Abstract
Poyang Lake, a large floodplain lake, plays a crucial role in the ecological safety and quality of life in surrounding areas. Over the past decade (2013–2022), amid economic development and environmental changes, the water environment of Poyang Lake has encountered complex challenges. This study evaluated the water quality of Poyang Lake in a recent 10-year span by the water quality index (WQI), trophic level index (TLI) and a newly constructed comprehensive evaluation index, and it analyzed the trend of water quality change under extreme events. Meanwhile, the main factors affecting the water quality of Poyang Lake were analyzed by partial least squares (PLS), a multivariate statistical method that accounts for multicollinearity. The results indicate that: (1) The water quality of Poyang Lake in summer and autumn is slightly worse than that in spring and winter. Each water quality index reflects the distinct states of the water environment in Poyang Lake. (2) Each water quality evaluation index responds differently to influencing factors. (3) Extreme flood and drought events have markedly different impacts on the water environment of Poyang Lake, exhibiting significant spatial heterogeneity. Domestic sewage discharge and total water resources have a relatively great impact on the water environment of Poyang Lake. The results of this study provide important insights for water quality management and policy formulation in Poyang Lake, supporting sustainable regional development.
1. Introduction
Lakes are essential for socioeconomic development and play a crucial role in maintaining ecological functions and biodiversity [1]. As important components of ecosystems, lakes not only regulate the climate, provide drinking water and provide flood control services but also directly affect the quality of life and economic activities in surrounding communities [2,3,4]. In recent years, under the influence of extreme climatic events and human activities, lake water environment problems and water ecology issues have become more severe [5,6]. In China, worsening water quality and environmental problems in lakes are increasingly hindering socioeconomic development and posing significant threats to ecological health [7]. Recent research has indicated that approximately 40% of lakes are experiencing varying degrees of eutrophication, resulting in water quality deterioration and a decline in biodiversity [8]. Particularly in regions facing water scarcity, water quality is becoming a major problem in lake management [9].
The existing water quality assessment methods mainly include dynamic modeling frameworks such as the water quality index (WQI), trophic level index (TLI) and others. Although these three methods can evaluate the water quality of lakes, rivers and other water bodies, each has its own focus. The WQI is mainly concerned with the overall quality of the water body, which is suitable for quickly judging the water quality status, and the results are intuitive and easy to understand for non-professionals. The TLI is specially used to evaluate the eutrophication degree of water body, which can provide basis for predicting bloom and controlling exogenous pollution. Water quality grades divide water bodies into different grades based on the comparison between the concentration of water quality parameters and the standard limits, emphasizing whether the water quality meets the management objectives, which can directly serve the water quality standard assessment and discharge permit management. Githaiga et al. [10] evaluated the water quality, heavy metal concentration and health risks of eight major lakes in Kenya using the WQI method. Song et al. [11] established a comprehensive and dynamic modeling framework that links land use changes to water quality, enabling accurate predictions of future water quality under different land use scenarios. Zhang et al. [12] studied the spatial and seasonal distribution patterns of total nitrogen, total phosphorus (TP) and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) in lakes and conducted an assessment of eutrophication, using the TLI and Chl-a concentrations to evaluate the effects of floods on these patterns. Wei et al. [13], using Landsat-8 satellite data and deep neural networks (DNN), identified the water quality levels of lakes in Wuhan and Huangshi in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River. However, through the analysis of existing studies, it can be found that almost all studies have only used one water quality assessment method and are also limited by the difficulty of selecting indicators and collecting data, which poses challenges fully reflecting the water quality status of the study area. Therefore, it is necessary to carry out comprehensive evaluation of water quality from various aspects.
On the basis of evaluating water quality, identifying the key factors affecting water quality is also crucial. Researchers have made some progress in studies related to identification of the key factors affecting water quality. Ariyan et al. [14] conducted the first comprehensive analysis of tap water quality and its associated human health risks in Dhaka City. Their study utilized indicator assessments and advanced technologies to identify pollution sources and quantify the associated risks. Lei [15] conducted a study in the typical rural lowland watershed of Stör in northern Germany, employing an integrated approach that utilized the SWAT3s hydrological model and multivariate statistical techniques to determine the impact of different land use types with varying slopes on water quality indicators. Liu et al. [16] investigated how urban green space patterns impact the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of river water quality in the Hangzhou section of the Beijing-Hangzhou Canal. Using exploratory regression analysis, geographically weighted regression and spatial interpolation, their study offers a new perspective for understanding the interaction between green space spatial patterns and the urban water environment, as well as valuable information for local green space planning policies. Zhu [17] combined partial least squares structural equation modeling with an excitation–emission matrix–parallel factor analysis of fluorescence fingerprint data to study nutrient sources in rivers in southeastern China.
In summary, current research predominantly relies on single-method approaches to assess lake water quality, which often yields incomplete or biased results due to the limited scope of individual methods. Although some studies have used multiple methods, their fragmented analytical focus during reanalysis often fails to capture the comprehensive lake water quality. To address this gap, our study integrates the WQI and TLI methods to enable a more comprehensive assessment and develops a new composite water quality evaluation index by leveraging the strengths of both methods, thereby providing a more accurate and holistic reflection of Poyang Lake’s overall water quality. This study first applies both the WQI and TLI methods to assess the water quality and trophic status of Poyang Lake. Building on this, a comprehensive water quality evaluation index was developed based on the non-compliance rate of individual water quality parameters and the entropy weight method to effectively characterize the overall water quality of Poyang Lake. This research not only elucidates the trends in lake water quality under extreme climatic events but also identifies the primary factors influencing the water quality of Poyang Lake. The findings of this study aim to inform lake water quality management practices and contribute to policy formulation, ultimately supporting regional sustainable development initiatives.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
Poyang Lake is located between longitudes 115°49′–116°46′ E and latitudes 28°24′–29°46′ N, as illustrated in Figure 1. It is the largest freshwater lake in China (average surface area: 3150 km2; maximum flood extent: 4125 km2) and an important wetland conservation area. It has an average water depth of 8.4 m (maximum depth: 25.1 m) and a drainage basin area of 162,000 km2. As a flood storage and water resource regulation zone in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River, Poyang Lake plays a vital role in mitigating extreme floods and droughts.
