Aquatic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impacts on Fisheries and Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
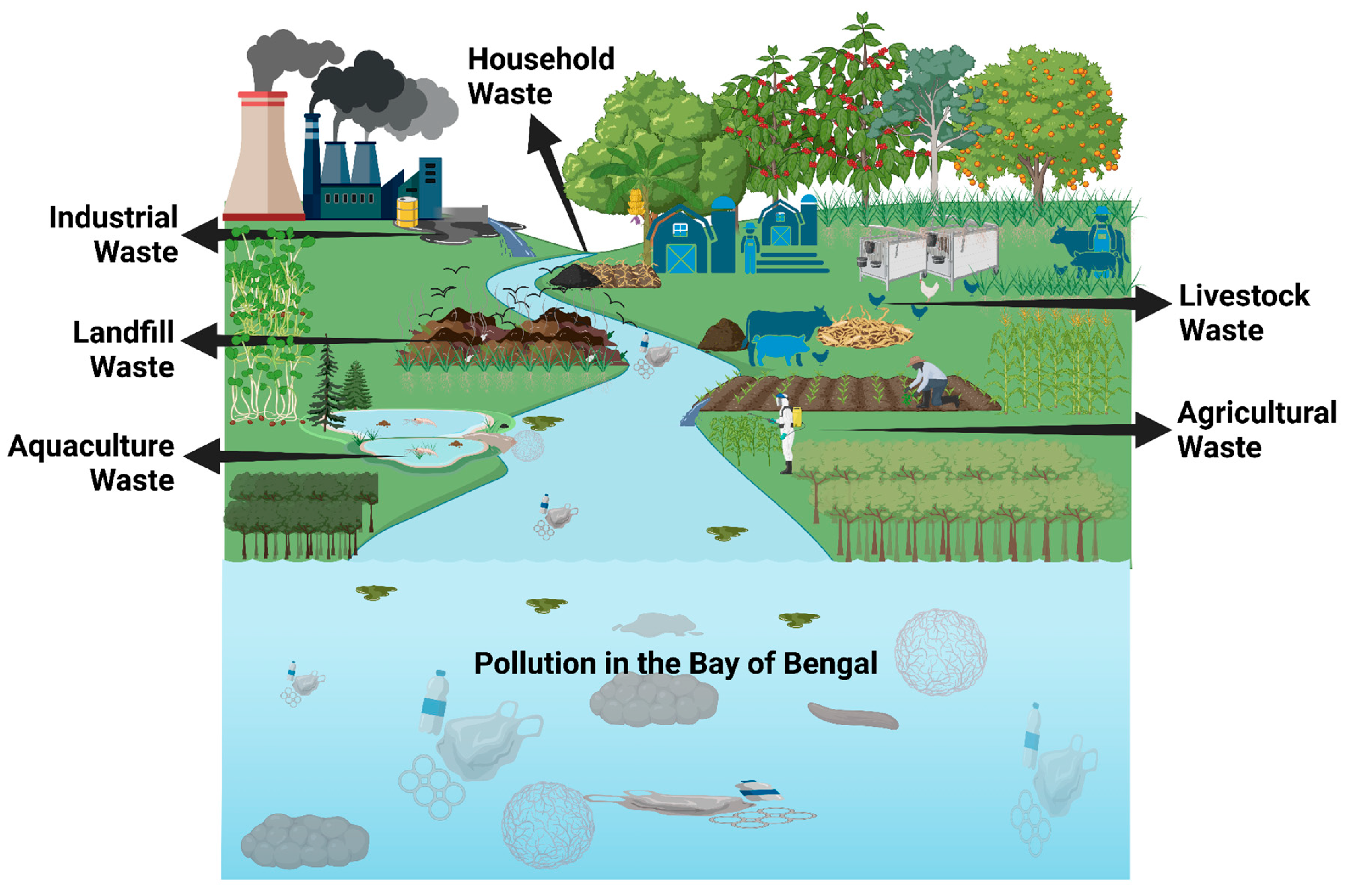
3. Major Sources of Aquatic Pollution in Bangladesh
3.1. Industrial Pollution
| Pollutants | Studied Industries and Areas | References |
|---|---|---|
| Microplastics | Dying, washing, pharmaceuticals, battery, and printing industries. | [27] |
| Persistent organic pollutants, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, Polychlorinated biphenyl, Polychlorinated Naphthalenes, organochlorine pesticides, Chlorinated paraffins | Landfills, industrial areas 1, mobile industry, agricultural lands, chemical industry, oil and fuel industry, and domestic sewage | [28,29] |
| Suspended solids | Textiles, tannery, steel rerolling, construction materials, pharmaceuticals, food processing, pulp and paper, fertilizer, and basic chemicals industries | [30,31] |
| Heavy metals (Fe, Mn, Cr, Cu, Ni, Co, Zn, Pb, and Cd) | Tannery industry, ship-breaking industry, mobile industry, aquaculture ponds, agricultural lands, landfills, and industrial areas. | [25,32,33,34,35] |
| Inorganic nutrient loading (NH4, NO2, NO3, PO4,) | Tannery industry, agricultural runoff, aquaculture discharge, paper industry, and landfills | [31] |
3.2. Domestic and Municipal Wastes
3.3. Agro-Chemicals
3.4. Algal Pollution
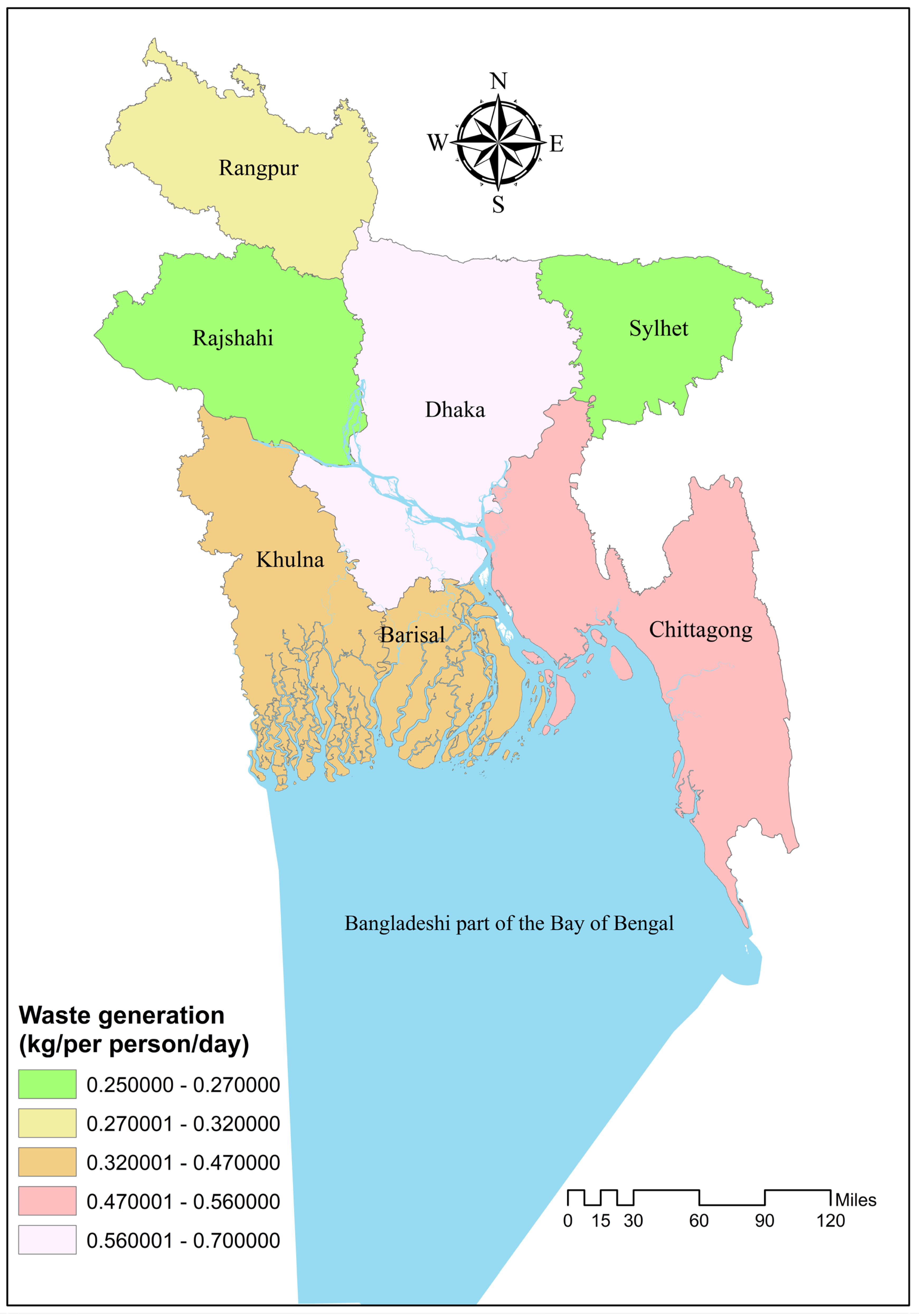
4. Pathways of Pollutants Toward the Bay of Bengal
5. Aquatic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh
| Pollutants | Amount, Concentration in Water and Sediment | References |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy metals | Mn concentration: water (2.94 μg/L), seaweed (32.9 μg/kg) | [81,82] |
| Zn concentration: water (2.66 μg/L), seaweed (34.5 μg/kg), fish (56.3–126.3 mg/kg), zooplankton (298 to 1160 µg/g) | [81,82,83,84] | |
| Cu concentration: water (0.66 μg/L), seaweed (16.6 μg/kg), fish (5–10 mg/kg), zooplankton (14.9–55.56 µg/g) | [81,82,83,84] | |
| Ni concentration: water (0.53 μg/L), fish (13.2–37.7 mg/kg) | [82,83] | |
| Cd concentration: water (0.09 μg/L), sediment (4.51 mg/kg), fish (0.25–1.5 mg/kg) | [82,84,85] | |
| Co concentration: water (0.05 μg/L), seaweed (0.26 μg/kg), zooplankton (9–22.1 µg/g) | [81,82,83] | |
| Pb concentration: water (0.05 μg/L), seaweed (2.6 μg/kg), sediment (65.31 mg/kg), fish (27.5–52.5 mg/kg) | [81,82,84,85] | |
