Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Lagged Hydrological Impacts of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events in the Poyang Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Definition of Compound Drought and Heatwave Event
2.3.2. Definition of Streamflow Drought and Lake Water Drought
2.3.3. Trend Analysis
2.3.4. Event-Based Coincidence Analysis
3. Results
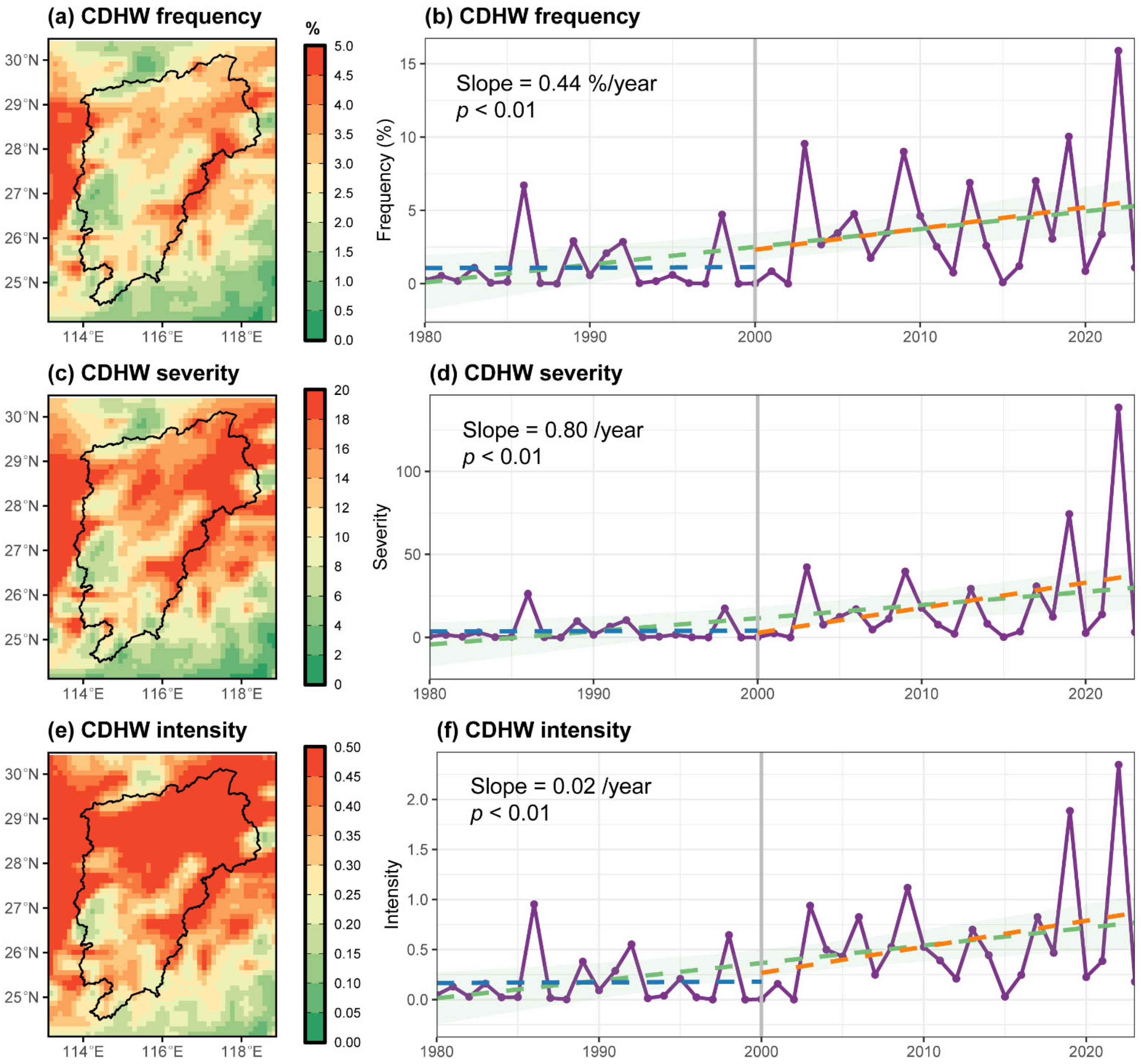
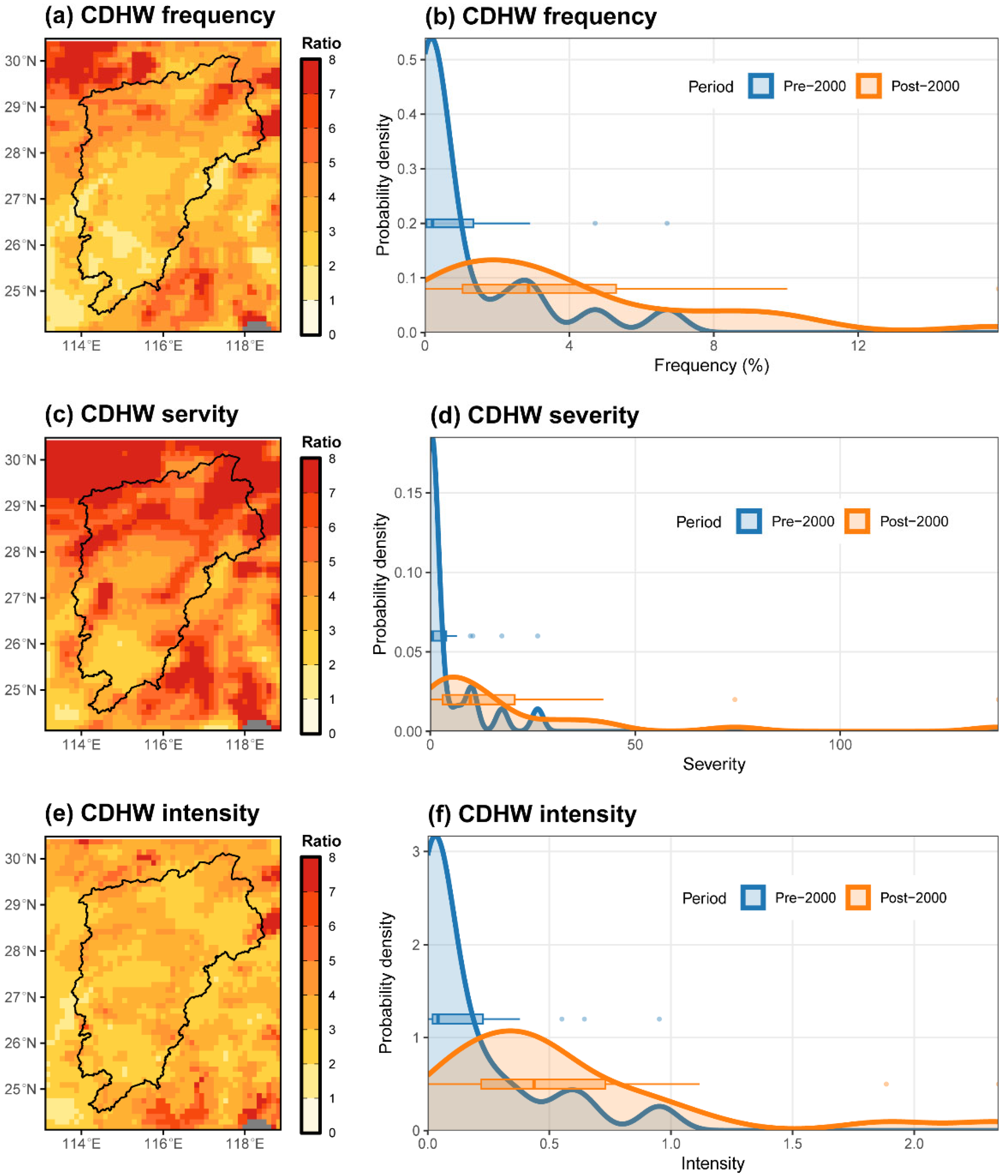
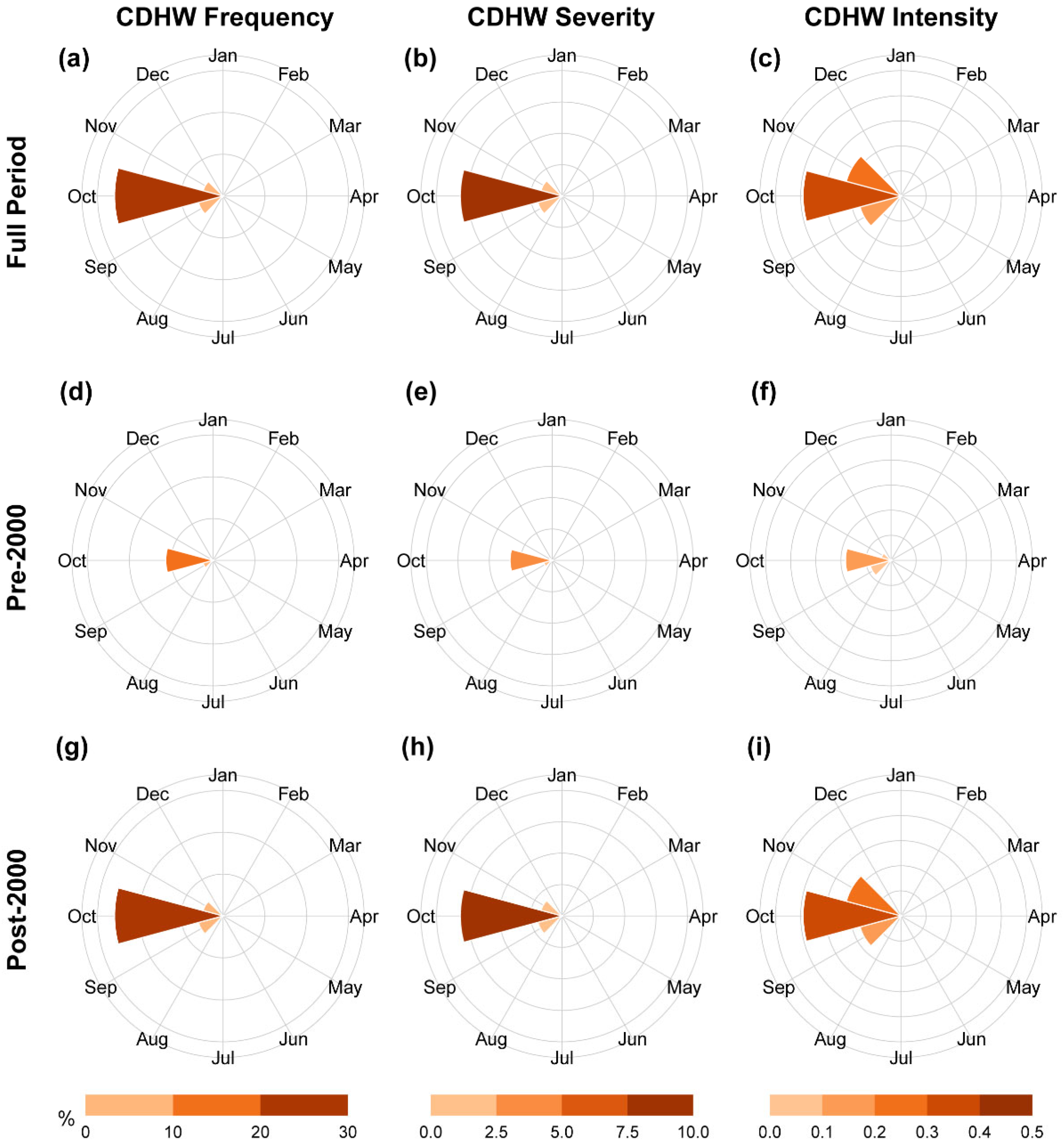
3.1. Spatiotemporal Trends of CDHW
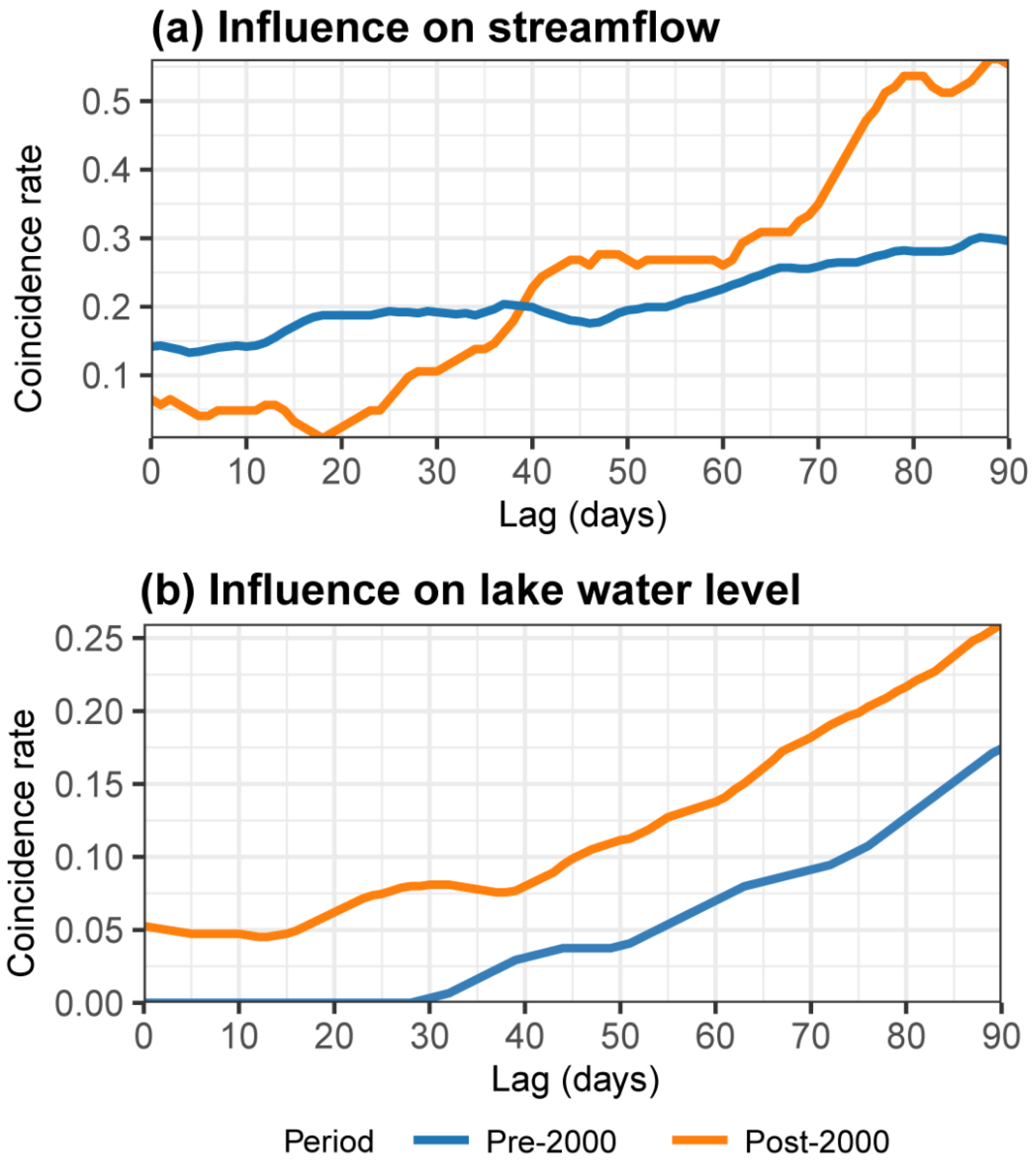
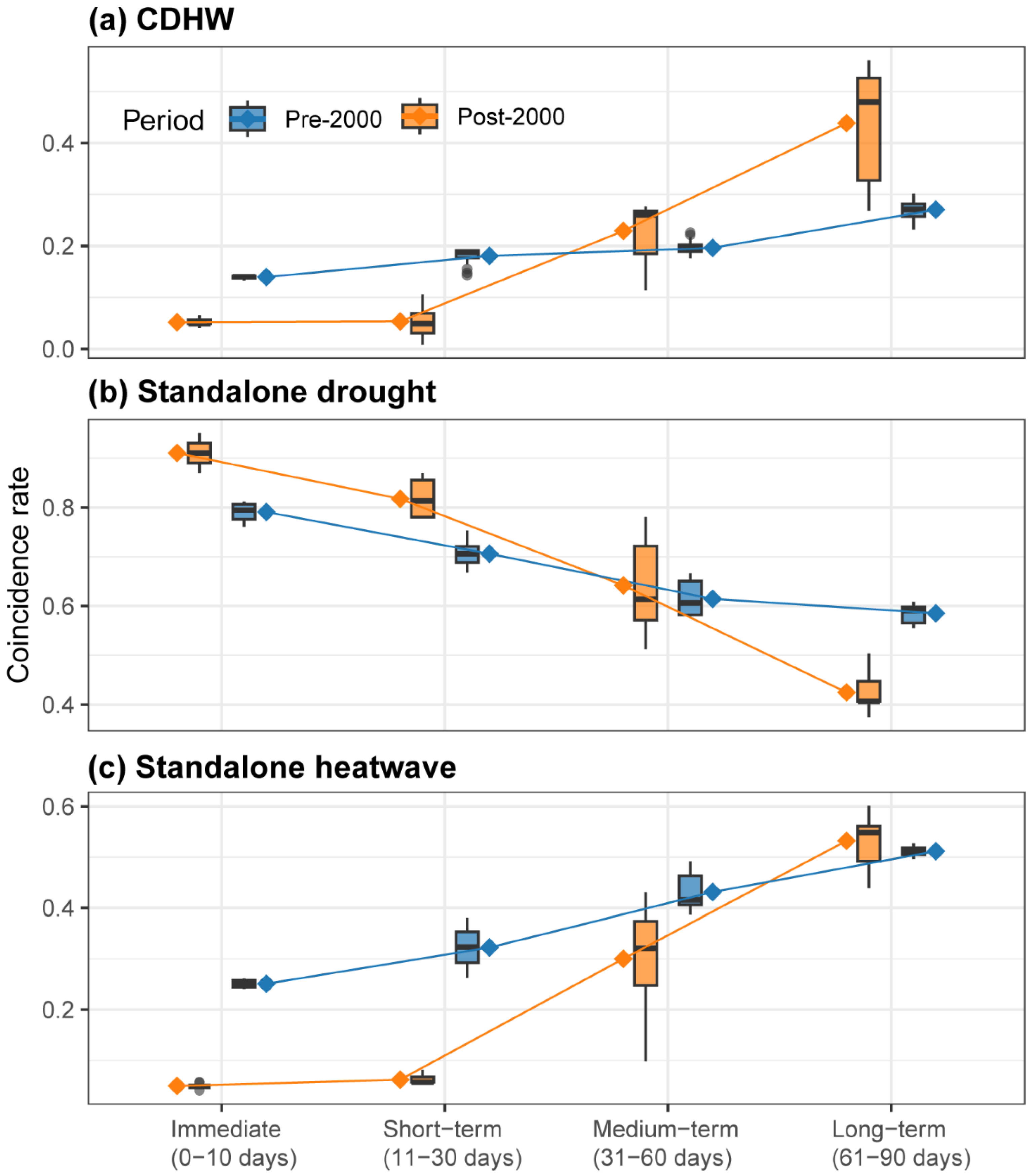
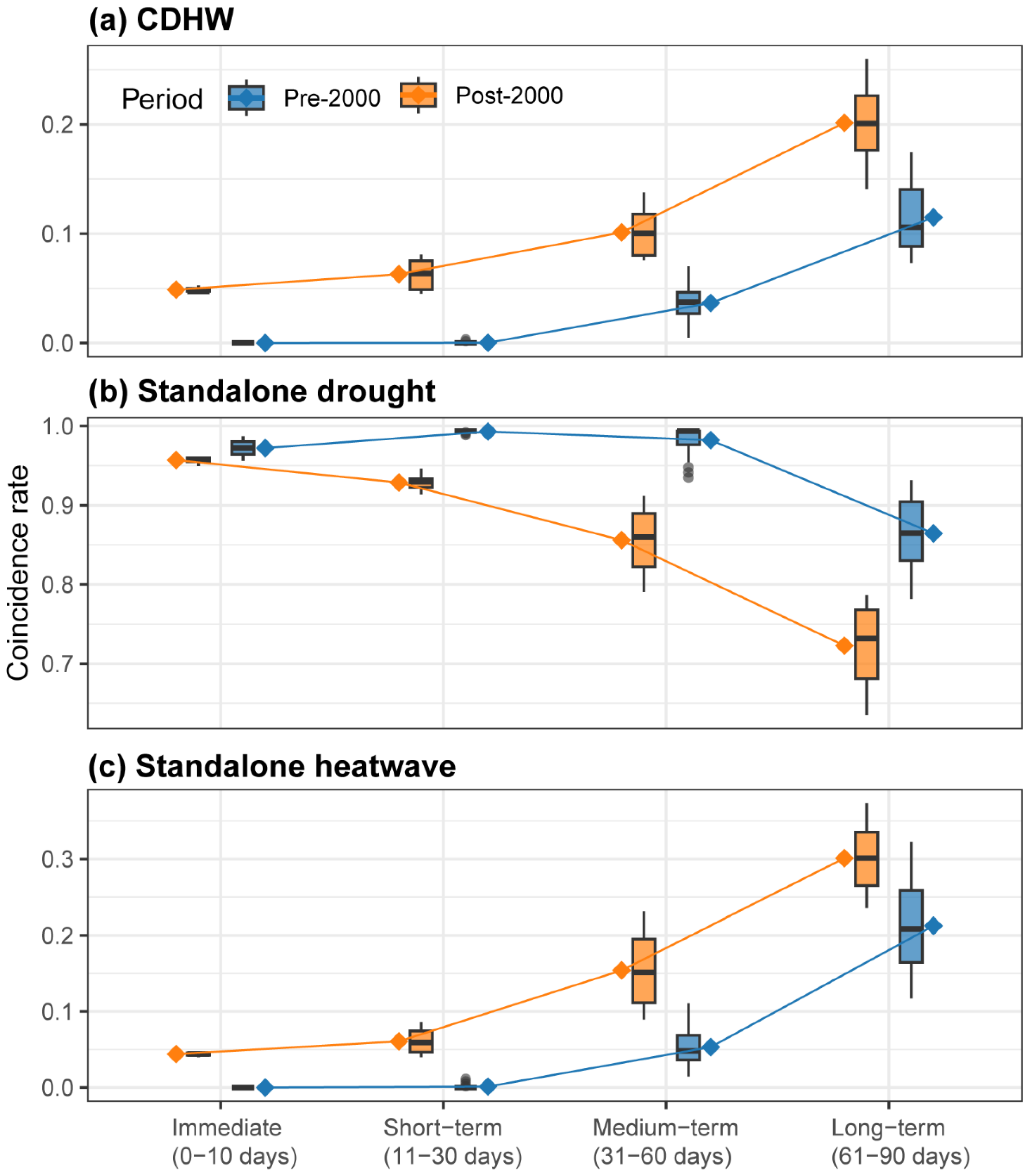
3.2. Lagged Influence of CDHW on Hydrological Drought
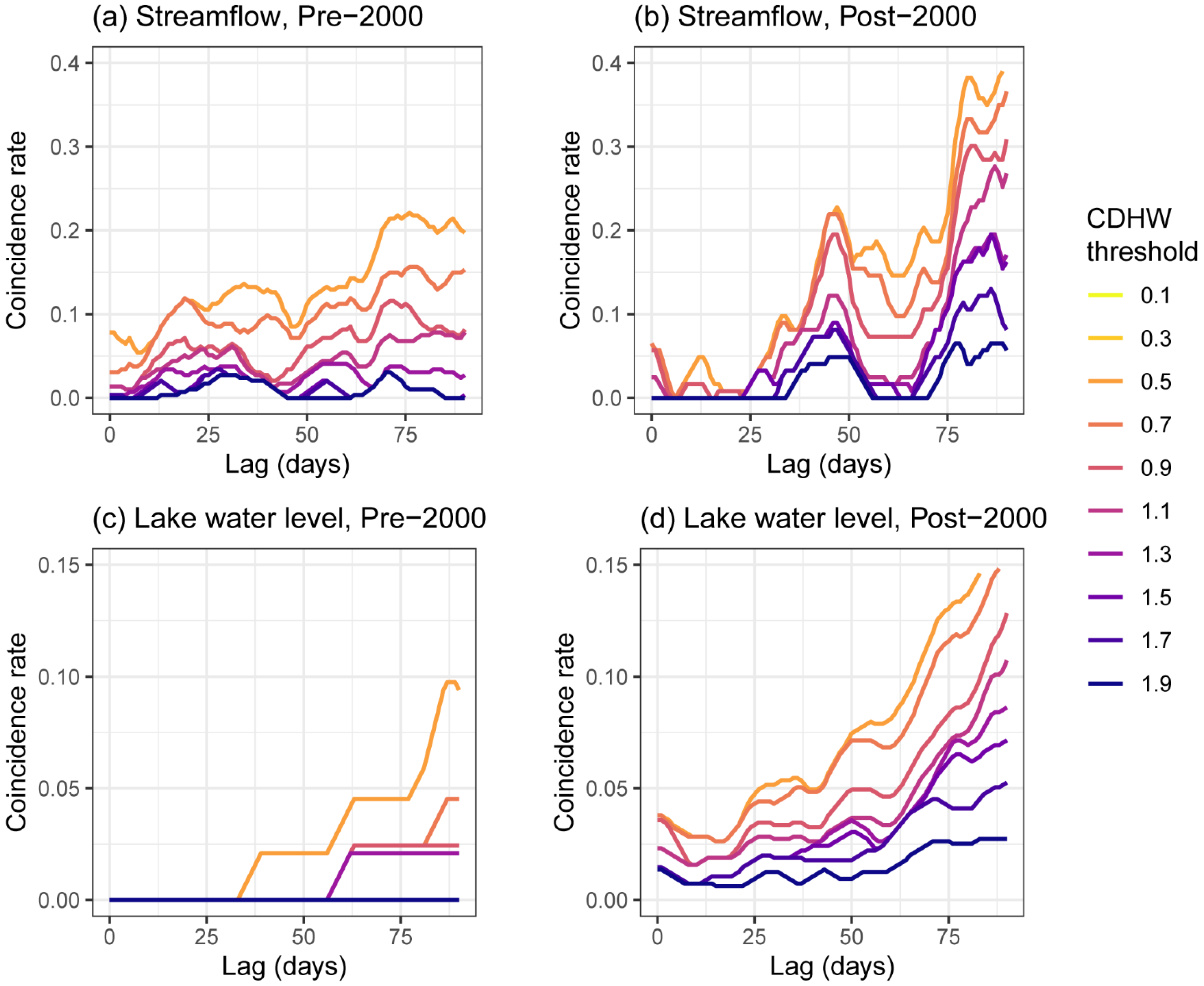
3.3. Sensitivity of CDHW’s Influence on Hydrological Regimes
4. Discussion
4.1. Increasing Threat of CDHW
4.2. Lagged Influence on Hydrological Drought
4.3. Implications, Limitations and Future Scope
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDHW | Compound drought and heatwave |
| ECA | Event coincidence analysis |
| PLB | Poyang Lake Basin |
| SPI | Standardized Precipitation Index |
| STI | Standardized Temperature Index |
| SRI | Standardized Runoff Index |
| SWI | Standardized Water-level Index |
References
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; King, A.D. Time of Emergence of Record-Shattering Compound Heatwave-Extreme Precipitation Events and Their Socio-Economic Exposures. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2025, 52, e2025GL116884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.K. Increase in Compound Drought and Heatwaves in a Warming World. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2020GL090617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Gu, X.; Slater, L.J.; Dembélé, M.; Tosunoğlu, F.; Guan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X.; Kong, D.; Xie, F.; et al. Amplification of Coupled Hot-Dry Extremes over Eastern Monsoon China. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Slater, L. Understanding Heatwave-Drought Compound Hazards and Impacts on Socio-Ecosystems. TIG 2023, 1, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, R.; Gu, X.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, X. Increasing Likelihood of Global Compound Hot-Dry Extremes from Temperature and Runoff during the Past 120 Years. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böhnisch, A.; Felsche, E.; Mittermeier, M.; Poschlod, B.; Ludwig, R. Future Patterns of Compound Dry and Hot Summers and Their Link to Soil Moisture Droughts in Europe. Earths Future 2025, 13, e2024EF004916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Ashfaq, M.; Kao, S.-C. Relative Effect of Anthropogenic Warming and Natural Climate Variability to Changes in Compound Drought and Heatwaves. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Cheng, L.; Zhou, P.; Liu, Z. Compound Hot Droughts over China: Identification, Risk Patterns and Variations. Atmos. Res. 2019, 227, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yin, J.; Su, T.; Xiong, L.; Xia, J. Understanding Compound Extreme Precipitations Preconditioned by Heatwaves over China under Climate Change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 064077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, S. The 2022-like Compound Dry and Hot Extreme in the Northern Hemisphere: Extremeness, Attribution, and Projection. Atmos. Res. 2023, 295, 107009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gu, X.; Bai, W.; Slater, L.J.; Li, J.; Kong, D.; Liu, J.; Li, Y. Asymmetric Response of Short- and Long-Duration Dry Spells to Warming during the Warm-Rain Season over Eastern Monsoon China. J. Hydrol. 2021, 603, 127114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Mujumdar, P.P. Spatial Synchrony, Temporal Clustering and Dominant Driver of Streamflow Droughts in Peninsular India. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 074056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Shi, L.; Su, X.; Song, S.; Feng, K.; Zhang, T.; Fu, X. Development of a Novel Daily-Scale Compound Dry and Hot Index and Its Application across Seven Climatic Regions of China. Atmos. Res. 2023, 287, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Ren, L.; Singh, V.P.; Yong, B.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, F.; Yang, X. Understanding the Spatiotemporal Links Between Meteorological and Hydrological Droughts from a Three-Dimensional Perspective. JGR Atmos. 2019, 124, 3090–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, I.; Zeng, X.