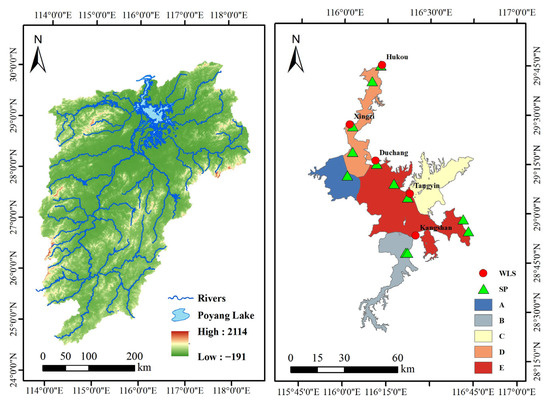
Figure 1.
Location of the study area and sampling points. (Note: XZ stands for XingZi Stations, SP stands for Sampling Points, A is the Ganjiang River Estuary Region, B is the Three Rivers Estuary Region, C is the Eastern Wetland Lake Region, D is the Northern Yangtze River-Connected Lake Region and E is the Southern Central Lake Region).
The watershed is influenced by five major rivers: Ganjiang River, Fuhe River, Xinjiang River, Raohe River and XiuShui River, resulting in significant seasonal variations in water levels. Land cover in the drainage basin, which critically mediates lake-water interactions, is dominated by five types (CORINE Land Cover 2018 data): agricultural land (42%, predominantly paddy fields), forest land (28%, subtropical evergreen forests), wetlands (15%, reed marshes), artificial surfaces (8%, urban/industrial zones) and grassland/shrubland (7%). These land cover types regulate nutrient inputs and pollutant loads. Agricultural runoff—which contributes approximately 60% of total nitrogen and phosphorus—significantly exacerbates eutrophication, whereas wetlands alleviate pollution through natural purification processes.
Winters are cold, spring is characterized by convective weather and summer often brings flooding and drought events, with an average annual temperature of 18.0 °C. The hydrological characteristics and ecological environment of Poyang Lake directly impact the socioeconomic development of the watershed, and it holds significant regional and international importance, especially in responding to extreme climate events. However, the ecological function of Poyang Lake has been potentially affected by extreme climatic events in recent years [18,19]. When extreme weather events occur, the hydrological exchange between Poyang Lake and the Yangtze River exhibits significant changes in water area and water level, which directly affects the concentration of nutrients and pollutants in the lake [20,21]. Recent climate change projection studies on Poyang Lake have demonstrated that different models (e.g., CMIP5 and CMIP6 scenarios) yield divergent predictions regarding future changes. Some models project a rise in annual average temperature of 1.5–3.0 °C, accompanied by intensified summer flooding, whereas others highlight that uneven precipitation spatial distribution may reduce effective dry-season recharge. However, recent studies have suggested that extreme climate events have likely impacted the ecological functions of Poyang Lake in recent years. During extreme weather events, hydrological exchanges between Poyang Lake and the Yangtze River undergo significant variations in water area and level, which directly alters nutrient and pollutant concentrations in the lake.
2.2. Data Sources
This study relies on monitoring data from the Poyang Lake Wetland Comprehensive Research Station of the Nanjing Institute of Geography and Limnology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, to analyze the health status of the Poyang Lake’s water environment based on the WQI, TLI and compliance with water quality standards. Given the unique hydrological conditions, lake morphology and functional characteristics of Poyang Lake, the research station has established 15 monitoring points across the lake, with samples collected quarterly (in January, April, July and October) at a seasonal temporal resolution, this sampling frequency may fail to capture short-term variations, including monthly fluctuations and acute pollution events. The main indicators monitored include dissolved oxygen (DO), pH, transparency (SD), water temperature (WT), chlorophyll a (Chl-a), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), Potassium Permanganate Index (CODMn), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N) and ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N). This study utilized water quality data from the Poyang Lake Wetland Observation Research Station for the 2013–2022 period. To address potential limitations in temporal resolution, we integrated analyses of interannual variations and extreme climate events (e.g., the 2020 extreme flood and 2022 extreme drought) to enhance our understanding of short-term water environment responses. Based on the hydrological connectivity and geographical position of Poyang Lake in relation to the Yangtze River and five other rivers, the Poyang Lake watershed was divided into five regions: the Northern Yangtze River-Connected Lake Region, the Ganjiang River Estuary Region, the Southern Central Lake Region and the Eastern Wetland Lake Region, along with the Three Rivers Estuary Region. This study also analyzed the interannual variations in the spatiotemporal distribution characteristics of the Poyang Lake’s water environment. Geographic data for the watershed were sourced from the Geospatial Data Cloud (https://www.gscloud.cn/search (accessed on 29 September 2024)). Additionally, the analysis of Poyang Lake’s water environment status was conducted using water quality condition data from extreme drought years and extreme flood years, with the independent variables for the influencing factors sourced from the Jiangxi Provincial Yearbook.
2.3. Method
This study used WQI and TLI to evaluate the water quality of Poyang Lake in recent 10 years. At the same time, a new comprehensive evaluation index was constructed to evaluate the overall water quality of Poyang Lake. Based on the evaluation results obtained, on the one hand, the water quality change trend of Poyang Lake under the influence of extreme events was analyzed. On the other hand, the main factors affecting the water quality of Poyang Lake were analyzed by partial least squares regression. The specific process is shown in Figure 2.
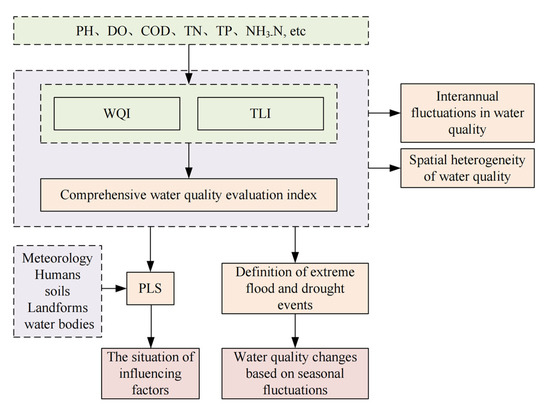
Figure 2.