| Cr concentration: seaweed (1.15 μg/kg), sediment (121.87 mg/kg), fish (15.3–89.3 mg/kg), zooplankton (0.14–2.3 µg/g) | [81,83,84,85] | |
| As concentration: seaweed (3.4 μg/kg), sediment (32.53 mg/kg) | [81,85] | |
| Microplastic | Abundance in water (60–820 items per m3), sediment (60–1620 items per kg) and beach sand (20–1540 items per kg), Hilsha (19.13 ± 10.77 particles/fish), Bombay duck (8.72 ± 1.54 particle/fish), Sardine (3.20 ± 1.16 particle/fish), Brown shrimp (7.80 ± 2 particle/shrimp), Tiger shrimp (6.60 ± 2 particle/shrimp), Salt (2676 MPs/kg), Sandy beach (248–402 items/m3), sediment of Saint martin island (0.33–317.67 items/kg), sediment of Saint Martin island (0.118 ± 0.034 items/m3), muscle (1.74 ± 0.23–3.79 ± 2.03 items/g), gastrointestinal tract (0.54 ± 0.22–5.96 ± 3.16 items/g), Surface water of estuary (150.00 ± 65.62 items/m3), sediment of estuary (30.56 ± 9.34 items/kg) | [86,87,88,89,90,91,92] |
| Marine Litter | 0.14 to 0.58 items/m2 | [93] |
| Plastic | Plastic debris in water (3.34 g/m2) | [94] |
| Plastic items on sandy beach (54,401 ± 184 items//m2) | [94] | |
| Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons | PAHs concentration in sediment (1.87 to 918.79 ng/g) | [95] |
| Plasticizers | Concentration in surface water (176.1 ± 104.8 ng/L), storm water (355.2 ± 232.5 ng/L) | [96] |
| Bisphenol A | Concentration in surface water (658.3 ± 1760 ng/L), storm water (459.3 ± 620.2 ng/L) | [96] |
| Petroleum hydrocarbons | Concentration in sediment (17–39.72 ppm) | [97] |
| Organochlorine pesticide | Concentration of hexachlorocyclohexane isomers (HCHs) in sediment (0.05–12 ng/g) | [98] |
| Concentration of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane and its six metabolites (DDTs) in sediment (0.05–1.4 ng/g), sediment (0.09–4.78 ng/g) | [98,99] | |
| Concentration of hexachlorobenzene (HCB) in sediments (0.05–11.5 ng/g) | [98] | |
| Concentration of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) in water (1.93–4.43 ng/L), Sediment (19.9–6570 pg/g) | [99] |
6. Effects of Pollution on Fish and Fisheries
7. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SDG | Sustainable Development Goal |
| HABs | Harmful Algal Blooms |
| BOBLME | Bay of Bengal Large Marine Ecosystem |
| BAPI | Bangladesh Association of Pharmaceutical Industries |
| DGDA | Directorate General of Drug Administration |
