Characterization of Water Level Variability of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area and Characteristics of the Lakes
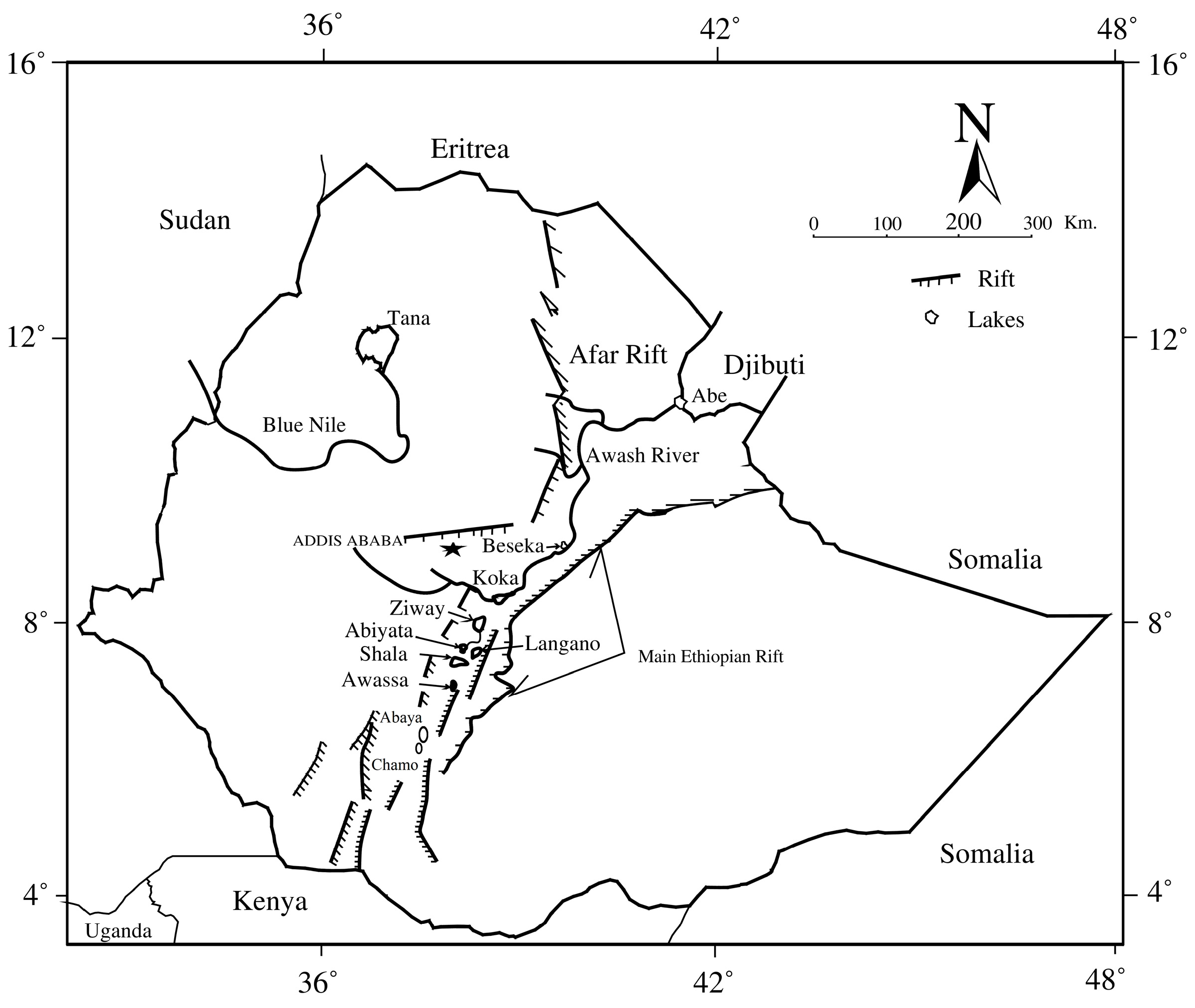
| Elevation (m.a.s.l) | Max. Depth (m) | Mean Depth (m) | Volume (km) | Surface Area (km) | Watershed Area (km) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lake Ziway | 1636 | 8.95 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 442 | 7025 |
| 2 | Lake Abiyata | 1578 | 14.2 | 7.6 | 1.1 | 176 | 1630 |
| 3 | Lake Shalla | 1558 | 266 | 87 | 36.7 | 329 | 3920 |
| 4 | Lake Langano | 1582 | 47.9 | 17 | 5.3 | 241 | 1600 |
| 5 | Lake Hawassa | 1680 | 22 | 11 | 1.34 | 90 | 1250 |
| 6 | Lake Abaya | 1285 | 13.1 | 7.1 | 8.2 | 1162 | 17,300 |
| 7 | Lake Chamo | 1233 | 13 | 6 | 3.3 | 551 | 2210 |
| 8 | Lake Beseka | 1200 | 11 | 8 | 0.280 (in 2010) | 2.7 (1969); 48.5 (2010) | 505 |
2.2. Available Data
| Name of the Lake | Inflow | Outflow | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P | Sin | Run | GWi | E | Sout | A | GWo | |||
| 1 | Ziway (in 106 m3) | 323 | 656.5 | 48 | 80.5 | 890 | 184 | 28 | 14.6 | Ayenew [7] |
| (mm) | 750 | 1530 | 1720 | Deganovsky and Getahun [21] | ||||||
| (mm) | 753 | 0.692 km3 | 0.05 km3 | 100 | 1740 | 200 (net) | Vallet-Coulomb et al. [24] | |||
| 2 | Langano (in ×106 m3) | 186 | 212 | 135.4 | 463 | 46 | 18.9 | Ayenew [7] | ||
| 3 | Abiyata (in ×106 m3) | 113 | 230 | 15 | 26.8 | 372 | 0 | 13 | 1.2 | Ayenew [7] |
| (in ×106 m3) | 97.2 | 179.87 | 13.92 | 290.97 | 0 | 0 | Ayalew [25] | |||
| 4 | Shalla (in ×106 m3) | 232 | 245 | 18 | 40 | 781 | 0 | Ayenew [7] | ||
| 5 | Hawassa (in ×106 m3) | 106 | 83.1 | 132 | 0 | 58 | Ayenew [7] | |||
| (mm) | 950 | 1440 | 1440 | 0 | 570 | Deganovsky and Getahun [21] | ||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 80.6 | 74 | 90 | 164.6 | 0 | 71 | WWDSE [20] | |||