-M.; Mukherjee, S.; Aadhar, S.; Mishra, A.K.; Syed, S.; Ayugi, B.O.; Iyakaremye, V.; Lv, H. Future Amplification of Multivariate Risk of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events on South Asian Population. Earths Future 2023, 11, e2023EF003688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Vrac, M. Time of Emergence of Compound Events: Contribution of Univariate and Dependence Properties. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 23, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Li, Y.; Sun, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Drought-Heatwave Compound Events Are Stronger in Drylands. Weather Clim. Extrem. 2023, 42, 100632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Gong, D.; Ding, M.; Zhong, W.; Deng, M.; Kang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J. Spatiotemporal Heterogeneity and Zonal Adaptation Strategies for Agricultural Risks of Compound Dry and Hot Events in China’s Middle Yangtze River Basin. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Yew Gan, T.; Su, X.; Wu, H.; Shi, L.; Xu, P.; Fu, X. Evaluating Vegetation Vulnerability under Compound Dry and Hot Conditions Using Vine Copula across Global Lands. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donges, J.F.; Schleussner, C.-F.; Siegmund, J.F.; Donner, R.V. Event Coincidence Analysis for Quantifying Statistical Interrelationships between Event Time Series: On the Role of Flood Events as Triggers of Epidemic Outbreaks. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2016, 225, 471–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, J.F.; Siegmund, N.; Donner, R.V. CoinCalc—A New R Package for Quantifying Simultaneities of Event Series. Comput. Geosci. 2017, 98, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Wei, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Yi, P.; Ju, Q.; Laux, P.; Kunstmann, H. Disentangling the Spatially Combined and Temporally Lagged Influences of Climate Oscillations on Seasonal Droughts in the East Asian Monsoon Influenced Poyang Lake Basin. Atmos. Res. 2024, 310, 107603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Knoche, H.R.; Kunstmann, H. Contribution of Transpiration and Evaporation to Precipitation: An ET-Tagging Study for the Poyang Lake Region in Southeast China. JGR Atmos. 