Reproducibility Limits of the Frequency Equation for Estimating Long-Linear Internal Wave Periods in Lake Biwa
Abstract
1. Introduction
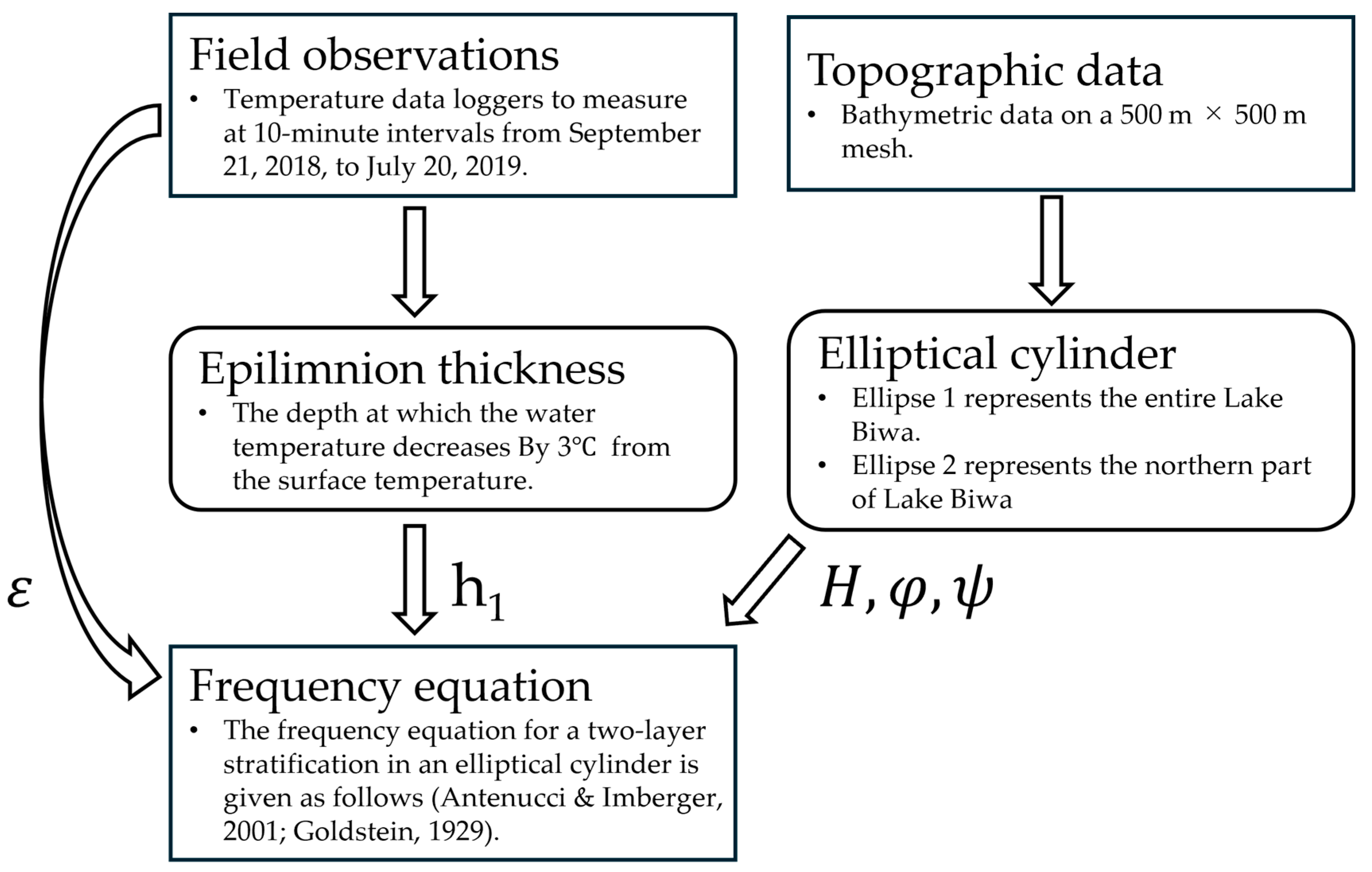
2. Methods
2.1. Field Observations
2.2. Estimation of Epilimnion Thickness
2.3. Frequency Equation in a Two-Layer Fluid
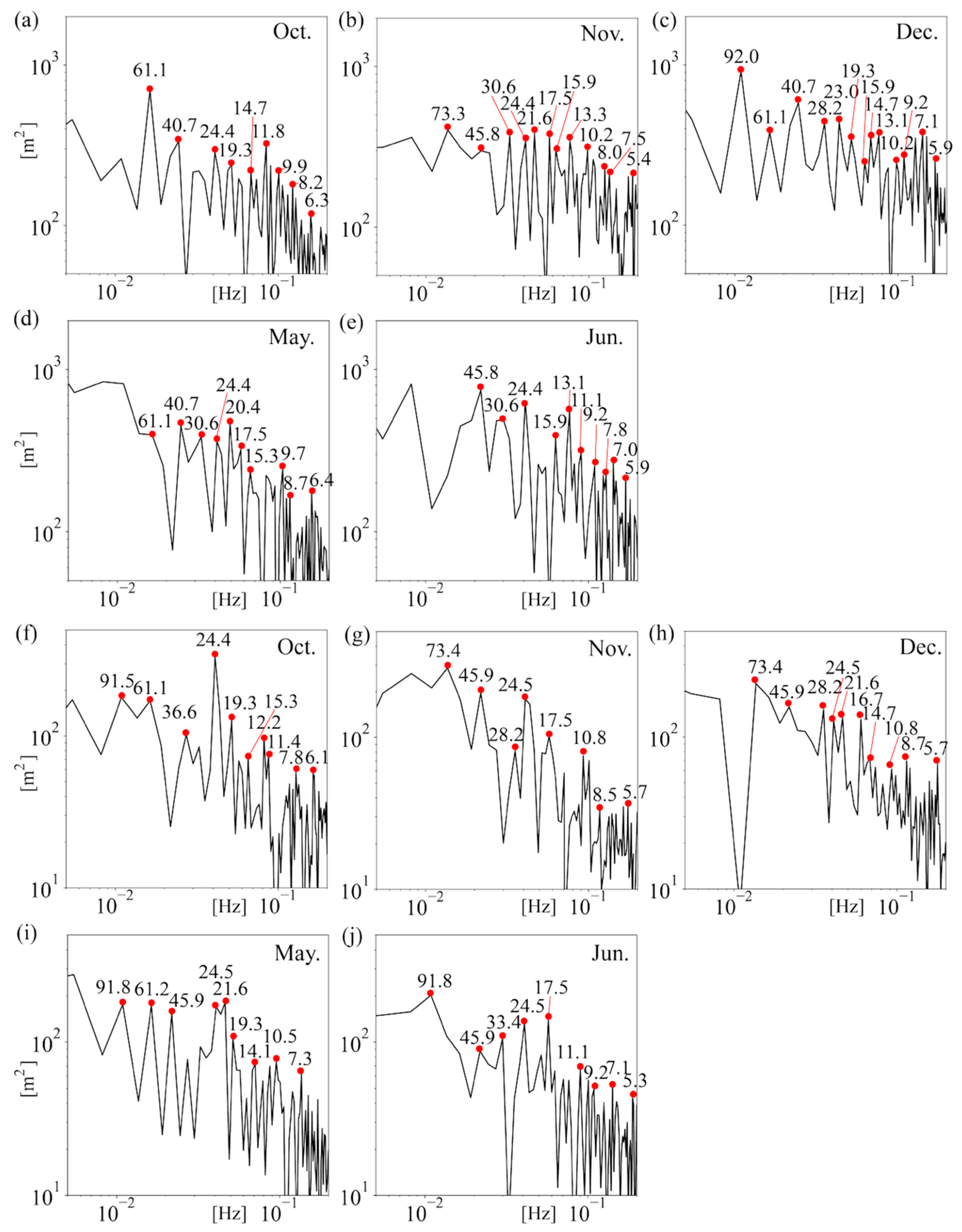
3. Results
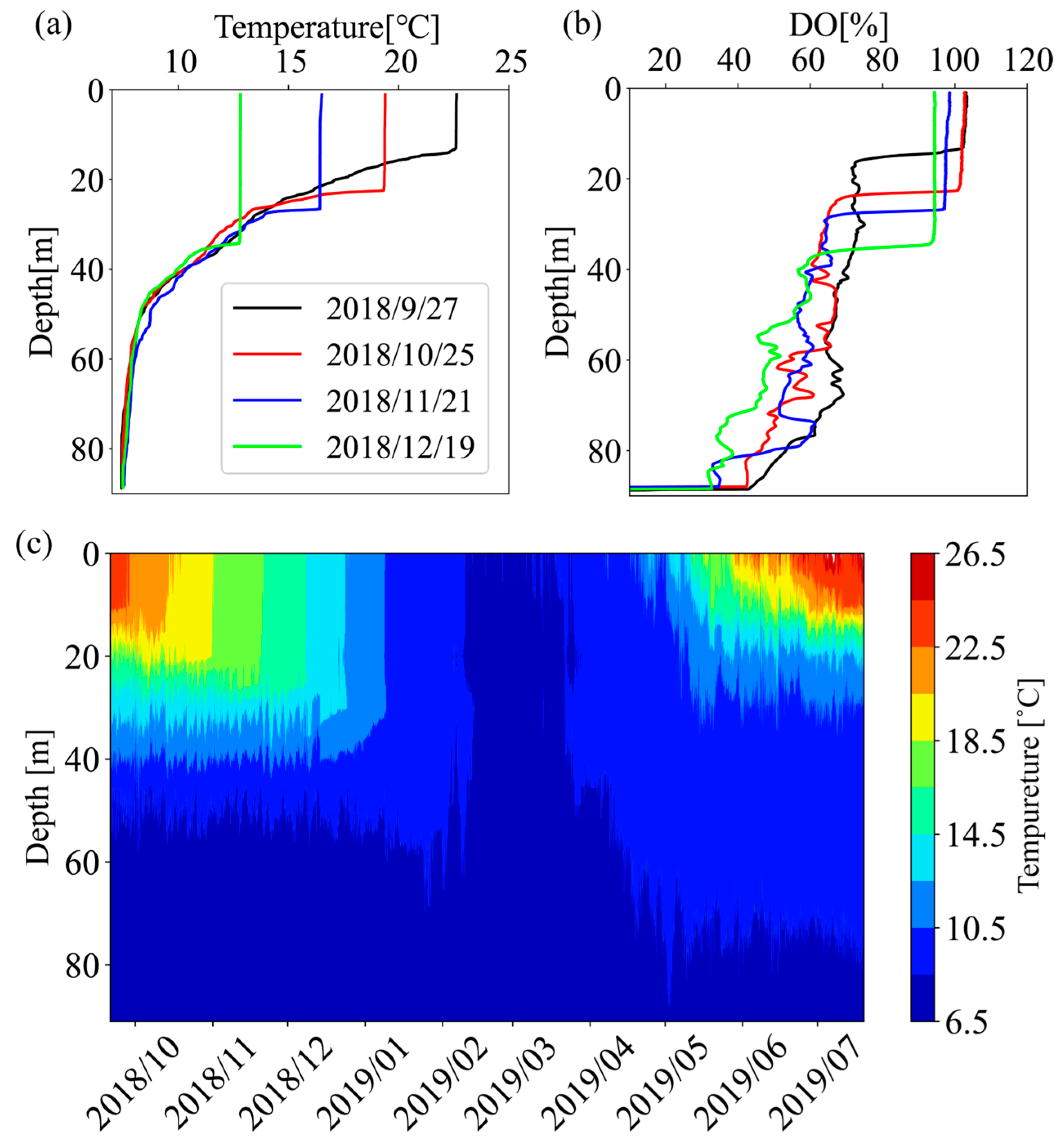
3.1. Annual Variations in Stratification in Lake Biwa
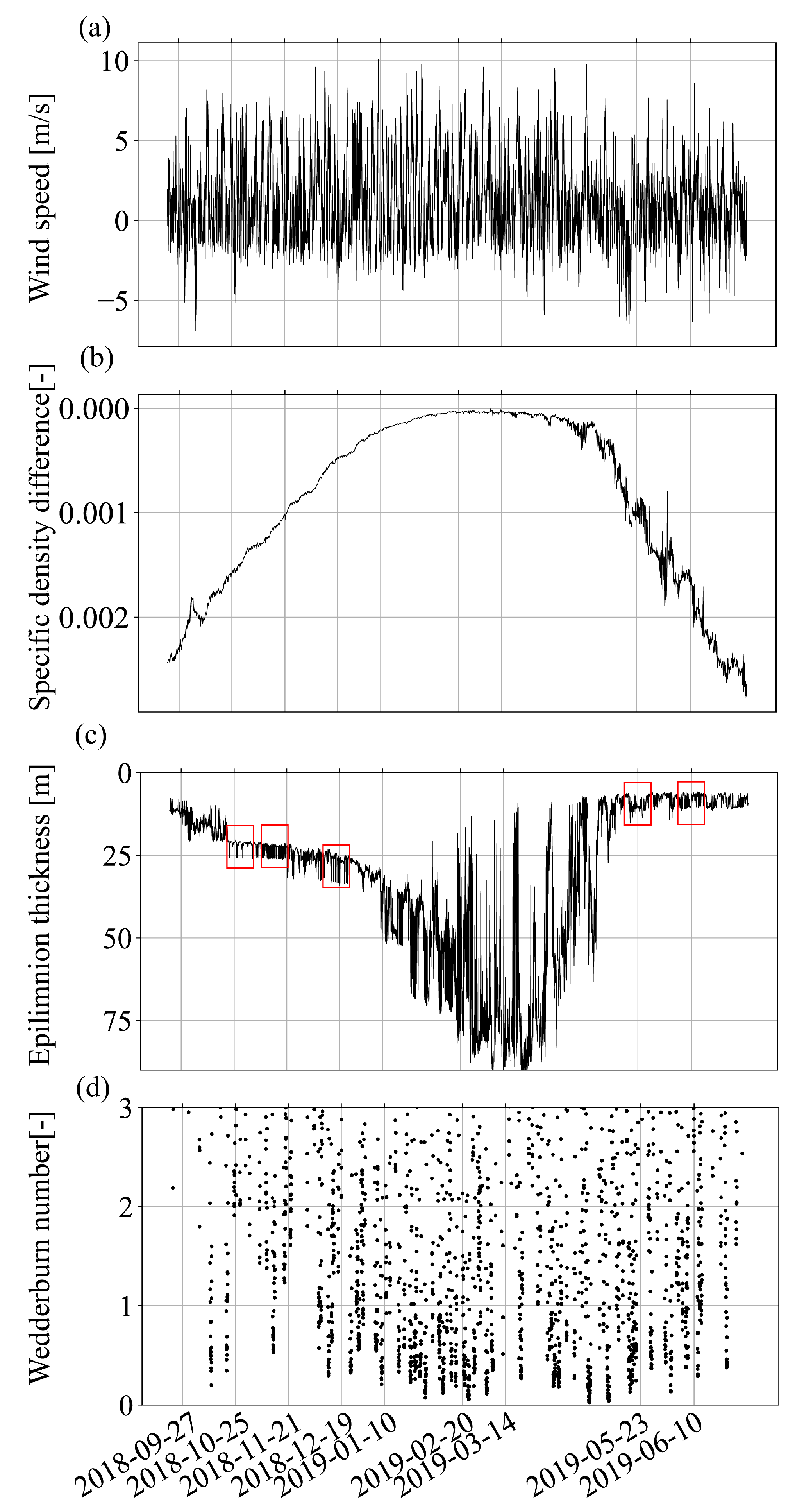
3.2. Linear Internal Wave Periods Obtained from Theoretical Solutions and Field Observations
3.3. Influence of Winds and Interference of Waves on Internal Wave Periods Using the Field Experiments
3.4. Validity of Theoretical Solutions for Internal Kelvin Waves in November and December 2018
3.5. Year-Round Internal Wave Periods Using the Frequency Equation
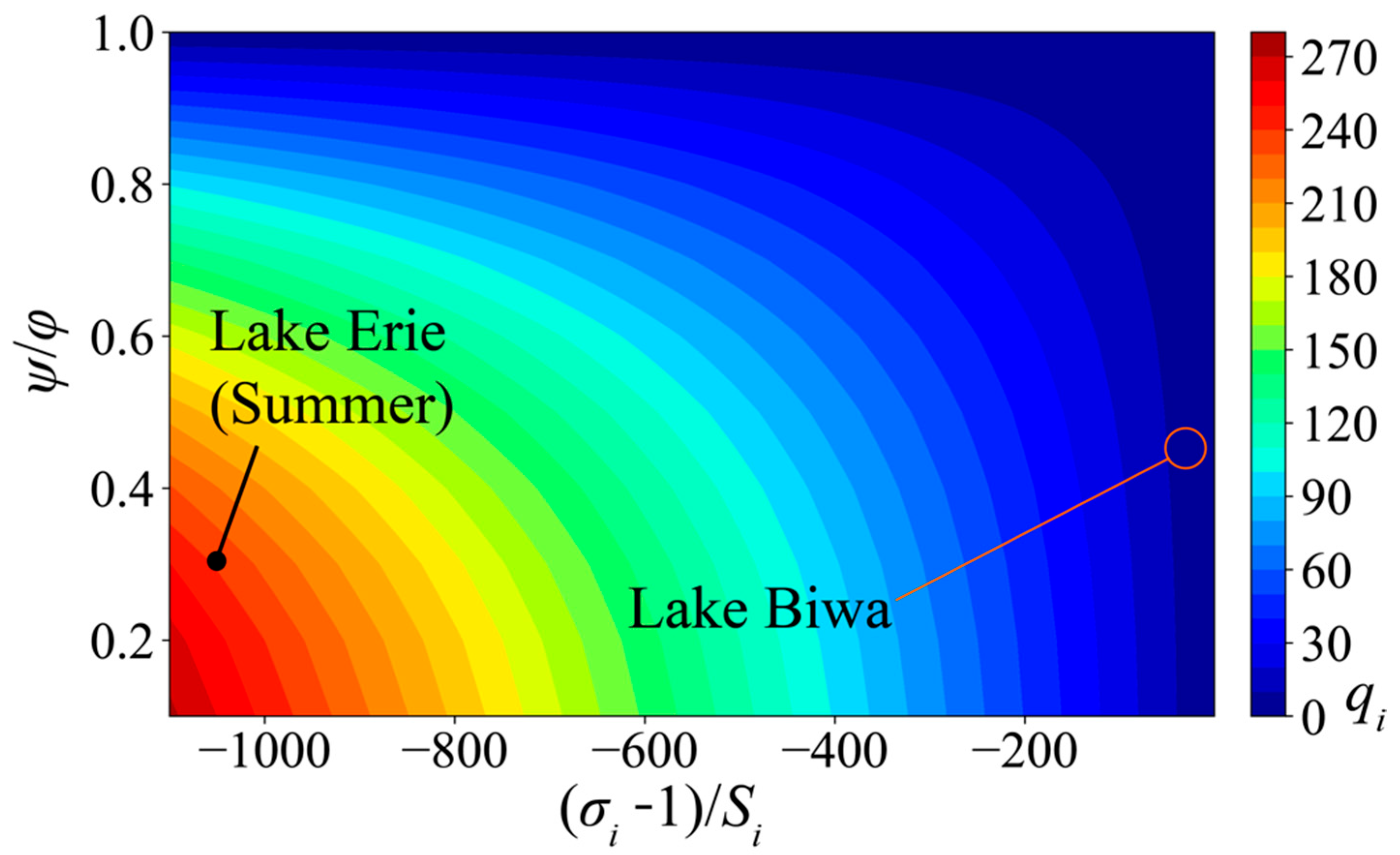
4. Discussion
4.1. Wind Effect on Internal Kelvin Waves
4.2. Applicability Limits of the Theoretical Solutions for Internal Kelvin Waves
4.3. Comparisons of the Frequency Equations for a Circular and Elliptical Cylinder
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartosiewicz, M.; Laurion, I.; Clayer, F.; Maranger, R. Heat-Wave Effects on Oxygen, Nutrients, and Phytoplankton Can Alter Global Warming Potential of Gases Emitted from a Small Shallow Lake. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6267–6275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinohara, R.; Matsuzaki, S.-I.S.; Watanabe, M.; Nakagawa, M.; Yoshida, H.; Kohzu, A. Heat Waves Can Cause Hypoxia in Shallow Lakes. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2023, 50, e2023GL102967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Jennings, E.; Carrea, L. Impact of the 2018 European heatwave on lake surface water temperature. Inland Waters 2020, 10, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y. Evaluation of ICESat-2 Laser Altimetry for Inland Water Level Monitoring: A Case Study of Canadian Lakes. Water 2025, 17, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Jin, X.; Li, W.; Cai, K.; Yang, G.; Chen, K.; Xu, J.; Johnson, A.C. Identifying Critical Land Use Thresholds for Biodiversity Conservation in China’s Lake Ecosystems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 5431–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gloor, M.; Wüest, A.; Münnich, M. Benthic boundary mixing and resuspension induced by internal seiches. Hydrobiologia 1994, 284, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, D.C.; Weyhenmeyer, G.A. High resolution measurements of sediment resuspension above an accumulation bottom in a stratified lake. Hydrobiologia 1994, 284, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shteinman, B.; Eckert, W.; Kaganowsky, S.; Zohary, T. Seiche-Induced Resuspension in Lake Kinneret: A Fluorescent Tracer Experiment. In The Interactions Between Sediments and Water; Evans, R.D., Wisniewski, J., Wisniewski, J.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1997; pp. 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüest, A.; Lorke, A. Small-scale hydrodynamics in lakes. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2003, 35, 373–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boegman, L.; Stastna, M. Sediment Resuspension and Transport by Internal Solitary Waves. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2019, 51, 129–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macintyre, S.; Flynn, K.M.; Jellison, R.; Romero, J.R. Boundary mixing and nutrient fluxes in Mono Lake, California. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1999, 44, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finlay, K.P.; Cyr, H.; Shuter, B.J. Spatial and temporal variability in water temperatures in the littoral zone of a multibasin lake. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanady, G.T. The Coastal Boundary Layer in Lake Ontario: Part II. The Summer-Fall Regime. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1972, 2, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, B.R.; Imberger, J.; Saggio, A.; Winters, K.B. Modeling basin-scale internal waves in a stratified lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2000, 45, 1603–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, W.; Nakayama, K.; Shintani, T. Coriolis effects on wind-driven upwelling in enclosed basins. Cont. Shelf Res. 2023, 256, 104956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laval, B.; Imberger, J.; Hodges, B.R.; Stocker, R. Modeling circulation in lakes: Spatial and temporal variations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffard, D.; Boegman, L.; Rao, Y.R. Poincaré wave–induced mixing in a large lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 1201–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valipour, R.; Bouffard, D.; Boegman, L.; Rao, Y.R. Near-inertial waves in Lake Erie. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2015, 60, 1522–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayami, Y.; Fujiwara, T. Recent warming of the deep water in Lake Biwa. Res. Sea 1999, 8, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamada, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Hichiri, S.; Okamoto, T.; Hayakawa, K. First observation of incomplete vertical circulation in Lake Biwa. Limnology 2021, 22, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumagai, M.; Jiao, C.; Ishikawa, K.; Aota, Y. Chapter 1, climate change and environmental change in Lake Biwa. In Final Report of the Committee for the Investigation of Northern Lakes of Lake Biwa; Lake Biwa Environmental Research Institute: Shiga, Japan, 2005; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Maruya, Y.; Nakayama, K.; Sasaki, M.; Komai, K. Effect of dissolved oxygen on methane production from bottom sediment in a eutrophic stratified lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2023, 125, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antenucci, J.P.; Imberger, J. Energetics of long internal gravity waves in large lakes. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2001, 46, 1760–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csanady, G.T. Motions in a model Great Lake due to a suddenly imposed wind. J. Geophys. Res. 1968, 73, 6435–6447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Imberger, J.; Kumagai, M. Horizontal structure and excitation of primary motions in a strongly stratified lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 2641–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoneda, H.; Nakayama, K.; Hirami, T.; Hayakawa, K.; Jiao, C. Internal wave mode in Lake Biwa. Jpn. J. JSCE 2025, 81, 24–16084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Chiu, C.Y.; Tsai, J.W.; Liu, W.C.; Tada, K.; Nakayama, K. Influence of Thermal Stratification on Seasonal Net Ecosystem Production and Dissolved Inorganic Carbon in a Shallow Subtropical Lake. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2021, 126, e2020JG005907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staehr, P.A.; Sand-Jensen, K. Temporal dynamics and regulation of lake metabolism. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2007, 52, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saggio, A.; Imberger, J. Internal wave weather in a stratified lake. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1998, 43, 1780–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antenucci, J.P.; Imberger, J. The seasonal evolution of wind/internal wave resonance in Lake Kinneret. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, S. On the vortex theory of screw propellers. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Contain. Pap. A Math. Phys. Character 1929, 123, 440–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedlosky, J. Geophysical Fluid Dynamics, 2nd ed.; Springer Science & Business Media: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imberger, J.; Patterson, J.C. Physical Limnology. In Advances in Applied Mechanics; Hutchinson, J.W., Wu, T.Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1989; pp. 303–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, C.; Imberger, J. The initial response of a stratified lake to a surface shear stress. J. Fluid Mech. 1996, 312, 39–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, J. Air-sea bulk transfer coefficients in diabatic conditions. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1975, 9, 91–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanari, S. On the Study of Numerical Experiments of Two Layer Lake Biwa. Jpn. Soc. Limnol. 1974, 35, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Boegman, L.; Rao, Y.R. Characterizing spatial and temporal distributions of turbulent mixing and dissipation in Lake Erie. J. Great Lakes Res. 2021, 47, 168–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, H.; Nakayama, K. Validity of theoretical solutions for a rotating rectangular basin with two-layer stratification due to a suddenly imposed wind. Phys. Fluids 2025, 37, 036602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanari, S. The long-period internal waves in Lake Biwa. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1975, 20, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birchfield, G.E. Response of a circular model great lake to a suddenly imposed wind stress. J. Geophys. Res. 1969, 74, 5547–5554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
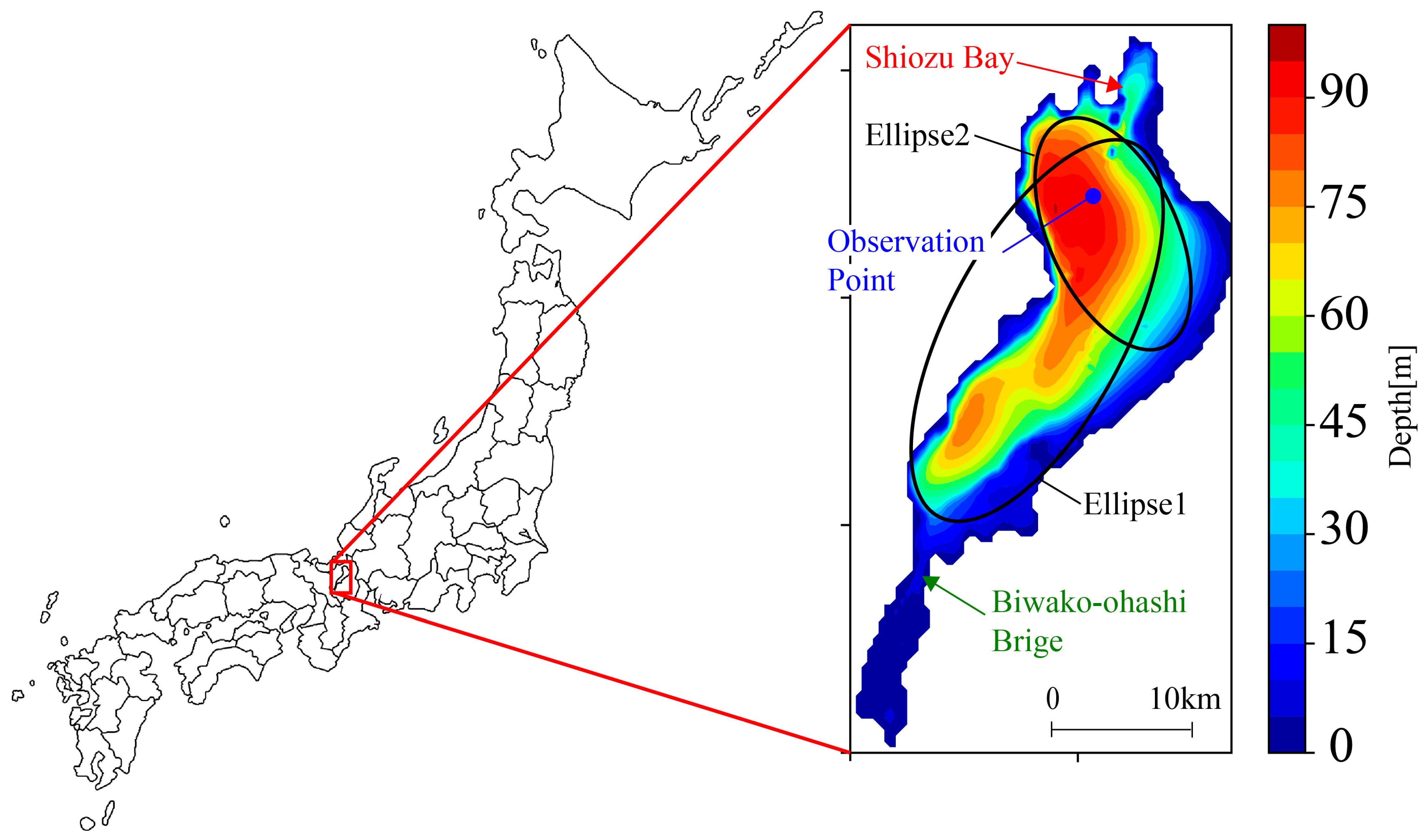

| (=Semi-Major Axis) (km) | (=Semi-Minor Axis) (km) | (=Representative Depth) (m) | |
| Ellipse1 | 19.0 | 8.3 | 43.4 |
| Ellipse2 | 11.9 | 7.2 | 66.6 |