| (in ×106 m3) | 106 | 83 | 131 | 0 | 58 | Ayenew and Gebreegziabher [26] | ||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 90 | 167 | 148 | Gebremichael [27] | ||||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 98.9 | 54.9 | 44.44 | 178.93 | 0 | Shewangizaw [28] | ||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 90.72 | 88.29 | 91.57 | 3.2 | 166.66 | 71.5 | WRDB [29] | |||
| (in ×106 m3) | 106 | 83.7 - | 132 | 0 | 58 | Gebreegziabher [10] | ||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 106 | 83.7 - | 132 | 58 | Ayenew [8] | |||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 52.5 | Ayenew and Tilahun [30] | ||||||||
| 6 | Abaya (in ×106 m3) | 556 | 1900 | Ayenew [7] | ||||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 980 | 750 | 691 | 2009 | Belete [31] | |||||
| (mm) | 730 | 1080 | 1700 | Deganovsky and Getahun [21] | ||||||
| 7 | Chamo (in ×106 m3) | 406 | 900.9 | Ayenew [7] | ||||||
| 8 | Beseka (in ×106 m3) | 22 | 30 | 52.8 | 98.8 | Ayenew [7] | ||||
| (in ×106 m3) | 24.4 | 7.7 | 33.8 | 61.8 | 0.22 | Belay [9] | ||||
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Water Balance Approach to Characterize the Lake Level Regimes
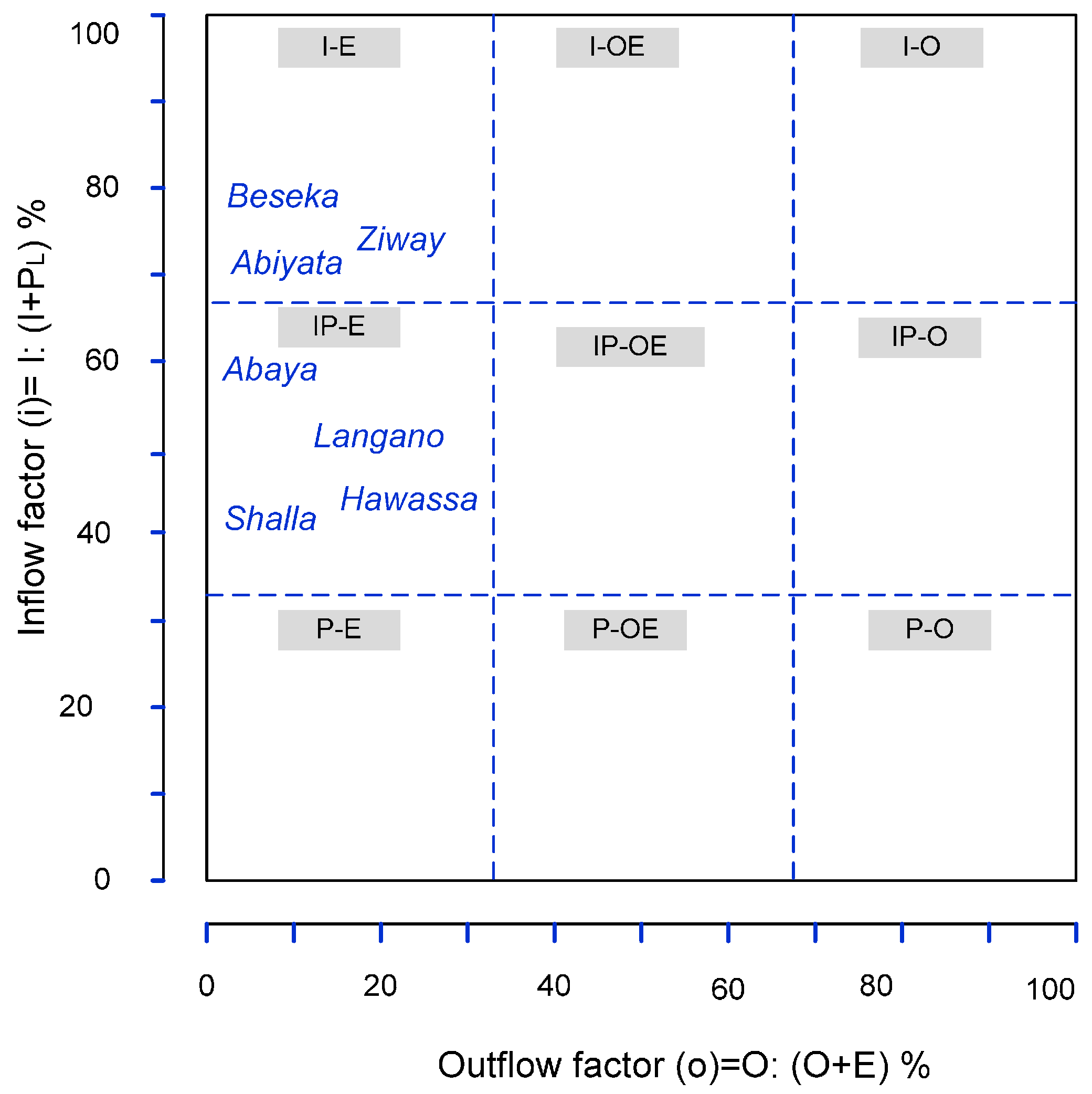
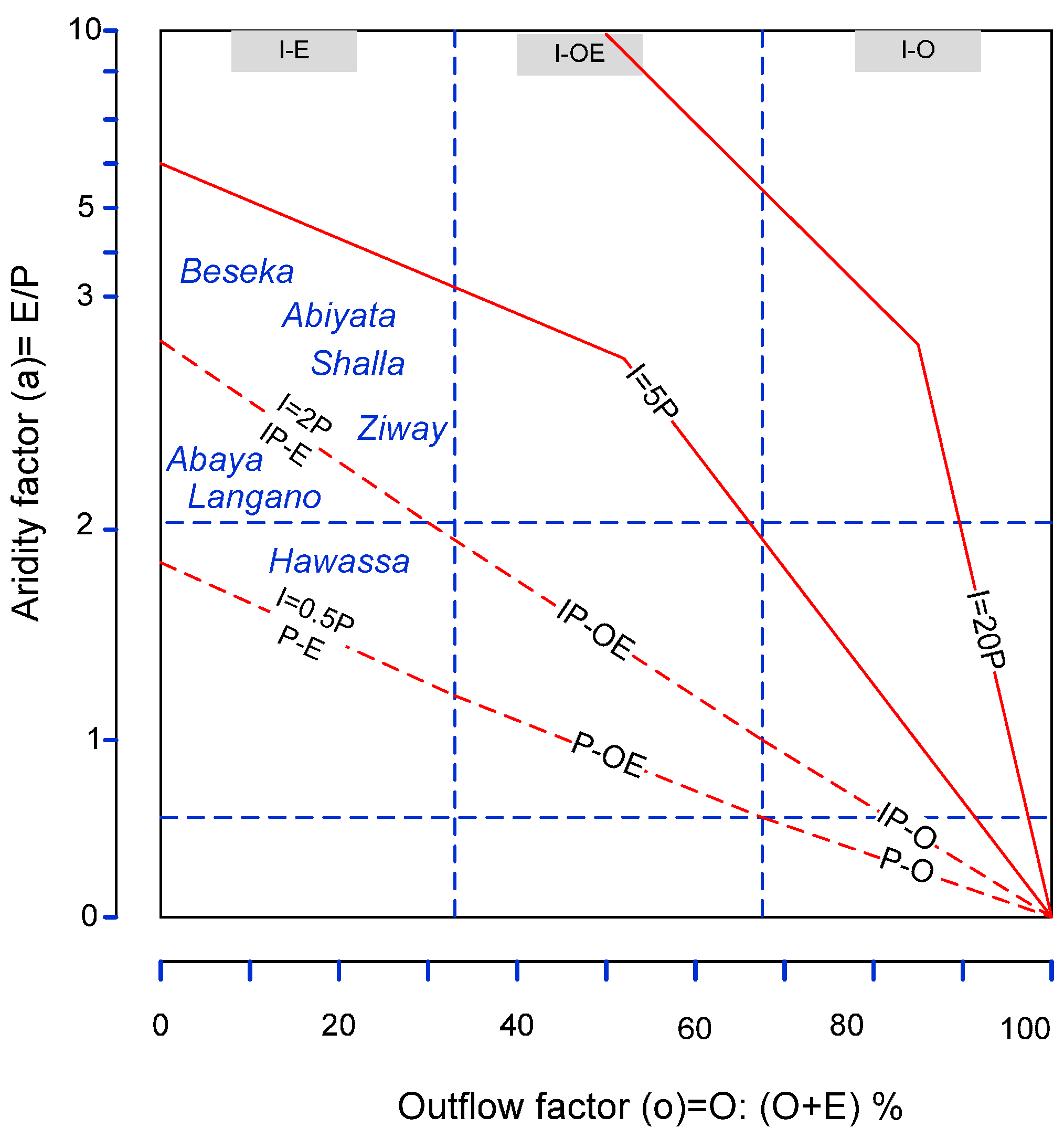
2.3.2. Morphological Approach to Characterize the Lake Level Regimes
2.3.3. Detection of Regime Shift (Pettit’s Homogeneity Test)
2.3.4. Trend Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Classification of the Lakes Based on Long-Term Water Balance
| Inflow Factor (i) | Outflow Factor (o) | Aridity (a) | Without Aridity Factor | With Aridity Factor | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lake Ziway | 69.0 | 22.6 | 2.5 | I-E * | IP-E * |