2015, 120, 6845–6864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, H.; Yao, J. Integrated Model Projections of Climate Change Impacts on Water-Level Dynamics in the Large Poyang Lake (China). Hydrol. Res. 2021, 52, 43–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, J.; Liu, Y. Meteorological Drought Migration in the Poyang Lake Basin, China: Switching among Different Climate Modes. J. Hydrometeorol. 2020, 21, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The Relationship of Drought Frequency and Duration to Time Scales. In Proceedings of the Eighth Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Singh, V.P.; Kwon, H.-H.; Kim, T.-W. Forecasting Compound Drought-Heatwaves Using Burg Entropy Spectral Analysis with Multi-Frequency Resolutions. J. Hydrol. 2025, 658, 133166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, P.; Teuling, A.J.; Zhu, Y. Spatial-Temporal Variations and Drivers of the Compound Dry-Hot Event in China. Atmos. Res. 2024, 299, 107160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, N.; Yang, M.; Yu, Z.; Wei, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Kunstmann, H. Water Resources Management in a Reservoir-Regulated Basin: Implications of Reservoir Network Layout on Streamflow and Hydrologic Alteration. J. Hydrol. 2020, 586, 124903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, Z.; Yao, J. On the Hydrodynamic Behavior of Floodplain Vegetation in a Flood-Pulse-Influenced River-Lake System (Poyang Lake, China). J. Hydrol. 2020, 585, 124852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xiao, M.; Singh, V.P.; Wang, Y. Spatiotemporal Variations of Temperature and Precipitation Extremes in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Theor. Appl. Clim. 2016, 124, 855–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Zhu, G.; Song, C.; Deng, J.; Xue, B.; Gong, Z.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Shi, K.; et al. Importance and Main Ecological and Environmental Problems of Lakes in China. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2022, 67, 3503–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Dutra, E.; Agustí-Panareda, A.; Albergel, C.; Arduini, G.; Balsamo, G.; Boussetta, S.; Choulga, M.; Harrigan, S.; Hersbach, H.; et al. ERA5-Land: A State-of-the-Art Global Reanalysis Dataset for Land Applications. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 4349–4383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, A.J.; Sobie, S.R.; Murdock, T.Q. Bias Correction of GCM Precipitation by Quantile Mapping: How Well Do Methods Preserve Changes in Quantiles and Extremes? J. Clim. 2015, 28, 6938–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Su, X.; Singh, V.P. Blended Dry and Hot Events Index for Monitoring Dry-Hot Events over Global Land Areas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2021, 48, e2021GL096181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, X.; Hao, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Hao, F. Propagation from Meteorological Drought to Hydrological Drought under the Impact of Human Activities: A Case Study in Northern China. J. Hydrol. 2019, 579, 124147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Sheng, X.; Yang, F. Spatiotemporal Evolution and Meteorological Triggering Conditions of Hydrological Drought in the Hun River Basin, NE China. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 22, 995–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinoni, J.; Barbosa, P.; Bucchignani, E.; Cassano, J.; Cavazos, T.; Christensen, J.H.; Christensen, O.B.; Coppola, E.; Evans, J.; Geyer, B.; et al. Future Global Meteorological Drought Hot Spots: A Study Based on CORDEX Data. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 3635–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; López-Moreno, J.I. A Multiscalar Drought Index Sensitive to Global Warming: The Standardized Precipitation Evapotranspiration Index. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 1696–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wei, J.; Zhang, X.; Ma, M.; Yi, P.; Ju, Q.; Wang, J.; Laux, P.; Kunstmann, H. Lagged Influence of ENSO Regimes on Droughts over the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 275, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, G.; He, H.; Wu, Z.; He, J. A Conceptual Prediction Model for Seasonal Drought Processes Using Atmospheric and Oceanic Standardized Anomalies: Application to Regional Drought Processes in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Lu, G.; He, H.; Wu, Z.; He, J. Understanding Atmospheric Anomalies Associated with Seasonal Pluvial-Drought Processes Using Southwest China as an Example. JGR Atmos. 2017, 122, 12210–12225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; Wood, A.W. Use of a Standardized Runoff Index for Characterizing Hydrologic Drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 2007GL032487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, R.R. Theil–Sen Estimator. In Introduction to Robust Estimation and Hypothesis Testing; Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005; pp. 423–427. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, G.J. Parametric and Nonparametric Sequential Change Detection in R: The Cpm Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2015, 66, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharwardi, M.S.; Hassan, W.U.; Dasari, H.P.; Gandham, H.; Ag, P.; Hoteit, I. Rising Occurrence of Compound Droughts and Heatwaves in the Arabian Peninsula Linked to Large-Scale Atmospheric Circulations. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 978, 179433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, S.A.; Irvine, D.J.; Rau, G.C.; Bayer, P.; Menberg, K.; Blum, P.; Jamieson, R.C.; Griebler, C.; Kurylyk, B.L. Global Groundwater Warming Due to Climate Change. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baez-Villanueva, O.M.; Zambrano-Bigiarini, M.; Miralles, D.G.; Beck, H.E.; Siegmund, J.F.; Alvarez-Garreton, C.; Verbist, K.; Garreaud, R.; Boisier, J.P.; Galleguillos, M. On the Timescale of Drought Indices for Monitoring Streamflow Drought Considering Catchment Hydrological Regimes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 1415–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Sheffield, J. Lagged Compound Occurrence of Droughts and Pluvials Globally over the Past Seven Decades. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2020, 47, e2020GL087924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Hong, S.; Liu, D.; Piao, S. Susceptibility of Vegetation Low-Growth to Climate Extremes on Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 331, 109323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegmund, J.F.; Sanders, T.G.M.; Heinrich, I.; Van Der Maaten, E.; Simard, S.; Helle, G.; Donner, R.V. Meteorological Drivers of Extremes in Daily Stem Radius Variations of Beech, Oak, and Pine in Northeastern Germany: An Event Coincidence Analysis. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Agathokleous, E.; Bao, G.; Iqbal, P.; Liu, Q. Grassland Growth Response to Drought in Dryland Inner Mongolia: Insights from a Two-Decade Analysis. Environ. Res. Lett. 2025, 20, 074038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, T. Super Drought under Global Warming: Concept, Monitoring Index, and Validation. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2023, 104, E943–E969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.; Chen, Y.; Feng, S.; Liao, Z.; An, N.; Li, P. The 2022 Sichuan-Chongqing Spatio-Temporally Compound Extremes: A Bitter Taste of Novel Hazards. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, G.; Chen, W.; Wang, T.; Chotamonsak, C.; Limsakul, A. Decadal Background for Active Extreme Drought Episodes in the Decade of 2010–2019 over Southeastern Mainland Asia. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 2785–2803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Yuan, D.; Lu, E.; Ma, Z. Causes of a Typical Southern Flood and Northern Drought Event in 2015 over Eastern China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2023, 40, 2092–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Zhou, W.; Tian, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Luo, J. A Stratospheric Precursor of East Asian Summer Droughts and Floods. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, D.O.; Dirmeyer, P.A. Characterizing the Relationship between Temperature and Soil Moisture Extremes and Their Role in the Exacerbation of Heat Waves over the Contiguous United States. J. Clim. 2021, 34, 2175–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, X.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Fan, X.; Yuan, C. Propagation from Atmospheric Water Deficit to Lake Drought in Lake Basins Across China: Implications for Lake Drought Management. Water Resour. Res. 2025, 61, e2024WR039641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Zhan, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Bu, L.; Chang, M.; Qiao, L. Land-Air Coupling Exacerbates the Future Risk of Concurrent Daytime-Nighttime Hot Extremes. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2025, 68, 1261–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Fan, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, D.; Zhao, F. Future Climate Change Exacerbates Streamflow Depletion in the Wei River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2025, 663, 134146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; AghaKouchak, A. Global Assessment and Hotspots of Lake Drought. Commun. Earth Environ. 