| KAFCO | Karnaphuli Fertilizer Company Limited |
| BCIC | Bangladesh Chemical Industries Corporation |
References
- Edo, G.I.; Itoje-akpokiniovo, L.O.; Obasohan, P.; Ikpekoro, V.O.; Samuel, P.O.; Jikah, A.N.; Nosu, L.C.; Ekokotu, H.A.; Ugbune, U.; Oghroro, E.E.A.; et al. Impact of Environmental Pollution from Human Activities on Water, Air Quality and Climate Change. Ecol. Front. 2024, 44, 874–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Sze-Yin Leung, K.; Elsner, M.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Pan, B.; Sun, H.; An, T.; Ying, G.; et al. Emerging Contaminants: A One Health Perspective. Innovation 2024, 5, 100612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zhu, S.; He, C. Intercity Personnel Exchange Is More Effective than Policy Transplantation at Reducing Water Pollution. Nat. Cities 2025, 2, 210–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- du Plessis, A. Persistent Degradation: Global Water Quality Challenges and Required Actions. One Earth 2022, 5, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yang, H.; Xu, X. Effects of Water Pollution on Human Health and Disease Heterogeneity: A Review. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 880246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateo-Sagasta, J.; Zadeh, S.M.; Turral, H. Water Pollution from Agriculture: A Global Review; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, A.E.V.; Hanjra, M.A.; Jiang, Y.; Qadir, M.; Drechsel, P. Water Quality: Assessment of the Current Situation in Asia. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2012, 28, 195–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S. Urban Waste Management in Bangladesh: An Overview with a Focus on Dhaka; ASEF Education Department: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Waste Concern. Bangladesh Waste Database 2021; Waste Concern: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- World Bank How Dialogue Is Shifting Bangladesh’s Textile Industry from Pollution Problem to Pollution Solution; World Bank Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2017.
- Khalilullah, M.I. Bangladesh’s Perilous Battle with Pollution, Pesticides and Plastics|Earth Journalism Network. Jamuna TV . 2022. Available online: https://earthjournalism.net/stories/bangladeshs-perilous-battle-with-pollution-pesticides-and-plastics (accessed on 17 March 2025).