| 2 | Lake Langano | 65.1 | 12.3 | 2.5 | IP-E * | IP-E * |
| 3 | Lake Abiyata | 68.6 | 3.7 | 3.1 | I-E * | I-E * |
| 4 | Lake Shalla | 56.6 | 0.0 | 3.4 | IP-E * | I-E * |
| 5 | Lake Hawassa | 53.3 | 23.2 ** | 1.5 | IP-E * | IP-E * |
| 6 | Lake Abaya | 59.5 | 0.0 | 2.6 | IP-E * | IP-E * |
| 7 | Lake Chamo | Incomplete | incomplete | 2.2 | ||
| 8 | Lake Beseka | 79.0 | 0.0 | 4.5 | I-E * | I-E * |
3.2. Classification of the Lakes Based on Morphology
| Surface Area (km) | Watershed Area (km) | Specific Watershed [–] | About Level-Regime | Expected Mean Annual Amplitude (cm) ** | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lake Ziway | 442 | 7025 | 16 | Moderately stable | 50–130 |
| 2 | Lake Langano | 241 | 1600 | 6.6 | stable | 30–65 |
| 3 | Lake Abiyata | 176 | 1630 | 9.3 | stable | 30–65 |
| 4 | Lake Shalla | 329 | 3920 | 12 | Moderately stable | 50–130 |
| 5 | Lake Hawassa | 90 | 1250 | 14 | Moderately stable | 50–130 |
| 6 | Lake Abaya | 1162 | 17,300 | 15 | Moderately stable | 50–130 |
| 7 | Lake Chamo | 551 | 2210 | 4 | stable | 30–65 |
| 8 | Lake Beseka | 43 | 505 | 11.7 | Moderately stable | 50–130 |
3.3. Results of Homogeneity and Trend Tests
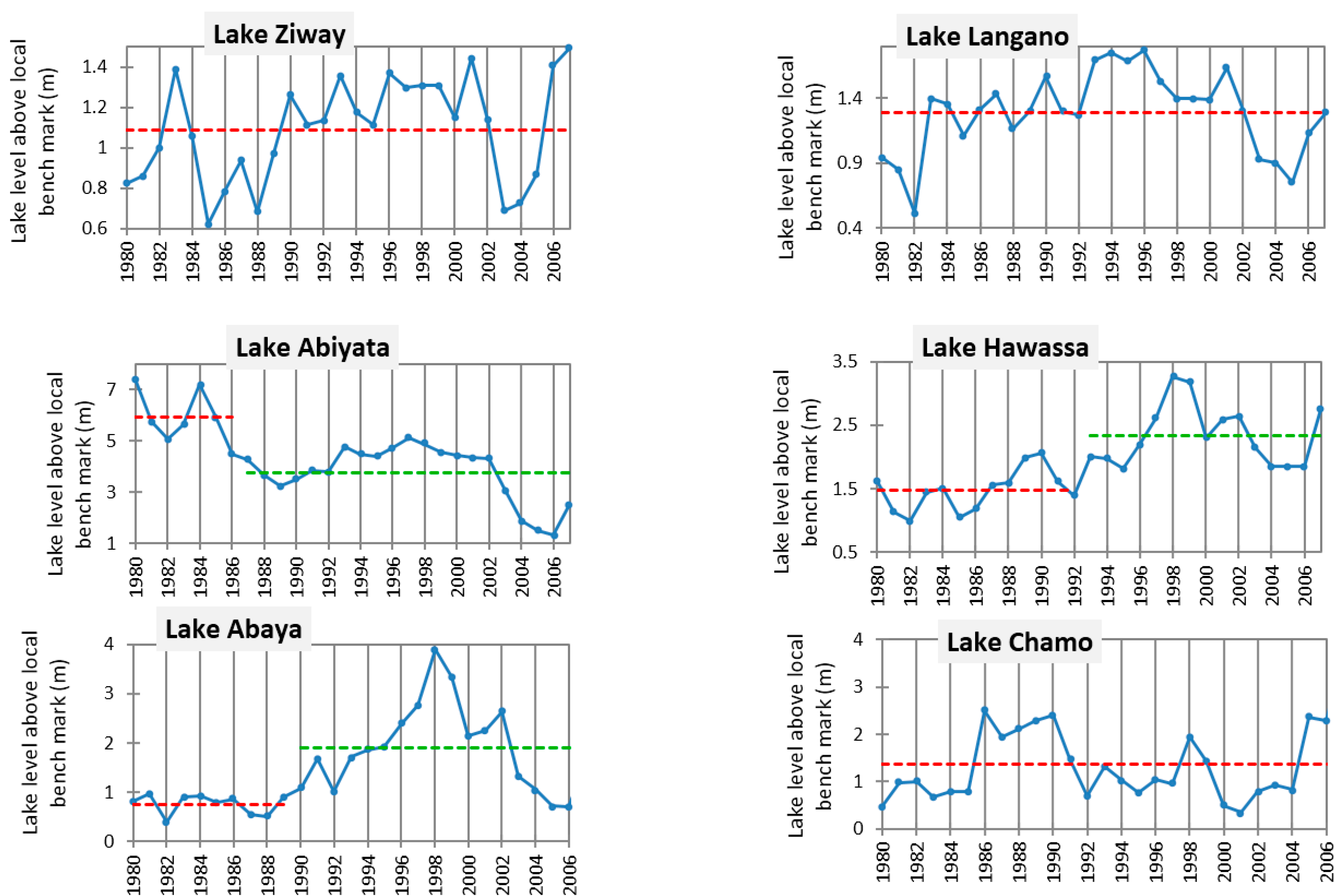
| MK τ** | Interpretation | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lake Ziway | 0.324 | Increasing |
| 2 | Lake Langano | 0.037 | No trend |
| 3 | Lake Abiyata | −0.492 | Decreasing |
| 4 | Lake Shalla | - | - |
| 5 | Lake Hawassa | 0.531 | Increasing |
| 6 | Lake Abaya | 0.363 | increasing |
| 7 | Lake Chamo | 0.106 | No trend |
| 8 | Lake Beseka | - | Increasing |
3.3.1. Lake Ziway
3.3.2. Lake Langano
3.3.3. Lake Abiyata
3.3.4. Lake Hawassa
3.3.5. Lake Abaya