| Observation Dates | Spectrum Analysis Period |
|---|---|
| 27 September 2018 | (Excluded due to typhoon) |
| 25 October 2018 | 22 October 2018–6 November 2018 |
| 21 November 2018 | 6 November 2018–21 November 2018 |
| 19 December 2018 | 8 December 2018–23 December 2018 |
| 10 January 2019 | (excluded) |
| 20 February 2019 | (excluded) |
| 14 March 2019 | (excluded) |
| 23 May 2019 | 15 May 2019–30 May 2019 |
| 10 June 2019 | 2 June 2019–17 June 2019 |
| Date | Mode | Ellipse1 | Ellipse2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 47.2 (61.1) | 27.6 | |
| 25 October | Mode2 | 14.4 (14.7) | 11.7 (11.8) |
| 2018 | Mode3 | 8.5 (8.2) | 6.1 (6.3) |
| Mode4 | 6.8 | 5.1 | |
| Mode1 | 58.1 (73.3) | 34.5 | |
| 21 November | Mode2 | 15.9 (15.9) | 13.3 (13.3) |
| 2018 | Mode3 | 10.1 (10.2) | 7.4 (7.5) |
| Mode4 | 8.2 | 6.2 | |
| Mode1 | 73.3 (92.0) | 51.0 (61.1) | |
| 19 December | Mode2 | 18.1 (19.3) | 15.8 (15.9) |
| 2018 | Mode3 | 13.3 (13.1) | 9.9 (9.2) |
| Mode4 | 11.3 | 8.4 | |
| Mode1 | 59.9 (61.1) | 38.8 (40.7) | |
| 23 May | Mode2 | 16.1 (17.5) | 14.1 (15.3) |
| 2019 | Mode3 | 10.4 (9.7) | 8.1 |
| Mode4 | 8.5 (8.7) | 6.8 (6.4) | |
| Mode1 | 52.3 (45.8) | 33.7 (30.6) | |
| 20 June | Mode2 | 15.2 (15.9) | 13.1 (13.1) |
| 2019 | Mode3 | 9.2 (9.2) | 7.2 (7.0) |
| Mode4 | 7.5 (7.8) | 6.1 (5.9) |
| 25 Oct. 2018 | 21 Nov. 2018 | 19 Dec. 2018 | 23 May 2019 | 20 June 2019 | Lake Erie | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ellipse1 | 0.438 | 0.304 | |||||
| 0.257 | 0.207 | 0.138 | 0.200 | 0.231 | 0.031 | ||
| −12.2 | −20.3 | −48.4 | −21.9 | −15.7 | −1051 | ||