Article structure diagram.
2.3.1. Water Quality Evaluation Method
This study used three methods for water quality assessment. The WQI is a comprehensive indicator used to assess and represent the quality of water bodies. This method effectively converts numerous physical and chemical parameters into a single value that reflects the water quality level, thereby eliminating discrepancies between parameters used individually in assessments and providing a complete representation of the overall water quality information [14], The WQI evaluation scoring criteria are as shown in Table S1.
TLI is an indicator used to assess the degree of eutrophication in water bodies. Eutrophication refers to the excessive concentration of nutrients in water, leading to the overgrowth of aquatic plants, which, in turn, affects the ecological balance and water quality. The evaluation factors include Chla, TP, TN, SD and CODMn [22], The TLI evaluation scoring criteria are as shown in Table S2.
Each of the two water quality analysis methods has its own characteristics. The WQI comprehensively reflects the overall water quality, incorporating multiple water quality indicators [23,24]. The TLI focuses primarily on the nutrient status of the water body, including parameters such as Chla, nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations [25].
In order to avoid the comprehensive evaluation index covering up the details of a single index (for example, if WQI meets the standard, but TLI exceeds the standard), this study proposed a combined weight method to calculate the weight of WQI and TLI by considering the substandard rate of water quality index and entropy weight. The weight distribution Table S3 of the comprehensive evaluation method, and Classification of lake health standards are as shown in Table S4. The formula is as follows:
The comprehensive evaluation index:
The weights of each index:
where Wi and qi are the combined weight and value of i-th comprehensive evaluation index (WQI and TLI) respectively, Wbdb and We are substandard rate of water quality index and entropy weight, rij is the standardized value of the two water quality evaluation indexes, Ei is the information entropy of i-th index, pij is the proportion of the j-th standardized value of the i-th index in all indexes.
2.3.2. Definition of Extreme Flood and Drought Events
According to information released by the Jiangxi Hydrological Monitoring Center, Poyang Lake typically maintains an average water level of approximately 13.5 m (based on long-term hydrological records from 2000 to 2022), which provides a key reference for defining extreme hydrological events. The center has explicitly defined water level standards to distinguish normal fluctuations from extreme conditions: Extreme flood threshold: when the water level at Xingzi Station exceeds 20.0 m, an orange alert is issued; a red alert (indicating emergency response measures) is activated if the level surpasses 21.0 m (historical records indicate that this threshold corresponds to “extreme flood events”). Extreme drought threshold: the warning water level is set at 19.0 m; sustained water levels below 19.0 m for ≥15 consecutive days are defined as “extreme drought events” (in accordance with the center’s drought classification standards).
Over the past decade (2013–2022), Poyang Lake experienced frequent extreme hydrological events, including extreme flood events: the 2016 flood (July–August), where water levels exceeded 20.0 m for 23 consecutive days (peaking at 21.38 m), and the 2020 flood (July), designated as a representative extreme flood year (study period: July 2020), with water levels reaching 20.50 m (exceeding the orange alert threshold). Notable cases of extreme drought events include the 2014 drought (duration: May–October (water levels <19.0 m for 153 days)), 2015 drought (June–September, <19.0 m for 112 days), 2019 drought (July–November, <19.0 m for 141 days) and 2022 drought (the most severe: September–December, <19.0 m for 118 days, with a record low of 7.10 m at Xingzi Station on September 23).
Based on the above water level data, this study analyzed the impact of extreme flooding and drought events on the water environment of Poyang Lake. The year 2020 was selected as a typical extreme flood year, with the study period being July 2020. In this study, 2022 was selected as a typical extreme drought year. The study period was October 2022. The water level of Poyang Lake exhibited periodic changes. It is usually low in January and February, peaks in July and August and then gradually decreases, reaching its lowest point by December. The water quality before and after the seasons of the same year in the extreme flood period was selected for comparison. Since the data were up to October 2022, the average data of October were used for comparison of extreme drought.
2.3.3. Partial Least Squares
Partial least squares (PLS) is a statistical method used to establish the relationship between dependent and independent variables, particularly suitable for situations with a large number of independent variables and issues of multicollinearity [26]. The PLS coefficient reflects the magnitude and direction of the direct contribution of each environmental impact factor to the target variable. A positive coefficient signifies a positive driving relationship with the target variable, whereas a negative coefficient implies an inhibitory relationship. A larger absolute coefficient value indicates a more substantial influence of the factor on the target variable. Although PLS effectively models high-dimensional data and linear-to-weakly nonlinear relationships by reducing dimensionality, it relies fundamentally on linear assumptions and may fail to capture complex nonlinear interactions in hydrological and ecological systems. To mitigate this limitation, we deliberately selected indicators spanning climatic factors, socioeconomic conditions, aquatic system characteristics and land use patterns—variables that capture not only key drivers of water quality but also potential nonlinear drivers.
Climate factors, including annual average temperature, annual precipitation, annual sunshine hours and annual average relative humidity, directly influence the temperature, recharge and ecological balance of water bodies. Social factors, such as watershed GDP, watershed population, tourist visits to Poyang Lake, approved sand extraction volume, domestic sewage discharge and total water resources, reflect the direct impacts of economic activities and population on water quality. Factors such as the annual average water level, maximum water level and minimum water level provide insights into the capacity and ecological health of a water body. Similarly, land use factors like agricultural sowing areas and afforestation areas can illustrate the impact of human activities on water bodies. A comprehensive analysis of these indicators helps identify sources of water pollution and provides a scientific foundation for further research. In this study, PLS analysis was performed on the independent and dependent variables using ORIGIN v.2024.