| Land Use/Land Cover | In the Year 1986 (ha) | In the Year 2000 (ha) | Change in Percent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bushland | 50,459.8 | 59,442.4 | 17.8 |
| Wetland | 31,512.7 | 20,790.8 | −34 |
| Forest | 180,832 | 143,195 | −20.8 |
| Agriculture | 24,506.7 | 72,254.3 | 194.84 |
| Water | 137,734 | 137,320 | −0.3 |
| Grassland | 17,150.2 | 9192.48 | −46.4 |
3.3.6. Lake Chamo
3.3.7. Lake Shalla
3.3.8. Lake Beseka
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Vuglinskiy, V. Water Level in Lakes and Reservoirs, Water Storage. Global Terrestrial Observing System: Rome, 2009; Available online: http://www.fao.org/gtos/doc/ECVs/T04/T04.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Zohary, T.; Ostrovsky, I. Ecological impacts of excessive water level fluctuations in stratified freshwater lakes. Inland Waters 2011, 1, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffer, M.; Carpenter, S.R. Catastrophic regime shifts in ecosystems: Linking theory to observation. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 648–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinshiro, N. Hydrological Regime on the Regulation of Lake-Level. A Contribution to the Paleolimnological Study of Lake Biwa. Available online: https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/pjab1945/50/9/50_9_665/_pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Hayashi, M.; van der Kamp, G. Water Level Changes in Ponds and Lakes: The Hydrological Processes. Available online: http://people.ucalgary.ca/~hayashi/um_may2007/Ch10_final.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Gasith, A.; Gafny, S. Effects of water level fluctuation on the structure and function of the littoral zone. In Large Lakes: Ecological Structure and Function; Tilzer, M.M., Serruya, C., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1990; pp. 156–171. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenew, T. Environmental implications of changes in the levels of lakes in the Ethiopian Rift since 1970. Regional Environ. Chang. 2004, 4, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, T. Water management problems in the Ethiopian rift: Challenges for development. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2007, 48, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belay, E.A. Growing Lake with Growing Problems: Integrated Hydrogeological Investigation on Lake Beseka, Ethiopia. Ph.D. Thesis, Rheinischen Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn, Bonn, Germany, 2009. Available online: http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/2009/1645/1645.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Gebreegziabher, Y. Assessment of the Water Balance of Lake Awassa Catchment, Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, International Institute for Geo-information Science and Earth Observation, Enschede, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bewketu, K. Hydrodynamics of Selected Ethiopian Rift Lakes. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- MoWR. The Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia-Ministry of Water Resources: Rift Valley Lakes Basin Integrated Resources Development Master Plan Study Project. Phase 3 Report: Lake Hawassa Sub-basin Integrated Watershed Management Feasibility Study. Part 1 and 2; Halcrow Group Limited and Generation Integrated Rural Development (GIRD) Consultants: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Alemayehu, T.; Ayenew, T.; Kebede, S. Hydrogeochemical and lake level changes in the Ethiopian Rift. J. Hydrol. 2006, 316, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.B.; Talling, J.F. Chemical and algal relationship in a salinity series of Ethiopian inland waters. Hydrobiologia 1988, 158, 29–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, E.; Zinabu, G.M.; Ahlgren, I. The Ethiopian rift-valley lakes: Chemical characters along a salinity-alkalinity gradient. Hydrobiologia 1994, 288, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernet, T. Hydrogeology of the Lakes Region, Ethiopia; Ministry of Mines and Energy: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1982; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenew, T. The Hydrogeological System of the Lake District Basin: Central Main Ethiopian Rift. Ph.D. Thesis, Free University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; p. 259. [Google Scholar]
- Tessema, Z. Hydrochemical and water balance approach in the study of high water level rise of Lake Beseka. Master’s Thesis, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, UK, 1998; p. 90. [Google Scholar]
- MoWR. Master Plan for the Development of Surface Water Resources in Ten Awash Basin; Ministry of Water Resources: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1989; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Water Works Design and Supervision Enterprise (WWDSE). The study of Lake Awassa Level Rise. Southern Nations Nationalities and Peoples Regional State; Water, Mines and Energy Resources Development Bureau: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Deganovsky, A.M.; Getahun, A. Water balance and level regime of Ethiopian lakes as integral indicators of climate change. In Proceedings of the 12th World Lake Conference (Taal 2007), Jaipur, India, 29 October–2 November 2007.