2025, 6, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Yuan, X.; Liu, X. Intensification of Drought Propagation over the Yangtze River Basin under Climate Warming. Int. J. Climatol. 2023, 43, 5640–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Villalobos, C.; Fu, D.; Loikith, P.C.; Neelin, J.D. Accelerating Increase in the Duration of Heatwaves under Global Warming. Nat. Geosci. 2025, 18, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
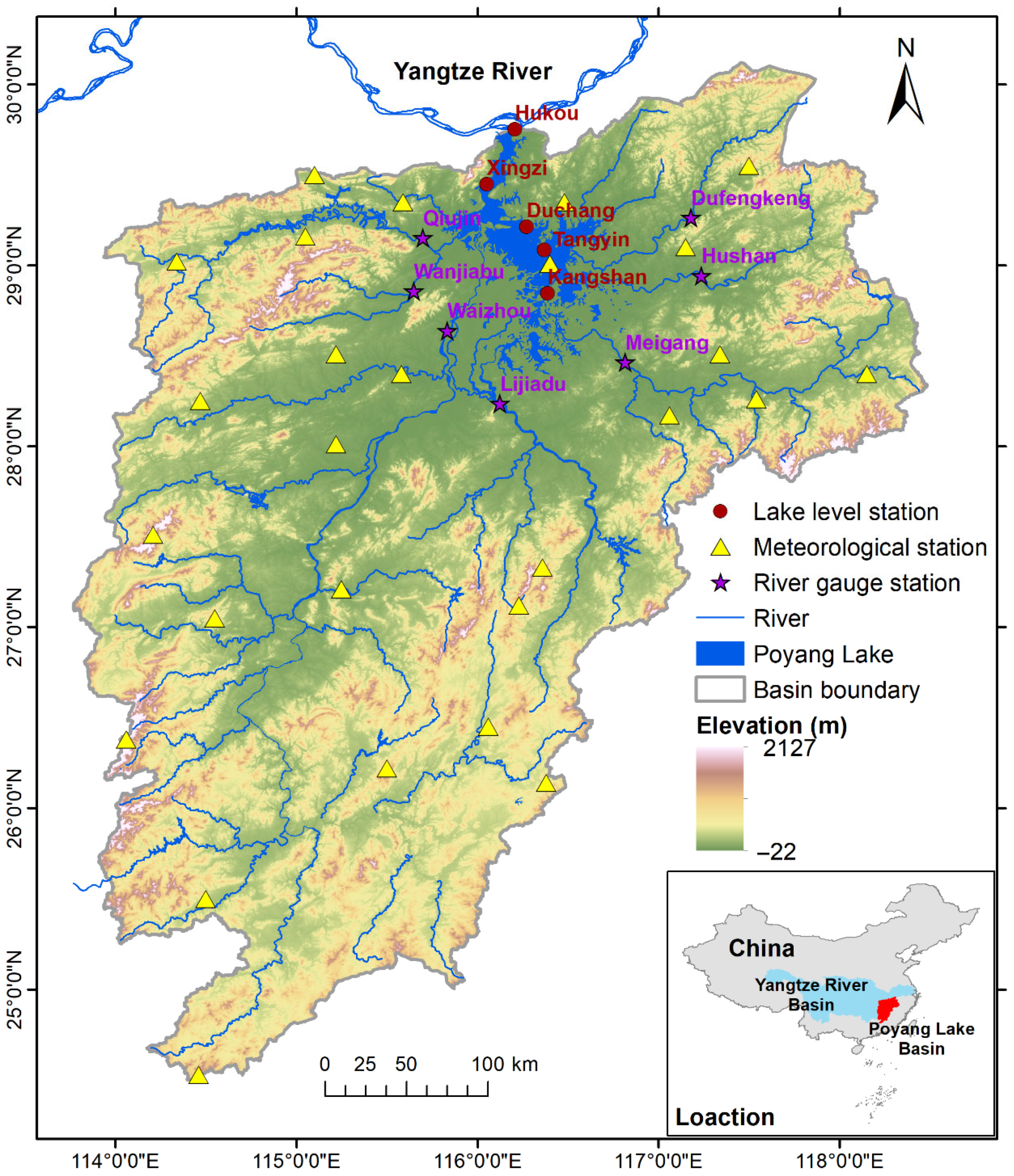
| Data Type | Source | Spatial Resolution | Temporal Resolution | Time Period | Variables Used |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reanalysis Data | ERA5-Land | 0.1° × 0.1° | Daily | 1980–2023 | Maximum temperature, precipitation |
| Meteorological stations | China Meteorological Administration | 27 stations | Daily | 1980–2023 | Maximum temperature, Precipitation |
| River gauge stations | Jiangxi Hydrological Bureau | 5 major tributaries (7 stations) | Daily | 1981–2016 | Runoff discharge |
| Lake Level stations | Jiangxi Hydrological Bureau | 5 main stations | Daily | 1981–2016 | Water level elevation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Li, N.; Yang, Y.; Xing, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, J.; Ma, M.; Zhang, X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Lagged Hydrological Impacts of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events in the Poyang Lake Basin. Hydrology 2026, 13, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010016
Li N, Yang Y, Xing Z, Zhao Y, Wei J, Ma M, Zhang X. Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Lagged Hydrological Impacts of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events in the Poyang Lake Basin. Hydrology. 2026; 13(1):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ningning, Yang Yang, Zikang Xing, Yi Zhao, Jianhui Wei, Miaomiao Ma, and Xuejun Zhang. 2026. "Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Lagged Hydrological Impacts of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events in the Poyang Lake Basin" Hydrology 13, no. 1: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010016
APA StyleLi, N., Yang, Y., Xing, Z., Zhao, Y., Wei, J., Ma, M., & Zhang, X. (2026). Spatiotemporal Dynamics and Lagged Hydrological Impacts of Compound Drought and Heatwave Events in the Poyang Lake Basin. Hydrology, 13(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology13010016