- Hasan, N.A.; Heal, R.D.; Bashar, A.; Haque, M.M. Face Masks: Protecting the Wearer but Neglecting the Aquatic Environment?—A Perspective from Bangladesh. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Kumar, U.; Kumar, I.; Dwivedi, A.; Singh, P.; Mishra, S.; Seth, C.S.; Sharma, R.K. Critical Review on Toxic Contaminants in Surface Water Ecosystem: Sources, Monitoring, and Its Impact on Human Health. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 56428–56462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, T.; Hoque, S.; Akter, S. Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impact on Marine Ecosystem. Open J. Mar. Sci. 2015, 05, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, M.Y.; Ali, S.E.; Abbas, W.T.; Algammal, A.M.; Abdelsalam, M. The Role of Marine Pollution on the Emergence of Fish Bacterial Diseases. Chemosphere 2023, 344, 140366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, F.; Fossi, C.; Weber, R.; Santillo, D.; Sousa, J.; Ingram, I.; Nadal, A.; Romano, D. Marine Litter Plastics and Microplastics and Their Toxic Chemicals Components: The Need for Urgent Preventive Measures. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thushari, G.G.N.; Senevirathna, J.D.M. Plastic Pollution in the Marine Environment. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ton Nu Hai, A.; Speelman, S. Economic-Environmental Trade-Offs in Marine Aquaculture: The Case of Lobster Farming in Vietnam. Aquaculture 2020, 516, 734593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquin, L.; Petitjean, Q.; Côte, J.; Laffaille, P.; Jean, S. Effects of Pollution on Fish Behavior, Personality, and Cognition: Some Research Perspectives. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020, 8, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, S.A.; Al-Rudainy, A.J.; Salman, N.M. Effect of Environmental Pollutants on Fish Health: An Overview. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2024, 50, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Jeong, Y.-K. Urban River Pollution in Bangladesh during Last 40 Years: Potential Public Health and Ecological Risk, Present Policy, and Future Prospects toward Smart Water Management. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahaduzzaman, -; Sarkar, P.; Anjum, A.; Khan, E.A. Overview of Major Industries in Bangladesh. J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 30, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, Z. Comprehensive Report 2017 on Bangladesh Leathergoods and Footwear Industry; Confederation of International Footwear Association: Hong Kong, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Howlader, S. Fertilizer Industry of Bangladesh Volume-I; Department of Research, Emerging Credit Rating Limited: Dhaka, Bangladesh, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.M.M.; Sarker, A.; Sarker, M.E.; Kabir, M.H.; Ahmed, F.T.; Yeasmin, M.; Islam, M.S.; Idris, A.M. Heavy Metals in Sediments of an Urban River at the Vicinity of Tannery Industries in Bangladesh: A Preliminary Study for Ecological and Human Health Risk. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2023, 103, 7909–7927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, R. Water pollution due to textile industry. Bangladesh Textile Today. 2020. Available online: https://www.textiletoday.com.bd/water-pollution-due-textile-industry (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Haque, M.M.; Nupur, F.Y.; Parvin, F.; Tareq, S.M. Occurrence and Characteristics of Microplastic in Different Types of Industrial Wastewater and Sludge: A Potential Threat of Emerging Pollutants to the Freshwater of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2022, 8, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigar, R.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Huang, H.; Tian, L.; Xiao, Y.; Habib, A.; Zhang, G. Screening Legacy and Emerging Organic Pollutants in the Contaminated Soil of Dhaka, Bangladesh. Emerg. Contam. 2024, 10, 100356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanand, M.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Subramanian, R.; Issac, P.K.; Nasr, M.; Khoo, K.S.; Rajagopal, R.; Greff, B.; Wan Azelee, N.I.; Jeon, B.-H.; et al. Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the Water Environment: A Review on Toxicity, Microbial Biodegradation, Systematic Biological Advancements, and Environmental Fate. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmaker, A.; Hasan, M.; Ahmed, S. A Modified Approach to Industrial Pollution Projection System for the Assessment of Sectoral Pollution Loads in Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saeed, T.; Afrin, R.; Muyeed, A.A.; Sun, G. Treatment of Tannery Wastewater in a Pilot-Scale Hybrid Constructed Wetland System in Bangladesh. Chemosphere 2012, 88, 1065–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shammi, S.A.; Salam, A.; Khan, M.A.H. Assessment of Heavy Metal Pollution in the Agricultural Soils, Plants, and in the Atmospheric Particulate Matter of a Suburban Industrial Region in Dhaka, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 193, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Hosain, S.; Poddar, P.; Chowdhury, A.A.; Katengeza, E.W.; Roy, U.K. Heavy Metal Toxicity from the Leather Industry in Bangladesh: A Case Study of Human Exposure in Dhaka Industrial Area. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Ahmed, M.S.; Adnan, R. Assessment of Physico-Chemical Characteristics of River Water Emphasizing Tannery Industrial Park: A Case Study of Dhaleshwari River, Bangladesh. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, N.; Reza, S.; Biswas, P.K. Assessment of Soil Heavy Metal Pollution by Environmental Indices at Surroundings of Ishwardi Export Processing Zone (IEPZ), Ishwardi, Pabna, Bangladesh. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWAP. The United Nations World Water Development Report, 2017: Wastewater: The Untapped Resource; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2017; Volume 53, ISBN 978-92-3-100201-4. [Google Scholar]
