. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, M.; Yilmaz, K.K. Evaluation and Bias Correction of Satellite-Based Rainfall Estimates for Modelling Flash Floods over the Mediterranean region: Application to Karpuz River Basin, Turkey. Water 2018, 10, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirpa, F.A.; Gebremichael, M.; Hopson, T. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite Precipitation Products over Very Complex Terrain in Ethiopia. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2010, 49, 1044–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitew, M.M.; Gebremichael, M.; Ghebremichael, L.T.; Bayissa, Y.A. Evaluation of High-Resolution Satellite Rainfall Products through Streamflow Simulation in a Hydrological Modeling of a Small Mountainous Watershed in Ethiopia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2012, 13, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, E.; Haile, A.T.; Sazib, N.; Zhang, Y.; Rientjes, T. Effect of Bias Correction of Satellite-Rainfall Estimates on Runoff Simulations at the Source of the Upper Blue Nile. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6688–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Sun, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, T.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, Q.; Deng, Z. Evaluation and Correction of GPM IMERG Precipitation Products over the Capital Circle in Northeast China at Multiple Spatiotemporal Scales. Adv. Meteorol. 2018, 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfagiorgis, K.; Mahani, S.E.; Krakauer, N.Y.; Khanbilvardi, R. Bias correction of satellite rainfall estimates using a radar-gauge product—A case study in Oklahoma (USA). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 2631–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Pineda, R.; Demaría, E.M.C.; Valdés, J.B.; Wi, S.; Serrat-Capdevilla, A. Bias correction of daily satellite-based rainfall estimates for hydrologic forecasting in the Upper Zambezi, Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2016, 2016, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimani, M.; Hoedjes, J.; Su, Z. Bayesian Bias Correction of Satellite Rainfall Estimates for Climate Studies. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, H.; Nordin, M.; Lakshmi, V.; Huffman, G.J.; Knight, R. Bias Correction of Long-Term Satellite Monthly Precipitation Product (TRMM 3B43) over the Conterminous United States. J. Hydrometeorol. 2017, 18, 2491–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douville, H.; Chauvin, F.; Broqua, H. Influence of Soil Moisture on the Asian and African Monsoons. Part I: Mean Monsoon and Daily Precipitation. JCli 2001, 14, 2381–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brocca, L.; Pellarin, T.; Crow, W.T.; Ciabatta, L.; Massari, C.; Ryu, D.; Su, C.-H.; Rüdiger, C.; Kerr, Y. Rainfall estimation by inverting SMOS soil moisture estimates: A comparison of different methods over Australia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 12062–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, Q.; Bi, H.; Qiu, J.; Zou, P. Evaluation of remotely sensed and reanalysis soil moisture products over the Tibetan Plateau using in-situ observations. RSEnv 2015, 163, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.-H.; Zhang, J.; Gruber, A.; Parinussa, R.; Ryu, D.; Crow, W.T.; Wagner, W. Error decomposition of nine passive and active microwave satellite soil moisture data sets over Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 182, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, W.; Pan, M.; Wanders, N.; Wood, E.F. Correction of real-time satellite precipitation with satellite soil moisture observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 4275–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, W.T.; van den Berg, M.J.; Huffman, G.J.; Pellarin, T. Correcting rainfall using satellite-based surface soil moisture retrievals: The Soil Moisture Analysis Rainfall Tool (SMART). Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Qiu, J.; Liao, W. Use of SMAP Soil Moisture and Fitting Methods in Improving GPM Estimation in Near Real Time. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.K.; Kwak, Y.-J.; Kumar, R.; Sarma, B. Analysis of Hydrological Sensitivity for Flood Risk Assessment. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).