3. Results
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
3.1. Interannual Variation of Water Quality
The results obtained by three different water quality assessment methods are shown in Figure 3. In the chart, green denotes years of extreme drought, while red indicates years of extreme flood events. All results are presented in Supplementary Tables S5–S7. Based on the WQI data of Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022, the trend of water quality changes showed obvious fluctuating characteristics. In 2013, the WQI was 48.04, indicating a relatively good water quality condition. Subsequently, in 2014 and 2015, the WQI slightly rose to 48.52 and 51.40 respectively, suggesting a deterioration in water quality. In 2016, the WQI dropped to 44.61, indicating an improvement in water quality. Entering 2017, the WQI rose again to 51.62, showing a clear trend of water quality deterioration. In 2018, the WQI reached 54.72, reflecting a significant deterioration in water quality and making it the worst year in terms of water quality over the decade. Although the WQI slightly decreased to 53.01 in 2019, the water quality still did not improve significantly. In 2020, the WQI was 51.63, remaining at a poor level. In 2021 and 2022, the WQI values dropped to 50.46 and 49.76, respectively, showing a gradual improvement in water quality, but still higher than the level in 2013. Overall, the WQI in the Poyang Lake area has experienced multiple fluctuations over the past decade.
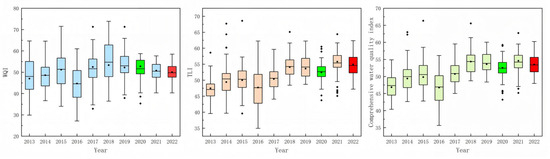
Figure 3.
Inter-annual variations of the water quality in Poyang Lake. (Note: green denotes years of extreme drought, while red indicates years of extreme flood events.)
Based on the TLI data of Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022, it can be observed that the eutrophication level of this area showed a fluctuating trend. In 2013, the TLI was 47.11, which was in the mesotrophic range, indicating relatively good water quality at that time. However, in the following years, the TLI gradually increased. In 2014 and 2015, the values were 50.42 and 50.29, respectively, still within the mesotrophic range. In 2017, the TLI exceeded 50 for the first time, reaching 50.62, entering the oligo-eutrophic range, indicating the initial manifestation of eutrophication problems. In 2018, the TLI further rose to 54.29, suggesting a worsening of eutrophication and a continuous decline in water quality. The subsequent data fluctuated between 54 and 55, especially in 2021, reaching 55.39, still within the oligo-eutrophic range, showing a further intensification of eutrophication problems. Overall, during the analysis period, the TLI of Poyang Lake were mostly in the oligo-eutrophic range in most years.
Based on the comprehensive water quality assessment results of Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022, the changes and trends in water quality can be observed. In 2013, the comprehensive water quality assessment score was 47.33, indicating that the water quality of the lake area was in a relatively good state. As time went by, the water quality slightly declined in 2014, with a score of 49.96, still remaining at a good level. In 2015, the water quality further improved to 50.56, entering a moderate state, showing a relatively stable trend. In 2016, the comprehensive water quality assessment score dropped back to 46.93, returning to a relatively good level. Subsequently, in 2017, the water quality score rose to 50.86, indicating an increase in eutrophication pressure. In 2018, the comprehensive water quality assessment score significantly increased to 54.39, reflecting a gradually more obvious trend of deterioration and entering a state of light eutrophication. The scores for 2019 and 2020 were 53.86 and 52.42, respectively; although there were slight fluctuations, the overall level remained relatively high, suggesting that water quality issues still existed. In 2021, the comprehensive water quality assessment score was 54.21, and in 2022, it was 53.41, indicating a slight decline in water quality during these two years. Overall, the comprehensive water quality assessment results of Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022 show a fluctuating trend, with water quality improving in some years.
Based on the comprehensive water quality assessment, as well as the TLI and WQI data of Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022, the results of the three evaluation methods showed a similar trend. From the overall trend, all indicators reached their peak in 2018, indicating the severity of eutrophication and pollution intensification problems faced by the Poyang Lake area. Specifically, the water quality comprehensive assessment rose to 54.39 in 2018, the TLI climbed to 54.29 and the WQI reached 54.72. Subsequently, the water quality comprehensive assessment and WQI slightly declined in 2022, but the overall level remained relatively high.
Based on the ANOVA results of the three indicators, the p-values for all intergroup differences were <0.001 (the statistically “highly significant” threshold), leading to the definitive conclusion that the three water quality evaluation methods—WQI, TLI and the composite index—yielded statistically distinct results. This indicates that the quantitative assessments of water quality derived from different methods are inconsistent. The integrated composite index (or alternative methods) may account for water quality characteristics—such as pollutant synergies/antagonisms that a single method cannot detect.
3.2. Analysis of Spatial Variations of Several Water Quality Evaluation Methods Under Extreme Flood and Drought Conditions
3.2.1. Spatial Variation of WQI
In this study, we conducted a systematic analysis of extreme flooding events in April 2020 and July 2020 and the WQI in October 2020. The results are shown in Figure 4a,d. When comparing the WQI data of different time periods, it is obvious to observe the impact of extreme flooding events on water quality in various regions. In the Southern Central Lake Region, WQI values decreased significantly during extreme flooding, with an average drop of more than 20 points and water quality increased from “moderate” to “good” at some points. In contrast, the WQI in the Northern Lake region, which connects the Yangtze River, changed relatively gently during extreme floods, and the water quality at most sites was similar to pre-flood levels. In the mouth of Ganjiang River, the WQI value increased after the extreme flood event. Finally, in the eastern Wetland Lake area and the Sanhe River into the Lake area, the changes of WQI after extreme flooding events were more complex, and the water quality at some sites showed a trend of improvement but declined in the later recovery process.
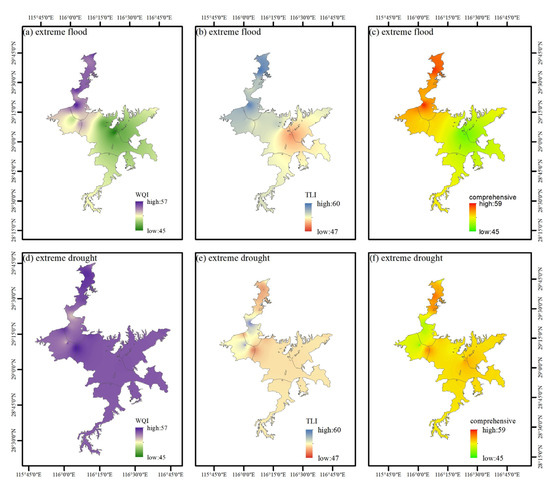
Figure 4.