- Goerner, A.; Jolie, E.; Gloaguen, R. Non-climatic growth of the saline Lake Beseka. Main Ethiopian Rift. J. Arid Environ. 2009, 73, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinka, M.O. Analysing the extent (size and shape) of Lake Basaka expansion (Main Ethiopian Rift Valley) using remote sensing and GIS. Lakes Reserv. Res. Manag. 2012, 17, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Legesse, D.; Gasse, G.; Travi, Y.; Chernet, T. Lake evaporation estimates in tropical Africa (Lake Ziway, Ethiopia). J. Hydrol. 2001, 245, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayalew, E. Application of Stable Isotopes in the Study of Lake Dynamics in Ziway-Shalla Basin. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenew, T.; Gebreegziabher, Y. Application of a spreadsheet hydrological model for computing the long-term water balance of Lake Awassa, Ethiopia. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2006, 51, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremichael, H. Modeling and Forecasting Hawassa Lake Level Fluctuation. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shewangizaw, D. Assessing the effect of land use changes on the hydraulic regime of Lake Hawassa. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Water Resources Development Bureau (WRDB). Study of Pollution of Lakes and Rivers; AG Consulting Hydrogeologists and Engineers Plc: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Ayenew, T.; Tilahun, N. Assessment of lake-groundwater interactions and anthropogenic stresses, using numerical groundwater flow model for a Rift lake catchment in central Ethiopia. Lakes Reservoirs Res. Manag. 2008, 13, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belete, A. Climate Change Impact on Lake Abaya Water Level. Master’s Thesis, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Szesztay, K. Water balance and water level fluctuation of lakes. Hydrol. Sci. Bull. 1974, 19, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litinskaya, K.D. Long-Term Water Stage Regime in Natural Lakes of Karelia and Its Changes in View of Conversion of Lakes into Storage Reservoirs. Available online: http://hydrologie.org/redbooks/a109/iahs_109_0486.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Pettitt, A.N. A non-parametric approach to change point problem. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, H.B. Non-parametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Measures; Charles Griffin: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Lukács, B.A.; Tóthmérészb, B.; Boricsa, G.; Várbíróa, G.; Juhászc, P.; Kissc, B.; Müller, Z.; G-Tóth, L.; Eros, T. Macrophyte diversity of lakes in the Pannon Ecoregion (Hungary). Limnologica 2015, 53, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muvundja, F.A.; Wüest, A.; Isumbisho, M.; Kaningini, M.B.; Pasche, N.; Rinta, P.; Schmid, M. Modelling Lake Kivu water level variations over the last seven decades. Limnologica 2014, 47, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buishand, T.A. Some methods for testing the homogeneity of rainfall records. J. Hydrol. 1982, 58, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Gupta, A.K. Parametric Statistical Change Point Analysis; Birkhauser: Boston, MA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Radziejewski, M.; Bardossy, A.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Detection of change in river flow using phase randomization. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2000, 45, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, L.; McVicar, T.R.; Chille, B.; Gau, P. Analysis of the impact of conservation measures on stream flow regime in catchments of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process 2007, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Mu, X.-M.; Wang, F.; Li, R. Changes in streamflow and sediment discharge and the response to human activities in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, S.N. A sequential algorithm for testing climate regime shifts. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, S.N. A Brief Overview of the Regime Shift Detection Methods. Available online: http://www.beringclimate.noaa.gov/regimes/rodionov_overview.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Wijngaard, J.; Klein, T.; Können, G.P. Homogeneity of 20th century European daily temperature and precipitation series. Int. J. Climatol. 2003, 23, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.M.; Yusof, F. Homogeneity Tests on Daily Rainfall Series in Peninsular Malaysia. Int. J. Contemp. Math. Sci. 2012, 7, 9–22. [Google Scholar]
- Salarijazi, M.; Ahmadianfar, I.; Ameriun, M.S.; Salari, A.; Najafpour, K. Non parametric spatial and temporal analysis of temperature characteristics in Karoun & Dez watershed. In Proceedings of the 4th National Conference on Water Resources, Tehran, Iran, 3–4 May 2011. (In Persian)