- Sakib, S.N. Bangladesh’s Polybag Ban Falls Flat in Stopping Production, Use. Asia-Pacific. 2021. Available online: https://www.aa.com.tr/en/asia-pacific/bangladesh-s-polybag-ban-falls-flat-in-stopping-production-use/2292293 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, V.; Shahzad, B.; Tanveer, M.; Sidhu, G.P.S.; Handa, N.; Kohli, S.K.; Yadav, P.; Bali, A.S.; Parihar, R.D.; et al. Worldwide Pesticide Usage and Its Impacts on Ecosystem. SN Appl. Sci. 2019, 1, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peluso, F.; Dubny, S.; Othax, N.; Castelain, J.G. Environmental Risk of Pesticides: Applying the DelAzulPestRisk Model to Freshwaters of an Agricultural Area of Argentina. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2014, 20, 1177–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, P.; Islam, A.; Sachi, S.; Islam, M.Z.; Islam, P. Pesticides in Vegetable Production in Bangladesh: A Systemic Review of Contamination Levels and Associated Health Risks in the Last Decade. Toxicol. Rep. 2023, 11, 199–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidullah, A.K.M.; Islam, A.; Rahman, M. Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice of Pesticide Use by Vegetable Growers in Bangladesh: A Health Literacy Perspective in Relation to Non-Communicable Diseases. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2023, 7, 1199871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Chowdhury, M.A.Z.; Pramanik, M.K.; Rahman, M.A.; Fakhruddin, A.N.M.; Alam, M.K. Determination of Selected Pesticides in Water Samples Adjacent to Agricultural Fields and Removal of Organophosphorus Insecticide Chlorpyrifos Using Soil Bacterial Isolates. Appl. Water Sci. 2015, 5, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suresh Kumar, K.; Dahms, H.-U.; Lee, J.-S.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, W.C.; Shin, K.-H. Algal Photosynthetic Responses to Toxic Metals and Herbicides Assessed by Chlorophyll a Fluorescence. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 104, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-S.; Wang, C.-L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.-W.; Li, W.-Y. Combined Toxicity of Pesticide Mixtures on Green Algae and Photobacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 95, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Brink, P.J.; Van Smeden, J.M.; Bekele, R.S.; Dierick, W.; De Gelder, D.M.; Noteboom, M.; Roessink, I. Acute and Chronic Toxicity of Neonicotinoids to Nymphs of a Mayfly Species and Some Notes on Seasonal Differences. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2015, 35, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessink, I.; Merga, L.B.; Zweers, H.J.; Van den Brink, P.J. The Neonicotinoid Imidacloprid Shows High Chronic Toxicity to Mayfly Nymphs. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 32, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjunatha, B.; Philip, G.H. Reproductive Toxicity of Chlorpyrifos Tested in Zebrafish (Danio Rerio). Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1808–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Emran, M.; Hasan, N.A.; Khan, M.P.; Islam, S.M.M.; Bashar, A.; Zulfahmi, I.; Shahjahan, M.; Sumon, K.A. Alterations in Hematological Parameters and the Structure of Peripheral Erythrocytes in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis Niloticus) Exposed to Profenofos. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021 2022, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ara, A.G.; Haque, W.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Detection of Organochlorine and Organophosphorus Pesticides Residues in Water Samples of Taragong Thana in Rangpur District in Bangladesh. Res. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 6, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. Pesticide Use Sees Decline|The Business Standard. The Business Standard. 2021. Available online: https://www.tbsnews.net/economy/pesticide-use-sees-decline-316849 (accessed on 12 March 2025).
- Khan, S.; Jahan, R.; Rahman, M.A.; Haque, M.M. Eutrophication Enhances Phytoplankton Abundance in the Maheshkhali Channel, Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Aust. J. Sci. Technol. 2019, 3, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, S.; Awal, S.; Shaika, N.A.; Khan, S. Cyanobacterial Blooms in Earthen Aquaculture Ponds and Their Impact on Fisheries and Human Health in Bangladesh. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 5129–5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaika, N.A.; Khan, S.; Sultana, S. Harmful Algal Blooms in the Coastal Waters of Bangladesh: An Overview. J. Aquac. Mar. Biol. 2022, 11, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bláha, L.; Babica, P.; Maršálek, B. Toxins Produced in Cyanobacterial Water Blooms—Toxicity and Risks. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 2009, 2, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilborn, E.; Beasley, V. One Health and Cyanobacteria in Freshwater Systems: Animal Illnesses and Deaths Are Sentinel Events for Human Health Risks. Toxins 2015, 7, 1374–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedde, S.; Kroeze, C.; Mayorga, E.; Seitzinger, S.P. Modeling Sources of Nutrients in Rivers Draining into the Bay of Bengal—A Scenario Analysis. Reg. Environ. Change 2017, 17, 2495–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinia, N.J.; Kroeze, C. Future Trends in Urbanization and Coastal Water Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: The Lived Experience. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2015, 17, 531–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pote, S.E.; Singal, S.K.; Srivastava, D.K. Assessment of Surface Water Quality of Godavari River at Aurangabad. Asian J. Water Environ. Pollut. 