Comparison of water quality zoning results for the main areas of Poyang Lake in extreme flood years and drought years.
The effects of extreme drought on WQI in different regions showed obvious spatial differences. The Southern Central Lake area was most affected, the Northern Lake area and the Ganjiang Estuary area showed a certain resilience, while the eastern Wetland Lake area and the three rivers into the lake area showed a greater fluctuation in water quality. WQI values in the Southern Central Lakes Region increased significantly during periods of extreme drought, with the average rising from 42.09 in July 2022 to 55.46. In contrast, water quality changes in the Northern Lakes were relatively stable. Although WQI increased during extreme droughts, it remained at “moderate” levels overall. The WQI value of Ganjiang River Estuary during the extreme drought period was 42.00, which was improved compared with 46.04 in July. In the eastern Wetland Lake District, the WQI during extreme drought was 54.94, compared with 50.76 in July, indicating the deterioration of effluent quality. The WQI of the Sanhe lake area during the extreme drought period was 55.32, which remained at the “medium” level, slightly increased compared with 54.86 in July, indicating that the water quality in this area remained at a low level under the drought conditions.
3.2.2. Spatial Variation of TLI
The degree of trophication varied across regions during extreme floods, with the Southern Central Lake District showing initial improvement followed by deterioration, The results are shown in Figure 4b,e, while the Northern lake District and Ganjiang River mouth experienced negative impacts, though the latter exhibited recovery potential, and the eastern Wetland Lake Region remained at risk of declining water quality. When comparing the water quality of extreme flooding events in 2020 with similar periods, the changes in nutrient levels in different regions showed significant differences. In April 2020, TLI in the Southern Central Lake District was 52.60, indicating light eutrophication, which improved to 47.20 during floods but rose to 52.32 by October. In the Northern Lakes, TLI was 51.13 in April, increasing to 54.12 during flooding and slightly dropping to 50.41 in October. The Ganjiang River Estuary had a TLI of 55.94 in April (medium eutrophication), rising to 57.05 during floods but improving to 45.23 by October. In the eastern Wetland Lake District, TLI was 51.98 in April, rising to 55.33 during flooding and slightly decreasing to 52.82 in October, remaining in light eutrophication.
When comparing the degree of trophication during the 2022 extreme drought period with similar periods, TLI data from different regions showed significant changes. The deterioration of water quality was more obvious in the Southern Central Lake District and the Northern Lake District under extreme drought, while the eastern Wetland Lake District showed a certain stability, and the Ganjiang Estuary area was between the two. In the Southern Central Lake Region, TLI values during extreme drought were generally higher than those during the other two ordinary periods, indicating deterioration of effluent quality. In the Northern Lakes, the region has also experienced significant water quality changes. The TLI values in October 2022 ranged from 51.29 to 58.90, a significant increase compared to the TLI values in July (53.19 to 56.39), with an average TLI value of 50.81 (moderate eutrophication). In the estuary of Ganjiang River, the TLI value of extreme drought period was 54.13 to 57.63, which decreased from 56.74 to 60.25 in July, and the average TLI value was 53.77 (mild eutrophication). Finally, in the eastern Wetland Lake District, TLI values ranged from 51.98 to 58.28 during extreme drought, with an average TLI of 51.96 (mild eutrophication), indicating that water quality was relatively stable and did not deteriorate significantly during extreme drought.
3.2.3. Spatial Variation of Comprehensive Evaluation
In the analysis of the comprehensive assessment index of water quality in 2020 and the extreme flood period and in October 2020, there were obvious differences among different regions, especially the water quality changes under the influence of extreme climate events. The comparative analysis between the extreme flood period and the ordinary period in different regions is shown in Figure 4c,f. Water quality in the Southern Central Lake area and the mouth of the Ganjiang River improved significantly during extreme floods, while the Northern Lake area showed adaptability to extreme conditions. Water quality in the eastern Wetland Lake area remained relatively stable.
In the Southern Central Lake Region, water quality improved during extreme flooding, with composite assessment indices of 45.55 and 45.80, significantly lower than the April 2020 levels of 52.59 and 54.99. However, in October 2020, the indices slightly decreased to 50.86 and 50.73 (sub-healthy). Conversely, the Northern Lakes maintained stable water quality during extreme flooding, with indices ranging from 51.80 to 53.76, similar to April 2020’s 52.21 to 52.55. A minor deterioration was noted in October 2020, with one point at 50.36 (sub-healthy). The Ganjiang River Estuary showed more fluctuation during floods, with an index of 55.86 in April 2020 rising slightly to 55.95 during floods but significantly improving to 45.11 (healthy) by October 2020. The eastern Wetland Lakes remained stable during floods, with indices of 54.10 to 56.76, higher than the April 2020 range of 51.60 to 52.82, indicating sub-healthy levels without significant deterioration.
In 2022, water quality varied significantly across regions during extreme climate events and drought periods. The Southern Central Lake District saw indices of 53.95 in July, 56.21 in the dry period, and 52.97 in October. The Northern Lakes showed similar trends, with a July index of 53.99 falling to 50.98 in October. The Ganjiang River mouth remained stable, while the eastern wetland area improved, with indices of 54.53 in July, 52.69 in the dry period and 50.56 in October. The three rivers entering the lake had an index of 57.35 in July, dropping to 53.02 in October, indicating potential for improvement but still at sub-healthy levels.