| −2.47 | −4.11 | −9.79 | −4.43 | −3.17 | −238 | ||
| Ellipse2 | 0.602 | ||||||
| 0.474 | 0.387 | 0.273 | 0.348 | 0.395 | |||
| −1.91 | −4.24 | −11.2 | −5.86 | −3.94 | |||
| −0.30 | −0.68 | −1.78 | −0.93 | −0.63 | |||
| Ellipse1 | Circle1 | Ellipse2 | Circle2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode1 | 47.2 | 42.3 | 27.6 | 26.2 |
| Mode2 | 14.4 | 15.6 | 11.7 | 12.4 |
| Mode3 | 8.5 | 9.2 | 6.1 | 6.2 |
| Mode4 | 6.8 | 9.0 | 5.1 | 4.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoneda, H.; Jiao, C.; Nakayama, K.; Matsumoto, H.; Hayakawa, K. Reproducibility Limits of the Frequency Equation for Estimating Long-Linear Internal Wave Periods in Lake Biwa. Hydrology 2025, 12, 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070190
Yoneda H, Jiao C, Nakayama K, Matsumoto H, Hayakawa K. Reproducibility Limits of the Frequency Equation for Estimating Long-Linear Internal Wave Periods in Lake Biwa. Hydrology. 2025; 12(7):190. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070190
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoneda, Hibiki, Chunmeng Jiao, Keisuke Nakayama, Hiroki Matsumoto, and Kazuhide Hayakawa. 2025. "Reproducibility Limits of the Frequency Equation for Estimating Long-Linear Internal Wave Periods in Lake Biwa" Hydrology 12, no. 7: 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070190
APA StyleYoneda, H., Jiao, C., Nakayama, K., Matsumoto, H., & Hayakawa, K. (2025). Reproducibility Limits of the Frequency Equation for Estimating Long-Linear Internal Wave Periods in Lake Biwa. Hydrology, 12(7), 190. https://doi.org/10.3390/hydrology12070190