2012, 9, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostakim, K.; Arefin, M.A.; Islam, M.T.; Shifullah, K.M.; Islam, M.A. Harnessing Energy from the Waste Produced in Bangladesh: Evaluating Potential Technologies. Heliyon 2021, 7, e08221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Islam, M.S.; Ju, M. Urban River Pollution in the Densely Populated City of Dhaka, Bangladesh: Big Picture and Rehabilitation Experience from Other Developing Countries. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 321, 129040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noman, A.A.; Rafizul, I.M.; Moniruzzaman, S.M.; Kraft, E.; Berner, S. Assessment of Municipal Solid Waste from Households in Khulna City of Bangladesh. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, I. 30,000 Tonnes of Plastic in 4 Rivers. Prothom Alo. 2020. Available online: https://en.prothomalo.com/environment/pollution/30000-tonnes-of-plastic-in-4-rivers (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Sarwar, M.I.; Majumder, A.K.; Islam, M.N. Water Quality Parameters: A Case Study of Karnafully River Chittagong, Bangladesh. Bangladesh J. Sci. Ind. Res. 1970, 45, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Kawser, A.; Xu, Y.; Ye, X.; Rani, S.; Chen, K. Heavy Metal Accumulation during the Last 30 Years in the Karnaphuli River Estuary, Chittagong, Bangladesh. Springerplus 2016, 5, 2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiquee, N.A.; Parween, S.; Quddus, M.M.A.; Barua, P. Heavy Metal Pollution in Sediments at Ship Breaking Area of Bangladesh. In Coastal Environments: Focus on Asian Regions; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Aktar, M. Heavy Metal Concentration in Pore Water of Salt Marsh along the Karnafully River Coast, Bangladesh. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 5, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.; Das, S.K.; Paul, S.C.; Islam, M.F.; Hossain, M.S. Water Quality Assessment of Karrnaphuli River, Bangladesh Using Multivariate Analysis and Pollution Indices. Asian J. Environ. Ecol. 2018, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.N.; Ahmed, M.J.; Hossain, M.A.; Siraj, S. Physicochemical Assessment of Water Pollutants Due to the Ship Breaking Activities and Its Impact on the Coastal Environment of Chittagong—Bangladesh. Eur. Chem. Bull. 2013, 2, 1053–1059. [Google Scholar]
- Iftehimul, M.; Manik, M.; Bashar, A.; Haque, M.M.; Sarker, J.; Hasan, N.A. Algae-Based Bioremediation of Emerging Pollutants. In Management and Mitigation of Emerging Pollutants; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 143–199. [Google Scholar]
- Nillesen, A.L.; zum Felde, M.; Pfannes, E.; Meyer, H.; Klijn, O. Water as Leverage: Design Studies for Khulna, Chennai and Semarang. In SeaCities; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 133–169. [Google Scholar]
- Bashar, A.; Heal, R.D.; Hasan, N.A.; Salam, M.A.; Haque, M.M. COVID-19 Impacts on the Bangladesh Shrimp Industry: A Sequential Survey-Based Case Study from Southwestern Bangladesh. Fish. Sci. 2022, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.M. Prediction of Dissolved Oxygen in Surma River by Biochemical Oxygen Demand and Chemical Oxygen Demand Using the Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs). J. King Saud. Univ. —Eng. Sci. 2017, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Financial Express Polluted Waters in Two Sylhet Rivers Threaten Fish, Aquatic Resources | The Financial Express. The Financial Express. 2021. Available online: https://thefinancialexpress.com.bd/national/country/polluted-waters-in-two-sylhet-rivers-threaten-fish-aquatic-resources-1609483595 (accessed on 15 March 2025).
- Chanda, A.; Akhand, A. Challenges towards the Sustainability and Enhancement of the Indian Sundarban Mangrove’s Blue Carbon Stock. Life 2023, 13, 1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, H.; Ahmed, M.; Islam, T.; Uddin, M.Z.; Ahmed, Z.U.; Saha, C. Paradigm Shift in the Management of the Sundarbans Mangrove Forest of Bangladesh: Issues and Challenges. Trees For. People 2021, 5, 100094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A. Persistent Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: An Emerging Issue for Regional Ocean Governance. SSRN Electron. J. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.W.; Xiangmin, X.; Ahamed, R. Protecting the Marine and Coastal Water from Land-Based Sources of Pollution in the Northern Bay of Bengal: A Legal Analysis for Implementing a National Comprehensive Act. Environ. Chall. 2021, 4, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.C.; Haque, M.M.; Maniruzzaman, M.; Kalra, N. Coastal and Marine Pollution in Bangladesh: Pathways, Hotspots and Adaptation Strategies. Eur. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 2, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, G.; Hossain, M.M.; Mallick, D.; Lau, T.C.; Wu, R. Monitoring of Metal Pollution in Waterways across Bangladesh and Ecological and Public Health Implications of Pollution. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuyan, M.S.; Islam, M.S. Status and Impacts of Industrial Pollution on the Karnafully River in Bangladesh: A Review. Int. J. Mar. Sci. 2017, 7, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakib, M.R.J.; Jolly, Y.N.; Dioses-Salinas, D.C.; Pizarro-Ortega, C.I.; De-la-Torre, G.E.; Khandaker, M.U.; Alsubaie, A.; Almalki, A.S.A.; Bradley, D.A. Macroalgae in Biomonitoring of Metal Pollution in the Bay of Bengal Coastal Waters of Cox’s Bazar and Surrounding Areas. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookan, V.P.; Machakalai, R.K.; Srinivasan, S.; Sigamani, S.; Kolandhasamy, P.; Gnanamoorthy, P.; Moovendhan, M.; Srinivasan, R.; Hatamleh, A.A.; AI-Dosary, M.A. Assessment of Metal Contaminants along the Bay of Bengal—Multivariate Pollution Indices. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 192, 115008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singaram, P.; Retnamma, J.; Cheruparambil, R.; Nagarathinam, A.; Loganathan, J.; Thangaraj, J.R.; Radhakrishnan, S.S. Heavy Metals Concentration in Zooplankton (Copepods) in the Western Bay of Bengal. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 101565–101584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, S.; Pradhan, U.; Karthikeyan, P.; Begum, M.; Panda, U.S.; Mishra, P.; Ramana Murthy, M.V. Heavy Metal Pollution Causes Mass Mortality of Fish in a Tropical Estuary in the Southwestern Bay of Bengal. Mar. Environ. Res. 2024, 199, 106595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.M.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Bhuyan, M.S.; Ahmed, A.S.S.; Rahman, M.Z.; Rahman, M.M. Toxic Metal Pollution and Ecological Risk Assessment in Water and Sediment at Ship Breaking Sites in the Bay of Bengal Coast, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 175, 113274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, P.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Marshall, D.J.; Yu, J.; Nur, A.-A.U.; Jolly, Y.N.; Mamun, M.A.-; Paray, B.A.; Bappy, M.M.M.; et al. Quantification, Characterization and Risk Assessment of Microplastics from Five Major Estuaries along the Northern Bay of Bengal Coast. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 342, 123036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Anisuzzaman, M.; Hossain, M.K.; Rana, M.S.; Paray, B.A.; Arai, T.; Yu, J.; Hossain, M.B. Ecological Risk Assessment of Microplastics and Mesoplastics in Six Common Fishes from the Bay of Bengal Coast. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 204, 116544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvin, F.; Nath, J.; Hannan, T.; Tareq, S.M. Proliferation of Microplastics in Commercial Sea Salts from the World Longest Sea Beach of Bangladesh. Environ. Adv. 2022, 7, 100173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Rahman, M.S.; Uddin, M.N.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Sarker, S.; Nawaz Chowdhury, M.S. Microplastic Contamination in Penaeid Shrimp from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Chemosphere 2020, 238, 124688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.S.; Sobhan, F.; Uddin, M.N.; Sharifuzzaman, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.R.; Sarker, S.; Chowdhury, M.S.N. Microplastics in Fishes from the Northern Bay of Bengal. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 690, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddique, M.A.M.; Uddin, A.; Rahman, S.M.A.; Rahman, M.; Islam, M.S.; Kibria, G. Microplastics in an Anadromous National Fish, Hilsa Shad Tenualosa Ilisha from the Bay of Bengal, Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 174, 113236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunitha, T.G.; Monisha, V.; Sivanesan, S.; Vasanthy, M.; Prabhakaran, M.; Omine, K.; Sivasankar, V.; Darchen, A. Micro-Plastic Pollution along the Bay of Bengal Coastal Stretch of Tamil Nadu, South India. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 144073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.S.; Phoungthong, K.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Ali, M.M.; Ismail, Z.; Shahid, S.; Kabir, M.H.; Idris, A.M. Sources and Management of Marine Litter Pollution along the Bay of Bengal Coast of Bangladesh. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 185, 114362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadanga, M.K.; Behera, A.K.; Swain, G.K.; Dora, D.P.; Padhi, C.P.; Mishra, R.K.; Pradhan, S.; Barik, S.; Mohanty, P.K.; Mishra, P.; et al. Evaluation of the Status of Marine Plastic Pollution along a Tourist Beach of Bay of Bengal during Lockdown and Post Lockdown. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2022, 182, 113970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furtado, C.M.; Gireeshkumar, T.R.; Vignesh, E.R.; Fahad Fathin, K.P.; Suresh, A.; Jyothibabu, R. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Surface Sediments of the Western Bay of Bengal: Distribution, Sources, and Ecological Risk Assessment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2025, 211, 117387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, M.; Chakraborty, P. Plasticizers and Bisphenol A: Emerging Organic Pollutants along the Lower Stretch of River Ganga, North-East Coast of the Bay of Bengal. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 276, 116697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalapathy, R.; Veerasingam, S.; Basavaiah, N.; Ramkumar, T.; Deenadayalan, K. Environmental Magnetic and Petroleum Hydrocarbons Records in Sediment Cores from the North East Coast of Tamilnadu, Bay of Bengal, India. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.K.; Binelli, A.; Riva, C.; Parolini, M.; Chatterjee, M.; Bhattacharya, A.K.; Bhattacharya, B.D.; Satpathy, K.K. Organochlorine Pesticide Residues in Sediment Cores of Sunderban Wetland, Northeastern Part of Bay of Bengal, India, and Their Ecotoxicological Significance. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2008, 55, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, R.B.; Imagawa, T.; Tao, H.; Ramesh, R. Distribution of PCBs, HCHs and DDTs, and Their Ecotoxicological Implications in Bay of Bengal, India. Environ. Int. 2005, 31, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, C.; Krauth, T.; Wagner, S. Export of Plastic Debris by Rivers into the Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 12246–12253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M. Alarming Plastic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal|The Daily Star. The Daily Star. 2019. Available online: https://www.thedailystar.net/opinion/environment/news/alarming-plastic-pollution-the-bay-bengal-1784278 (accessed on 16 March 2025).