3.3. The Driving Mechanism of Water Quality Changes
This study utilized PLS to analyze the impact of multiple independent variables on water quality indexes. The research results are shown in Figure 5, highlighting the influence of various factors on water quality assessment. The independent variables included climate factors (such as annual average temperature, annual precipitation, annual sunshine hours and annual average relative humidity), socioeconomic factors (including watershed GDP, watershed population, tourism numbers in Poyang Lake, approved sand extraction volume in Poyang Lake, domestic wastewater discharge and total water resources), as well as water and land use factors (such as annual average water level, length of embankments, agricultural planting area and afforestation area).
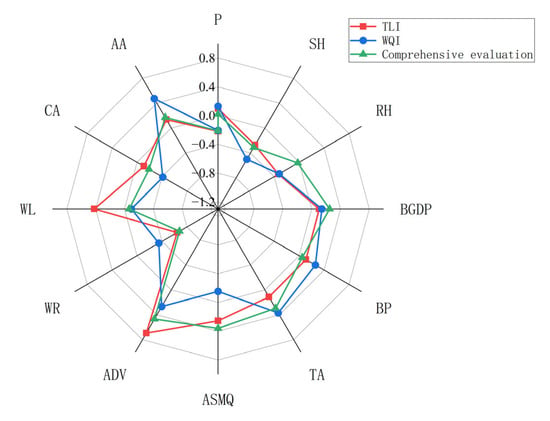
Figure 5.
PLS coefficients of environmental impact factors. (Note: The abbreviations used include AT for average annual temperature, P for annual precipitation, SH for annual sunshine hours and RH for average annual relative humidity. Additionally, BGDP represents basin GDP, while BP indicates basin population. TA refers to tourist visits to Poyang Lake, ASMQ denotes approved sand extraction volume (in ten thousand tons) and ADV signifies domestic sewage discharge (in ten thousand tons). Furthermore, WR stands for total water resources (in hundred million cubic meters), WL denotes average annual water level, CA represents agricultural sown area and AA refers to afforested area.).
According to the results of PLS analysis, AT had little effect on water quality, and the coefficients of TLI and WQI were −0.21 and −0.20, respectively, indicating that temperature rise may have had a certain positive impact on water quality, but the overall impact was not significant [27]. The relationship between P and water quality was more complex, and the positive coefficients of P (0.097 and 0.12) indicate that moderate precipitation may help dilute pollutants and thus improve water quality, but excessive precipitation will lead to deterioration of water quality, especially in extreme climate situations [28]. The negative coefficients of SH (−0.27 and −0.50) suggest that the long-term sunshine may accelerate the evaporation and eutrophication process of water and further affect the water quality.
The influence of social and economic factors on water quality was more obvious and complex. There was a positive correlation between BGDP and water quality, indicating that economic development may improve water quality through investment in environmental governance and infrastructure construction. However, both BP and TA showed a negative effect, which was closely related to the increasing pressure of human activities on the water body, with coefficients of 0.10 and 0.25, respectively, indicating that the enhancement of human activities may lead to the decline of water quality [29]. In addition, the correlation between ADV and water quality was particularly prominent, with negative coefficients (0.69 and 0.26) indicating that the increase of domestic sewage directly affects water quality, emphasizing the importance of treating sewage discharge.
The influence of hydrological factors is particularly significant in this study. The negative effect of WL on water quality (−0.64 and −0.34) indicates that the change of water level was directly related to the health of the water body, and the decrease of water level may have led to the deterioration of water quality, especially in the dry season. In addition, the negative effect of WR on water quality (coefficient −0.11) suggests that water scarcity may also have had a negative impact on water quality.
3.4. Discussion
This study employed the WQI, TLI and comprehensive water quality assessment methods to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the water quality changes in Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022 (Figure 6). It analyzed the regional impact of extreme climate events on the water quality of Poyang Lake and explored the changing patterns of the water quality index, eutrophication index and comprehensive water quality assessment of Poyang Lake. The results indicated that despite significant seasonal fluctuations, the water quality of Poyang Lake showed a downward trend in 2019 and 2021, which might be related to eutrophication, pollutant accumulation and climate change. The studies by Huang et al. [30] on the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River and You [31] on Dianchi Lake pointed out that water quality has seasonal fluctuations and is affected by floods and droughts. In contrast, the water quality of Poyang Lake fluctuated within the “healthy” range, suggesting that despite eutrophication issues, the overall water quality remained in a relatively good state, similar to the results of Peng [32] in their study of Taihu Lake.
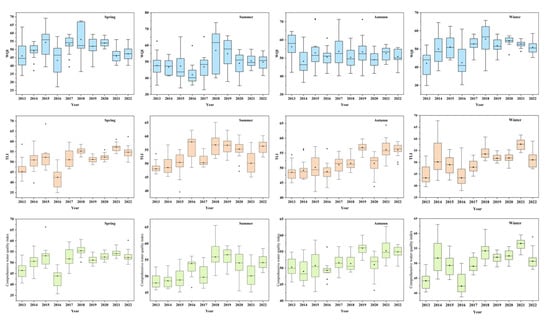
Figure 6.
Seasonal variation charts of the three water quality indices.
In terms of the impact of floods on water quality, the monitoring data showed that the WQI values were higher in autumn and winter, but the water quality was poorer. The WQI values were lower in summer and spring, and the water quality was better. This is consistent with the research results of Li [33]. In terms of regional studies, the water quality in the entire Poyang Lake improved significantly during the flood season, especially in the southern part of the central lake area. This is also consistent with the flood dilution effect proposed by Van [34] and Wang [35]. The eutrophication state of Poyang Lake also fluctuated year by year, which is consistent with the research results of Li [36], who believed that the eutrophication degree of Poyang Lake was affected by external inputs, water volume changes and climate factors. Floods can improve water quality, but they may also introduce additional nutrients, increasing the risk of eutrophication [12,37]. In terms of the overall water quality score, the influence of extreme weather events in different regions showed significant spatial differences. This is consistent with the research content of Zhu [38], who believed that the flood risk in the Poyang Lake basin was relatively low, with a higher spatial distribution characteristic in the central and northern regions, and a lower spatial distribution characteristic in the surrounding areas.