- Kahya, E.; Kalayci, S. Trend analysis of stream flow in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2004, 289, 128–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NNSMP-National Non-Point Source Monitoring Program. Statistical Analysis for Monotonic Trends. Technical Note 6, 2011. Available online: http://www.bae.ncsu.edu/programs/extension/wqg/319monitoring/TechNotes/technote6_trend_analysis.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Texas State Auditor’s Office (TSOA). Data Analysis: Analyzing Data—Trend Analysis-2.Methodology Manual, Rev. 5/95, 1995. Available online: http://www.sputtr.com/trend+analysis (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Partal, T.; Kahya, E. Trend analysis in Turkish precipitation data. Hydrol. Process 2006, 20, 2011–2026. [Google Scholar]
- Tereshchenko, I.; Filonov, A.; Gallegos, A.; Monzón, C.; Rodríguez, R. El Niño 1997–98 and the hydrometeorological variability of Chapala, a shallow tropical lake in Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2002, 264, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strub, P.T.; James, C. Altimeter-Derived Surface Circulation in the Large-Scale NE Pacific Gyres. Part 2. 1997–1998 anomalies. Progress Oceanogr. 2002, 53, 185–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, D.; Ayenew, T. Effect of improper water and land resource utilization on the central Main Ethiopian Rift lakes. Quat. Int. 2006, 148, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilalta, E.R. Water resources management in the central Rift Valley of Ethiopia. Master’s Thesis, Civil Engineering, Barcelona, Spain, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Billi, P.; Dramis, F. Geomorphological Investigation on Gully Erosion in the Rift Valley and Northern Highlands of Ethiopia. Catena 2003, 50, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, T. Numerical groundwater flow modeling of the Central Main Ethiopian Rift lakes basin. SINET Ethiop. J. Sci. 2001, 24, 167–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, D.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Gasse, F. Analysis of the hydrological response of a tropical terminal lake, Lake Abiyata (Main Ethiopian Rift Valley) to changes in climate and human activities. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagesho, N.; Goel, N.K.; Jain, M.K. Investigation of non-stationarity in hydro-climatic variables at Rift Valley lakes basin of Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. 2012, 444–445, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, A.L.; Leng, M.J.; Lamb, H.F.; Telford, R.J.; Mohammed, M.U. Climatic and non-climatic effects on the δ O and δ C compositions of Lake Awassa, Ethiopia, during the last 6.5 ka. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2002, 21, 2199–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayenew, T. Vulnerability of Selected Ethiopian Lakes to Climatic Variability, Tectonism and Water Use: Global Change System for Analysis, Research and Training (START), 2006. Available online: http://start.org/download/gec05/ayenew-final.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Esayas, Y. Evaluating the Impact of Land Use/Land Cover Change on Soil Erosion Runoff Using SWAT Model at Tikur Wuha Watershed. Available online: http://etd.aau.edu.et/bitstream/123456789/993/3/Yacob%20Esayas.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2015).
- Awulachew, S.B. Characteristics Investigation of physical and bathymetric characteristics of Lakes Abaya and Chamo and their management implications. Lakes Reservoirs Res. Manag. 2006, 11, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, M.A.; Williams, F.M.; Bishop, P.M. Late Quaternary history of Lake Beseka, Ethiopia. Palaeoecol. Afr. Surround. Islands Antarct. 1981, 13, 93–104. [Google Scholar]
- Water Works Design and Supervision Enterprise (WWDSE). Study of Lake Beseka; Ministry of Water Resources: Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 1999; Volume 1, p. 203. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Belete, M.D.; Diekkrüger, B.; Roehrig, J. Characterization of Water Level Variability of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes. Hydrology 2016, 3, 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010001
Belete MD, Diekkrüger B, Roehrig J. Characterization of Water Level Variability of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes. Hydrology. 2016; 3(1):1. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleBelete, Mulugeta Dadi, Bernd Diekkrüger, and Jackson Roehrig. 2016. "Characterization of Water Level Variability of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes" Hydrology 3, no. 1: 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010001
APA StyleBelete, M. D., Diekkrüger, B., & Roehrig, J. (2016). Characterization of Water Level Variability of the Main Ethiopian Rift Valley Lakes. Hydrology, 3(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology3010001