- Hall, N.M.; Berry, K.L.E.; Rintoul, L.; Hoogenboom, M.O. Microplastic Ingestion by Scleractinian Corals. Mar. Biol. 2015, 162, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landos, M.; Lloyd-Smith, M.; Immig, J. Aquatic Pollutants in Oceans and Fisheries. Int. Pollut. Elimin. Netw. 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Hou, J.; Deng, R. Co-Exposure of Environmental Contaminants with Unfavorable Temperature or Humidity/Moisture: Joint Hazards and Underlying Mechanisms. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 264, 115432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez-Vázquez, E.J.; Gárate-Lizarraga, I.; Band-Schmidt, C.J.; Cordero-Tapia, A.; Lopez-Cortes, D.J.; Sandoval, F.E.H.; Heredia-Tapia, A.; Bustillos-Guzman, J.J. Impact of Harmful Algal Blooms on Wild and Cultured Animals in the Gulf of California. J. Environ. Biol. 2011, 32, 413–423. [Google Scholar]
- Patiño, R.; Christensen, V.G.; Graham, J.L.; Rogosch, J.S.; Rosen, B.H. Toxic Algae in Inland Waters of the Conterminous United States—A Review and Synthesis. Water 2023, 15, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Wali, A.F.; Yatoo, A.M.; Majid, S.; Rasool, S.; Khan, R.; Ali, M.N.; Wani, J.A.; Farooq, S.; Rasool, S.; et al. Effect of Pesticides on Fish Fauna: Threats, Challenges, and Possible Remedies. In Bioremediation and Biotechnology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 27–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dhaka Tribune Toxicity Levels in Shitalakkhya, Banar Rivers Reach Critical Point. Dhaka Tribune e-paper. 2021. Available online: https://www.dhakatribune.com/bangladesh/nation/244070/toxicity-levels-in-shitalakkhya-banar-rivers (accessed on 20 March 2025).
- Ali, H.; Khan, E.; Ilahi, I. Environmental Chemistry and Ecotoxicology of Hazardous Heavy Metals: Environmental Persistence, Toxicity, and Bioaccumulation. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 6730305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadim, M.K.; Risjani, Y. Biomarker for Monitoring Heavy Metal Pollution in Aquatic Environment: An Overview toward Molecular Perspectives. Emerg. Contam. 2022, 8, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, B.D.; Jenkins, S.R.; Boig, C.; Sinfield, C.; Kennington, K.; Brand, A.R.; Lart, W.; Kröger, R. Metal Pollution as a Potential Threat to Shell Strength and Survival in Marine Bivalves. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 143019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akter, T.; Foysal, M.J.; Alam, M.; Ehsan, R.; Paul, S.I.; Momtaz, F.; Siddik, M.A.B.; Tay, A.C.Y.; Fotedar, R.; Gupta, S.K.; et al. Involvement of Enterococcus Species in Streptococcosis of Nile Tilapia in Bangladesh. Aquaculture 2021, 531, 735790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.K.; Parvin, E.; Islam, M.M.; Akter, M.S.; Khan, S.; Al-Mamun, M.H. Lead- and Cadmium-Induced Histopathological Changes in Gill, Kidney and Liver Tissue of Freshwater Climbing Perch Anabas Testudineus (Bloch, 1792). Chem. Ecol. 2014, 30, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, H.; Bhat, R.A.; Mehmood, M.A.; Dar, G.H. Fresh Water Pollution Dynamics and Remediation; Qadri, H., Bhat, R.A., Mehmood, M.A., Dar, G.H., Eds.; Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2020; ISBN 978-981-13-8276-5. [Google Scholar]
- Moxness Reksten, A.; Rahman, Z.; Kjellevold, M.; Garrido Gamarro, E.; Thilsted, S.H.; Pincus, L.M.; Aakre, I.; Ryder, J.; Ariyawansa, S.; Nordhagen, A.; et al. Metal Contents in Fish from the Bay of Bengal and Potential Consumer Exposure—The EAF-Nansen Programme. Foods 2021, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.C.; Akter, S.M.; Islam, R.M.; Habib, A.; Chakraborty, T.K.; Zaman, S.; Kabir, A.H.M.E.; Shipin, O.V.; Wahid, M.A. Microplastics Contamination in Commercial Marine Fish from the Bay of Bengal. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2021, 44, 101728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.A.R.; Olden, J.D. Global Meta-analysis Reveals Diverse Effects of Microplastics on Freshwater and Marine Fishes. Fish Fish. 2022, 23, 1439–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarquoy, J. Microplastics and Microbiota: Unraveling the Hidden Environmental Challenge. World J. Gastroenterol. 2024, 30, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudud, H.J. St. Martin’s Island and its unique biodiversity face serious threats. IUCN Press Release. 2010. Available online: https://iucn.org/content/st-martins-island-and-its-unique-biodiversity-face-serious-threats (accessed on 16 March 2025).


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shaika, N.A.; Khan, S.; Awal, S.; Haque, M.M.; Bashar, A.; Simsek, H. Aquatic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impacts on Fisheries and Ecosystems. Hydrology 2025, 12, 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070191
Shaika NA, Khan S, Awal S, Haque MM, Bashar A, Simsek H. Aquatic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impacts on Fisheries and Ecosystems. Hydrology. 2025; 12(7):191. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070191
Chicago/Turabian StyleShaika, Nowrin Akter, Saleha Khan, Sadiqul Awal, Md. Mahfuzul Haque, Abul Bashar, and Halis Simsek. 2025. "Aquatic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impacts on Fisheries and Ecosystems" Hydrology 12, no. 7: 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070191
APA StyleShaika, N. A., Khan, S., Awal, S., Haque, M. M., Bashar, A., & Simsek, H. (2025). Aquatic Pollution in the Bay of Bengal: Impacts on Fisheries and Ecosystems. Hydrology, 12(7), 191. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070191