During drought years, water quality generally declined. This was because drought led to a reduction in water volume and an increase in pollutant concentration, thereby causing the deterioration of water quality. This is consistent with the research results of Lin [34,39]. The eutrophication index showed that the risk of water body eutrophication increased during drought periods, especially in the Central South Lake area, reflecting that drought increases the risk of water body eutrophication. Yin [40] further pointed out that extreme climate events have an impact on water quality, causing instability in water quality, especially significant degradation of water quality after drought and subsequent recovery.
Based on the above research results, the water quality of Poyang Lake was significantly affected by seasonal changes and extreme climate events from 2013 to 2022. Although the overall water quality remained within the “healthy” range, attention still needs to be paid to the fluctuations in water quality caused by extreme weather. The water quality in the southern and central lake areas changed dramatically. The water quality improved during the flood season and deteriorated during the dry season. In the northern part of the Yangtze River, the water quality at the Ganjiang estuary deteriorated due to agricultural non-point source pollution. In the eastern wetland lake area, the sensitivity to drought periods was high, and the water quality improved during the flood period, indicating that ecological restoration has a compensatory effect [41].
4. Conclusions
Based on the WQI and TLI, a new comprehensive evaluation index was constructed to evaluate the water quality of Poyang Lake in a recent 10-year span, and the trend of water quality change in Poyang Lake under extreme events was analyzed. At the same time, partial least squares regression was used to analyze the main factors affecting the water quality of Poyang Lake. The main conclusions are as follows:
- (1)
- The water quality of Poyang Lake was slightly worse in summer and autumn than in spring and winter. Each water quality index reflects the different states of the water environment of Poyang Lake, among which the WQI of Poyang Lake from 2013 to 2022 was in the “medium” level, the TLI was in the “medium” and “eutrophic” state and the comprehensive water quality was in the “healthy” and “sub-healthy” state.
- (2)
- Each water quality evaluation index showed different response states to the influencing factors. SH, CA and AA had the most obvious influence on WQI. ADV, WR and WL had the greatest influence on TLI. The influence of WR and ADV on the comprehensive evaluation index was relatively large.
- (3)
- Extreme flood and drought events had significant effects on the water environment of Poyang Lake and have obvious spatial heterogeneity. WQI had an obvious positive response to flood, while TLI had both positive and negative responses to flood. Drought had a negative effect on the water quality evaluation index.
Based on the research results, we propose the following practical recommendations for water management policies and local stakeholders: enhance seasonal monitoring, particularly targeting TP and domestic sewage during summer and autumn; mitigate pollution sources by reducing domestic sewage discharge and agricultural runoff; develop adaptive management strategies for extreme hydrological events, including flood diversion in the northern region and water supplementation in the southern region; incorporate the newly developed composite index into regional water quality monitoring systems to facilitate holistic policy development.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/hydrology12070192/s1, Table S1. Water quality index (WQI) assessment scoring standards. Table S2. Trophic level index (TLI) evaluation grades. Table S3. Weight allocation for the comprehensive evaluation method. Table S4. Classification of lake health standards. Table S5. The result of WQI. Table S6. The result of TLI. Table S7. The result of comprehensive water quality. Figure S1: Water level at Xingzi station in Poyang Lake. Figure S2: Comparison of water quality index (WQI) partition results in the main area of Poyang Lake during extreme flood and drought years. Figure S3: Comparison of the trophic level index (TLI) in Poyang Lake during extreme flood and drought years vs. average years. Figure S4: Comparison of water quality grade (WQG) zones in the main area of Poyang Lake during extreme flood and drought years.
Author Contributions
Z.M.: data curation, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. J.C.: resources, conceptualization, project administration, supervision, funding acquisition, writing—review and editing. L.X.: supervision, funding acquisition, project administration. M.J.: methodology, visualization, writing—review and editing. H.Y.: formal analysis. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (Grant Numbers 2024YFE0106400, 2023YFF0807204), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Numbers U2444221, U2240224), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2024M751237), Jiangxi Province Key Laboratory of Watershed Ecological Process and Information (Grant Number 2023SSY01052), Key R&D Program of Jiangxi Province, China (Grant Numbers 20243BBH81035, 20223BBG74003), Project of Jiujiang Science and Technology Bureau (Grant Number S2024QNZZ0006, S2024TDJS0009), and Science and Technology Planning Project of NIGLAS (Grant numbers NIGLAS2022TJ13; NIGLAS2022GS09) and Science and Technology Plan Project of Jilin Province (2025SYHZ0021).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Liu, D.; Zhang, C.; Yan, N.; Yan, Y.; Duan, H. Eutrophication exacerbated organic pollution in lakes across China during the 1980s–2010s. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Yuan, Z.; Sun, K.K.; Lin, Y.R. Evolution characteristics research on summer-autumn consistent drought of Poyang Lake based on the copula in the changing environment. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 612, 012024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Kraemer, B.M.; Lenters, J.D.; Merchant, C.J.; O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S. Global lake responses to climate change. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.; Zhang, Q.; Melack, J.M.; Tang, H.; Yuan, S.; Jia, Y.; Xue, C.; Song, Y. Floodplain lakes: Linking hydrology to ecology and conservation. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2024, 258, 104967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Sun, J.; Zhou, Q.; Sojka, M.; Ptak, M.; Luo, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhu, S.; Tóth, V.R. 150-year daily data (1870–2021) in lakes and rivers reveals intensifying surface water warming and heatwaves in the Pannonian Ecoregion (Hungary). J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 101985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, T.; Deng, F.; Fan, Y.; De Maeyer, P. Dynamics of the risk of algal blooms induced by surface water temperature in an alpine eutrophic lake under climate warming: Insights from Lake Dianchi. J. Hydrol. 2024, 643, 131949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Hu, Y.; Ma, H. China’s strictest water policy: Reversing water use trends and alleviating water stress. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Gao, G. Eutrophication control of large shallow lakes in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Ni, Z.; Dong, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. Watershed sustainable phosphorus management involving the resilience assessment: Framework and application. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2025, 212, 107907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Githaiga, K.B.; Njuguna, S.M.; Gituru, R.W.; Yan, X. Water quality assessment, multivariate analysis and human health risks of heavy metals in eight major lakes in Kenya. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, G. Quantitative prediction of water quality in Dongjiang Lake watershed based on LUCC. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 284, 117005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Tang, H.; Jin, G.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Stewart, R.A.; Bertone, E.; Yuan, S. Evaluating nutrient distribution and eutrophication pattern in a shallow impounded lake: Exploring the influence of floods. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2024, 39, 375–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Wei, L.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xu, G. Water Quality Grade Identification for Lakes in Middle Reaches of Yangtze River Using Landsat-8 Data with Deep Neural Networks (DNN) Model. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyan, T.N.; Quraishi, S.B.; Nur, E.A.M.; Khan, M.S.R.; Faria, F.F.; Kabir, A. Comprehensive analysis and human health risk assessment of tap water quality in Dhaka City, Bangladesh: Integrating source identification, index-based evaluation, and heavy metal assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 485, 136837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C. Evaluating coupled influences of slope class and land use change on water quality using single and composite indices in an agricultural basin. Catena 2025, 248, 108584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X. Influence of urban green space landscape pattern on river water quality in a highly urbanized river network of Hangzhou city. J. Hydrol. 2023, 621, 129602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tong, G.; Duan, N.; Ma, H.; Song, Q.; Wang, J.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, X.; Jin, S.-Q. Analysis of the complex correlations between land use and water quality using the PLS-SEM method combined with fluorescence fingerprinting data. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, N.; Guo, W.; Lan, J.; Yu, Z.; Wang, H. The impact of human activities and climate change on the eco-hydrological processes in the Yangtze River basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 53, 101753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Duo, L.; Zhao, D.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, X. The response of ecosystem vulnerability to climate change and human activities in the Poyang lake city group, China. Environ. Res. 2023, 233, 116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Goyal, M.; Poonia, V.; Jain, V. Three decadal urban drought variability risk assessment for Indian smart cities. J. Hydrol. 2023, 625, 130056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, X.; Shao, Y.; Guo, X. Impact of Extreme Drought on Vegetation Greenness in Poyang Lake Wetland. Forests 2024, 15, 1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhao, J.; Peng, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Q.; Fu, Y.; Duan, M. Stochastic trophic level index model: A new method for evaluating eutrophication state. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 280, 111826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quevedo-Castro, A.; Bustos-Terrones, Y.A.; Bandala, E.R.; Loaiza, J.G.; Rangel-Peraza, J.G. Modeling the effect of climate change scenarios on water quality for tropical reservoirs. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 322, 116137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, M.; Awasthi, A.; Kumar, M. Global water quality indices: Development, implications, and limitations. Total Environ. Adv. 2024, 9, 200095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.A.; Rohlfs, A.M.; Facey, J.A.; Colville, A.; Mitrovic, S.M. Long-term study of phytoplankton dynamics in a supply reservoir reveals signs of trophic state shift linked to changes in hydrodynamics associated with flow management and extreme events. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Zhang, F.; Leong, T.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xin, H. Evaluation of impacts of environmental factors and land use on seasonal surface water quality in arid and humid regions using structural equation models. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.; Song, Y.; Fu, Q.; Qi, R.; Wu, Z.; Ge, F.; Lu, X.; An, W.; Han, W. Reclaimed water use improved polluted water’s self-purification capacity—Evidenced by water quality factors and bacterial community structure. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 386, 135736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, B.; Deng, J.; Shi, K.; Wang, J.; Brookes, J.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, G.; Paerl, H.W.; Wu, L. Extreme Climate Anomalies Enhancing Cyanobacterial Blooms in Eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR029371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salomon, K.Y.; Brahima, S.; Maxime, K.N.g. Impacts of Anthropogenic Activities on Water Quality of Ouangolodougou Dam, Côte d’Ivoire. Int. J. Environ. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 64–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Xia, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; She, D.; Lei, J. Pollution loads in the middle-lower Yangtze river by coupling water quality models with machine learning. Water Res. 2024, 263, 122191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, R.; Wang, S.; Wan, L.; Dong, F. Towards the development of a ‘land-river-lake’ two-stage deep learning model for water quality prediction and its application in a large plateau lake. J. Hydrol. 2024, 645, 132173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wu, P.; Lu, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Y. Influence of river structure and hydrodynamics on water quality in the upper Taihu Basin, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 453, 142262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wan, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, S.; Wagner, P.D. Exploring the spatiotemporal water quality variations and their influencing factors in a large floodplain lake in China. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Thorslund, J.; Strokal, M.; Hofstra, N.; Flörke, M.; Ehalt Macedo, H.; Nkwasa, A.; Tang, T.; Kaushal, S.S.; Kumar, R.; et al. Global river water quality under climate change and hydroclimatic extremes. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2023, 4, 687–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ding, L.; Wu, Y.; Bol, R. Combined effects of flood, drought and land use dominate water quality and nutrient exports in Jialing River basin, SW China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 954, 176733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, G.; Wan, R. Multidecadal water quality deterioration in the largest freshwater lake in China (Poyang Lake): Implications on eutrophication management. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 260, 114033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, P.; Xia, J.; Zhang, S.; Hu, S. Changes in the water environment and its major driving factors in Poyang Lake from 2016 to 2019, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 30, 3182–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.; Feng, X.; Jin, H.; Gao, Y. Flood risk transfer analysis based on the “Source-Sink” theory and its impact on ecological environment: A case study of the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 921, 171064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-I.; Pan, S.-Y.; Chang, H.-H.; Yu, M.-S.; Lin, W.-L. Will extreme drought impact the reservoir water quality? A 30-year observational study. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Xia, R.; Chen, Y.; Jia, R.; Zhong, N.; Yan, C.; Hu, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, H. Non-steady state fluctuations in water levels exacerbate long-term and seasonal degradation of water quality in river-connected lakes. Water Res. 2023, 242, 120247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Jin, G.; Tang, H.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.-G.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, S. Spatiotemporal variations of water levels and river-lake interaction in the Poyang Lake basin under the extreme drought. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).